Research progress and prospect of carbon sink in karst region of China
-
摘要: 20世纪90年代,我国率先开展了岩溶作用与碳循环研究。文章在系统总结相关研究进展的基础上,阐明岩溶碳汇的原理,提出基于地球系统科学理念的岩溶流域6种碳循环过程模式,揭示了岩溶碳汇的稳定性并回答有关学者对岩溶碳汇的质疑,从四大圈层的碳循环角度提出发掘岩溶地区碳汇潜力的新理念。在综述岩溶地区碳汇人工干预研究进展的基础上,分析了石漠化综合治理、岩溶土壤改良、水生生物固碳、加速岩溶过程等人工干预措施的碳汇潜力及研究应用方面的不足。提出了下一步岩溶流域碳汇调查研究监测和技术创新发展方向,以及固碳增汇试验示范工作思路。Abstract: In the 1990s, karst scientists in China took the lead in the study of karst processes and carbon cycle. Based on systematically summarizing research progresses of the carbon cycle and carbon sink in the karst regions, this paper illustrates the principle of the karst carbon sink, puts forward the six kinds of carbon cycle models on the base of the earth system science idea, reveals the stability of karst carbon sink and answers the question of some geological scholars about karst carbon sink, and proposes a new idea to explore carbon sink potential of karst regions from the carbon cycle angle among earth atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere. Based on the review of research progresses on carbon sink in the karst regions, the carbon sink potential and shortage of the artificial intervention measure on the comprehensive treatment of rocky desertification, improvement of karst soil, carbon sequestration of aquatic plants and accelerating of karst processes have been analyzed. In the last of the paper, the development direction on investigation, researches and monitoring of carbon sink and technological innovation in the karst basins are given, meanwhile, the working idea for test and demonstration of carbon sequestration and carbon sink increase in karst basin are proposed.
-
Key words:
- carbon cycle /
- carbon dioxide sink /
- karst basin /
- research progress /
- China
-
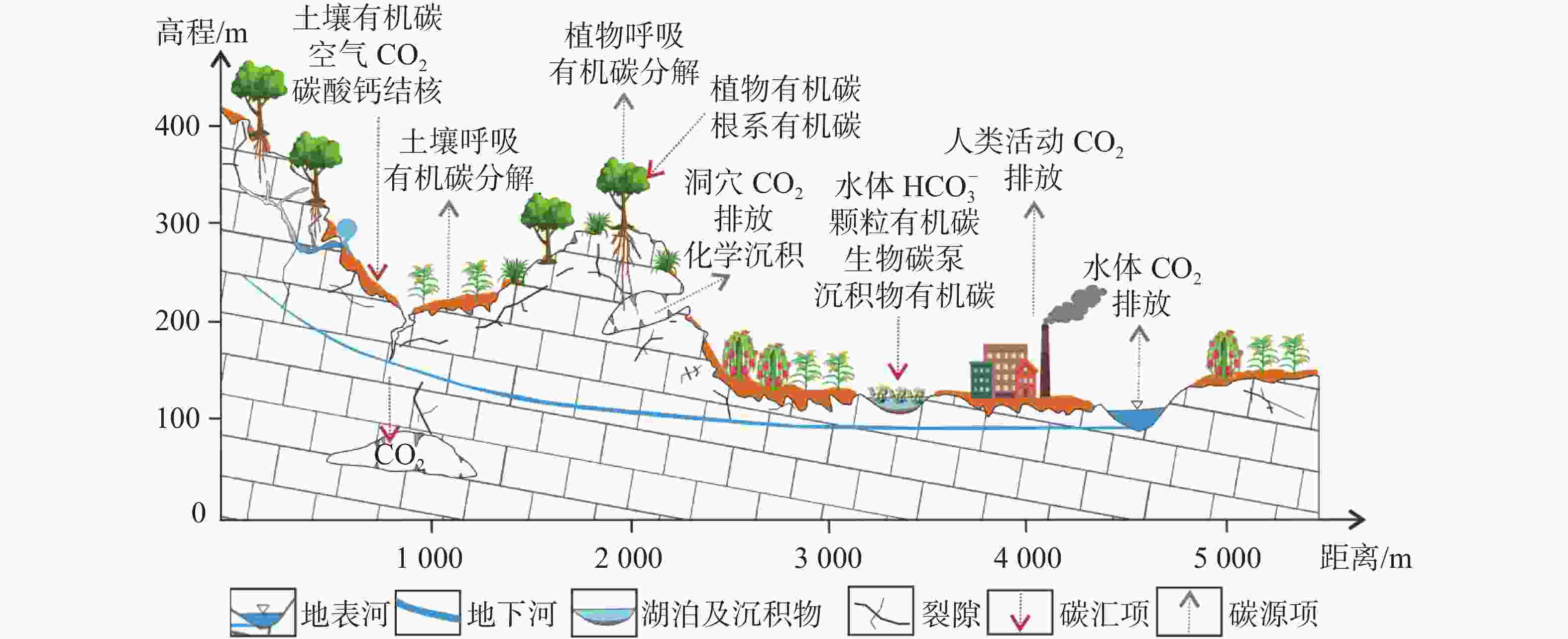
表 1 流域尺度岩溶系统碳循环过程及其碳源汇效应
Table 1. Carbon cycle process and carbon source sink effect of karst system at watershed scale
序号 碳循环过程 碳源项 碳汇项 碳源汇效应 1 岩溶空间CO2循环 洞穴碳排放 洞穴空气碳封存 汇大于源 2 岩溶水系统碳循环 水体碳排放 重碳酸根、颗粒有机碳、生物碳泵 汇大于源 3 岩溶土壤系统碳循环 土壤呼吸、土壤有机碳分解 土壤有机碳、土壤空气CO2、碳酸钙结核无机碳 汇大于源 4 岩溶植物系统碳循环 植物呼吸、植物有机碳分解 植物有机碳、根系有机碳 汇大于源 5 岩溶沉积物碳循环 沉积过程碳排放 沉积物有机碳 源大于汇 6 岩溶区人类活动碳循环 产业碳排放、人类活动碳排放 碳排放岩溶吸收、碳地质封存 源大于汇 -
[1] Yuan Daoxian, Zhu Dehao, Weng Jintao, et al. Karst of China. Beijing: Geological Publishing Hourse, 1991 [2] 袁道先. 碳循环与全球岩溶[J]. 第四纪研究, 1993, 13(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001YUAN Daoxian. Carbon cycle and global karst[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1993, 13(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001 [3] 袁道先. 中国岩溶动力系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.YUAN Daoxian. Karst dynamic system in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002. [4] 袁道先. 地球系统的碳循环和资源环境效应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(3):223-232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.03.004YUAN Daoxian. Carbon cycle in earth system and its effects on environment and resources[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(3):223-232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.03.004 [5] 袁道先. 道岩溶作用与碳循环”研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(5):425-432. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.05.001YUAN Daoxian. Progress in the study on karst processes and carbon cycle[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(5):425-432. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.05.001 [6] JIANG Z, YUAN D. Source-sink in karst processes in karst areas of China[J]. Episodes, 1999, 22:33-35. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1999/v22i1/005 [7] 袁道先, 蒋忠诚. IGCP3792岩溶作用与碳循环”在中国的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000, 27(1):49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.01.016YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Zhongcheng. Review on the research progress of the IGCP 379 project“Karst Processes and the Carbon Cycles”in China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2000, 27(1):49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.01.016 [8] 章程, 汪进良, 肖琼, 等. 岩溶碳循环与流域地球化学过程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021.ZHANG Chen, WANG Jinliang, XIAO Qiong. Karst carbon cycle and basin geochemical process[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021. [9] 蒋忠诚, 蒋小珍, 雷明堂. 运用GIS和溶蚀试验数据估算中国岩溶区大气CO2的汇[J]. 中国岩溶, 2000, 19(3):212-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2000.03.003JIANG Zhongcheng, JIANG Xiaozhen, LEI Mingtang. Estimation of atmospheric CO2 sink of karst areas in China based on GIS and limestone tablet loss data[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2000, 19(3):212-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2000.03.003 [10] 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 曹建华, 覃小群, 何师意, 章程. 中国岩溶碳汇潜力研究[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(4):129-134.JIANG Zhongcheng, YUAN Daoxian, CAO Jianhua, QIN Xiaoqun, HE Shiyi, ZHANG Cheng. A Study of carbon sink capacity of karst processes in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(4):129-134. [11] 章程, 蒋忠诚, Chris Groves, 袁道先. 岩溶IGCP 国际合作30 年与岩溶关键带研究展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(3):301-306.ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Zhongcheng, Chris Groves, YUAN Daoxian. 30 years international cooperation with IGCP and perspectives of karst critical zone research[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(3):301-306. [12] 李强. 基于文献计量学分析2016年度岩溶学研究热点[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(5):535-545. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.05.0535LI Qiang. Research hotspots of karst in 2016 based on bibliometrics analysis[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(5):535-545. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.05.0535 [13] 蒋忠诚, 覃小群, 曹建华, 蒋小珍, 何师意, 罗为群. 中国岩溶作用产生的大气 CO2碳汇的分区计算[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.002JIANG Zhongcheng, QIN Xiaoqun, CAO Jianhua, JIANG Xiaozhen, HE Shiyi, LUO Weiqun. Calculation of atmospheric CO2 sink formed in karst progresses of the karst divided regions in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4):363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.002 [14] 刘再华, 曾庆睿, 陈波, 贺海波. 碳酸盐风化碳汇研究. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.LIU Zaihua, ZENG Qingrui, CHEN Bo, HE Haibo. Research on carbonate weathering carbon sink[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. [15] Curl R L. Carbon shifted but not sequestered[J]. Science, 2012, 335:655. [16] 徐胜友, 蒋忠诚. 我国岩溶作用与大气温室气体CO2源汇关系的初步估算[J]. 科学通报, 1997, 42(9): 953-956.XU Shengyou, JIANG Zhongcheng. Preliminary estimation of the relationship between karst process and the source sink of atmospheric greenhouse gas CO2 in China [J]. Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(9): 953-956. [17] 何师意, 徐胜友, 张美良. 岩溶土壤中CO2浓度、水化学观测及其与岩溶作用的关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 1997, 16(4):319-324.HE Shiyi, XU Shengyou, ZHANG Meiliang. Observation on soll CO2 concentration, hydrochemistry, and theirrelationship with karst processes[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1997, 16(4):319-324. [18] Liu Z, Macpherson G L, Groves G et al. Large and active CO2 uptake by coupled carbonate weathering. Earth Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 42-49. [19] 蒋忠诚. 中国南方表层岩溶带的特征及形成机理[J]. 热带地理, 1998, 18(4):322-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.1998.04.007JIANG Zhongcheng. Fatures of epikarst zone in south China and formation mechanism[J]. Troplcal Geography, 1998, 18(4):322-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.1998.04.007 [20] Hoffer-French K J, Herman J S. Evaluation of hydrological and biological influences on CO2 fluxes from a karst stream[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1989, 108(1):189-212. [21] Zhongcheng Jiang, Yanqing Lian, Xiaoqun Qin. Carbon cycle in the epikarst systems and its ecological effects in South China. Environmental earth sciences, 2013(68): 151-158. [22] 曹建华, 周莉, 杨慧, 卢茜, 康志强. 桂林毛村岩溶区与碎屑岩区林下土壤碳迁移对比及岩溶碳汇效应研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(3):431-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.03.05CAO Jianhua, ZHOU Li, YANG Hui, LU Qian, KANG Zhiqiang. Comparison of soil carbon migration and karst carbon sink effect between Maocun karst area and clastic rock area in Guilin[J]. Quaternary Research, 2011, 31(3):431-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.03.05 [23] 张 莹, 李 强. 是“岩溶碳汇”还是“岩溶碳通量”?[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(6): 539-542.ZHANG Ying, LI Qiang. Is it karst carbon sink or karst carbon flux?[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(6): 539-542. [24] 王世杰, 刘再华, 倪健, 闫俊华, 刘秀明. 中国南方喀斯特地区碳循环研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(1):2-9.WANG Shijie, LIU Zaihua, NI Jian, YAN Junhua, LIU Xiuming. A review of research progress and future prospective of carbon cycle in karst area of South China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(1):2-9. [25] JIANG Zhongcheng, ZHANG Cheng, QIN Xiaoqun, PU Junbing, BAI Bing. Structural Features and Function of Karst Critical Zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2019 , 93(supp. 1): 109-112. [26] 吴泽燕, 章程, 蒋忠诚, 罗为群, 曾发明. 岩溶关键带及其碳循环研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(5):488-498. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.05.0488WU Zeyan, ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Zhongcheng, LUO Weiqun, ZENG Faming. Advance of karst critical zone and its carbon cycle[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(5):488-498. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.05.0488 [27] Atkinson T C. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of the unsaturated zone: An important control of groundwater hardness in limestones[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1977, 35(1):111-123. [28] 刘再华, Chris G, 袁道先, Joe Meiman, 姜光辉, 何师意. 水—岩—气相互作用引起的水化学动态变化研究: 以桂林岩溶试验场为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2003, 3(4):13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.04.003LIU Zaihua, Chris GROVES, YUAN Daoxian, Joe MEIMAN, JIANG Guanghui, HE Shiyi. Study on the hydrochemical variations caused by the water-rock-gas interaction: An example from the Guilin Karst Experimental Site[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2003, 3(4):13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.04.003 [29] Liu Z, Li Q, Sun H, et al. Seasonal, diurnal and storm-scale hydrochemical variations of typical epikarst springs in subtropical karst areas of SW China: Soil CO2 and dilution effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337:207-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.01.034 [30] 莫雪, 蒲俊兵, 袁道先, 章程, 何师意, 于奭, 刘文, 张陶, 周建超, 杨会, 唐伟. 亚热带典型岩溶区地表溪流溶解无机碳昼夜变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(4):873-880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.04.20MO Xue, PU Junbing, YUAN Daoxian, ZHANG Cheng, HE Shiyi, YU Shi, LIU Wen, ZHANG Tao, ZHOU Jianchao, YANG Hui, TANG Wei. Diurnal variation characteristics and influencing factors of dissolved inorganic carbon in surface streams in typical karst areas of subtropical zone[J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 34(4):873-880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.04.20 [31] ZHANG Tao, Li Jianhong, PU Junbing, Jonathan B. Martin, Mitra B. Khadka, Wu Feihong, LI Li, JIANG Feng, HUANG Siyu, YUAN Daoxian. River sequesters atmospheric carbon and limits the CO2 degassing in karst area, Southwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 92-102 [32] Khadka M B, Martin J B, Jin J. Transport of dissolved carbon and CO2 degassing from a river system in a mixed silicate and carbonate catchment[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 513:391-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.070 [33] 章程. 岩溶区河流水化学昼夜变化与生物地球化学过程[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(1):1-8. doi: 10.11932/karst20150101ZHANG Cheng. Diel aqueous chemistry and biogeochemical processes in streams of karst areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(1):1-8. doi: 10.11932/karst20150101 [34] 李瑞, 于奭, 孙平安, 何师意, 原雅琼, 熊志斌. 贵州茂兰板寨水域水生植物δ13C 特征及光合作用固定HCO3− 碳量估算[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(1):9-16. doi: 10.11932/karst20150102LI Rui, YU Shi, SUN Ping'an, HE Shiyi, YUAN Yaqiong, XIONG Zhibin. Characteristics of δ13C in typical aquatic plants and carbon sequestration by plant photosynthesis in the Banzhai catchment, Maolan of Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(1):9-16. doi: 10.11932/karst20150102 [35] LI Qiang, SONG Ang, PENG Wenjie, JIN Zhenjiang, Müller Werner E G, WANG Xiaohong. Contribution of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria to total organic carbon pool in aquatic system of subtropical karst catchments, Southwest China: Evidence from hydrochemical and microbiological study[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2017, 93(6):1-8. [36] ZHAO Haijuan, XIAO Qiong, ZHANG Cheng, ZHANG Xinghua, WU Xia. Transformation of DIC into POC in a karst river system: evidence from δ13C DIC and δ13C POC in Lijiang, Southwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79:295. doi: 10.1007/s12665-020-09039-7 [37] Baldini J U L, Baldini L M, Mcdermott F, Clipson N. Carbon dioxide sources, sinks, and spatial variability in shallow temperate zone caves: Evidence from Ballynamintra Cave, Ireland[J]. Journal of Cave & Karst Studies, 2006, 68(1):4-11. [38] PU Junbing, YUANG Daoxian, ZHAO Heping, SHEN Licheng. Hydrochemical and pCO2 variations of a cave stream in a subtropical karst area, Chongqing, SW China: Piston effects, dilution effects, soil CO2 and buffer effects[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(9):4039-4049. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2787-z [39] 王晓晓, 殷建军, 徐尚全, 沈立成. 雪玉洞上覆土壤CO2 变化及对表层岩溶泉水化学特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(2):85-89.WANG Xiaoxiao, YIN Jianjun, XU Shangquan, SHEN Lichen. The Variations of Soil CO2 and Hydrochemistry of Epikarst Sping Above Xueyu cave[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(2):85-89. [40] 邱冬生, 庄大方, 胡云锋, 姚锐. 中国岩石风化作用所致的碳汇能力估算[J]. 地球科学, 2004, 29(2):177-182.QIU Dongsheng, ZHUANG Dafang, HU Yunfeng, YAO Rui. Estimation of Carbon Sink Capacity Caused by Rock Weathering in China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(2):177-182. [41] ZENG C, LIU Zaihua, ZHAO Min, YANG Rui. Hydrologically-driven variations in the karst-related carbon sink fluxes: Insights from high resolution monitoring of three karst catchments in Southwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 533:74-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.049 [42] 曹建华, 杨慧, 康志强. 区域碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用碳汇通量估算初探: 以珠江流域为例[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(26):2181-2187. doi: 10.1360/csb2011-56-26-2181CAO Jianhua, YANG Hui, KANG Zhiqiang. Preliminary regional estimation of carbon sink flux by carbonate rock corrosion: A case study of the Pearl River Basin[J]. Chinese Sci Bull, 2011, 56(26):2181-2187. doi: 10.1360/csb2011-56-26-2181 [43] 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 黄奇波, 张连凯. 珠江流域岩石风化作用消耗大气\土壤CO2量的估算[J]. 地球学报, 2013, 34(4):455-462. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.04.08QIN Xiaoqun, LIU Pengyu, HUANG Qibo, ZHANG Liankai. Estimation of atmospheric/soil CO2 consumptionby rock weathering in the Pearl River valley[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2013, 34(4):455-462. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.04.08 [44] JIANG Zhongcheng, QIN Xiaoqun, CAO Jianhua, HE Shiyi, ZHANG Cheng ZHANG Qiang. Carbon sink effects of karst processes in global carbon cycle[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35 (Supp. ): 1-12 [45] PU Junbing, LI Jianhong, ZHANG Tao, XIONG Xiaofeng, YUAN Daoxian. High spatial and seasonal heterogeneity of Pco2 and CO2 emissions in a karst groundwater –stream continuum, Southern China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2019, 26(11):11029-11041. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04456-z [46] Zhang Tao, LI Jianhong, PU junbing, YUAN Daoxian. Carbon dioxide exchange and the controlling factors in Guijiang River, SW China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 578:124073. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124073 [47] LIU Zaihua, Dreybrodt W. Significance of the carbon sink produced by H2O-carbonate-CO2-aquatic phototroph interaction on land[J]. Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(2):182-191. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0682-y [48] 章程, 谢运球, 宁良丹, 玉宏, 汪进良, 李凤. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地典型水生植物δ13C 特征与固碳量估算[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(3):247-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.03.001ZHANG Cheng, XIE Yunqiu, NING Liangdan, YU Hong, WANG Jinliang, LI Feng. Characteristics of δ13C in typical aquatic plants and carbon sequestration in the Huixian karst wetland, Guilin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(3):247-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.03.001 [49] Jiao N, Herndl G J, Hansell D A, et al. Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: Long-term carbon storage in the global ocean[J]. Nature Review Microbiology, 2012, 8(8):593-599. [50] 章程. 岩溶作用时间尺度与碳汇稳定性[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):368-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.003ZHANG Cheng. Time-scale of karst processes and the carbon sink stability[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4):368-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.003 [51] 张强. 岩溶地质碳汇的稳定性: 以贵州草海地质碳汇为例[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(6):947-952. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.06.14ZHANG Qiang. The stability of carbon sink effect related to carbonate rock dissolution: A case study of the Caohai Lake geological carbon sink[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(6):947-952. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.06.14 [52] 蒲俊兵, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 章程 . 岩石风化碳汇研究进展: 基于IPCC第五次气候变化评估报告的分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(10): 1081-1090.PU Junbing, JIANG Zhongcheng, YUAN Daoxian, ZHANG Cheng. Some opinions on rock-weathering-related carbonsinks from the IPCC fifth assessment report[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(10) : 1081-1090 [53] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 张连凯,苏春田. 非岩溶水和硫酸参与溶蚀对湘南地区地下河流域岩溶碳汇通量的影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(3):307-318. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.03.0307HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun, LIU Pengyu, ZHANG Liankai, SU Chuntian. The influence of allogenic water and sulfuric acid to karst carbon sink in karst subterranean river in Southern Hu’nan[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(3):307-318. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.03.0307 [54] 孙平安, 李秀存, 于奭, 原雅琼, 何师意, 王艳雪. 酸雨溶蚀碳酸盐岩的源汇效应分析: 以广西典型岩溶区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(1):101-108. doi: 10.11932/karst20170113SUN Ping’an, LI Xiucun, YU Shi, YUAN Yaqiong, HE Shiyi, WANG Yanxue. Study on source-sink effect in the process of carbonate rock dissolved by acid rain: An example of typical karst regions in Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(1):101-108. doi: 10.11932/karst20170113 [55] 覃小群, 蒋忠诚, 黄奇波, 张连凯, 刘朋雨, 梁永平. 硫化物风化产酸对流域岩石风化和碳循环的影响: 以黄河支流三川河流域为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(4): 1070-1082QIN Xiaoqun, JIANG Zhongcheng, HUANG Qibo, ZHANG Liankai, LIU Pengyu, LIANG Yongping. The influence of sulfide acid on rock weathering and carbon cycle in catchment scale: A case study in Sanchuan River basin of Huanghe River tributary[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(4): 1070-1082. [56] WANG Jing, LIANG Feng, Palmer P I,LIU YI, FANG Shuangxi, Hartmut Bösch, Christopher W. O’Dell, TANG Xiaoping, YANG Dongxu, LIU Lixin , XIA ChaoZong Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data[J]. Nature, 2020, 586:720-723. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2849-9 [57] TONG Xiaowei, Martin Brandt, YUE Yuemin, Stephanie Horion, WANG Kelin, DE Wanda Keersmaecker, TIAN Feng, Guy Schurgers, XIAO Xiangming, LUO Yiqi, CHEN Chi, Ranga Myneni, SHI Zheng, CHEN Hongsong & Rasmus Fensholt. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2018(1):44-50. [58] TANG Xuguang, XIAO Jingfeng, MA Mingguo, YANG Hong, LI Xing, DING Zhi, YU Pujia, ZHANG Yongguang, WU Chaoyang, HUANG Jing, Julian R. Thompson. Satellite evidence for China’s leading role in restoring vegetation productivity over global karst ecosystems[J]. Forest Ecology and Management. 2022, 507 (1): 1-13. [59] 吴沿友, 邢德科, 刘莹. 植物利用碳酸氢根离子的特征分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 39(2):273-277.WU Yanyou‚XING Deke‚LIU Ying. The Characteristics of Bicarbonate Used by Plants[J]. Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(2):273-277. [60] 潘根兴. 中国土壤有机碳和无机碳库量研究[J]. 科技通报, 1999(5):330-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.1999.05.002PAN Genxing. Study on carbon reservoir in soils of china[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 1999(5):330-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.1999.05.002 [61] 潘根兴, 曹建华, 何师意, 滕永忠, 徐胜友. 岩溶土壤系统对空气 CO2 的吸收及其对陆地系统碳汇的意义:以桂林丫吉村岩溶试验场的野外观测和模拟实验为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(4):580-587. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.028PAN Genxing, CAO Jianhua, HE Shiyi, TENG Yongzhong, Xu Shengyou. Sink effect of karst soil system on atmospheric CO2: Evidence from field observation and simulation experiment[J]. Earth Science Frontiers (China University of Geosciences Beijing), 2000, 7(4):580-587. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.028 [62] 潘根兴, 孙玉华, 滕永忠, 陶于祥, 韩富顺, 曹建华, 何师意. 湿润亚热带峰丛洼地岩溶土壤系统中碳分布及其转移[J]. 应用生态学报, 2000, 11(1):70-73.PAN Genxing, SUN Yuhua, TENG Yongzhong, TAO Yuxiang, HAN Fushun. Distribution and transferring of carbon in kast soil system of peak forest depression inhumid subtropical regon[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2000, 11(1):70-73. [63] 王霖娇, 李瑞, 盛茂银 . 典型喀斯特石漠化生态系统土壤有机碳时空分布格局及其与环境的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(5): 1367-1378.WANG Linjiao, LI Rui, SHENG Maoyin. Distribution of soil organic carbon related to environmental factors in typical rocky desertification ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(5) : 1367-1378. [64] 任坤, 沈立成, 袁道先, 王晓晓, 徐尚全. 2012-2013 年重庆雪玉洞洞穴系统碳循环特征[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(8): 1424-1434.REN Kun, SHEN Licheng, YUAN Daoxian, WANG Xiaoxiao, XU Shangquan. Carbon cycle characteristics in karst cave system of Xueyu cave from 2012 to 2013[J]. Earth Scince, 2016, 41(8): 1424-1434. [65] Duc A. Trinh, Quan H. Trinh, Angel Fernández-Cortés, David Mattey, Javier G. Guinea. First assessment on the air CO2 dynamic in the show caves of tropical karst, Vietnam[J]. International Journal of Speleology, 2018, 47(1):93-112. doi: 10.5038/1827-806X.47.1.2141 [66] Bergel S J, Carlson P E, Larson T E, Wood C T, Johnson K R. , Banner J L, Breecker D O. Constraining the subsoil carbon source to cave-air CO2 and speleothem calcite in central Texas[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 217:112-127. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.08.017 [67] 宋贤威, 高扬, 温学发, 郭大立, 于贵瑞, 何念鹏, 张进忠 . 中国喀斯特关键带岩石风化碳汇评估及其生态服务功能[J]. 地理学报, 2016, 71(11): 1926-1938.SONG Xianwei, GAO Yang, WEN Xuefa, GUO Dali, YU Guirui, HE Nianpeng, ZHANG Jinzhong. Rock-weathering-related carbon sinks and associated ecosystem service functions in the karst critical zone in China[J]. Acta Geographica sinica , 2016, 71(11): 1926-1938. [68] Covington M D. The importance of advection for CO2 dynamics in the karst critical zone: An approach from dimensional analysis[J]. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2016, 26(6):431-433. [69] 张春来, 黄芬, 蒲俊兵, 曹建华. 中国岩溶碳汇通量估算与人工干预增汇途径[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4): 42-50.Zhang C L, Huang F, Pu J B, CAO Jianhua. Estimation of karst carbon sink fluxes and manual intervention to increase carbon sinks in China [J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(4): 40-52. [70] Xiaoqun Qin, Zhongcheng Jiang, Liankai Zhang, et al. Chemical weathering and atmospheric CO2 consumption intensity between carbonate rock and silicate rock in the Pearl River Basin, China[J]. Modern Environmental Science and Engineering, 2017, 3(2): 858-863 [71] 曾发明, 吴泽燕, 章 程, 杨奇勇. 峰丛洼地区石漠化治理的碳汇研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):67-73.ZENG Faming, WU Zeyan, ZHANG Cheng, YANG Qiyong. Carbon sink in rocky desertification restoration, Southwest China: A case of the peak-cluster depression areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):67-73. [72] 张明阳, 王克林, 刘会玉, 章春华,段亚锋. 基于遥感影像的桂西北喀斯特区植被碳储量及密度时空分异[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(12):1545-1553.ZHANG MingYang, WANG KeLin, LIU HuiYu, ZHANG ChunHua, DUAN YaFeng. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation carbon storage and density in karst areas of Northwest Guangxi based on remote sensing images[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(12):1545-1553. [73] 钟银星, 周运超, 李祖驹. 印江槽谷型喀斯特地区植被碳储量及固碳潜力研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2014, 42(1):82-89.ZHONG Yinxing,ZHOU Yunchao,LI Zhuju. Research on the Carbon Storage and Potential Carbon Sequestration of Vegetation in the Trough Valley of a Karst Area, Yinjiang[J]. Earth and Environment, 2014, 42(1):82-89. [74] 刘九缠, 孙玉川, 沈立成, 唐廉, 刘宁坤, 游贤慧. 石漠化治理对土壤中CO2、CH4变化特征及碳汇效应的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5):733-741.LIU Jiuchan, SUN Yuchuan, SHEN Licheng, TANG Lian, LIU Ningkun, YOU Xianhui. Effects of rocky desertification control on CO2, CH4 variation and carbon sink in soil[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5):733-741. [75] 陈伟杰, 熊康宁, 任晓冬, 周文龙. 岩溶地区石漠化综合治理的固碳增汇效应研究: 基于 实地监测数据的分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(3):229-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.03.003CHEN Weijie, XIONG Kangning, REN Xiaodong, ZHOU Wenlong. Study on the carbon-sink effect by treatment to karst rock desertification: An analysis in light of field monitoring data[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(3):229-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.03.003 [76] 宋同清, 王克林, 曾馥平, 等. 西南喀斯特植物与环境[M].北京: 科学出版社, 2015 [77] 曾发明. 岩溶石漠化治理对碳汇的影响研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.ZENG Faming. The effects of carbon sinks in karst rocky desertification restoration: A case study from Guohua site, Guangxi, P.R. China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2018. [78] 覃小群, 蒙荣国, 莫日生. 土地覆盖对岩溶地下河碳汇的影响: 以广西打狗河流域为例. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4): 372-378QIN Xiaoqun, MENG Rongguo, MO Risheng. Influence of land covers on carbon sink of underground river: A case in the Dagouhe Basin in Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. [79] 中国地质调查局. 应对气候变化地质调查研究取得重要阶段性成果[N]. 地质调查专报, 2012,60. [80] 张明, 张凤海. 茂兰喀斯特森林下的土壤. 茂兰喀斯特森林科学考察集[M]. 贵阳: 贵州人民出版社. 1987 [81] 王世杰, 卢红梅, 周运超, 谢丽萍,肖德安. 茂兰喀斯特原始森林土壤有机碳的空间变异性与代表性土样采集方法[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(3):475-483. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.03.014WANG Shijie,LU Hongmei,ZHOU Yunchao,XIE Dean. Spatial variability of soil organic carbon and representative soil sampling method in Maolan karst virgin forest[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(3):475-483. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.03.014 [82] 吴敏, 刘淑娟, 叶莹莹, 张伟,王克林,陈洪松. 喀斯特地区坡耕地与退耕地土壤有机碳空间异质性及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(6):1619-1627.WU Min,LIU Shujuan,YE Yingying,ZHANG Wei,WANG Kelin,CHEN Hongsong. Spatial variability of surface soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in cultivated slopes and abandoned lands in a Karst peak-cluster depression area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(6):1619-1627. [83] 金琳, 李玉娥, 高清竹, 刘运通, 万运帆, 秦晓波, 石锋. 中国农田管理土壤碳汇估算[J]. 中国农业科学. 2008, 41(3): 734-743.JIN Lin, LI Yue, GAO Qingzhu, LIU Yuntong, WAN Yunfan, QIN Xiaobo, SHI Feng.Estimate of Carbon Sequestration Under Cropland Management in China[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(3): 734-743. [84] 冯婷. 土壤改良对岩溶碳汇影响的试验研究: 以广西平果果化示范区为例[D]. 南宁: 广西师范学院, 1985.FENG Ting.Experimental study of soil improvement impact on karst carbon sink:A case study at Guohua Ecological Experimental Area Pingguo Guangxi[D].Nanning:Guangxi Teachers Education University,1985. [85] Jiang Y. The contribution of human activities to dissolved inorganic carbon fluxes in a karst underground river system: Evidence from major elements and δ13C DIC in Nandong, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2013, 152:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.05.010 [86] 罗为群, 蒋忠诚, 邓艳, 吴华英. 石灰土改良试验及其岩溶作用响应研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(3):221-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.03.005LUO Weiqun, JIANG Zhongcheng, DENG Yan, WU Huaying. Contrast experimental study on calcareous soil amelioration and karst processes responseand karst processes response[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(3):221-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.03.005 [87] 严毅萍, 曹建华, 杨慧, 尹辉,梁毅,王培. 岩溶区不同土地利用方式对土壤有机碳碳库及周转时间的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(2):144-149.YAN Yiping,CAO Jianhua,YANG Hui,YIN Hui,LIANG YI,WANG Pei. The impact of different soil types on soil organic carbon pool and turnover in karst area[J]. Journal of soil and water conser vartion, 2012, 26(2):144-149. [88] 李建鸿, 蒲俊兵, 袁道先, 刘文,肖琼,于奭,张陶,莫雪,孙平安,潘谋成. 岩溶区地下水补给型水库表层无机碳时空变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(8):2833-2842.LI Jianhong,PU Junbing,YUAN Daoxian,LIU Wen,XIAO Qiong,YU Shi,ZHANG Tao,MO Xue,SUN Pingan,PAN Moucheng. Variations of inorganic carbon and its impact factors in surface-layer waters in a groundwater-fed reservoir in karst area,SW China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(8):2833-2842. [89] 章程, 肖琼, 苗迎, 郭永丽,汤庆佳,郝玉培. 广西桂林漓江典型河段水化学昼夜动态变化及其对岩溶碳循环的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5):613-621. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.042001ZHANG Cheng, XIAO Qiong, MIAO Ying, GUO Yongli, TANG Qingjia, HAO Yupei. Day and Night Aqueous Chemical Changes and Their Impact on Karst Carbon Cycle at Typical Monitoring Sites of the Lijiang River,Guilin, Guangxi[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(5):613-621. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.042001 [90] 严壮, 汪夏雨, 李为, 等. 岩溶区水生生态系统微藻的生物碳泵效应[J]. 微生物学报, 2019, 59(6):1012-1025.YAN Zhuang, WANG Xiayu,LI Wei,YU Longjiang. Biological carbon pump effect of microalgae in aquatic ecosystems of karst areas[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2019, 59(6):1012-1025. [91] Yang M X, Liu Z H, Sun H L, et al. Organic carbon source tracing and DIC fertilization effect in the Pear River: insights from lipid biomarker and geochemical analysis[J]. Appl Geochem, 2016, 73:132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.08.008 [92] Yang R, Chen B, Liu H, et al. Carbon sequestration and decreased CO2 emission caused by terrestrial aquatic photosynthesis: Insights from diel hydrochemical variations in an epikarst spring and two spring-fed ponds in different seasons[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 63(3):248-260. [93] Sun HG, Han JT, Zhang SR, et al. Carbon isotope evidence for transformation of DIC to POC in the lower Xijiang River, SE China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380-381:288-296. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.01.018 [94] 杨玉雪, 向鹏, 卢玮琦, 王仕禄. 贵州乌江渡水库沉积速率及碳氮埋藏通量估算[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(1):66-73.YANG Yuxue,XIANG Peng,LU Weiqi,WANG Shilu. The sedimentation rate and burial fluxes of carbon and nitrogen in Wujiangdu reservoir,Guizhou,China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(1):66-73. [95] 张陶, 李建鸿, 蒲俊兵, 李 瑞, 吴飞红, 李 丽. 小球藻对岩溶水体Ca2+、HCO3_ 利用效率实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):81-90.ZHANG Tao, LI Jianhong, PU Junbing, LI Rui, WU Feihong, LI Li. Experimental study on the utilization efficiency of Chlorella to Ca2+ and HCO3- in karst water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):81-90. [96] 王培, 胡清菁, 王朋辉, 李斌,曹建华. 桂林寨底地下河沉水植物群落结构调查及影响因子分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2015, 36(1):34-39.WANG Pei,HU Qingjing,WANG Penghui,LI Bin,CAO Jianhua. Effect of karst geology on the submerged macrophyte community in Zhaidi river,Guilin[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2015, 36(1):34-39. [97] 熊志斌, 王万海, 玉屏, 于奭. 板寨地下河大型水生植物调查及其固碳评价[J]. 热带地理, 2018, 38(4):557-564.XIONG Zhibin,WANG Wanhai,YU Ping,YU Shi. Large aquatic plants survey and evaluation of carbon sequestration of the Banzhai underground river[J]. Tropical Geography, 2018, 38(4):557-564. [98] Liu Z. Role of carbonic anhydrase as an activator in carbonate rock dissolution and its implication for atmospheric CO2 Sink[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2001, 75(3):347-353. [99] 李为, 余龙江, 袁道先, 吴云. 不同岩溶生态系统土壤及其细菌碳酸酐酶的活性分析及生态意义[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(3):438-443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.03.007LI Wei,YU Longjiang,YUAN Daoxian,WU Yun. Researches on activity of carbonic anhydrase from soil and its bacteria in different Karst ecosystems and its ecological significance[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(3):438-443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2004.03.007 [100] 余龙江, 吴云, 李为, 曾宪东, 付春华. 微生物碳酸酐酶对石灰岩的溶蚀驱动作用研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2004, 23(3):59-62.YU Longjiang, WU Yun, LI Wei, ZENG Xiandong, FU Chunhua. Study on the driving effects on limestionge corrosion bymicrobial carbonic anhydrase[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2004, 23(3):59-62. [101] 李强, 何媛媛, 曹建华, 梁建宏,朱敏洁. 植物碳酸酐酶对岩溶作用的影响及其生态效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(12):1867-1871. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.015LI Qiang, HE Yuanyuan, CAO Jianhua, LIANG Jianhong, ZHU Minjie. The plant carbonic anhydrase at karst area and its ecological effects[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(12):1867-1871. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.015 [102] WANG Chenwei, LI Wei, SHEN Taiming, CHENG Weili,YU Longjiang. Influence of soil bacteria and carbonic anhydrase on karstification intensity and regulatory factors in a typical karst area[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 313:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.016 -




 下载:
下载:


