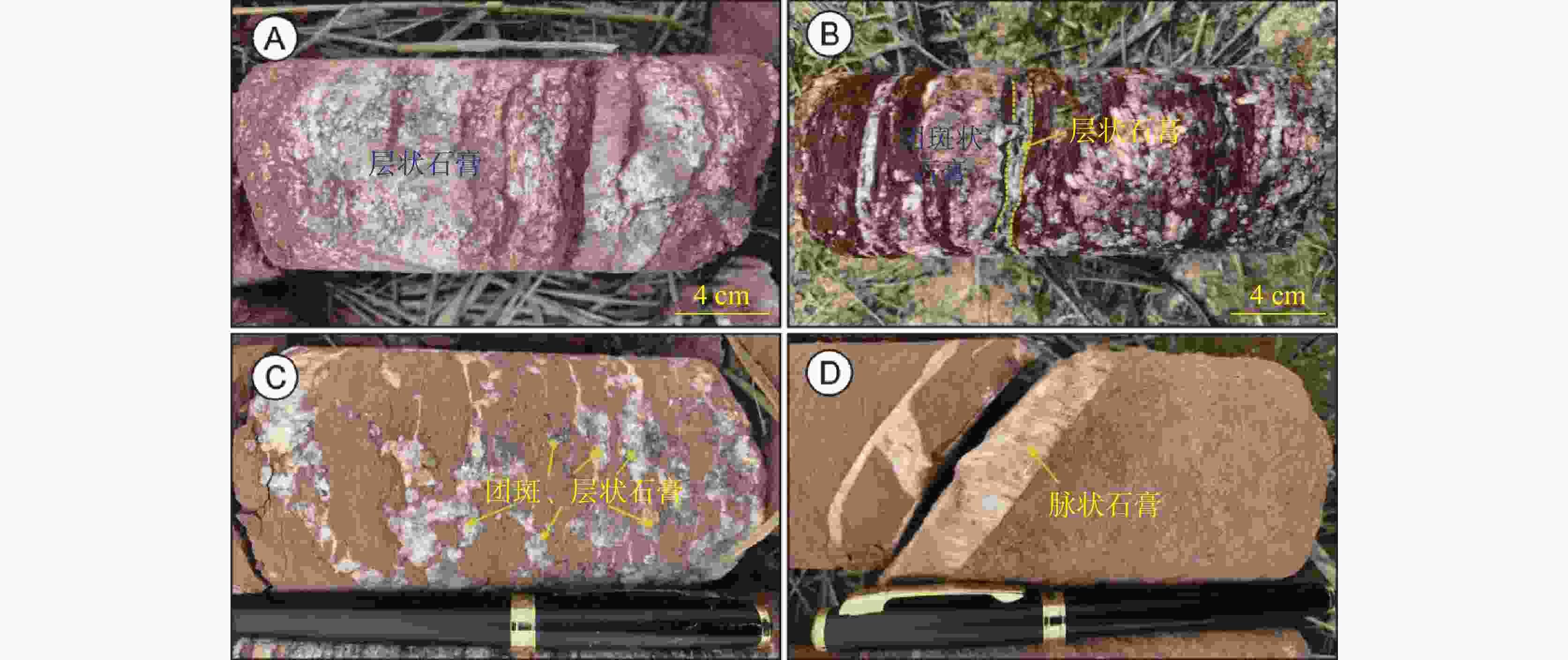
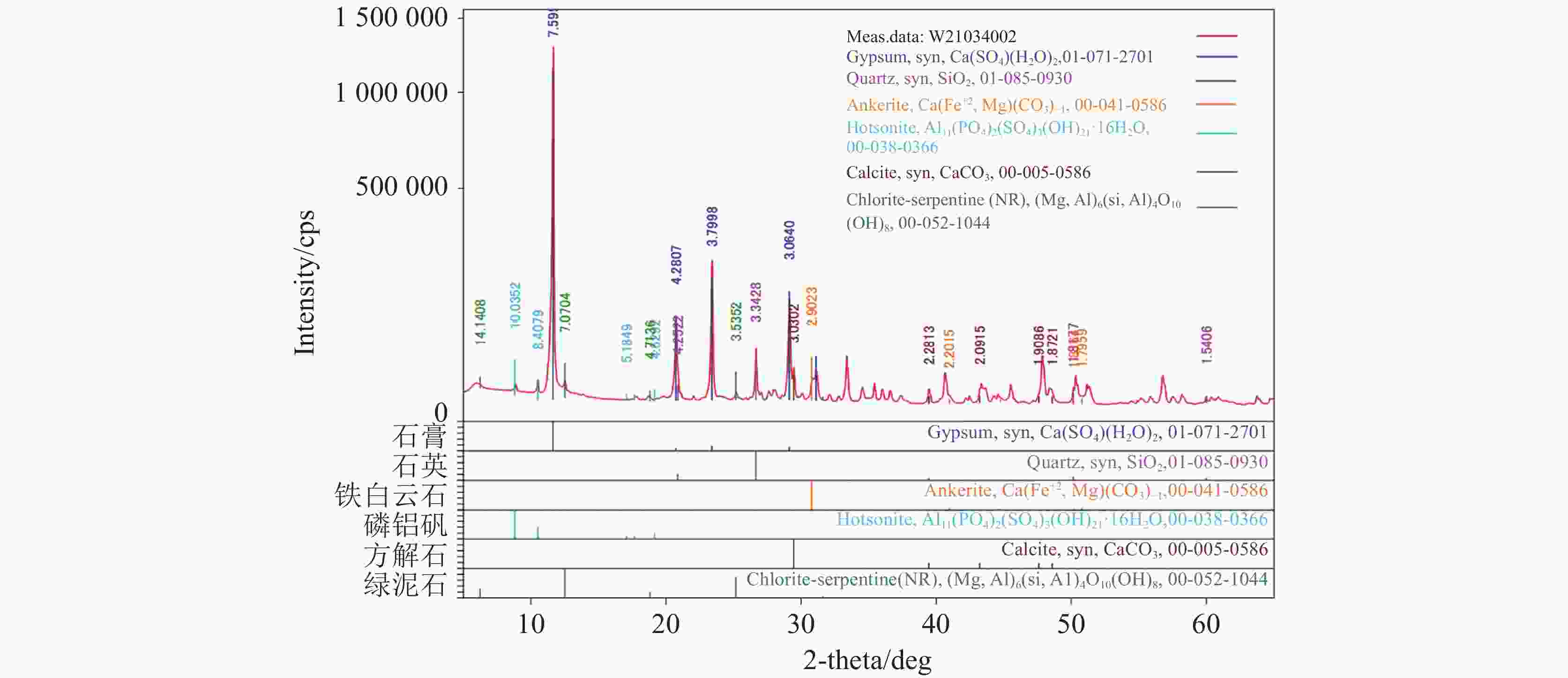
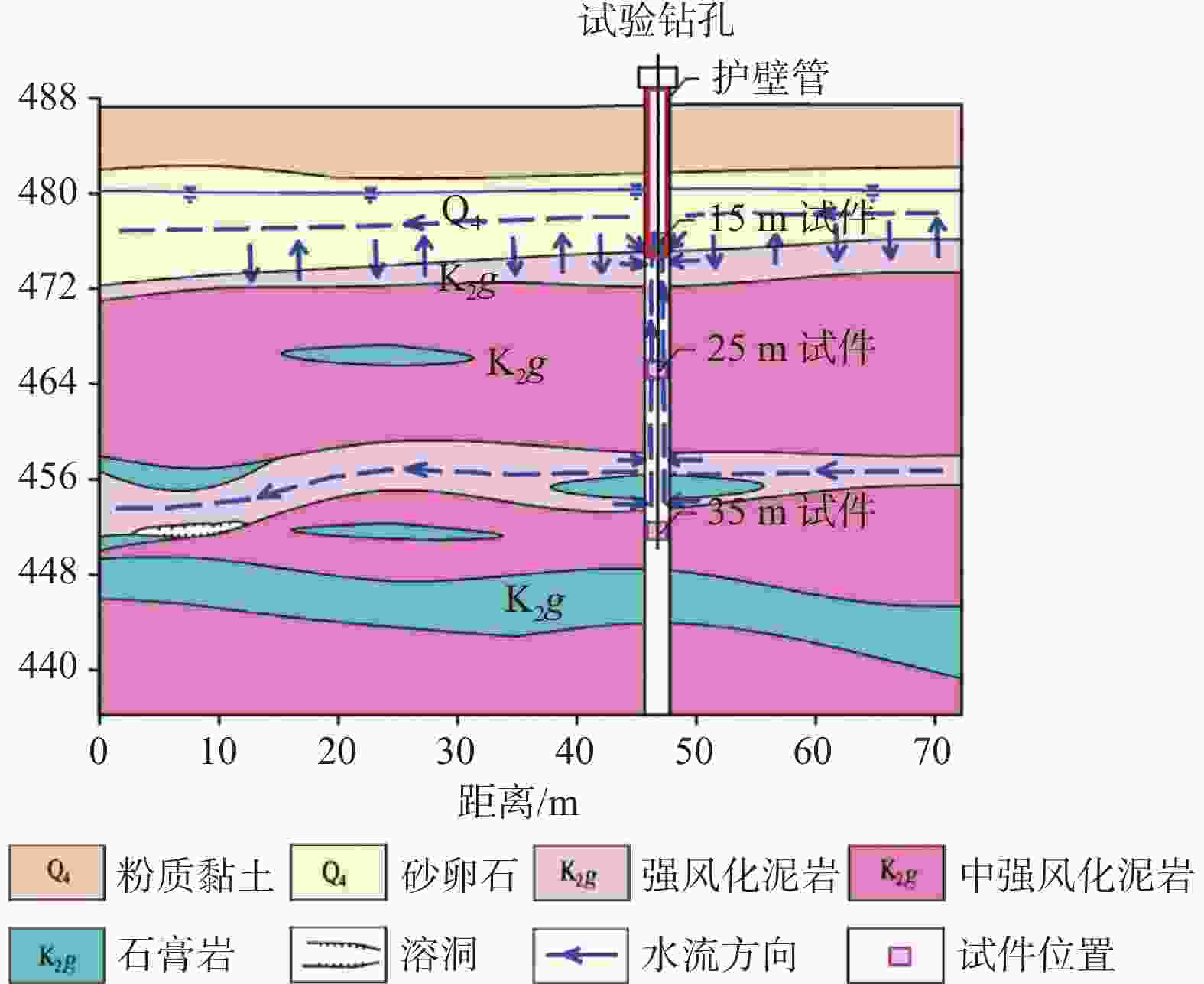
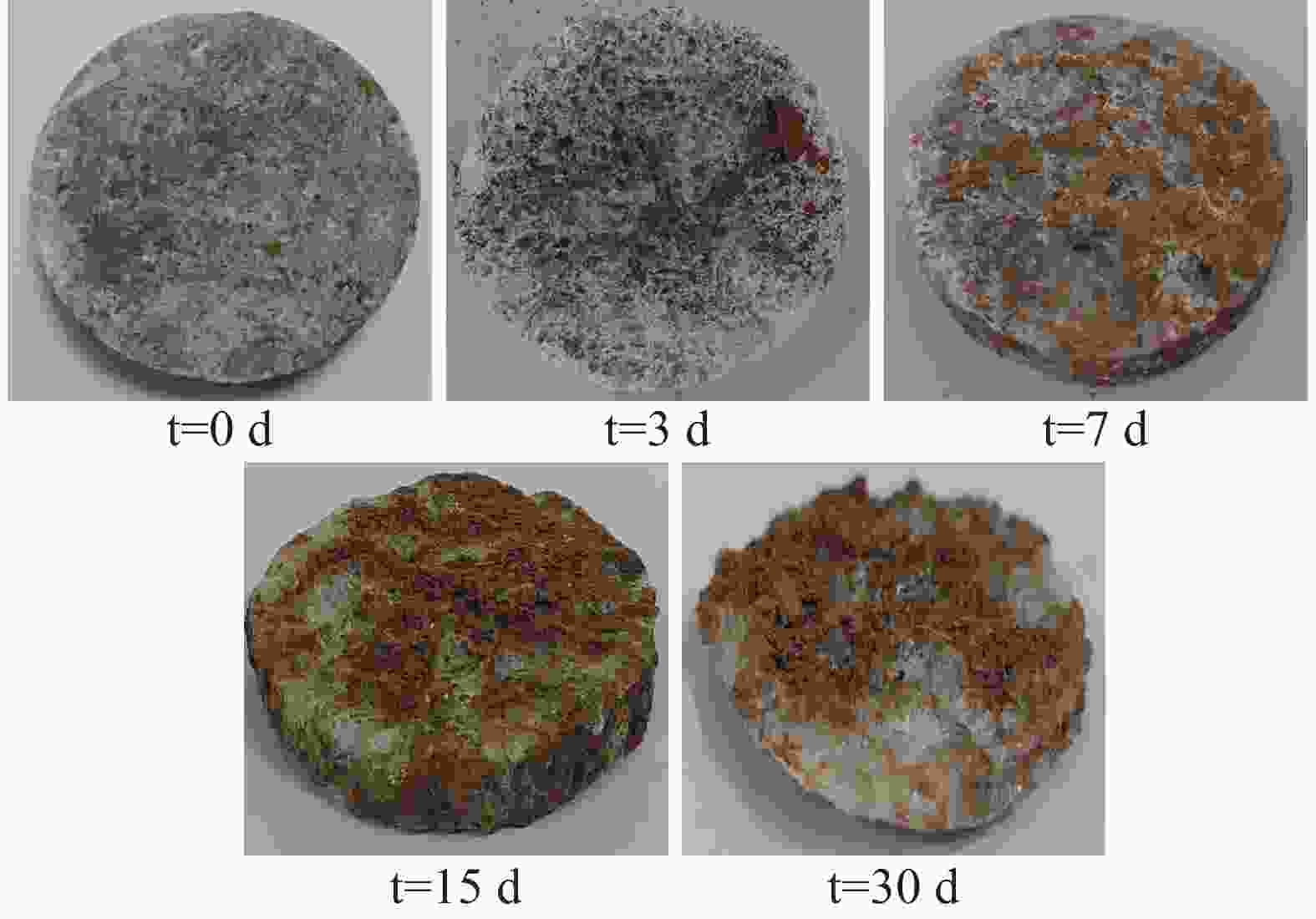
Study on an in-situ dissolution experiment of gypsum boreholes
-
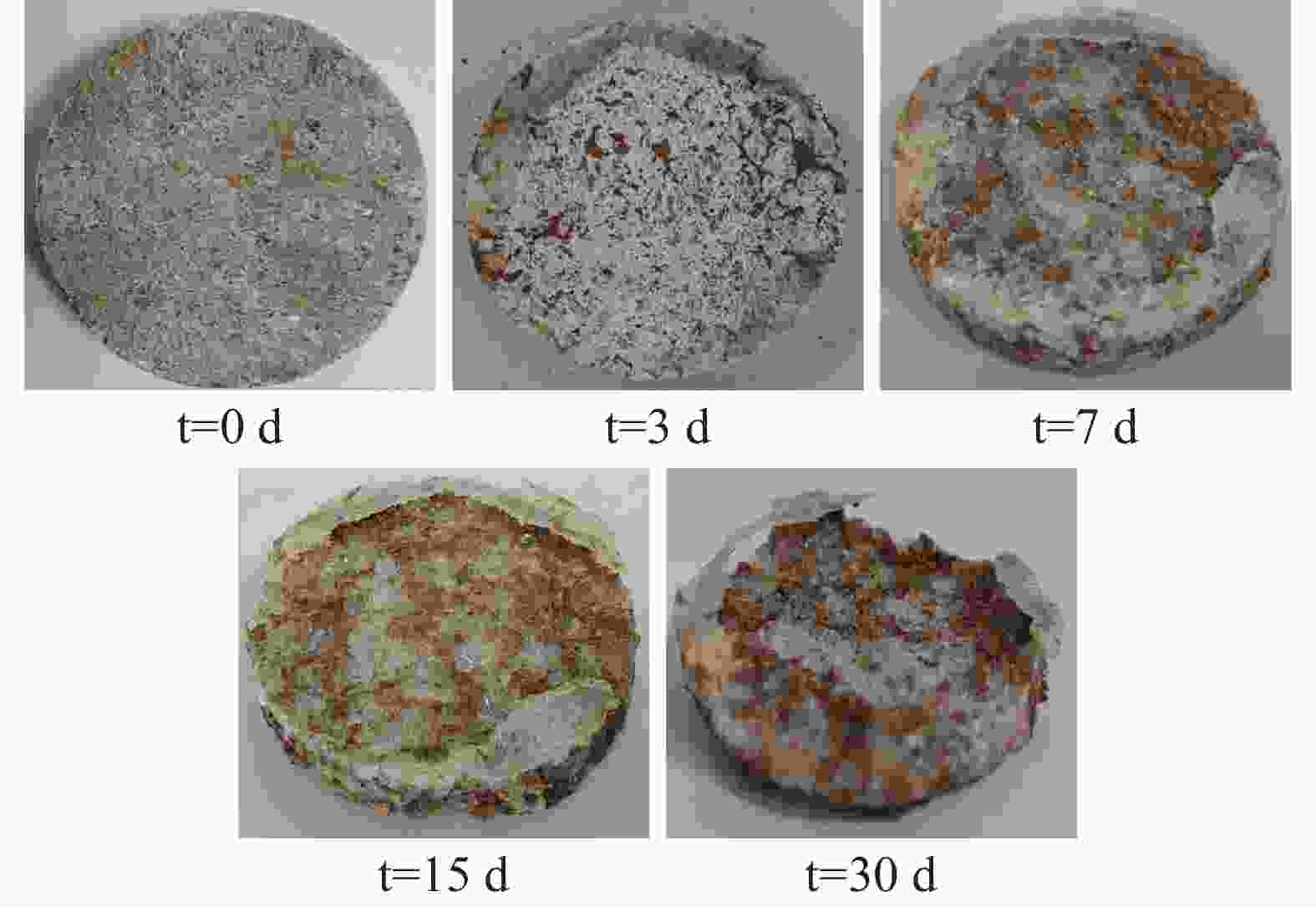
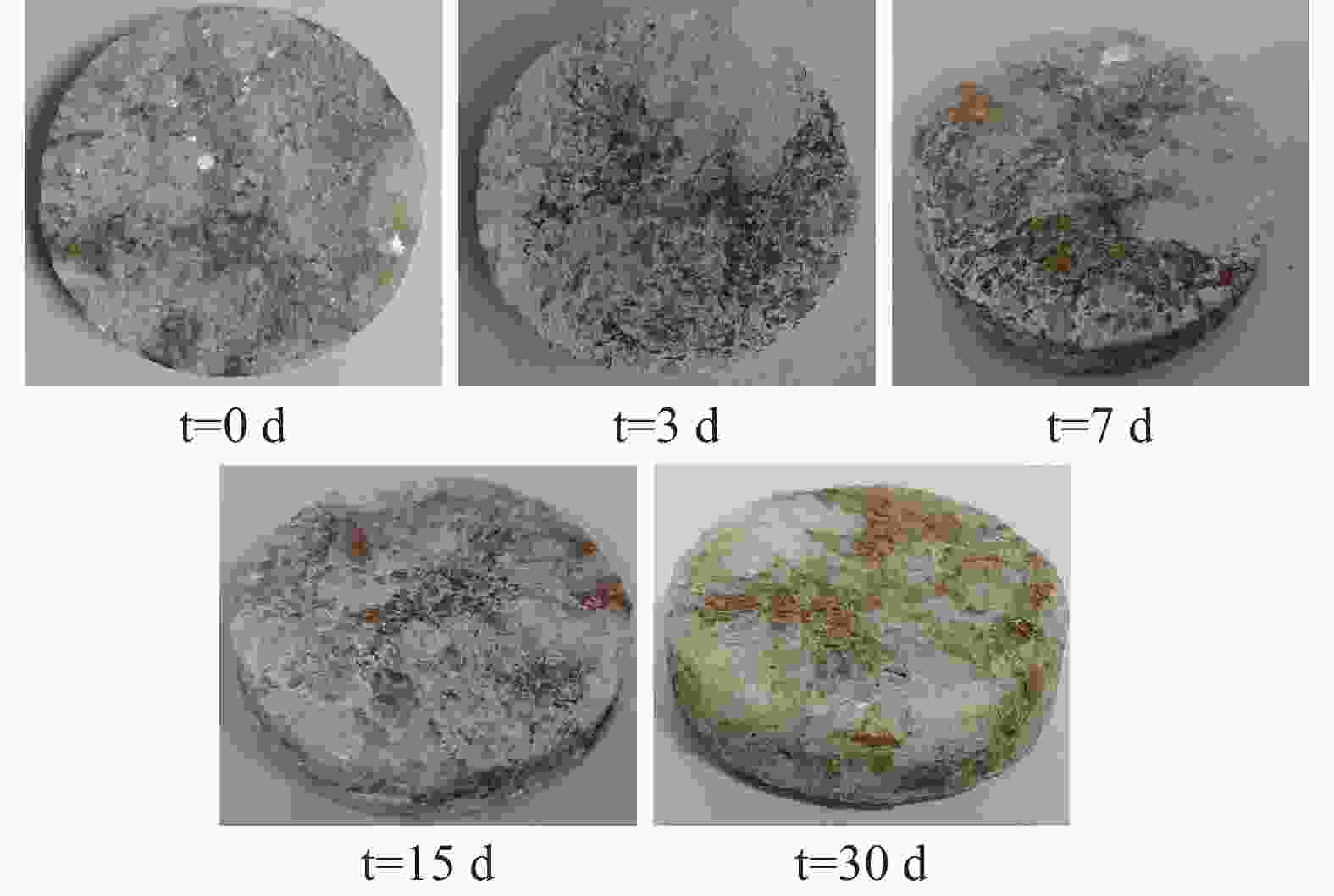
摘要: 以往针对石膏岩溶蚀试验多局限于室内环境,难以全面反映深部石膏溶蚀的真实情况。钻孔原位溶蚀试验方法是在石膏岩场地的钻孔内不同深度放置石膏岩标准试件,模拟石膏岩在原位水动力、水化学、温度等环境下的动态溶蚀过程。目前,国内鲜有公开该方法的研究成果,本文以白垩系灌口组石膏岩为研究对象,通过试验首次获取该石膏岩原位溶蚀宏观形态、溶蚀速率、水化学变化特征,深度剖析原位环境下石膏岩的溶蚀主控因素和机理。研究结果表明:钻孔原位环境中,石膏岩溶蚀的宏观特征、溶蚀速率具有显著垂向分层效应,主要受水动力条件控制,水化学影响次之;钻孔内15 m和25 m深度处试件溶蚀速率高达0.25 mm·d−1(约90 mm·a−1),而35 m深度处试件溶蚀速率仅为上述位置的1/4;15 m和25 m处试件的溶蚀主要受水动力物理驱动作用,溶蚀过程经历吸附饱水、浅层凹坑、横向并坑、纵深解体的四个阶段;35 m处试件在近似于封闭地下水环境下,溶蚀速率缓慢,主要受控于化学溶解。通过本试验研究,构建了石膏岩钻孔原位溶蚀试验流程和评价方法,可为石膏岩场地岩溶风险评价提供重要的参考依据。Abstract:
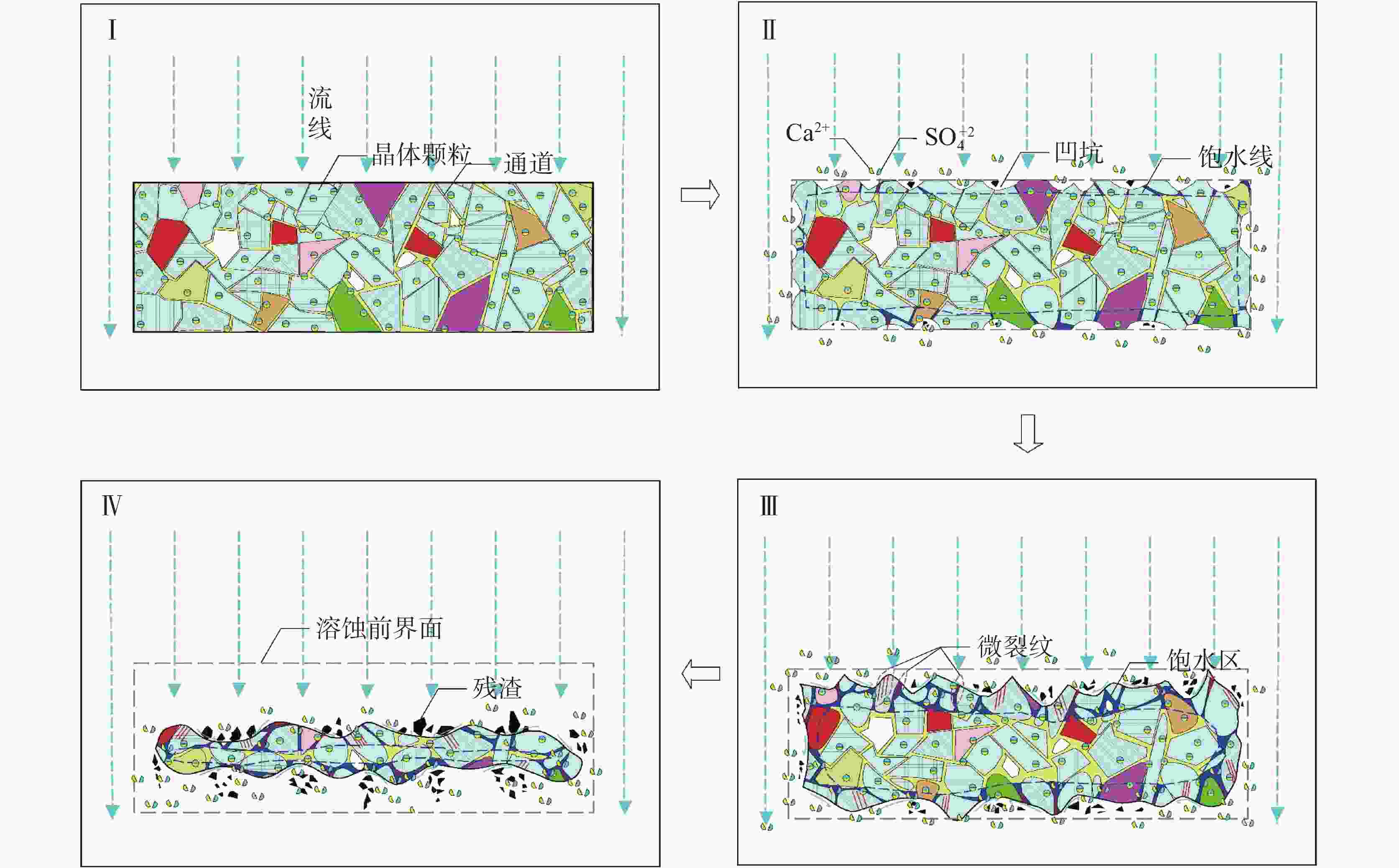
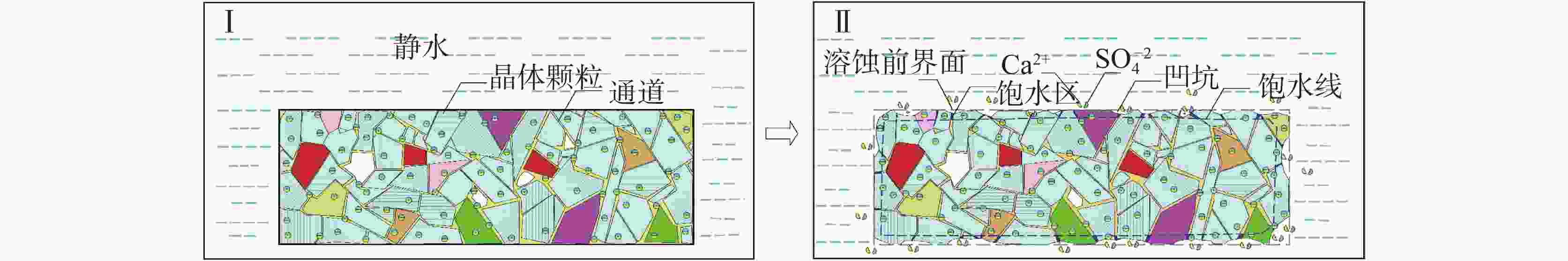
Gypsum is characterized by high solubility and a rapid dissolution rate, which can trigger geological disasters such as subsidence and collapse, especially under the influence of inappropriate human engineering activities like groundwater extraction and drainage. However, most research on gypsum has focused on itsn occurance in the marine sedimentary environments, with relatively few studies addressing gypsum in the lacustrine sedimentary settings. The latter is generally considered to exhibit rare karst phenomena and to occur on a smaller scale. The gypsum in the Cretaceous Guankou Formation (K2g) is a typical example of lacustrine sedimentary gypsum. Its dissolution has caused abnormal settlement of buildings constructed on it. However, most research on the dissolution of the gypsum has been limited to laboratory experiments, such as the static water and flowing water dissolution tests, which do not fully capture the actual dissolution conditions of gypsum. Some in-situ dissolution tests on gypsum have been carried out in Russia, Ukraine, Spain and Italy with the use of tablet or the MEM method in boreholes and cavities. But no in-situ dissolution research on gypsum has been conducted in China. In this study, three groups of standard gypsum (K2g) tablet specimen, packed in nylon bags, were suspended at depth of 15 m, 25 m and 35 m within the borehole. Steel pipe were used to prevent the upper sandy and gravel aquifer from directly entering to the borehole. This setup simulated the dynamic dissolution process of gypsum under the in-situ hydrodynamic, hydrochemical and temperature conditions representative of the real stratigraphy environment. After 3 days, 7 days, 15 days and 30 days, the specimens were retrieved from the borehole for measurement and observation, and the chemistry of groundwater was analyzed simultaneously. The tests showed that the specimens at the depths of 15 m and 25 m exhibited intense dissolution phenomena, while the specimens at the depth of 35 m showed only slight dissolution. After 30 days of in-site testing, the average mass loss rates of the specimens at 15 m and 25 m reached 73.9% and 73.7% respectively, with average dissolution rates of 1.16×10−2 g·cm−2·d−1 and 1.13×10−2 g·cm−2·d−1, respectively. The recession rates at 15 m and 25 m were 0.246 mm·d−1 and 0.245 mm·d−1, respectively. The average mass loss rate of the specimens at 35 m was only 18.4%, and the average dissolution rate was 0.39×10−2 g·cm−2·d−1, which was only a quarter of that of the specimens at 15 m and 25 m, and was comparable to the dissolution rate of the gypsum reported by other researchers in static water environments. This dissolution rate was much greater than that of gypsum specimens in boreholes measured by Calligaris C. The dissolution rates of the specimens at 15 m and 25 m initially increased and then decreased over time,while the dissolution rate of the specimens at 35m did not change significantly with time. Groundwater samples were collected from the borehole for chemical analysis both before and during the test. It was observed that the concentrations of SO$_4^{2-}$ and Ca2+ in the groundwater at 15 m and 35 m were lower than those at 25 m. Nevertheless, neither the concentration of SO$_4^{2-}$ nor that of Ca2+ reached saturation at any point during the experiment. The dissolution rate constants (K) at the site were approximately 0.030×10−5 to 0.114×10−5 m·s−1. Influenced by hydrogeological conditions at various depths, the rapid dissolution rate of gypsum was primarily controlled by mass transport driven by the hydraulic gradient, with surface reactions driven by ion concentration playing a secondary role. The dissolution processes of the specimens at 15 m and 25 m were affected by both mechanical erosion and chemical dissolution, progressing through four stages: adsorption and saturation, shallow pit formation, lateral pit merging, and deep disintegration. In contrast, the dissolution of the specimens at 35 m was mainly controlled by chemical dissolution and only underwent the first two stages: adsorption and saturation, and shallow pit formation. This in-situ dissolution experiment and evaluation method for gypsum supplements the existing dissolution data of gypsum in China, providing an important reference for karst risk assessment in gypsum-rich areas. -
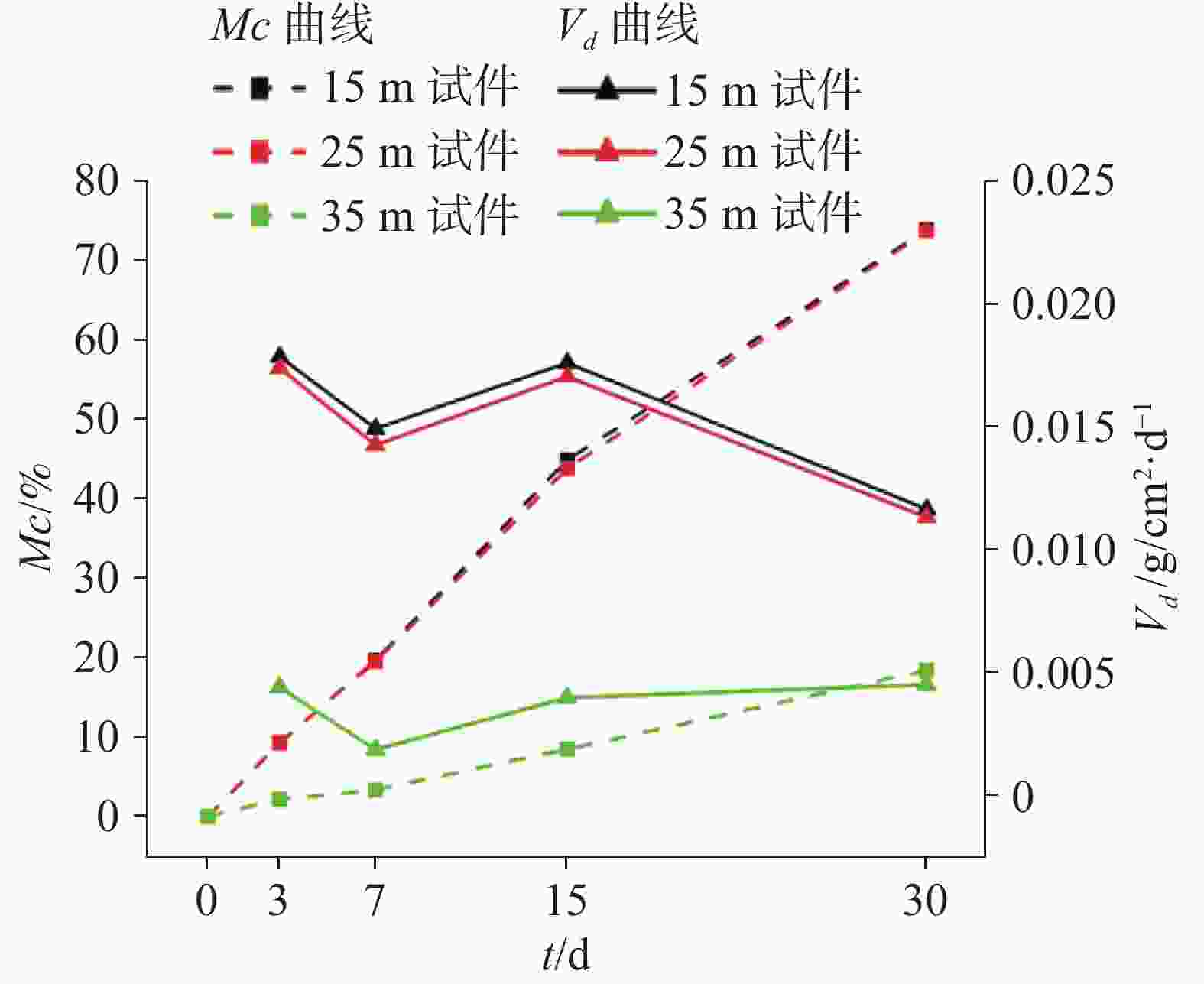
表 1 试件溶蚀平均质量变化统计表
Table 1. Statistics of average quality variation in specimen dissolution
试验
时间 t/d质量损失率 Mc/% 溶蚀速率Vd / ×10−2 g cm2·d−1 15 m 25 m 35 m 15 m 25 m 35 m 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 − − − 3 9.3 9.3 2.2 1.78 1.74 0.44 7 19.7 19.5 3.4 1.49 1.43 0.18 15 44.9 43.8 8.5 1.76 1.70 0.40 30 73.9 73.7 18.4 1.16 1.13 0.45 表 2 地下水化学特征统计表
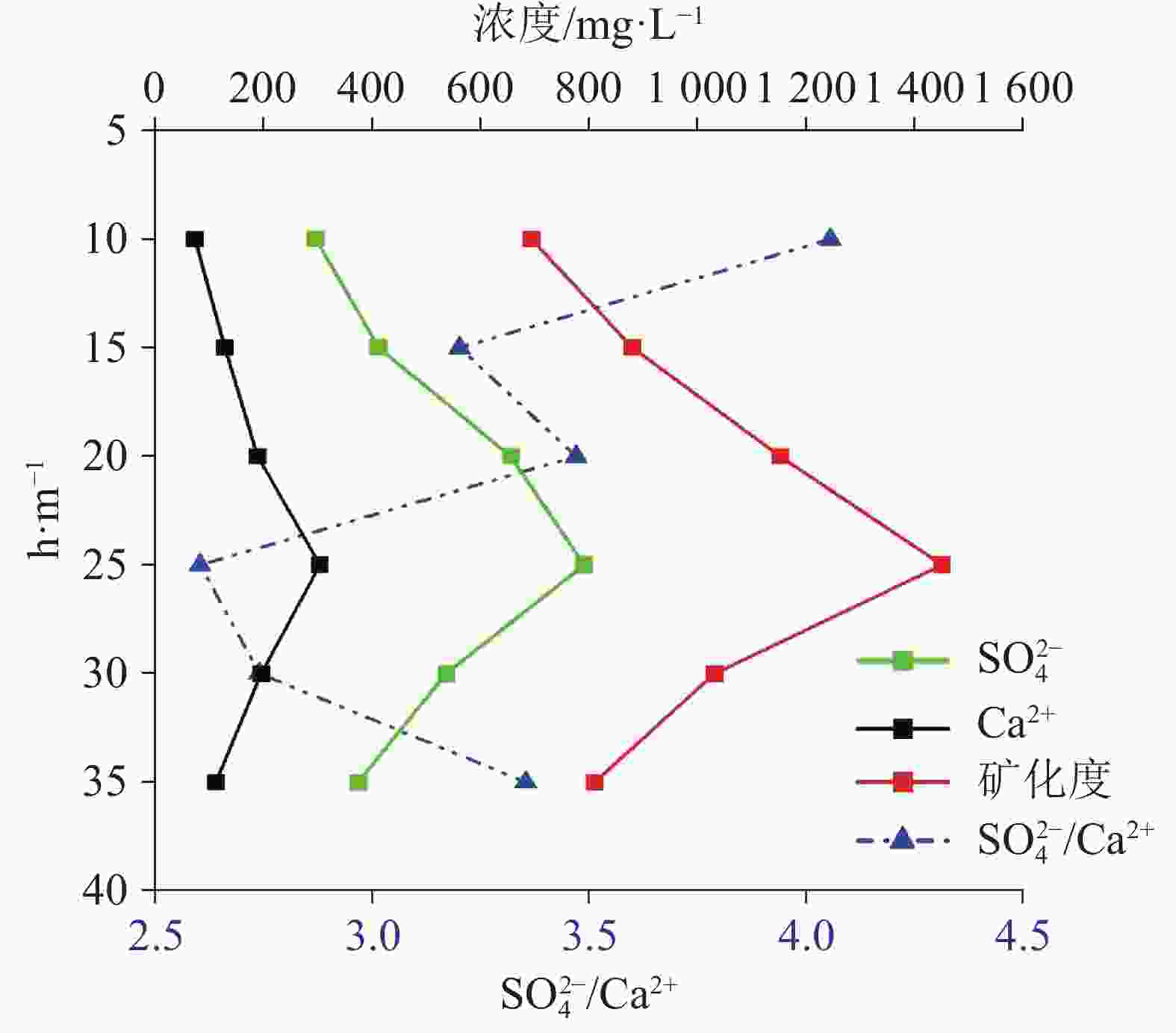
Table 2. Statistics of groundwater chemistry
取样
深度/mpH ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ /mg·L−1 Ca2+/mg·L−1 总矿化度/mg·L−1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$/Ca2+ 0 d 7 d 0 d 7 d 0 d 7 d 0 d 7 d 10 7.48 296 73 693 4.1 15 7.63 412 532 129 280 879 1098 3.2 1.9 20 8.06 655 189 1152 3.5 25 7.95 790 858 304 476 1450 1590 2.6 1.8 30 7.81 536 196 1030 2.7 35 7.32 374 428 112 306 809 1054 3.4 1.4 表 3 石膏岩溶蚀速率常数与径流速度统计表
Table 3. Statistics of dissolution rate constants and water velocity of gypsum
试件
环境dM×10−3
/kgdt×105
/sCs-C
/kg·m−3K×10−5/m·s−1 15 m 6.22 6.048 1.67 0.114 25 m 5.99 6.048 1.21 0.075 35 m 1.02 6.048 1.81 0.030 -
[1] Gutiérrez F, Ortí F, Gutiérrez M, Pérez-González A, Benito G, Prieto J G, Durán Valsero J J. The stratigraphical record and activity of evaporite dissolution subsidence in Spain[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2001, 16(1): 46-70. doi: 10.1007/BF03176226 [2] Cooper A H. Environmental problems caused by gypsum karst and salt karst in Great Britain[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2002, 17(2): 116-120. [3] Farrant A R, Cooper A H. Karst geohazards in the UK: the use of digital data for hazard management[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 2008, 41(3): 339-356. doi: 10.1144/1470-9236/07-201 [4] Schwendel A C, Cooper A H. Meander chute cutoff at an alluvial river facilitated by gypsum sinkholes[J]. Geomorphology, 2021, 393(3): 107944. [5] Doğan U. Land subsidence and caprock dolines caused by subsurface gypsum dissolution and the effect of subsidence on the fluvial system in the Upper Tigris Basin (between Bismil-Batman, Turkey)[J]. Geomorphology, 2005, 71(3/4): 389-401. [6] Johnson K S. Subsidence hazards due to evaporite dissolution in the United States[J]. Environmental geology: International journal of geosciences, 2005, 48(3): 395-409. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-1283-5 [7] Johnson K S. Evaporite karst in the USA[J]. Environmental geology, 2008, 53: 937-943. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0716-8 [8] 卢耀如, 张凤娥, 阎葆瑞, 郭秀红. 硫酸盐岩岩溶发育机理与有关地质环境效应[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.01.001LU Yaoru, ZHANG Fenge, YAN Baorui, GUO Xiuhong. Mechanism of karst development in sulphate rocks and its main Geo environmental Impacts[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2002, 23(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.01.001 [9] 王光亚, 施斌, 徐玉琳, 顾阿明. 南京石膏矿特大突水灾害机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 16(5): 651-656.Wang Guangya, Shi Bin, Xu Yulin, GU Aming. Case study and mechanism of water invasion hazard in Nanjing gypsum mine at deep depth[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(5): 651-656. [10] 张玲玲. 石膏原岩静水溶蚀时间-温度效应试验初步研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(2): 265-268. doi: 10.11932/karst20190211ZHANG Lingling. Preliminary experimental study on time-temperature effects of gypsum rock corrosion in static water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(2): 265-268. doi: 10.11932/karst20190211 [11] Pando L, Pulgar J A, Gutierrez-Claverol M. A case of man-induced ground subsidence and building settlement related to karstified gypsum (Oviedo, NW Spain)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68(2): 507-519. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1755-3 [12] Laouafa F, Guo J, Quintard M. Modeling of salt and gypsum dissolution: applications, evaluation of geomechanical hazards[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2019: 1-22. [13] 孟涛, 梁卫国, 陈跃都, 于永军. 层状盐岩溶腔建造过程中石膏夹层周期性垮塌理论分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, Z1: 3267-3273.MENG Tao, LIANG Weiguo, CHEN Yuedu, YU Yongjun. Theoretical analysis of periodic fracture for gypsum interlayer during construction of bedded salt cavern[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, Z1: 3267-3273. [14] Zaier I, Billiotte J, De Windt L, Charmoille A . The impact of common impurities present in gypsum deposits on in situ dissolution kinetics[J]. Environ Earth Sci, 2023, 82, 31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10710-4. [15] Feng P, Brand A S, Chen L, Bullard J W. In situ nanoscale observations of gypsum dissolution by digital holographic microscopy[J]. Chemical geology, 2017, 46025-36. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.04.008. [16] Meng T, Meng X, Zhang D H, Hu Y. Using micro-computed tomographyand scanning electron microscopy to assess the morphologicalevolution and fractal dimension of a salt-gypsum rock subjectedto a coupled thermal-hydrological-chemical environment[J]. Mar Petrol Geol, 2018, 98: 316-334. DOI: 10. 1016/j. marpe tgeo.2018. 8. 24. [17] 周其健, 郭永春, 屈智辉, 郑立宁, 许福周, 任跃勤. 某红层地基差异沉降原因分析[J]. 建筑科学, 2020, 36(11): 101-106.ZHOU Qijian, GUO Yongchun, QU Zhihui, ZHENG Lining, XU Fuzhou, REN Yueqin. Causes analysis of differential settlement of a red bed foundation[J]. Building Science, 2020, 36(11): 101-106. [18] 韩浩东, 王春山, 王东辉, 李鹏岳, 李华, 杨涛. 成都市白垩系灌口组富膏盐红层溶蚀特征与机理[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5): 768-782.HAN Haodong, WANG Chunshan, WANG Donghui, LI Pengyue, LI Hua, YANG Tao. Dissolution characteristics and mechanism of gypsum-salt-rich-red beds in Cretaceous Guankou formation in Chengdu[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5): 768-782. [19] 周其健. 成都隐伏石膏岩建筑地基异常沉降机理及处治技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021.Zhou Qijian. Study on mechanism and treatment technology of abnormal settlement of concealed gypsum rock building foundation in Chengdu[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021. [20] 周其健, 郭永春, 屈智辉, 郑立宁, 许福周, 谢强. 水热综合作用下钙芒硝盐岩强度等参数的衰减规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(4): 1019-1027.ZHOU Qijan, GUO Yongcun, QU Zhihui, ZHEN Lining, XU Fuqiang, XIE qiang. Strength decay law of glauberite salt rock with water and temperature[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(4): 1019-1027. [21] 徐文斌. 成都天府新区灌口组芒硝/石膏溶蚀规律研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020.Xu Wenbin. Study on dissolution of mirabilite/gypsum in Guankou Formation, Tianfu New Area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2020. [22] 钟志彬, 冯杰, 吕蕾, 周其健, 李思嘉, 薛昌汭. 红层石膏夹层静动水溶蚀特性试验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2025,44(1): 15-23.ZHONG Zhibin, FENG Jie, LYU Lei, ZHOU Qijian, LI Sijia, XUE Changrui. Experimental study on static and dynamic water dissolution characteristics of red layer gypsum interlayer[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2025,44(1):15-23. [23] 王子忠, 许模. 四川盆地含膏盐红层特征及坝基工程地质问题(I)[J]. 水利水电技术, 2011, 42(3): 10-12.Wang Zizhong, Xu Mo. Characteristics of red bed containing saline deposit and engineering geological issues of dam foundation in Sichuan Basin(I)[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2011, 42(3): 10-12. [24] 韩继伟. 某场地红层岩溶发育特征及工程影响研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015.HAN Jiwei. Study on Project Impact and Development Features of the Red layer of karst of the venue[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. [25] James A N, Cooper A H, Holliday D W. Solution of the gypsum cliff Permian, Middle Marl. by the River Ure at Ripon Parks, North Yorkshire[J]. Yorkshire Geol. 1981, 43, 433−450. [26] Klimchouk A B, Aksem S D. Hydrochemistry and solution rates in gypsum karst: case study from the Western Ukraine[J]. Environ Geology, 2005, 48: 307-319. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-1277-3 [27] Aljubouri Z A, Al-Kawaz H A. Dissolution rate of gypsum under different environments[J]. Iraqi Journal of Earth Sciences, 2007, 7(2): 11-18. [28] Calligaris C, Ghezzi L, Petrini R, Lenaz D, Zini L. Evaporite Dissolution Rate through an on-site Experiment into Piezometric Tubes Applied to the Real Case-Study of Quinis (NE Italy)[J]. Geosciences, 2019, 9(7): 298. doi: 10.3390/geosciences9070298 [29] Busetti A, Calligaris C, Zini L. Gypsum Dissolution Rate, New Data and Insights[A]//EuroKarst 2022, Málaga. Advances in Karst Science[C]. Springer, Cham.2023:207-213 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16879-6_30. [30] 魏玉峰, 聂德新. 第三系红层中石膏溶蚀特性及其对工程的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2005(2): 62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.02.013WEI Yufeng, NIE Dexin. The speciality of gypsum dissolution of the Neogene red clay and its influence to engineering[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2005(2): 62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.02.013 [31] Jin Q X, Perry L N, Bullard J W. Temperature dependence of gypsum dissolution rates[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 129, 105969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2019.105969. [32] Peruffo M, Mbogoro M M, Edwards M A, Unwin P R. Holistic approach to dissolution kinetics: linking direction-specific microscopic fluxes, local mass transport effects and global macroscopic rates from gypsum etch pit analysis[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2013, 15(6): 1956-65. doi: 10.1039/c2cp43555a -




 下载:
下载: