Comprehensive evaluation and restoration management of ecological issues in abandoned mines in plateau-mountainous areas: A case study of Qujing City, Yunnan Province
-
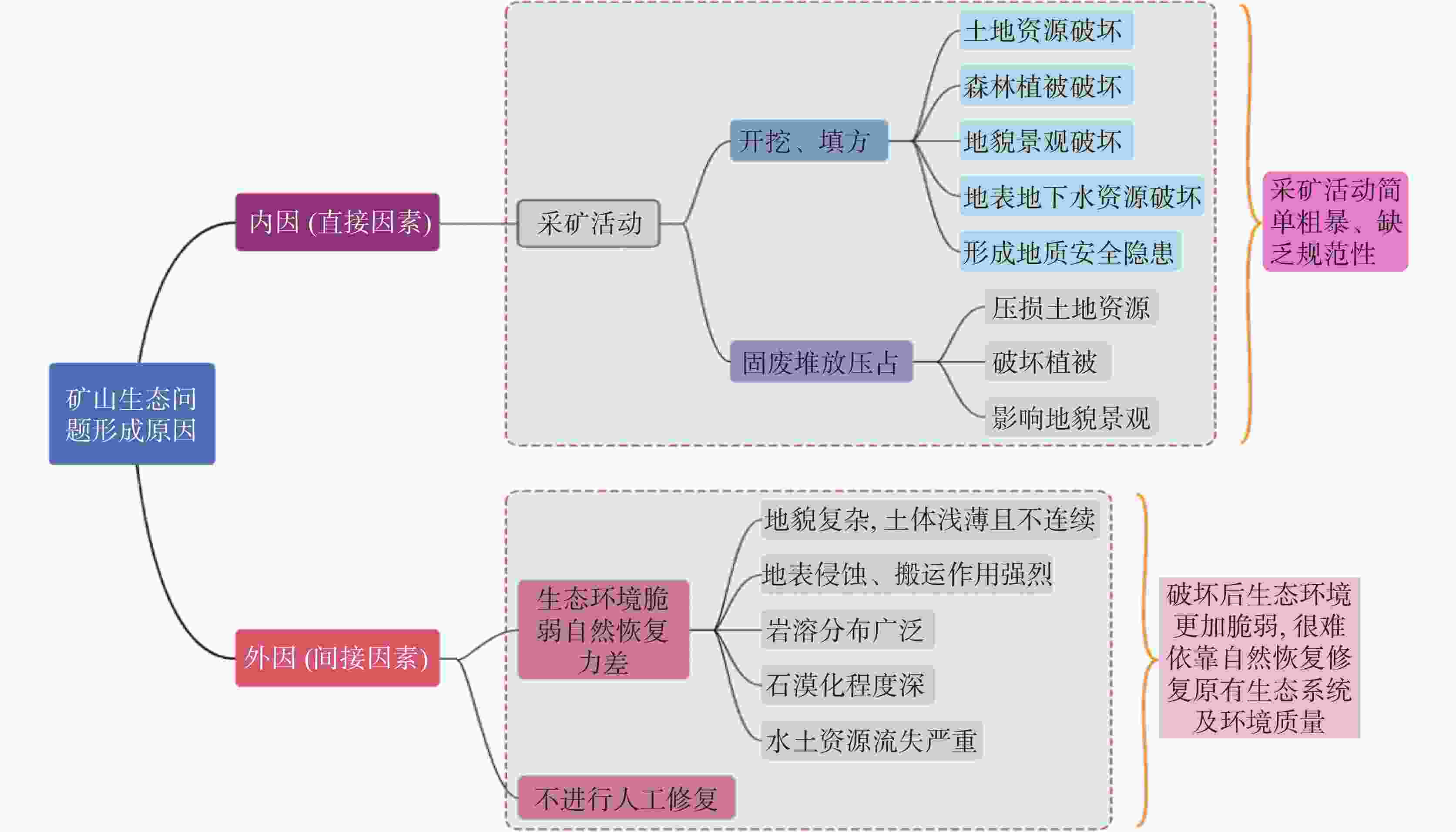
摘要: 由于早期粗放式开发,加之高原山地生态环境脆弱,历史遗留废弃矿山生态问题已严重影响当地生态环境、制约着区域发展。近年来,持续开展的修复工作使生态环境质量显著改善,但部分废弃矿山因调查不充分,生态问题综合评价不足,导致修复目标不明、治理措施不当、修复成效不佳。文章以滇东高原山地典型区曲靖市为研究区,通过系统分析地质环境问题与生态环境条件,运用多因素分析、图层叠加等方法综合评价发现:生态问题严重(Ⅰ级)图斑面积占35.29%,较严重(Ⅱ级)图斑占54.89%;一般(Ⅲ级)占比9.82%。根据评价,划分4个修复分区,并分区分类提出地质环境隐患消除、植被恢复及地形地貌重塑、废弃物清运与土壤改良、地形地貌重塑与土地转型、水土流失治理与石漠化减缓等针对性修复措施,为其他高原山地区生态保护修复提供参考。Abstract:
Due to the early extensive development, the geomorphic landscape, land resources, and forest vegetation have been severely damaged. Coupled with the fragile ecological environment in the plateau-mountainous areas, the ecological problems caused by abandoned mines have significantly affected the regional natural ecosystem and human settlements, thereby restricting economic and social development. In recent years, China has continued to promote the ecological restoration of mines, resulting in a marked improvement in environmental quality. However, some abandoned mines suffer from unclear restoration goals, improper management practices, and poor restoration outcomes due to insufficient investigation and inadequate comprehensive evaluation of ecological issues. In this study, Qujing City, a typical area in the plateau-mountainous region of eastern Yunnan, was selected as the research object. We systematically analyzed the geological environmental issues caused by abandoned mines in the area, as well as the ecological and environmental conditions of the sites where these mines are located. A comprehensive evaluation of the ecological issues associated with abandoned mines within the region was conducted. The ecological issues in the mining areas in the study area have been classified into different severity levels. The assessment results indicate that areas with severe (Level I) and moderately severe (Level II) ecological problems in the abandoned mines cover a total area of 999.01 hectares, accounting for 90.18% of the total area. Among these, areas with severe ecological problems (Level I) are mainly located in Shizong, Luoping, and Fuyuan Counties along the Nanpanjiang River Basin, whereas areas with moderately severe ecological problems (Level II) are primarily found in Shizong County and Fuyuan County along the Nanpanjiang River Basin, as well as in Xuanwei City along the Beipanjiang River Basin. Based on the comprehensive evaluation of the ecological issues associated with abandoned mines in the study area, and in conjunction with territorial spatial planning, the Nanpanjiang River Basin, which is identified as the most prominent and representative in terms of environmental problems, is prioritized. Additionally, considering the natural geographical patterns and focusing on the protection of the ecological barriers at the source of the Pearl River and the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, as well as addressing key ecological challenges such as soil erosion and rocky desertification, the study area is divided into four restoration zones: (1) the restoration area for water conservation and rocky desertification prevention and control in the Nanpanjiang River Basin at the source of the Pearl River; (2) the restoration area for water conservation in the Beipanjiang River Basin in the upper reaches of the Pearl River; (3) the restoration area for soil and water conservation in the Xiaojiang River Basin in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River; and (4) the restoration area for biodiversity conservation in the Niulanjiang River Basin in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. For areas classified as Type I, which face severe ecological problems, the main strategy is to carry out ecological restoration, expand forests and grasslands, and enhance the overall function and value of the ecosystem. In contrast, for areas classified as Type II and Type III, where ecological issues are relatively concentrated but less severe, the focus is on balancing development with ecological protection while meeting land use needs. By categorizing regions based on the severity of ecological problems, more precise and targeted ecological restoration measures can be proposed, thereby providing valuable reference and guidance for ecological protection and restoration in other similar plateau-mountainous areas. -
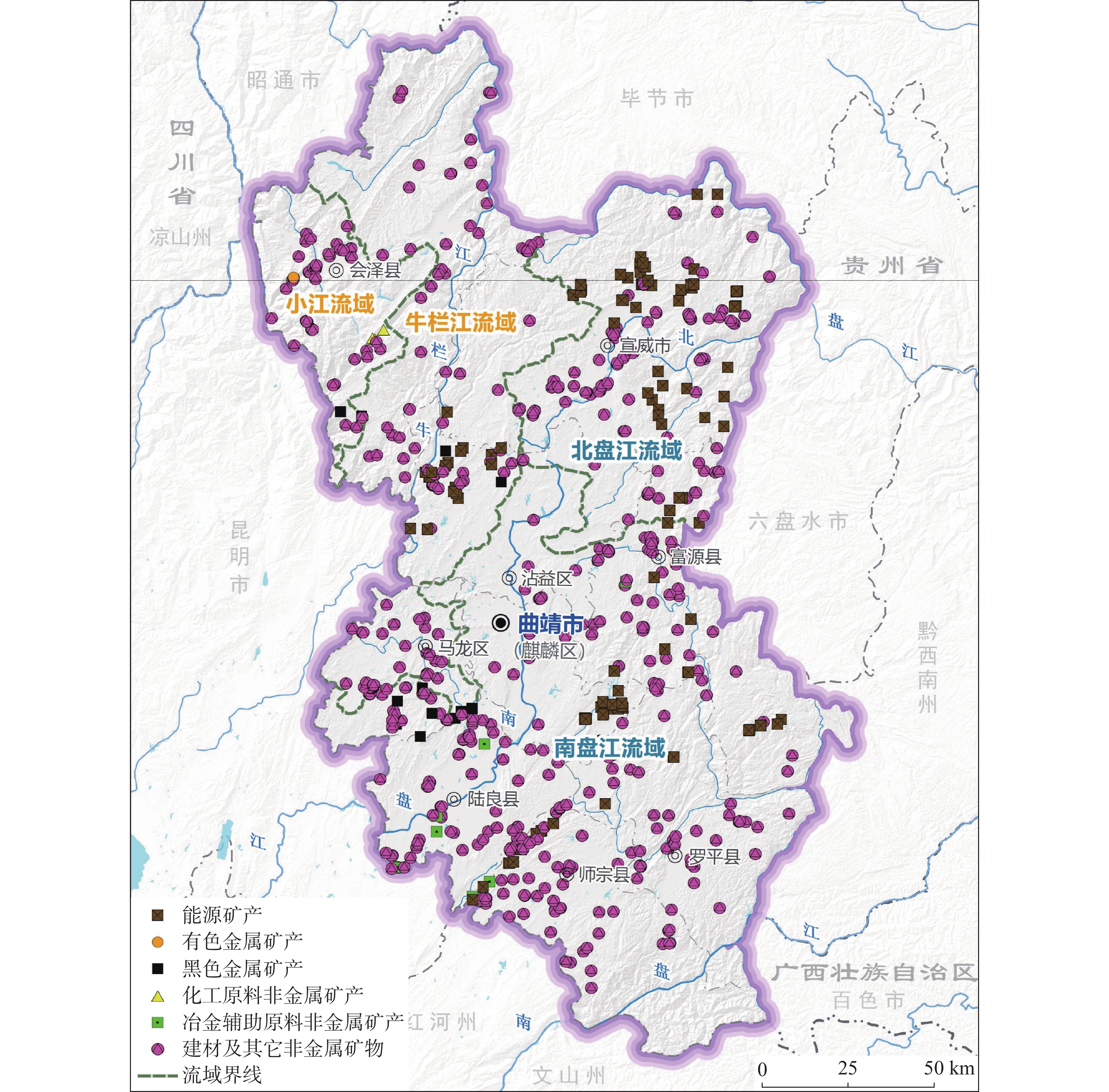
表 1 研究区历史遗留废弃矿山主要成因分区统计表
Table 1. Statistics of zoning for abandoned mines in the study area based on main genesis
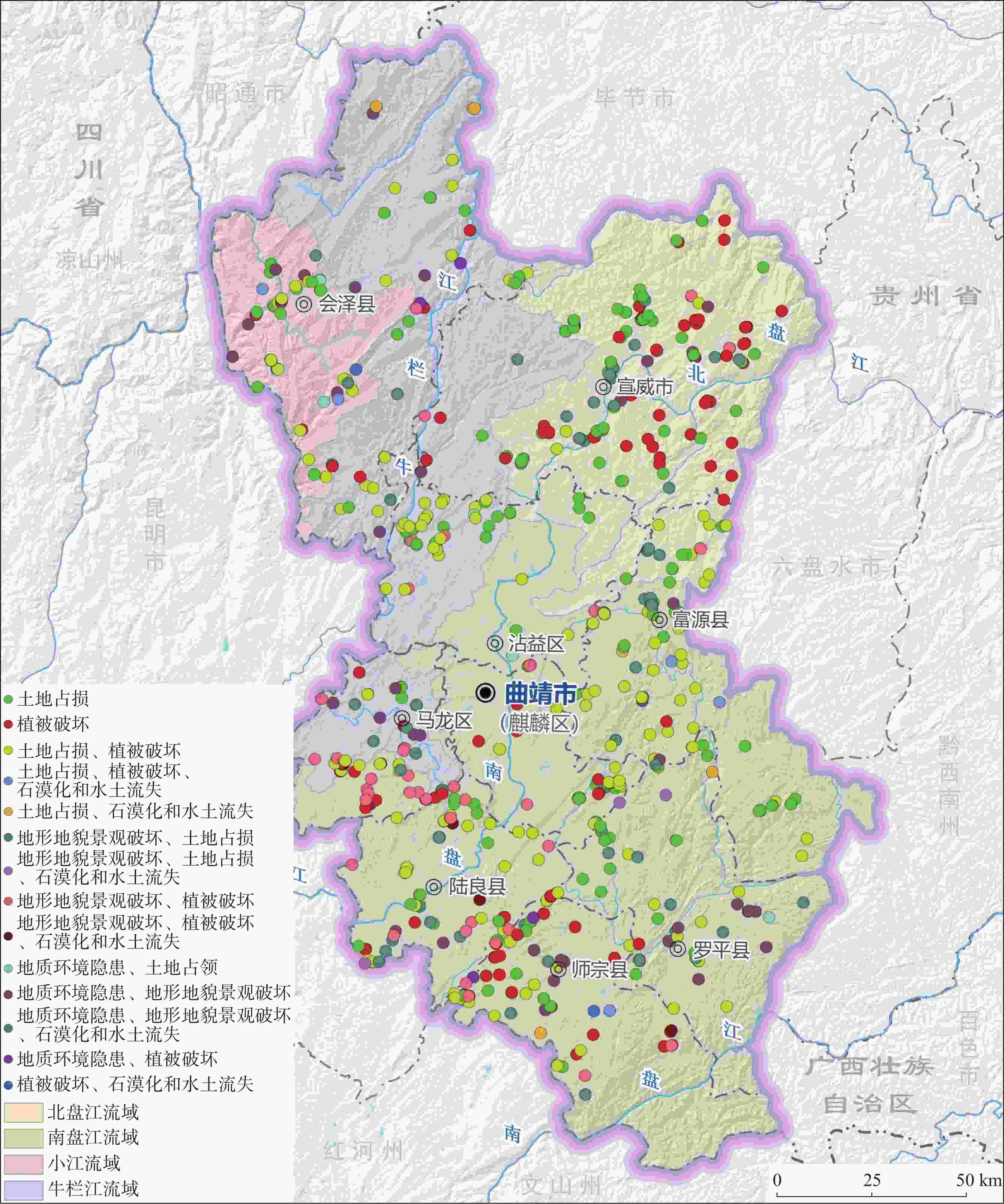
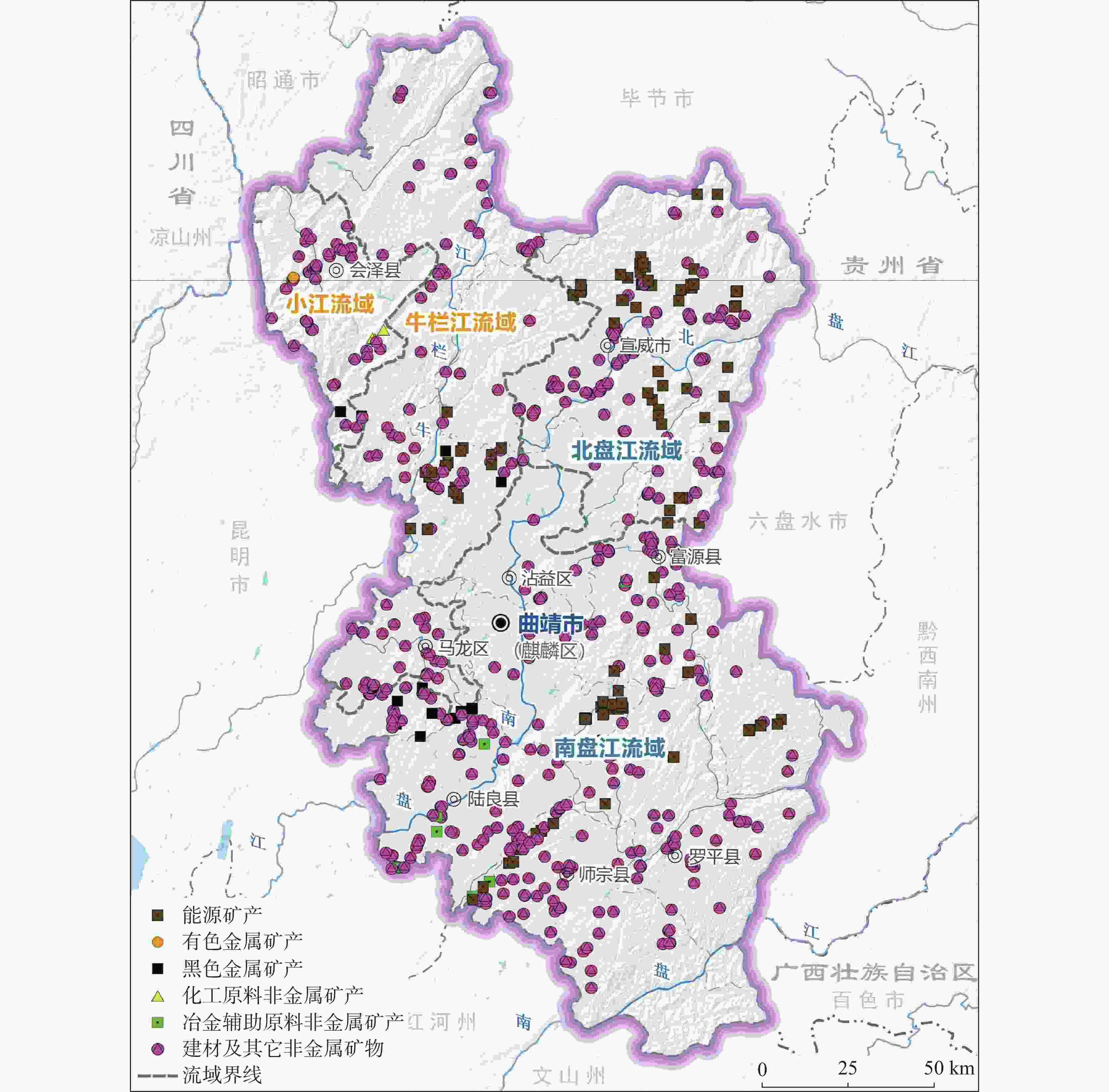
成 因 分 区 面积/km2 所属县(市、区) 主要成因类型 长江上游小江流域 2069.84 会泽县 矿山开挖是直接因素 长江上游牛栏江流域 7288.53 会泽县、宣威市、沾益区、马龙区 生态环境脆弱是间接因素 珠江上游北盘江流域 5758.04 宣威市 矿山固废压占和开挖是直接因素 珠江源头南盘江流域 13819.58 沾益区、富源县、麒麟区、陆良县、
师宗县、罗平县矿山开挖、压占和脆弱的
生态环境是综合影响因素表 2 挖损地损毁程度评价因素及等级标准表
Table 2. Evaluation factors and grade criteria for the damage degree of excavated land
评价因素 评价因子 评价等级 轻度损毁 中度损毁 重度损毁 挖损 挖掘深度/m <2 2~5 >5 挖掘面积/hm2 <1 1~10 >10 表 3 压占地损毁程度评价因素及等级标准表
Table 3. Evaluation factors and grade criteria for the damage degree of pressed area
评价因素 评价因子 评价等级 轻度损毁 中度损毁 重度损毁 压占 压占面积/hm2 <1 1~10 >10 边坡坡度/° <20 20~30 >30 压占物砾石含量/% <10 20~30 >30 压占物厚度/cm <20 20~50 >50 表 4 地貌景观破坏评价因素及等级标准表
Table 4. Evaluation factors and grade criteria of geomorphic landscape damage
评价因素 评价因子 评价等级 一般 较严重 严重 地貌景观破坏 破坏面积/hm2 <5 5~10 >10 与城市面山、主要交通干线距离/km >5 1.5~5 <1.5 表 5 生态系统服务功能重要性评价指标及等级
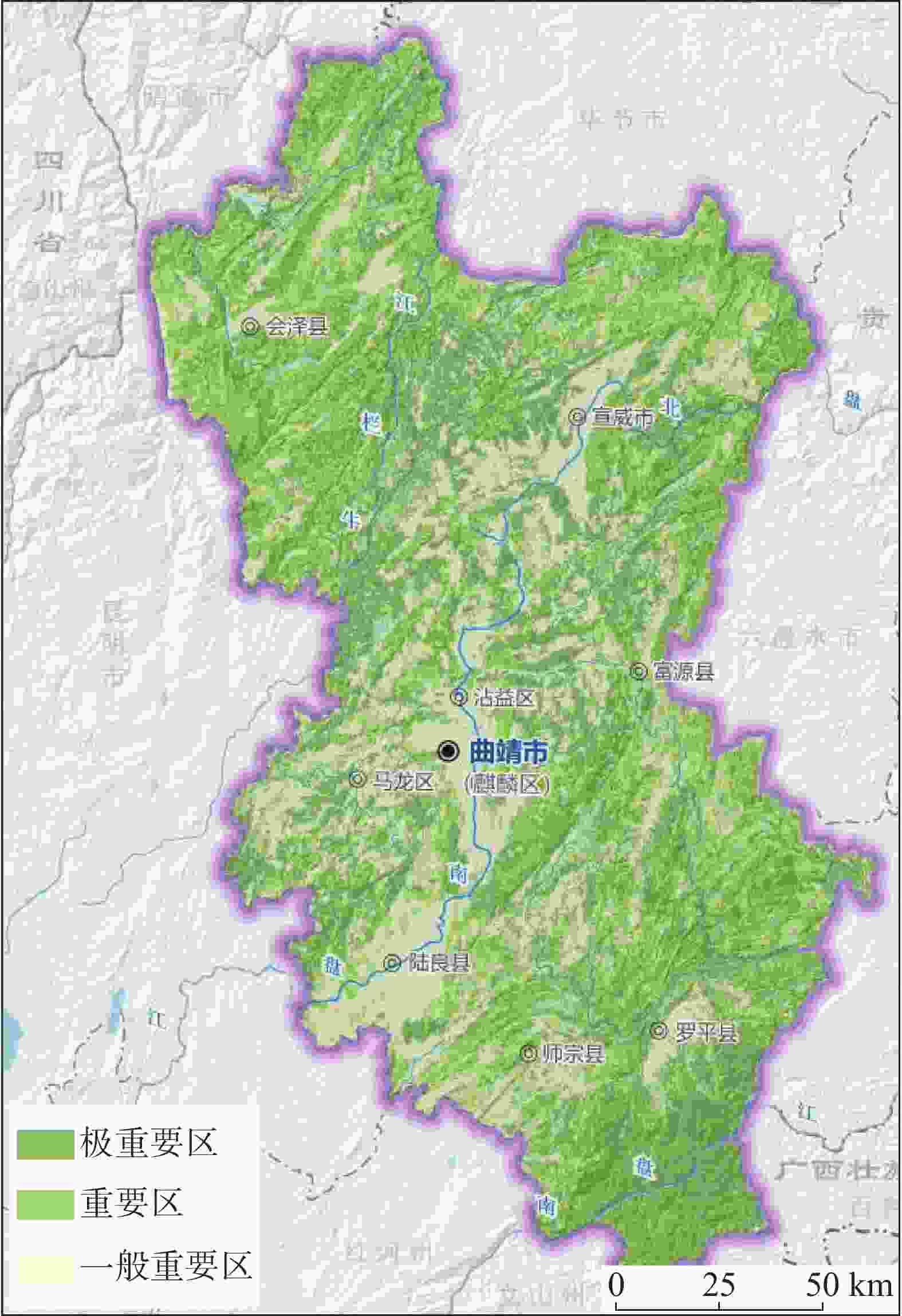
Table 5. Evaluation indexes and levels of importance of ecosystem service functions
数据名称 面积/km2 数据时效性 极重要 重要 一般重要 水源涵养的重要性 3907.3 4892.35 20136.34 2021年11月 水土保持的重要性 2422.99 8266.02 18246.98 生物多样性维护的重要性 7757.87 5518.77 15659.35 生态系统服务功能的重要性 11221.57 8405.80 9308.62 注:数据引自《曲靖市资源环境承载能力和国土空间开发适宜性评价》 表 6 生态系统脆弱性评价指标及等级
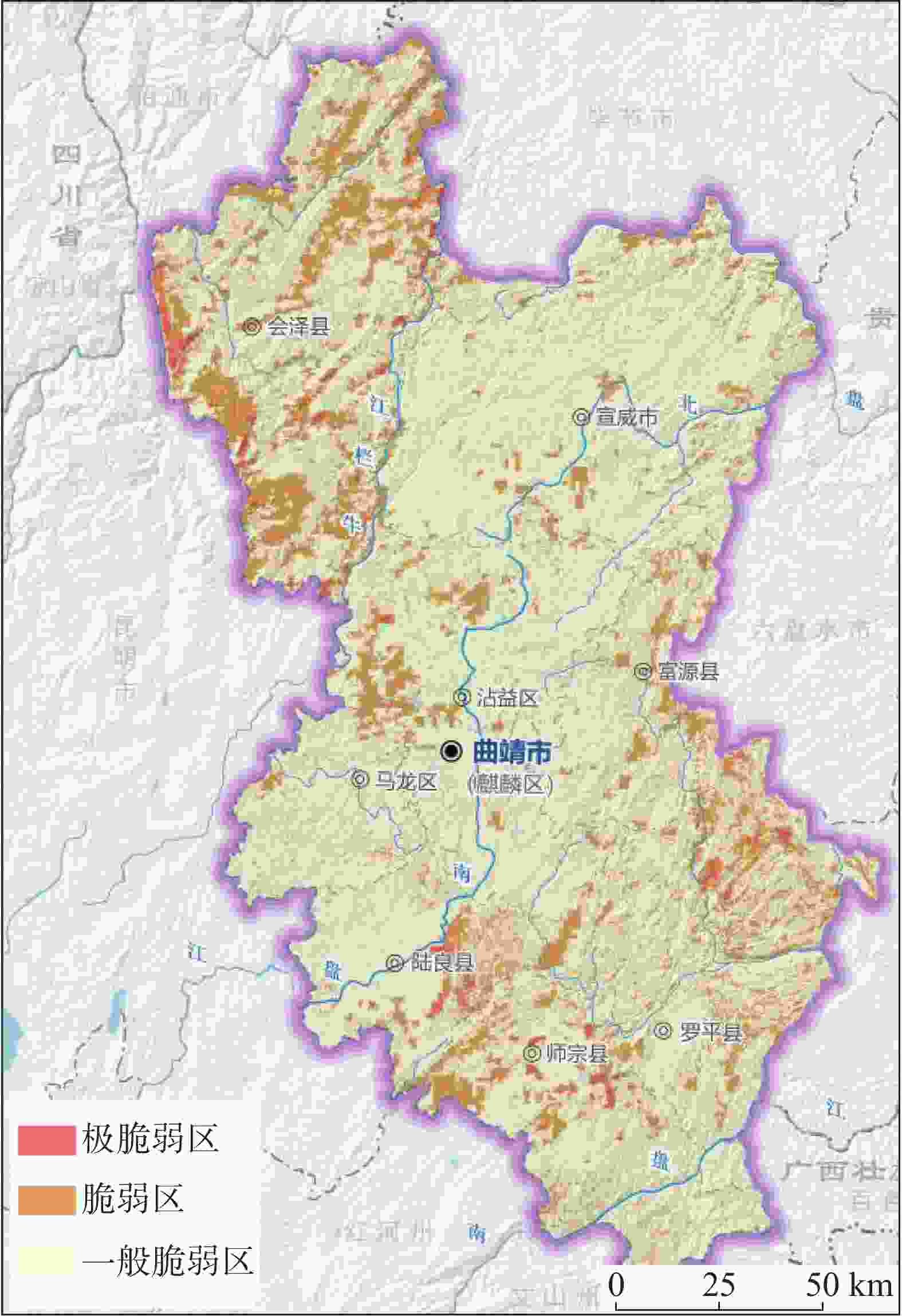
Table 6. Indexes and levels of ecosystem vulnerability assessment
数据名称 面积/km2 数据时效性 极脆弱 脆弱 一般脆弱 水土流失脆弱性 403.65 1600.06 26932.28 2021年11月 石漠化脆弱性 258 1517.75 27160.24 土地沙化脆弱性 29.76 2656.59 26249.64 生态系统脆弱性 672.30 5163.74 23099.95 注:数据引自《曲靖市资源环境承载能力和国土空间开发适宜性评价》。 表 7 历史遗留废弃矿山评价指标赋值表
Table 7. Index assignment for evaluating ecological issues in abandoned mines
评价指标 废弃矿山本身生态环境问题 废弃矿山所处区域环境 地质环境
隐患(A)土地资源
损毁程度(B)地形地貌
景观破坏(C)植被及动物
生境破坏(D)石漠化及
水土流失(E)生态系统服务功能
重要性评价(F)生态脆弱
性评价(G)有 无 重度 中度 轻度 严重 较严
重一般 严重 较严
重一般 严重 较严
重一般 极重
要重要 一般
重要极脆
弱脆弱 一般
脆弱赋值 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 表 8 历史遗留废弃矿山生态问题综合评价等级取值范围表
Table 8. Value range of comprehensive evaluation grades for ecological issues in abandoned mines
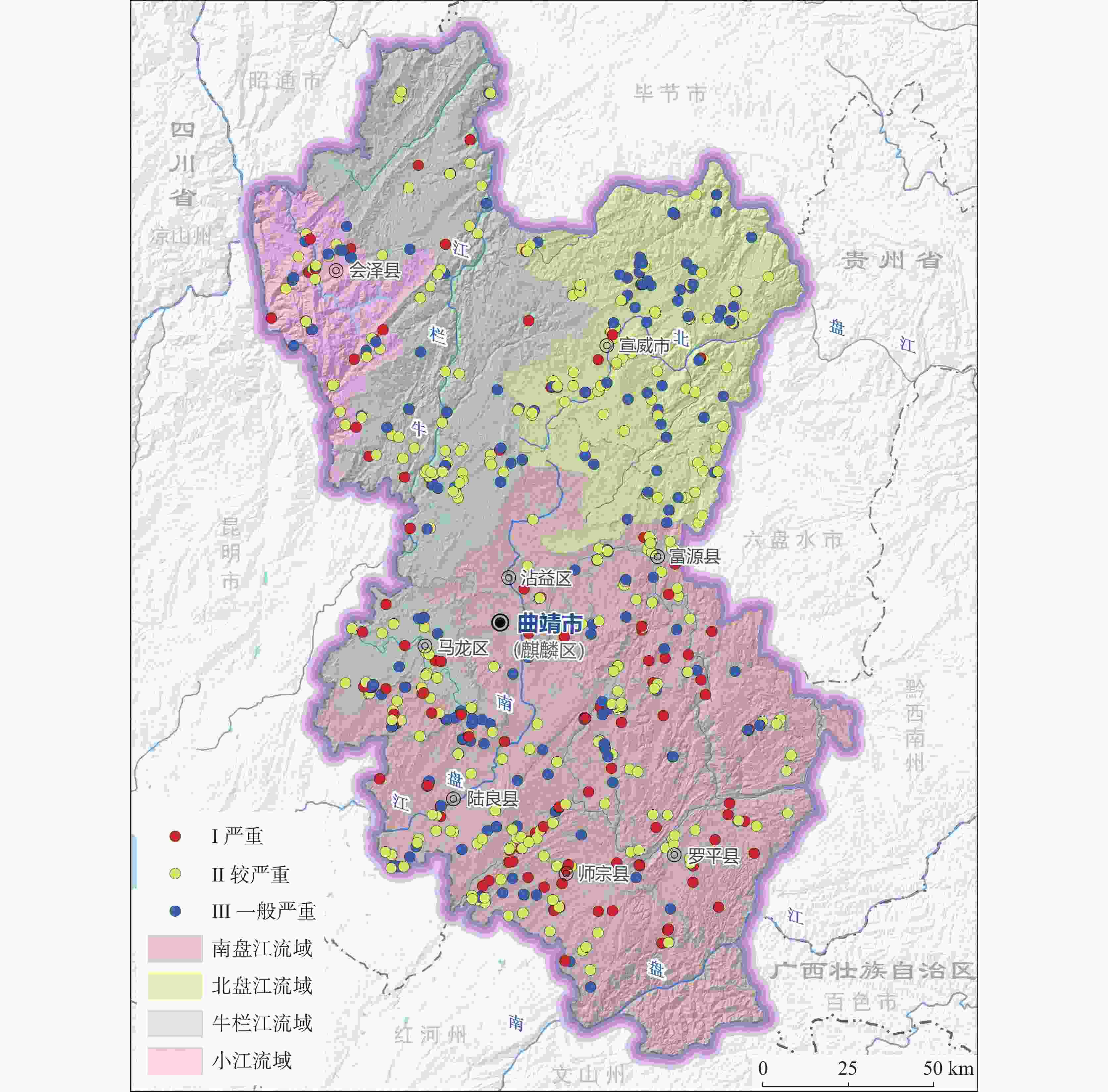
历史遗留废弃矿山生态问题综合评价等级 严重(Ⅰ级) 较严重(Ⅱ级) 一般(Ⅲ级) 取值范围 >60 ≥30,≤60 <30 表 9 历史遗留废弃矿山生态问题综合评价等级
Table 9. Comprehensive evaluation grades of ecological issues in abandoned mines
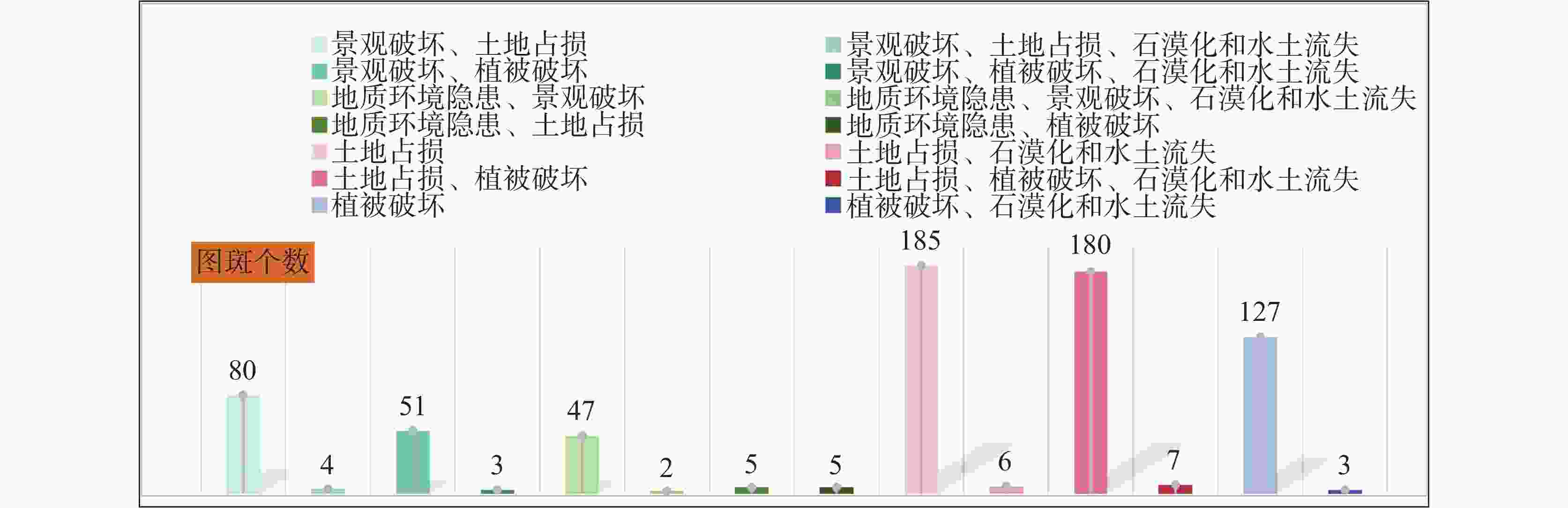
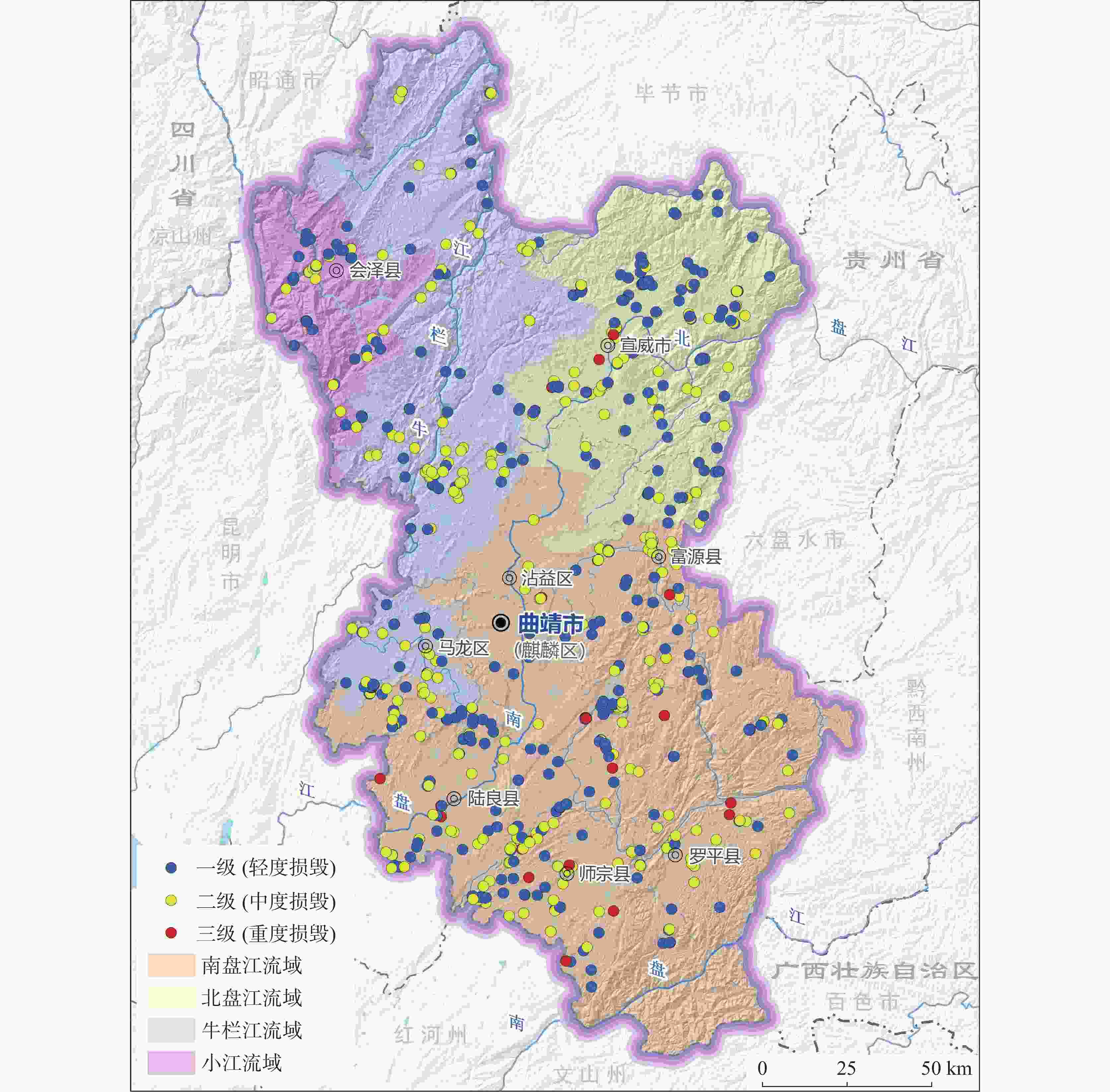
等级类别 划分依据 面积/hm2 面积占比/% Ⅰ 级 场地存在较大地质环境隐患,地质条件不稳定,或土地破坏程度重度损毁,或水资源破坏严重,或生态系统服务功能极重要、生态系统极脆弱,大部分植被盖度与质量遭受破坏,地表植被生境、动植物栖息地等受到严重影响,生态退化严重。 390.92 35.29 Ⅱ级 场地存在一定的地质环境隐患,地质稳定性较差,或土地破坏程度中度损毁,或水资源破坏较严重,或生态系统服务功能重要、生态系统脆弱,或局部植被盖度与质量遭受破坏,地表植被生境、动植物栖息地等受到影响,物种生境条件相对稳定。 608.09 54.89 Ⅲ 级 场地不存在地质环境隐患,地质稳定性总体较好,土地破坏程度轻度损毁,或水资源破坏较小,或生态系统服务功能一般、生态系统一般脆弱,局部植被盖度与质量受到影响,物种生境条件总体较稳定。 108.76 9.82 合计 1107.77 100 -
[1] 王自威. 典型工矿区受损土地修复技术与整治规划设计[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2013.WANG Ziwei Remediation Technologies and Consolidation Planning and Design of Typical Land Damaged in Industrial and Mining Areas[D]. Beijing. China University of Geosciences, 2013. [2] 王佳红. 矿山地质环境综合评价方法研究与管护对策建议:以广东省为例[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2018(11): 135-137, 141.WANG Jiahong. Research on Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Mine Geological Environment and Suggestions on Management and Protection Countermeasures--Taking Guangdong Province as an Example[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2018(11): 135-137, 141. [3] 范振林. 安徽省矿产资源开发环境影响评价研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(s1): 75-79.FAN Zhenlin, Chinese Academy of Land and Resource Economics. Study on the environmental impact assessment of mineral resources development in Anhui province[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(S1): 75-79. [4] 杨梅忠, 刘亮, 高让礼. 模糊综合评判在矿山环境影响评价中的应用[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2006, 26(4): 439-442.YANG Meizhong, LIU Liang, GAO Rangli. Application of Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation to the Environmental Influence of the West Mineral Exploration[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2006, 26(4): 439-442. [5] 赵娟. 矿山环境评价与治理恢复[J]. 煤炭与化工, 2019, 42(2), 96-103.ZHAO Juan. Mine environmental assessment and governance restoration[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry. 2019, 42(2), 96-103. [6] 江松林, 孙世群, 王辉. 安徽省矿山环境质量综合评价研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 31(1): 112-115.JIANG Songlin, SUN Shiqun, WANG Hui. Comprehensive assessment of mine environmental quality of Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science), 2008, 31(1): 112-115. [7] 陈艳玲, 王国文, 宋安安. 阜平县生态系统服务功能重要性评价_陈艳玲[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(9): 166-167,172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2021.09.066CHEN Yanling, WANG Guowen, SONG An′an. Importance Evaluation on Ecosystem Services in Fuping County[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021(9): 166-167,172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2021.09.066 [8] Anawar H M. Sustainable rehabilitation of mining waste and acid mine drainage using geochemistry, mine type, mineralogy, tex-ture, ore extraction and climate knowledge[J]. Journal of Envi-ronmental Management, 2015(158): 111-121. [9] Lisa, Zillig, Naomi, etal. Mining Rehabilitation in New South Wales (Australia) and Germany[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Engineering, 2015(8): 499-511. [10] Ana T. Lima, Kristen Mitchell, David W. O’Connell, Jos Verhoeven, Philippe Van Cappellen. The legacy of sur-face mining: Remediation, restoration, reclamati on and rehabili-tation[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2016(66): 227-233. [11] Jordán M M, García-Sánchez E, Almendro-Candel M B, et Al. Technosolsu-specially designed for the resumption of mining activities Sing my lots and biosolids. Ion fluidity and related use Penetration column[J]. Catena, 2017(148): 74-80. [12] 海俊杰, 苏梨, 张林, 刘正军. 湖南省宁乡县矿山地质环境现状分区评估研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(S1): 50-52.HAI Junjie, SU Li, ZHANG Lin, LIU Zhengjun. Study on zoning evaluation of mine geological environment situation in Ningxiang county, Hunan province[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019, 28(S1): 50-52. [13] 王波, 王宇, 张贵, 张华, 代旭升, 康晓波. 滇东南泸江流域岩溶地下水质量及污染影响因素研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(3): 352-362.WANG Bo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, DAI Xusheng, KANG Xiaobo. A Study of Quality and Pollution Factors of Karst Groundwater in Lujiang River Basin in Southeast Yunnan[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 352-362. [14] 云南省地质环境监测院. 云南省珠江流域重要历史遗留矿山详细调查报告[R]. 云南省自然资源厅, 2022. [15] 王宇, 张贵, 柴金龙, 王波, 何绕生, 彭淑惠, 康晓波, 周翠琼. 云南岩溶石山地区重大环境地质问题及对策[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2013: 17-27. [16] 张永安. 黄河流域兰州段废弃矿山主要生态环境问题及成因分析[J]. 资源信息与工程, 2024, 39(4): 118-121+126.ZHANG Yongan, Design and Research Institute Gansu Nonferrous Engineering Survey. Analysis on main ecological and environmental problems and causes of abandoned mines in Lanzhou section of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resource Information and Engineering, 2024, 39(4): 118-121+126. [17] 王孟本. “生态环境”概念的起源与内涵[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 23(9): 1910-1914.Wang Meng Ben(Institute of Loess Plateau. The origin of the term "ecological environment (eco-environment)" in Chinese and its connotation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(9): 1910-1914. [18] 袁丽梅, 董志升. 提高曲靖森林生态系统服务功能的对策研究[J]. 中国集体经济, 2024, 26: 116-120. [19] 自然资源部. 资源环境承载能力和国土空间开发适宜性评价指南(试行)[Z]. 自然资办函〔2020〕127号. 2020年1月19日. [20] 苏悦, 刘洪, 杨武年, 欧阳渊, 张景华, 张腾蛟, 黄勇. 高原山地区域生态脆弱性研究: 以四川省康定市为例[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2024, 36(3): 206-215.SU Yue, LIU Hong, YANG Wunian, OUYANG Yuan, ZHANG Jinghua, ZHANG Tengjiao, HUANG Yong. Ecological vulnerability of highland mountain areas: A case study of Kangding City, Sichuan Province[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2024, 36(3): 206-215. [21] 王亨利, 谢道雷, 刘咏明, 倪深海. 废弃矿山地质环境影响评价与生态修复[J]. 绿色科技, 2019, 24: 79-82.WANG Hengli, XIE Daolei, LIU Yongming, NI Shenhai. Geological Environmental Impact Assessment and Ecological Restoration of Abandoned Mines[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2019, 24: 79-82. [22] 李梦露, 何舸, 王成坤. 新时期国土空间矿山生态修复规划研究: 以南宁市为例[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(7): 71-77.LI Menglu, HE Ge, WANG Chengkun. Research on mines ecological restoration plan of territorial spatial in the new period: a case of Nanning city[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(7): 71-77. [23] 胡兆鑫, 罗为群, 蒋忠诚, 吴泽燕, 汤庆佳. 基于生态系统脆弱性评价的典型岩溶区生态治理分区[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(3): 661-671, 703.HU Zhaoxin, LUO Weiqun, JIANG Zhongcheng, WU Zeyan, TANG Qingjia. Zoning of ecological treatment in typical karst areas based on ecosystem vulnerability assessment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(3): 661-671, 703. [24] 卢泓杏, 赵宇鸾. 基于生态安全格局的岩溶山地国土空间生态修复关键区识别:以贵州省关岭县为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(2): 349-363.LU Hongxing, ZHAO Yuluan, Identification of key areas for the ecological restoration of karst mountainous territorial space based on the construction of ecological security pattern: A case study of Guanling, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(2): 349-363. -




 下载:
下载: