Research on the resolution of cross-hole electromagnetic wave CT method for small karst caves under different working patterns
-
摘要: 跨孔电磁波CT法是一种原位无损的探测方法,因其具有较高的分辨率及施工效率,能够直观、清晰地反映出地下局部异常体的空间分布,被广泛应用于溶洞探测、路基注浆质量检测等领域。但目前关于该方法对小型溶洞分辨能力的影响因素研究并不多见。文章利用电磁波数值模拟系统和自编添加电磁噪声程序,通过控制变量的方法分别对不同介质吸收系数、不同定点距、孔间距工作模式情况下,研究了电磁波CT法对小型溶洞探测的分辨能力。结果表明,围岩与探测目标体的吸收系数差异越大,越有利于电磁波CT法对异常体的分辨,但该过程也受环境电磁噪声干扰的影响。随着环境电磁噪声干扰的增强,CT成像的分辨能力会明显降低;定点距越大方法的分辨能力也降低。对小型溶洞进行探测时,为确保成像的精度,建议定点间距最好不要超过4 m;过大的钻孔间距会降低电磁波CT法对小型溶洞的分辨能力,数值模拟结果表明,利用CT法对小型溶洞进行探测时,钻孔间距一般不要超过30 m。Abstract:
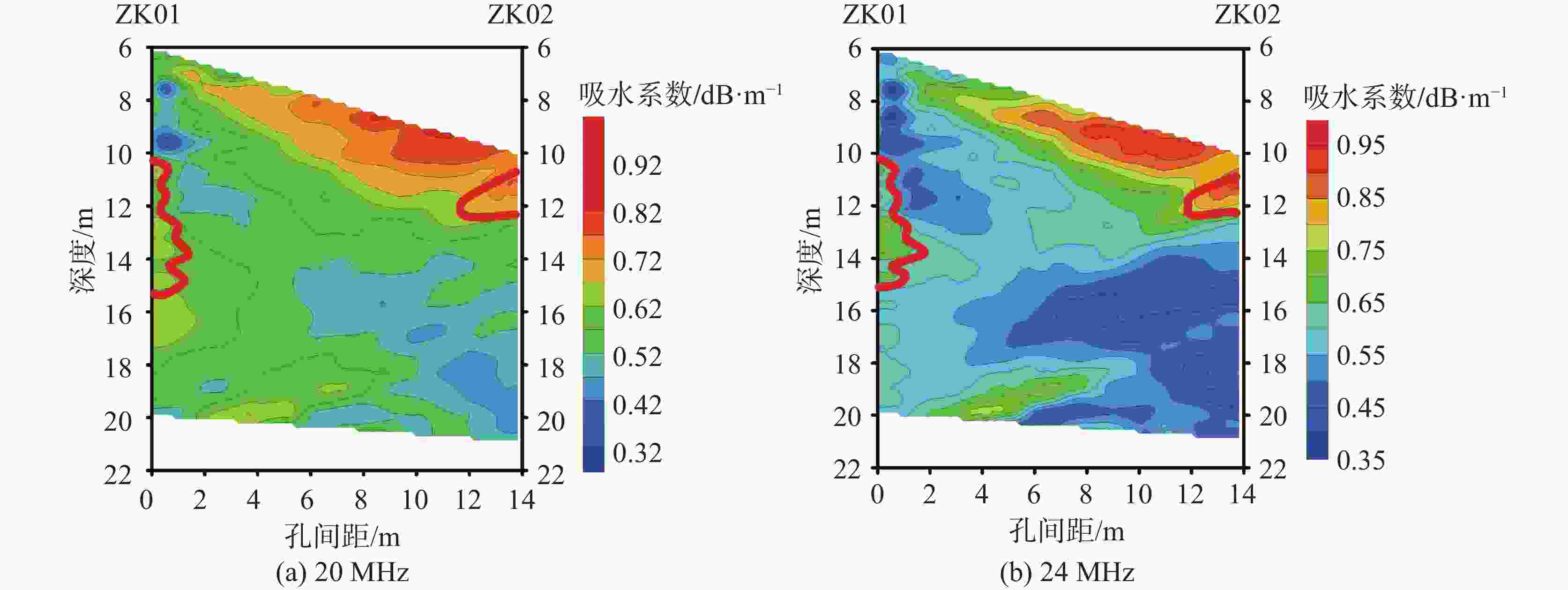
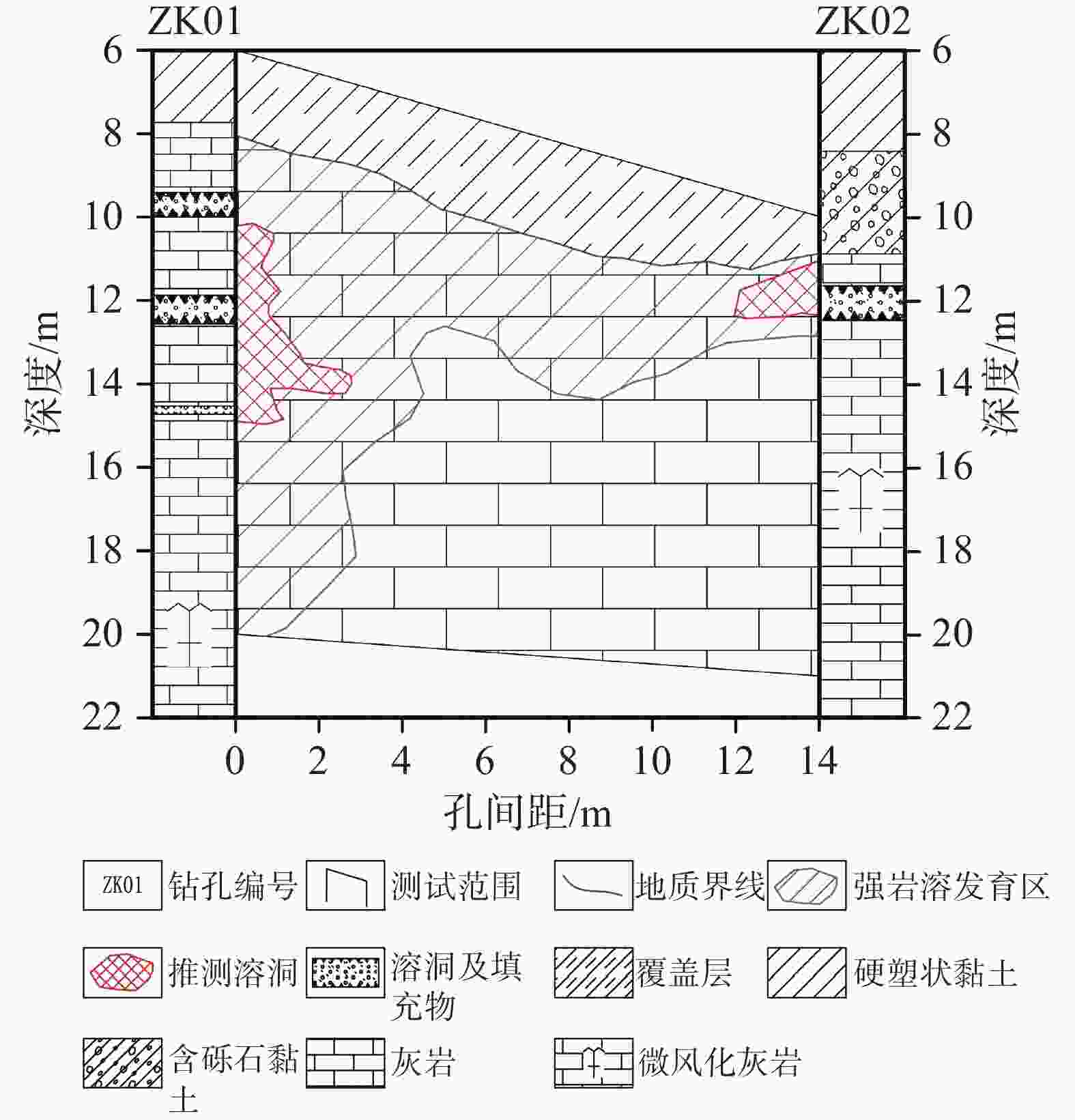
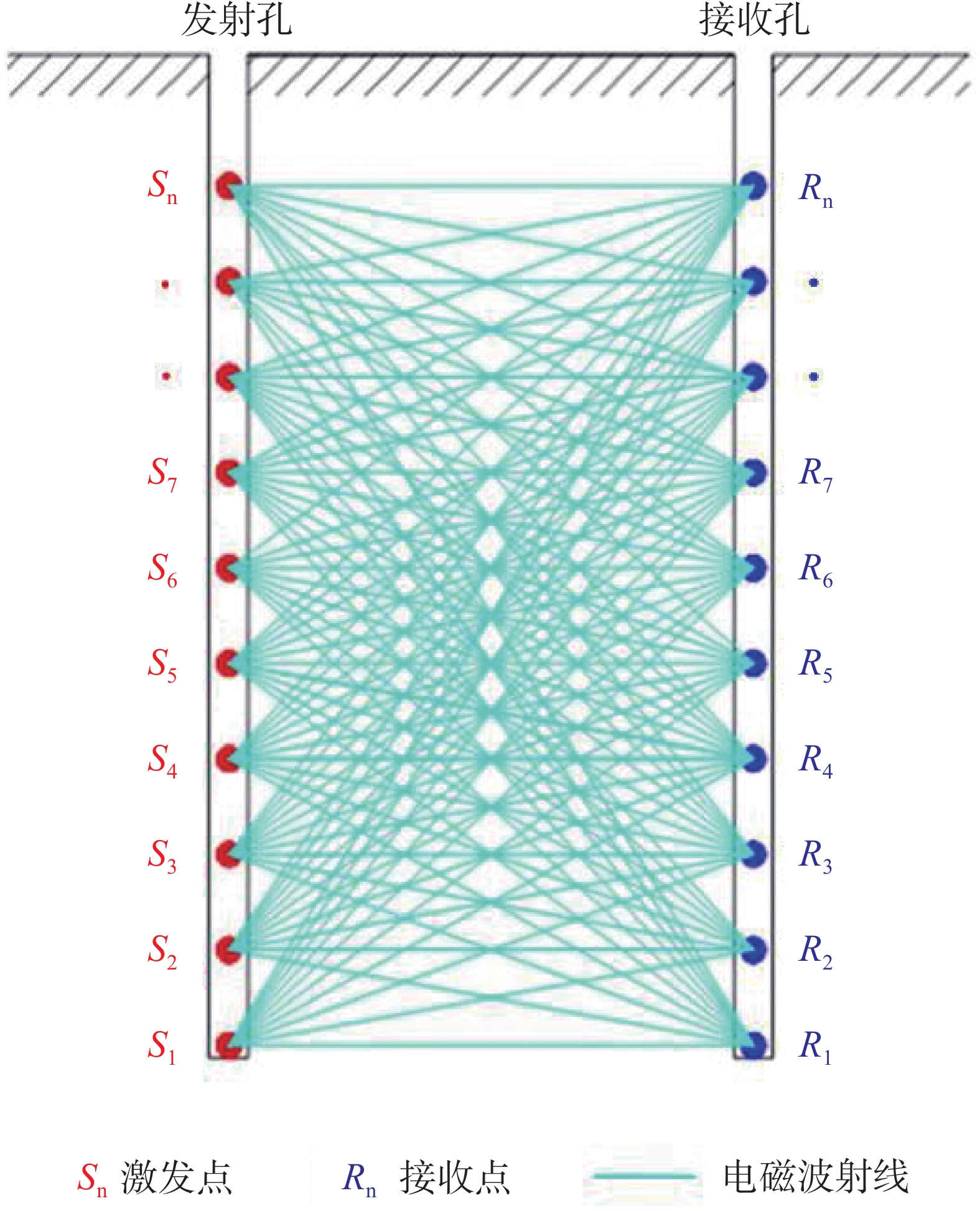
The cross-hole electromagnetic wave CT method, as an in-situ and non-destructive geophysical exploration technology, utilizes the propagation characteristics of high-frequency electromagnetic waves between boreholes to intuitively reflect the spatial distribution of underground anomalies. With advantages such as high resolution, efficient operation, and minimal restrictions by surface topography, it has been widely applied in engineering fields such as karst cave detection, roadbed grouting quality assessment, and mined-out area investigation in coal mines. However, in practical applications, the imaging quality of the electromagnetic wave CT method is affected by multiple factors, particularly in the detection of small karst cavities, where resolution capacity is closely tied to the selection of working parameters. Currently, there is a lack of systematic studies on the resolution capability of this method for small cavities, which to some extent restricts its precise application under complex geological conditions. This study adopts a combined approach of numerical simulation and engineering validation to thoroughly investigate the resolving capability of the cross-hole electromagnetic wave CT method under different working configurations for detecting small karst cavities. The research provides a solid theoretical foundation and technical reference for its practical engineering application.The research follows a technical route that integrates theoretical analysis, numerical modeling, and on-site testing. In terms of numerical simulation, a professional cross-hole electromagnetic tomography processing system was used along with a self-developed program for adding electromagnetic noise. Detection models were constructed under varying conditions, focusing on how key parameters-such as differences in medium absorption coefficients, transmission-reception spacing, and borehole spacing-affect the imaging outcome. The interference effects of ambient electromagnetic noise were also systematically analyzed. The model settings were designed to reflect typical engineering conditions. For example, the absorption coefficient of surrounding rock was set to 0.1 dB·m−1, and that of the target body (representing the karst cavity) was varied between 0.2 dB·m−1 and 0.7 dB·m−1 to simulate different filling conditions. The transmitting spacing ranged from 1 m to 10 m, and borehole spacing was controlled within 10 m to 30 m, covering a comprehensive range of commonly encountered engineering parameters. Based on the forward modeling, random electromagnetic noise at levels of 1% to 3% was also added to better replicate real field environments. For the engineering validation phase, a typical karst-developed area near Jingna Road in Guangxi was selected for on-site testing, and the absorption coefficient cross-sections were compared against borehole data for verification. The research results indicate that the resolution capability of electromagnetic wave CT for small karst cavities shows strong dependence on parameter selection. Regarding the absorption coefficient contrast, when the difference between the target body and surrounding rock reaches 0.6 dB·m−1, cavity anomalies can still be clearly identified even under 3% noise interference. However, when the difference is only 0.1 dB·m−1, the imaging quality deteriorates significantly once the noise level exceeds 1%. This suggests that in practical applications, working frequency bands with pronounced electromagnetic contrast should be prioritized, and effective noise suppression measures must be taken. With respect to transmission-reception spacing, the study shows that increasing the spacing leads to reduced ray path coverage density. When the spacing exceeds 4 m, the imaging quality for cavities of 2 m × 2 m in size becomes noticeably worse. At 8 m, the target is almost entirely unresolvable. This indicates that observation systems in practical projects must be designed according to the size of the target anomaly. For small cavity detection, it is recommended that transmitting spacing be kept within 4 m. Regarding borehole spacing, modeling data demonstrate that when the absorption coefficient difference is 0.6 dB·m−1, resolution remains acceptable at borehole spacing up to 30 m. However, when the difference decreases to 0.4 dB·m−1, cavity anomalies become blurred when spacing exceeds 20 m. This suggests that in regions with weak karst development or minimal contrast between the filling material and the surrounding rock, borehole spacing should be reduced appropriately to ensure detection effectiveness. The field validation further confirms the reliability of the simulation conclusions. In the actual survey conducted near Jingna Road in Guangxi, the electromagnetic wave CT method accurately delineated a cavity development zone between depths of 10m and 15 m. The inversion results closely matched the cavity positions revealed by borehole drilling. This study systematically identifies the key influencing factors and corresponding mechanisms that affect the resolution capability of electromagnetic wave CT in detecting small karst cavities. Firstly, it confirms that the absorption coefficient contrast is the fundamental determinant of resolution, providing theoretical guidance for frequency selection. Secondly, it quantifies reasonable values for transmitting spacing and borehole spacing, establishing technical standards for observation system design. Finally, it analyzes the interference mechanisms of ambient noise, offering guidance for improving data acquisition quality control. Based on the research findings, the following engineering recommendations are proposed for typical small karst cavity detection scenarios: transmission spacing should be kept within 4 meters, and borehole spacing should not exceed 30 meters. These results not only enrich the theoretical framework of electromagnetic wave CT method but also offer direct and practical guidance for improving the detection accuracy of karst cavities in real-world engineering contexts. -
Key words:
- electromagnetic wave CT /
- resolution /
- absorption coefficient /
- small karst caves
-
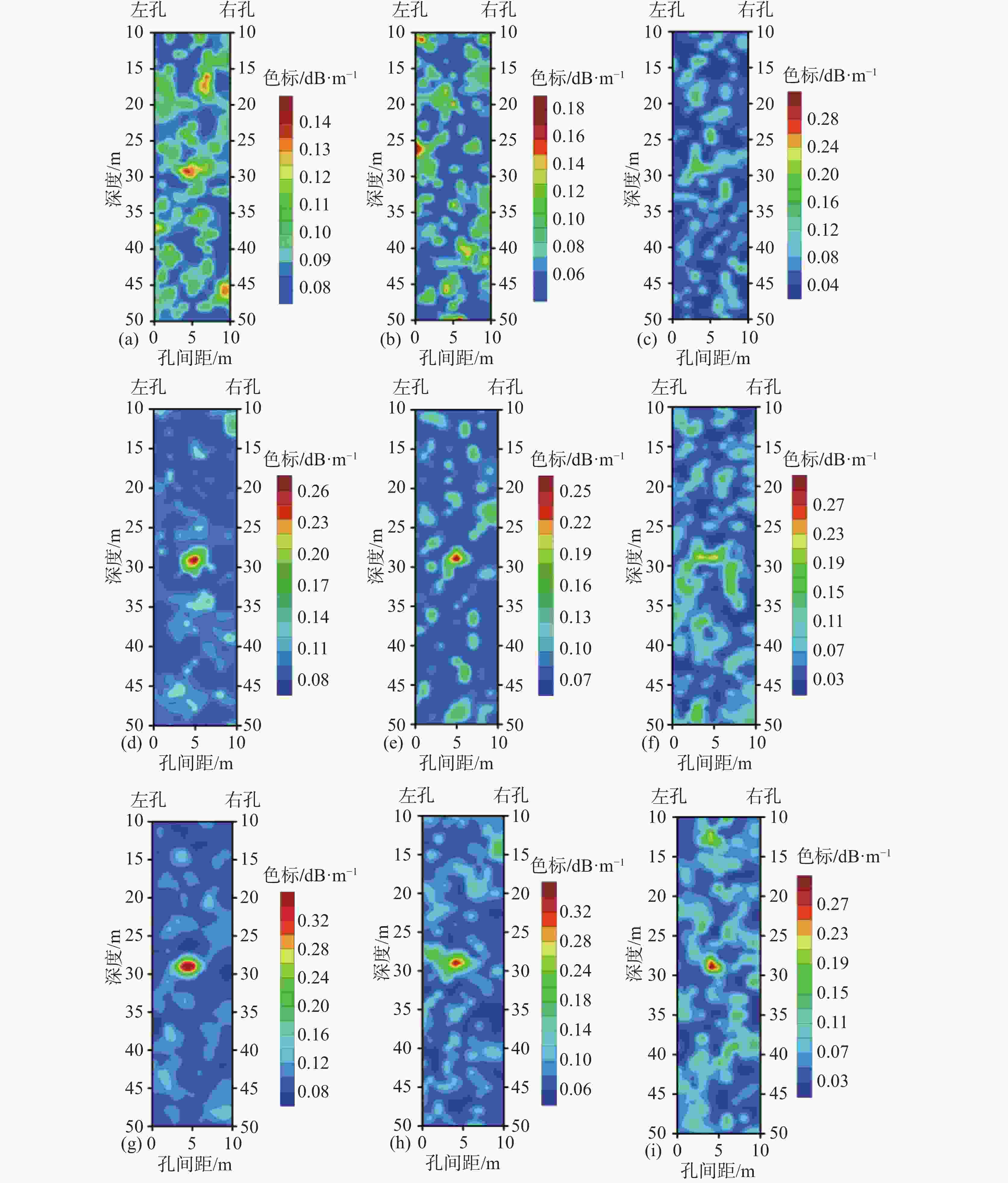
图 3 不同吸收系数差异及不同电磁噪声干扰情况下的电磁波CT法的反演成像图
(a)、(b)、(c)吸收系数差异为0.1 dB·m−1,电磁噪声分别为1%、2%、3% (d)、(e)、(f) 吸收系数差异为0.3 dB·m−1,电磁噪声分别为1%、2%、3% (g)、(h)、(i) 吸收系数差异为0.6 dB·m−1,电磁噪声分别为1%、2%、3%
Figure 3. Inversion results of electromagnetic wave CT method under different absorption coefficients and noise disturbances
(a) The difference in absorption coefficients for (b) and (c) is 0.1 dB·m−1, while the difference in absorption coefficients for electromagnetic noise is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively. The difference in absorption coefficients for (d), (e), and (f) is 0.3 dB·m−1, while the difference in absorption coefficients for electromagnetic noise is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively. The difference in absorption coefficients for electromagnetic noise is 0.6 dB·m−1, and the difference in absorption coefficients for electromagnetic noise is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively
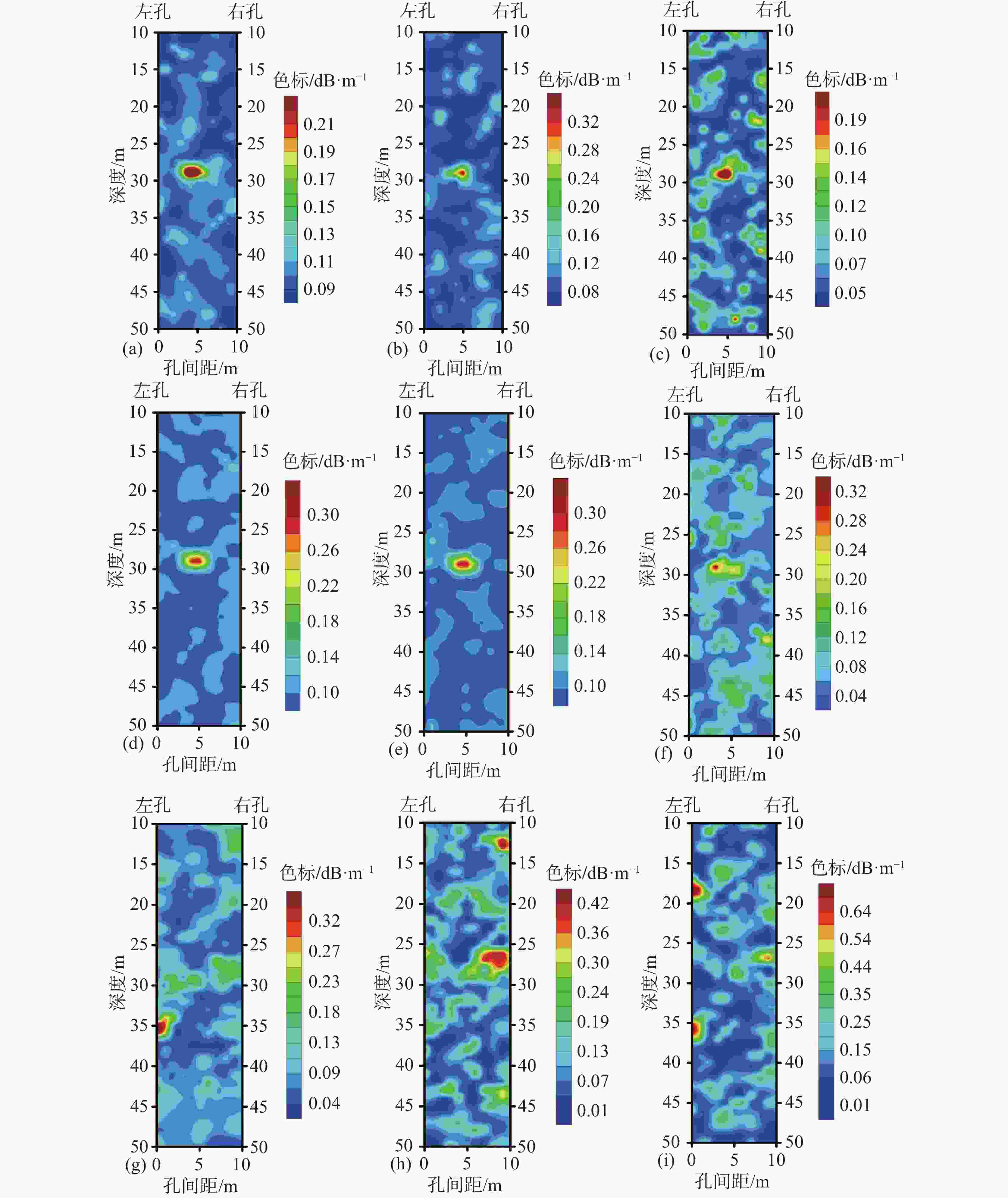
图 4 不同定点距及不同噪声干扰情况下电磁波CT法的反演成像图
(a)、(b)、(c)定点距为1 m,噪声干扰分别为1%、2%、3% (d)、(e)、(f) 定点距为4 m,噪声干扰分别为1%、2%、3% (g)、(h)、(i) 定点间距为8 m,噪声干扰分别为1%、2%、3%
Figure 4. Inversion results of electromagnetic wave CT method under different transmitting spacings and noise disturbances
(a) The fixed-point distance for (b) and (c) is 1 m, and the noise interference is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively. The fixed-point distance for (d), (e), and (f) is 4 m, and the noise interference is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively. The fixed-point distance for (g), (h), and (i) is 8 m, and the noise interference is 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively
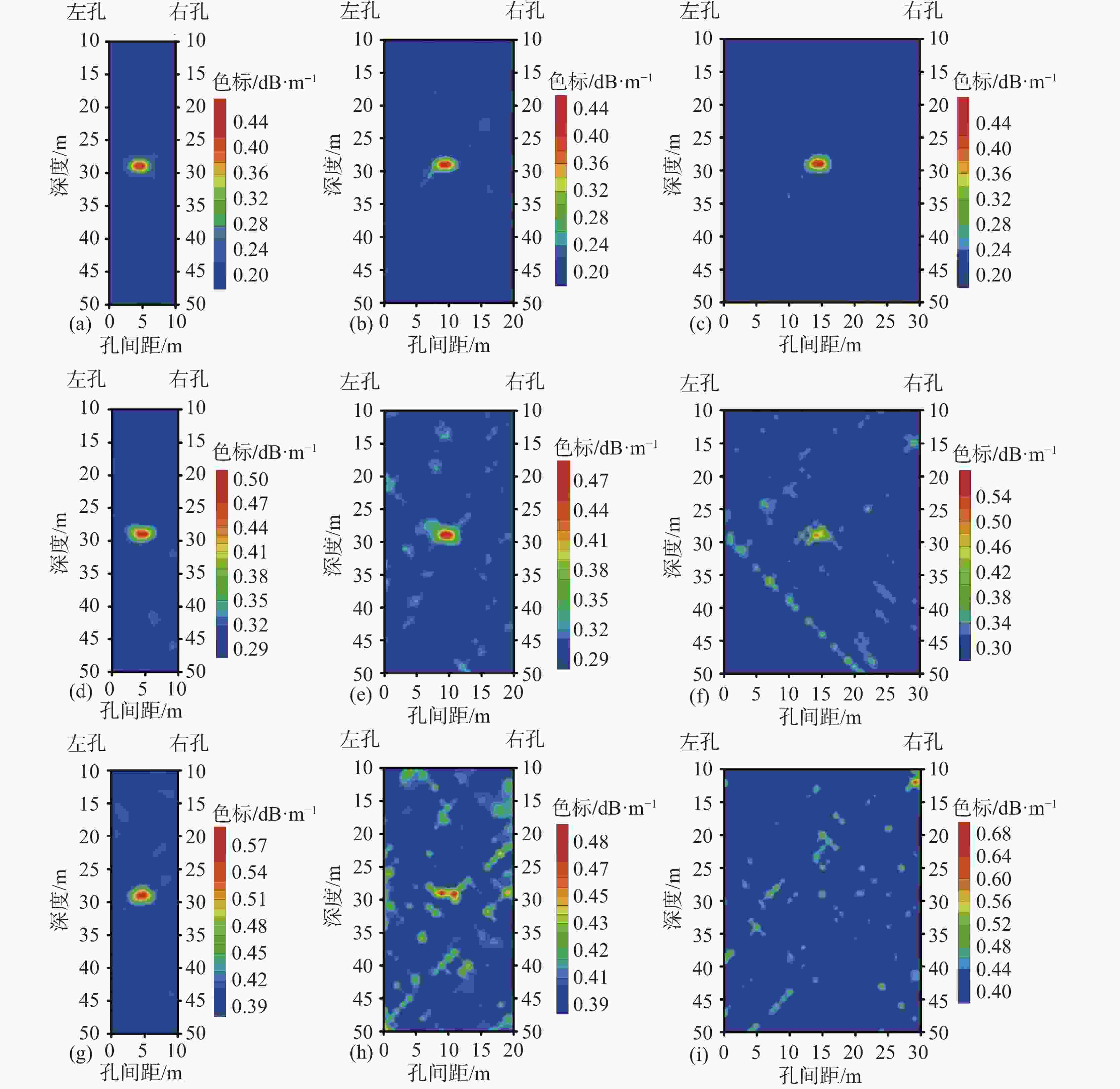
图 5 不同孔间距及不同吸收系数差异下电磁波CT法的反演结果成像图
(a)、(b)、(c)吸收系数差异为0.6 dB·m−1,孔间距分别为10 m、20 m、30 m (d)、(e)、(f) 吸收系数差异为0.5 dB·m−1,孔间距分别为10 m、20 m、30 m (g)、(h)、(i) 吸收系数差异为0.4 dB·m−1,孔间距分别为10 m、20 m、30 m
Figure 5. Inversion results of electromagnetic wave CT method under different borehole spacings and absorption coefficients
(a) The difference in absorption coefficients between (b) and (c) is 0.6 dB·m−1, with hole spacing of 10 m, 20 m, and 30 m, respectively. The difference in absorption coefficients between (d), (e), and (f) is 0.5 dB·m−1, with hole spacing of 10 m, 20 m, and 30 m, respectively. The difference in absorption coefficients between (g), (h), and (i) is 0.4 dB·m−1, with hole spacing of 10 m, 20 m, and 30 m, respectively
-
[1] 陈贻祥, 覃小群, 黄奇波, 甘伏平, 韩凯, 郑智杰, 贺德煌, 黄德健, 付昱, 蒋莹. 桂南陇瑞洼地浅层岩溶自然电场特征剖析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):130-138. doi: 10.11932/karst2017y36CHEN Yixiang, QIN Xiaoqun, HUANG Qibo, GAN Fuping, HAN Kai, ZHENG Zhijie, HE Dehuang, HUANG Dejian, FU Yu, JIANG Ying. Analysis of the characteristics of self-potential anomalous in shallow karst area of Longrui valley, southern Guangxi, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1): 130-138. doi: 10.11932/karst2017y36 [2] 刘天云, 罗锐恒, 胡顺强, 赵永宾, 潘晓东, 刘伟. 文山小河尾水库岩溶渗漏水文地质条件与管道位置识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1):88-99. doi: 10.11932/karst20220104LIU Tianyun, LUO Ruiheng, HU Shunqiang, PAN Xiaodong, LIU Wei. Hydrogeological conditions of karst leakage and identification of pipeline location in Xiaohewei reservoir, Wenshan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1): 88-99. doi: 10.11932/karst20220104 [3] 李志义, 白明洲, 许兆义, 陈祥,王成亮,郭蒙. 深长桩基础施工期岩溶处置实时效果无损检测方法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2012, 34(5):91-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.05.015LI Zhiyi, BAI Mingzhou, XU Zhaoyi, CHEN Xiang, WANG Chengliang, GUO Meng. Study on Real-time NDT Method Applied in Evaluating the Performance of Karst Cave Treatment in the Course of Construction of Deep Bridge Piles Foundation[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(5): 91-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.05.015 [4] Lapierre L, Zapata R, Lepinay P, et al. Karst exploration: Unconstrained attitude dynamic control for an AUV-Science Direct[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 219. [5] Chalikakis K, Plagnes V, Guerin R, Valois R,Bosch F. Contribution of geophysical methods to karst-system exploration: An overview[J]. Hydrogeology journal, 2011, 19(6): 1169-1180. doi: 10.1007/s10040-011-0746-x [6] 张银松, 曹聪, 康世海, 刘家富. 重庆市中梁山地区隐伏塌陷特征及物探勘测的思路[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):918-927. doi: 10.11932/karst20200611ZHANG Yinsong, CAO Cong, KANG Shihai, LIU Jiafu. Characteristics of hidden karst collapse in the Zhongliangshan area of Chongqing and an approach of geophysical surveys[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 918-927. doi: 10.11932/karst20200611 [7] YI Hu, MENG Yizhao, SHU Liang. Research on detection standard of Karst Roadbed Grouting effect based on the Geophysical Methods[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 3207(1118): 659-662. [8] HE Tuan, LI Guodong, LUO Feng. Research on Mining-Induced stress distribution of extrathick coal seams based on electromagnetic wave CT technology[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2022, 2022. [9] 岳崇旺. 井间电磁波层析成像研究与应用[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2007.YUE Chongwang. Study on the Cross-Well Electromagnetic Tomography and lts Application [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2007. [10] 谢朋. 基于SPAC法和电磁波CT法探测城市地下岩溶结构的对比研究[D].北京: 中国地震局地震研究所, 2019.XIE Peng. Based on SPAC method and electromagnetic wave CT method comparative study on detecting urban karst [D]. Beijing: China Earthquake Administration, 2019. [11] 胡熠. 电磁波层析法在南广铁路岩溶路基注浆质量检测上的应用[D].成都: 西南交通大学, 2010.HU Yi. Application of electromagnetic tomography in grouting quality detection of carst subgrade in Naning-Guangzhou railway[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010. [12] 郑立宁, 谢强, 胡熠, 徐飞飞, 任新红. 电磁波CT岩溶路基注浆质量检测试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(6):71-75, 125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.014ZHENG Lining, XIE Qiang, HU Yi, XU Feifei, REN Xinhong. Test study of electromagnetic CT for detecting grouting effect of Karst roadbed[J]. Hydrogeology and engineering geology, 2010, 37(6): 71-75, 125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.014 [13] 陈杭, 邢亚东, 邓超云. 跨孔电磁波CT在煤矿采空区探测中的应用探究[J]. 矿山测量, 2022, 50(1):21-23, 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2022.01.006CHEN Hang, XING Yadong, DENG Chaoyun. Application of borehole electromagnetic wave CT in coal mine goaf detection[J]. Mine Surveying, 2022, 50(1): 21-23, 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2022.01.006 [14] 赵旭辰, 李雪健, 曹芳智, 雷晓东, 李晨, 韩宇达. 井间电磁波CT在煤矿采空区探测效果分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):1088-1094.ZHAO Xuchen, LI Xuejian, CAO Fangzhi, LEI Xiaodong, LI Chen, HAN Yuda. An analysis of the detection effect of cross-well electromagnetic wave CT in coal mine goaf[J]. geophysical and geochemical exploration, 2021, 45(4): 1088-1094. [15] TAN Hanhua, HUANG Jiahui, Qi Shengwen. Application of cross-hole radar tomograph in karst Area[J]. Environmental earth sciences, 2012, 66(1): 355-362. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1244-0 [16] 黄生根, 刘东军, 胡永健. 电磁波CT技术探测溶洞的模拟分析与应用研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(S1):544-550.HUANG Shenggen, LIU Dongjun, HU Yongjian. Simulation analysis and application study of electromagnetic wave computed tomography in detecting karst caves[J]. Geotechnical mechanics, 2018, 39(S1): 544-550. [17] 代方园, 高扬, 宿庆伟, 胡韬, 耿付强, 董亚楠. 瞬变电磁与跨孔CT成像探测岩溶分布及形态特征的应用: 以山东省济南地区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(2):308-317, 328.DAI Fangyuan, GAO Yang, SU Qingwei, HU Tao,GENG Fuqiang, DONG Yanan. Application of transient electromagnetism and cross-hole CT imaging to detect karst distribution and morphological characteristics: A case study of Jinan, Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(2): 308-317, 328. [18] 袁永榜, 易洪春. 基于多频同步电磁波CT技术的煤层水力压裂范围探测试验[J]. 工矿自动化, 2020, 46(8):51-57.YUAN Yongbang, YI Hongchun. Detection test of coal seam hydraulic fracturing range based on multi-frequency synchronous electromagnetic wave CT technology[J]. Industrial and mining automation, 2020, 46(8): 51-57. [19] 付晖. 电磁波CT在水利水电工程岩溶探测中的应用[J]. 人民长江, 2003(11):26-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.11.011FU Hui. Application of Electromagnetic Wave CT in Karst Exploration of Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering[J]. Yangtze River, 2003(11): 26-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.11.011 [20] 刘少虹, 潘俊锋, 秦子晗, 王书文, 张震, 高晓进, 李根. 基于电磁波CT探测的掘进工作面冲击危险性评价技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(S2):4093-4101.LIU Shaohong, PAN Junfeng, QIN Zihan, WANG Shuwen, ZHANG Zhen, LI Geng. Research on the risk assessment of rock burst of heading face based on electromagnetic wave CT detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S2): 4093-4101. [21] YANG Zhen, CHANG Shuai, WU Xiang . Mining Safety Mechanisms Adopting CT Projection Matrix Measured by Electromagnetic Wave Imaging in a Longwall Panel[J]. Disaster Advances, 2013, 6: 144-153. [22] 刘少虹, 潘俊锋, 王洪涛, 唐忠义, 夏永学, 曹延福, 张晨阳. 基于冲击启动过程的近场围岩冲击危险性电磁波CT评估方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(2):384-396.LIU Shaohong, PAN Junfeng, WANG Hongtao, TANG Zhongyi, XIA Yongxue, CAO Yanfu, ZHANG Chenyang. Electromagnetic wave CT evaluation method for rock burst hazard in near field based on rock burst start-up process[J]. Journal of Coal, 2019, 44(2): 384-396. [23] 邓小虎, 傅焰林. 跨孔电磁波层析成像在岩溶三维空间分布上的应用[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2022, 31(1):13-22.DENG Xiaohu, FU Yanlin. Application of Cross-hole Electromagnetic Wave Tomography in Three Dimensional Spatial Distribution of Karst[J]. CT theory and application, 2022, 31(1): 13-22. -




 下载:
下载: