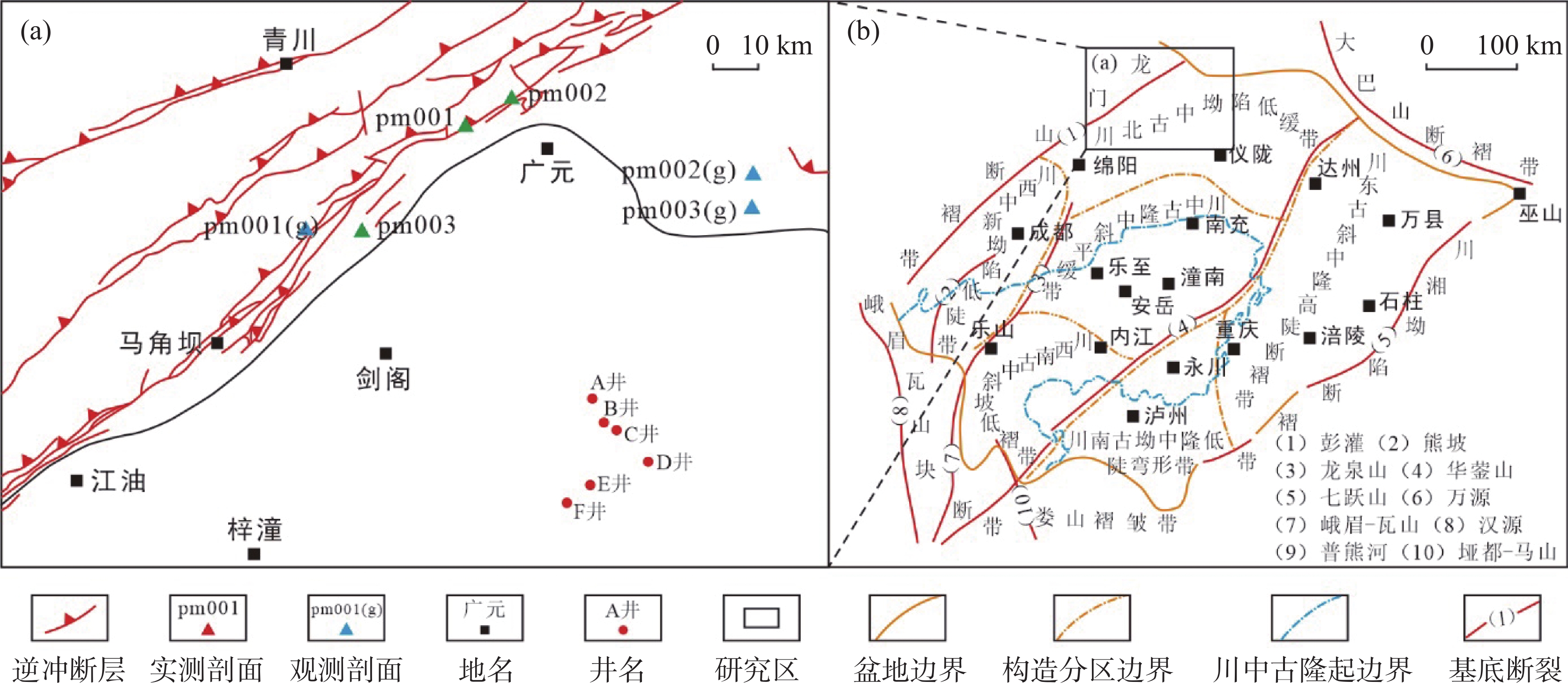
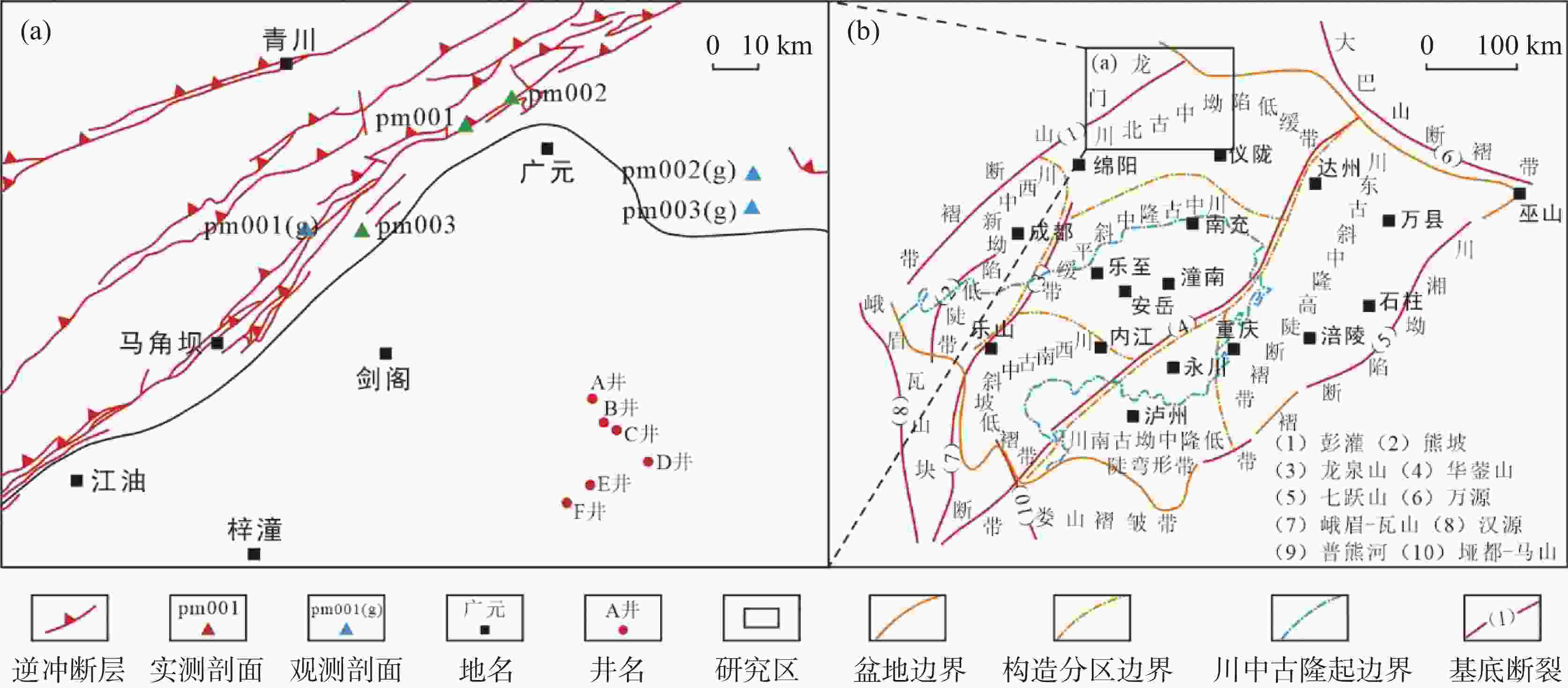
Characteristics of paleokarst processes and reservoir development of the middle Permian Maokou Formation in the Yuanba area,Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 元坝地区茅口组岩溶储层是该区重要储层类型之一。在古岩溶作用地质背景研究基础上,基于野外剖面、钻井岩心、测井及测试分析等资料,对四川盆地元坝地区茅口组岩溶储层发育特征、分布规律等进行研究,探讨古岩溶作用期次及对岩溶储层的影响。结果表明:①元坝地区茅口组顶面岩溶古地貌整体属微地貌形态,为岩溶地貌形成演化初期特征。②茅口组岩溶储层垂向上可划分为表层岩溶带、垂向渗滤溶蚀带、径流溶蚀带和潜流溶蚀带等四个岩溶发育带,岩溶储层主要分布在表层岩溶带,且横向上连续性较好。③茅口组古岩溶缝洞系统形成于同生期或准同生期岩溶环境、表生期淡水岩溶环境、浅埋藏期岩溶环境和深埋藏期高温岩溶环境等四种岩溶环境。④有利沉积相是茅口组岩溶储层发育的物质基础,表生岩溶作用是茅口组岩溶储层发育的关键因素。Abstract:
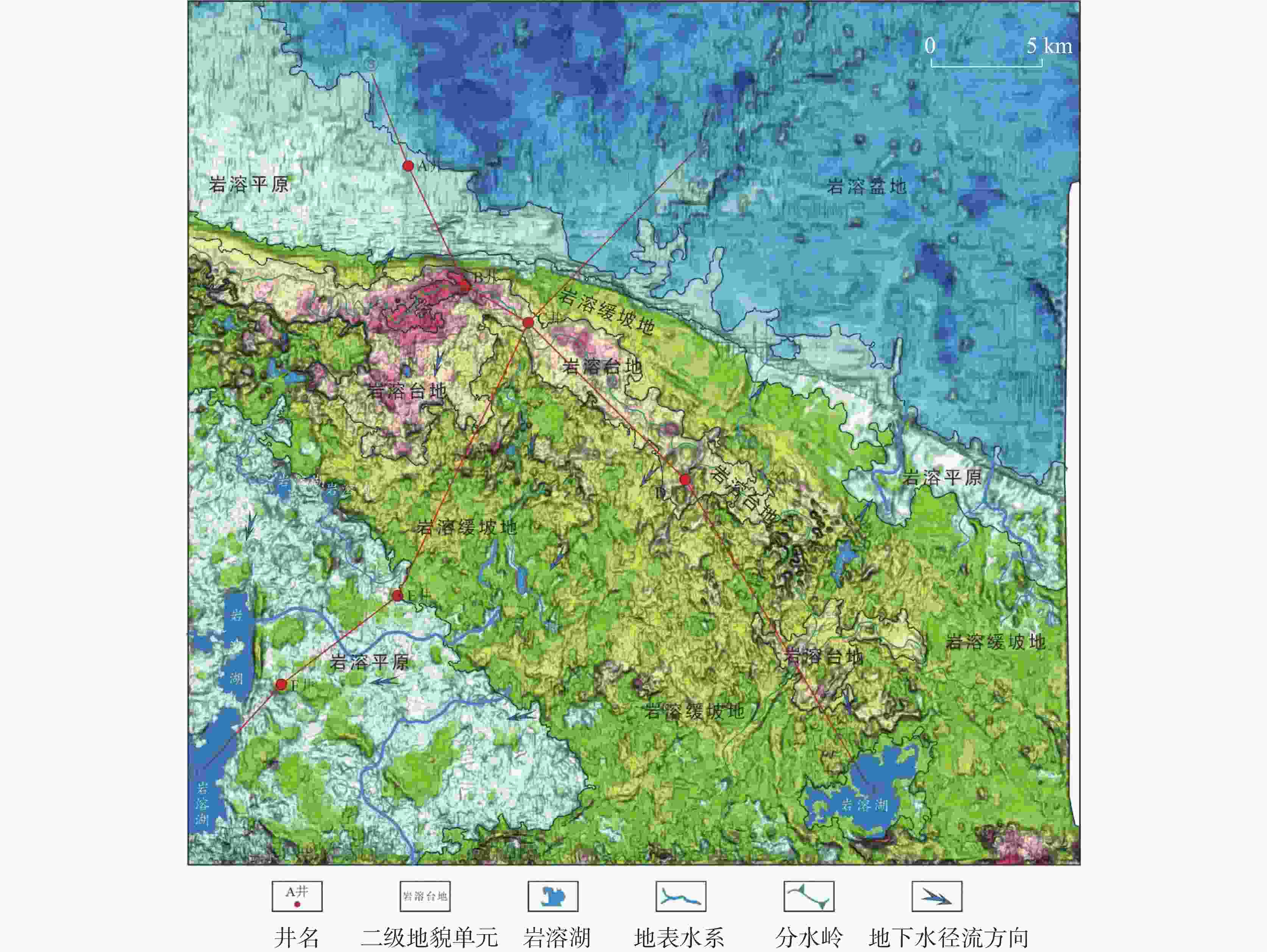
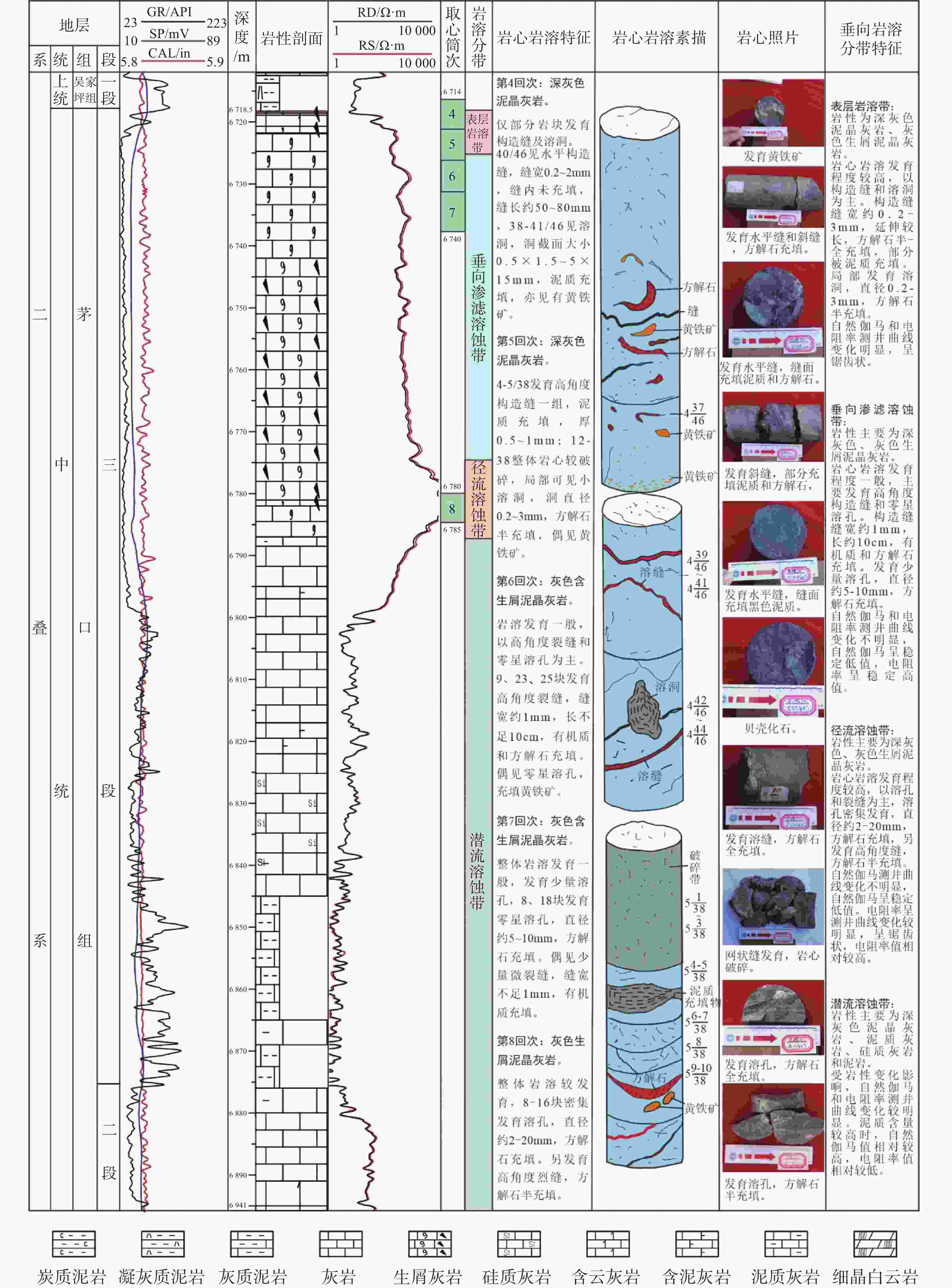
In recent years, the Maokou Formation of the middle Permian in the Yuanba area of Northwest Sichuan has consistently yielded high-flow industrial gas, indicating significant exploration potential for the Maokou Formation in this area. Drilling has confirmed the presence of exposed karst features within the Maokou Formation, indicating that the reservoir space mainly consists of fracture-pore types. The karst fracture-pore reservoir type is one of the important reservoir types found in the Maokou Formation in this area. Previous studies have been conducted on the stratigraphic division, lithofacies paleogeography, karst layer groups, and karst paleogeomorphology of the Maokou Formation in Northwest Sichuan. However, systematic research on paleokarst stages of the Maokou Formation in the Yuanba Area, as well as its impacts and other related aspects, has been limited. This study investigates the development characteristics and distribution patterns of karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation of the Yuanba area in the Sichuan Basin, based on a study on the geological background of ancient rock dissolution. The investigation utilizes field profiles, drilling cores, logging, and analytical testing data. This study combines geochemical analyses of the filling materials found in paleokarst fractures and pores, to explore the stages of ancient rock dissolution and its impacts on karst reservoirs. The findings will support predictions regarding the karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation in the Yuanba area in subsequent research. The research results indicate, (1) Taking the top surface of a section in the Maokou Formation as the underlying reference surface, the residual thickness method was used to restore the karst paleogeomorphology of the top surface of the Maokou Formation in the study area. The karst paleogeomorphology of the top surface was categorized into four secondary geomorphological units and six tertiary geomorphological units. Overall, the karst paleogeomorphology on the top surface of the Maokou Formation in the study area is characterized by micro-geomorphological features, with locally developed mature landforms that indicate the initial stages of karst formation and evolution. The surface drainage system is not fully developed and is influenced by the topography, with runoff flowing northward and southwestward from the central region. (2) Based on the results of field profiles, drilling core observations, thin section identification, and scanning electron microscopy observations, the rock types of reservoirs in the Maokou Formation within the study area are mainly mud-crystal bioclastic limestone, bright-crystal bioclastic limestone, and a minor amount of bioclastic mud-crystal limestone. The types of storage space are classified into three categories: dissolved pores, caves, and fractures. (3) According to the classification guidance formulated by the Institute of Karst Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation are vertically classified into four karst development zones, that is, surface karst zone, vertical infiltration and dissolution zone, runoff dissolution zone, and phreatic dissolution zone. This classification was based on the observation of field profiles, drilling core samples, logging, and the analysis of well logging and drilling records in the study area. The vertical distribution of karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation is primarily concentrated within 0–20 m below the weathering crust surface, corresponding to the surface karst zone. (4) The analysis of carbon and oxygen isotopes, along with inclusion testing of the filling materials in the paleokarst fracture-pore of the Maokou Formation in the study area indicates that the paleokarst fracture-pore system of the Maokou Formation was formed in four distinct karst environments, a contemporaneous or pene-contemporaneous karst environment, a freshwater karst environment in the hypergene period, a karst environment in the shallow-burial period, and a high-temperature karst environment in the deep-burial period. (5) Comprehensive analysis suggests that favorable sedimentary facies such as open platforms or platform edges are the material basis for the development of karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation in the study area. Epigenetic karstification is a key factor in the development of karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation in the study area, and its degree of development is controlled by conditions such as the karst layer group, ancient landforms, and ancient water systems. The shallow-deep-burial process has transformed and adjusted the early reservoir space, further increasing the heterogeneity of the reservoir. -
Key words:
- karst reservoir /
- paleokarst process /
- Maokou Formation /
- middle Permian /
- Yuanba area /
- Sichuan Basin
-
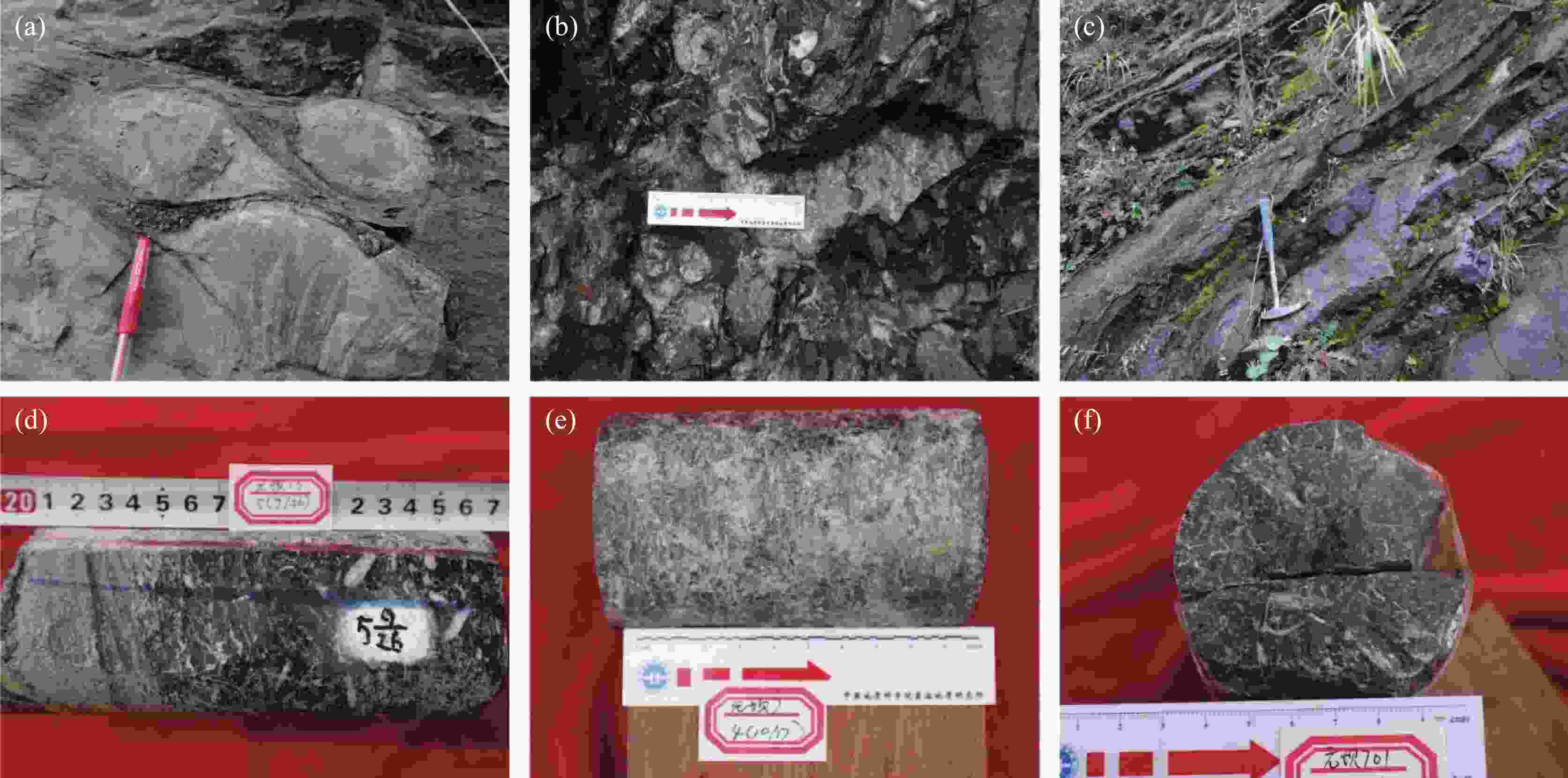
图 3 研究区茅口组碳酸盐岩岩石学特征
(a) 眼皮眼球状灰岩,茅一段,三堆镇剖面 (b) 生屑泥晶灰岩,茅二段,王家沟剖面 (c) 硅质岩,孤峰段,王家沟剖面 (d) 含砂屑生屑灰岩,茅二段,G井 (e) 生屑灰岩,茅三段,B井 (f) 生屑泥晶灰岩,茅三段,C井
Figure 3. Petrological characteristics of carbonate rocks of the Maokou Formation in the study area
(a) Eyelid-eyeball shaped limestone, Mao Member 1, Section Sanduizhen (b) Biogenic mitrite, Mao Member 2, Section Wangjiagou (c) Siliceous rock, Gufeng Member, Section Wangjiagou (d) Sandstone containing bioclastic limestone, Mao Member2,Well G (e) Bioclastic limestone, Mao Member 3,Well B (f) Bioclastic mitrite, Mao Member 3, Well C
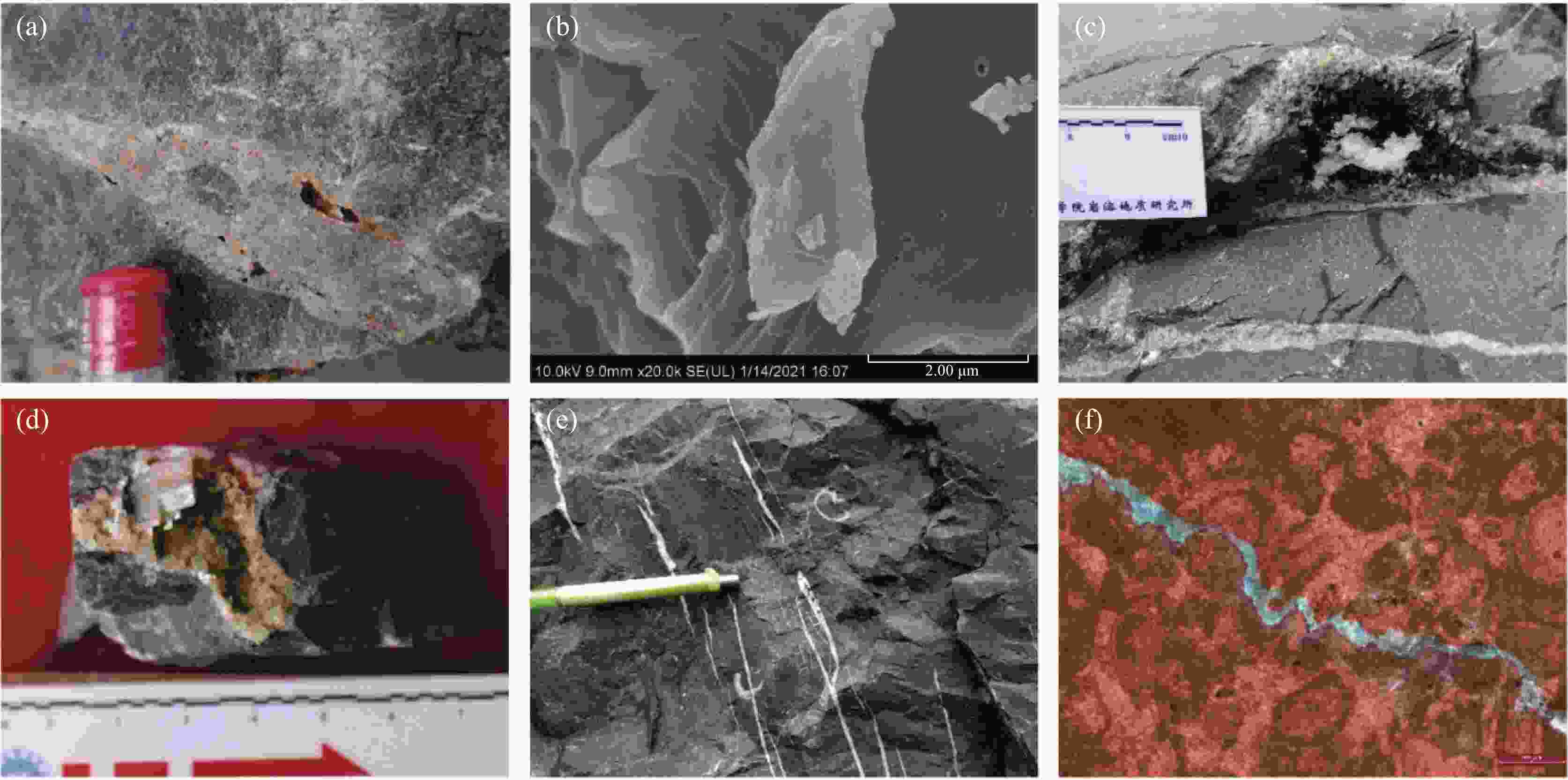
图 4 研究区茅口组碳酸盐岩储集空间特征
(a) 溶孔发育,泥晶灰岩,茅一段,马鹿乡剖面 (b) 方解石粒内溶孔,泥晶生屑灰岩,茅三段,C井 (c) 溶洞,方解石、沥青充填,泥晶灰岩,茅二段,唐家沟剖面 (d) 溶洞,方解石充填,茅三段,D井 (e) 构造缝,方解石充填,泥质灰岩,茅一段,唐家沟剖面 (f) 溶蚀缝,亮晶生屑灰岩,茅三段,D井
Figure 4. Characteristics of reservoir space of carbonate rocks in the Maokou Formation in the study area
(a) Developed dissolved pores, mitrite, Mao Memeber 1, Section Maluxiang (b) Dissolved pores in calcite grains, bioclastic mitrite, Mao Memeber 3, Well C (c) Cave filled with calcite and asphalt, bioclastic mitrite, Mao Memeber 2, Section Tangjiagou (d) Cave filled with calcite, Mao Memeber 3, Well D (e) Structural factures filled with calcite, argillaceous limestone, Mao Memeber 1, Section Tangjiagou (f) Dissolved fractures, sparry bioclastic limestone, Mao Memeber 3, Well D
表 1 研究区茅口组古岩溶形成环境及同位素特征
Table 1. Paleokarst environment and isotope characteristics of the Maokou Formation in the study area
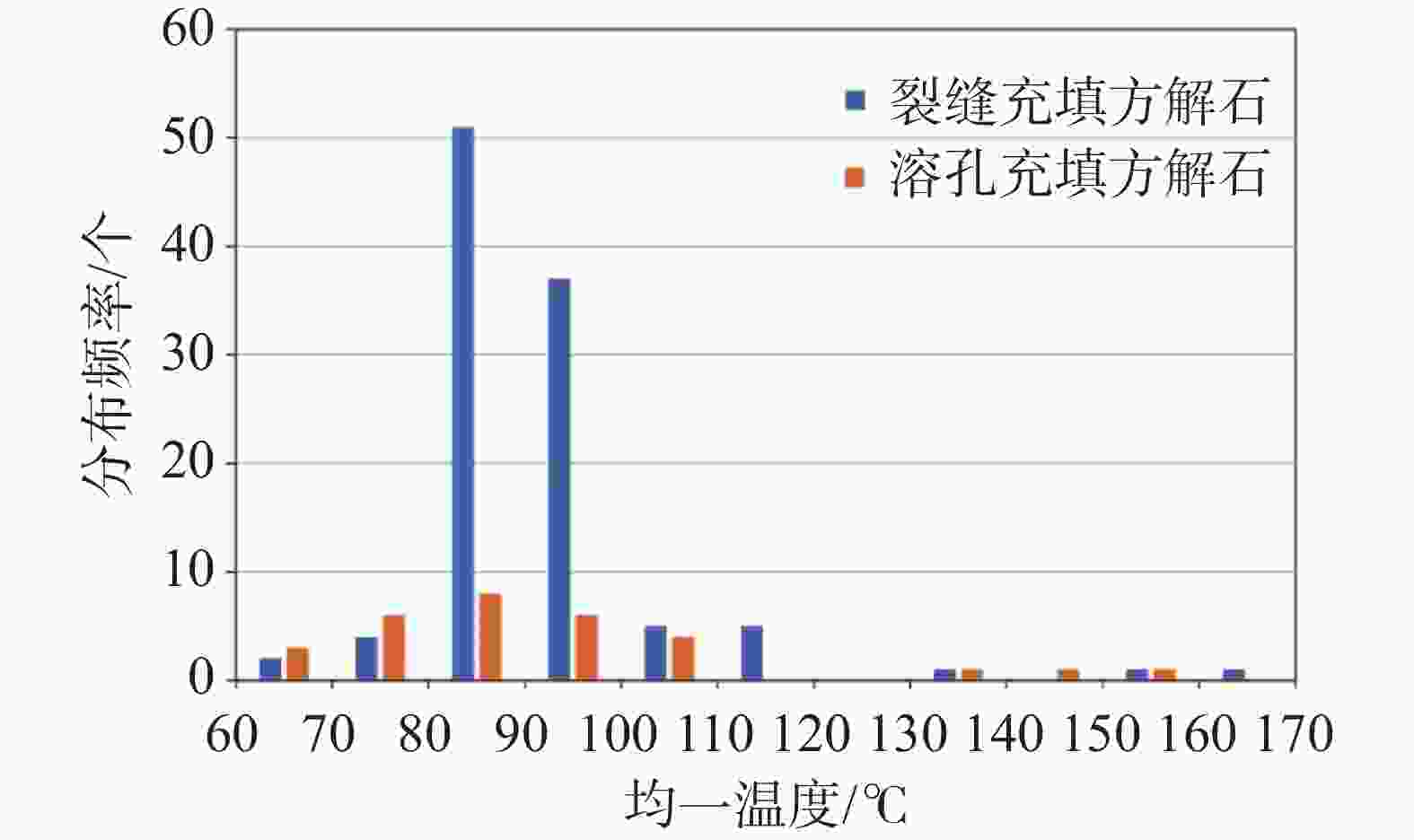
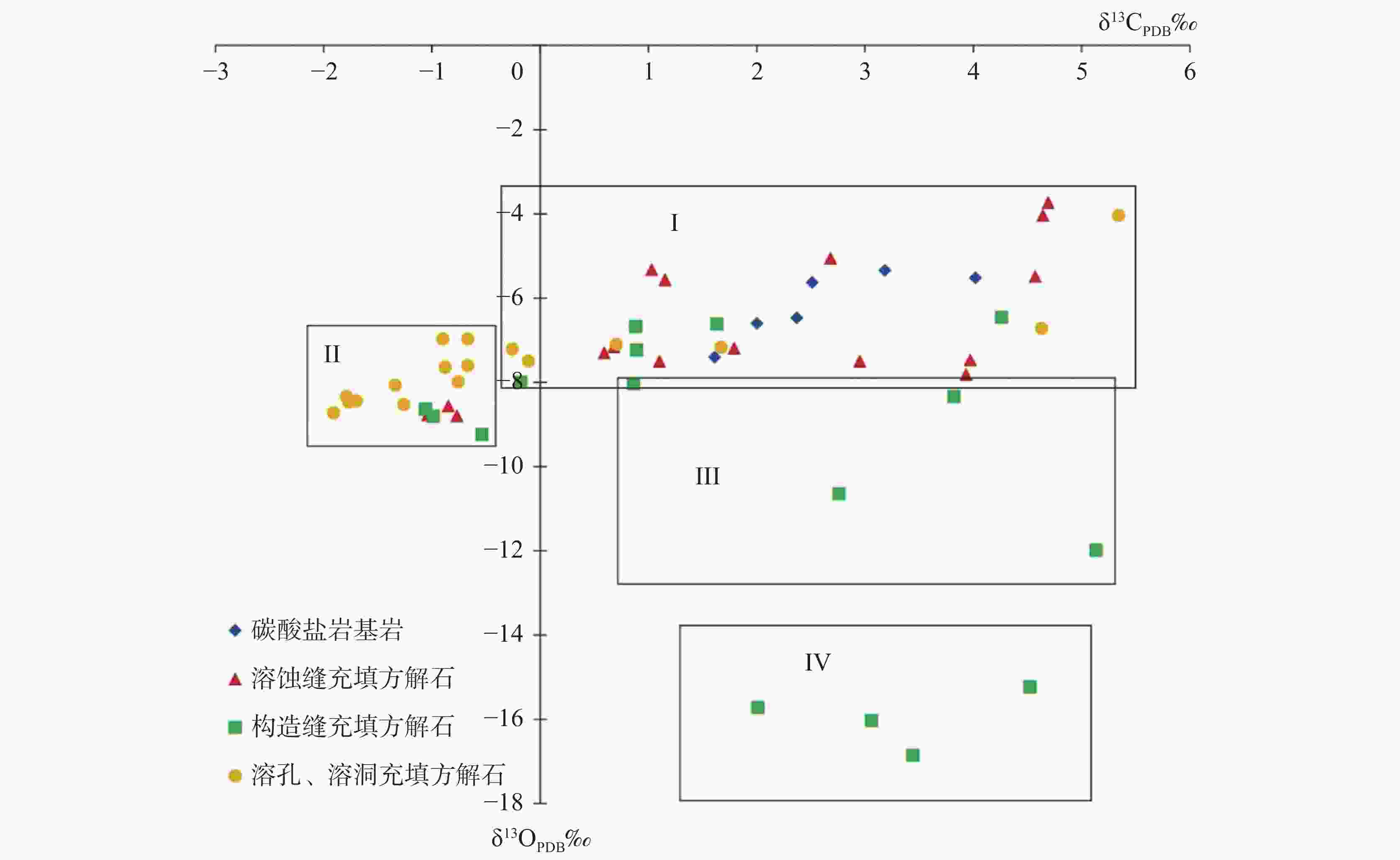
发育期次 形成环境 同位素特征 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ I 同生期或准同生期岩溶环境 −0.26~5.34 −8.00~−3.73 Ⅱ 表生期淡水岩溶环境 −1.91~−0.54 −9.24~−6.97 Ⅲ 浅埋藏期岩溶环境 0.86~5.13 −11.99~−8.03 Ⅳ 深埋藏期高温岩溶环境 2.01~4.52 −16.86~−15.23 -
[1] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 段金宝. 中国南方海相油气勘探展望[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5):675-686. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005675GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, DUAN Jinbao. Marine petroleum exploration in South China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 675-686. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005675 [2] 胡东风. 四川盆地元坝地区茅口组台缘浅滩天然气勘探的突破与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(3):1-10.HU Dongfeng. Breakthrough in natural gas exploration in the platform margin shoal at the Maokou Fm in the Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin, and its implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(3): 1-10. [3] 张宇, 曹清古, 罗开平, 李龙龙, 刘金连. 四川盆地二叠系茅口组油气藏勘探发现与启示[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(3):610-620. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220310ZHANG Yu, CAO Qinggu, LUO Kaiping, LI Longlong, LIU Jinlian. Reservoir exploration of the Permian Maokou Formation in the Sichuan Basin and enlightenment obtained[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(3): 610-620. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220310 [4] 施泽进, 张瑾, 李文杰, 田亚铭, 王勇, 尹观. 四川盆地Guadalupian统碳酸盐岩稀土元素和碳-锶同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4):1095-1106. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.08SHI Zejin, ZHANG Jin, LI Wenjie, WANG Yaming, WANG Yong, YI Guan. Characteristics of rare earth element and carbon-strontium isotope and their geological significance of Guadalupian carbonate in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1095-1106. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.08 [5] 霍飞, 杨西燕, 王兴志, 黄荟文, 张凤玲. 川西北地区茅口组储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(1): 45-52.HUO Fei, YANG Xiyan, WANG Xingzhi, HUANG Huiwen, ZHANG Fengling. Characteristics and main controlling factors of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation reservoir in northwestern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2018, 45(01): 45-52. [6] 张本健, 谢继容, 尹宏, 胡 欣,王宇峰,杨 迅, 裴森奇. 四川盆地西部龙门山地区中二叠统碳酸盐岩储层特征及勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(2):33-42. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.02.005ZHANG Benjian, XIE Jirong, YIN Hong, HU Xin, WANG Yufeng, YANG Xun, PEI Senqi. Characteristics and exploration direction of the Middle Permian carbonate reservoirs in the Longmenshan mountain areas, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(2): 33-42. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.02.005 [7] 钟原, 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰,肖笛, 李明隆,陈聪,赵立可,芦飞凡,谭秀成. 四川盆地西北部中二叠统茅口组岩相古地理、古岩溶地貌恢复及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1):81-93. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.07ZHONG Yuan, YANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, XIAO Di, LI Minglong, CHEN Cong, ZHAO Like, LU Feifan, TAN Xiucheng. Reconstruction and petroleum geological significance of lithofacies paleogeography and paleokarst geomorphology of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1): 81-93. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.07 [8] 王兴志, 李博, 杨西燕, 文龙, 徐亮, 谢圣阳, 杜垚, 冯明友, 杨雪飞, 王雅萍, 裴森奇. 四川盆地北部中二叠世晚期“广元—旺苍”海槽特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3):562-574.WANG Xingzhi, LI Bo, YANG Xiyan, WEN Long, XU Liang, XIE Shengyang, DU Yao, FENG Mingyou, YANG Xuefei, WANG Yaping, PEI Senqi. Characteristics of “Guangyuan-Wangcang” trough during late Middle Permian and its petroleum geological significance in northern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 562-574. [9] 曾韬, 季少聪, 夏文谦, 张庆玉, 巴俊杰, 董红琪, 聂国权. 川北元坝地区茅口组顶面古地貌恢复与岩溶发育特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(6):860-868, 879. doi: 10.11932/karst20220602ZENG Tao, JI Shaocong, XIA Wenqian, ZHANG Qingyu, BA Junjie, DONG Hongqi,NIE Guoquan. Reconstruction of karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system on the top of Maokou formation in Yuanba area, northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(6): 860-868, 879. doi: 10.11932/karst20220602 [10] 张庆玉, 季少聪, 曾韬, 夏文谦, 巴俊杰, 董红琪, 梁彬. 四川盆地北部中二叠统茅口组碳酸盐岩溶蚀模拟实验与岩溶层组特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(1):175-184. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301175ZHANG Qingyu, JI Shaocong, ZENG Tao,XIA Wenqian, BA Junjie, DONG Hongqi,LIANG Bin. Experimental dissolution and karst strata association of Middle Permian Maokou carbonate rocks in the northern part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(1): 175-184. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301175 [11] 李乾, 徐胜林, 陈洪德, 林良彪, 杨帅, 余瑜, 孙逢瑞, 董翼昕, 邓翔. 川北旺苍地区茅口组地球化学特征及古环境记录[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(3): 268-281.LI Qian, XU Shenglin, CHEN Hongde,LIN Liangbiao, YANG Shuai,YU Yu, SUN Fengrui,DONG Yixin, DENG Xiang. Geochemical characteristics and palaeo-environmental implication of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in Wangcang region, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2018, 45(3): 268-281. [12] 何斌, 徐义刚, 王雅玫, 肖龙. 东吴运动性质的厘定及其时空演变规律[J]. 地球科学, 2005(1):89-96. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.01.012HE Bin, XU Yigang, WANG Yamei, XIAO Long. Nature of the Dongwu movement and its temporal and spatial evolution[J]. Earth Science, 2005(1): 89-96. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.01.012 [13] 张玺华, 陈聪, 张亚, 文龙, 罗冰, 陈双玲, 王丽英, 李亚, 杨雨然.川西北地区茅口组海槽相地质特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2018, 41(3):42-50.ZHANG Xihua, CHEN Cong, ZHANG Ya,WEN Long, LUO Bing, CHEN Shuangling, WANG Liying, LI Ya, YANG Yuran. Geological characteristics of trough facies, Maokou Formation, northwestern Sichuan Basin: Implications for geology[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2018, 41(3): 42-50. [14] 袁道先. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1994.YUAN Daoxian. Chinese karst Science[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. [15] 袁道先. 中国岩溶动力系统[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 2002.YUAN Daoxian. Karst dynamic system in China[M].Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002. [16] 赵宽志, 淡永, 郑多明, 梁彬, 张庆玉, 李景瑞. 塔北哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系潜山岩溶储层发育特征及控制因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(2):171-178. doi: 10.11932/karst20150211ZHAO Kuanzhi, DAN Yong, ZHENG Duoming, LIANG Bin, ZHANG Qingyu, LI Jingrui. Characteristics of karst reservoirs in the Ordovician buried hills of the Halahatang area, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(2): 171-178. doi: 10.11932/karst20150211 [17] 夏日元. 塔里木盆地奥陶系碳酸盐岩缝洞系统模式及成因研究[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 2011.XIA Riyuan. Study on the Patterns and Forming Mechanism of Fracture-cavity Systems in Ordovician Carbonate, Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011. [18] 夏日元, 唐健生, 关碧珠, 罗伟权, 马振芳, 周树勋, 于忠平, 潘令红. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系古岩溶地貌及天然气富集特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999(2):37-40. doi: 10.11743/ogg19990208XIA Riyuan, TANG Jiansheng, GUAN Bizhu, LUO Weiquan, MA Zhenfang, ZHOU Shuxun, YU Zhongping, PAN Linghong. Ordovician palaeokarst landform in Ordos Basin and natural gas enrichment characteristics[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999(2): 37-40. doi: 10.11743/ogg19990208 [19] 邹胜章, 夏日元, 刘莉, 唐建生, 梁彬. 塔河油田奥陶系岩溶储层垂向带发育特征及其识别标准[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(9):2490-2501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.09.026ZOU Shengzhang, XIA Riyuan, LIU Li, TANG Jiansheng, LIANG Bin. Vertical zone characteristics and identification standard of Ordovician karst reservoirs in the Tahe oilfield[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(9): 2490-2501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.09.026 [20] 淡永. 塔中地区奥陶系鹰山组早成岩岩溶作用与储层特征研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2017.DAN Yong. Eogenetic karstification and reservoir characteristics study of the Ordovician Yingshan Formation in the central Tarim Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. [21] 张恒. 塔里木盆地中下奥陶统岩溶储层形成机制及其与二叠盆地相似储层对比[D]. 北京:中国地质大学, 2016.ZHANG Heng. Formation Mechanism of Middle-Lower Ordovician karst reservoirs in Tarim Basin and the comparison with similar reservoirs in Permian Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016. [22] 段金宝, 金民东, 范志伟, 朱祥, 刘雁婷. 四川盆地东北部中三叠统雷口坡组四段优质储层发育特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4):898-908. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210411DUAN Jinbao, JIN Mindong, FAN Zhiwei, ZHU Xiang, LIU Yanting. Characteristics and favorable plays for high-quality reservoirs in the Middle Triassic Lei 4 Member, Yuanba area, northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 898-908. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210411 [23] 刘存革, 李国蓉, 朱传玲, 刘国勇, 卢宇峰. 塔河油田中下奥陶统岩溶缝洞方解石碳、氧、锶同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2008(3):377-386.LIU Cunge, LI Guorong, ZHU Chuanling, LIU Guoyong, LU Yufeng. Geochemistry characteristics of carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopes of calcites filled in karstic fissure-cave in lower-middle Ordovician of Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008(3): 377-386. [24] 张庆玉. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩古岩溶发育机理[D]. 北京:中国地质大学, 2018.ZHANG Qingyu. Development mechanism of Ordovician carbonate paleokarst in the Halahatang area of the Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018. [25] O'Neil J R, Clayton R N and Mayeda T K. Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1969, 51: 5547-5558. doi: 10.1063/1.1671982 [26] 何治亮, 马永生, 朱东亚, 段太忠, 耿建华, 张军涛, 丁茜, 钱一雄, 沃玉进, 高志前. 深层-超深层碳酸盐岩储层理论技术进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(3):533-546. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210301HE Zhiliang, MA Yongsheng, ZHU Dongya, DUAN Taizhong, GENG Jianhua, ZHANG Juntao, DING QIAN, QIAN Yixiong, WO Yujin, GAO Zhiqian. Theoretical and technological progress and research direction of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(3): 533-546. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210301 [27] 胡文革. 塔里木盆地塔河油田潜山区古岩溶缝洞类型及其改造作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1):43-53. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220104HU Wenge. Paleokarst fracture-vug types and their reconstruction in buried hill area, Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 43-53. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220104 [28] 钟怡江, 陈洪德, 林良彪, 侯明才,李秀华, 徐胜林, 王峻. 川东北地区中三叠统雷口坡组四段古岩溶作用与储层分布[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(8):2272-2280.ZHONG Yijiang,CHEN Hongde,LIN Liangbiao,HOU Mingcai,LI Xiuhua,XU Shenglin, WANG Jun. Paleokarstification and reservoir distribution inthe Middle Triassic carbonates of the 4th member of the Leikoupo Formation,northeastern Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(8): 2272-2280. -




 下载:
下载: