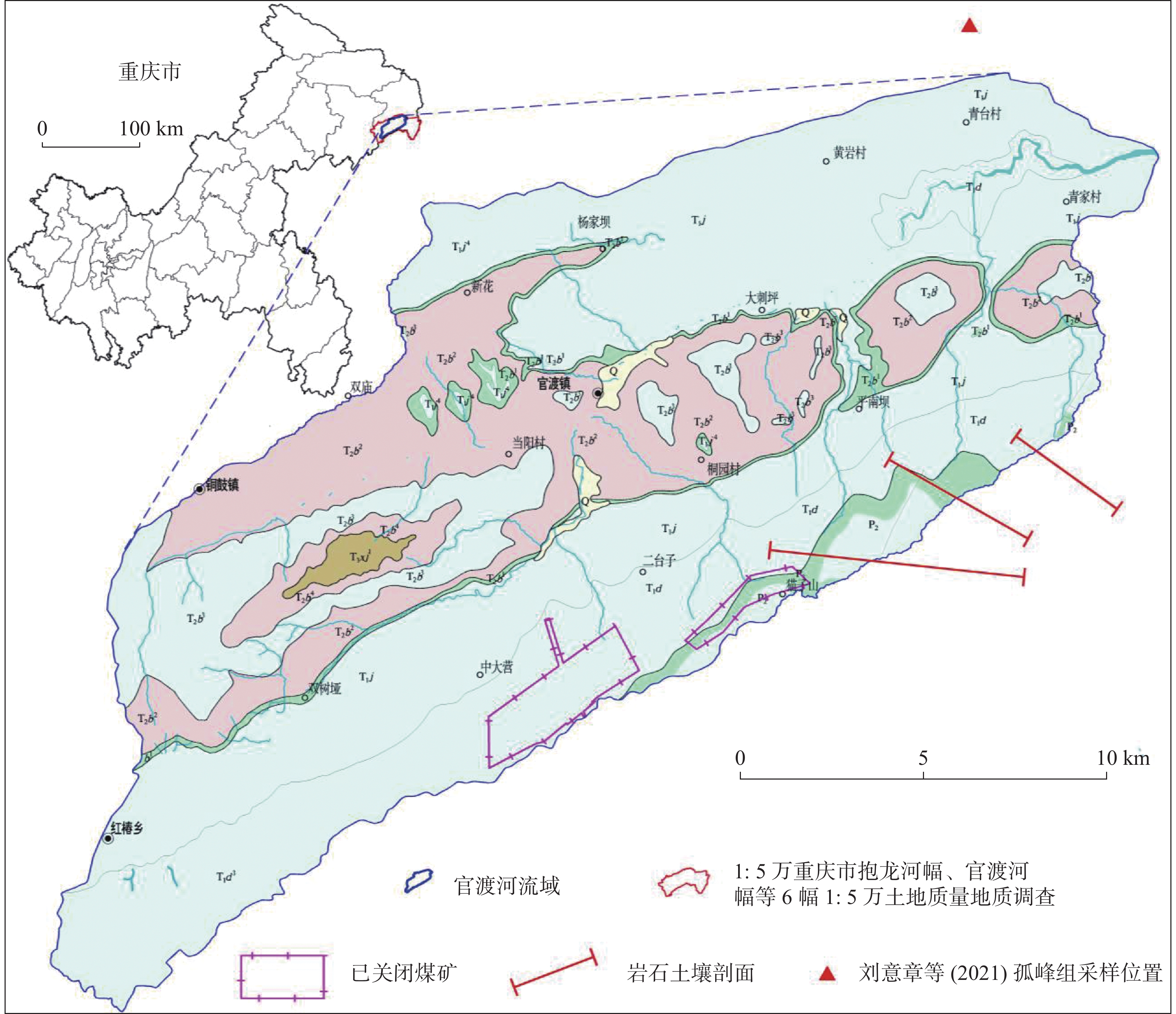
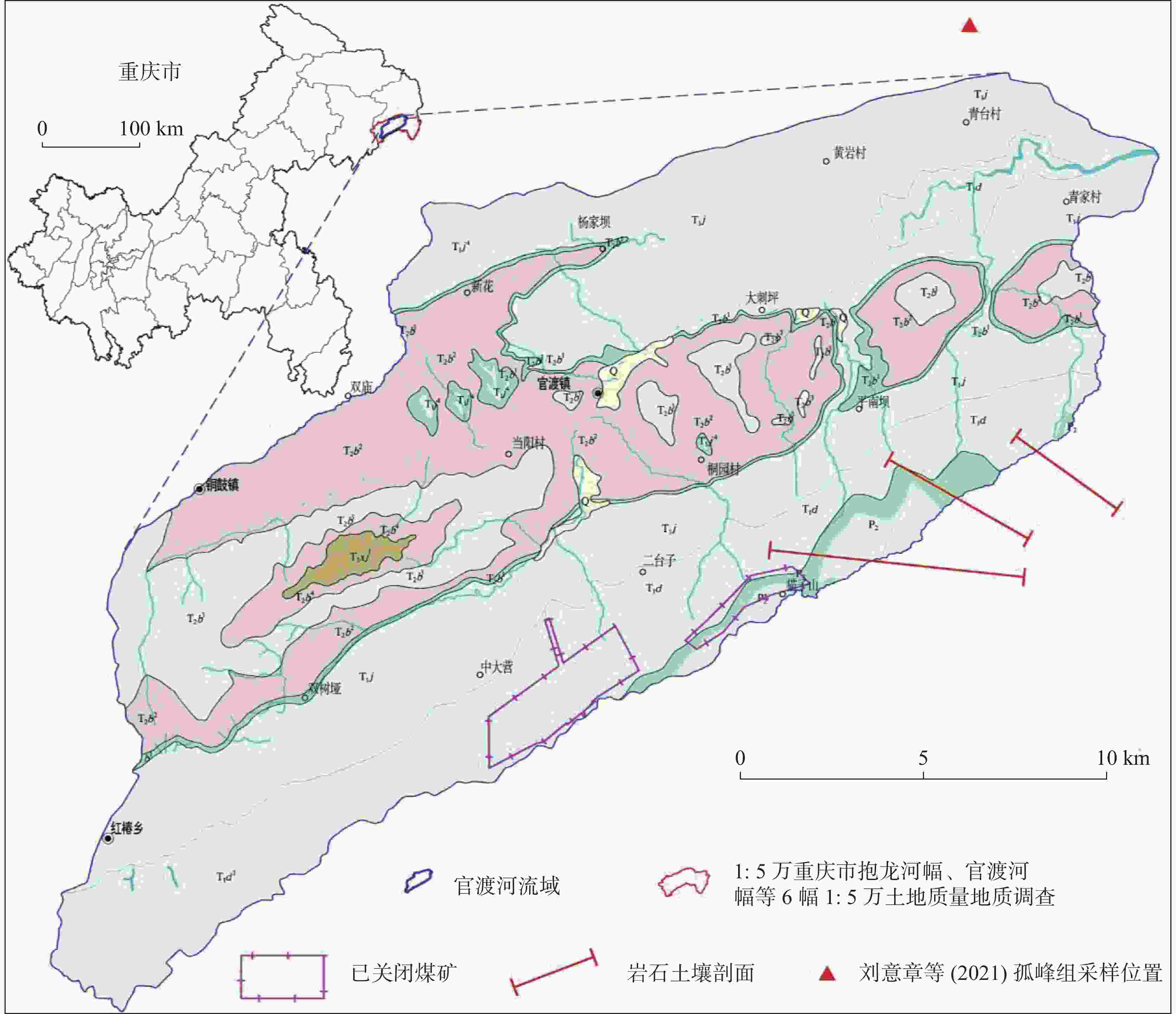
Study on the migration characteristics of cadmium element in the black shales of the groundwater system in the Guandu River Basin of Wushan area
-
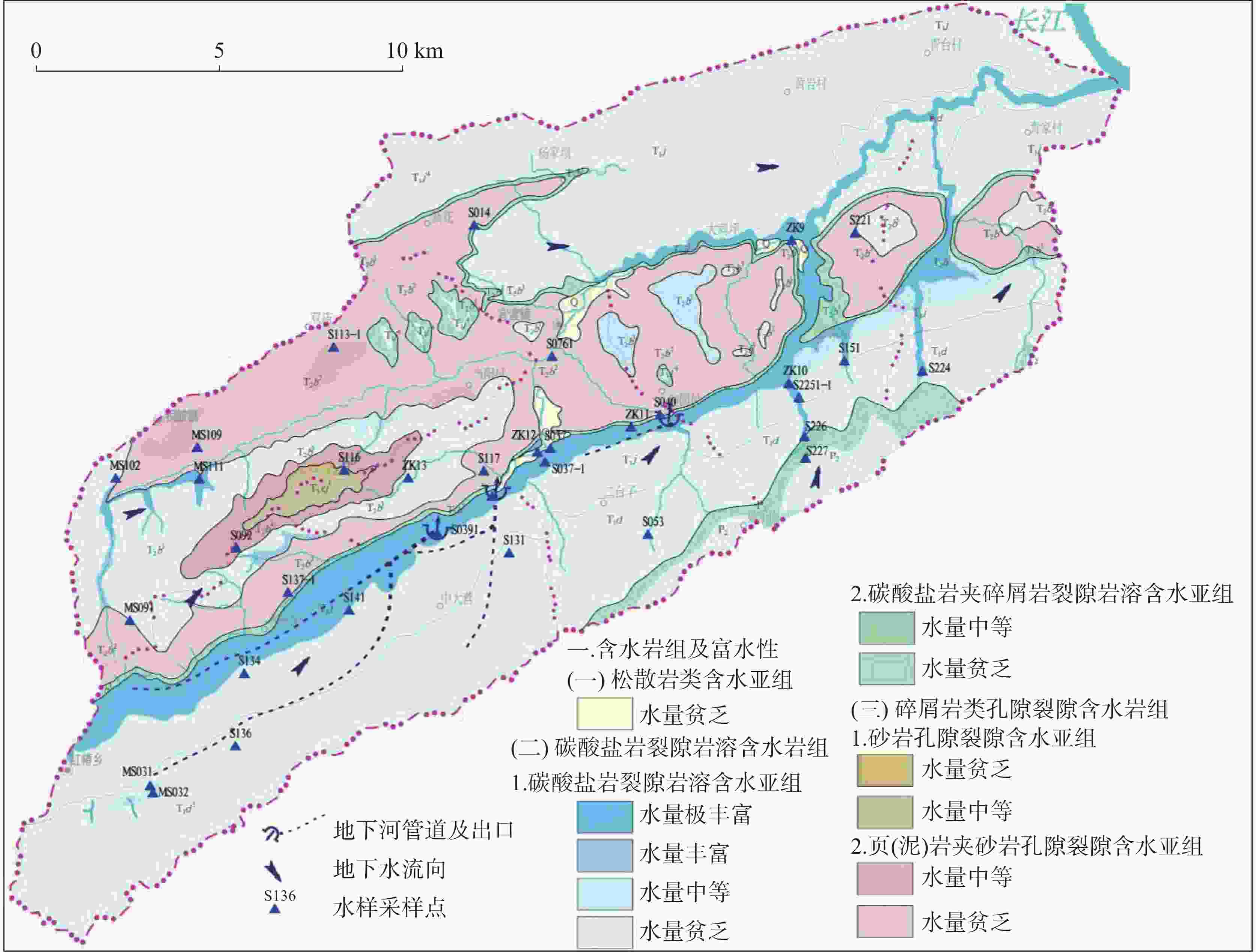
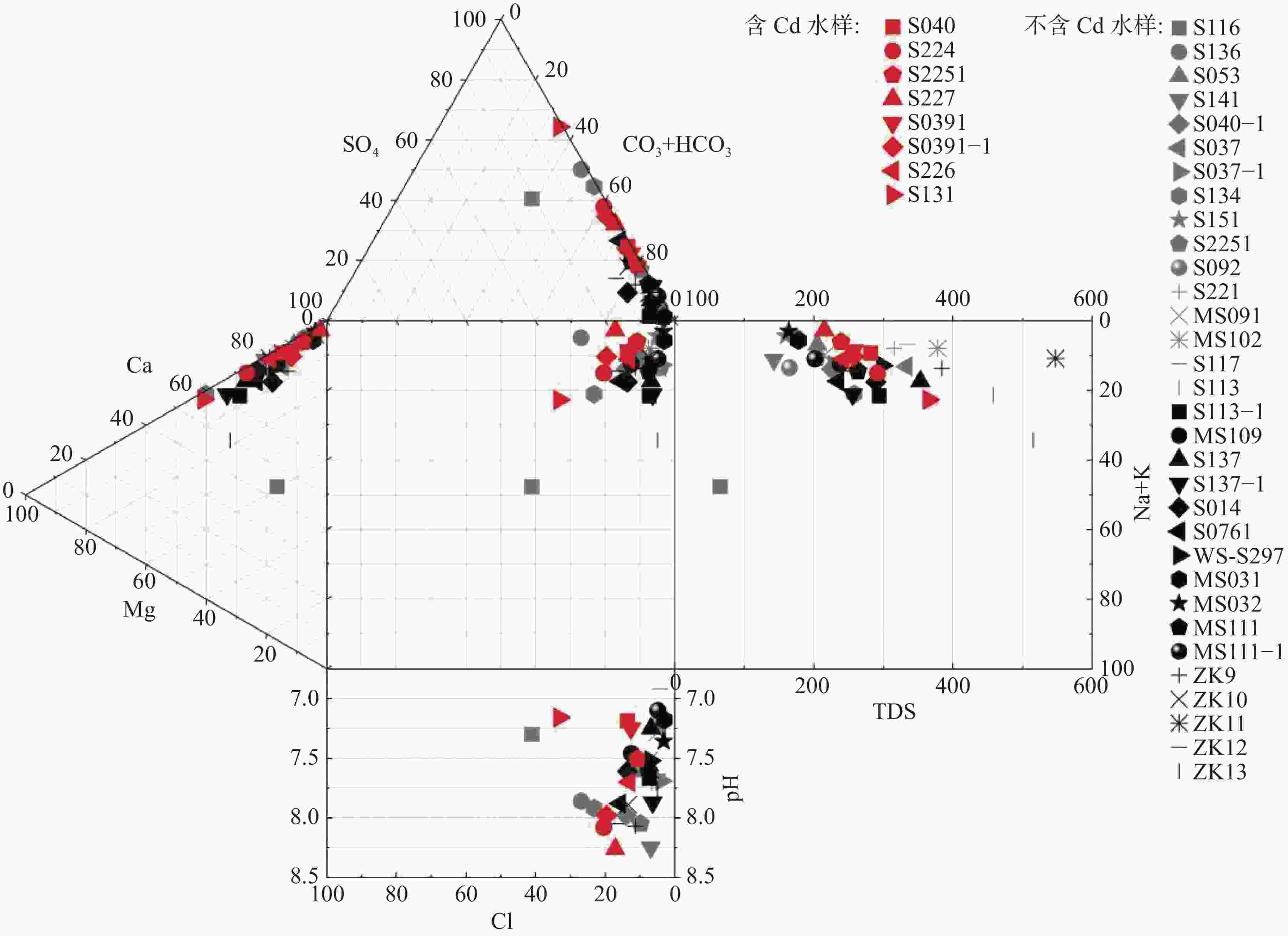
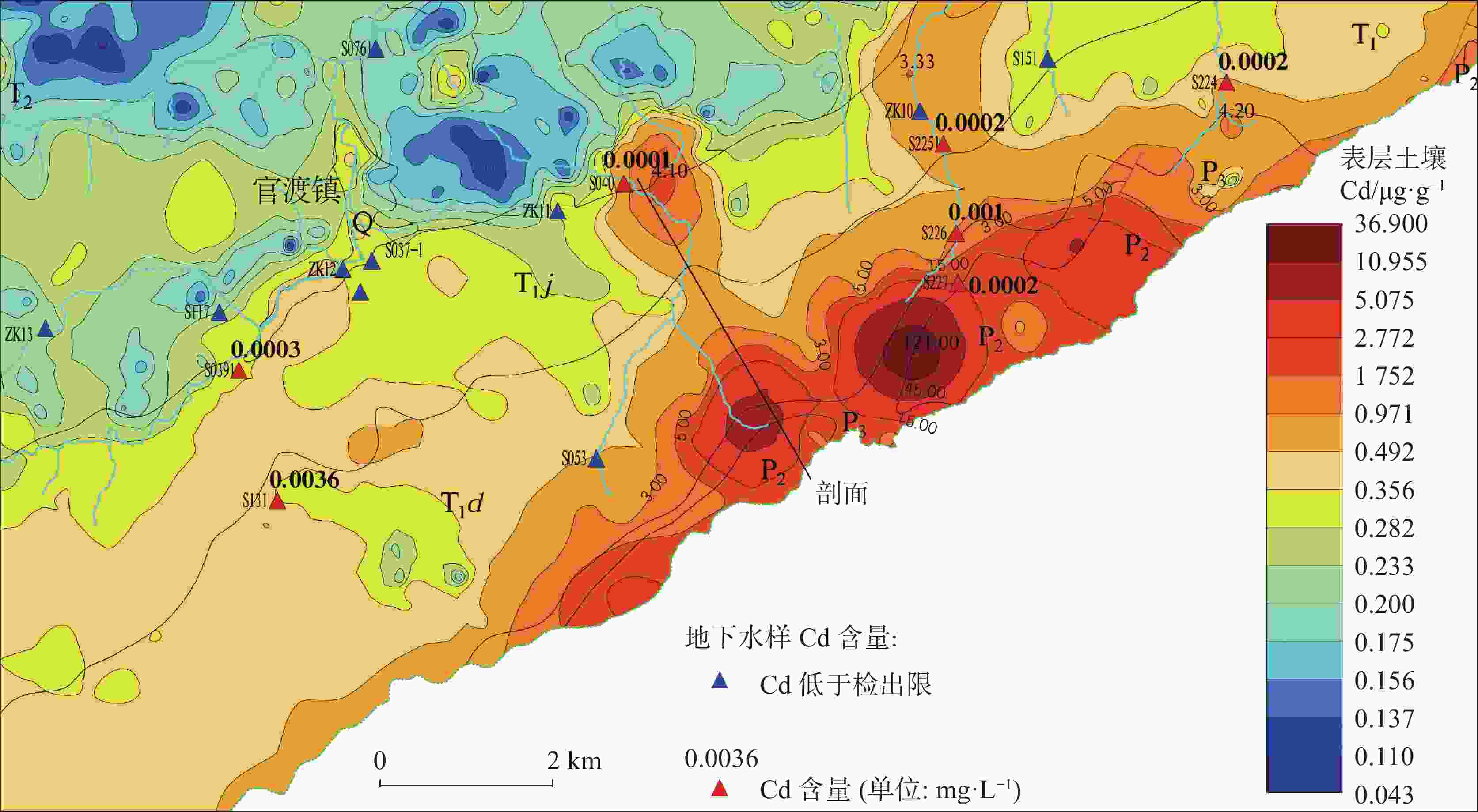
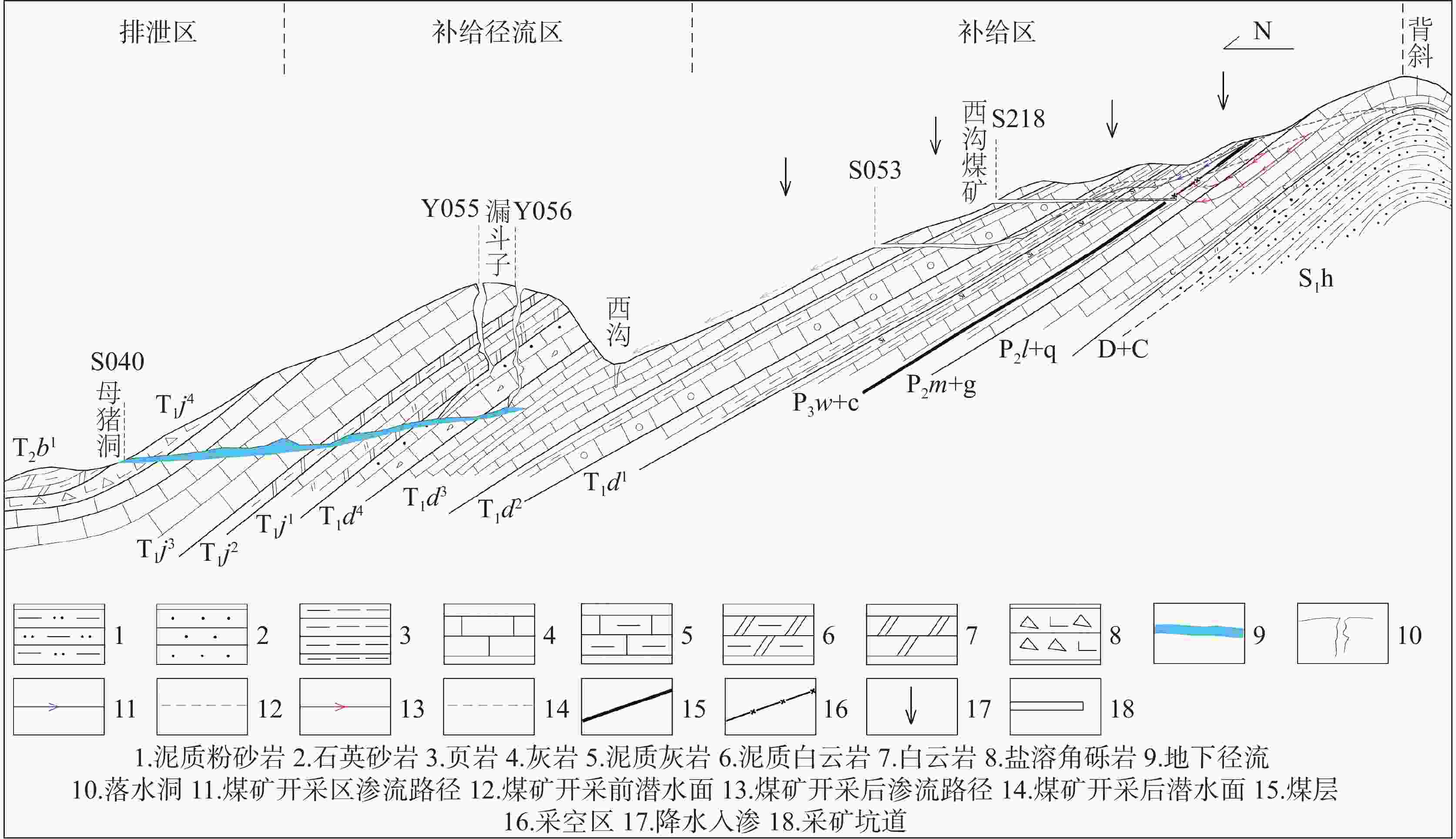
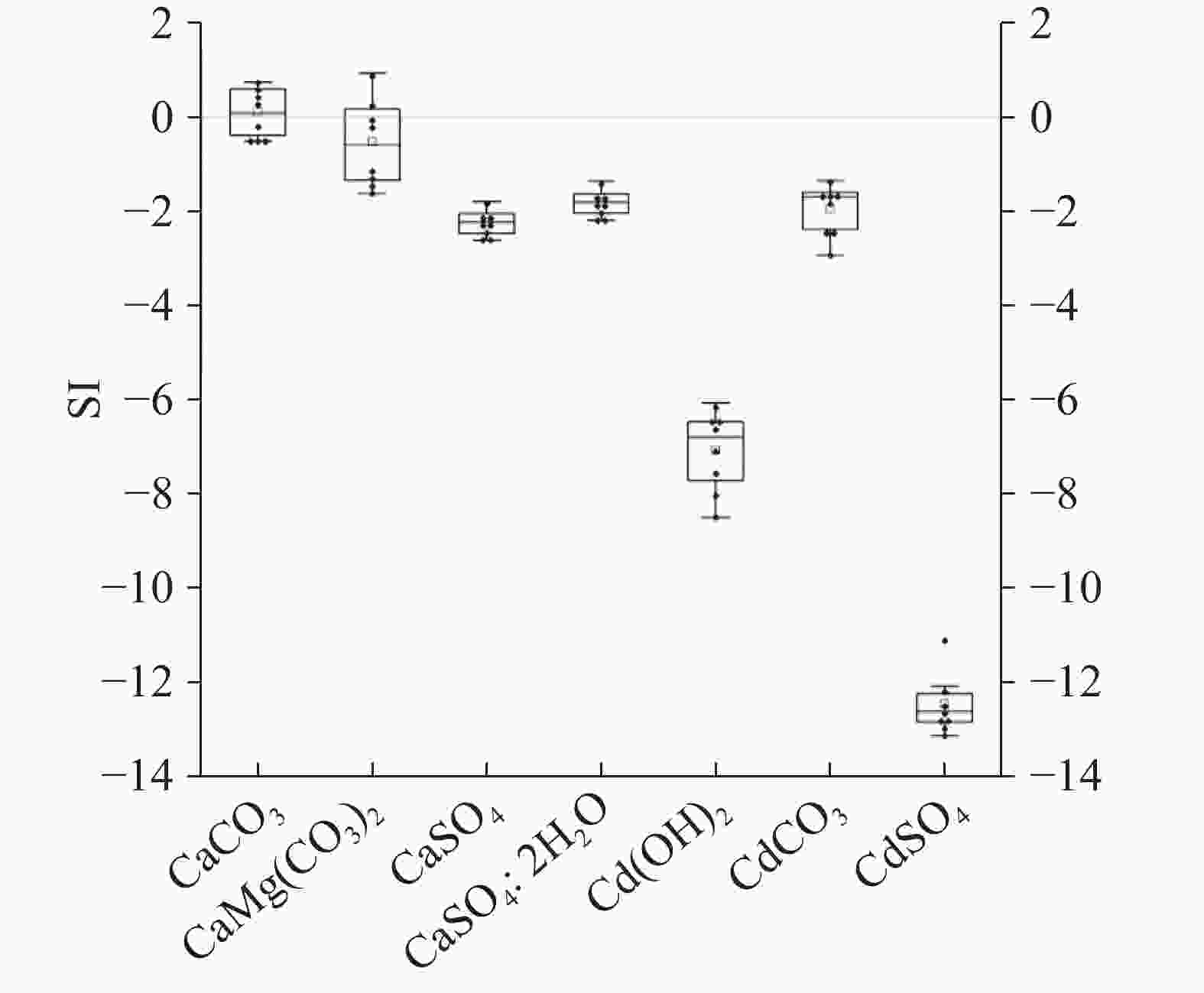
摘要: 巫山地区二叠系黑色岩系有害元素Cd高背景值突出,表层土壤已受到污染,对地下水的影响尚不清楚。本次工作以巫山官渡河流域为研究区,通过野外调查、资料收集、数据分析、水样测试等方法,分析研究区二叠系黑色岩系有害元素Cd对地下水的影响,以期揭示Cd在岩石—土壤—水中的运移特征。结果表明:(1)研究区含Cd地下水样均来自该流域发源于二叠系黑色岩系的岩溶地下水系统,水样具有典型的碳酸盐岩岩溶的化学特征,含Cd水样与不含Cd水样最显著的差别是含Cd水样${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$平均含量是不含Cd水样的3倍。(2)研究区内二叠系黑色岩性中的Cd含量较高,以二叠系孤峰组为最高,岩石风化成土壤后Cd依旧富集,但含量大幅降低;Cd通过溶滤作用进入地下水系统,是研究区含地下水中Cd的主要来源,Cd与${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$具有极显著正相关。(3)煤矿开采改变了地下水的运动路径,强化了溶滤作用,Cd在坑道涌水中富集作用加强,煤矿坑道涌水中Cd含量迅速增高,相应TDS也增高,水质变差,具有潜在风险,不宜作为引用水源。研究区三叠系岩溶地下水系统水量丰富,稀释了二叠系岩溶地下水中Cd的浓度,降低了Cd污染的风险。(4)Cd在岩石中赋存状态以碳酸盐矿物为主,风化后Cd多数溶解或转化其它可迁移形态,土壤的酸化使得Cd容易迁入水体,增加环境风险。通过饱和指数分析Cd地下水在迁移过程中尚未达到饱和。Abstract:
The Permian black shale in the Wushan area is characterized by high background values of harmful trace elements, among which cadmium (Cd) is particularly prominent. These elements can easily enter groundwater systems through rock weathering, soil erosion, and human activities such as coal mining, thus posing potential threats to regional ecosystems and public health. However, previous studies have predominantly focused on Cd accumulation in soil and crops, while paying less attention to the migration characteristics and pollution mechanisms of Cd in groundwater systems. This study employs a multidisciplinary approach, integrating techniques from geology, hydrology, geochemistry, and environmental science, to systematically investigate the migration characteristics of Cd in the Guandu River Basin. The primary research methods include field surveys, water sampling and testing, data analysis, and geochemical modeling. By examining the pathways and mechanisms of Cd migration from black shale to groundwater, this study reveals the transport patterns of Cd within the rock–soil–groundwater system, clarifies its pollution mechanisms, and provides a scientific basis for environmental protection and resource utilization. Analysis of 40 groundwater samples revealed that eight samples contained detectable levels of Cd, ranging from 0.0001 mg·L−1 to 0.0036 mg·L−1, while Cd was undetectable in the other 32 samples. The pH values of Cd-containing samples ranged from 7.16 to 8.26, indicating neutral conditions. The average sulfate (SO$_4^{2-} $) concentration in Cd-containing samples was 67.84 mg·L−1, three times higher than that in Cd-free samples (22.81 mg·L−1), highlighting a strong correlation between SO$_4^{2-} $ and Cd migration. Additionally, the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) values in Cd-containing samples ranged from 215 mg·L−1 to 365 mg·L−1, with an average of 268.56 mg·L−1, indicating moderately hard to hard water. Research findings show that Cd-containing groundwater in the Guandu River Basin primarily originates from the karst groundwater system of the Permian black shale. The Gufeng Formation within the Permian System exhibited the highest Cd content. Although Cd remained enriched in soils derived from weathered rocks, its concentration significantly decreased. Cd entered the groundwater system through leaching, which is the main source of Cd in the groundwater of the study area. Coal mining activities have significantly altered the groundwater flow paths and intensified leaching effects, leading to Cd enrichment in mine gushing water. The highest Cd concentration detected was 0.0036 mg·L−1 in gushing water (Sample S131) in an abandoned coal mine, indicating that coal mining activities are a significant anthropogenic factor contributing to Cd contamination. Additionally, TDS values in mine gushing water increased sharply, resulting in water quality deterioration and posing potential environmental risks. The Triassic karst groundwater system can effectively dilute Cd concentrations. This system is characterized by abundant water resources and demonstrates significant dilution effects on Cd concentrations in Permian karst water. For example, Cd was detected in the Longdong Underground River (Sample S039) during both the dry season and wet season, but its concentration was only 0.0003 mg·L−1, which is far lower than that in mine gushing water. This dilution effect effectively reduces the risk of Cd contamination. Geochemical modeling revealed that calcite and dolomite in groundwater are close to saturation, while cadmium sulfate and cadmium carbonate have not yet reached saturation. This indicates that Cd has the potential for further enrichment in groundwater. Cd in rocks mainly exists in carbonate minerals (19%−66%). Analysis of Cd speciation in soil shows that Cd primarily exists in the forms of iron-manganese oxide-bound (25.03%) and residual (24.22%) fractions, with the smallest proportion in the water-soluble fraction (0.63%), indicating that soluble Cd in soils is mostly leached into groundwater through weathering, and soil acidification further enhances the dissolution and migration of Cd. This study elucidates the migration mechanisms and contamination risks of Cd within the black shale–soil–groundwater system, offering essential theoretical support for controlling Cd contamination in similar regions. The findings regarding Cd enrichment in coal mine gushing water provide scientific evidence for groundwater protection and pollution management in mining areas. By clarifying the impact of soil acidification on Cd migration, this study underscores the significance of controlling soil acidification for regional ecological restoration and environmental protection. Additionally, this study also highlights the dilution effect of Triassic karst groundwater on Cd pollution, offering guidance for the sustainable development and utilization of groundwater in the region. The results of this study can serve as a reference for ecological conservation in the Wushan area and other regions characterized by black shale. -
表 1 含镉水样主要化学指标
Table 1. Main chemical indicators of Cd-containing water samples
编号 pH Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ Cl− ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ TDS 镉 S040 7.19 1.37 0.41 57.43 6.08 149.62 39.33 1.46 0.67 281.81 0.0001 S224 8.08 1.65 0.66 72.94 16.4 183.47 89.94 2.61 1.15 291.50 0.0002 S2251 7.51 1.16 0.47 51.96 2.76 131.67 24.04 1.46 0.67 238.84 0.0002 S227 8.26 1.15 0.32 69.67 0.99 145.25 55.07 1.3 0.66 215.00 0.0002 S0391 7.25 1.77 0.3 51.51 4.15 131.67 30.59 1.46 1.2 257.34 0.0003 S0391-1 7.98 4.19 0.51 73.84 6.27 163.43 70.80 3.48 1.25 257.00 0.0003 S226 7.70 1.55 0.25 69.67 9.94 191.11 47.72 1.74 1.28 242.00 0.001 S131 7.16 2.72 0.59 67.21 29.32 126.14 185.22 2.17 1.08 365.00 0.0036 均值 7.64 1.95 0.44 64.28 9.49 152.80 67.84 1.96 1.00 268.56 0.00074 标准差 0.43 1.03 0.15 9.22 9.33 24.47 52.05 0.76 0.28 45.86 0.00119 变异系数 0.06 0.53 0.34 0.14 0.98 0.16 0.77 0.39 0.28 0.17 1.61 最大值 8.26 4.19 0.66 73.84 29.32 191.11 185.22 3.48 1.28 365.00 0.0036 最小值 7.16 1.15 0.25 51.51 0.99 126.14 24.04 1.30 0.66 215.00 0.0001 注:指标含量单位为mg·L−1,pH无量纲。下表同上。 表 2 研究区各地质单元表层土壤及岩石中Cd元素分布特征表
Table 2. Distribution characteristics of Cd in surface soils and rocks from different geological units in the study area
元素/指标 统计参数 P2l P2q P2m P2g P3w P3d T1d T1j T2b T3xj Q 土壤 样品件数 − 68 50 10 129 63 367 479 946 14 83 Cd X − 1.945 2.332 6.671 1.697 1.582 0.461 0.327 0.223 0.162 0.3 CV − 1.14 0.92 0.77 2.00 1.26 1.04 0.45 0.50 0.36 0.59 pH X − 6.044 5.973 6.728 5.63 6.511 6.62 7.224 7.319 5.176 7.845 CV − 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.17 0.18 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.07 0.07 岩石 样品件数 1 1 37 21 59 9 22 − − − − Cd X 0.42 0.28 1.03 24.41 1.16 0.19 0.06 − − − − 注:X为平均值,CV为变异系数,括号内为样品数,Cd含量单位为mg/kg,pH无量纲。 表 3 含Cd水样水化学参数相关系数矩阵(样品数8)
Table 3. Correlation coefficient matrix of hydrochemical parameters in Cd-containing water samples (eight samples)
pH Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ Cl− ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ TDS Cd pH 1 Na+ 0.336 1 K+ 0.557 0.634* 1 Ca2+ 0.931** 0.514 0.663* 1 Mg2+ 0.069 0.588* 0.667* 0.296 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 0.898** 0.430 0.580* 0.929** 0.231 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 0.168 0.685* 0.702* 0.397 0.957** 0.254 1 Cl− 0.519 0.917** 0.798** 0.696* 0.571 0.655* 0.637* 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$N 0.657* 0.671* 0.555 0.762** 0.460 0.784** 0.450 0.759** 1 TDS 0.790** 0.575 0.809** 0.819** 0.602* 0.754** 0.641* 0.665* 0.724** 1 Cd −0.038 0.564 0.438 0.150 0.914** 0.054 0.917** 0.410 0.315 0.478 1 **. 在0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关。*. 在 0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 4 土壤Cd元素地球化学形态组成
Table 4. Geochemical speciation composition of Cd element in soil
元素形态 全量 水溶态 离子交换态 碳酸盐结合态 腐殖酸结合态 铁锰氧化物结合态 强有机结合态 残渣态 最小值 0.123 0.001 0.019 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.007 0.022 平均值 1.598 0.010 0.249 0.163 0.249 0.400 0.081 0.387 最大值 8.737 0.061 1.158 0.845 1.857 2.339 0.399 1.781 标准离差 2.044 0.014 0.275 0.206 0.437 0.556 0.096 0.502 变异系数 1.279 1.400 1.104 1.264 1.755 1.390 1.185 1.297 占比(%) 100.00 0.63 15.58 10.20 15.58 25.03 5.07 24.22 注:含量单位mg·kg−1,样品数n=16。 -
[1] Parviainen A, Loukola-Ruskeeniemi K. Environmental impact of mineralised black shales[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 65-90. [2] Peng B, Song Z L, Tu X L, Xiao M L, Wu F C, Lv H Z. Release of heavy metals during weathering of the Lower Cambrian black shales in western Hunan, China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 45(8): 1137-1147. [3] Ling S X, Wu X Y, Ren Y, Sun C W, Liao X, Li X N, Zhu B L. Geochemistry of trace and rare earth elements during weathering of black shale profiles in Northeast Chongqing, Southwestern China: Their mobilization, redistribution, and fractionation[J]. Geochemistry, 2015, 75(3): 403-417. [4] Liu Y Z, Xiao T F, Perkins R B, Zhu J M, Zhu Z J, Xiong Y, Ning Z P. Geogenic cadmium pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 176: 42-49. [5] Duan Y R, Yang Z F, Yu T, Yang Q, Liu X, Ji W B, Jiang H Y, Zhuo X X, Wu T S, Qin J X, Wang L. Geogenic cadmium pollution in multi-medians caused by black shales in Luzhai, Guangxi[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 260: 113905. [6] Nganje T N, Edet A, Cuthbert S, Adamu C I, Hursthouse A S. The concentration, distribution and health risk from potentially toxic elements in the soil-plant-water system developed on black shales in SE Nigeria[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2020, 165: 103806. [7] Ulf Lavergren, Mats E. Åström, Bo Bergbäck, Henning Holmström. Mobility of trace elements in black shale assessed by leaching tests and sequential chemical extraction[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2009, 9(1): 71-79. [8] Tuttle M L W, Breit G N, Goldhaber M B. Weathering of the New Albany Shale, Kentucky: II. Redistribution of minor and trace elements[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(8): 1565-1578. [9] Perkins R B, Mason C E. The relative mobility of trace elements from short-term weathering of a black shale[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 56: 67-79. [10] Falk H, Lavergren U, Bergbäck B. Metal mobility in alum shale from Öland, Sweden[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 90(3): 157-165. [11] Lavergren U, Åström M E, Falk H, Bergback B. Metal dispersion in groundwater in an area with natural and processed black shale: Nationwide perspective and comparison with acid sulfate soils[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24: 359-369. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.11.022 [12] 唐将, 刘安云, 邓富银, 雷家立.长江三峡库区土壤与水系沉积物Cd地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(8): 750-754.TANG Jiang, LIU Anyun, DENG Fuyin, LEI Jiali. Geochemical characteristics of cadmium in soils and stream sediments in the Three Gorges reservoir area, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(8): 750-754. [13] 赵万伏, 宋垠先, 管冬兴, 马强, 郭超, 文宇博, 季峻峰. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7):1332-1341. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0595ZHAO Wanfu, SONG Yinxian, GUAN Dongxing, MA Qiang, GUO Chao, WEN Yubo, JI Junfeng. Pollution status and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of a typical black shale area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1332-1341. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0595 [14] 杨连升, 周明忠, 熊康宁, 杨桦, 张迪, 姚成斌, 张先荣. 贵州黑色页岩土壤地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(5): 1023-1037.YANG Liansheng, ZHOU Mingzhong, XIONG Kangning, YANG Hua, ZHANG Di, YAO Chengbin, ZHANG Xianrong. Geochemical characteristics of black-shale soils in Guizhou Province, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1023-1037. [15] 范德廉, 张焘, 叶杰. 中国的黑色岩系及其有关矿床[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2004: 1-441.FAN Delian, ZHANG Tao, YE Jie. China's black shales and their associated mineral deposits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004:1-441. [16] 周东晓, 彭渤, 王勤, 方小红, 邬思成, 赵亚方, 刘静, 陈丹婷, 王欣, 谭长银, 万大娟. 扬子地台西缘下寒武统黑色页岩土壤元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(1): 59-71.ZHOU Dongxiao, PENG Bo, WANG Qin, FANG Xiaohong, WU Sicheng, ZHAO Yafang, LIU Jing, CHEN Danting, WANG Xin, TAN Changyin, WAN Dajuan. Elemental Geochemical characteristics of soils derived from the lower Cambrian black shales in the western Yangtze Platform, china[j]. bulletin of mineralogy, petrology and geochemistry, 2020, 39(1): 59-71. [17] 骆永明, 滕应. 我国土壤污染的区域差异与分区治理修复策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2):145-152. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2018.02.003LUO Yongming, TENG Ying. Regional difference in soil pollution and strategy of soil zonal governance and remediation in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 145-152. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2018.02.003 [18] 刘意章, 陈梓杰, 叶太平, 朱正杰, 宁增平, 肖唐付. 重庆巫山地区上二叠统黑色岩系中镉等有害元素赋存状态及环境意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(4):938-945.LIU Yizhang, CHEN Zijie, YE Taiping, ZHU Zhengjie, NING Zengping, XIAO Tangfu. Occurrences of toxic elements in upper permian black shales at Wushan area and their environmental implication[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(4): 938-945. [19] 余飞, 罗恺, 王佳彬, 李瑜, 周皎, 王锐, 余亚伟, 张云逸. 重庆岩溶地质高背景区土壤—农作物系统重金属累积特征及影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(1):71-83. doi: 10.11932/karst20230106YU Fei, LUO Kai, WANG Jiabin, LI Yu, ZHOU Jiao, WANG Rui, YU Yawei, ZHANG Yunyi. Characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal accumulation in soil-crop system in the karst area with high geological background of Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(1): 71-83. doi: 10.11932/karst20230106 [20] 刘浩, 田茂中, 陈再谦. 水文地质条件对岩溶地下暗河污染的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(2):314-325. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y040LIU Hao, TIAN Maozhong, CHEN Zaiqian. Influence of hydrogeological conditions on the pollution of karst underground rivers[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(2): 314-325. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y040 [21] 段逸凡, 贺秋芳, 刘子琦, 张远瞩, 张弘, 赵瑞一. 岩溶区地下水微生物污染特征及来源:以重庆南山老龙洞流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(4):504-511. doi: 10.11932/karst20140416DUAN Yifan, HE Qiufang, LIU Ziqi, ZHANG Yuanzhu, ZHANG Hong, ZHAO Ruiyi. Characteristics and source of microbial contamination of groundwater in Laolongdong basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(4): 504-511. doi: 10.11932/karst20140416 [22] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 高列波, 张建友, 张松涛, 李成城, 姜春芳. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):287-298. doi: 10.11932/karst2020y25GAO Xubo, WANG Wanzhou, HOU Baojun, GAO Liebo, ZHANG Jianyou, ZHANG Songtao, LI hengcheng, JIANG Chunfang. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 287-298. doi: 10.11932/karst2020y25 [23] 孙 斌, 邢立亭, 李常锁. 趵突泉泉域岩溶水典型污染组分变化特征及污染途径[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(6):810-818.SUN Bin, XING Liting, LI Changsuo. Variation of typical pollution components and pollution way of karst water in Baotu Spring region[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(6): 810-818. [24] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-148.CHI Qinghua, YAN Mingcai. The data book of the application geochemical element contents[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 1-148. [25] 张文强, 滕跃, 唐飞, 王金晓, 许庆宇, 张海林. 山东省肥城断块岩溶水系统地下水水化学特征及演化分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(5):1047-1060, 1084. doi: 10.11932/karst20230515ZHANG Wenqiang, TENG Yue, TANG Fei, WANG Jinxiao, XU Qingyu, ZHANG Hailin. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of the karst water system in the Feicheng fault block in Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(5): 1047-1060, 1084. doi: 10.11932/karst20230515 [26] 涂光炽. 分散元素地球化学及成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.XU Guangchi. Geochemistry and metallogenic mechanism of dispersed elements [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004. [27] 双燕, 李航, 杨振鸿, 易宗旺, 李海. 三峡库区二叠系孤峰组硅质岩分布区土壤-农作物重金属元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2024, 52(2): 188-198.SHUANG Yan , LI Hang, YANG Zhenhong , YI Zongwang, LI Hai. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops in the Permian Gufeng Formation siliceous rock distribution region in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Earth and Environment, 2024, 52(2): 188-198. [28] 刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊燕, 宁增平, 双燕, 李航, 马良, 陈海燕. 西南高镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2877-2884.LIU Yizhang, XIAO Tangfu, XIONG Yan, NING Zengping, SHUANG Yan, LI Hang, MA Liang, CHEN Haiyan. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium, Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2877-2884. [29] 吴吉春, 孙媛媛, 徐红霞. 地下水环境化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2019: 1-295.WU Jichun, SUN Yuanyuan, XU Hongxia. Environmental chemistry of groundwater[M]. Beijing: Science Press. 2019: 1-295. -




 下载:
下载: