Characteristics and influencing factors of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus nutrients in the soil-plant-litter continuum of typical communities in mid-high mountain karst areas
-
摘要: 中高山岩溶区具有独特的地理和环境特征,生态系统脆弱,研究土壤–植物–凋落物的物质循环和能量流动在各个典型植被群落之间的变化,对于理解该地区的生态恢复和可持续发展具有重要意义。文章以滇西北中高山岩溶石漠化区的5种典型群落类型(草地、灌草、乔灌草–柏、纯松、乔灌草–松)选取的23个不同群落共69块样地为研究对象,分析土壤、植物和凋落物的碳(C)、氮(N)、磷(P)含量与化学计量特征,以及环境因素的影响。结果表明:(1)不同群落类型土壤C、N、P含量均值为7.46~43.25 g·kg−1、1.05~2.96 g·kg−1、0.39~0.53g·kg−1,土壤C/N、C/P、N/P计量比为8.82~23.25、21.74~105.25、2.89~6.33;植物C、N、P含量为373.79~622.87 g·kg−1、10.47~15.56 g·kg−1、1.43~2.14 g·kg−1,植物C/N、C/P、N/P计量比为27.10~65.13、272.85~624.26、7.23~10.72;凋落物C、N、P含量为334.93~491.73 g·kg−1、7.00~16.61 g·kg−1、1.16~1.53 g·kg−1,凋落物C/N、C/P、N/P计量比为23.70~72.17、238.49~499.18、7.61~17.49,不同群落类型土壤、植物和凋落物的C、N、P含量及化学计量比差异显著;(2)土壤与植物的C、N养分基本上表现出随群落类型由草地到乔木逐渐丰富的趋势,乔灌草–松、纯松、灌草阶段普遍大于草地和乔灌草–柏阶段,而凋落物则与之相反;土壤普遍缺P,但植物与凋落物中未表现出缺P;(3)土壤C/N值、C/P值、N/P值在纯松、乔灌草–松、灌草类型显著大于乔灌草–柏和草地;植物与凋落物的C/N值、C/P值乔灌草–柏类型显著大于其他类型;(4)土壤、植物和凋落物之间的养分含量呈现相关关系,群落类型、海拔、石漠化程度等环境因子对化学计量特征有显著影响,且各因子间相关性复杂,影响重要性排序为海拔>生态修复措施>石漠化程度>群落类型>土壤厚度>植被覆盖度;(5)中高山岩溶区植被生长受到N、P的共同制约,乔木群落相较草本与矮灌群落,更多受到N素的制约。
-
关键词:
- 岩溶区 /
- 典型群落类型 /
- 土壤–植物–凋落物连续体 /
- 碳氮磷化学计量特征 /
- 影响因子
Abstract:This study focuses on the mid-high mountain karst rocky desertification areas in northwestern Yunnan, aiming to elucidate the stoichiometric characteristics and influencing mechanisms of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) within the soil-plant-litter continuum in this region. It is of great significance for an in-depth understanding of ecosystem cycles in mid-high mountain karst areas and provides theoretical support for ecological restoration efforts. The study area is located in Shuhe town and Jiuhe township, south of Yulong Snow Mountain, on the southeastern edge of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. It lies within the transition zone between China's first and second terrain steps. The region features complex terrain with numerous high mountains and valleys, and an altitude ranging from 2,544 m to3,090 m. Carbonate rocks are widely distributed, with limestone as the main soil-forming parent material, resulting in an extremely slow rate of soil formation through weathering; The predominant soil type is brown soil. The area experiences a plateau monsoon climate characterized by distinct dry and wet seasons, an annual average temperature of 13℃ to 20 ℃, and an annual average rainfall of 950 mm to1200 mm, over 85% of which occurs between May and October. Solar radiation remains strong throughout the year. Vegetation is characterized by xerophytism, lithophytism, and calciphilia, with key species including Arundinella hookeri Munro ex Keng, Tripogon yunnanensis J. L. Yang ex S. M. Phillips & S. L., Festuca ovina L., Lespedeza forrestii Schindl., Rhododendron racemosum Franch., Quercus guyavifolia H. Lév., Cotoneaster microphyllus Wall. ex Lindl., Pinus yunnanensis Franch., Juniperus formosana Hayata, Cupressus duclouxiana Hickel.Targeting the ecological vulnerability of mid-high mountain karst areas and addressing existing research gaps, this study analyzes the C, N, and P contents and stoichiometric characteristics of soil, plants, and litter under different vegetation community types. It further explores the impacts of community types and environmental factors on nutrient cycling. This study focuses on answering two core questions: first, the variation patterns of C, N, and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics in the soil-plant-litter continuum; Second, the specific effects of vegetation community types on C, N, and P contents within this continuum.From July to August 2023, the survey was conducted in the study area encompassing five typical community types: grassland, shrub-grass, arbor-shrub-grass-cypress, pure pine, and arbor-shrub-grass-pine. The grassland type includes three communities, while the shrub-grass, arbor-shrub-grass-cypress, pure pine, and arbor-shrub-grass-pine types each included five communities, totaling 23 communities. For each community, three parallel sample plots were selected, resulting in a total of 69 sample plots. In each sample plot, a standard 10 m×10 m quadrat was established, along with a representative 5 m×5 m shrub quadrat and five 1 m×1 m herb quadrats arranged using the plum-point method. Indicators such as geographical location, altitude, community type, ecological restoration measures, soil thickness, vegetation coverage, rock exposure rate, and degree of rocky desertification were recorded. Community diversity was assessed using indices such as species richness and the Shannon-Wiener diversity index. Samples were analyzed for C, N, and P contents and stoichiometric characteristics of soil, plants, and litter, as well as the influence of environmental factors.The research results show that the average contents of soil C, N, and P across different community types were 7.46 to 43.25 g·kg−1, 1.05 to 2.96 g·kg−1, and 0.39 to 0.53 g·kg−1, respectively. The soil C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios ranged from 8.82 to 23.25, 21.74 to 105.25, and 2.89 to 6.33, respectively. Plant C, N, and P contents were 373.79 to 622.87 g·kg−1, 10.47 to 15.56 g·kg−1, and 1.43 to 2.14 g·kg−1, with plant C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios of 27.10 to 65.13, 272.85 to 624.26, and 7.23 to 10.72, respectively. Litter C, N, and P contents were 334.93 to 491.73 g·kg−1, 7.00 to 16.61 g·kg−1, and 1.16 to1.53 g·kg−1, with litter C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios of 23.70 to 72.17, 238.49 to 499.18, and 7.61 to 17.49, respectively. Significant differences were observed in the C, N, P contents and stoichiometric ratios of soil, plants, and litter among different community types. Soil and plant C and N nutrients generally showed a trend of gradual enrichment as community types transitioned from grassland to arbor, Specifically, the arbor-shrub-grass-pine, pure pine, and shrub-grass stages generally showed higher nutrient levels than the grassland and arbor-shrub-grass-cypress stages, while litter exhibited the opposite trend. Soil was generally deficient in P, but plants and litter did not exhibit signs of P deficiency. In terms of stoichiometric ratios, and soil C/N, C/P, and N/P ratios in pure pine, arbor-shrub-grass-pine, and shrub-grass types were significantly higher than those in arbor-shrub-grass-cypress and grassland types. Conversely, plant and litter C/N and C/P ratios in arbor-shrub-grass-cypress type were significantly higher than those in other types. There were widespread correlations in nutrient contents among soil, plants, and litter. Environmental factors such as community type, altitude, and degree of rocky desertification had significant impacts on stoichiometric characteristics, with complex correlations among factors. The relative importance of these influences was ranked as follows, altitude > ecological restoration measures > degree of rocky desertification > community type > soil thickness > vegetation coverage.Vegetation growth in mid-high mountain karst areas is jointly limited by N and P, with the degree of limitation varying among different community types. Compared with herbaceous and low shrub communities, arbor communities are more strongly constrained by N. -
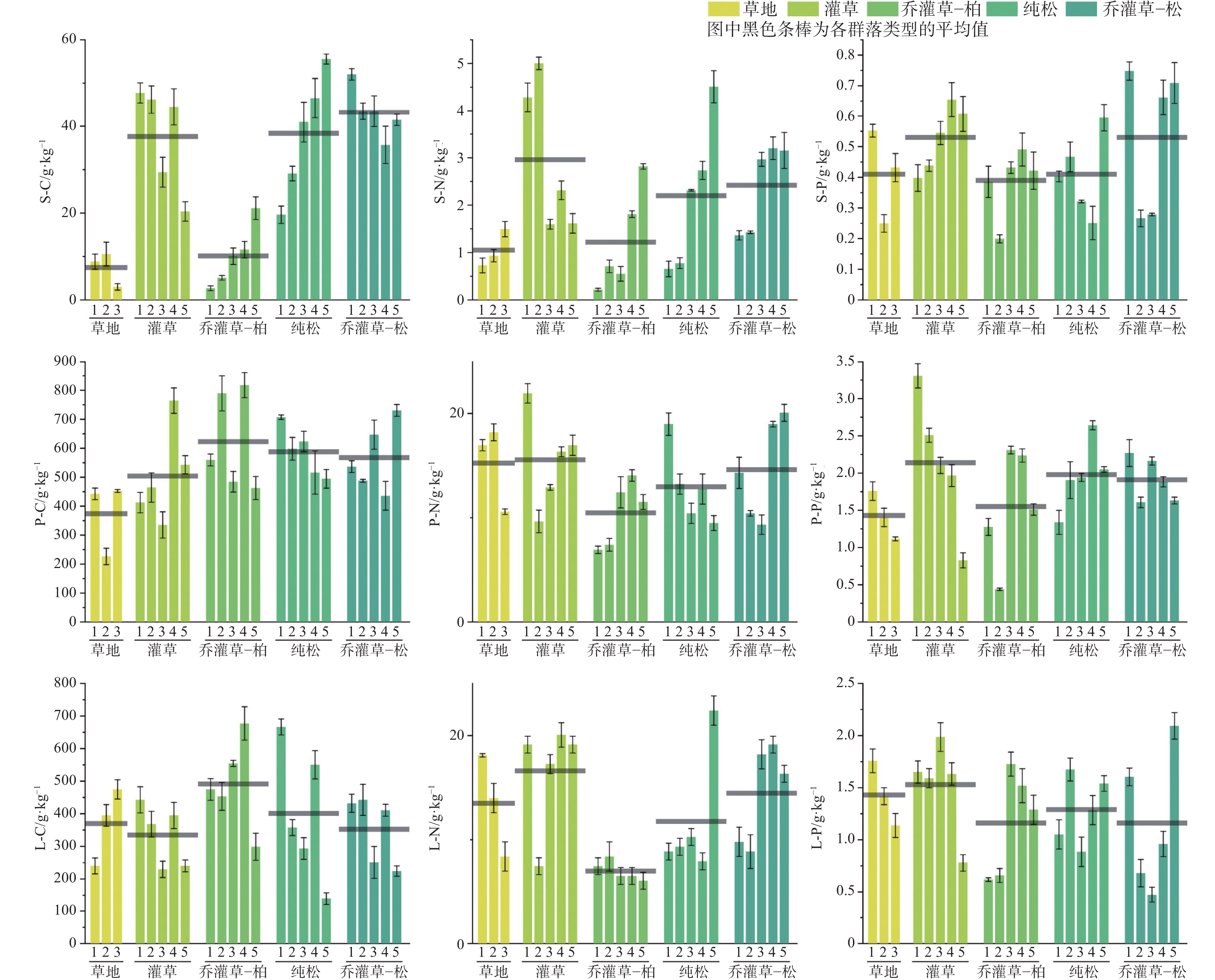
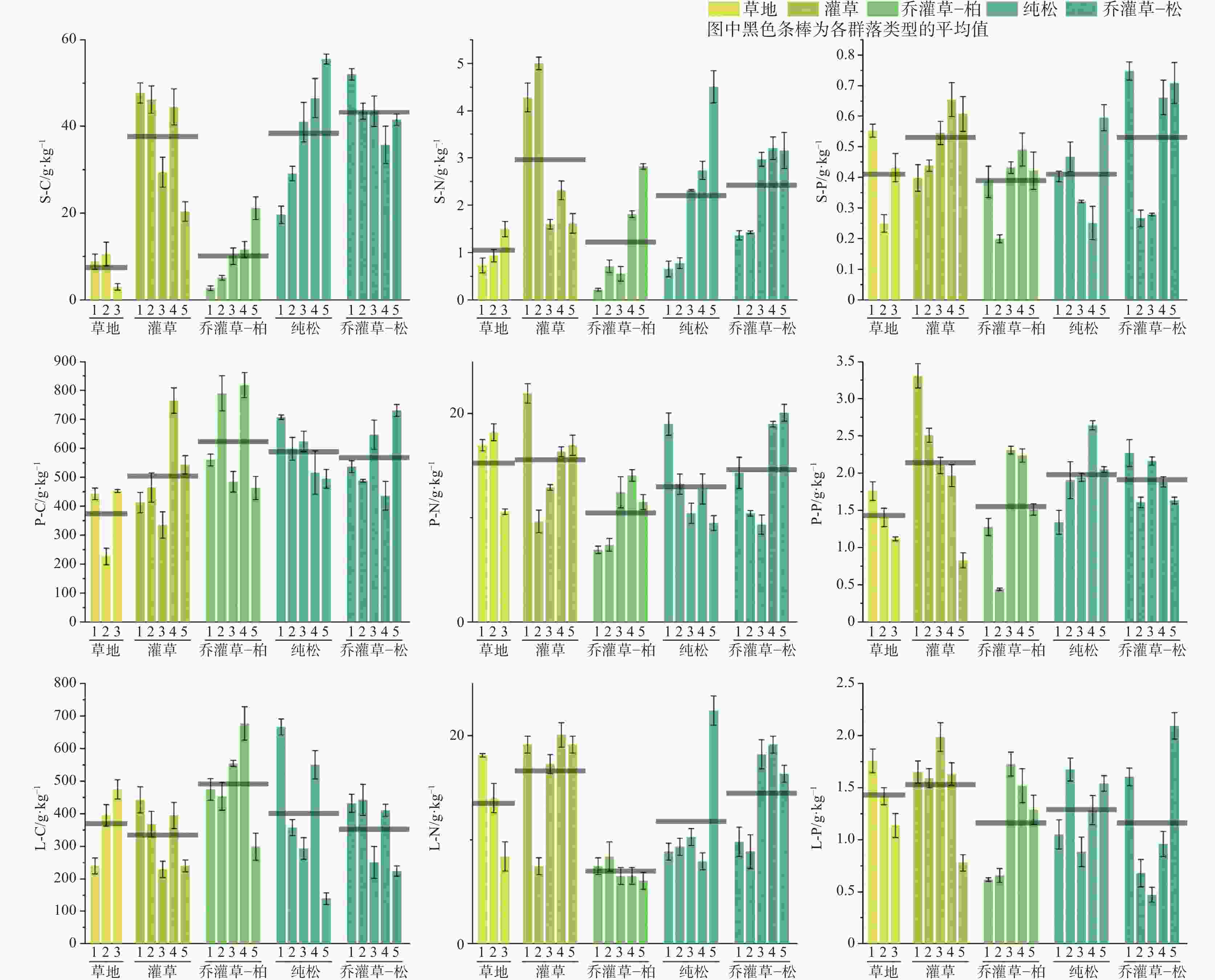
图 1 典型群落类型土壤-植物-凋落物C、N、P含量
注:图中S-C为土壤C含量,S-N为土壤N含量,S-P为土壤P含量;P-C为植物C含量,P-N为植物N含量,P-P为植物P含量;L-C为凋落物C含量,L-N为凋落物N含量,L-P为凋落物P含量。
Figure 1. Contents of C, N, and P of soil-plant-litter at different typical community types
Note: S-C represents soil carbon content, S-N represents soil nitrogen content, and S-P represents soil phosphorus content. P-C represents plant carbon content, P-N represents plant nitrogen content, and P-P represents plant phosphorus content. L-C represents litter carbon content, L-N represents litter nitrogen content, and L-P represents litter phosphorus content.
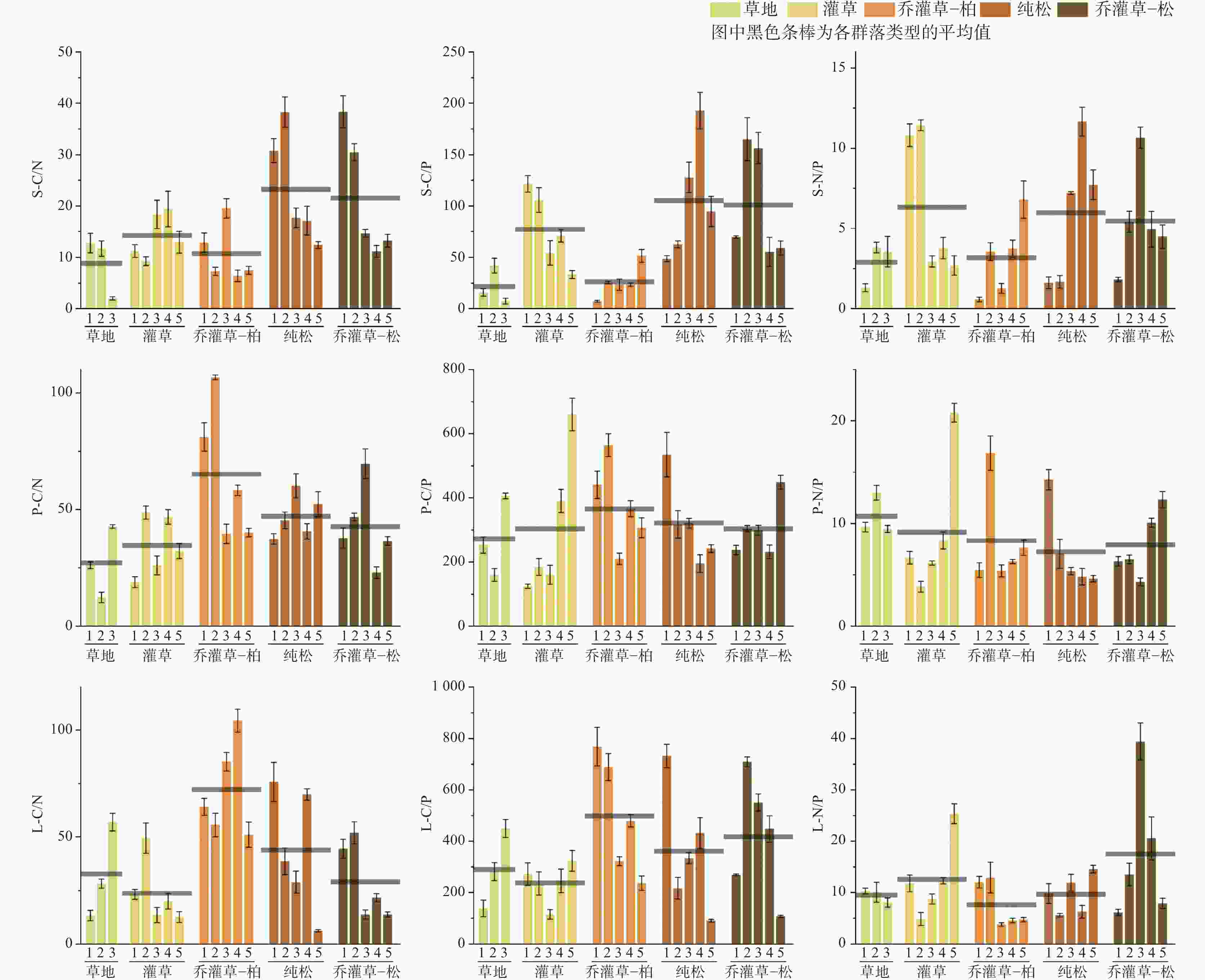
图 2 典型群落类型土壤–植物–凋落物C/N、C/P、N/P比值
注:图中S-C/N为土壤碳氮比,S-C/P为土壤碳磷比,S-N/P为土壤氮磷比;P-C/N为植物碳氮比,P-C/P为植物碳磷比,P-N/P为植物氮磷比;L-C/N为凋落物碳氮比,L-C/P为凋落物碳磷比,L-N/P为凋落物氮磷比。
Figure 2. Ratios of C/N, C/P, and N/P of soil-plant-litter at different typical community types
Note: S-C/N represents the soil carbon-nitrogen ratio, S-C/P represents the soil carbon-phosphorus ratio, and S-N/P represents the soil nitrogen-phosphorus ratio. P-C/N represents the plant carbon-nitrogen ratio, P-C/P represents the plant carbon-phosphorus ratio, and P-N/P represents the plant nitrogen-phosphorus ratio. L-C/N represents the litter carbon-nitrogen ratio, L-C/P represents the litter carbon-phosphorus ratio, and L-N/P represents the litter nitrogen-phosphorus ratio.
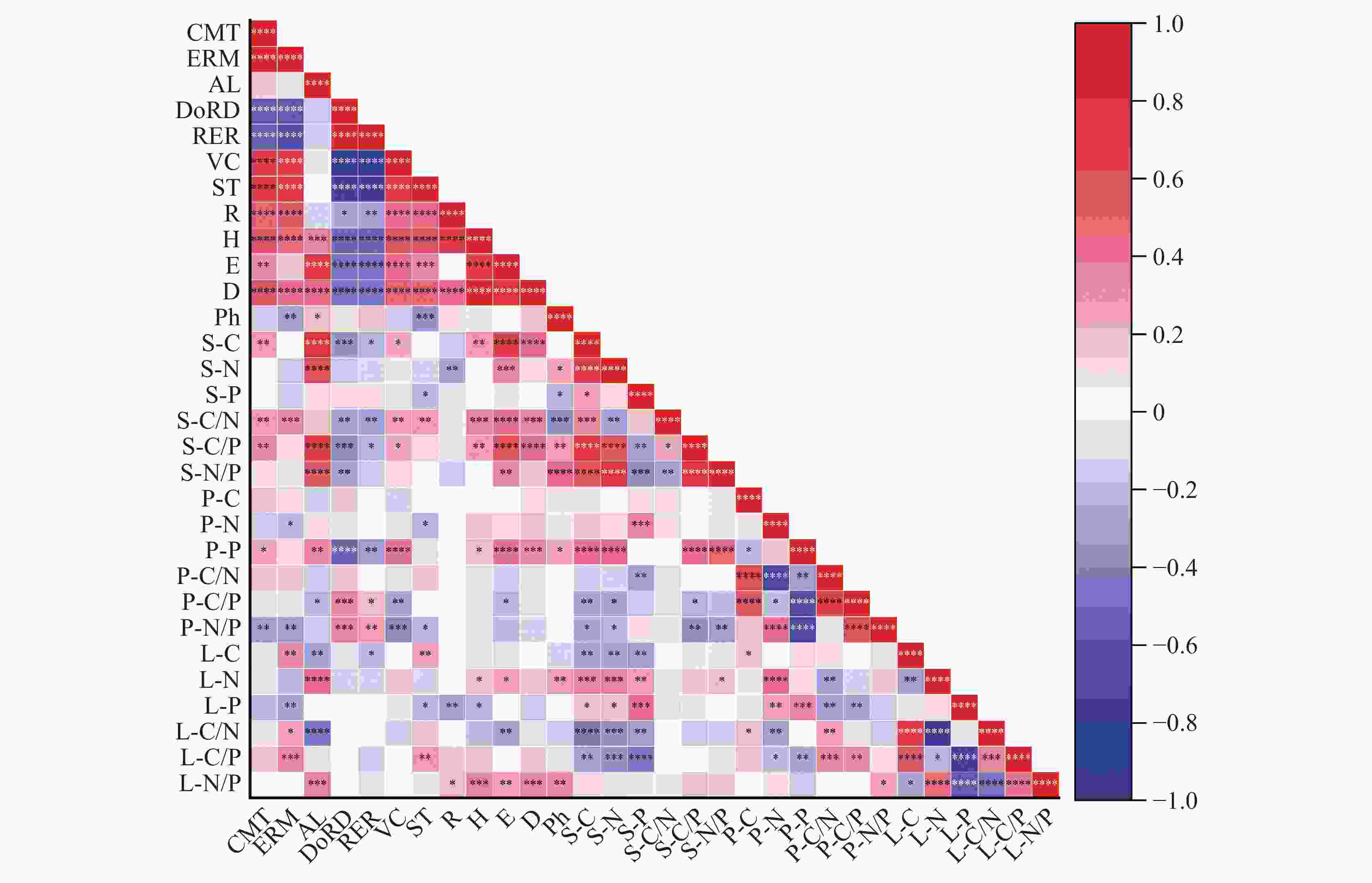
图 3 土壤–植物–凋落物C、N、P化学计量特征与环境因子的相关性
注:图中CMT为群落类型,ERM为生态修复措施,AL为海拔高度,DoRD为石漠化程度,RER为岩石裸露率,VC为植被覆盖度,ST为土壤厚度,R为丰富度指数,H为香农–威尔指数,E为均匀度指数,D为优势度指数;“*”表示显著性P<0.05,“**”表示显著性P<0.01,“***”表示显著性P<0.001,“****”表示显著性P<0.0001。
Figure 3. Correlation between the stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, and P in soil-plant-litter and environmental factors
Note: CMT represents community type, ERM represents ecological restoration measure, AL represents altitude, DoRD represents degree of rocky desertification, RER represents rock exposure rate, VC represents vegetation coverage, ST represents soil thickness, R represents richness index, H represents Shannon-Wiener index, E represents evenness index, and D represents dominance index. “*” indicates significance with P < 0.05, “**” indicates significance with P < 0.01, “***” indicates significance with P < 0.001, and “****” indicates significance with P < 0.0001.
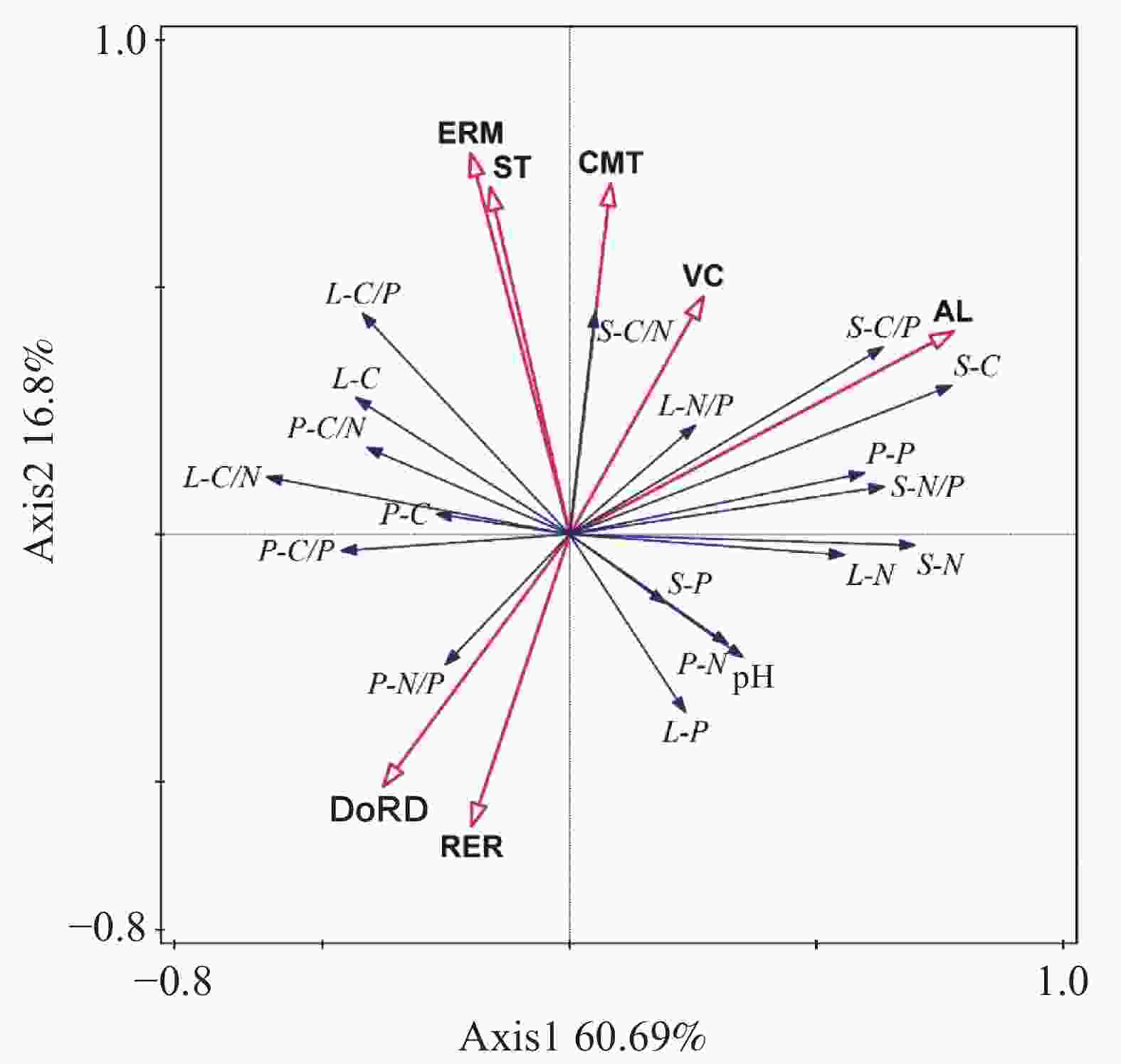
图 4 土壤-植物-凋落物C、N、P及化学计量比与主要环境因子的RDA分析
注:图中CMT为群落类型,ERM为生态修复措施,AL为海拔高度,DoRD为石漠化程度,RER为岩石裸露率,VC为植被覆盖度,ST为土壤厚度。
Figure 4. RDA analysis of soil-plant-litter C, N, P and stoichiometric ratios with main environmental factors
Note: CMT represents community type, ERM represents ecological restoration measure, AL represents altitude, DoRD represents degree of rocky desertification, RER represents rock exposure rate, VC represents vegetation coverage, ST represents soil thickness.
表 1 样点概况信息
Table 1. Basic information of sample plots
群落
名称群落
类型经度 纬度 海拔/m 石漠化
程度生态修
复措施pH 岩石裸
露率/%植被覆
盖度/%土壤厚
度/cm小叶栒子–旱茅群落 草地1 100°10′32.36″E 26°39′56.56″N 2612 中度 无措施 6.34±0.02ab 60 28 6 矮生胡枝子–西南野古草群落 草地2 100°10′31.68″E 26°39′55.79″N 2677 中度 无措施 6.18±0.10b 42 31 8 西南野古草群落 草地3 100°10′17.72″E 26°39′24.54″N 2648 重度 无措施 6.08±0.03b 52 25 15 刺叶高山栎–西南野古草群落 灌草1 100°16′59.78″E 27°02′15.11″N 3049 轻度 无措施 6.61±0.06a 35 51 15 刺叶高山栎–狼毒群落 灌草2 100°16′59.82″E 27°02′13.18″N 3040 中度 无措施 6.02±0.13b 32 40 8 帽斗栎–西南野古草群落 灌草3 100°17′22.74″E 27°01′42.11″N 3090 重度 无措施 6.33±0.17ab 58 40 10 帽斗栎–西南野古草群落 灌草4 100°18′48.30″E 27°00′52.49″N 2795 重度 无措施 6.29±0.11ab 68 38 8 帽斗栎–灯心草群落 灌草5 100°18′50.58″E 27°00′49.19″N 2794 重度 无措施 6.45±0.08ab 65 35 8 刺柏–腋花杜鹃–西南野古草群落 乔灌草–柏1 100°10′13.08″E 26°39′36.89″N 2669 重度 植树造林 5.80±0.23c 51 29 15 刺柏–小叶栒子–西南野古草群落 乔灌草–柏2 100°10′11.52″E 26°39′35.87″N 2660 重度 植树造林 6.28±0.14ab 55 28 18 干香柏–川滇野丁香–西南野古草群落 乔灌草–柏3 100°10′36.11″E 26°39′49.36″N 2584 重度 植树造林 6.17±0.14b 56 25 9 干香柏–小叶栒子–西南野古草群落 乔灌草–柏4 100°10′33.51″E 26°39′44.65″N 2570 重度 植树造林 6.29±0.07ab 55 25 10 干香柏–小叶鼠李–西南野古草群落 乔灌草-柏5 100°13′4.04″E 26°42′33.89″N 2544 重度 植树造林 5.62±0.15cd 65 35 8 云南松–西南野古草群落 纯松1 100°10′32.75″E 26°39′54.89″N 2637 轻度 封山育林 5.38±0.06d 8 52 30 云南松-西南野古草群落 纯松2 100°13′28.54″E 26°42′52.41″N 2600 轻度 封山育林 5.63±0.38cd 10 74 25 云南松–西南野古草群落 纯松3 100°18′45.49″E 27°01′26.42″N 2843 中度 植树造林 6.14±0.08ab 49 47 15 云南松–矮生胡枝子群落 纯松4 100°17′25.29″E 27°01′35.70″N 3078 轻度 植树造林 6.22±0.11ab 42 40 20 云南松–矮生胡枝子群落 纯松5 100°17′04.59″E 27°02′14.67″N 3057 轻度 植树造林 5.87±0.21bc 15 60 25 云南松–高山栎–云南草沙蚕群落 乔灌草–松1 100°16′57.52″E 27°02′11.38″N 3084 轻度 封山育林 5.39±0.05d 25 60 20 云南松–高山栎–云南草沙蚕群落 乔灌草–松2 100°16′57.29″E 27°02′9.92″N 3060 中度 封山育林 5.68±0.07d 42 48 20 云南松–帽斗栎–羊茅群落 乔灌草-松3 100°17′26.55″E 27°01′34.91″N 3080 轻度 封山育林 6.18±0.18b 20 60 18 云南松–帽斗栎–羊茅群落 乔灌草–松4 100°17′17.36″E 27°01′40.27″N 3070 中度 封山育林 5.77±0.05cd 41 42 18 云南松–柊树–西南野古草群落 乔灌草–松5 100°18′42.20″E 27°01′9.08″N 2821 中度 植树造林 6.02±0.10b 40 44 13 注:群落类型数字1~3与1~5表示在该群落类型内的每一个群落样点,与图1和图2中的数字相对应;“abcd”表示显著性差异(P<0.05)。
Note: The numbers 1 to 3 and 1 to 5 in community succession stages represent each community sample point within that succession stage and correspond to the numbers in Figure 1 and 2; “abcd” indicates significant differences (P < 0.05). -
[1] James J. Elser, Matthew E. S. Bracken, Elsa E. Cleland, Daniel S. Gruner, W. Stanley Harpole, Helmut Hillebrand, Jacqueline T. Ngai, Eric W. Seabloom, Jonathan B. Shurin, Jennifer E. Smith. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary production in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Ecology Letters, 2007, 10(12): 1135-1142. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01113.x [2] Sterner Robert W, James J Elser. Ecological stoichiometry: The biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2002. [3] 刘娜, 喻理飞, 赵庆, 武亚楠, 严令斌. 喀斯特高原石漠化区次生林叶片–凋落物–土壤连续体碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(3): 681-688.LIU Na, YU Lifei, ZHAO Qing, WU Yanan, YAN Lingbin. C∶N∶P stoichiometry of leaf-litter-soil continuum in secondary forests of the rocky desert regions of the karst plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2020, 26(3): 681-688. [4] LIN Degen, HAN Yu, FANG Lian, WANG Jing’ai, ZHU A-Xing and YUE Yaojie. Quantifying the hazardous impacts of human-induced land degradation on terrestrial ecosystems: A case study of karst areas of south China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75: 1-18. [5] 胡林安, 邱江梅, 李强. 云南岩溶断陷盆地植被演替土壤碳氮磷化学计量学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(6): 1213-1223.HU Lin'an, QIU Jiangmei, LI Qiang. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in different stages of vegetation succession at karst graben basin of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(6): 1213-1223. [6] 陶慧敏, 孙宁骁, 温家豪, Umair Muhammad, 袁俊, 杜红梅, 刘春江. 滇南喀斯特地区灌木群落和人工林土壤元素化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(24): 9119-9130.TAO Huimin, SUN Ningxiao, WEN Jiahao, Umiar Muhammad, YUAN Jun, DU Hongmei, LIU Chunjiang. Characteristics of soil stoichiometry in native shrub and plantation communities in karst regions of Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(24): 9119-9130. [7] 岳祥飞, 李衍青, 刘 鹏. 广西岩溶区灌木林地凋落物–土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(5): 1106-1116.YUE Xiangfei, LI Yanqing, LIU Peng. Stoichiometric characteristics of C, N and P in soil and litter of shrublands in karst areas of Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(05): 1106-1116. [8] 吴丽芳, 王紫泉, 王妍, 刘云根, 杨波, 张叶飞. 喀斯特高原不同石漠化程度土壤C、N、P化学计量特征和酶活性的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(12): 2332-2340.WU Lifang, WANG Ziquan, WANG Yan, LIU Yungen, YANG Bo, ZHANG Yefei. Relationship between soil C, N, P stoichiometric characteristics and enzyme activity in karst plateau soils with different degree of rocky desertification[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(12): 2332-2340. [9] 张水琳, 马丽娜, 王妍, 李成荣, 刀明宽, 刘云根. 断陷盆地不同石漠化生态修复类型下土壤碳氮磷化学计量及酶活性特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(4): 69-74.ZHANG Shuilin, MA Lina, WANG Yan, LI Chengrong, DAO Mingkuan, LIU Yungen. Characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus enzyme stoichiometry and activity under different fcological restoration types of rocky desertificaton in faut basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservaton, 2023, 30(4): 69-74. [10] 王亚娟, 陈云明, 孙亚荣, 赵敏, 薛文艳, 刘乐. 黄土丘陵区油松人工林植物器官—凋落物—土壤化学计量特征的季节变化[J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(4): 350-356.WANG Yajuan, CHEN Yunming, SUN Yarong, ZHAO Min, XUE Wenyan, LIU Le. Seasonal variation of plant organ-litter-soil stoichiometry in Pinus Tabulaeformis plantation in loess hilly region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(4): 350-356. [11] 陈飞, 刘方, 白晓永, 吴路华, 陈祖拥, 王金凤. 喀斯特山地不同微地貌下土壤碳氮磷空间异质性及生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(24): 10201-10213.CHEN Fei, LIU Fang, BAI Xiaoyong, WU Luhua, CHEN Zuyong, WANG Jinfeng. Spatial heterogeneity and ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus under different micro-geomorphology in karst mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(24): 10201-10213. [12] 蓝家程, 王俊贤, 王莎莎, 祁雪, 龙启霞. 喀斯特石漠化治理措施对土壤颗粒有机碳与团聚体有机碳的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(5): 773-783.LAN Jiacheng, WANG Junxian, WANG Shasha, QI Xue, LONG Qixia. Impact of controlling karst rocky desertification on soil particulate organic carbon and aggregate-associated organic carbon[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(5): 773-783. [13] LIU Liling, HE Ting, ZHU Ninghua, PENG Yuanying, GAO Xiaoqian, LIU Zongxin, DANG Peng. Effects of Afforestation Patterns on Soil Nutrient and Microbial Community Diversity in Rocky Desertification Areas[J]. Forests, 2023,14(12): 2370. doi: 10.3390/f14122370 [14] 袁成军, 熊康宁, 容丽, 翁应芳. 喀斯特石漠化生态恢复中的生物多样性研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(3): 336-345.YUAN Chengjun, XIONG Kangning, RONG Li, WENG Yingfang. Research progress on the biodiversity during the ecological restoration of karst rocky desertification[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(3): 336-345. [15] 王克林, 岳跃民, 陈洪松, 吴协保, 肖峻, 祁向坤, 张伟, 杜虎. 喀斯特石漠化综合治理及其区域恢复效应[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7432-7440.WANG Kelin, YUE Yuemin, CHEN Hongsong, WU Xiebao, XIAO Jun, QI Xiangkun, ZHANG Wei, DU Hu. The comprehensive treatment of kart rocky desertification and its regional restoration eflects[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7432-7440. [16] ZHENG Wei, GUO Xiaobin, ZHOU Ping, TANG Li, LAI Jiaxin, DAI Yuting, YAN Wende, WU Jinshui. Vegetation restoration enhancing soil carbon sequestration in karst rocky desertification ecosystems: A meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 370: 122530. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122530 [17] XIAO Qiang, XIAO Yang, LIU Yuanliu, TAO Jianping. Driving forest succession in karst areas of Chongqing municipality over the past decade[J]. Forest Ecosystems, 2020, 7(3): 1-11. [18] 李森, 魏兴琥, 张素红, 李红兵, 王明刚, 罗红波, 王金华. 典型岩溶山区土地石漠化过程: 以粤北岩溶山区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(3): 674-684.LI Sen, WEI Xinghu, ZHANG Suhong, LI Hongbing, WANG Minggang, LUO Hongbo, WANG Jinhua. The processes of land rocky desertification in typical karst mountain area: A case study in the karst mountain area of North Guangdong[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(3): 674-684. [19] TANG Jing, TANG Xiaoxin, QIN Yangmei, HE Qiushun, YI Yin, JI Zhiliang. Karst rocky desertification progress: Soil calcium as a possible driving force[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 1250-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.242 [20] 熊康宁, 黎平, 周忠发. 喀斯特石漠化的遥感: GIS典型研究: 以贵州省为例[M] . 北京: 地质出版社, 2002. [21] 曾昭霞, 王克林, 刘孝利, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 杜虎. 桂西北喀斯特森林植物–凋落物–土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(7): 682-693. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0065ZENG Zhaoxia, WANG Kelin, LIU Xiaoli, ZENG Fuping, SONG Tongqing, PENG Wanxia, ZHANG Hao, DU Hu. Stoichiometric characteristics of plants, litter and soils in karst plant communities of Northwest Guangxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(7): 682-693. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0065 [22] SUN Yuan, WANG Cuiting, CHEN Xinli, LIU Shirong. Phosphorus additions imbalance terrestrial ecosystem C∶N∶P stoichiometry[J]. Global Change Biology, 2022, 28(24): 7353-7365. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16417 [23] 董晓蕾, 王元忠, 张金渝, 金航, 张霁. 植物氮磷化学计量特征及其在药用植物研究中的应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(6): 1671-1677.DONG Xiaolei, WANG Yuanzhong, ZHANG Jinyu, JIN Hang, ZHANG Ji. Nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in plants and its application to research on medicinal plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(6): 1671-1677. [24] 张子琦, 焦菊英, 陈同德, 陈玉兰, 林红, 徐倩, 程玉卓, 赵文婷. 拉萨河流域中下游洪积扇土壤养分评价[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(11): 2082-2096.ZHANG Ziqi, JIAO Juying, CHEN Tongde, CHEN Yulan, LIN Hong, XU Qian, CHENG Yuzhuo, ZHAO Wenting. Soil nutrient evaluation of alluvial fan in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River Basin[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(11): 2082-2096. [25] 陈秋帆, 卢琦, 王妍, 刘云根. 西南石漠化区林下土壤养分特征及差异性[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(2): 290-300.CHEN Qiufan, LU Qi, WANG Yan, LIU Yungen. Nutrient characteristics and differences of forest soil in rocky desertification areas of Southwest China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(2): 290-300. [26] 郑帷婕, 包维楷, 辜彬, 何晓, 冷俐. 陆生高等植物碳含量及其特点[J]. 生态学杂志, 2007,26(3): 307-313.ZHENG Weijie, BAO Weikai, GU Bin, HE Xiao, LENG li. Carbon concentration and its characteristics in terrestrial higher plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(3): 307-313. [27] DUAN Xiangguang. Stoichiometric characteristics of woody plant leaves and responses to climate and soil factors in China[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(9): e0291957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291957 [28] 武燕, 李歆玉, 张奕婷, 丁波, 张运林, 符裕红, 刘讯. 西南喀斯特地区不同龄组马尾松人工林枯落物碳氮磷化学计量特征及其影响因子[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2024, 46(2): 87-94.WU Yan, LI Xinyu, ZHANG Yiting, DING Bo, ZHANG Yunlin, FU Yuhong, LIU Xun. Litter carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics and their influencing factors of Pinus massoniana plantation with different age groups in karst region of southwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2024, 46(2): 87-94. [29] 喻林华, 方晰, 项文化, 石俊, 刘兆丹, 李雷达. 亚热带4种林分类型凋落物层和土壤层的碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(10): 10-21.YU Linhua, FANG Xi, XIANG Wenhua, SHI Jun, LIU Zhaodan, LI Leida. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in litter layer and soil layer of four subtropical forest types[J]. Forestry Science, 2016, 52(10): 10-21. [30] KANG Hongzhang, XIN Zaijun, Björn Berg, Paul Burgess, LIU Qunlun, LIU Zhicheng, LI Zhaohua, LIU Chunjiang. Global pattern of leaf litter nitrogen and phosphorus in woody plants[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2010, 67(8): 811. doi: 10.1051/forest/2010047 [31] 王霖娇, 汪攀, 盛茂银. 西南喀斯特典型石漠化生态系统土壤养分生态化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(18): 6580-6593.WANG Linjiao, WANG Pan, SHENG Maoyin. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil nutrient elements and its influencing factors in typical karst rocky desertification ecosystems, Southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(18): 6580-6593. [32] 杨全, 陈志飞, 周俊杰, 赖帅彬, 简春霞, 王智, 徐炳成. 黄土丘陵区草地植被群落优势种叶片功能性状对氮磷添加的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(11): 3697-3706.YANG Quan, CHEN Zhifei, ZHOU Junjie, LAI Shuaibin, JIAN Chunxia, WANG Zhi, XU Bingcheng. Responses of leaf functional traits of dominant plant species in grassland communities to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in loess hilly-gully region[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(11): 3697-3706. [33] 盛茂银, 刘洋, 熊康宁. 中国南方喀斯特石漠化演替过程中土壤理化性质的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6303-6313. doi: 10.5846/stxb201305080979SHENG Maoyin, LIU Yang, XIONG Kangning. Response of soil physical-chemical properties to rocky desertification succession in South China Karst[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 6303-6313. doi: 10.5846/stxb201305080979 [34] LIANG Yueming, PAN Fujing, JIANG Zhongcheng, LI Qiang, PU Junbing, LIU Kunping. Accumulation in nutrient acquisition strategies of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant roots in poor and heterogeneous soils of karst shrub ecosystems[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22: 1-12. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03514-y [35] GENG Yuanyuan, PAN Shang, ZHANG Lin, QIU Jingjing, HE Kun, GAO Hongjian, LI Zhen, TIAN Da. Phosphorus biogeochemistry regulated by carbonates in soil[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 214(2): 113894. [36] 陈浏寰, 覃英凤, 王紫莹, 黄德周, 张苑, 梁建宏, 朱婧. 土地利用方式下岩溶湿地土壤无机磷形态特征及分析方法适用性探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6): 845-853.CHEN Liuhuan, QIN Yingfeng, WANG Ziying, HUANG Dezhou, ZHANG Yuan, LIANG Jianhong, ZHU Jing. Occurrence forms of inorganic phosphorus in soils of karst wetland under different landuses and comparison of two analysis methods[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 845-853. [37] TIAN Hanqin, CHEN Guangsheng, ZHANG Chi, Melillo Jerry M, Hall Charles A S. Pattern and variation of C∶N∶P ratios in China's soils: A synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98: 139-151. [38] Reich P B, Oleksyn J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(30): 11001-11006. [39] 陈柯豪, 杜红梅, 刘春江. 云南喀斯特断陷盆地典型群落植物生态化学计量学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6): 883-893.CHEN Kehao, DU Hongmei, LIU Chunjiang. Characteristics of leaf ecological stoichiometry in typical plant communities in karst fault-depression basins of Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 883-893. [40] 张万年, 杨子, 严玉鹏, 王小明, 殷辉, 徐仁扣, 谭文峰, 冯雄汉. 土壤有机磷的矿化及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2025, 62(2): 334-347.ZHANG Wannian, YANG Zi, YAN Yupeng, WANG Xiaoming, YIN Hui, XU Renkou, TAN Wenfeng, FENG Xionghan. Research progress on soil organic phosphorus mineralization and its regulation [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2025, 62(2): 334-347. [41] WEI Hongxu, HE Xingyuan. Foliar C/N stoichiometry in urban forest trees on a global scale[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2021, 32: 1429-1443. doi: 10.1007/s11676-020-01188-6 [42] 陈培云, 范弢, 何停, 户红红. 滇东岩溶高原不同恢复阶段云南松林叶片–枯落物–土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(6): 1549-1556.CHEN Peiyun, FAN Tao, HE Ting, HU Honghong. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in leaf litter soil of Pinus yunnanensis forest during different restoration stages in the karst plateau of eastern Yunnan[J]. Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 2022, 28(6): 1549-1556. [43] Megan EMcGroddy, Tanguy Daufresne, Lars O Hedin. Scaling of C∶ N∶P stoichiometry in forest worldwide: Implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios[J]. Ecology, 2004, 85(9): 2390-2401. doi: 10.1890/03-0351 [44] 王小平, 杨雪, 杨楠, 辛晓静, 曲耀冰, 赵念席, 高玉葆. 凋落物多样性及组成对凋落物分解和土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(17): 6264-6272.WANG Xiaoping, YANG Xue, YANG Nan, XIN Xiaojing, QU Yaobing, ZHAO Nianxi, GAO Yubao. Effects of litter diversity and composition on litter decomposition characteristics and soil microbial community[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(17): 6264-6272. [45] 李志安, 邹碧, 丁永祯, 曹裕松. 森林凋落物分解重要影响因子及其研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2004, 23(6): 77-83.LI Zhi'an, ZOU Bi, DING Yongzhen, CAO Yusong. Key factors of forest litter decomposition and research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2004, 23(6) : 77-83. [46] GUO Yun, HE Yuejun, WU Pan, WU Bangli, LIN Yan, HE Minhong, HAN Xu, XIA Tingting, SHEN Kaiping, KANG Liling, TAN Qiyu, REN Wenda, SUN Yan, LI Qing. The interspecific competition presents greater nutrient facilitation compared with intraspecific competition through AM fungi interacting with litter for two host plants in karst soil[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 15: 399-412. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtab110 [47] 张瑞香, 李强, 冯雪琦, 赵星辉, 郭二辉. 黄河下游4种典型草本植物与土壤碳、氮含量的关系研究[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2023, 57(1): 65-72, 95.ZHANG Ruixiang, LI Qiang, FENG Xueqi, ZHAO Xinghui, GUO Erhui. Relationship of carbon and nitrogen content of four typical herbs and soil in the lower reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2023, 57(1): 65-72, 95. [48] 肖琼, 赵丽芳, 陆来谋, 孙平安, 张 陶, 郭永丽. 漓江源头大溶江流域土壤理化性质[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5): 815-824.XIAO Qiong, ZHAO Lifang, LU Laimou, SUN Ping’an, ZHANG Tao, GUO Yongli. Spatial differences of soil physical and chemical properties in Darongjiang river watershed[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5): 815-824. [49] 王玉珏, 赵佳宁, 于洋, 张敬莉, 张钰舒, 冯金朝, 肖春旺. 不同纬度兴安落叶松林土壤碳氮含量特征及影响机制[J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 29(2): 13-20.WANG Yujue, ZHAO Jianing, YU Yang, ZHANG Jingli, ZHANG Yushu, FENG Jinchao, XIAO Chunwang. Characteristics and influence factors of soil carbon and nitrogen content in Gmelin larch forests at different latitudes[J]. Journal of MUC (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 29(2): 13-20. [50] 苏同庆, 崔婷婷, 张建兵, 罗为群, 胡宝清. 土地利用方式对广西平果喀斯特土壤碳氮磷全量与易利用组分的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(2): 311-320.SU Tongqing, CUI Tingting, ZHANG Jianbing, LUO Weiqun, HU Baoqing. Effect of land utilization patterns on total and easy-to-use components of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the karst area of Pingguo, Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(2): 311-320. -




 下载:
下载: