Analysis of chemical substance sources in the groundwater of karst-fissure groundwater system in the Qinglian River, Guangdong Province, China
-
摘要: 作为国家“两屏三带”生态安全格局中典型流域的基本单元,掌握青莲水流域地下水水质状况,对筑牢南方丘陵山地带生态安全屏障、维护粤港澳大湾区生态安全具有重要意义。结合水文地质调查和地下水化学指标特征分析,采用正矩阵因子分解模型(PMF)分析方法,追踪地下水化学物质来源并定量分析影响地下水质量的因子贡献率。研究结果表明,流域内地下水化学物质主要来源于含镁碳酸盐和硅酸盐矿物的风化溶解(F1)、生活废水、农用肥料等人类活动(F2)、碳酸盐矿物的水−岩作用(F3)、含硫化肥的使用(F4)以及硅酸盐矿物和岩盐的风化溶解(F5)。各类矿物的风化和含水层水−岩作用等自然因素的贡献率为64%,是流域内地下水化学物质的主要来源,人类活动影响的来源仅占36%。水化学指标高含量分布区域和来源因子贡献率的空间分布区域有显著相关性,表明水化学对岩性和土地利用空间分布有响应关系。整体而言,岩溶水化学成分来源主要是碳酸盐、硅酸盐和岩盐矿物等风化溶解,局部地区还受生活废水和农用化肥的使用等人为活动的影响;火成岩裂隙水来源主要为硅酸盐矿物的风化溶解。地下水离子来源贡献率的定量分析有助于加深对研究区裂隙和岩溶含水层的认识,为地下水的科学管理提供依据。Abstract:
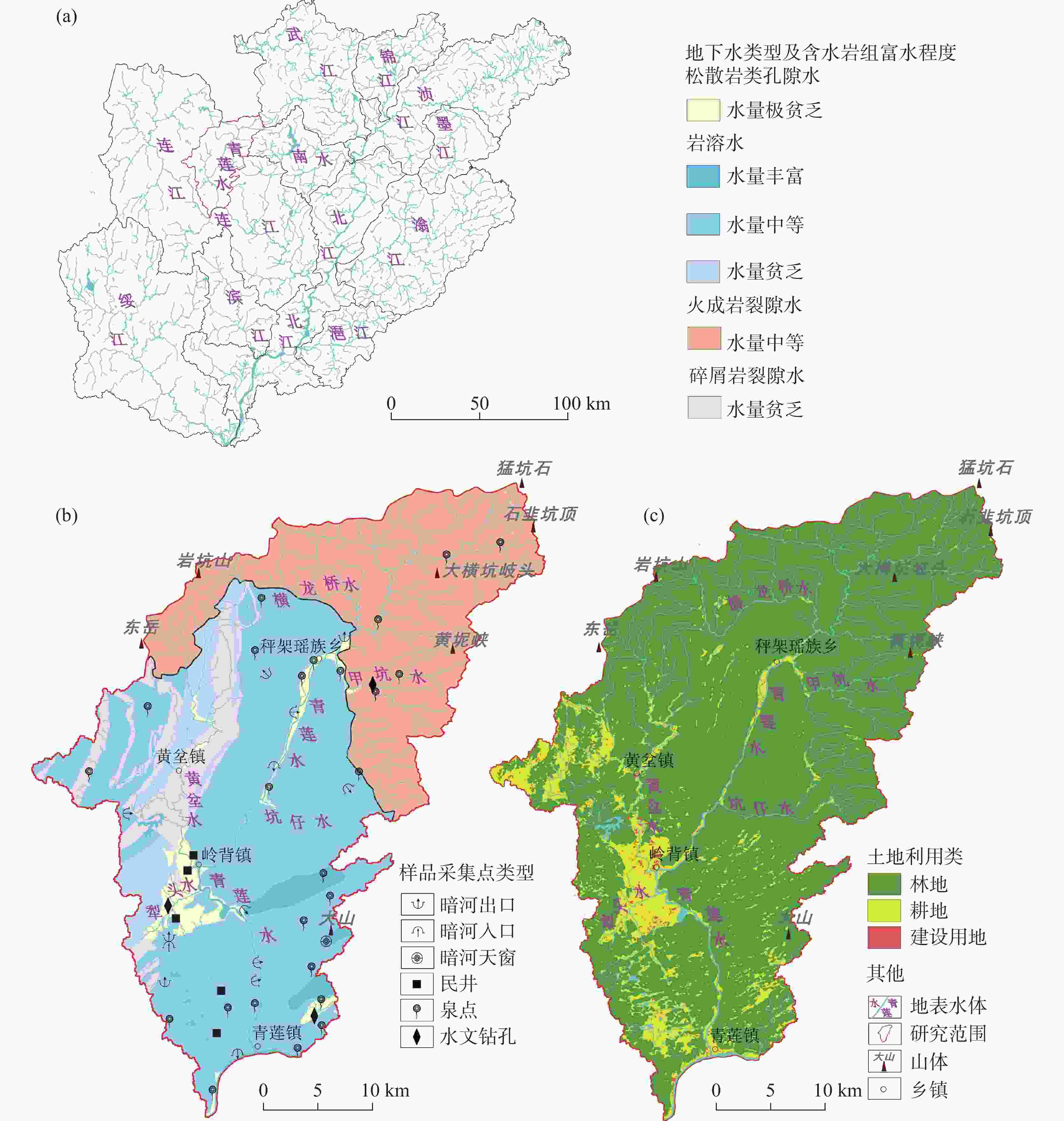
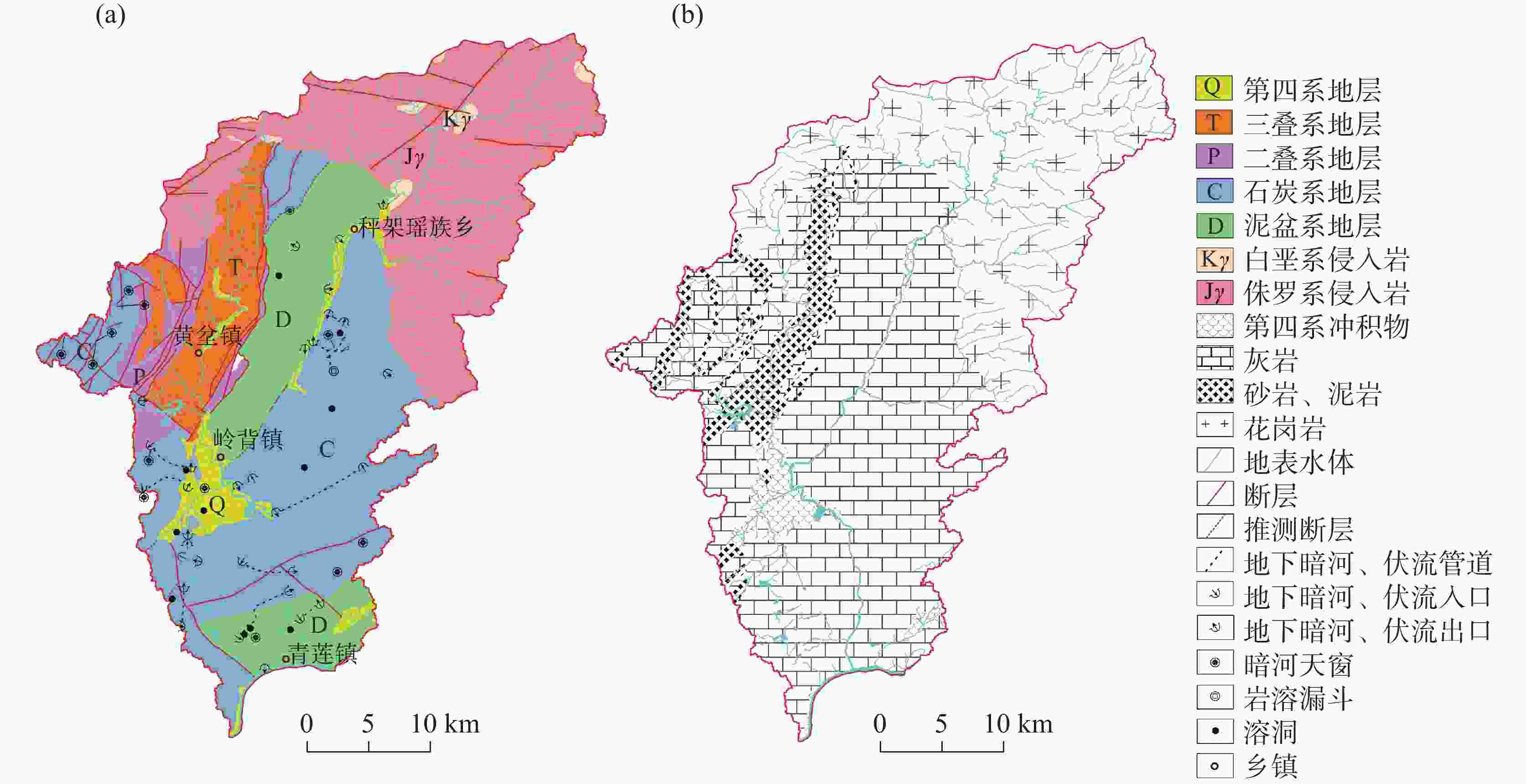
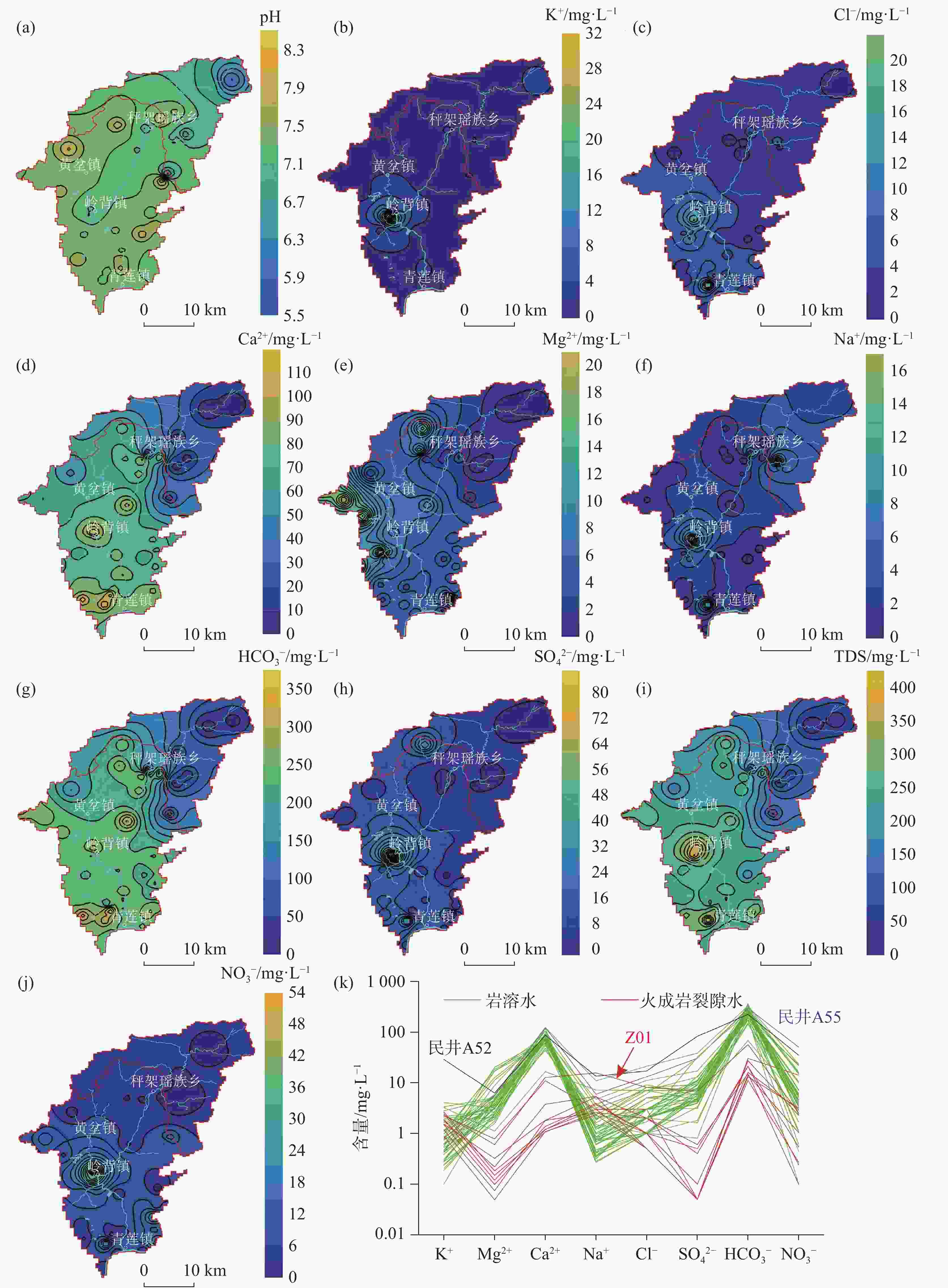
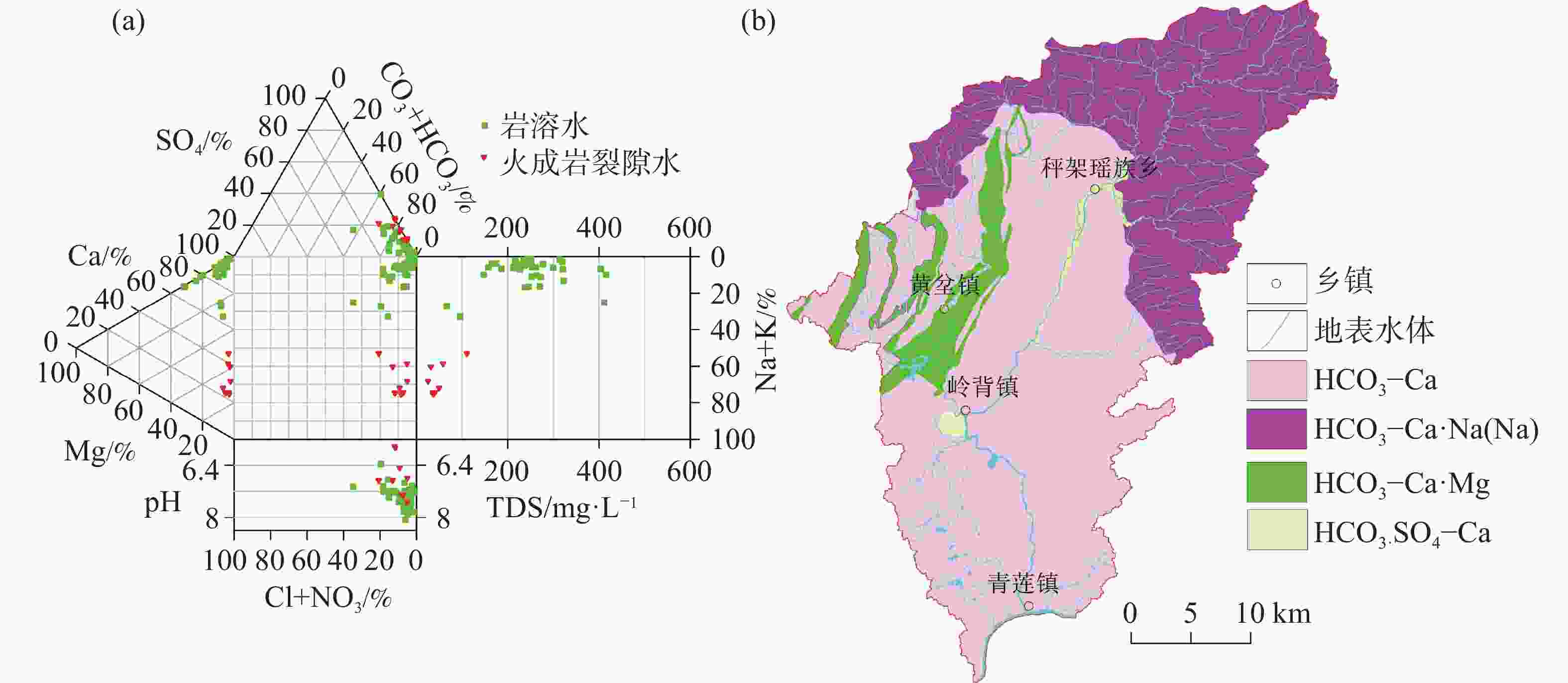
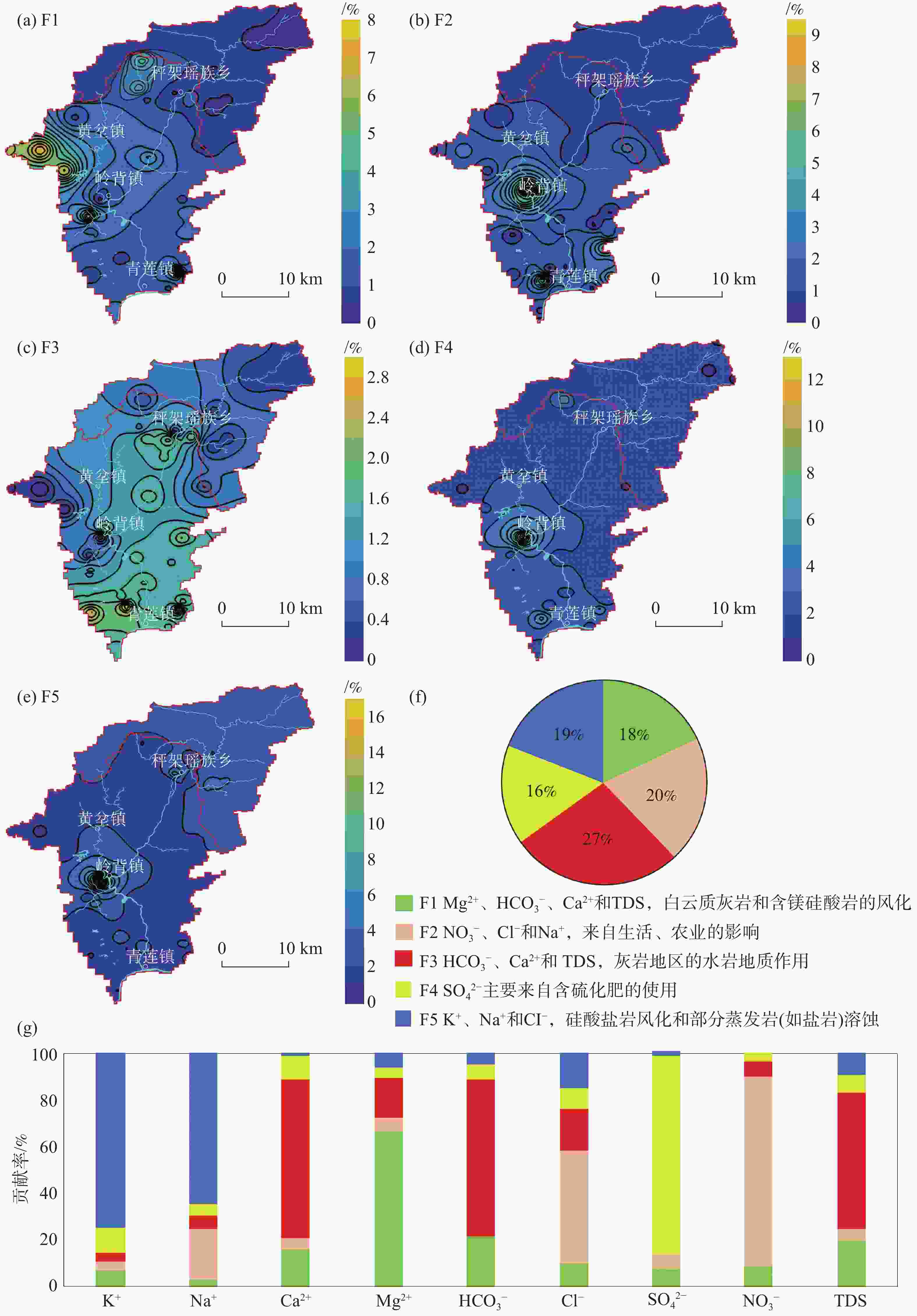
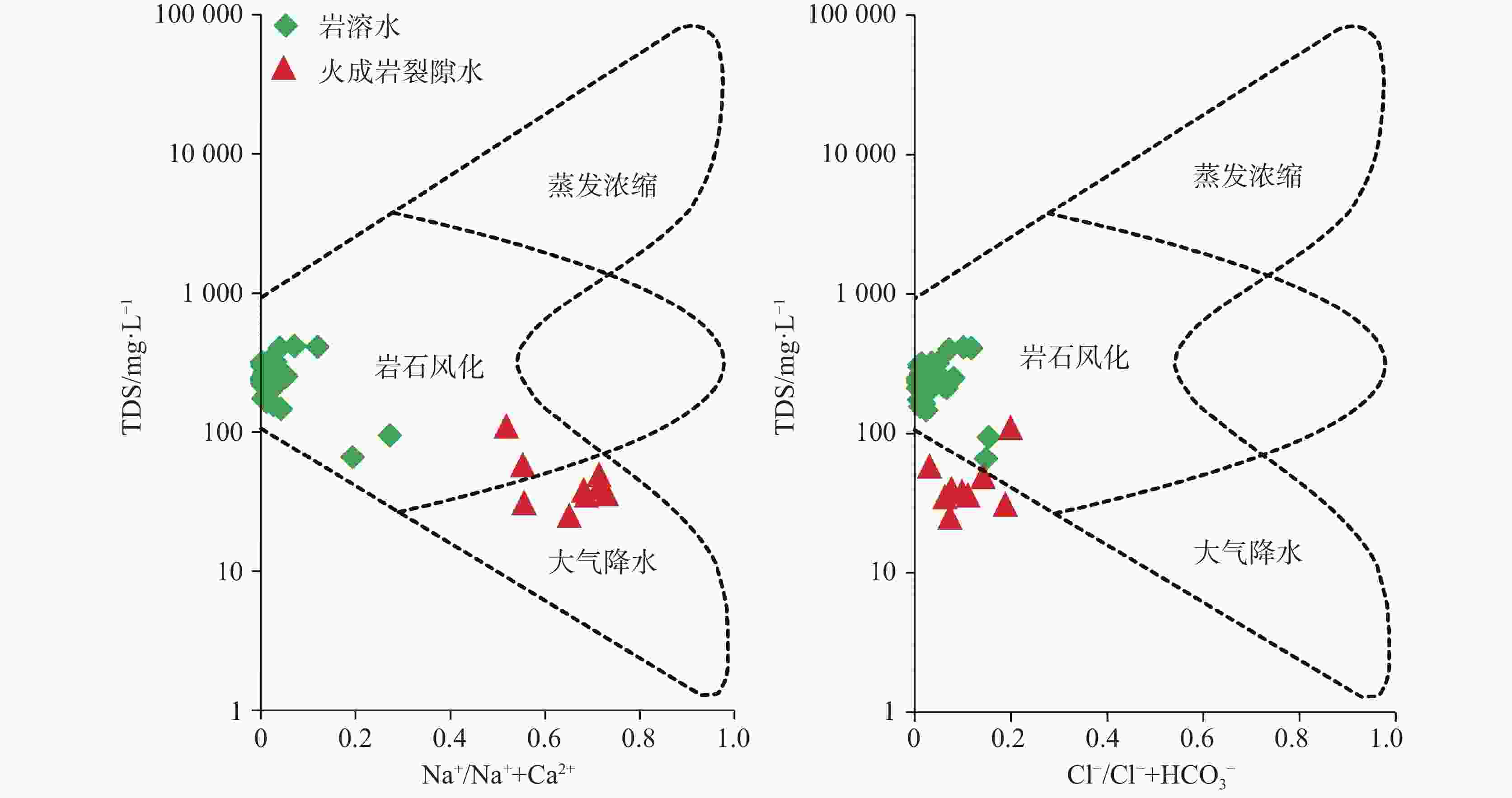
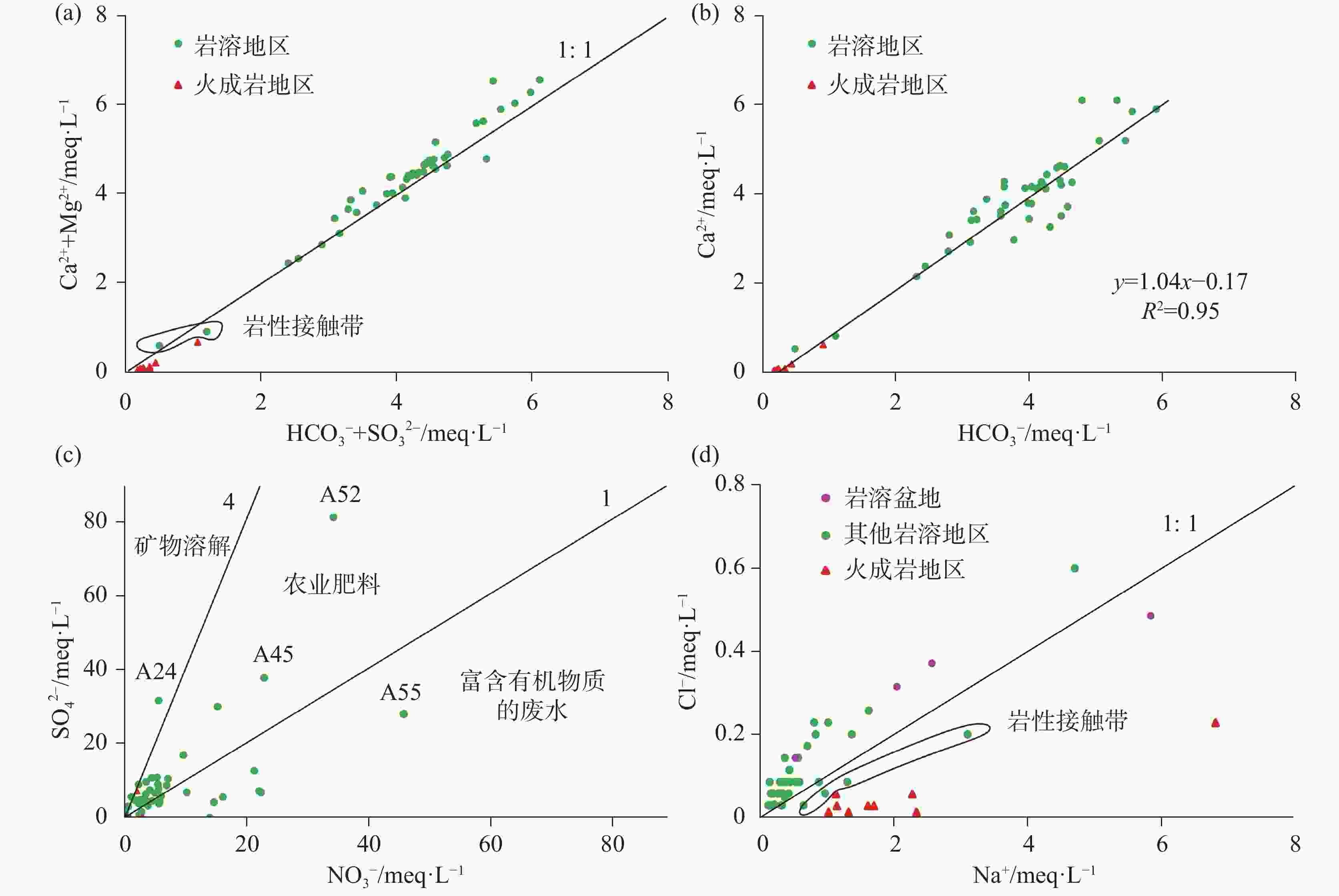
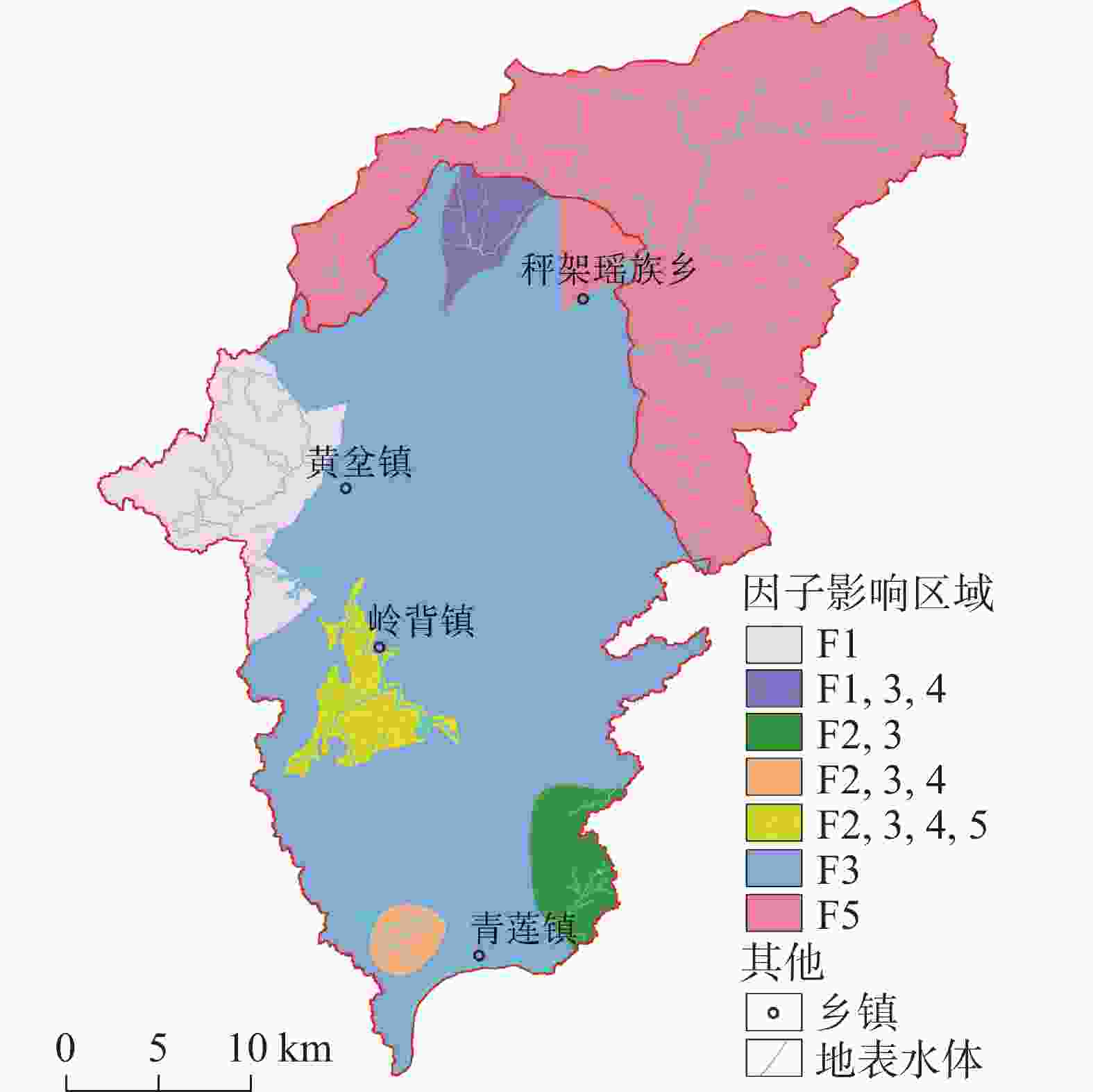
The Qinglian River Basin is a typical basin unit within the ecological security pattern. Therefore, clarifying its groundwater quality is crucial for strengthening the ecological security barrier of the hilly and mountainous areas in South China and for maintaining the ecological security of the Guangdong−Hong Kong−Macao Greater Bay Area. The chemical composition of water is significantly related to water potability, availability for agriculture and tourism, and interaction with biological systems. However, the lack of understanding regarding the nature of groundwater has presented some challenges for the scientific management of groundwater in the Qinglian Basin, particularly concerning irrational spatial exploitation of groundwater. To address these challenges, methods such as hydrochemical parameters and multivariate statistical techniques-including Durov diagram, Gibbs plot, Schoeller diagram and Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) model-were employed to trace the sources of chemical substances in groundwater and quantify the contribution rates of various factors affecting groundwater quality. The main land use types in the study area include forest land, cultivated land, construction land, and water bodies, which account for 87.30%, 11.31%, 1.14%, and 0.27%, respectively. Based on the deposit conditions of groundwater and the characteristics of water-bearing media, the types of groundwater are mainly classified as karst water, igneous-fissure water, clastic-fissure water, and pore water. According to the extended Durov diagram, the pore water in Quaternary sediments predominantly exhibits HCO3·SO4−Ca characteristics, while the igneous-fissure water is classified as HCO3−Ca·Na (Na). The groundwater in areas with dolomitic limestone and clastic rocks is primarily of HCO3−Ca·Mg types, whereas the other karst water is mainly classified as HCO3−Ca type. In the PMF model, a total of 53 groundwater samples were used for the identification and apportionment of groundwater chemical sources. Five major factors of groundwater chemical sources within the basin were identified. Factor 1 (F1) is characterized by Mg2+, ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$, and total dissolved solids (TDS), originating from weathering and dissolution of dolomitic limestone and Mg-containing silicate minerals, with a contribution rate of 18%. Factor 2 (F2) is characterized by ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$, Cl−, and Na+, which are derived from anthropogenic activities such as domestic and agriculture practices, with a contribution rate of 20%. In addition, agricultural activities on sloping farmland can cause substances such as ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ to be discharged into the karst basin through underground runoff, further increasing the concentrations of chemical substances in the groundwater of the karst basin. Factor 3 (F3), is characterized by ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$, Ca2+, and TDS, resulting from the weathering and dissolution of carbonate minerals, and it is the factor with the highest contribution rate (27%). The dominance of F3 among the five factors corresponds to the largest proportion of karst area in the basin (55%), making it the primary source of chemical substances in the groundwater of the Qinglian River Basin. The most relevant parameter of Factor 4 (F4) is mainly ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$, and its apportioned contribution rate is 16%. The majority of ratios of ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ to ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$− in groundwater fall between one and four, indicating that the primary source is the use of sulfur-containing fertilizers in agricultural activities. Notably, the pore water in loose rock formations within the karst basin has a relatively high concentration of ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$, with a maximum value of 81.30 mg·L−1, showing a significant impact from human activities. However, the underlying karst water has a lower concentration of ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ (6.90 mg·L−1), indicating less influence from human activities. F5 is characterized by Na+, K+, Cl−, and TDS, which are derived from the weathering of silicate minerals and the dissolution of a small amount of halite, with a contribution rate of 19%. The distribution areas with high concentrations of chemical parameters are significantly correlated with the spatial distribution of contribution rates of source factors, which indicates that water chemistry responds to the spatial distribution of lithology and land use. F1, F3 and F5, belonging to natural factors such as rock weathering and water−rock interaction, contribute 64% and have a significant correlation with lithology. F2 and F4 are significantly correlated with the distribution of cultivated land and construction land, and are considered to be influenced by human activities, with a contribution rate of 36%. In general, the main sources of the chemical substances in karst water are the weathering and dissolution of carbonate, and silicate and halite minerals. In some areas, human activities such as domestic wastewater and the use of fertilizers areas also have an impact. The main source of igneous-fissure water is the weathering and dissolution of silicate minerals. The quantitative analysis of the contribution rates of groundwater ion sources helps to deepen the understanding of fissures and karst aquifers in the study area, and provide a basis for the scientific management of groundwater. -
图 8 (Ca2+ + Mg2+)−(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ + ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$)(a)、Ca2+−${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$(b)、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$−${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$(c)、Na+−Cl−(d)关系图
Figure 8. Relationship plot of (Ca2+ + Mg2+) − (${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ + ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$) (a),Ca2+−${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ (b),${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$−${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ (c),and Na+−Cl− (d)
表 1 青莲水流域地下水样品的化学参数统计汇总表
Table 1. Statistical summary of chemical parameters of the groundwater samples in Qinglian River Basin
化学指标 pH K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ TDS 无量纲 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 mg·L−1 地下水质量标准a 6.50~8.50 − 100.00 − − − 250.00 250.00 20.00 1000.00 岩溶水 最大值 8.09 28.60 13.40 122.00 20.10 360.00 21.00 81.30 49.80 415.00 最小值 6.87 0.10 0.27 16.50 1.10 67.00 1.00 0.80 0.10 95.00 平均值 7.40 1.62 1.91 79.55 5.40 242.46 4.39 10.73 8.31 249.88 标准偏差 0.27 4.31 2.73 20.45 4.70 55.38 4.37 13.81 9.97 63.33 火成岩裂隙水 最大值 7.57 2.64 15.60 12.60 0.78 56.00 8.00 6.80 14.10 110.00 最小值 5.86 0.88 2.32 1.06 0.05 11.00 0.50 0.05 0.10 25.00 平均值 6.76 1.83 4.72 3.66 0.26 22.40 1.95 0.87 2.72 48.80 标准偏差 0.59 0.58 3.96 4.33 0.24 13.32 2.28 2.10 4.17 24.85 注: a,GB/T 14848 −2017《地下水质量标准》[28],“−”表示不是评价指标,无限值。 -
[1] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 全国地下水污染防治规划(2011-2020年)[R]. 2011.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. National groundwater pollution control plan (2011-2020) [R]. 2011. [2] 廖驾, 朱振华, 彭毅, 韦珊瑚, 罗朝晖, 刘状, 徐强强, 谢亘. 湘西北地区岩溶地下水水化学与氘氧同位素特征分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3):425-435, 481. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y003LIAO Jia, ZHU Zhenhua, PENG Yi, WEI Shanhu, LUO Zhaohui, LIU Zhuang, XU Qiangqiang, XIE Gen. Analysis on D/18O and hydrochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in northwestern Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 425-435, 481. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y003 [3] 张海月, 杨平恒, 王建力, 蓝家程, 詹兆君, 任娟, 张宇. 城市化对岩溶水系统化学组分演化的影响:以重庆市南山老龙洞地下河为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(4):541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416ZHANG Haiyue, YANG Pingheng, WANG Jianli, LAN Jiacheng, ZHAN Zhaojun, REN Juan, ZHANG Yu. Effect of urbanization on the hydrogeochemical evolution of karst groundwater system: A case of the Laolongdong watershed, Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(4): 541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416 [4] 卢丽, 王喆, 裴建国, 杜毓超, 林永生, 樊连杰. 红水河中上游流域岩溶地下水水质影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4):415-419.LU Li, WANG Zhe, PEI Jianguo, DU Yuchao, LIN Yongsheng, FAN Lianjie. R-mode analysis for influencing factors of karst groundwater quality in middle and upper reaches of the Hongshuihe river[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 415-419. [5] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2023中国生态环境状况公报[R]. 2023.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. 2023 Bulletin of the State of Ecological Environment in China [R]. 2023. [6] Wang Liangjie, Ma Shuai, Jiang Jiang, Zhao Yuguo, Zhang Jinchi. Spatiotemporal variation in ecosystem services and their drivers among different landscape heterogeneity units and terrain gradients in the southern hill and mountain belt, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 1375. [7] Zhu Chen, Schwartz Franklin. Hydrogeochemical processes and controls on water quality and water management[J]. Elements, 2010, 7: 169-174. [8] Xu Lanfang, Ni Zehua, Huang Wenlong, Tu Shiliang, Jiang Shoujun, Zhuang Zhuohan, Zhao Libo, Yang Hongyu. Groundwater geochemistry in the karst-fissure aquifer system of the Qinglian River Basin, China[J]. Hydrology, 2024, 11(11): 184. [9] Paatero Pentti, Tapper Unto. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values[J]. Environmetrics, 1994, 5(2): 111-126. doi: 10.1002/env.3170050203 [10] Brown Steven G. , Eberly Shelly, Paatero Pentti, Norris Gary A. Methods for estimating uncertainty in PMF solutions: Examples with ambient air and water quality data and guidance on reporting PMF results[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 518-519: 626-635. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.022 [11] Paatero P, Eberly S, Brown S G, Norris G A. Methods for estimating uncertainty in factor analytic solutions[J]. Atmos. Meas. Tech., 2014, 7(3): 781-797. doi: 10.5194/amt-7-781-2014 [12] Haji Gholizadeh Mohammad, Melesse Assefa M. , Reddi Lakshmi. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 566-567: 1552-1567. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.046 [13] Argyropoulos Georgios, Samara Constantini. Development and application of a robotic chemical mass balance model for source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2011, 26(4): 469-481. [14] Koçak Ebru, Balcılar İlker. Spatio-temporal variation of particulate matter with health impact assessment and long-range transport - case study: Ankara, Türkiye[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 938: 173650. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173650 [15] Chen Kai, Liu Qimeng, Peng Weihua, Liu Xianghong. Source apportionment and natural background levels of major ions in shallow groundwater using multivariate statistical method: A case study in Huaibei Plain, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 301: 113806. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113806 [16] Zhang Han, Cheng Siqian, Li Hongfei, Fu Kang, Xu Yi. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140383. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140383 [17] Wang Xiaoping, Zong Zheng, Tian Chongguo, Chen Yingjun, Luo Chunling, Li Jun, Zhang Gan, Luo Yongming. Combining positive matrix factorization and radiocarbon measurements for source apportionment of PM2.5 from a national background site in north China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 10648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10762-8 [18] Saba Tarek, Su Steave. Tracking polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) congener patterns in Newark Bay surface sediment using principal component analysis (PCA) and positive matrix factorization (PMF)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 260: 634-643. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.046 [19] Wei Rongfei, Meng Zirui, Zerizghi Teklit, Luo Jie, Guo Qingjun. A comprehensive method of source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals: A case study in Qingyuan city, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 882: 163555. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163555 [20] Chen Ruihui, YanguoTeng, Chen Haiyang, Hua Bin, Yang Jie, Yue Weifeng. Groundwater pollution and risk assessment based on source apportionment in a typical cold agricultural region in Northeastern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 696: 133972. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133972 [21] 郑悦华, 张晓远, 刘协亭. 基于GIS的粤北青莲水流域水土流失成因分析[J]. 广东水利水电, 2016(5):24-28. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2016.05.007ZHENG Yuehua, ZHANG Xiaoyuan, LIU Xieting. Causes analysis of soil erosion in Qinglian River Satershed of north area of Guangdong Province based on GIS[J]. Guangdong Water Resources and Hydropower, 2016(5): 24-28. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2016.05.007 [22] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. DZ/T 0064-2021《地下水质量分析方法》[S].2021.Ministry of Natural Resources, People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0064-2021 Methods for groundwater quality analysis [S]. 2021. [23] Piper A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1944, 25(6): 914-928. doi: 10.1029/TR025i006p00914 [24] Gibbs Ronald J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [25] 姜守俊, 许兰芳, 倪泽华, 杨宏宇, 涂世亮. 广东清远盆地地下水水文地球化学及流场特征[J]. 华南地质, 2023, 39(4):672-685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2023.04.008JIANG Shoujun, XU Lanfang, NI Zehua, YANG Hongyu, TU Shiliang. Hydrogeochemical characterization and flow field of groundwater in the Qingyuan Basin of Guangdong Province, China[J]. South China Geology, 2023, 39(4): 672-685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2023.04.008 [26] Li Peiyue, Wu Jianhua, Qian Hui. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 69(7): 2211-2225. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5 [27] Pu Junbing, Yuan Daoxian, Xiao Qiong, Zhao Heping. Hydrogeochemical characteristics in karst subterranean streams: a case history from Chongqing, China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2015, 30(3): 307-319. doi: 10.1007/s13146-014-0226-1 [28] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局和中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 14848−2017《地下水质量标准》[S]. 中国, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China and Standardization Administration of China. GB /T 14848−2017 Groundwater quality standard [S]. China, 2017. [29] Cui Yuhuan, Wang Jie, Hao Shuang. Spatial variability of nitrate pollution and its sources in a hilly basin of the Yangtze River based on clustering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 16752. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96248-0 [30] Jiang Yongjun, Wu Yuexia, Groves Chris, Yuan Daoxian, Kambesis Pat. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2009, 109(1-4): 49-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2009.08.001 [31] 王若帆, 赵良杰, 李强, 吉勤克补子, 焦恒, 江峰, 陈刚. 黔中洋水背斜分散排泄系统地下水化学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4):733-741. doi: 10.11932/karst20230409WANG Ruofan, ZHAO Liangjie, LI Qiang, JI Qinkebuzi, JIAO Heng, JIANG Feng, CHEN Gang. Chemical characteristics of groundwater in the dispersed drainage system of Yangshui anticline in central Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 733-741. doi: 10.11932/karst20230409 [32] Chen Kai, Liu Qimeng, Yang Tingting, Ju Qiding, Hou Xikang, Gao Wei, Jiang Shaojie. Groundwater pollution source identification and health risk assessment in the North Anhui Plain, eastern China: Insights from positive matrix factorization and Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 895: 165186. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165186 [33] Xing Jianwei, Song Jinming, Yuan Huamao, Li Xuegang, Li Ning, Duan Liqin, Qu Baoxiao, Wang Qidong, Kang Xuming. Chemical characteristics, deposition fluxes and source apportionment of precipitation components in the Jiaozhou Bay, North China[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 190: 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.02.001 [34] Su Yong Hong, Feng Qi, Zhu Gao Feng, Si Jian Hua, Zhang Yan Wu. Identification and evolution of groundwater chemistry in the Ejin Sub-Basin of the Heihe River, Northwest China[J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(3): 331-342. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60040-X [35] Sun Houyun, Sun Xiaoming, Wei Xiaofeng, Chen Ziran, Liu Wei, Huang Xingkai, Li Xia, Yin Zhiqiang, Liu Wenbo. Formation mechanism of metasilicate mineral water in Chengde, Hebei Province: Evidence from rock weathering and water-rock interaction[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(4): 1088-1113. [36] 孙厚云, 孙晓明, 卫晓锋, 陈自然, 刘卫, 黄行凯, 李霞, 殷志强, 刘文波. 河北承德偏硅酸矿泉水成因模式: 岩石风化与水岩作用证据[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(4):1088-1113. doi: 10.12029/gc20220405SUN Houyun, SUN Xiaoming, WEI Xiaofeng, CHEN Zan, LIU Wei, HUANG Xingkai, LI Xia, YIN Zhiqiang, LIU Wenbo. Formation mechanism of metasilicate mineral water in Chengde, Hebei Province: Evidence from rock weathering and water-rock interaction[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(4): 1088-1113. doi: 10.12029/gc20220405 [37] Mao Meng, Wang Xia, Zhu Xueqin. Hydrochemical characteristics and pollution source apportionment of the groundwater in the east foothill of the Taihang Mountains, Hebei Province[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(1): 14. doi: 10.1007/s12665-020-09341-4 [38] Shen Zhenyao, Hou Xiaoshu, Li Wen, Aini Guzhanuer, Chen Lei, Gong Yongwei. Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanised watershed in China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 48: 417-427. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.019 [39] Federico Cinzia, Aiuppa Alessandro, Favara Rocco, Valenza Mariano. Geochemical monitoring of groundwaters (1998−2001) at Vesuvius volcano (Italy)[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2004, 133: 81-104. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(03)00392-5 [40] Abascal E, Gómez-Coma L, Ortiz I, Ortiz A. Global diagnosis of nitrate pollution in groundwater and review of removal technologies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 810: 152233. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152233 [41] Cuoco E, Darrah T H, Buono G, Verrengia G, De Francesco S, Eymold W K, Tedesco D. Inorganic contaminants from diffuse pollution in shallow groundwater of the Campanian Plain (Southern Italy). Implications for geochemical survey[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(2): 46. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4307-y [42] Subramani T, Rajmohan N, Elango L. Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2010, 162(1-4): 123-137. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-0781-4 -




 下载:
下载: