Mechanism of karst Waterlogging formation and effective control
-
摘要: 岩溶内涝灾害给岩溶地区人们带来重大损失,严重威胁人们的生产生活,其综合治理已成为国家重大现实需求。内涝灾害具有周期性、群发性和突发性的特征,封闭的岩溶地貌及岩溶含水层特殊的溶隙–管道“二元”结构是产生内涝的内部因素,降雨集中的湿润季风气候是内涝发生的直接外因,不合理的工程活动造成水土大量流失阻塞地下岩溶管道,是导致内涝日趋严重的人为外部因素。严重的内涝主要分布在有地下河管道发育的峰丛谷地、洼地地貌区,补给区、径流区、排泄区具有不同内涝成因模式。目前主要采取水利工程措施对内涝进行治理,大部分工程未达到预期成效,后期应以地下河流域为单元,采取水利工程措施与生态环境措施进行综合防治,形成流域岩溶内涝综合防治体系;另外,还需开展内涝灾害形成的水文动态、水土流失动态系统观测,精细刻画洼地岩溶含水层裂隙–管道“二元”结构,明确引发内涝的降雨量阈值及变化特征,阐明内涝灾害形成水文过程和水土流失过程及控制因素,系统揭示内涝形成机制、演变规律和机理;准确掌握岩溶内涝的主控因素和可调控的因素,提出科学有效的内涝调控对策建议,实现流域岩溶内涝灾害标本兼治。Abstract:
The global karst area is about 22 million km2, accounting for 15% of the global land area. The people in karst areas are threatened to varying degrees by droughts and floods. Waterlogging is a geological hazard formed by the superposition of karst geological and geomorphological environment and human activities. The closed karst terrain combined with strong human engineering activities causes serious soil erosion. Soil leaks into the lower karst pipeline through the sinkhole, causing underground pipeline blockage , drainage obstruction, and frequent occurrence of waterlogging; With the increase of extreme weather, human activities, soil erosion in low-lying areas, and blockage of karst pipelines, if left untreated for a long time, the waterlogging time in low-lying areas will become more frequent and severe. Karst Waterlogging disasters have caused significant losses to people in karst areas, seriously threatening their production and life. The comprehensive management of these disasters has a major national demand. The characteristics of Waterlogging disasters are periodicity, group occurrence, and suddenness. The enclosed karst landform and the special "binary" structure of the karst aquifer are the internal factors that cause karst Waterlogging. The subtropical monsoon climate with concentrated rainfall is the external condition for the occurrence of karst Waterlogging. Unreasonable engineering activities have caused a large amount of soil and water loss, blocking underground karst channels, which is the human factor leading to increasingly karst Waterlogging. Severe karst Waterlogging mainly occurs in karst valleys and depressions where underground rivers and pipelines are developed. The recharge area, runoff area, and discharge area of an underground river have different mechanisms for causing internal Waterlogging. At present, there is a lack of systematic research and characterization of the "binary" structure of karst aquifers. Soil erosion leads to a decrease in the rainfall threshold for causing Waterlogging, and no relevant studies have been conducted on the impact of soil erosion on degeneration of underground pipeline water conveyance capacity. There is a lack of in-depth research on the formation mechanism of karst Waterlogging disasters, and it is even more impossible to predict the extent of karst Waterlogging disasters and the losses caused under extreme climate events, which seriously affects the effectiveness of karst Waterlogging control. In the later stage, systematic observations of the hydrological dynamics and soil erosion dynamics that lead to urban Waterlogging should be carried out, characterize the karst aquifer fracture-cave "dual" structure in detail, clarify the rainfall threshold and its changing characteristics that cause urban Waterlogging, elucidate the hydrological processes and soil erosion processes and their controlling factors that lead to the formation of karst Waterlogging disasters, analyze the relationship between reduction coefficient of outlet flow and the amount of soil erosion in low-lying areas, and systematically reveal the mechanism, evolution laws, and principles of karst Waterlogging formation, and then propose scientifically effective countermeasures for karst Waterlogging regulation. -
Key words:
- karst waterlogging /
- karst aquifer /
- underground river /
- soil and water loss /
- effective governance
-
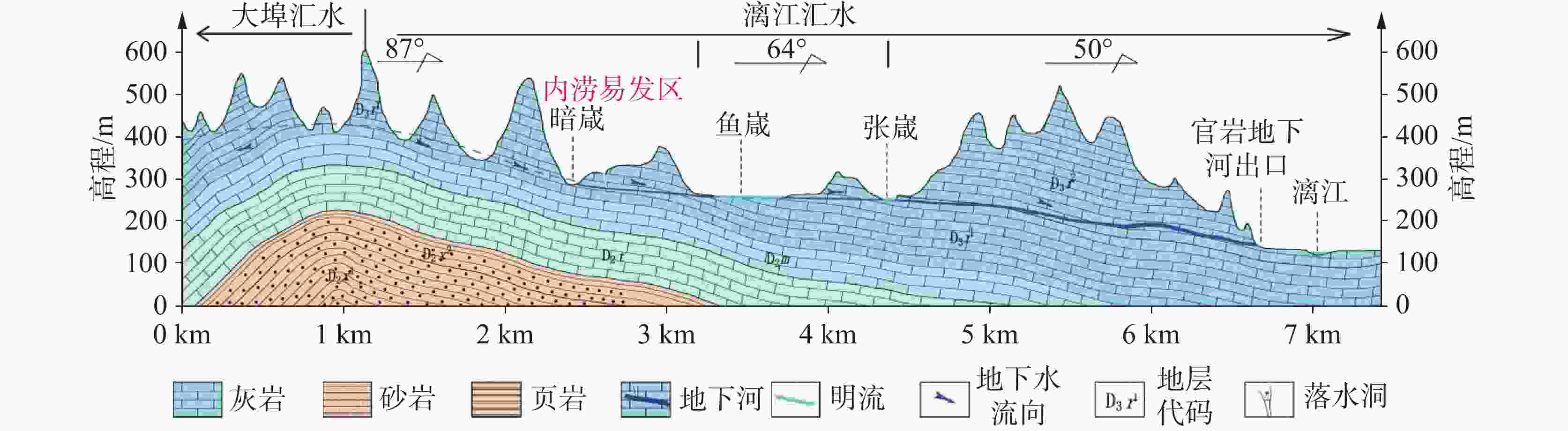
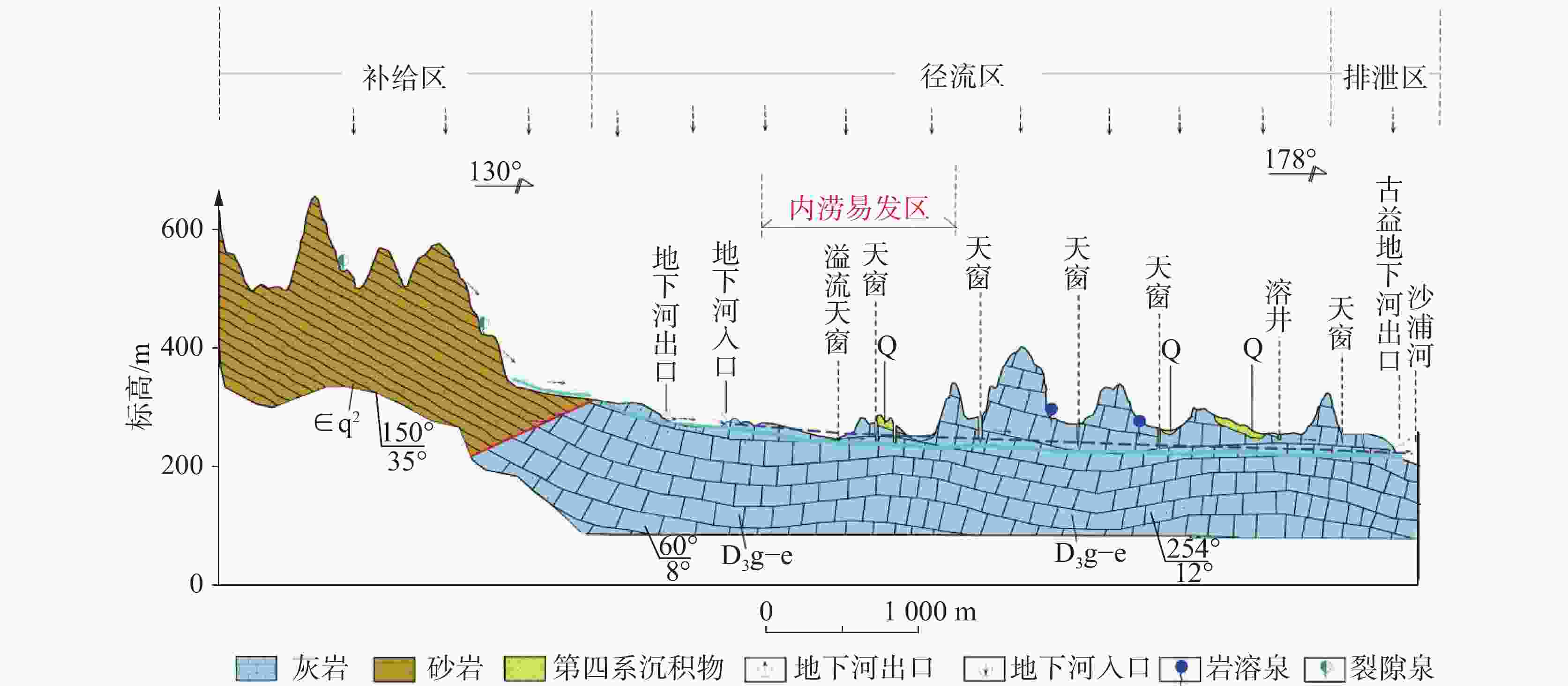
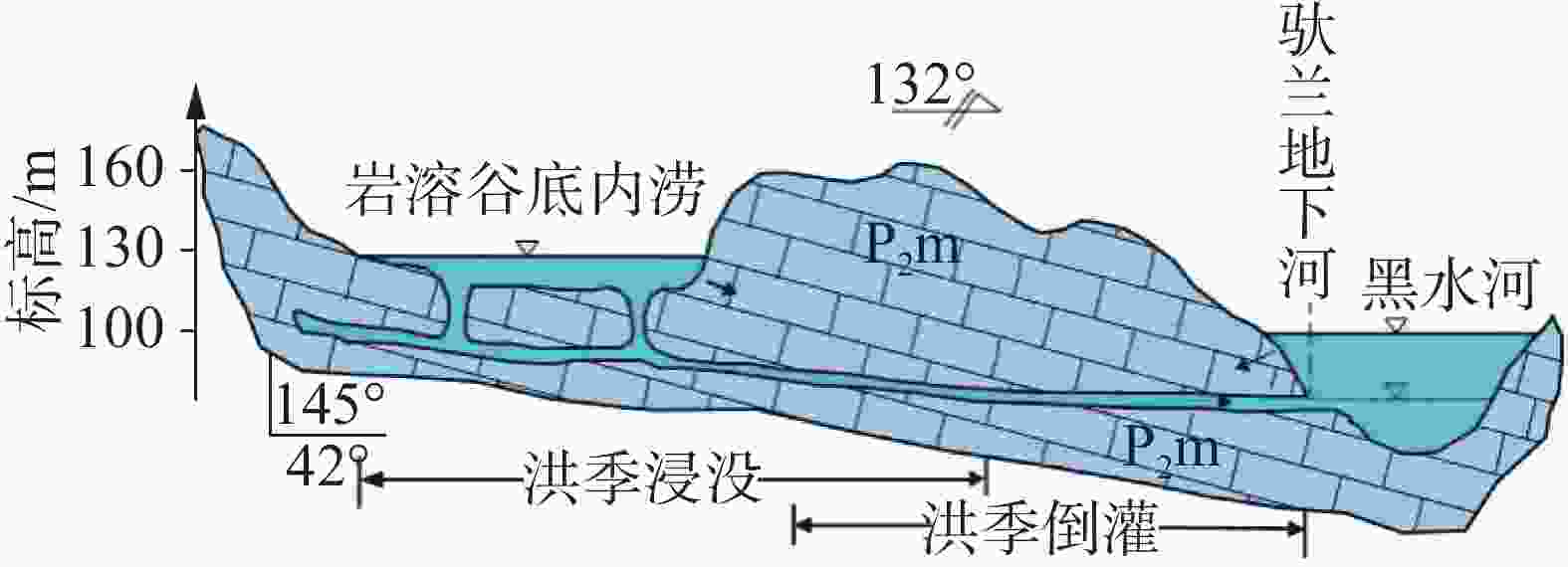
图 2 地下河补给区内涝成因模式 [42]
Figure 2. Mechanism of karst waterlogging formation in the recharge area of the underground river
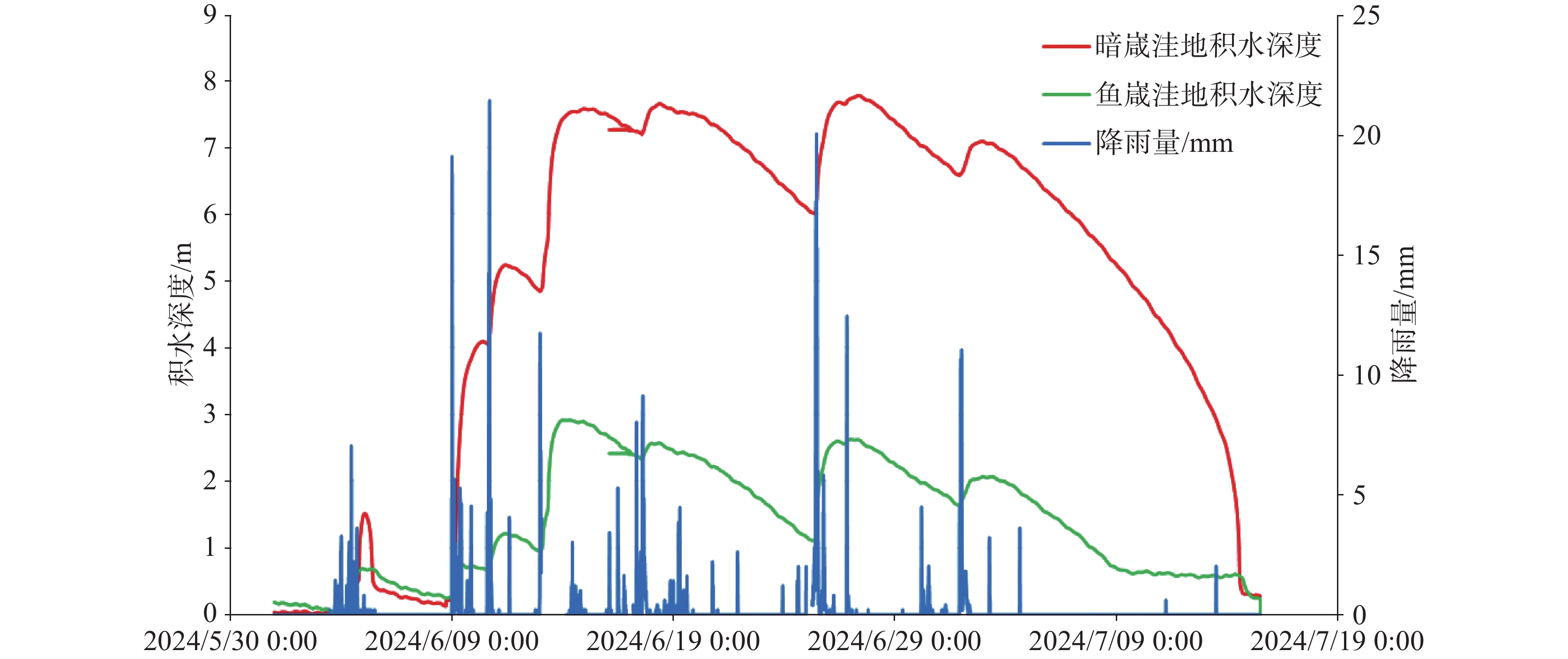
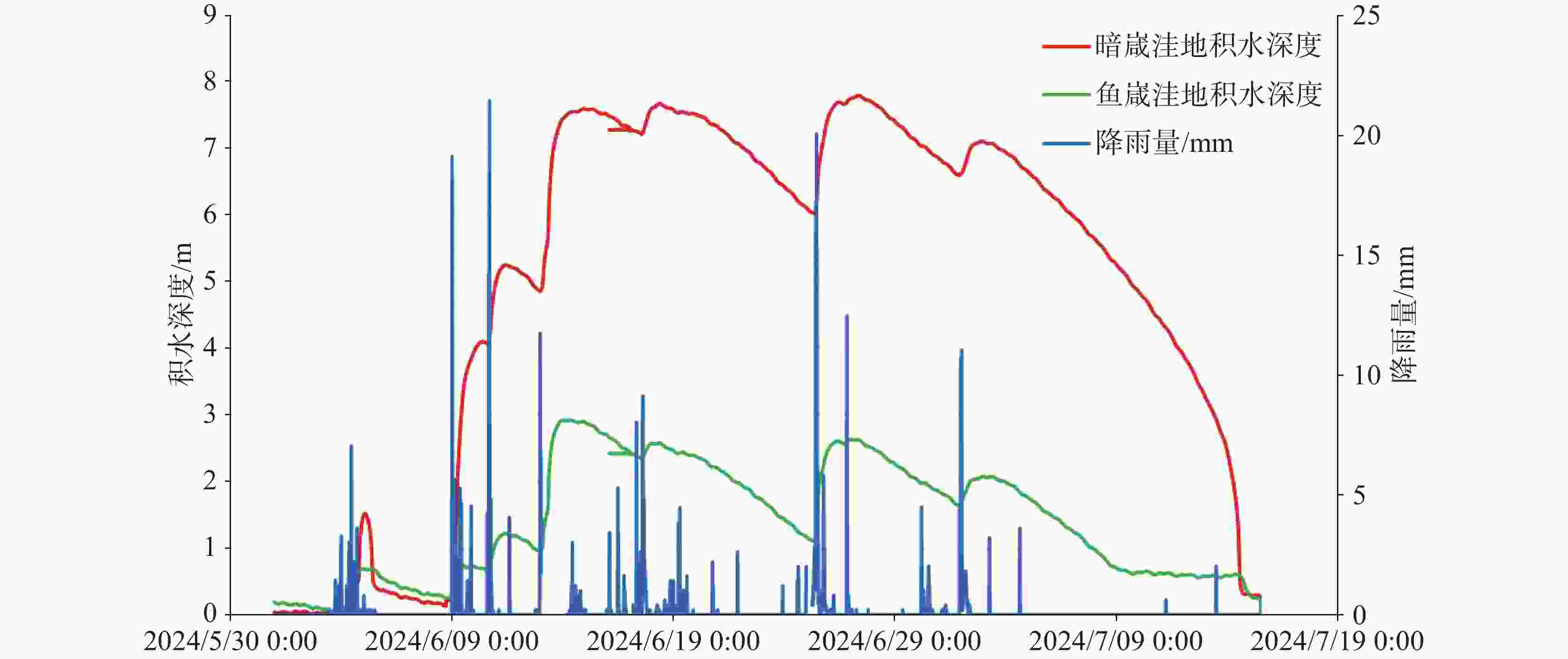
表 1 2024年6月漓江峰丛片区暗嵅洼地积水情况
Table 1. Water depth in the Andang depression of the Lijiang Peak Cluster area in June 2024
集中降雨时间 降雨量/mm 最大积水时刻 最大积水深度/m 6月9日—10日 223.2 6月11日17:30 5.22 6月12—13日 235.6 6月14日19:30 7.55 6月16—17日 97.4 6月18日6:00 7.60 6月25日 190.8 6月27日13:30 7.74 7月1—2日 91.6 7月3日3:15 7.06 -
[1] FORD D. C, WILLIAMS P. W. Karst geomorphology and hydrology [M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989. [2] LUO Mingming, CHEN Zhihua, CRISS Robert E, ZHOU Hong, HUANG He, HAN Zhaofeng, SHI Tingting. Dynamics and anthropogenic impacts of multiple karst flow systems in a mountainous area of south china[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(8): 1993-2002. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1462-3 [3] PARK Kiyong, LEE Man Hyung. The development and application of the urban flood risk assessment model for reflecting upon urban planningelements[J]. Water, 2019, 11(5): 920. doi: 10.3390/w11050920 [4] TOM Randa O, GEORGE Krhoda O, JOANES Atela O, HARON Akala. Review of flood modelling and models in developing cities and informal settlements: a case of Nairobi City[J]. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 2022, 43: 101188. [5] QI Wenchao, MA Chao, XU Hongshi, ZHAO kai, CHEN Zifan. A comprehensive analysis method of spatial prioritization for urban flood management based on source tracking[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 135: 108565. [6] 蒋忠诚, 罗为群, 邓艳, 曹建华, 覃星铭, 李衍青, 杨奇勇. 岩溶峰丛洼地水土漏失及防治研究[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(5): 535-542.JIANG Zhongcheng, LUO Weiqun, DENG Yan, CAO Jianhua, QIN Xingming, LI Yanqing, YANG Qiyong. Study on soil leakage and prevention of water and soil leakage in karst peak cluster depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 35(5): 535-542. [7] Mahler Barbara J, JIANG Yongjun , PU Junbing, MARTIN Jonathan B. Editorial: Advances in hydrology and the water environment in the karst critical zone under the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities[J]. Journal of Hydrology. 2021, 703: 125982. [8] 罗为群, 张辉旭, 蒋忠诚, 金克谟, 李衍青, 王志广. 岩溶峰丛洼地不同环境水土流失差异及防治研究: 以广西果化岩溶生态研究基地为例[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(4): 473-480. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.04.09LUO Weiqun, ZHANG Huixu, JIANG Zhongcheng, JN Kemo, LI Yanqing, WANG Zhiguang. The difference in soil erosion in different environments of karst peak-cluster depression and the study of soil erosion prevention: A case study of Guohua karst ecological experimental site, Guangxi[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(4): 473-480. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.04.09 [9] 彭旭东, 戴全厚, 李昌兰. 中国西南喀斯特坡地水土流失/漏失过程与机理研究进展[J], 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(5): 1-8.PENG Xudong, DAl Quanhou, LI Changlan. Research progress on the process and mechanism of soil water loss or leakage on slope in southwest karst of China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(5): 1-8. [10] 蒋忠诚, 罗为群, 邓艳, 杨奇勇, 覃星铭, 喻琦雯. 广西岩溶区的水土流失特点及其防治[J]. 广西科学, 2018, 25(5): 449-455.JIANG Zhongcheng, LUO Weiqun, DENG Yan, YANG Qiyong, QIN Xingming, YU Qiwen, Features and treatment of soil erosion in karst areas of Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2018, 25(5): 449-455 [11] 李远强, 李中蔚. 岩溶山区内涝灾害成因分析及对策[J], 长江水利教育, 1995, (4): 64-65.LI Yuanqiang, Li Zhongwei. Analysis of the Causes of Waterlogging Disasters in Karst Mountainous Areas and Countermeasures[J]. Journal of Changjiang Engineering Vocational College, 1995, (4): 64-65. [12] 袁道先. 岩溶地区的地质环境和水文生态问题[J]. 南方国土资源, 2003, (1): 22- 24.YUANG Daoxian. Geological environment and hydroecological problems in karst areas[J]. Land resources in the South, 2003, (1): 22~-24. [13] 王浩, 杜伟, 刘家宏, 王佳, 梅超. 基于知识图谱的城市内涝灾害链推演及时空特性解析[J]. 水科学进展, 2024, 35(2): 185-196.WANG Hao, DU Wei, LIU Jiahong, WANG Jia, MEI Chao. Derivation and transmission analysis of urban flood disaster chain based on knowledge graph[J]. Advances in water science, 2024, 35(2): 185-196. [14] 黎廷宇, 王世杰. 贵州岩溶洼地内涝灾害加重的原因分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2001, 21(3): 1-4.LI Tingyu, WANG Shijie. Analysis of flood aggravation in Guizhou karst depression[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 21(3): 1-4. [15] 梁聪, 荣明书, 李超瑜. 广西岩溶内涝灾害风险普查报告[R], 广西壮族自治区地质环境监测站, 广西水文地质工程地质勘察院, 2023. [16] 欧阳资文, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 曾馥平. 广西岩溶峰丛洼地内涝现状分析与综合治理对策研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2011, 32(1): 107-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0275.2011.01.024OUYANG Ziwen, SONG Tongqing, PENG Wanxia, ZENG Fuping. Analysis of waterlogging in karst peaks and depressions in Guangxi Province and comprehensive treatment countermeasures[J]. Agricultural Modernization, 2011, 32(1): 107-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0275.2011.01.024 [17] 郭纯青. 岩溶浸没内涝灾害风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2005(S1): 337-342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.z1.069GUO Chunqing. Risk of waterlogging disaster by karst inundation[J]. Earth and Emviromment, 2005(S1): 337-342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.z1.069 [18] 罗为群, 蒋忠诚, 欧阳然, 李衍青. 典型岩溶峰丛洼地水土保持技术研究[J]. 中国水土保持, 2013(1): 37-41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2013.01.012LUO Weiqun, JIANG Zhongcheng, OUYANG Ran, LI Yanqing. Typical soil and water conservation technology of karst peak-cluster depression[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2013(1): 37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2013.01.012 [19] 肖攀, 万军伟, 曹雪琴, 黄小琴. 湖北宣恩岩底河流域内涝灾害成因分析及防治对策[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2012, 32(4): 500-504.XIAO Pan, WAN Junwei, CAO Xueqin, HUANG Xiaoqin. Analysis of the causes of flood disasters and prevention and control measures in the Yandi River Basin of Xuan'en, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2012, 32(4): 500-504. [20] 罗锦珠, 黄联锋. 广西北部地区“85·5”特大暴雨洪水分析[J]. 广西水利水电, 2001(4): 42-45.LUO Jinzhu, HUANG Lianfeng. Analysis of "85·5" heavy rainstorm and flood in Northern Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Water Resources and Hydropower, 2001(4): 42-45. [21] 光耀华. 关于岩溶浸没性内涝灾害初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1996, 7(4): 27-34.GUANG Yaohua. A sort of geological haxard-karst immedsion and waterlogging[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Haxard and Control, 1996, 7(4): 27-34. [22] 苏昌, 陈海波, 董炳维. 岩溶内涝灾害成因机制分析及防治建议[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2008, 22(2): 193-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2008.02.013SU Chang, CHEN Haibo, DONG Bingwei. Analysis of the causal mechanism of karst flood disaster and suggestions for prevention and control[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2008, 22(2): 193-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2008.02.013 [23] 郭纯青, 胡君春, 潘林艳. 中国西南典型岩溶洼地旱涝灾害演变规律: 以西南块所岩溶区为例[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2013(11): 160-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2013.11.041GUO Chunqing, HU Junchun, PAN Linyan. Evolution of drought and flood disasters in typical karst depressions in southwest China: A case study of karst areas in southwest China[J]. China Rural Water Resources and Hydropower, 2013(11): 160-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2013.11.041 [24] 黄秀凤. 下牙谷地岩溶内涝成因分析与治理工程方案设计[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(4): 52-57.HUANG Xiufeng. Analysis of the causes of karst waterlogging in Xiaya Valley and design of treatment engineering[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(4): 52-57. [25] MO Chongxun, WANG Yafang, RUAN Yuli, QIN Junkai, ZHANG Mingshan, SUN Guikai, JIN Juliang. The effect of karst system occurrence on flood peaks in small watersheds, southwest China. Hydrology Research, 2021. 52 (1): 305-322. [26] 罗明明, 尹德超, 张亮, 陈植华, 周宏, 韩兆丰, 史婷婷. 南方岩溶含水系统结构识别方法初探[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(6): 543-550.LUO Mingming, YIN Dechao, ZHANG Liang, CHEN Zhihua, ZHOU Hong, HAN Zhaofeng, SHI Tingting. Identifying methods of karst aquifer system structure in South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(6): 543-550. [27] ZHAO Liangjie, YANG Yang, XIA Riyuan, SHAO Jingli, CAO Jianwen, FAN Lianjie, CHEN Hongfeng. Evaluation of a hydrodynamic threshold in the Zhaidi karst aquifer (Guangxi Province, China)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(12): 424. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7599-8 [28] OW Lai Fern, CHAN Eugenie. Deferring waterlogging through stormwater control and channelling of runoff[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2021, 65: 127351. [29] DING Wei, WU Jindong. Interregional economic impacts of an extreme storm flood scenario considering transportation interruption: a case study of Shanghai, China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2023, 88: 104296. [30] WAN Hanna Melini Wan Mohtar, ABDULLAH Jazuri, ABDUL MAULUD Khairul Nizam, MUHAMMAD Nur Shazwani. Urban flash flood index based on historical rainfall events[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2020, 56: 102088. [31] 裴建国. 广西溶洼系统结构特征及其对岩溶内涝的影响[J]. 广西科学, 2002, 9(3): 193-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2002.03.011PEI Jianguo. Structural characteristics of karst depression system in Guangxi and its influence on karst waterlogging[J]. Guangxi Science, 2002, 9(3): 193-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2002.03.011 [32] MARÉCHAL JC, LADOUCHE B, DORFLIGER. Karst flash flooding in a Mediterranean karst, the example of Fontaine de Nîmes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 99(3-4): 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.11.013 [33] ATKINSON Timothy Christopher. Diffuse flow and conduit flow in limestone terrain in the mendip hills, somerset (great britain)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1977, 35(1-2): 93-110. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(77)90079-8 [34] 李庆松, 李兆林, 裴建国, 覃小群, 易连兴, 梁茂珍. 马山东部岩溶洼地谷地内涝特征与治理规划[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(4): 359-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.04.011LI Qingsong, LI Zhaolin, PEI Jianguo, QIN Xiaoqun, YI Lianxing, LIANG Maozhen. Waterlogging characteristics and management planning of karst depression valley in eastern Madong[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(4): 359-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.04.011 [35] 罗贵荣, 李兆林, 梁小平. 广西岩溶石山区内涝灾害成因与防治对策研究: 以马山岩溶地下河流域为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2010, 17(1): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.002LUO Guirong, LI Zhaolin, LIANG Xiaoping. Research on the causes and prevention and control countermeasures of flood disasters in karst mountainous areas of Guangxi: A case study of Mashan karst underground river basin[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2010, 17(1): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.002 [36] ZANG Yawen, MENG Yu, GUAN Xinjian, LV Hong, YAN Denghua. Study on urban flood early warning system considering flood loss[ J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2022, 77: 103042. [37] WANG Qiyuan, HOU Jundong. Hazard assessment of rainstorm- geohazard disaster chain based on multiple scenarios[ J]. Natural Hazards, 2023, 118(1): 589-610. [38] CHEN Wenjie, HUANG Guoru, ZHANG Han, WANG Weiqi. Urban inundation response to rainstorm patterns with a coupled hydrodynamic model: a case study in Haidian Island, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 564: 1022-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.069 [39] 裴建国, 李庆松. 生态环境破坏对岩溶洼地内涝的影响—以马山古寨乡为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2001, 20(4): 52-55.PEI Jianguo, LI Qingsong. Effects of ecological environment damage on waterlogging in karst depressions: A case study of Mashan Guzhai Township[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2001, 20(4): 52-55. [40] 王恒松, 熊康宁, 刘云. 西南岩溶区地下水土流失浅析[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2008(32): 144-146.WANG Hengsong, XIONG Kangning, LIU Yun. Analysis of groundwater soil erosion in karst area of southwest China[J]. Science and Technology Information Development and Economy, 2008(32): 144-146. [41] 黄琨, 武亚遵, 万军伟, 肖攀. 落马洞暗河发育特征及其内涝成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(4): 385-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.04.006HUANG Kun, WU Yazun, WAN Junwei, XIAO Pan. Development characteristics of Luomadong dark river and its flood cause analysis[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(4): 385-388. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.04.006 [42] 普政功, 黄奇波, 吴华英, 李腾芳, 邹昌霈, 廖红为. 漓江峰丛片区高位岩溶洼地洪涝水文过程及有效治理[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(4): 831-842. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y004PU Zhenggong, HUANG Qibo, WU Huaying, LI Tengfang, ZOU Changpei, LIAO Hongwei. Flood hydrological process and its effective control measures in the high-altitude depressions of peak-cluster areas in Lijiang River[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(4): 831-842. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y004 [43] CHEN Hongsong, LLU Jianwei, WANG Kelin, ZHANG Wei. Spatial distribution of rock fragments on steep hillslopes in karst region of northwest Guangxi, China[J]. Catena, 2011, 84(l): 21-28. [44] HERMAN Ellen K, TORAN Laura, WHITE William B. Clastic sediment transport and storage in fluviokarst aquifers: An essential component of karst hydrogeology[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2012, 27(3): 211-241. [45] WANG Jianxiu, ZOU Baoping, LIU Yan, TANG Yiqun, ZHANG Xinbao, YANG Ping. Erosion- creep-collapse mechanism of underground soil loss for the karst rocky desertification in Chenqi village, Puding county, Guizhou, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(8): 2751-2764. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3182-0 [46] 熊康宁, 李晋, 龙明忠. 典型喀斯特石漠化治理区水土流失特征与关键问题[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(7): 878-888. doi: 10.11821/xb201207002XIONG Kangning, LI Jin, LONG Mingzhong. Features of Soil and Water Loss and Key Issues in Demonstration Areas for Combating Karst Rocky Desertification[J]. Acta geographica sinica, 2012, 67(7): 878-888. doi: 10.11821/xb201207002 [47] LIANG Dongfang, FALCONER Roger A, LIN Binliang. Coupling surface and subsurface flows in a depth averaged flood wave model[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337(1/2): 147-158. [48] 覃小群, 蒙荣国, 莫日生. 土地覆盖对岩溶地下河碳汇的影响-以广西打狗河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.004QIN Xiaoqun, MENG Rongguo, MO Risheng. Influence of land covers on carbon sink of underground river: A case in the Dagouhe Basin in Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.004 [49] 光耀华, 项式均, 李文兴, 郭纯青. 水库周边岩溶浸没—内涝灾害研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 1997, 16(1): 25-34.GUANG Yaohua, XIANG Shijun, LI Wenxing, GUO Chunqing. Karst immersion around reservoir-research on waterlogging disaster[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1997, 16(1): 25-34. -




 下载:
下载: