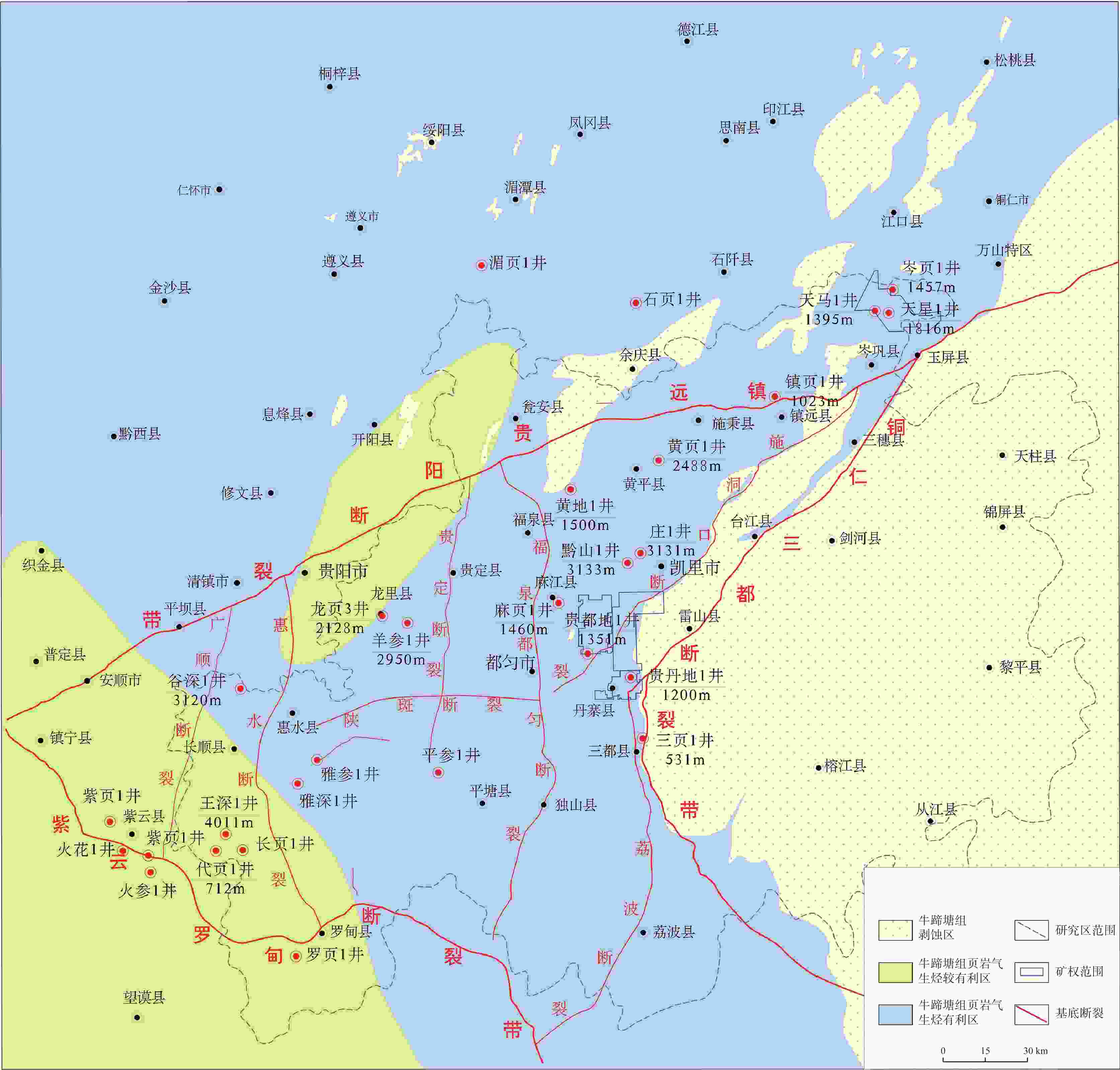
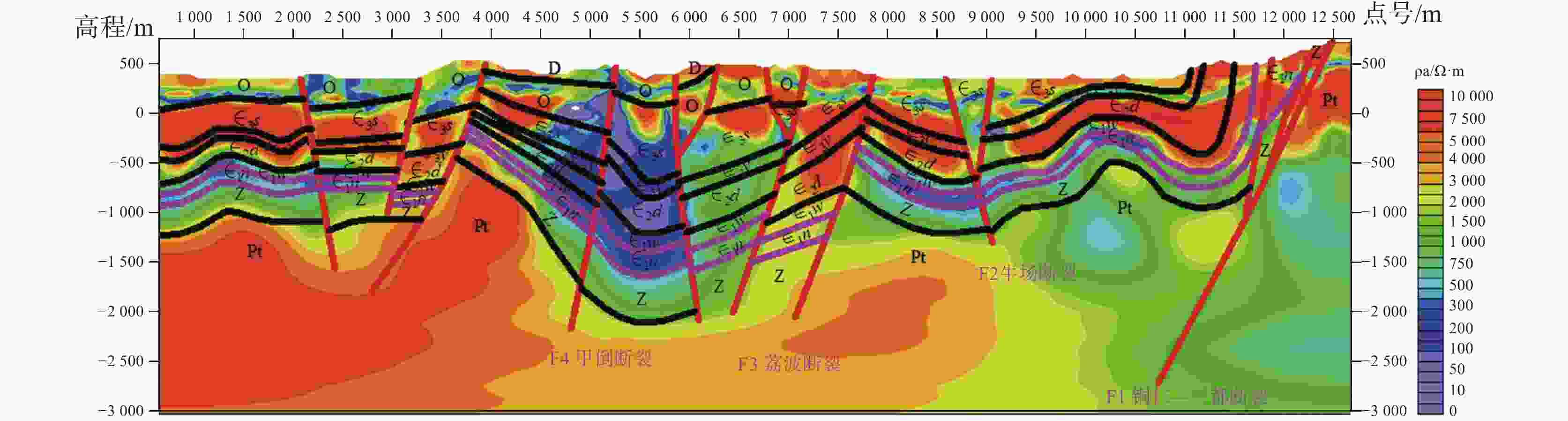
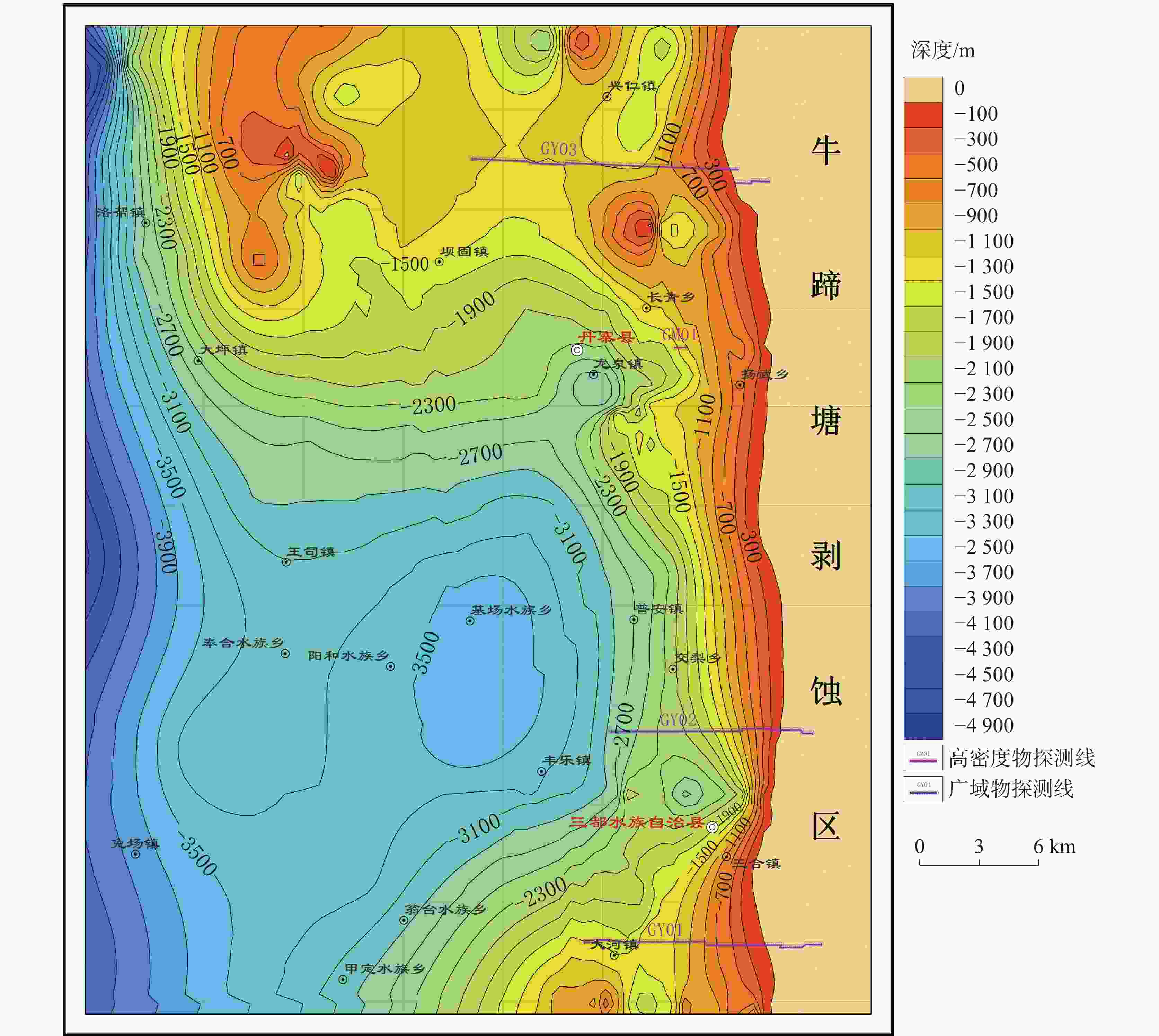
Geological conditions and geochemical characteristics of favorable shale gas zones in Danzhai of the Qiannan depression
-
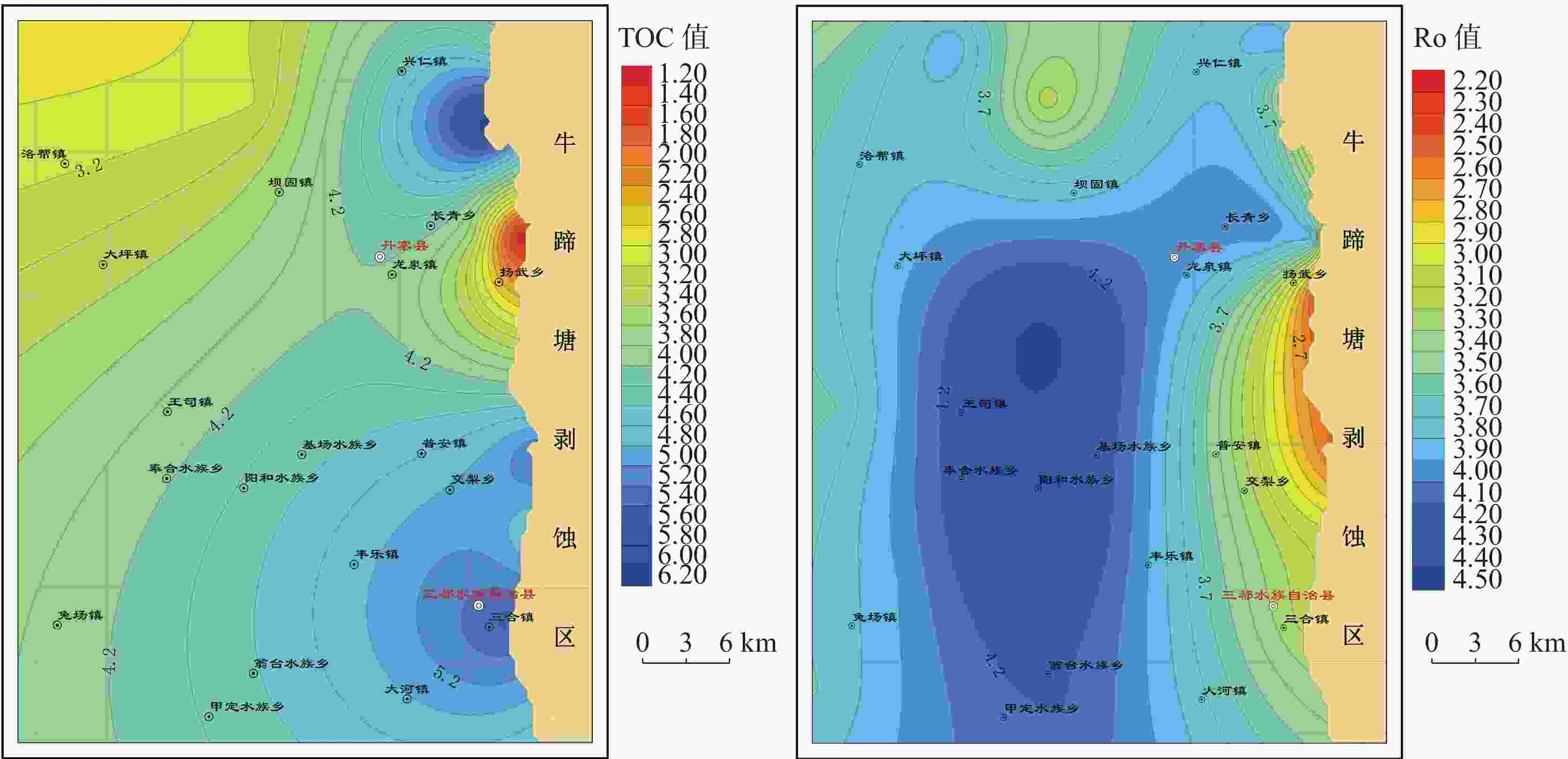
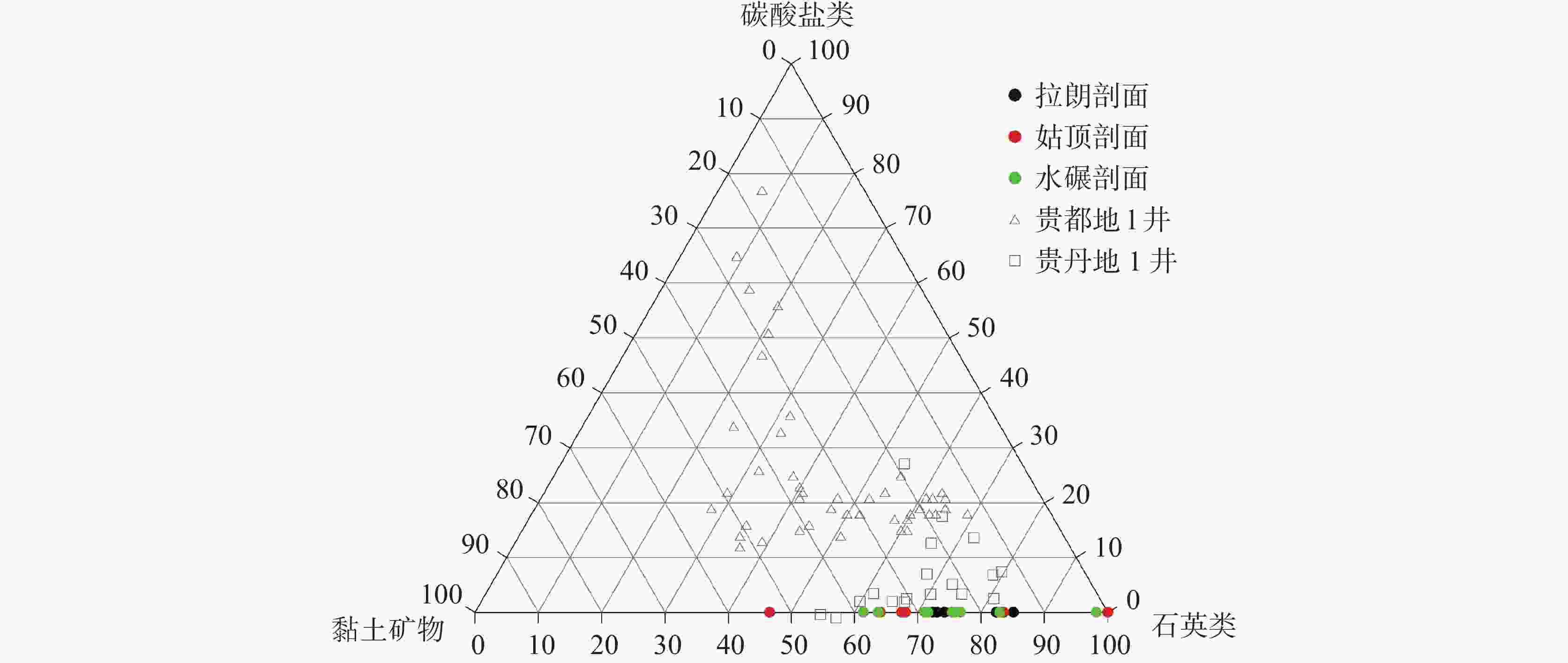
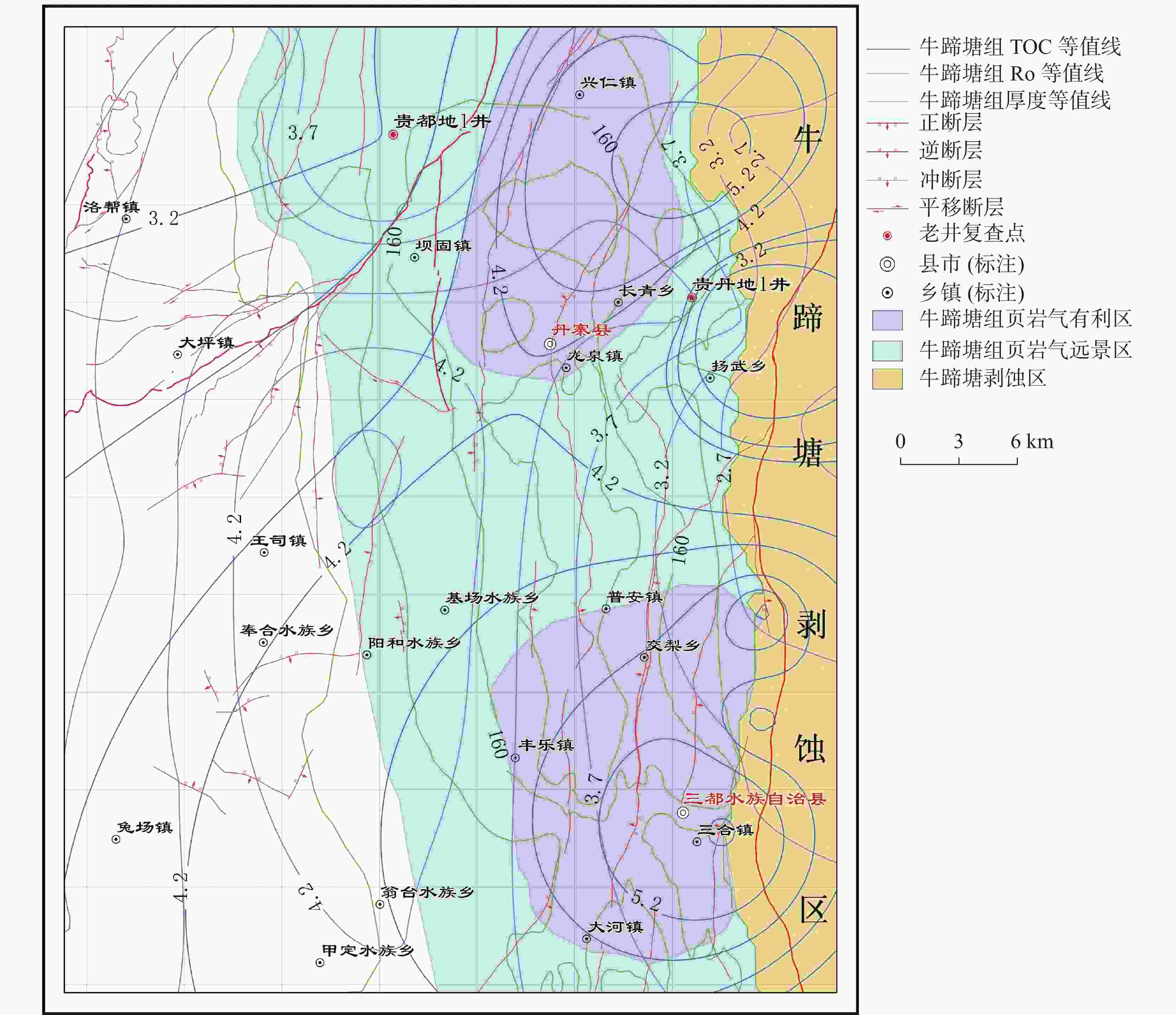
摘要: 黔南坳陷区域寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩分布广泛,层厚较大,富集有机质,处于成熟阶段,页岩气勘探和开发潜力较好,因此查明不同地区富有机质页岩层段有利区地质条件及其地球化学特征已成为页岩气勘探的关键问题。文章利用沉积学、有机岩石学和地球化学等综合手段,绘制丹寨有利区分布图,重点探讨了研究区有利区地质条件及优质烃源岩的生烃潜力和时空分布。结果表明:丹寨地区有利区显示该区牛蹄塘组页岩主体沉积环境为深水陆棚至深水盆地;富有机质页岩厚度为60~200 m,整体呈现出由西北向东南逐渐增厚的趋势;总有机碳含量主要介于4.5%~6.0%,有机质成熟度则主要在2.5%~2.7%之间,且从东北向西南方向逐渐降低,构造活动对地层保存条件和页岩气富集程度产生了重要影响;揭示黔南丹寨地区寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩地质条件较好,具有进一步深入开展页岩气调查勘探的潜力。Abstract:
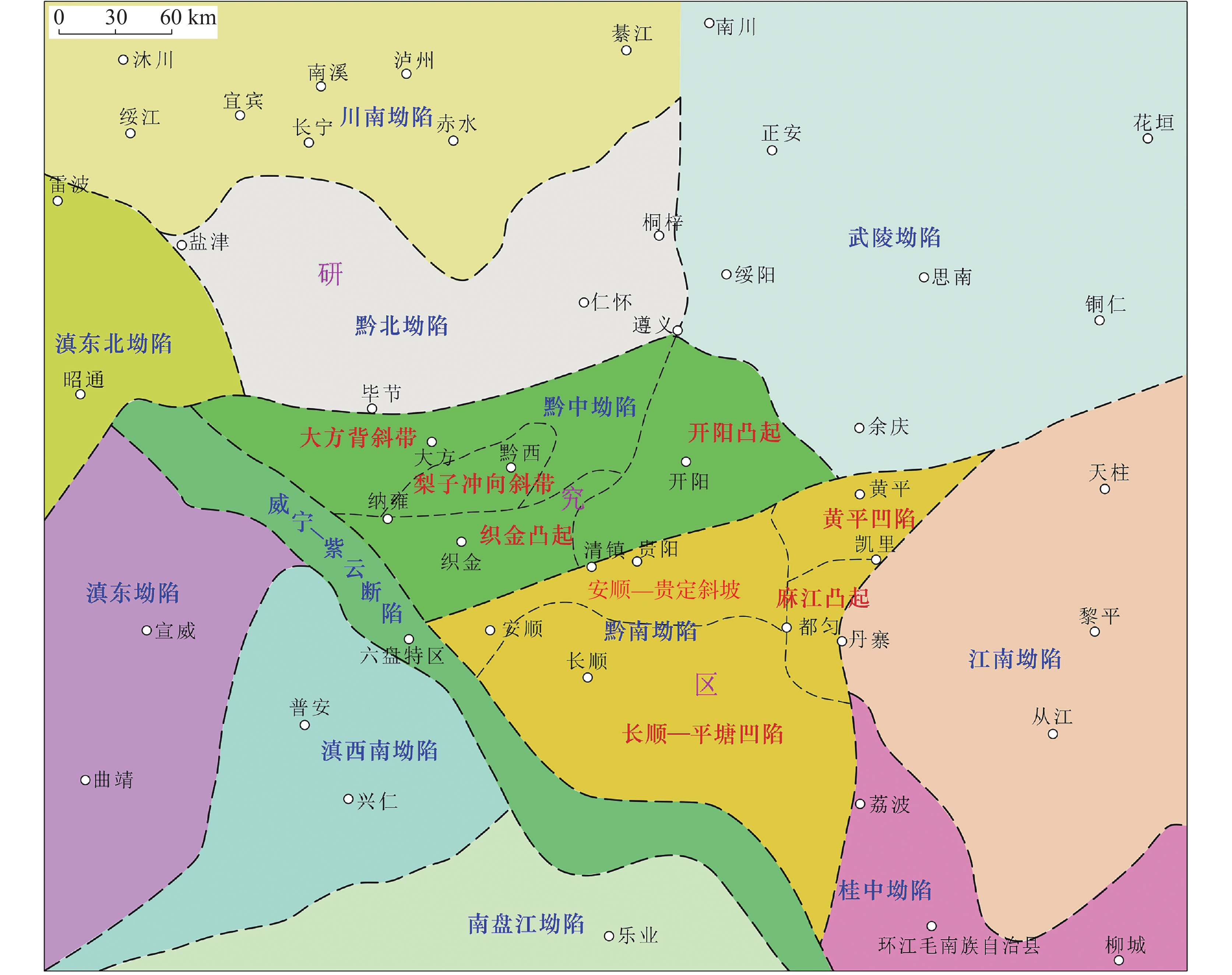
The Qiannan depression is located on the southwestern edge of the Yangtze block and is an important area of shale gas resources in South China. In recent years, significant progress has been made in shale gas exploration in this region. The shale in Cambrian Niutitang formation of the Qiannan depression is widely distributed, characterized by thick layers and abundant organic matter. Shale is developed in the mature stage and possesses significant potential for shale gas exploration and development. Although some progress has been made in the studies on shale in the Qiannan region, there is still a relative lack of in-depth research on the geological conditions, soluble organic matter, and reservoir formation mechanisms of the favorable zones. By measuring and collecting samples from typical profiles and survey wells of shale gas, this study systematically analyzed the geological conditions and organic geochemical characteristics of the favorable zones in Danzhai of the Qiannan depression. It also explored the distribution and development patterns of high-quality hydrocarbon source rocks in the Cambrian Niutitang formation. The results indicate that the Cambrian Niutitang formation in Danzhai is abundant in organic shale with a thickness of about 60 meters to 200 meters, showing an overall trend of gradually thickening from northwest to southeast. The total organic carbon content (TOC) of the Niutitang formation mainly ranges from 4.5% to 6.0%, while the organic matter maturity (Ro) predominantly varies from 2.5% to 2.7%, gradually decreasing from the northeast to the southwest. The mineral composition of shale in the Niutitang formation primarily consists of quartz, followed by clay minerals, and a small amount of carbonate minerals. The types of shale reservoir spaces include organic pores, inorganic pores, and microfractures, among which inorganic pores primarily consists of intergranular pores, intragranular pores, dissolution pores, etc. The shale matrix typically exhibits low porosity and permeability, categorizing the study area as a low porosity and low permeability shale reservoir. However, the development of local fractures can enhance both the porosity and permeability of shale. The tectonic activity has significantly influenced the preservation conditions of the strata and the degree of shale gas enrichment. Tectonic preservation continues to be a key factor affecting the shale gas enrichment of the Niutitang formation in Danzhai of the Qiannan depression. Due to relatively unfavorable enrichment conditions and the complex preservation of structures, the large-scale industrial development of shale gas in the Cambrian Niutitang formation faces significant challenges. However, the geological conditions of the shale in the Cambrian Niutitang formation in Danzhai are relatively favorable, indicating potential for further exploration of shale gas. -
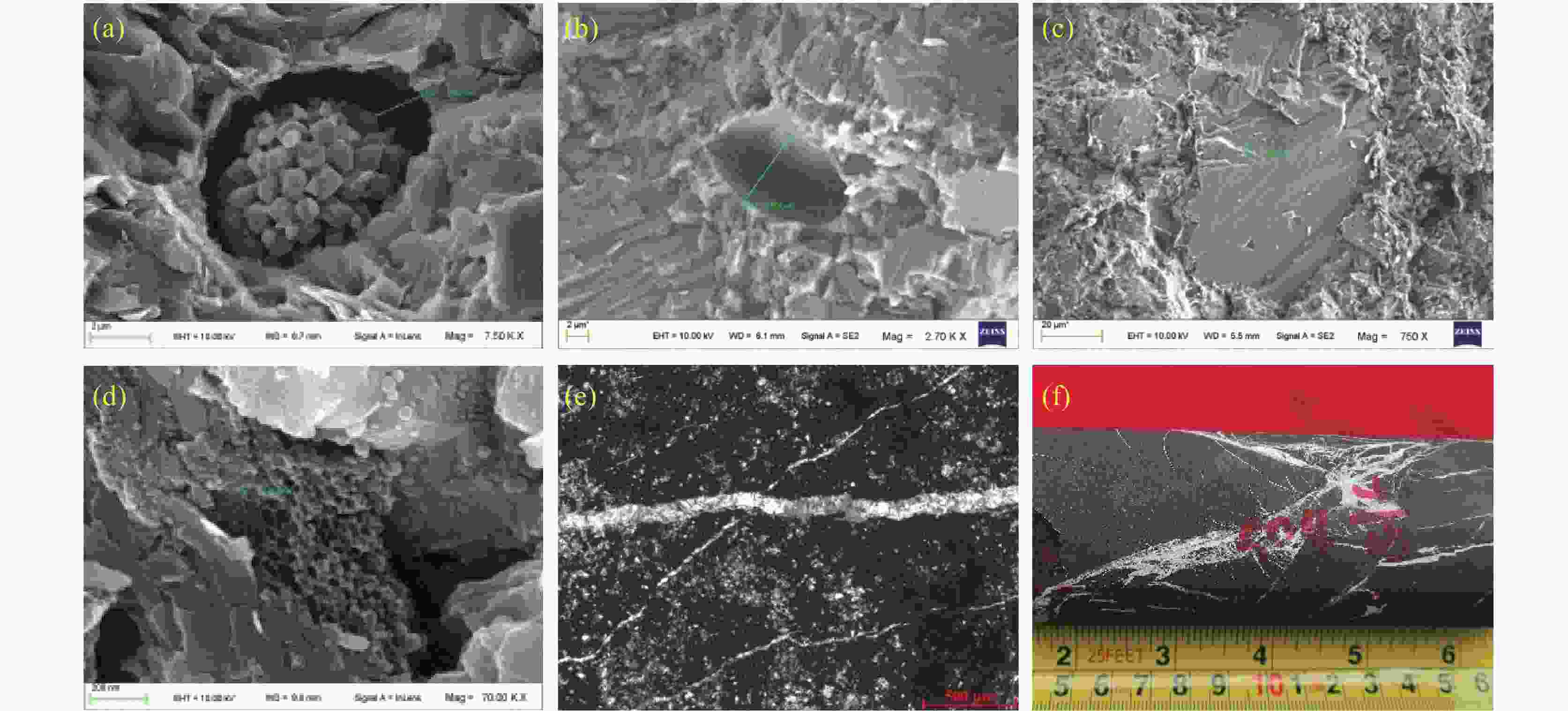
图 8 丹寨地区牛蹄塘组/渣拉沟组储集空间类型特征
(a) 草莓状黄铁矿发育晶间孔,牛蹄塘组,三都拉郎剖面 (b) 铸膜孔,牛蹄塘组,贵都地1井 (c) 钠长石粒内溶孔,牛蹄塘组,贵都地1井 (d) 有机孔发育,渣拉沟组,三都水碾剖面 (e) 裂缝,方解石充填,牛蹄塘组,贵丹地1井 (f) 裂缝,方解石充填,牛蹄塘组,贵都地1井
Figure 8. Characteristics of reservoir space types in the Niutitang formation/the Zhalagou formation in Danzhai
(a) strawberry-shaped pyrite with intergranular pores, Sandulalang section in the Niutitang Formation (b) cast film pore, Guidudi Well 1 in the Niutitang Formation (c) intragranular dissolution pore of sodium feldspar, Guidudi Well 1 in the Niutitang Formation (d) development of organic pore, Sandushuinian section in the Zhalagou Formation (e) cracks filled with calcite, Guidandi Well 1 in the Niutitang Formation (f) cracks filled with calcite, Guidudi Well 1 in the Niutitang Formation
表 1 贵州黔南坳陷及周缘地区下寒武统地层对比[29]
Table 1. Comparison of lower Cambrian strata in the Qiannan depression and its surrounding areas of Guizhou Province[29]
统 阶 地 层 川西南 川东南、黔北—黔中 黔东南皋 黔南黄平 黔南丹寨 中寒武统 毛庄阶 陡坡寺组 高台组 高台组 凯里组 下寒武统 龙王庙组 龙王庙组 清虚洞组 清虚洞组 乌训组 沧浪铺组 沧浪铺组 金顶山组 杷榔组 杷榔组 明心寺组 变马冲组 变马冲组 筇竹寺组 筇竹寺组 牛蹄塘组 九门冲组 九门冲组 九门冲组 牛蹄塘组 梅树村阶 麦地坪组 老堡组 牛蹄塘组 上震旦统 灯影组 灯影组 灯影组 灯影组 表 2 丹寨研究区牛蹄塘组沉积环境划分方案
Table 2. Division scheme for the sedimentary environment of the Niutitang formation in the study area of Danzhai
目标层系 沉积微相 沉积亚相 沉积相 沉积体系 牛蹄塘组 泥棚 浅水陆棚 陆棚 海洋沉积体系 粉砂质泥棚 粉砂质碳质泥棚 深水陆棚 碳质泥棚 表 3 黔南坳陷海相页岩气有利区优选参考指标
Table 3. Reference indicators for optimal selection of the favorable zones of marine shale gas in the Qiannan depression
评价参数 评价指标 调查区目的层段对应指标 牛蹄塘组 富有机质泥页岩厚度/m 厚度稳定,30~50 厚度稳定,60~200 TOC/% >3.0 4.50~6.35 Ro/% 1.30~3.50 2.50~2.70 储集性 脆性矿物含量/% >40 64.0~81.3 黏土矿物含量/% <30 17.5~30.0 孔隙度/% >2.0 2.0~8.0 总含气量/m3·t−1 ≥1.0 0.09~2.7 保存条件 埋藏深度/m 1000 ~4500 0~ 2500 区域盖层厚度/m
区域盖层分布>150
大面积连片259~652
大面积连片顶、底板厚度/m
顶、底板均质程度>30
均质顶70~125、底10~15
顶板均质,底板较均质地层倾角/° <30 4~48 距目的层露头距离/km >2 >2 距通天断裂距离/km ≥5 0~10 断裂密度/条·km−1 <0.5 0.2~0.5 地层压力系数 >0.9 0.91~1.06 -
[1] 张金川, 王香增, 李中明, 刘树根, 牛嘉亮, 袁天姝, 李兴起, 唐玄. 页岩含气量现场测试技术进展与发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(1):315-326.ZHANG Jinchuan, WANG Xiangzeng, LI Zhongming, LIU Shugen, NIU Jialiang, YUAN Tianshu, LI Xingqi, TANG Xuan. Technological progress and trend in shale gas on-site testing: A critical review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(1): 315-326. [2] 陈孝红, 李海, 苗凤彬, 罗胜元. 中扬子古隆起周缘寒武系页岩气赋存方式与富集机理[J]. 华南地质, 2022, 38(3):394-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2022.03.003CHEN Xiaohong, LI Hai, MIAO Fengbin, LUO Shengyuan. Occurrence model and enrichment mechanism of Cambrian shale gas around paleo-uplift in the mid-Yangtze region[J]. South China Geology, 2022, 38(3): 394-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2022.03.003 [3] 罗超, 刘树根, 孙玮, 冉波, 雍自权, 杨迪, 张旋, 王世玉, 叶玥豪, 邓宾. 上扬子区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气基本特征研究:以贵州丹寨南皋剖面为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(3):453-470.LUO Chao, LIU Shugen, SUN Wei, RAN Bo, YONG Ziquan, YANG Di, ZHANG Xuan, WANG Shiyu, YE Yuehao, DENG Bin. Basic characteristics of shale gas in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in the upper Yangtze region: Taking Nangao section in Danzhai as an Example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(3): 453-470. [4] 李世臻, 刘卫彬, 王丹丹, 张文浩, 林燕华. 中美陆相页岩油地质条件对比[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(Suppl.1):39-40.LI Shizhen, LIU Weibin, WANG Dandan, ZHANG Wenhao, LIN Yanhua. Continental shale oil geological conditions of China and the United States[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(Suppl.1): 39-40. [5] 邹才能, 潘松圻, 荆振华, 高金亮, 杨智, 吴松涛, 赵群. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(1):1-12. doi: 10.7623/syxb202001001ZOU Caineng, PAN Songqi, JING Zhenhua, GAO Jinliang, YANG Zhi, WU Songtao, ZHAO Qun. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 1-12. doi: 10.7623/syxb202001001 [6] 陈方文, 卢双舫, 丁雪. 泥页岩吸附气能力评价模型:以黔南坳陷牛蹄塘组吸附气含量为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2015, 44(3):508-513.CHEN Fangwen, LU Shuangfang, DING Xue. Evaluation model of gas adsorption capacity of shale: A case of adsorbed gas content from Niutitang Formation in Qiannan depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2015, 44(3): 508-513. [7] Bao S J, Zhai G Y, Zhou Z, Yu S F, Chen K, Wang Y F, Wang H, Liu Y M. The evolution of the Huangling uplift and its control on the accumulation and preservation of shale gas[J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(3): 346-353. [8] 蒙炳坤, 李靖, 周世新, 淡永, 张庆玉, 聂国权. 黔南坳陷震旦系—寒武系页岩解析气中氦气成因及来源[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4):647-655.MENG Bingkun, LI Jing, ZHOU Shixin, DAN Yong, ZHANG Qingyu, NIE Guoquan. Origin and source of helium in the resolved gas of Sinian–Cambrian shale in the Qiannan depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 647-655. [9] 魏小松, 严德天, 龚银, 牛杏, 梁万乐, 伏海蛟, 刘紫璇, 杨向荣, 张宝. 鄂西—黔南地区下寒武统页岩旋回地层学研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2024, 42(3):823-838.WEI Xiaosong, YAN Detian, GONG Yin, NIU Xing, LIANG Wanle, FU Haijiao, LIU Zixuan, YANG Xiangrong, ZHANG Bao. Cyclostratigraphic analysis of the Lower Cambrian shales in western Hubei and southern Guizhou[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2024, 42(3): 823-838. [10] 曹慧, 孙东生, 苑坤, 李阿伟, 张光晗. 黔南地区~3km油气深孔地应力测量与构造应力场分析[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1):88-98.CAO Hui, SUN Dongsheng, YUAN Kun, LI Awei, ZHANG Guanghan. In-situ stress determination of 3 km oil-gas deep hole and analysis of the tectonic stress field in the southern Guizhou[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 88-98. [11] Ge M N, Chen K, Chen X L, Wang C, Bao S J. The influence factors of gas-bearing and geological characteristics of Niutitang Formation shale in the southern margin of Xuefeng mountain ancient uplift: A case of Well Huangdi 1[J]. China Geology, 2020, 3(4): 533-544. [12] 谢舟, 卢双舫, 于玲, 陈瑜鹏, 王民, 陈方文, 何希鹏. 泥质气源岩层内天然气扩散损失量评价:以黔南坳陷黄页1井九门冲组页岩为例[J]. 矿物学报, 2014, 34(1):137-143.XIE Zhou, LU Shuangfang, YU Ling, CHEN Yupeng, WANG Min, CHEN Fangwen, HE Xipeng. Assessment of natural gas loss from mudstone gas source rocks: An example from Jiumenchong Formation of Huangye 1 Well, Lower Cambrian, southern Guizhou Sag[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2014, 34(1): 137-143. [13] 陈方文, 卢双舫, 丁雪. 黔南坳陷牛蹄塘组富有机质页岩生气期和生气量[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 40(3):55-62.CHEN Fangwen, LU Shuangfang, DING Xue. Gas generation period and quantity of organic-rich Niutitang shale in Qiannan depression, China[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2016, 40(3): 55-62. [14] 淡永, 卢炳雄, 梁彬, 张庆玉, 李景瑞. 中国南方古生界碳酸盐岩发育对页岩气成藏和开发控制问题[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(3):343-350. doi: 10.11932/karst20180304DAN Yong, LU Bingxiong, LIANG Bin, ZHANG Qingyu, LI Jingrui. Effects of Paleozoic carbonate rock on shale gas accumulation and exploitation in Southern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 343-350. doi: 10.11932/karst20180304 [15] 朱继良, 许模, 孙建平, 康小兵, 史箫笛. 重庆涪陵页岩气勘查开发区岩溶水文地质结构研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(1):1-10. doi: 10.11932/karst2019y32ZHU Jiliang, XU Mo, SUN Jianping, KANG Xiaobing, SHI Xiaodi. Karst hydrogeologic structures of the shale-gas exploration and exploitation area in Fuling, Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11932/karst2019y32 [16] 聂国权, 李小盼, 淡永, 梁彬, 张庆玉, 李景瑞, 季少聪. 黔南坳陷下寒武统牛蹄塘组泥页岩埋藏史与热史研究:以贵都地1井为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):760-767.NIE Guoquan, LI Xiaopan, DAN Yong, LIANG Bin, ZHANG Qingyu, LI Jingrui, JI Shaocong. Burial and thermal history of mud shale in Niutitang Formation of Lower Cambrian in southern Guizhou depression: A case study of Guidudi Well 1[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5): 760-767. [17] 马龙, 徐学金, 闫剑飞, 曹竣锋, 门玉澎, 淡永, 熊国庆, 孙媛媛, 邓奇, 杨菲. 古隆起边缘页岩气富集规律与选区:以雪峰西南缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2022, 42(3):426-443.MA Long, XU Xuejin, YAN Jianfei, CAO Junfeng, MEN Yupeng, DAN Yong, XIONG Guoqing, SUN Yuanyuan, DENG Qi, YANG Fei. Enrichment laws and regional selection of shale gas at the edge of palaeohigh: A case study on the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation on the southwestern margin of Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2022, 42(3): 426-443. [18] 何贵松, 何希鹏, 高玉巧, 张培先, 万静雅, 黄小贞. 中国南方3套海相页岩气成藏条件分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(1):57-68. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190102HE Guisong, HE Xipeng, GAO Yuqiao, ZHANG Peixian, WAN Jingya, HUANG Xiaozhen. Analysis of accumulation conditions of three sets of marine shale gas in Southern China[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(1): 57-68. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190102 [19] Wei S L, He S, Pan Z J, Zhai G Y, Dong T, Guo X W, Yang R, Han Y J, Yang W. Characteristics and evolution of pyrobitumen-hosted pores of the overmature Lower Cambrian Shuijingtuo shale in the south of Huangling anticline, Yichang area, China: Evidence from FE-SEM petrography[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 116: 104303. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104303 [20] Xi Z D, Tang S H, Li J, Zhang Z Y, Xiao H Q. Pore characterization and the controls of organic matter and quartz on pore structure: Case study of the Niutitang Formation of northern Guizhou Province, South China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 61: 18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.11.001 [21] 包书景, 陈科, 周志, 余谦, 陈孝红, 李世臻, 刘伟, 苑坤, 淡永, 冯兴强, 周道容. 南方公益性页岩气调查研究进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2023, 10(6):1-12.BAO Shujing, CHEN Ke, ZHOU Zhi, YU Qian, CHEN Xiaohong, LI Shizhen, LIU WEI, YUAN Kun, DAN Yong, FENG Xingqiang, ZHOU Daorong. Progress of investigation and research on public welfare shale gas in Southern China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2023, 10(6): 1-12. [22] 张培先. 黔中隆起及邻区下寒武统页岩气成藏特殊性分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):162-179. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702162ZHANG Peixian. Peculiar accumulation conditions for shale gas in the Lower Cambrian in Qianzhong uplift and its periphery[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 162-179. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702162 [23] 卢树藩, 陈厚国. 黔南地区麻页1井寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩特征及页岩气勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(3):81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010LU Shufan, CHEN Houguo. Shale characteristics and shale gas exploration prospect in Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Well MY-1, southern Guizhou[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(3): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010 [24] 门玉澎, 闫剑飞, 戚明辉, 熊国庆, 马龙, 杨菲, 康建威. 黔南地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气顶底板特征研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(1):53-59.MEN Yupeng, YAN Jianfei, QI Minghui, XIONG Guoqing, MA Long, YANG Fei, KANG Jianwei. Effects of bottom and top layers of Niutitang Formation on preservation of shale gas in southern Guizhou[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(1): 53-59. [25] 孟江辉, 潘仁芳, 陈浩, 唐小玲. 滇黔桂盆地泥盆系页岩气成藏条件及资源潜力分析[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1):181-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.01.020MENG Jianghui, PAN Renfang, CHEN Hao, TANG Xiaoling. Shale gas accumulation condition and resource potential analysis of Devonian in Dian-Qian-Gui basin[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(1): 181-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.01.020 [26] 张本杰, 姚玲, 罗沙, 赵芸, 孙维. 贵州省页岩气勘探开发现状与展望[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2016, 10(3):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1132.2016.03.016ZHANG Benjie, YAO Ling, LUO Sha, ZHAO Yun, SUN Wei. Current status and outlook of shale gas exploration and development in Guizhou Province[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2016, 10(3): 57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1132.2016.03.016 [27] 万梦, 苗宝, 杜继成. 黔南下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏条件及勘探前景分析[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2017, 31(3):19-22, 131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2017.03.005WAN Meng, MIAO Bao, DU Jicheng. Shale gas accumulation conditions and exploration prospect in Niutitang Formation of Lower Cambrian in southern Guizhou[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2017, 31(3): 19-22, 131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2017.03.005 [28] 易同生, 赵霞. 贵州下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩储层特征及其分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(8):8-14. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.08.002YI Tongsheng, ZHAO Xia. Characteristics and distribution patterns of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale reservoirs in Guizhou, China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(8): 8-14. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.08.002 [29] 戴传固. 贵州省区域地质志 上下册[R]. 贵州省地质调查院, 2013. [30] 丰国秀, 陈盛吉. 岩石中沥青反射率与镜质体反射率之间的关系[J]. 天然气工业, 1988, 8(3):20-25.FENG Guoxiu, CHEN Shengji. The relationship between asphalt reflectance and vitrinite reflectance in rocks[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1988, 8(3): 20-25. [31] 张志飞, 刘璠, 梁悦, 胡亚洲, 陈飞扬, 张志亮, 陈延龙, 任心宜, 姚金龙, 李国祥, 郭俊锋, 华洪. 寒武纪生命大爆发与地球生态系统起源演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(6):1065-1106.ZHANG Zhifei, LIU Fan, LIANG Yue, HU Yazhou, CHEN Feiyang, ZHANG Zhiliang, CHEN Yanlong, REN Xinyi, YAO Jinlong, LI Guoxiang, GUO Junfeng, HUA Hong. The Cambrian Explosion of animals and theevolution of ecosystems on Earth[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 51(6): 1065-1106. -




 下载:
下载: