Causes of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and assessment of health risk to humans in the karst area of southeastern Chongqing
-
摘要: 岩溶水是重要的水资源,揭示其成因机制,开展质量评价及健康风险评估,对于岩溶水的合理开发利用与保护具有至关重要的意义。文章以渝东南岩溶水为研究对象,采用Gibbs图、多元统计分析、熵权水质指数(EWQI)和人类健康风险评估模型等方法研究该区域地下水水化学组成、水质状况,并开展健康风险评价。结果表明:(1)渝东南岩溶区地下水呈弱碱性,以HCO3-Ca型水为主;(2)水化学组分主要受控于水岩作用和人类活动,阳离子交换作用不明显;(3)渝东南岩溶区地下水总体水质优良,EWQI值范围为7.29~182.68,均值为21.83;(4)健康风险评估结果表明渝东南岩溶区个别地下水的TFe和${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$超过儿童非致癌风险的可接受限值。研究成果可为渝东南岩溶水资源的开发利用和保护提供基础数据,也能为类似岩溶区地下水的研究提供可借鉴的方法手段。
-
关键词:
- 水化学 /
- 熵权水质指数(EWQI) /
- 人类健康风险 /
- 岩溶水 /
- 渝东南
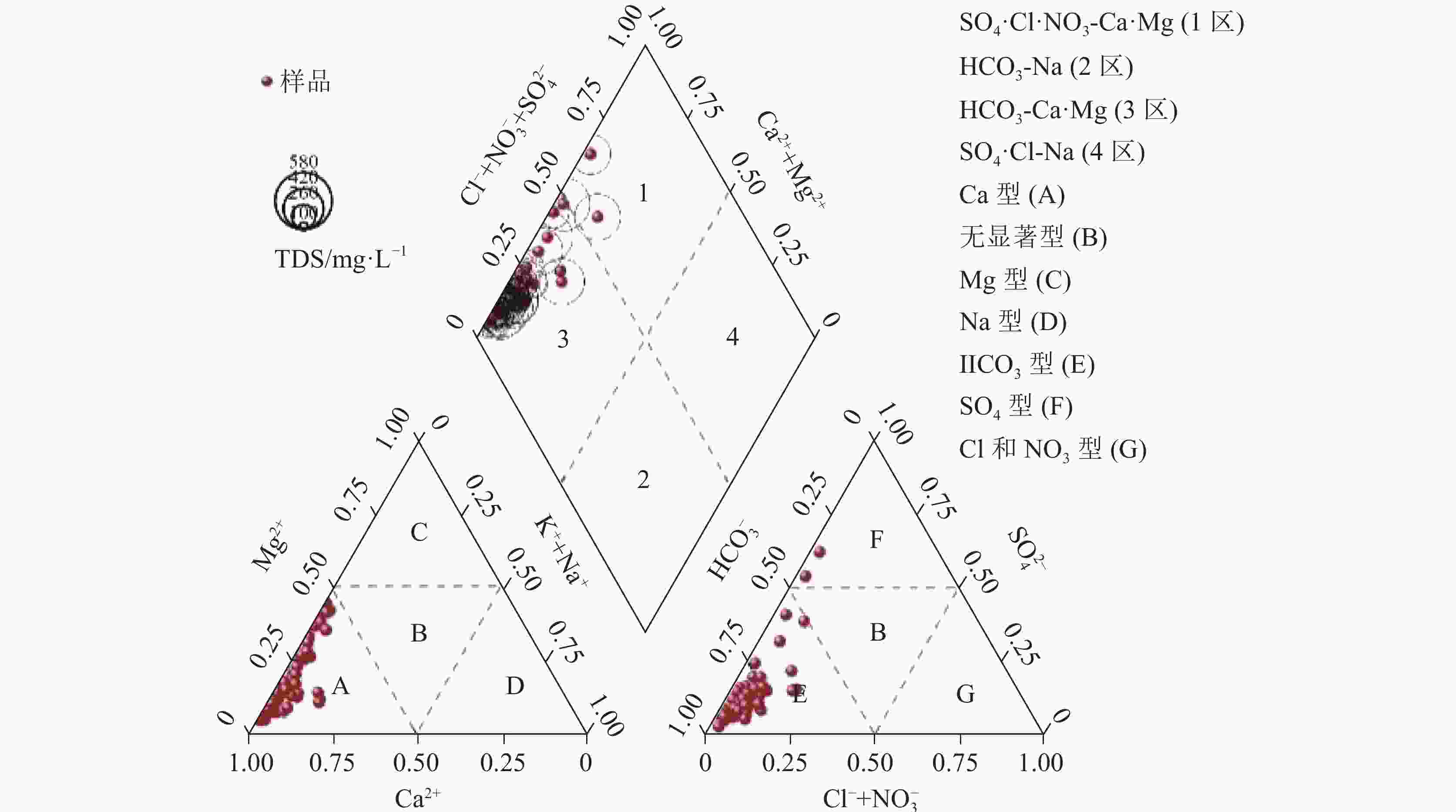
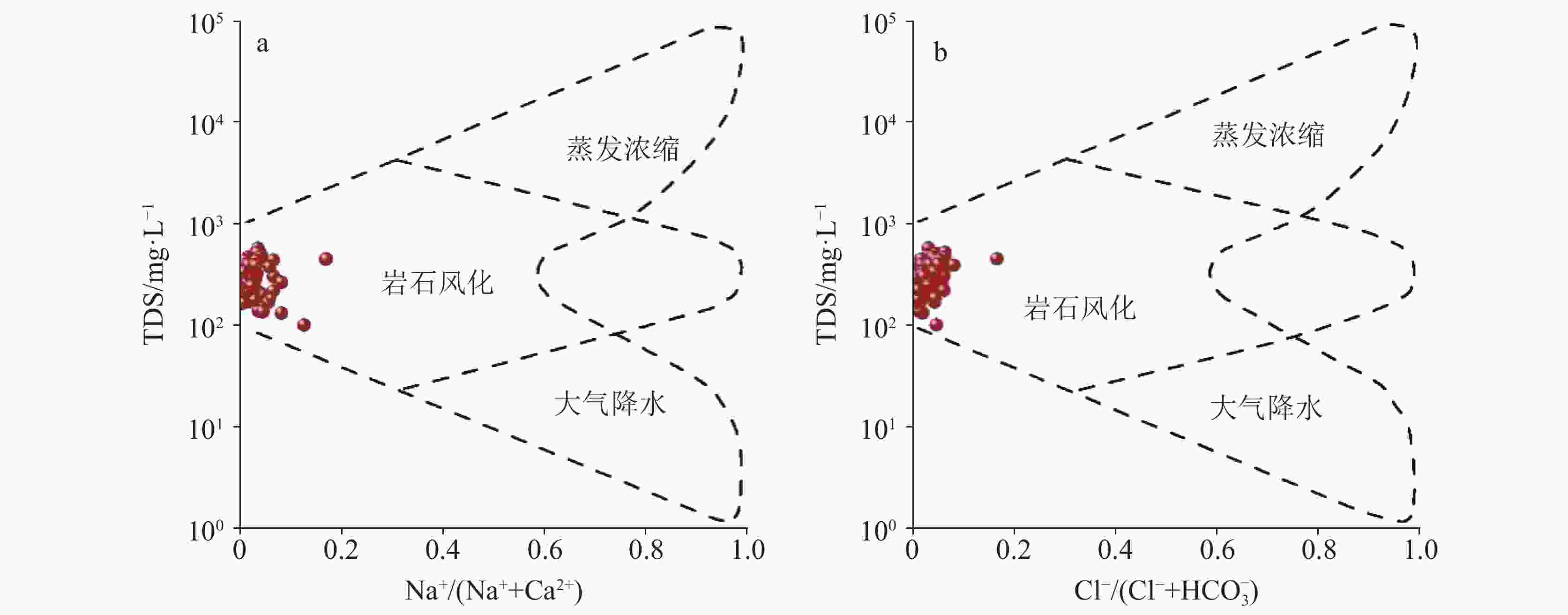
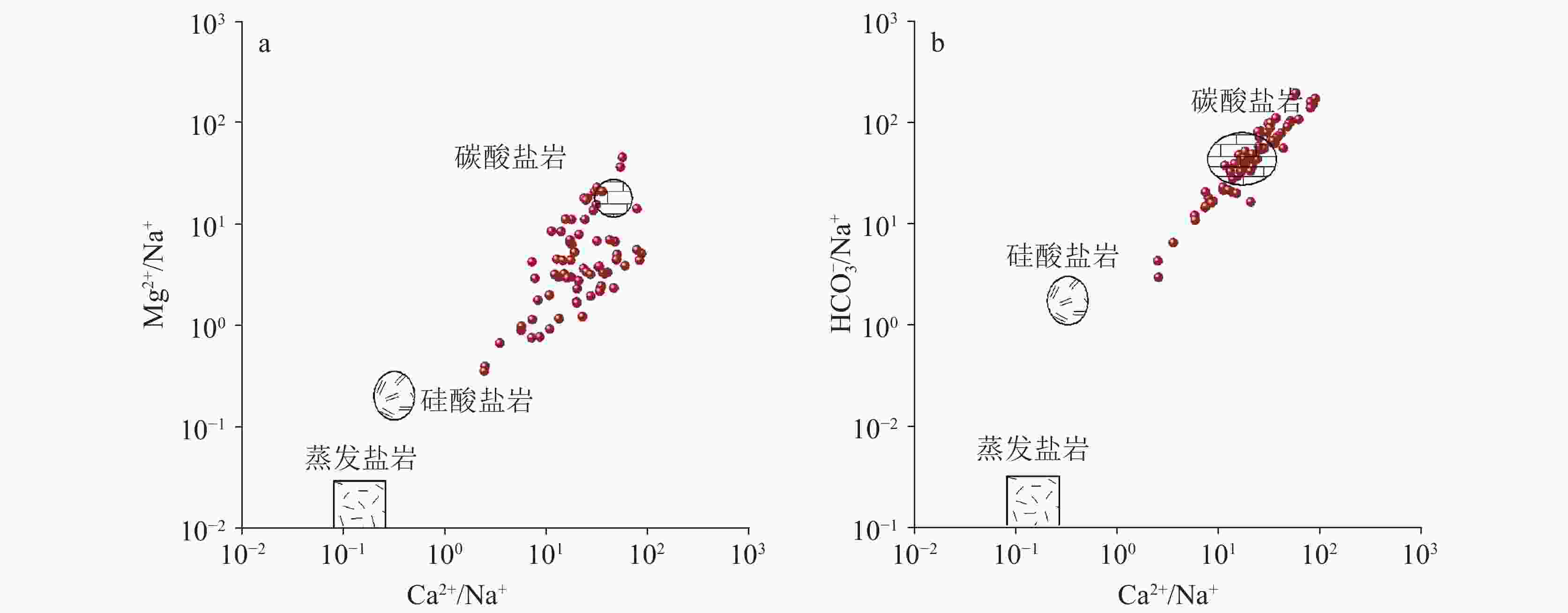
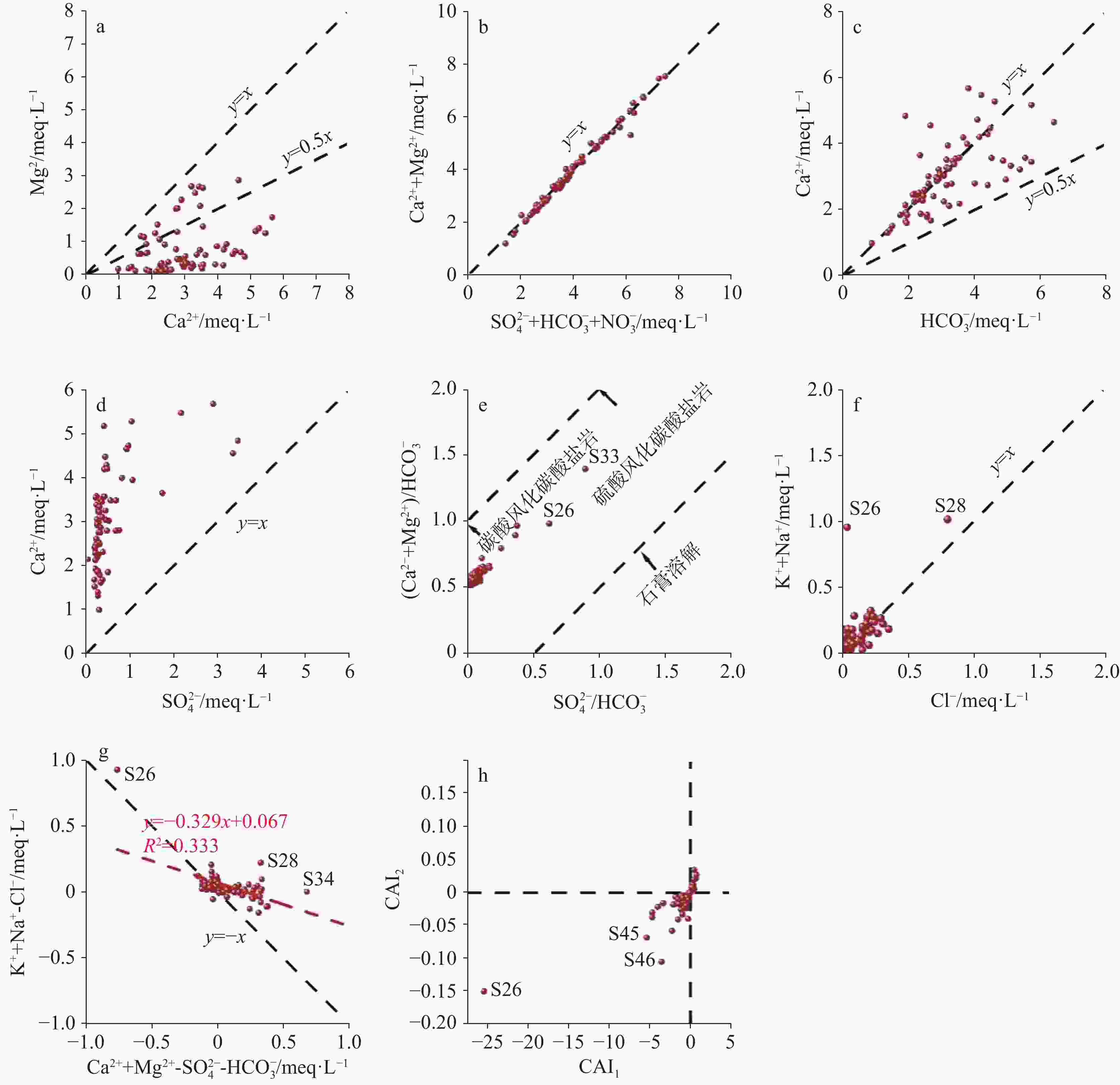
Abstract:This study conducted comprehensive water sampling and testing at 71 groundwater sites in a typical karst area of southeastern Chongqing during the summer. The research utilized methods including Gibbs diagrams, ion ratios analysis, multivariate statistical technique, the entropy-weighted water quality index (EWQI), and assessment models of human health risk to investigate the hydrochemical composition, water quality status, and health risks of groundwater in the region. The results indicate that the hydrochemical type of groundwater in the karst area of southeastern Chongqing is predominantly HCO3-Ca (61.97%), followed by mixed types of HCO3-Ca·Mg (30.98%) and a small proportion of HCO3·SO4-Ca(7.04%). The dominant cations is Ca2+, while the primary anions is HCO$_3^{-}$. The average cation concentrations follow the order: Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ > K+ (60.67 mg·L−1, 10.09 mg·L−1, 2.45 mg·L−1, and 1.23 mg·L−1, respectively), while the average anion concentrations are ranked as HCO$_3^{-}$ > SO$_4^{2}$− > NO$_3^{-}$ > Cl− (195.04 mg·L−1, 26.95 mg·L−1, 9.04 mg·L−1, and 3.69 mg·L−1, respectively). The pH values range from 6.98 to 8.17, with a mean of 7.58, indicating weakly alkaline conditions. The total dissolved solids (TDS) range from 101.48 to 578.44 mg·L−1, with an average value of 300.13 mg·L−1. The coefficients of variation (CV) of the major ions Cl−, SO$_4^{2}$−, and Na+ in the groundwater exceed 100%, suggesting complex sources. The hydrochemistry of groundwater in the karst area of southeastern Chongqing is predominantly controlled by rock weathering. The ions of K+ and Na+ primarily originate from dissolution of and halite, with a limited role played by cation exchange. In some localized areas, elevated Na+ levels are influenced by domestic sewage inputs. Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO$_3^{-}$ are mainly derived from the weathering and dissolution of carbonate rocks such as calcite and dolomite. Cl− is partly sourced from halite dissolution but predominantly reflects anthropogenic contamination from domestic wastewater. NO$_3^{-}$ is primarily attributed to the application of agricultural fertilizer. SO$_4^{2}$− originates from the dissolution of sulfur-bearing minerals, industrial and mining activities, and gypsum dissolution, with the gypsum dissolution contributing minimally. The water quality evaluation of the karst area in the southeastern Chongqing was conducted using the EWQI method. The EWQI values range from 7.29 to 182.68, with an average value of 21.83, indicating overall high water quality. Specifically, the proportions of high-quality, good, and poor are 92.96%, 5.63%, and 1.41%, respectively. Correlation analysis revealed a strong relationship between TDS, TFe, Mn, Al, and the EWQI. Multivariate linear regression further confirmed that groundwater is mainly affected by TFe, TDS, Al, Mn, and NO$_3^{-}$. Some sampling points exhibited poor water quality (Class IV), greatly affected by elevated levels of TFe, Mn, and Al. According to the Groundwater Quality Standard (GB/T 14848-2017), the single-factor evaluation classified water quality as Class I to V in proportions of 7.04%, 47.89%, 32.39%, 9.86%, and 2.82% respectively. Overall, groundwater quality is mainly affected by industrial and mining activities associated with local mining operations. The assessment of health risk of groundwater in southeastern Chongqing show that most of the risks are within safe levels,with an exceedance rate of 4.23%.However, in some areas, TFe and ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ surpass the comprehensive health risk threshold for children(HI=1),indicating elevated hazard risks,with the highest risk value of ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ reaching HInitate= 2.17277 . Therefore, these areas require increased attention. -
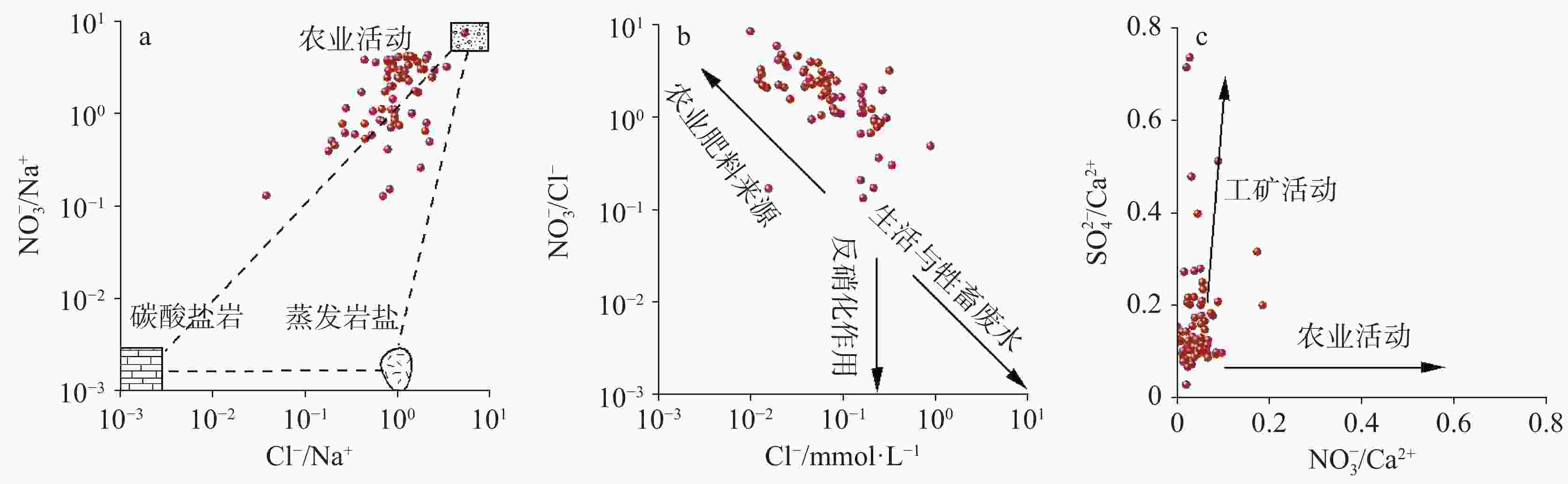
图 6 地下水的$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{a}}^{+} $与$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{a}}^{+} $(a)、$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $与$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $(b)、$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}}^{2+} $与$ {\mathrm{S}\mathrm{O}}_{4}^{2-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}}^{2+} $(c)的关系图
Figure 6. Relationship between the ratios of $ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{a}}^{+} $ vs $ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{a}}^{+} $(a), $ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $ vs $ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{l}}^{-} $(b), $ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}}^{2+} $ vs $ {\mathrm{S}\mathrm{O}}_{4}^{2-} $/$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}}^{2+} $(c) in groundwater
表 1 EWQI等级分类
Table 1. Classification of EWQI levels
EWQI 值 等级分类 描述 50≤EWQI 1 优质 50<EWQI≤100 2 良好 100<EWQI≤150 3 中等 150<EWQI≤200 4 差 EWQI>200 5 极差 表 2 暴露剂量计算参数
Table 2. Calculation parameters of exposure dose
表 3 研究区地下水水化学参数
Table 3. Groundwater hydrochemical parameters in the study area
统计参数 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 变异系数 WHO(2017) 超标率 pH 8.17 6.98 7.58 0.28 3.72 6.50~8.50 0.00 Cl− 28.31 0.24 3.69 4.14 112.21 250 0.00 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 166.53 2.85 26.95 31.48 116.79 250 0.00 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 392.34 56.89 195.04 70.17 35.98 400 0.00 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 60.38 <0.05 9.04 8.30 91.77 50 1.41 K+ 4.06 0.1 1.23 0.81 66.39 30 0.00 Na+ 22.2 0.3 2.45 3.55 144.76 200 0.00 Ca2+ 113.7 20.22 60.67 20.95 34.53 200 0.00 Mg2+ 34.99 1.36 10.09 8.91 88.22 150 0.00 TDS 578.44 101.48 300.13 107.69 35.88 1000 0.00 TFe 5.16 <0.005 0.1829 0.6332 346.22 0.3 8.45 Mn 0.3750 < 0.00006 0.0204 0.0562 275.06 0.1 4.23 Al 0.8840 < 0.0006 0.0840 0.1454 173.09 0.2 9.86 Pb 0.0219 < 0.00007 0.00041 0.00257 632.48 0.01 1.41 注:表中各元素的单位均为 mg·L−1(pH除外),变异系数(%);超标率(%):超过世界卫生组织 (WHO)饮用水标准值的样品百分比(%);WHO提供的临时指导值(WHO,2017)。 表 4 逐步多元线性回归结果
Table 4. Results for stepwise multiple linear regression
模型 线性 R2 P 1 EWQI=15.682+33.644TFe 0.874 <0.001 2 EWQI=0.007+32.445TFe+0.053TDS 0.936 <0.001 3 EWQI=2.255+27.680TFe+0.042TDS+94.677Mn 0.968 <0.001 4 EWQI=-0.933+19.514TFe+0.046TDS+84.927Mn+44.753Al 0.992 <0.001 5 EWQI=-0.688+19.782TFe+0.039TDS+85.010Mn+44.482Al+0.260$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $ 0.997 <0.001 表 5 Fe、Mn、Al、$ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $和Pb人类健康非致癌风险值统计
Table 5. Statistical values of non-carcinogenic risks of Fe, Mn, Al, $ {\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{-} $and Pb to humans
金属 统计项目 HQoral HQdermal HI 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 TFe 最大值 0.24201 0.98724 0.01635 0.04081 0.25836 1.02805 最小值 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 平均值 0.00858 0.03499 0.00058 0.00145 0.00916 0.03644 Mn 最大值 0.11471 0.46792 0.01635 0.11517 0.11517 0.46907 最小值 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 平均值 0.00625 0.02549 0.00003 0.00006 0.00627 0.02555 Al 最大值 0.08885 0.36243 0.00450 0.01124 0.09335 0.37366 最小值 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 平均值 0.00844 0.03444 0.00043 0.00107 0.00887 0.03551 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 最大值 0.53099 2.16606 0.00269 0.00672 0.53368 2.17277 最小值 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 平均值 0.07729 0.31529 0.00039 0.00098 0.07768 0.31627 Pb 最大值 0.22010 0.89787 0.00000 0.00001 0.22011 0.89788 最小值 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 平均值 0.00414 0.01689 0.00000 0.00000 0.00414 0.01689 注:参数与计算过程见2.3节(11)~(13)式和表2。 -
[1] DUAN Yan, GAO Xubo, LI Chengcheng, WANG Hong, KANG Caiqin, WANG Wanzhou, ZHANG Xin, SUN Zhuang, XIONG Yinzheng, WANG Yanxin. Combining hydrodynamics, geochemical and multiple isotopic tracers to understand the hydrogeological functioning of karst groundwater system in Jinci, Northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2025, 648: 132375. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.132375 [2] 任坤, 曾洁, 彭聪, 潘晓东, 于正良, 吴华英. 玉龙雪山—丽江水体水化学和同位素特征及其变化规律与成因[J]. 地理学报, 2024, 79(11): 2864-2879. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202411011REN Kun, ZENG Jie, PENG Chong, PAN Xiaodong, YU Zhengliang, WU Huaying. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics, changes and controlling factors of waters in the Yulong Snow Mountain-Lijiang area, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2024, 79(11): 2864-2879. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202411011 [3] 袁道先, 薛禹群, 傅家谟. 防止我国西南岩溶地区地下河变成“下水道”的对策与建议[R]. 中国科学院院士建议, 2007, 4: 114. [4] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [5] WANG Ping, ZHANG Wei, ZHU Yuchen, LIU Yaci, LI Yasong, CAO Shengwei, HAO Qichen, LIU Shenghua, KONG Xiangke, HAN Zhantao, LI Binghua. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism during groundwater recharge: A case study in the Hutuo River alluvial−pluvial fan, North China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 915: 170159. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170159 [6] Ariyan N T , Quraishi B S , Alam E N M, Khan R S M, Faria F F, Kabir A. Comprehensive analysis and human health risk assessment of tap water quality in Dhaka City, Bangladesh: Integrating source identification, index-based evaluation, and heavy metal assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 485: 136837. [7] Ioannis M, Christian M, Yuliya V, Hannu M, Natalie O, Søren J, Jaivime E, Mathieu S, Gerbrand K, Elias D, Sasha M, Yiannis P, Michael P S. Nitrate isotopes in catchment hydrology: Insights, ideas and implications for models[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 626(PB): 130326. [8] Vesković J, Timotić D I, Lučić M, Miletić A, Đolić M, Ra·ić S, Onjia A. Entropy-weighted water quality index, hydrogeochemistry, and Monte Carlo simulation of source-specific health risks of groundwater in the Morava River plain (Serbia)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2024, 201: 1116277. [9] Zahra A, Ali M, Ali N, Khan A, Zairov R, Sinyashin O, WANG Yan, Zafar S, Khan A F. A comprehensive analysis of the impact of arsenic, fluoride, and nitrate−nitrite dynamics on groundwater quality and its health implications[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2025, 487: 137093. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137093 [10] SHENG Danrui, MENG Xianhong, WEN Xiaohu, WU Jun, YU Haijiao, WU Min, ZHOU Ting. Hydrochemical characteristics, quality and health risk assessment of nitrate enriched coastal groundwater in northern China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 403: 136872. [11] Vesković J, Onjia A. Two-dimensional Monte Carlo simulation coupled with multilinear regression modeling of source-specific health risks from groundwater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2025, 488: 137309. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137309 [12] LI Rui, YAN Yuting, XU Jiaqian, YANG Chang, CHEN Si, WANG Yangshuang, ZHANG Yunhui. Evaluate the groundwater quality and human health risks for sustainable drinking and irrigation purposes in mountainous region of Chongqing, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2024, 264: 104344. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2024.104344 [13] YUAN Ruiqiang, LI Zhibin, GUO Siyu. Health risks of shallow groundwater in the five basins of Shanxi, China: Geographical, geological and human activity roles[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 316(P1): 120524. [14] 樊连杰, 裴建国, 邹胜章, 杜毓超, 卢丽. 重庆市南川区南部岩溶地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5): 697-703.FAN Lianjie, PEI Jianguo, ZOU Shengzhang, DU Yuchao, LU Li. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in southern Nanchuan district of Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 697-703. [15] 肖旭芳, 张双龙, 郭雯, 王敬富, 杨海全, 廖鹏. 西南喀斯特地区地表水和地下水环境污染特征与研究展望[J]. 地球与环境, 2023, 51(5): 564-573.XIAO Xufang, ZHANG Shuanglong, GUO Wen, WANG Jingfu, YANG Haiquan, LIAO Peng. Environmental Pollution Characteristics of Surface Water and Groundwater in Southwest China and Its Research Prospects[J]. Earth and Environment, 2023, 51(5): 564-573. [16] 肖成芳, 魏兴萍, 张爱国, 陈英. 重庆市岩溶泉发育特征与流量控制机制分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41(4): 693-706. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.013XIAO Chengfang, WEI Xingping, ZHANG Aiguo, CHEN Ying. Development characteristics and flow control mechanism of karst springs in Chongqing Municipality[J]. Progress in Geography, 2022, 41(4): 693-706. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.013 [17] 刘兴兵, 程军, 唐本锋, 张丽红. 重庆市上二叠统硫铁矿沉积环境及成矿模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(1): 148-154.LIU Xingbing, CHENG Jun, TANG Benfeng, ZHANG Lihong. Upper Permian sedimentary environment and metallogenic model of pyrite in Chongqing[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(1): 148-154. [18] 田欢欢, 樊海峰, 何明勤, 刘喜强, 杨若飞, 梁坤萍, 郑茂尧. 重庆秀山地区大塘坡组锰矿稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2022, 41(3): 557-571.TIAN Huanhuan, FAN Haifeng, HE Mingqin, LIU Xiqiang, YANG Ruofei, LIANG Kunping, ZHENG Maoyao. A study on REE geochemistry of the Datangpo Formation-hosted manganese deposits in the Xiushan area, Chongqing, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2022, 41(3): 557-571. [19] 刘平, 韩忠华, 聂坤. 黔中—渝南岩溶型铝土矿含矿岩系特征、控制条件及生成发展模式[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(6): 147-174.LIU Ping, HAN Zhonghua, NIE Kun. Characteristics of ore-bearing rock series, control conditions and generative development model of karst bauxite deposit in central Guizhou—southern Chongqing[J]. Geological Reviw, 2022, 68(6): 147-174. [20] LI Jun, YANG Guoli, ZHU Danni, XIE Hao, ZHAO Yi, FAN Lianjie, ZOU Shengzhang. Hydrogeochemistry of karst groundwater for the environmental and health risk assessment: The case of the suburban area of Chongqing (Southwest China)[J]. Geochemistry, 2022, 82(2): 125866. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2022.125866 [21] LIU Jiutan, LOU Kexin, GAO Zongjun, WANG Yabo, LI Qiang, TAN Menghan. Comprehending hydrochemical fingerprint, spatial patterns, and driving forces of groundwater in a topical coastal plain of Northern China based on hydrochemical and isotopic evaluations[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 461: 142640. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142640 [22] ZHANG Shuai, HAN Yingyue, PENG Jingyu, CHEN Yunmin, ZHAN Liangtong, LI Jinlong. Human health risk assessment for contaminated sites: A retrospective review[J]. Environment International, 2023, 171: 107700. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107700 [23] 王袆曼, 葛勤, 危超, 李翔, 刘海燕, 李昕妍. 南方某尾矿区地下水金属元素来源解析及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(6): 3429-3439.WANG Yiman, GE Qin, WEI Chao, LI Xiang, LIU Haiyan, LI Xinyan. Source and health risk assessment of groundwater metal elements of a tailings mining area in Southern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2025, 46(6): 3429-3439. [24] 谷志琪, 卞建民, 王宇, 马丽欣, 孙晓庆, 阮冬梅. 长白山源头区地下水质评价及监测指标优化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(10): 5257-5264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.10.024GU Zhiqi, BIAN Jianmin, WANG Yu, MA Lixin, SUN Xiaoqing, RUAN Dongmei. Groundwater quality assessment and index optimization of water quality monitoring in the water source area of Changbai Mount[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(10): 5257-5264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.10.024 [25] Piper A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1944, 25(6): 914-928. doi: 10.1029/TR025i006p00914 [26] 令狐昌卫, 邹石林, 管继云, 柴楚, 杨浪浪, 和成忠, 朱平平, 寸得欣, 刘振南, 朱星强, 徐磊. 滇东富源典型煤矿区地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J/OL]. 中国地质, 1-21[2025-02-11].LINGHU Changwei, ZOU Shilin, GUAN Jiyun, CHAI Chu, YANG Langlang, HE Chengzhong, ZHU Pingping, CUN Dexin, LIU Zhennan, ZHU Xingqiang, XU Lei. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in typical coal mining areas of Fuyuan, Eastern Yunnan[J/OL]. Geology in China, 1-21[2025-02-11]. [27] Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Louvat P, Allègre J C. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1-4): 3-30. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5 [28] XIAO Jun, WANG Lingqing, CHAI Ningpan, LIU Ting, JIN Zhangdong, Rinklebe Jörg. Groundwater hydrochemistry, source identification and pollution assessment in intensive industrial areas, eastern Chinese loess plateau[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 278: 116930. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116930 [29] 曹明达. 运用多同位素识别典型农业小流域水环境硝酸盐来源及生物地球化学过程[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.CAO Mingda. Identification of nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in typical agricultural watershed with multi-isotope analysis: A case study of Quanshui River watershed[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2022. [30] 王楠, 胥芹, 孙小艳, 武显仓, 李常锁, 高帅. 趵突泉泉域岩溶水化学特征及成因研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(2): 279-290. doi: 10.11932/karst20240203WANG Nan, XU Qin, SUN Xiaoyan, WU Xiancang, LI Changsuo, GAO Shuai. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanismof karst water in Baotu Spring watershed[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(2): 279-290. doi: 10.11932/karst20240203 [31] LIU Jiutan, GAO Zongjun, FENG Jianguo, WANG Min. Identification of the hydrochemical features, genesis, water quality and potential health hazards of groundwater in Dawen River Basin, North China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 149: 110175. [32] 江峰, 吉勤克补子, 曹建文, 王若帆, 赵良杰. 黔中岩溶区地下水水化学来源特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(4): 889-899. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y028JIANG Feng, JIQIN Kebuzi, CAO Jianwen, WANG Ruofan, ZHAO Liangjie. Source characteristics and influencing factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in the karst areas of central Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(4): 889-899. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y028 [33] 张文强, 滕跃, 唐飞, 王金晓, 许庆宇, 张海林. 山东省肥城断块岩溶水系统地下水水化学特征及演化分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(5): 1047-1060, 1084. doi: 10.11932/karst20230515ZHANG Wenqiang, TENG Yue, TANG Fei, WANG Jinxiao, XU Qingyu, ZHANG Hailin. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of the karst water system in the Feicheng fault block in Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(5): 1047-1060, 1084. doi: 10.11932/karst20230515 [34] 戈德沙伊德, 德鲁, 陈宏峰, 何愿. 岩溶水文地质学方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.GOLDSCHEIDER Nico, DREW David, CHEN Hongfeng, HE Yuan. Methods in Karst Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [35] 苏丹, 周忠发, 龚晓欢, 丁圣君, 董慧, 闫利会, 熊勇. 岩溶洞穴水中硝酸盐浓度变化及其来源与估算[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(11): 5812-5822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.11.019SU Dan, ZHOU Zhongfa, GONG Xiaohuan, DING Shengjun, DONG Hui, YAN Lihui, XIONG Yong. Variation of nitrate concentration in karst cave water and its sources and estimation[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(11): 5812-5822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.11.019 [36] LIU Jiutan, PENG Yuming, LI Changsuo, GAO Zongjun, CHEN Shaojie. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assess-ment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268(B): 115947. [37] WANG Wenlin, YANG Jiasen, YANG Fang, YANG Liu, XU Xiaoguang, TAO Yulong, AO Wen, LIU Bo, JIN Qiu, WANG Guoxiang. Mixed nitrogen inputs affected nitrate distribution and biogeochemical processes during ice-covered and ice-free periods in a boreal eutrophic steppe lake basin[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2025, 182: 106333. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2025.106333 [38] 吴华英, 李腾芳, 程瑞瑞, 黄奇波, 潘晓东. 我国岩溶地下水受污染的原因与污染特征[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(S1): 101-104. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.S1.095WU Huaying, LI Tengfang, CHENG Ruirui, HUANG Qibo, PAN Xiaodong. Causes and characteristics of the pollution of karst groundwater in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(S1): 101-104. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.S1.095 -




 下载:
下载: