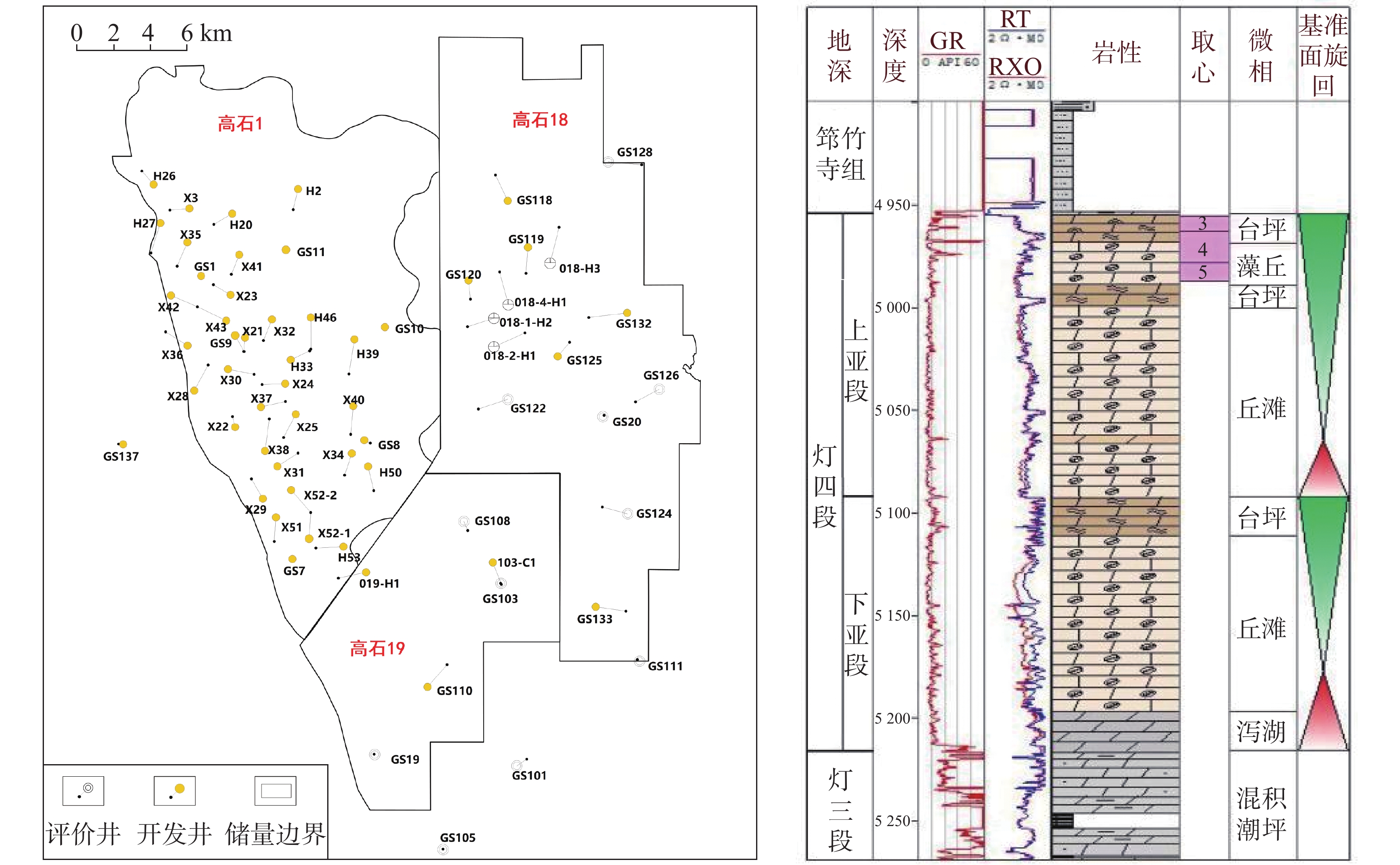
Comprehensive comparison and development strategy suggestions between the edge and interior of the fourth section of the Sinian series lamps in the Gaoshiti block
-
摘要: 安岳气田高石梯区块震旦系灯影组四段储层岩性复杂、非均质性强,台缘带和台内区单井产能差异大,生产效果也存在明显的差异。为实现台缘带灯四段气藏的长期稳产开发,台内区灯四段气藏高效建产。基于大量的地质、测井、气藏工程等资料,应用动静态相结合的方法全面剖析台缘带-台内区气藏共性及差异性特征,明确导致其差异性的控制因素。结果表明:① 台缘带与台内区储层岩石类型、储集空间及类型差异不大,但两者的储层发育规模、溶蚀孔洞发育程度、储层物性、渗流特征和气井生产特征存在差异性。② 有利丘滩沉积岩体的发育规模、表生岩溶作用和源储匹配程度是决定差异性的因素。③ 基于上述气藏的差异性认识,结合目前开发生产的需求形势,有针对性的提出了台缘带精细开发,实现持续稳产;台内区落实高产井模式和有利区分布,加快效益建产的开发建议。笔者提出的台缘带和台内区气藏差异性对比和主控因素分析的思路,为高石梯区块灯四气藏的有效开发,提供了科学开发的依据。Abstract:
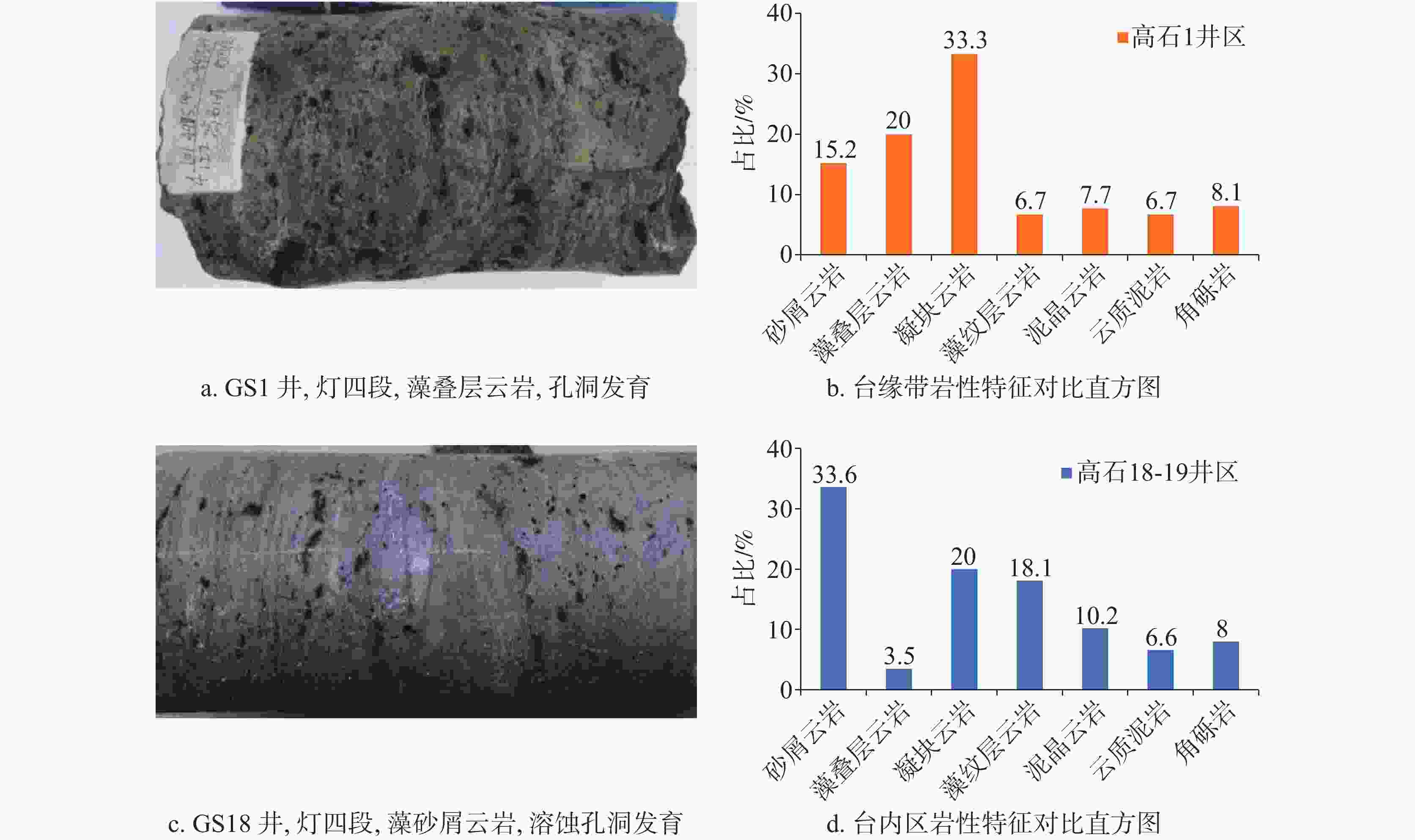
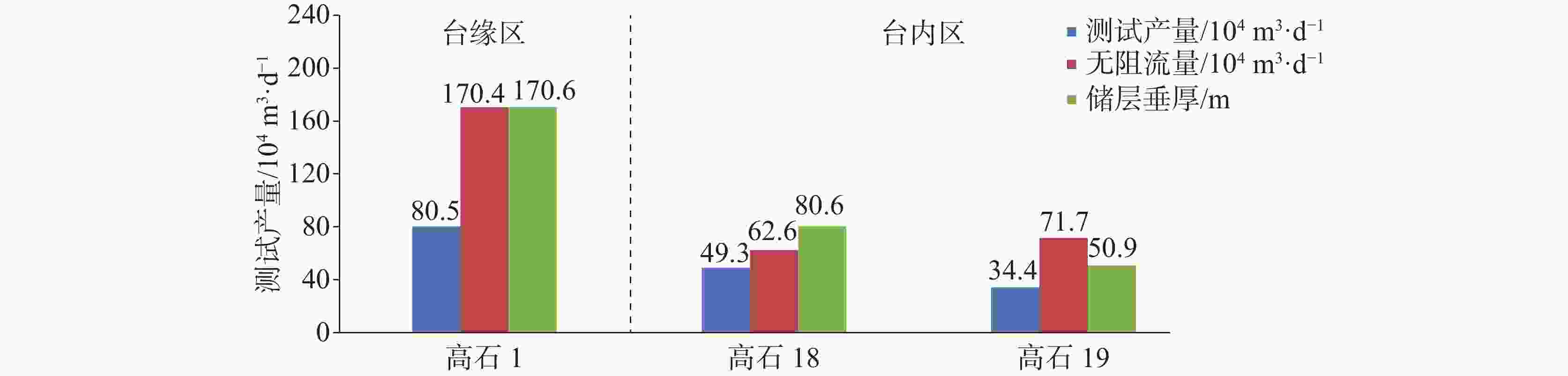
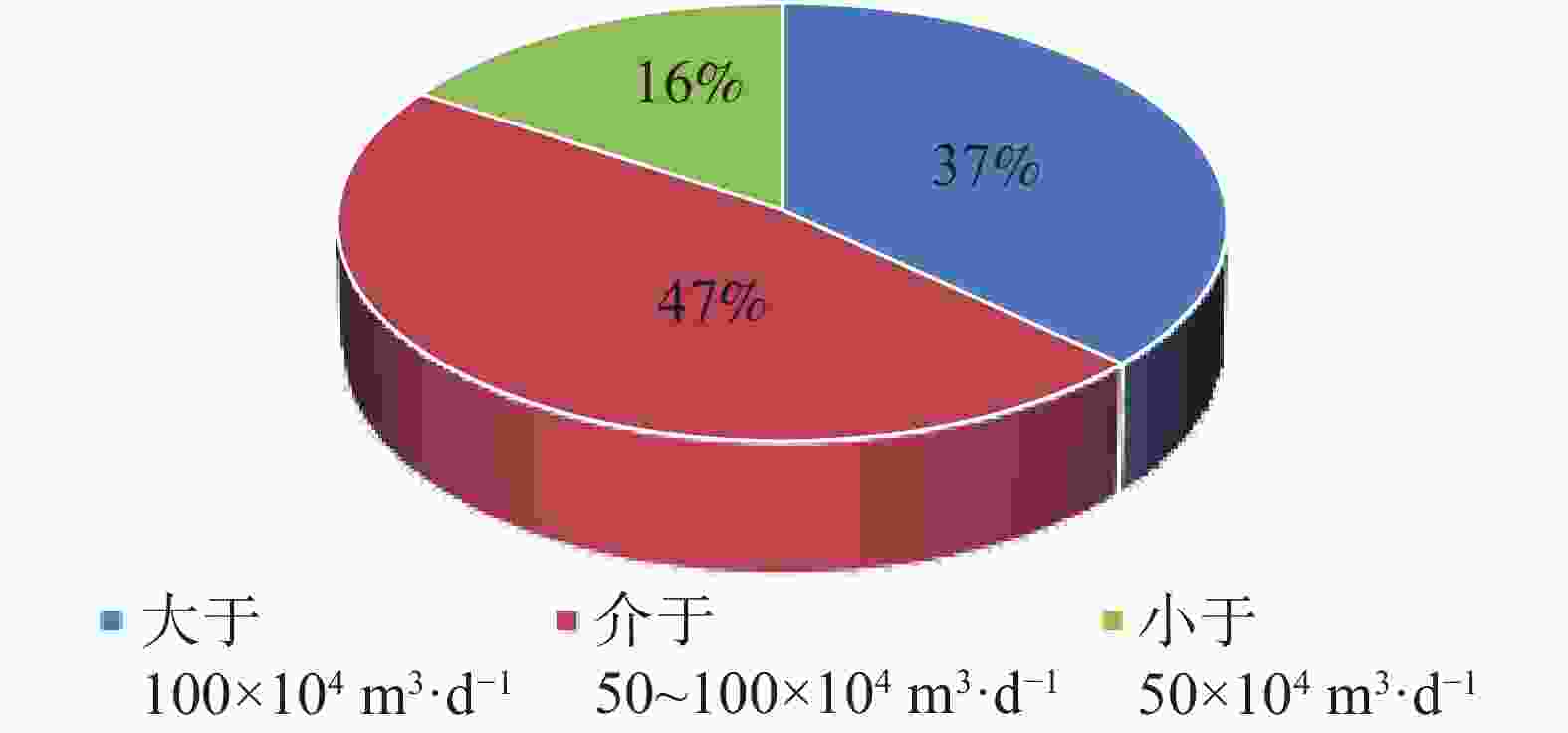
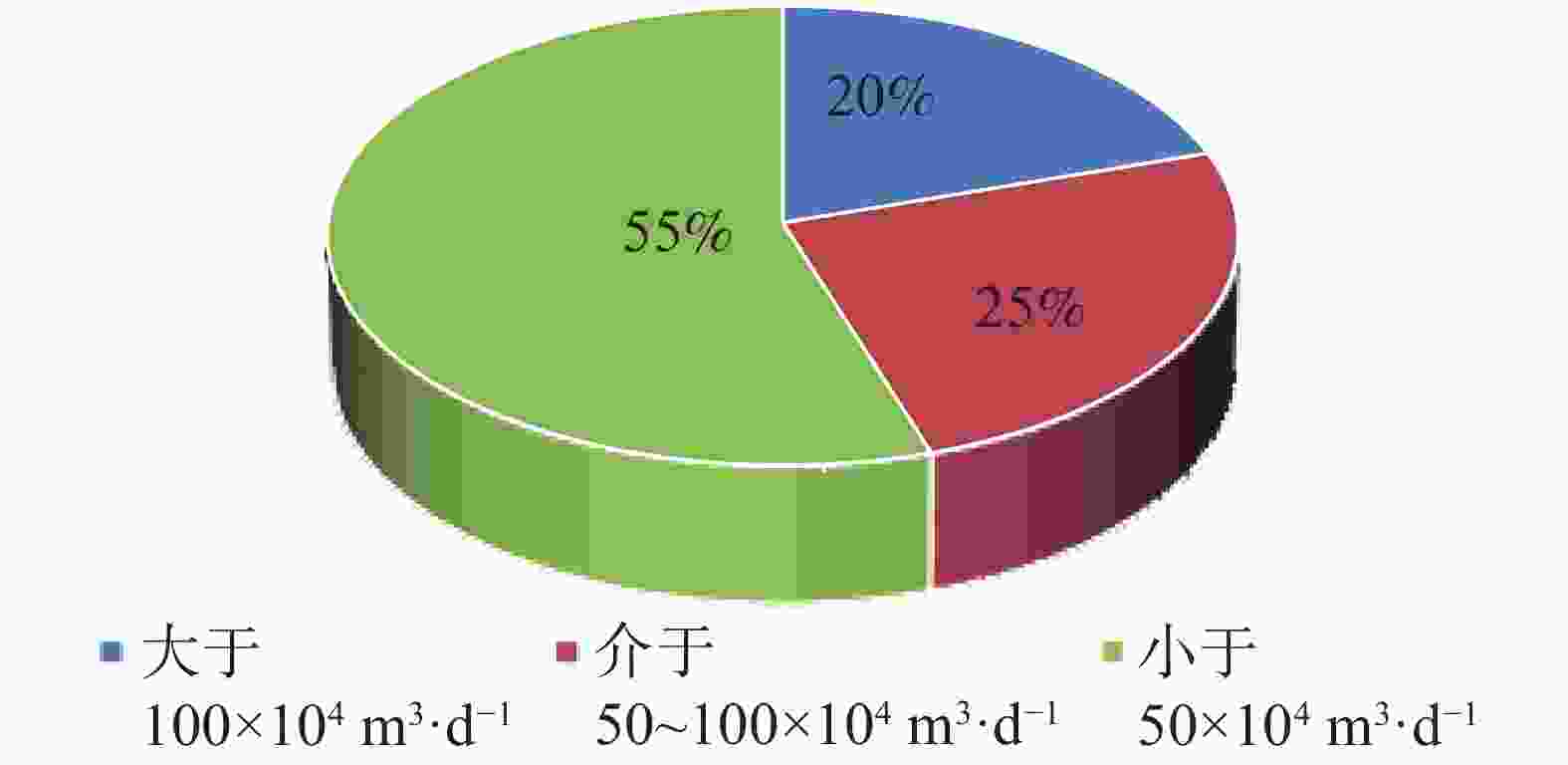
The fourth section of Dengying Formation in the Gaoshiti block of the Anyue Gas Field is of complex lithology and strong heterogeneity. There is a significant difference in the single-well production capacity as well as in production efficiency between the platform margin and the intra-platform. To achieve long-term stable development of the gas reservoir in the fourth section of Dengying Formation at the platform margin, as well as efficient production of the corresponding section in the intra-platform, the controlling factors leading to the observed differences have been identified. This was accomplished through a combination of dynamic and static methods, which allowed for a comprehensive analysis of the common and distinct characteristics of the gas reservoirs in both the platform margin and intra-platform. This analysis was based on a substantial amount of geological, logging, gas reservoir engineering and other relevant data. The reservoir rock types and reservoir space in both the platform margin and the intra-platform share common characteristics. The lithology is primarily composed of doloarenite, algal-laminated dolomite, and algal-clotted dolomite. These rocks are all well developed in terms of dissolution pores. The porosity of the reservoir core ranges from 2.0% to 7.3%, with an average of 3.5%. The permeability ranges from 0.1 mD to 113 mD, with an average of 5.832 mD. The reservoir properties exhibit low porosity and low permeability, and the reservoir type is primarily characterized as fracture-pore (cave) type. However, there are differences between the platform margin and the intra-platform in terms of reservoir development scale, degree of dissolution pore development, reservoir physical properties, seepage characteristics, and characteristics of gas well production. At the platform margin, the proportion of wells with single-well test output larger than 500,000 cubic meters of gas is higher. The development degree of large pores and caves is greater, and the density of fracture development is also higher. In terms of production, the gas wells at the platform margin generally exhibit high and stable production, with an average daily gas production of 233,000 cubic meters per well. In contrast, the gas wells in the intra-platform show significant production differences, with a daily gas production of 145,000 cubic meters. In terms of seepage characteristics, the reservoir type at the platform margin is primarily classified as fracture-pore type, with fractures and fracture-cave systems serving as the main seepage channels. These wells exhibit relatively high test production rates and are capable of maintaining high and stable production. This paper comprehensively analyzes the reasons for the differences from four aspects, sedimentary environment, diagenesis, matching of reservoir conditions, and karst transformation. It clarifies that the sedimentary environment and reservoir conditions control the scale of reservoir development, while karst transformation in later stages plays a decisive role in the seepage characteristics and production differences of gas wells. The favorable shoal and lagoon bodies control the distribution of high-quality reservoirs, and the intensity of epigenetic karst transformation during the Tongwan Period determines the strength of dissolution and transformation. Additionally, the relationship between source and reservoir affects the efficiency of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. Therefore, the development scale of shoal and lagoon deposits, the intensity of epigenetic karst transformation, and the source-reservoir relationship are the primary controlling factors determining the differences between the platform margin and the intra-platform. Based on a comprehensive comparison between the platform margin and the intra-platform, the former exhibits the thicker reservoir, superior physical properties, and dominant storage space types characterized by fracture-pore (cave) patterns. It also features a larger controlled radius, better fluid flow, a higher proportion of high-yield wells, and the potential for long-term, stable high production. In contrast, the intra-platform has the relatively thinner reservoir, comparable physical properties, and greater horizontal heterogeneity, resulting in more significant differences in the development of high-quality reservoirs. The production capacity of gas wells primarily comes from medium-and-low-yield wells, with a smaller proportion of wells capable of stable production. Given this comparison between the two zones and the production and development needs of the Gaoshiti block, the differentiated production suggestions are proposed. For the platform margin, the detailed characterization of high-quality seepage bodies within reservoir should be conducted, and the development of supplementary wells should be implemented to achieve stable production of gas reservoirs. For the intra-platform, the identification of favorable site distributions should be prioritized, and the production wells should be deployed to ensure efficient production. -
Key words:
- Gaoshiti area /
- platform margin belt /
- inner platform area /
- difference /
- transfusion characteristic
-
表 1 台缘区和台内区生产井统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of production wells in platform margin and inner platform area
区块 投产井数/口 开井数/口 开井率/% 日产气/104 m3 单井日产气/104 m3 累产气/108 m3 台缘区 35 35 100.00 814.98 23.29 98.01 台内区 9 4 44.44 58.18 14.54 2.24 表 2 高石梯地区灯四气藏储层分类综合图版
Table 2. Comprehensive map of reservoir classification for Member 4 gas reservoir in Gaoshiti block
区带 储层
类型典型井 井型 试井曲线 井控半
径/m渗透率
/mD渗流特征 台缘 裂缝—孔洞型 H27 水平井 
400 4.47↑44.7 采用“水平井+径向复合”模型解释,井控半径大,远井区物性变好,反映储层物性变好,该井目前日产气54×104 m3·d−1,生产效果好 X25 水平井 
450 5.57↓0.51 采用“水平井+径向复合”模型解释,井控半径大,近井区存在高渗介质,渗透性较好,该井目前日产气60×104 m3·d−1,生产效果好 台内 孔洞型 103C1 水平井 
160 0.54↓0.24 采用“水平井+无限大边界”模型解释,探测半径较近,远井区物性变差,该井目前日产气17×104 m3·d−1,生产效果较稳定 孔隙型 G10 水平井 
50 0.02↑0.08 采用“无限导流+复合”模型解释,探测半径较近,整体物性较差,该井目前日产气仅5×104 m3·d−1,生产效果一般 -
[1] 马新华. 四川盆地天然气发展进入黄金时代[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(2):1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.02.001MA Xinhua. A golden era for natural gas development in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(2): 1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.02.001 [2] 罗文军, 季少聪, 刘曦翔, 淡永, 梁彬, 聂国权. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组白云岩溶蚀差异实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(6):1312-1321. doi: 10.11932/karst20230612LUO Wenjun, JI Shaocong, LIU Xixiang, DAN Yong, LIANG Bin, NIE Guoquan. Experiment for the differential dissolution of dolomite of Sinian Dengying Formation in the Gaoshiti−Moxi area, the Sichuan basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(6): 1312-1321. doi: 10.11932/karst20230612 [3] 罗冰, 杨跃明, 罗文军, 文龙, 王文之, 陈康. 川中古隆起灯影组储层发育控制因素及展布[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(4):416-426. doi: 10.7623/syxb201504003LUO Bing, YANG Yuemin, LUO Wenjun, WEN Long, WANG Wenzhi, CHEN Kang. Controlling factors and distribution of reservoir development in Dengying Formation of palco-uplift in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. doi: 10.7623/syxb201504003 [4] 魏国齐, 杨威, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 邹才能, 谢武仁, 曾富英, 武赛军. 四川盆地震旦纪—早寒武世克拉通内裂陷地质特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(1):24-35. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.01.003WEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, DU Jinghu, XU Chunchun, ZOU Caineng, XIE Wuren, ZENG Fuying, WU Saijun. Geological characteristics of the Sinian-Early Cambrian intracratonic rift, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(1): 24-35. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.01.003 [5] 罗平, 王石, 李朋威, 宋金民, 金廷福, 王果谦, 杨式升. 微生物碳酸盐岩油气储层研究现状与展望[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(5):807-823.LUO Ping, WANG Shi, LI Pengwei, SONG Jingmin, JING Tingfu, WANG Guoqian, YANG Shishen. Review and prospective of microbial carbonate reservoirs[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(5): 807-823. [6] 胡修权, 鲁洪江, 易驰, 李江寒, 陈克勇, 鲁杰, 肖陈静. 川中高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组储层构型研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(6):847-859. doi: 10.11932/karst20220601HU Xiuquan, LU Hongjiang, YI Chi, LI Jianghan, CHEN Keyong, LU Jie, XIAO Chenjing. A study of reservoir architecture of Dengying formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area in Sichuan Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(6): 847-859. doi: 10.11932/karst20220601 [7] 周正, 李大华, 张烨, 陈洪凯, 王兴志, 廖云平, 祁永爱, 王宝亮 . 川中地区震旦系灯影组优质储层的形成条件研究 [J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42 (4): 853-862.ZHOU Zheng, LI Dahua, ZHANG Ye, CHEN Hongkai, WANG Xingzhi6, LIAO Yunping, QI Yongai, WANG Baoliang [J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42 (4): 853-862. [8] 刘曦翔, 淡永, 罗文军, 梁 彬, 徐 亮, 聂国权, 季少聪. 四川盆地高石梯地区灯影组四段顶岩溶古地貌、古水系特征与刻画[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(2):206-214. doi: 10.11932/karst20200210LIU Xixiang, DAN Yong, LUO Wenjun, LIANG Bin, XU Liang, NIE Guoquan, JI Shaocong. Characterization of karst paleo-geomorphology and the paleo-water system on the top of the 4th member of the Dengying formation in the Gaoshiti area, Sichuan basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(2): 206-214. doi: 10.11932/karst20200210 [9] 田兴旺, 彭瀚霖, 王云龙, 杨岱林, 孙奕婷, 张玺华, 文 龙, 罗 冰, 洪海涛, 王文之, 马 奎, 叶 茂, 薛玖火. 川中安岳气田震旦系灯影组四段台缘—台内区储层差异及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(9):1225-1238.TIAN Xing-wang, PENG Han-lin, WANG Yun-long, YANG Dailin, SUN Yiting, ZHANG Xihua, WEN Long, LUO Bing, HONG Haitao, WANG Wenzhi, MA Kui, YE Mao, XUE Jiuhuo. Analysis of reservoir difference and controlling factors between the platform margin and the inner area of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Anyue Gas Field, central Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(9): 1225-1238. [10] 田兴旺, 张玺华, 彭瀚霖, 马奎, 杨岱林, 孙奕婷. 川中高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组四段气藏产能差异[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(6):673-679.TIAN Xingwang, ZHANG Xihua, PENG Hanlin, MA Kui, YANG Dailin, SUN Yiting. Productivity differences of gas reservoirs in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, central Sichuan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(6): 673-679. [11] 夏青松, 黄成刚, 杨雨然, 彭军, 陶艳忠, 周翔. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组储层特征及主控因素[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(2):441-458.XIA Qingsong, HUANG Chenggang, YANG Yuran, PENG Jun, TAO Yanzhong, ZHOU Xiang. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of oil and gas accumulation of Dengying Formation, Sinian System, in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(2): 441-458. [12] :张哲夫. 高石梯—磨溪区块碳酸盐岩储层测井评价研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.ZHANG Zhefu. Research on well logging evaluation of carbonate reservoir in Gaoshiti-Moxi Block[D]. QingDao: China University of Petroleum (EastChina), 2019. [13] 谷一凡, 周 路, 蒋裕强, 倪 佳, 李俊良, 朱 讯, 付永红, 蒋增政. 四川盆地高石梯区块震旦系灯影组四段储层类型及气井产能模式[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(5):574-583. doi: 10.7623/syxb202005006GU Yifan, ZHOU Lu, JIANG Yuqiang, NI Jia, LI Junliang, ZHU Xun, FU Yonghong, JIANG Zengzheng. Reservior types and gas well productivity models for Member 4 of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(5): 574-583. doi: 10.7623/syxb202005006 [14] 杨雨, 黄先平, 张健, 杨光, 宋家荣, 宋林珂, 洪海涛, 谭秀成, 文龙. 四川盆地寒武系沉积前震旦系顶界岩溶地貌特征及其地质意义[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3):38-43. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.0016YANG Yu, HUANG Xianping, ZHANG Jian, YANG Guang, SONG JIarong, SONG Linke, HONG Haitao, TAN Xiucheng, WEN Long. Features and geologic significances of the top Sinian karst landform before the Cambrian deposition in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 38-43. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.0016 [15] 朱讯, 谷一凡, 蒋裕强, 唐廷科, 徐伟, 李开鸿, 邓惠. 川中高石梯区块震旦系灯影组岩溶储层特征与储渗体分类评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(3):38-46. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.03.005ZHU Xun, GU Yifan, JIANG Yuqiang, TANG Tingke, XU Wei, LI Kaihong, DENG Hui. Characteristics and reservoir body classification&evaluation of Sinian Dengying karst reservoirs in the Gaoshiti Block of central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(3): 38-46. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.03.005 [16] 姚根顺, 郝毅, 周进高, 蒋伟雄, 文龙, 倪超, 潘立银, 张建勇. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组储层储集空间的形成与演化[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3):31-37. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.005YAO Genshun, HAO Yi, ZHOU Jingao, JIANG Weixiong, WEN Long, NI Chao, PAN Liyin, ZHANG Jianyong. Formation and evolution of reservoir spaces in the Sinian Dengying Formation of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 31-37. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.005 [17] 陈元千. 确定气井绝对无阻流量和产能的一个简易方法[J]. 天然气工业, 1987, 7(4):38-43.CHEN Yuanqian. A Simple method to determine absolute open flow and capacity of gas well[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1987, 7(4): 38-43. [18] 国家经济贸易委员会. 碳酸盐岩气藏开发地质特征描述: SY/T6110-2002[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002.State Economic and Trade Commission. The description of exploitation geologic characteristics for carbonate gas reservoir: SY/T 6110-2002[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002. [19] 严鸿, 商绍芬, 张铭, 季晓婧. 安岳气田高石梯区块上震旦统灯四段气藏动态监测及认识[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2020, 14(4):5-11.YAN Hong, SHANG Shaofen, ZHANG Ming, JI Xiaojing. Performance monitoring and understandings on gas reservoirs of the Upper Sinian Dengying 4 Member, Gaoshiti block, Anyue gasfield, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2020, 14(4): 5-11. [20] 王文之, 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 罗文军, 夏茂龙, 孙赛男. 微生物碳酸盐岩沉积特征研究: 以四川盆地高磨地区灯影组为例[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(1):306-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.023WANG Wenzhi, YANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, LUO Wenjun, XIA Maolong, SUN Sainan. A study of sedimentary characteristics of microbial carbonate: A case study of the Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaomo area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(1): 306-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.023 [21] 郭恒玮, 伏美燕, 宋荣彩. , 刘文, 赵亮, 沈秋媛 . 川中高石梯地区灯四段藻丘类型与沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(1): 217-228.GUO HengWei, FU MeiYan, SONG RongCai, LIU Wen, ZHAO Liang, SHEN Qiuyuan. Algal Type and Sedimentary Model of the 4th Member, Dengying Formation in the Gaoshiti Area of Chuanzhong[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(1): 217-228. [22] 李启桂, 李克胜, 周卓铸, 燕继红, 唐欢阳. 四川盆地桐湾不整合面古地貌特征与岩溶分布预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(4):516-521. doi: 10.11743/ogg20130413LI Qigui, LI Kesheng, ZHOU Zhuozhu, YAN Jihong, TANG Huanyang. Palaeogeomorphology and karst distribution of Tongwan unconformity in Sichuan Basin[J]. OIL & GAS GEOLOGY, 2013, 34(4): 516-521. doi: 10.11743/ogg20130413 [23] 李忠权, 刘记, 李应, 杭文艳, 洪海涛, 应丹琳, 陈骁, 刘冉, 段新国, 彭戟. 四川盆地震旦系威远—安岳拉张侵蚀槽特征及形成演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(1):26-33. doi: 10.11698/PED.2015.01.03LI Zhongquan, LIU Ji, LI Ying, HANG Wenyan, HONG Haitao, YING Danlin, CHEN Xiao, LIU Ran, DUAN Xinguo, PENG Ji. Formation and evolution of Weiyuan-Anyue extension-erosion groove in Sinian system, Sich- uan basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(1): 26-33. doi: 10.11698/PED.2015.01.03 [24] 聂国权, 淡永, 徐亮, 梁彬, 李景瑞. 蜀南Z工区茅口组顶岩溶古地貌、古水系特征与刻画[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):911-917. doi: 10.11932/karst20200610NIE Guoquan, DAN Yong, XU Liang, LIANG Bin, LI Jingrui. Characteristics and characterization of karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system on the top of the Maokou formation in the Z area in southern Sichuan basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 911-917. doi: 10.11932/karst20200610 -




 下载:
下载: