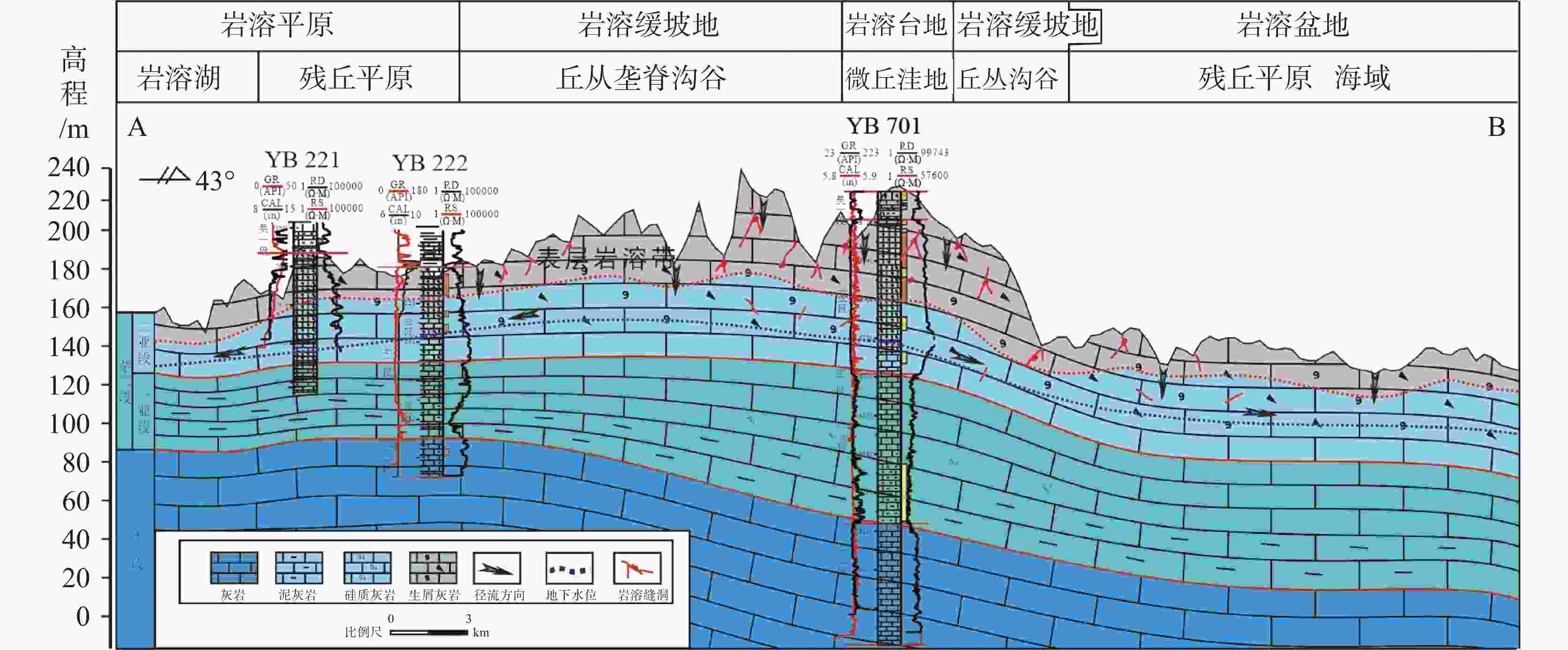
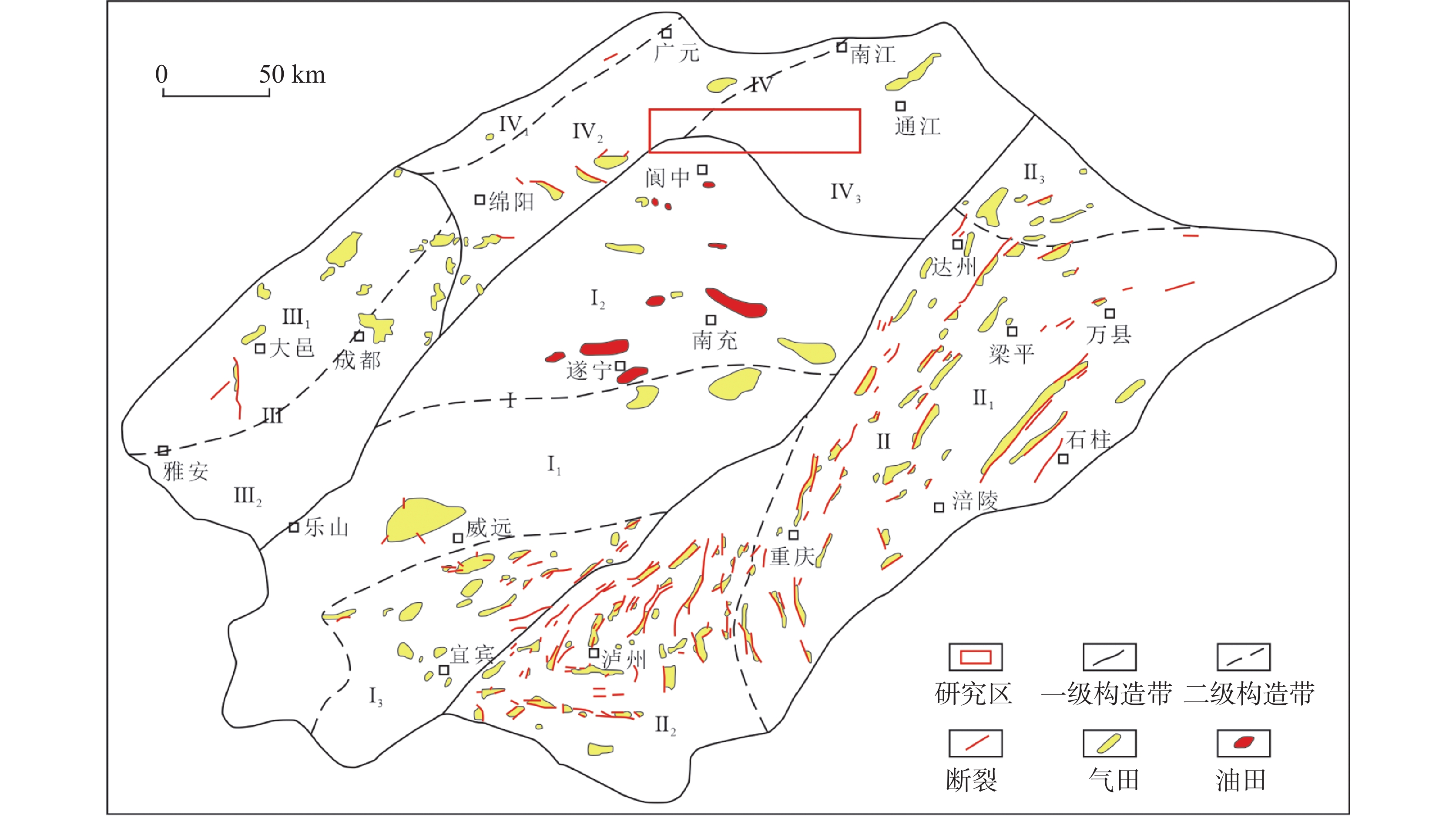
Reconstruction of karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system on the top of Maokou formation in Yuanba area, northern Sichuan Basin
-
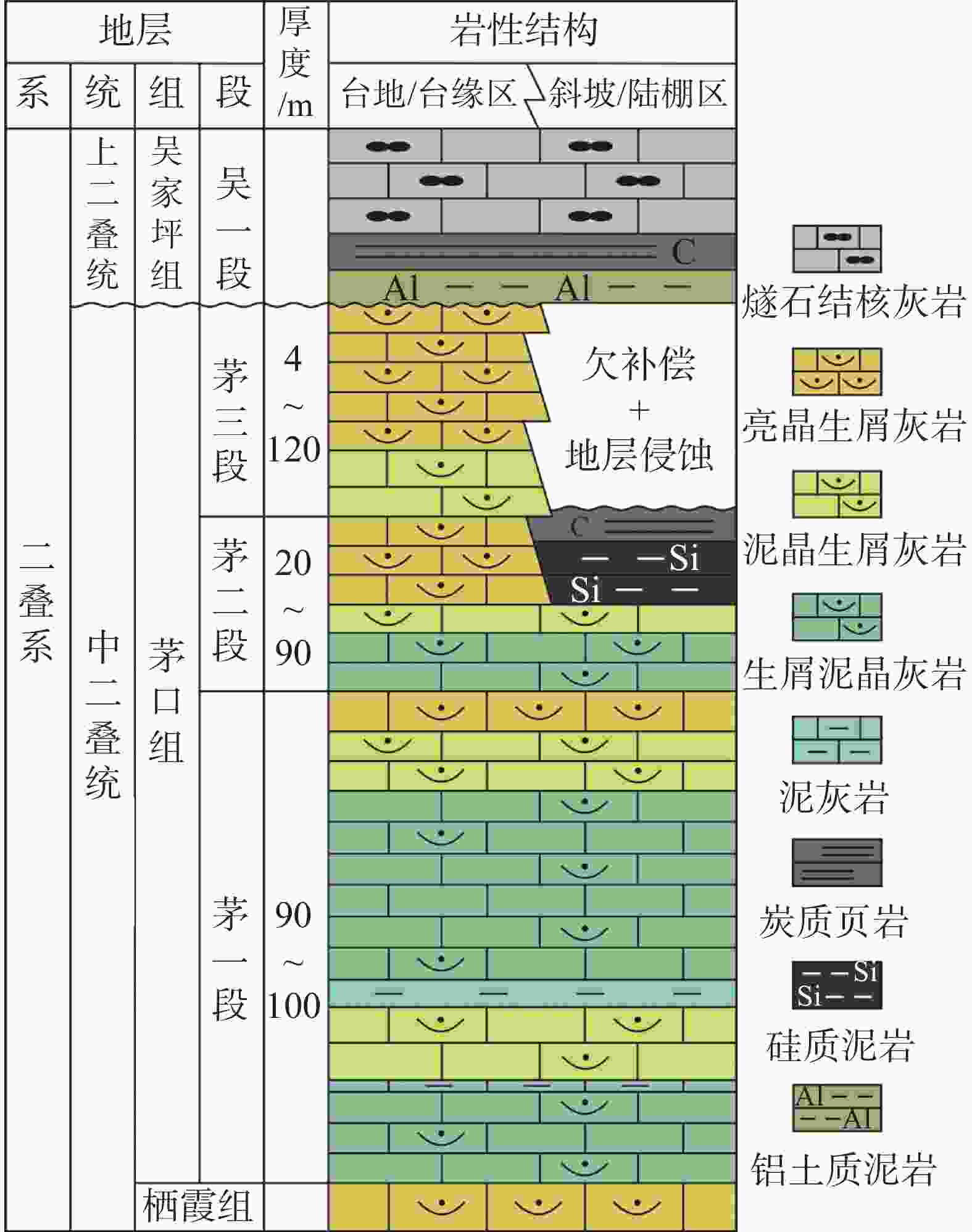
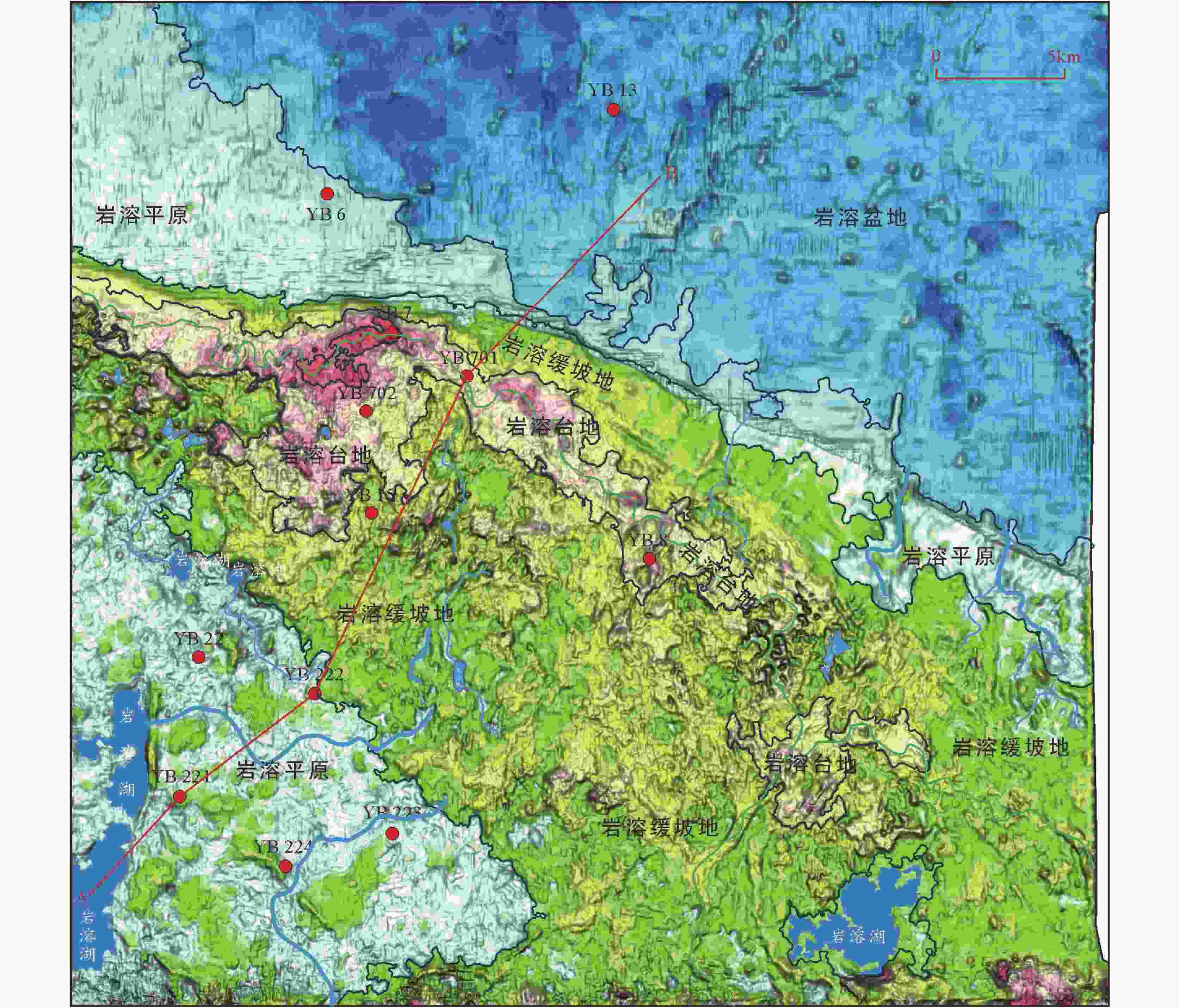
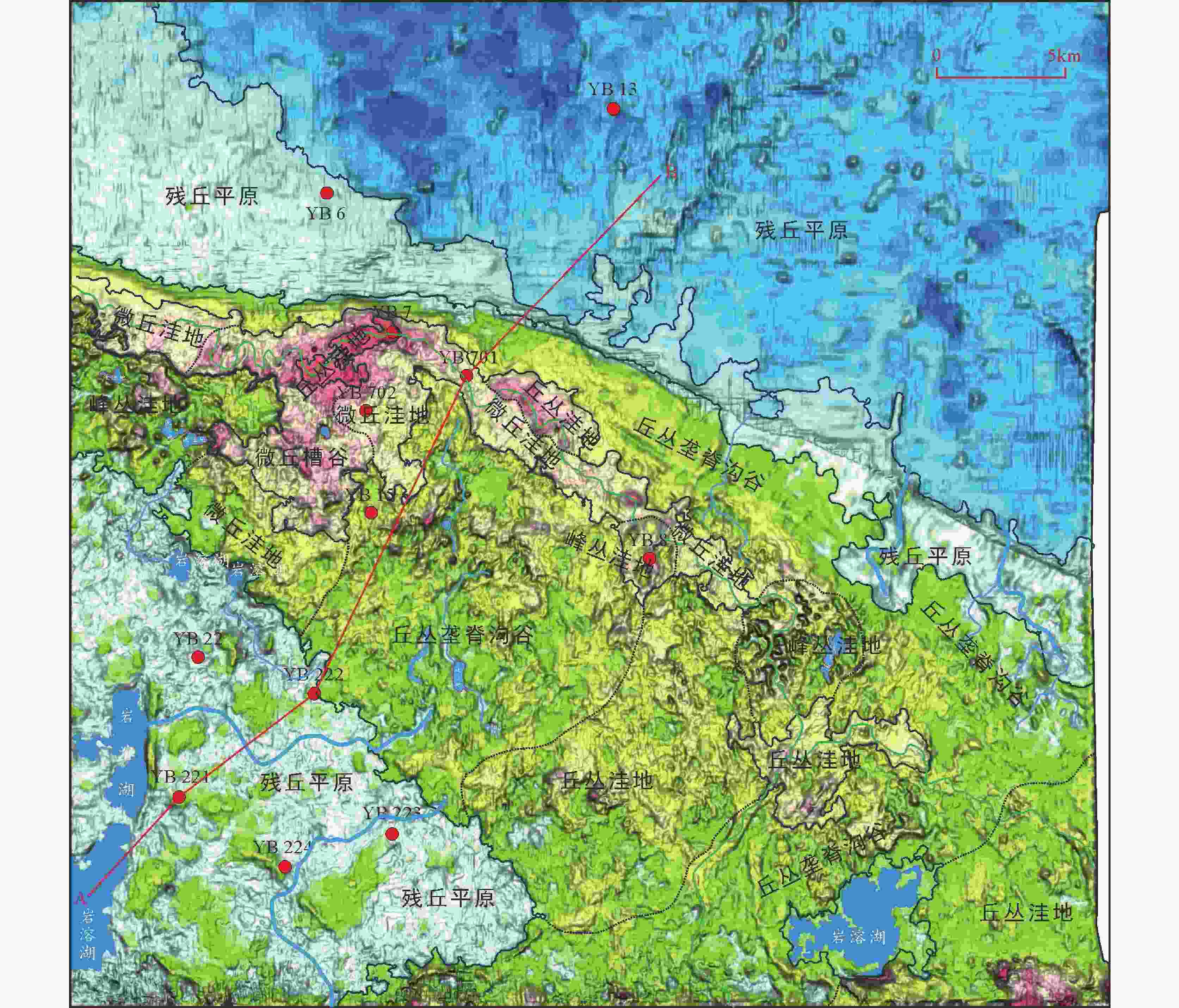
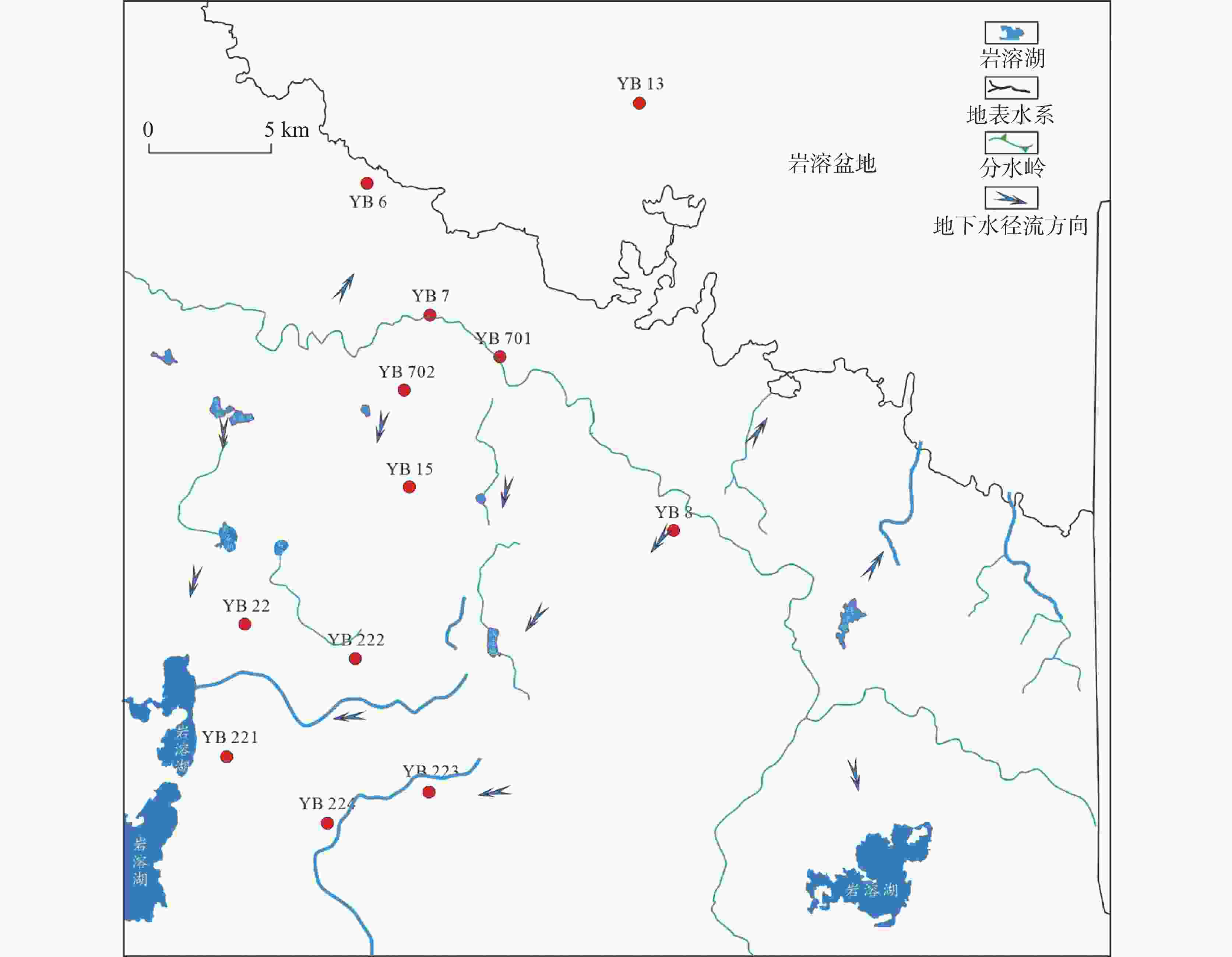
摘要: 川北元坝地区茅口组碳酸盐岩岩溶储层发育,但该套储层非均质性强,储层预测有较大困难,需要进一步恢复岩溶古地貌、古水系,从而掌握储层分布规律,指导下一步油气勘探开发。文章选用残厚法恢复了元坝地区茅口组顶面岩溶古地貌,并结合现代岩溶学和岩溶动力学理论,划分了岩溶台地、岩溶缓坡地、岩溶平原和岩溶盆地4类二级地貌单元。应用现代岩溶分类方法,根据微地貌组合形态,划分了6类三级地貌单元,并对古水系进行了刻画。分析认为元坝地区茅口组顶面岩溶古地貌属岩溶地貌形成演化的初期阶段,不同地貌位置岩溶发育有较大差异,岩溶缓坡地属地下水径流区,水动力条件最强,孔洞最发育,是下一步储层勘探方向。Abstract: The carbonate karst reservoir of Maokou formation is developed in the Yuanba area, northern Sichuan Basin. However, it is difficult to predict this set of reservoir because of its strong heterogeneity. Therefore, for the guidance of future oil and gas exploration and development, it is necessary for us to further restore karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system so as to master the law of reservoir distribution. In order to better depict the micro karst landform, the ''the trend surface of residual thickness and impression residual" are combined to restore the ancient landform. According to the characteristics of karst paleo-geomorphology on the top of Maokou Formation in Yuanba area and the thickness from the top of Maokou formation to the top of its first section in Yuanba area, an index system for the classification of karst paleo-geomorphology types is established. Based on the thickness mentioned above, the paleogeographic environment and paleo-hydrodynamic conditions, the study area is divided into four second-tier geomorphic units—karst platform, gentle karst slope, karst plain and karst basin. Then, in terms of modern karst classification, a third-tier geomorphic units are subdivided into six types—micro hill depression, hill-cluster depression, micro hill trough, cluster-peak depression, hill-cluster ridge valley and monadnock plain, according to the micro geomorphic combination form of karst paleo-geomorphology on the top of Maokou Formation in Yuanba area. Based on the characteristics of paleo-topography as well as the plane distribution and mutual configuration relationship of the six third-tier geomorphic units, the surface water system of the paleo-karst surface at the top of Maokou formation in Yuanba and its adjacent areas is constructed. In general, controlled by the ancient topography, the surface runoff is mainly the scattered runoff from the karst platform to both sides. The ancient water system is not well developed with no centralized runoff system, and only small gullies and karst lakes are locally developed. On the whole, the ancient karst landform on the top of Maokou formation in the study area belongs to the initial stage of the formation and evolution of karst landform. The relative elevation difference of the regional terrain which is slightly undulating is generally less than 120 m. The relative elevation difference of hills (peaks) and depressions is generally less than 10-30 m, which belongs to the initial stage of tectonic uplift and denudation and is characterized by coastal (island) karst landform, and the surface water system is not fully formed. The karstification time of the study area is relatively short, belonging to the initial stage of epigenetically exposed karst which is characterized by the joint karstification of atmospheric fresh water and seawater. The karstification mode is mainly the leaching and infiltration of atmospheric fresh water, which is difficult to form concentrated lateral runoff. Karstification mainly occurs in the shallow part, and karst is dominated by dissolution holes. Large-scale karst fractures and caves have not been formed. There are great differences in karst development in different geomorphic locations, among which the karst platform belongs to the groundwater recharge area; the atmospheric precipitation is mainly vertical infiltration; and the lateral runoff of groundwater is slow. The karst plain belongs to groundwater runoff and discharge area, where groundwater runoff is slow, and the intensity of karstification is relatively weak. The karst basin belongs to groundwater drainage area with long water-rock interaction cycle and weak karstification intensity. The gentle karst slope belongs to groundwater runoff area with the strongest hydrodynamic force and the most developed holes, which is suitable for the future reservoir exploration.
-
表 1 元坝及邻区茅口组顶面岩溶古地貌类型划分表
Table 1. Classification of karst paleo-geomorphology in Yuanba area and on the top of Maokou formation
二级地貌类型 类别 主要指标/m 岩溶台地 215≤Hc<265 岩溶缓坡地 185≤Hc<215 岩溶平原 145≤Hc<185 岩溶盆地 Hc<145 注:Hc为茅口组顶面至茅口组一段顶面的厚度。 表 2 元坝及邻区茅口组顶面岩溶古地貌类型划分表
Table 2. Classification of karst paleo-geomorphology in Yuanba area and on the top of Maokou formation
岩溶古地貌类型 分布位置 二级地貌 三级地貌 主要微地貌形态 岩溶台地 微丘洼地 微丘、浅洼地、沟谷 YB 701井-YB 702井-YB 8井一带 微丘槽谷 微丘、浅洼地、槽谷、沟谷 YB 702井西南侧 丘丛洼地 溶丘、洼地、沟谷 YB 7井一带、YB 701井东侧、研究区东部 峰丛洼地 溶峰、洼地、沟谷 YB 8井一带 岩溶缓坡地 丘丛龙脊沟谷 溶丘、垄脊、沟谷、槽谷 研究区中部、YB 8井东南侧 峰丛洼地 溶峰、洼地、沟谷 研究区中部西侧、YB 8井东南侧 微丘洼地 微丘、浅洼地 YB 22井北侧 岩溶平原 残丘平原 溶丘、浅洼地、平原 YB 22井-YB 222井-YB 223井-YB 221井-YB 224井一带、研究区北部 岩溶盆地 残丘平原 溶丘、浅洼地、平原 研究区北部 -
[1] 肖笛, 谭秀成, 山述娇, 陈韵骐, 夏吉文, 杨坚, 周涛, 程遥. 四川盆地南部中二叠统茅口组古岩溶地貌恢复及其石油地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(10):1992-2002.XIAO Di, TAN Xiucheng, SHAN Shujiao, CHEN Yunqi, XIA Jiwen, YANG Jian, ZHOU Tao, CHENG Yao. The restoration of palaeokarst geomorphology of Middle Permian Maokou Formation and its petroleum geological significance in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(10):1992-2002. [2] 施泽进, 夏文谦, 王勇, 田雪松, 王长城. 四川盆地东南部茅口组古岩溶特征及识别[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(3):622-630.SHI Zejin, XIA Wenqian, WANG Yong, TIAN Xuesong, WANG Changcheng. Characteristics and identification of paleokarst in the Maokou Formation in the southeastern Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(3):622-630. [3] 胡修权, 施泽进, 田亚铭, 王长城. 川东南地区茅口组岩溶古地貌恢复及特征[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(6):874-882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.06.010HU Xiuquan, SHI Zejin, TIAN Yaming, WANG Changcheng. The restoration of karst ancient landform of the Maokou Formation in southeastern Sichuan basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(6):874-882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.06.010 [4] 聂国权, 淡永, 徐亮, 梁彬, 李景瑞. 蜀南Z工区茅口组顶岩溶古地貌、古水系特征与刻画[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):911-917.NIE Guoquan, DAN Yong, XU Liang, LIANG Bin, LI Jingrui. Characteristics and characterization of karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system on the top of the Maokou formation in the Z area in southern Sichuan basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6):911-917. [5] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 段金宝. 中国南方海相油气勘探展望[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5):675-686. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005675GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, DUAN Jinbao. Marine petroleum exploration in South China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5):675-686. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005675 [6] 胡东风. 四川盆地元坝地区茅口组台缘浅滩天然气勘探的突破与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(3):1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.03.001HU Dongfeng. Breakthrough in natural gas exploration in the platform margin shoal at the Maokou Fm in the Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin, and its implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(3):1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.03.001 [7] 段金宝. 普光与元坝礁滩气田天然气成藏特征对比[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(4):9-18.DUAN Jinbao. The comparative study of natural gas accumulation characteristics between Puguang and Yuanba reef-bank gas field[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 38(4):9-18. [8] 唐大海, 肖笛, 谭秀成, 李海云, 谢继容, 刘宏, 杨迅, 张本健. 古岩溶地貌恢复及地质意义: 以川西北中二叠统茅口组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(5):689-695.TANG Dahai, XIAO Di, TAN Xiucheng, LI Haiyun, XIE Jirong, LIU Hong, YANG Xun, ZHANG Benjian. Restoration of paleokarst landform and its geological significance: A case from Middle Permian Maokou Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(5):689-695. [9] 夏日元, 唐健生, 关碧珠, 罗伟权, 马振芳, 周树勋, 于忠平, 潘令红. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系古岩溶地貌及天然气富集特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999(2):37-40. doi: 10.11743/ogg19990208XIA Riyuan, TANG Jiansheng, GUAN Bizhu, LUO Weiquan, MA Zhenfang, ZHOU Shuxun, YU Zhongping, PAN Linghong. Ordovician palaeokarst landform in Ordos Basin and natural gas enrichment characteristics[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999(2):37-40. doi: 10.11743/ogg19990208 [10] 张庆玉, 陈利新, 梁彬, 陈宏峰, 曹建文. 轮古西地区前石炭纪古岩溶微地貌特征及刻画[J]. 海相油气地质, 2012, 17(4):23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.04.004ZHANG Qingyu, CHEN Lixin, LIANG Bin, CHEN Hongfeng, CAO Jianwen. Characterization of Precarboniferous karst microgeomorphology in the west part of Lungu Oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2012, 17(4):23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.04.004 [11] 淡永, 邹灏, 梁彬, 张庆玉, 曹建文, 李景瑞, 郝彦珍. 塔北哈拉哈塘加里东期多期岩溶古地貌恢复与洞穴储层分布预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(3):304-312. doi: 10.11743/ogg20160302DAN Yong, ZOU Hao, LIANG Bin, ZHANG Qingyu, CAO Jianwei, LI Jingrui, HAO Yanzhen. Restoration of multistage paleogeomorphology during Caledonian Period and paleokarst cavernous reservoir prediction in Halahatang area, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(3):304-312. doi: 10.11743/ogg20160302 [12] 钟原, 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 肖笛, 李明隆, 陈聪, 赵立可, 芦飞凡, 谭秀成. 四川盆地西北部中二叠统茅口组岩相古地理、古岩溶地貌恢复及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1):81-93. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.07ZHONG Yuan, YANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, XIAO Di, LI Minglong, CHEN Chong, ZHAO Like, LU Feifan, TAN Xiucheng. Reconstruction and petroleum geological significance of lithofacies paleogeography and paleokarst geomorphology of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1):81-93. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.07 [13] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 元坝气田长兴组—飞仙关组礁滩相储层特征和形成机理[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(6):1001-1011. doi: 10.7623/syxb201406001MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of reef-shoal carbonate reservoirs of Changxing-Feixianguan formations, Yuanba gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(6):1001-1011. doi: 10.7623/syxb201406001 [14] 张庆玉. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩古岩溶发育机理[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018.ZHANG Qingyu. Development Mechanism of Ordovician Carbonate Paleokarst in the Halahatang Area of the Tarim Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018. [15] 邓兴梁, 张庆玉, 梁彬, 淡永, 李景瑞, 郝彦珍. 塔中Ⅱ区奥陶系鹰山组岩溶古地貌恢复方法研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(2):154-158. doi: 10.11932/karst20150208DENG Xingliang, ZHANG Qingyu, LING Bin, DAN Yong, LI Jingrui, HAO Yanzhen. Reconstruction of karst palaeogeomorphology for the OrdovicianYingshan formation in the central Tarim basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(2):154-158. doi: 10.11932/karst20150208 [16] 刘曦翔, 淡永, 罗文军, 梁彬, 徐亮, 聂国权, 季少聪. 四川盆地高石梯地区灯影组四段顶岩溶古地貌、古水系特征与刻画[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(2):206-214.LIU Xixiang, DAN Yong, LUO Wenjun, LIANG Bin, XU Liang, NIE Guoquan, JI Shaochong. Characterization of karst paleo-geomorphology and the paleo-water system on the top of the 4th member of the Dengying Formation in the Gaoshiti area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(2):206-214. [17] 袁道先. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994.YUAN Daoxian. Chinese karst Science[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. [18] 袁道先. 中国岩溶动力系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.YUAN Daoxian. Karst dynamic system in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002. -




 下载:
下载: