Analysis and prediction of spatial and temporal variation of carbon storage in limestone area in recent 30 years:A case study of the Hongshui River Basin
-
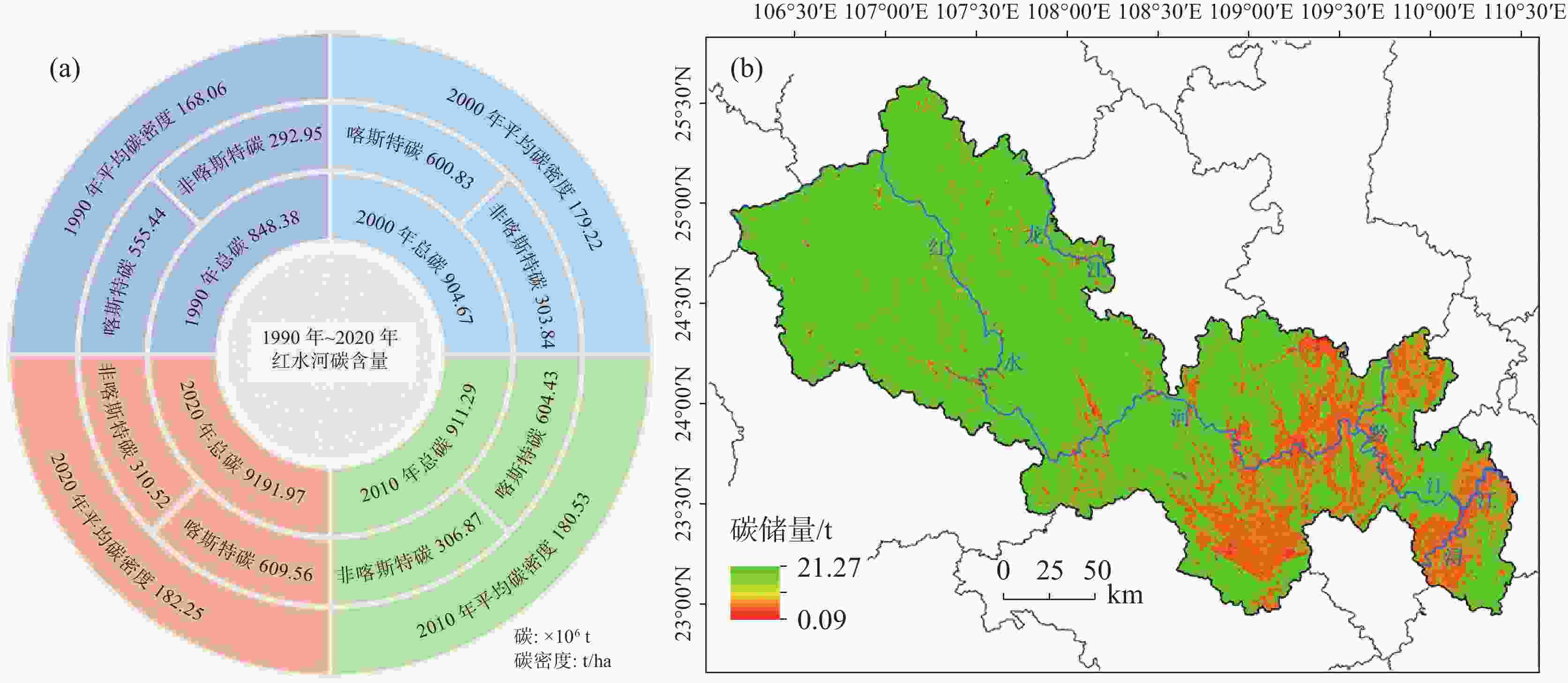
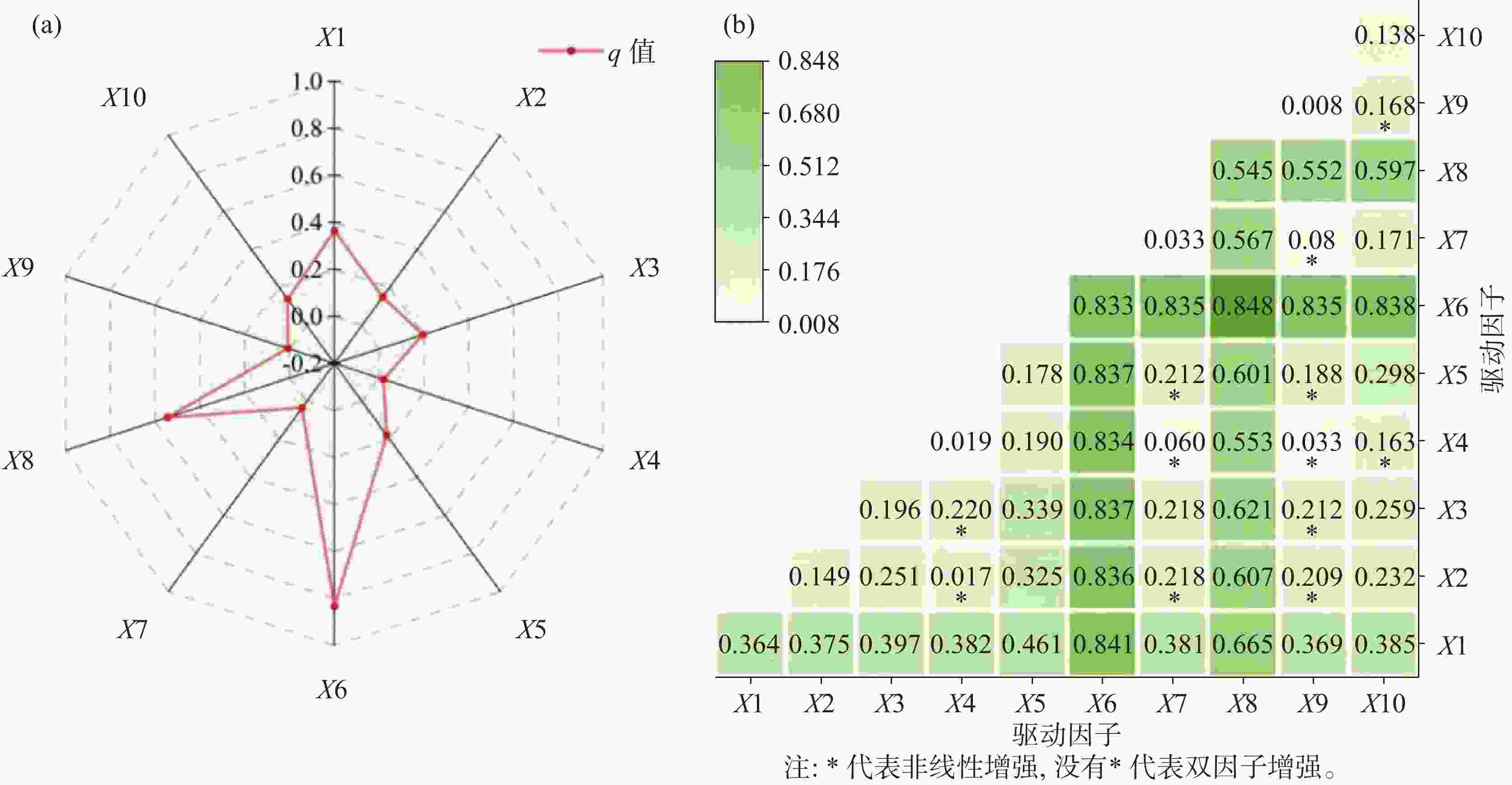
摘要: 岩溶地区具有生态脆弱、环境容量小、土地承载力低、抗干扰能力差等特征,了解岩溶地区生态系统碳储量变化的原因对于预防和控制生态系统退化和支持可持续发展至关重要。本研究以红水河流域为例,基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型评估其1990年至2020年的岩溶地区碳储量,并预测了2030年不同情景下岩溶地区碳储量的变化。研究结果表明:(1) 1990-2020年30年间红水河流域岩溶地区碳储量总体呈递增趋势,空间分布特征由东南向西北逐渐升高,总体的碳源/汇效应为汇大于源,总增加量为71.59×106 t;(2) 相较于2020年,在自然发展情景和生态保护情景下,2030年红水河流域的岩溶地区碳储量分别将增加7.69×106 t和10.74×106 t;而城镇发展情景下碳储量将减少5.14×106 t,城镇发展会导致岩溶地区固碳能力较强的林地减少,导致岩溶流域固碳能力失衡;(3) 根据地理探测器结果显示土地利用对碳储量的空间异质性解释力最强,解释力q值为0.833,以及土地利用与年均NDVI因子之间的相互作用对红水河流域碳储量的变化影响最显著,交互作用解释力为0.848,土地利用变化是使得岩溶碳储量升高主要原因。此研究结果可为红水河流域实现岩溶地区生态系统服务碳储量的可持续性发展、为土地利用管理优化提供科学指导提供理论和数据支持。Abstract:
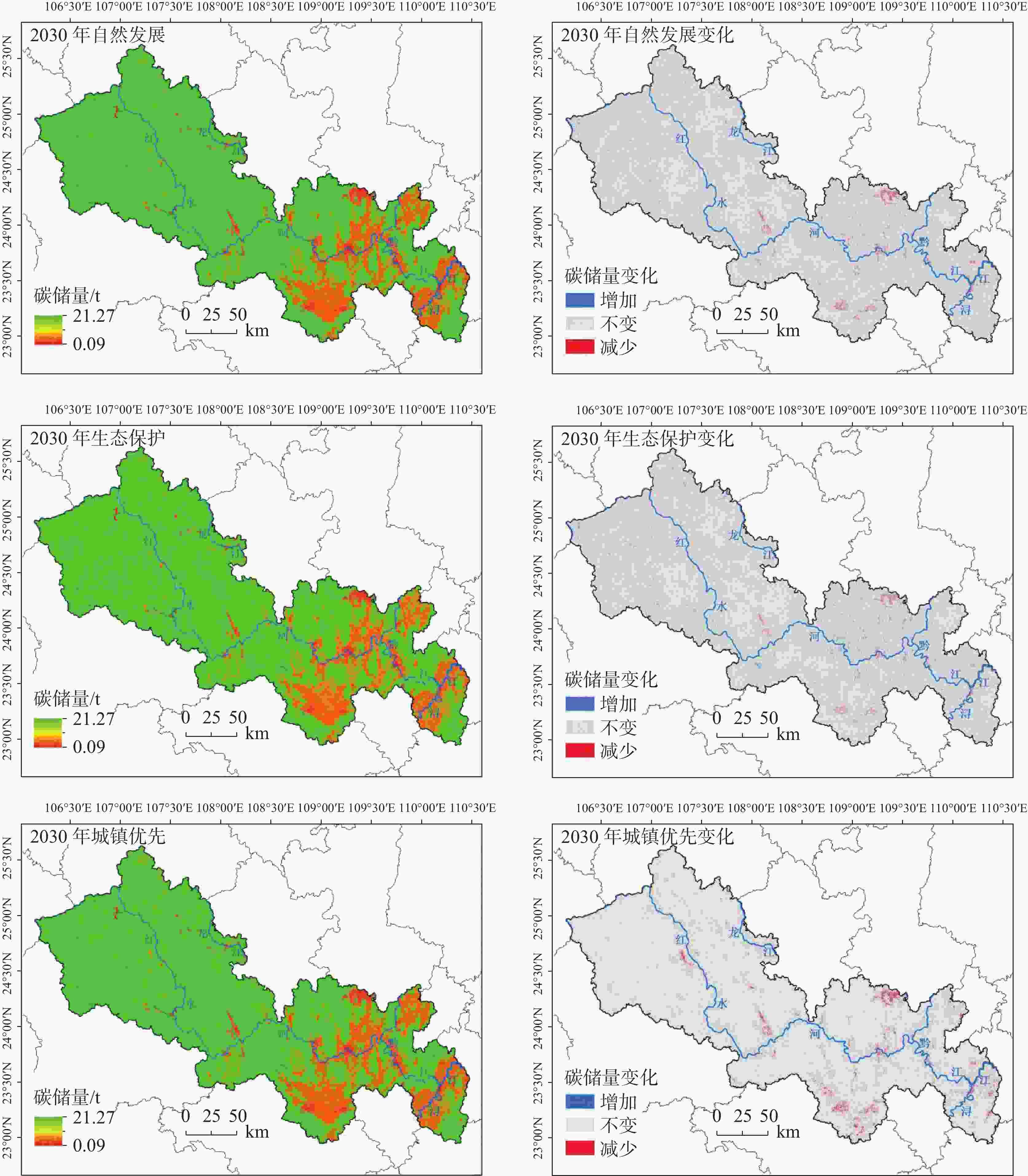
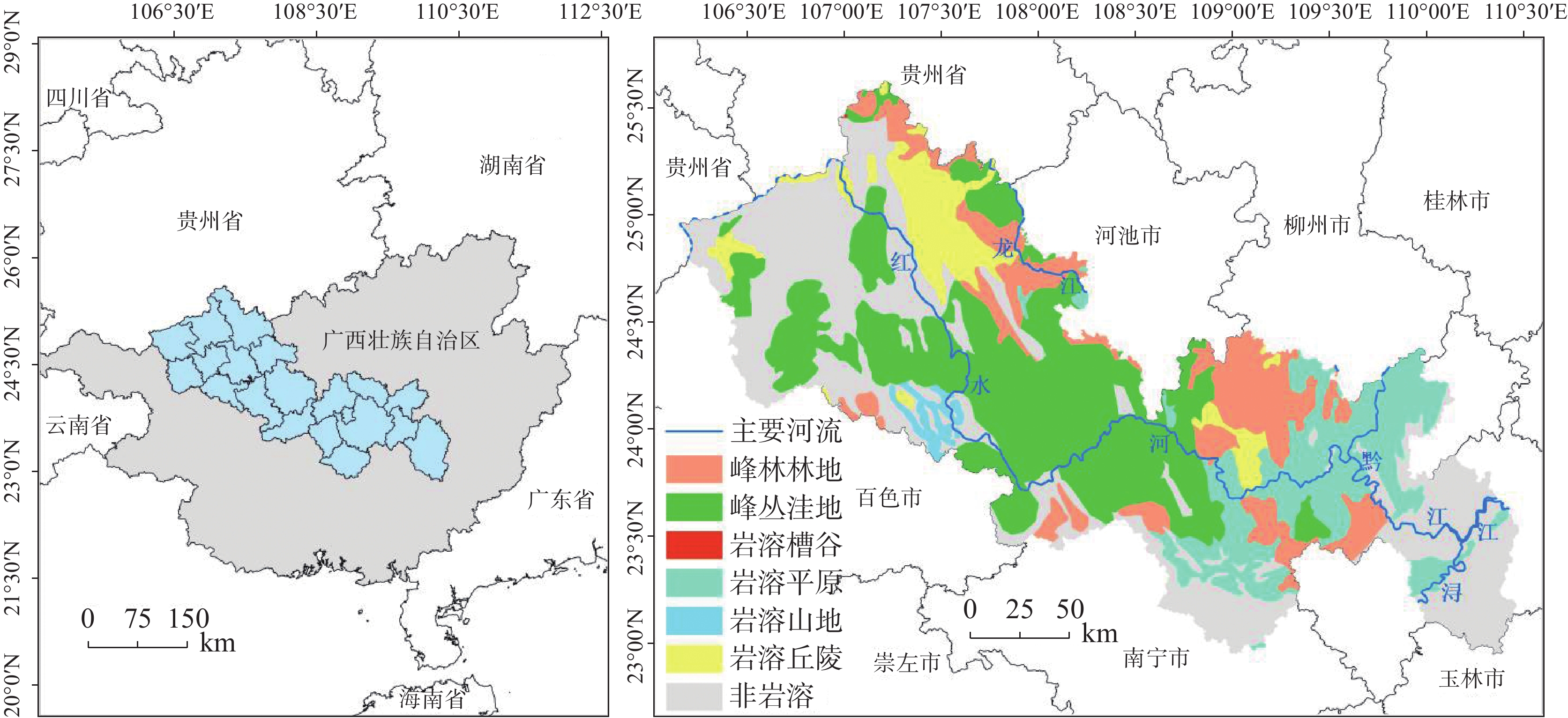
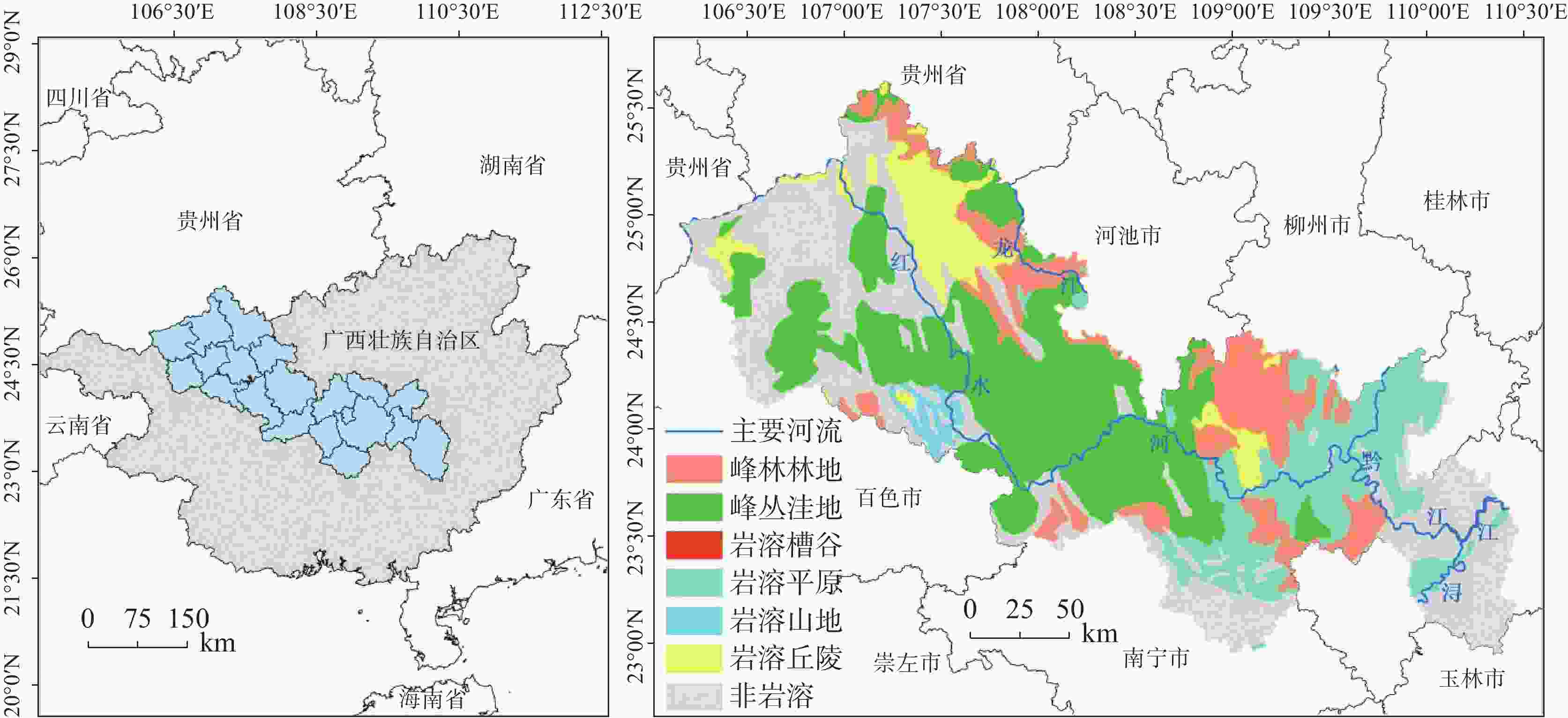
The vulnerable ecology of karst areas is characterized by limited environmental capacity, poor soil quality, insufficient water resources, low land carrying capacity, and high yet vulnerable biodiversity. These factors contribute to low ecosystem productivity and a diminished ability to withstand disturbances. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the causes of changes in ecosystem carbon storage to prevent and mitigate ecosystem degradation and to support sustainable development in karst areas. The Hongshui River Basin is located in the northwest and central regions of Guangxi, characterized by high terrain in the northwest and low terrain in the southeast. It is the main tributary of the Pearl River Basin and encompasses the largest contiguous karst area in Guangxi, covering an area of 50,479.745 km2. Of this, the karst landform area spans 33,942.048 km2, accounting for 67% of the total area. The Hongshui River Basin is a typical karst basin located in Southwest China. It features widely distributed karst landforms, significant altitude variations, and generally thin soil with low fertility and poor water retention capacity. As a result, the ecological environment in this regions is extremely fragile. The vulnerability of natural attributes such as carbon storage function and soil erosion in karst basins, combined with human activities, has led to severe ecological degradation in karst areas. Based on the InVEST model, this study took the Hongshui River Basin as an example to evaluate changes in ecosystem carbon storage in the karst area for the years 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020. At the same time, the PLUS model was employed to simulate the trend of carbon storage changes in the study area under three future scenarios: natural development, urban prioritization and ecological protection. A geographical detector was utilized to identify the main driving factors influencing land use, precipitation, temperature, population density, and other elements affecting the spatial heterogeneity of carbon storage in the karst region of the study area. The conclusions are as follows, (1) From 1990 to 2020, the spatial distribution characteristics of carbon storage in the Hongshui River Basin showed a gradual increase from the southeast to the northwest. Over the past 30 years, the total carbon storage in the basin gradually increased by 71.59×106 t. The most significant increase in carbon storage occurred between 1990 and 2000, indicating that the carbon sink capacity of the Hongshui River Basin was stronger than its carbon source over this period. Overall, the carbon sink effect surpassed the carbon source effect in the basin. (2) In the year 2030, the carbon storage in the Hongshui River Basin is projected to be 927.67×106 t, 914.84×106 t and 930.71×106 t under the scenarios of natural development, urban development and ecological protection, respectively. Compared with 2020, both the natural development scenario and ecological protection scenario for the Hongshui River Basin are expected to demonstrate a generally increasing trend in carbon storage. This indicates that the carbon sink capacity under these scenarios in the future will be stronger than that of the carbon source. In 2030, the carbon storage of the Hongshui River Basin will increase by 7.69×106 t and 10.74×106 t, respectively. Compared with the natural development scenario, the ecological protection scenario shows advantages in areas where the overall spatial distribution of carbon storage increases. Under the urban development scenario for the year 2030, the carbon storage in the Hongshui River Basin is projected to decrease by 5.14×106 t. As urban socio-economic development necessitates the expansion of urban construction land, urban development will lead to a reduction in forest land, which has a significant capacity for carbon sequestration in karst areas. This reduction will disrupt the ecological balance in this regions, further diminishing the carbon sequestration capacity of the basin and gradually shifting its carbon source-sink effect from a carbon sink to a carbon source.(3) The single-factor detection results from the geographic detector indicate that land use is the main driving factor influencing the spatial heterogeneity of carbon storage in the Hongshui River Basin, with a q value of 0.833. Additionally, the average annual NDVI has been shown to explain the spatial heterogeneity of carbon storage, with a q value of 0.545. The interactive detection results show that the interaction between land use and the annual average NDVI factor have the most significant effect on the change in carbon storage within the Hongshui River Basin, with an explanatory power of 0.833. This indicates that the specific combination of the land use interactions, annual average NDVI and other factors—such as annual average temperature, annual average rainfall, digital elevation model, and population density—will influence the spatial distribution of carbon storage. The land use change factor is the main contributor to the increase of carbon storage in the Hongshui River Basin, followed by the annual average NDVI factor. The findings of this study may provide significant theoretical and data support for the sustainable development of carbon storage within ecosystem services in the Hongshui River Basin. Furthermore, they will assist in the formulation of more effective ecological protection and resource management policies aimed at enhancing the carbon sink capacity of the ecosystem and promoting environmental health and sustainable development. -
Key words:
- carbon storage /
- driving factors /
- inVEST model /
- karst area /
- Hongshui River Basin
-
表 1 红水河流域各土地利用类型碳密度/·hm−2
Table 1. Carbon density of land use types in Hongshui River Basin
土地利用
类型地上碳
密度地下碳
密度土壤碳
密度死亡有机
碳密度耕地 13.50 2.70 35.00 1.00 草地 3.01 13.53 10.00 1.00 林地 105.90 67.50 59.40 3.50 湿地 37.00 11.80 56.71 3.00 建设用地 1.20 0.93 12.48 0 水域 1.02 0 0 0 表 2 PLUS模型转移成本矩阵
Table 2. PLUS model transfer cost matrix
自然发展情景 城镇优先情景 生态保护情景 A B C D E F A B C D E F A B C D E F 土地利
用类型A 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 B 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 C 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 D 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 E 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 F 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 注:A-耕地 B-草地 C-林地 D-湿地 E-建设用地 F-水域 表 3 两个因子对因变量的交互作用
Table 3. Interaction of two factors on dependent variables
判断依据 交互作用 q(X1∩X2) < Min(q1,q2) 非线性减弱 Min(q1,q2) < q(X1∩X2) < Max(q1,q2) 单因子非线性减弱 q(X1∩X2) > Max(q1,q2) 双因子增强 q(X1∩X2) = q1+q2 独立 q(X1∩X2) > q1+q2 非线性增强 *表中Min(q1,q2)表示取q1,q2中的最小值,Max(q1,q2)表示取q1,q2中的最大值,q1+q2表示取q1,q2的和。 表 4 1990、2000、2010和2020年各土地类型面积及占比
Table 4. Area and proportion of each land type in 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020
土地类型 1990年 2000年 2010年 2020年 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 耕地 17751.434 35.165 14210.221 28.150 13505.526 26.754 12689.366 25.138 草地 12.246 0.024 54.542 0.108 56.851 0.113 61.225 0.121 林地 31947.882 63.289 35094.401 69.522 35514.595 70.354 36044.503 71.404 湿地 0.149 0.000 1.923 0.004 2.094 0.004 2.374 0.005 建设用地 500.090 0.991 684.471 1.356 930.969 1.844 1206.539 2.390 水域 267.944 0.531 434.187 0.860 469.709 0.930 475.737 0.942 表 5 1990年~2020年土地利用转移矩阵
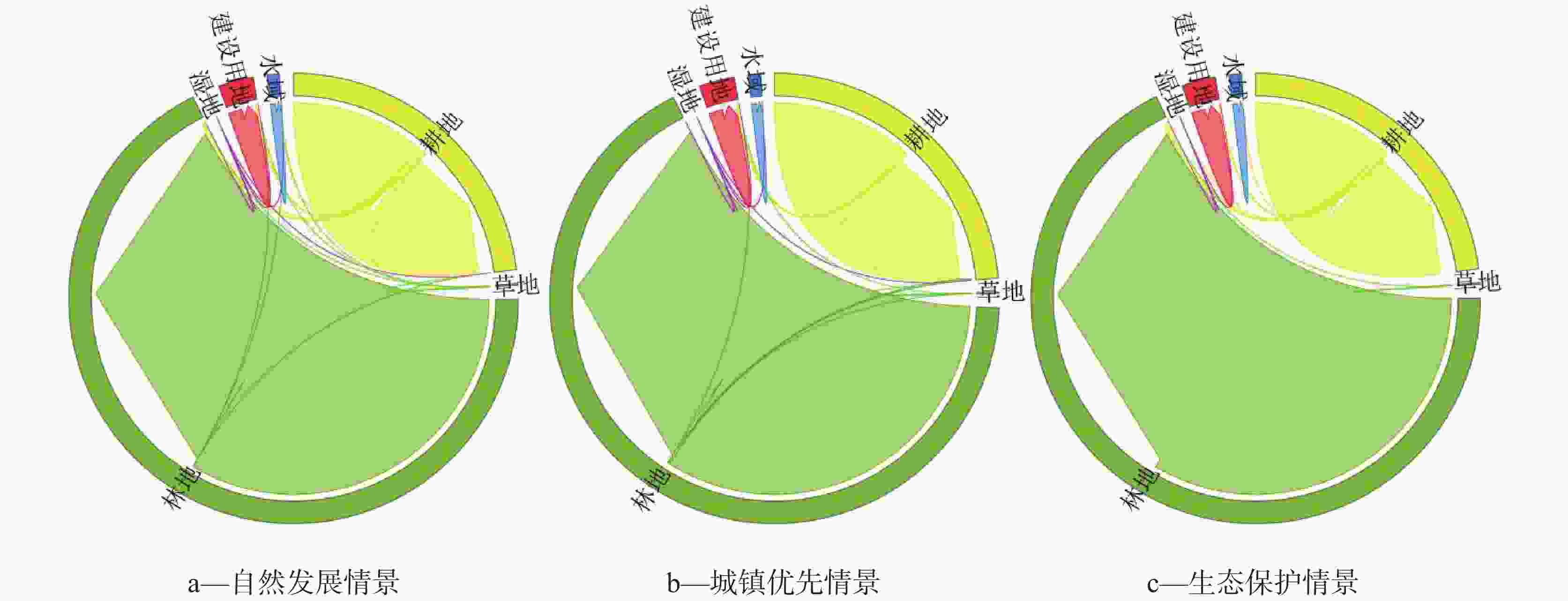
Table 5. Land use transfer matrix from 1990 to 2020
2020年土地利用面积/km2 耕地 草地 林地 湿地 建设用地 水域 总面积 1990年土地利
用面积/km2耕地 10896.853 13.354 6032.528 1.598 624.868 182.234 10896.853 草地 0.439 9.961 1.803 0.002 0.030 0.012 0.439 林地 1772.772 37.847 30002.547 0.074 80.328 54.315 1772.772 湿地 0 0 0 0.149 0 0 0 建设用地 0 0 0 0 500.090 0 0 水域 19.301 0.063 7.626 0.553 1.224 239.177 19.301 总面积 10896.853 13.354 6032.528 1.598 624.868 182.234 10896.853 表 6 未来各情景土地利用面积
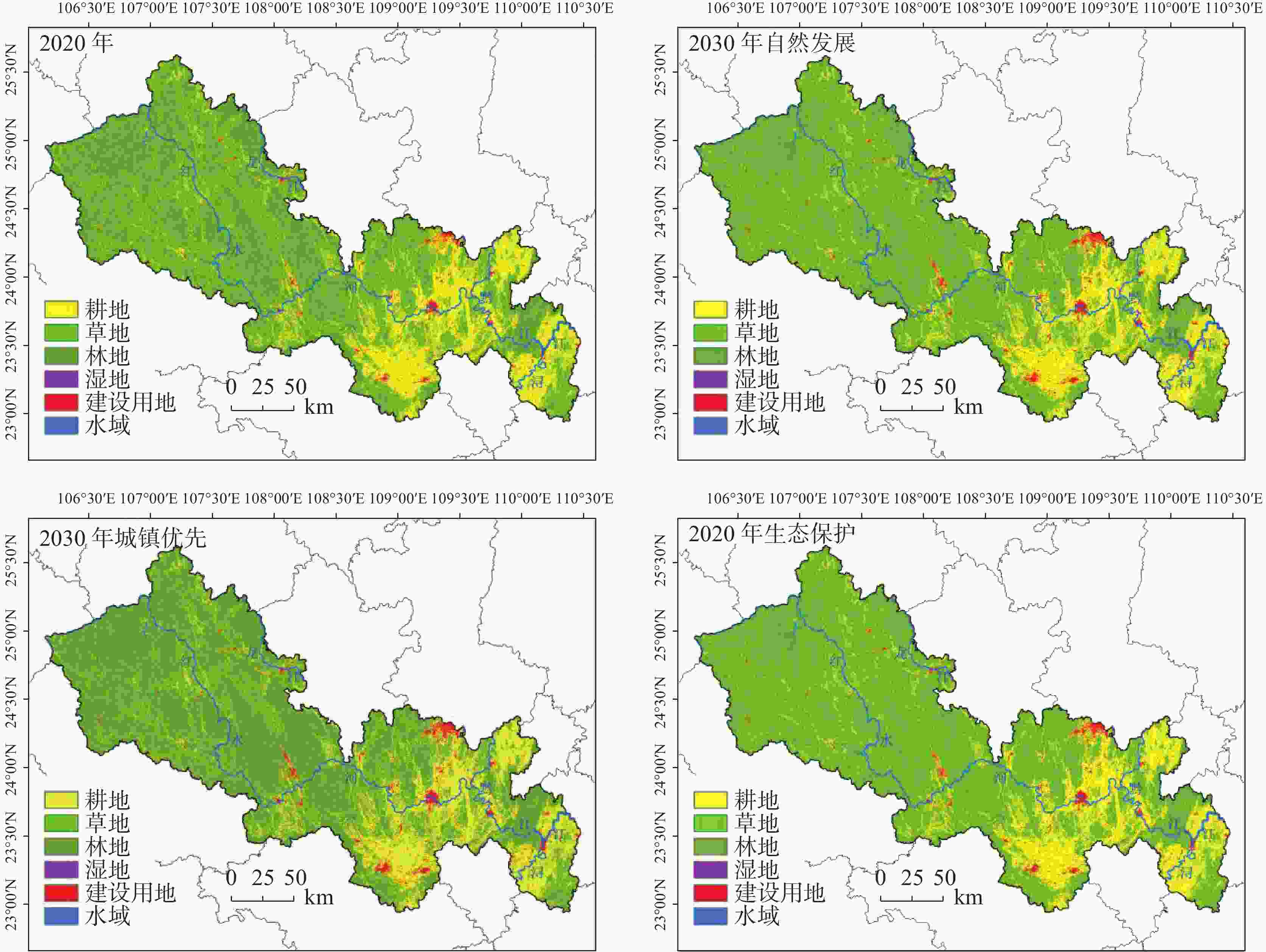
Table 6. Future land use area under different scenarios
2020年 2030年自然
发展情景2030年城镇
优先情景2030年生态
保护情景耕地 12689.366 11956.148 12591.183 11887.438 草地 61.225 55.096 59.988 53.656 林地 36044.503 36516.677 35829.470 36665.501 湿地 2.374 2.093 2.238 2.348 建设用地 1206.539 1468.697 1521.123 1390.058 水域 475.737 481.033 475.743 480.744 -
[1] ZHU Guofeng, QIU Dongdong, ZHANG Zhuanxia, SANG Liyuan, LIU Yuwei, WANG Lei, ZHAO Kailiang, MA Huiying, XU Yuanxiao, WAN Qiaozhuo. Land-use changes lead to a decrease in carbon storage in arid region, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 127: 107770. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107770 [2] LI L, SONG Y, WEI X H, DONG J. Exploring the impacts of urban growth on carbon storage under integrated spatial regulation: A case study of Wuhan, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 111: 106064. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106064 [3] 王深, 吕连宏, 张保留, 王斯一, 吴静, 付加锋, 罗宏. 基于多目标模型的中国低成本碳达峰、碳中和路径[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(9):2044-2055.WANG Shen, LV Lianhong, ZHANG Baoliu, WANG Siyi, WU Jing, FU Jiafeng, LUO Hong. Multi Objective Programming Model of Low-Cost Path for China's Peaking Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Carbon Neutrality[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(9): 2044-2055. [4] 于奭, 蒲俊兵, 刘凡, 杨慧. 岩溶碳汇效应对植被的响应研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4):418-428.YU Shi, PU Junbing, LIU Fan, YANG Hui. Effect of vegetation on carbon sequestration in karst systems:a critical review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4): 418-428. [5] ZENG S B, LIU Z H, Goldscheider N, Frank S, Goeppert N, Kaufmann G, Zeng C, Zeng Q, Sun H. Comparisons on the effects of temperature, runoff, and land-cover on carbonate weathering in different karst catchments: insights into the future global carbon cycle[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2021, 29(1): 331-345. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02252-5 [6] 闫伟, 曾成, 肖时珍, 蓝家程, 代林玉, 邰治钦, 何江湖, 何春, 狄永宁. 湿润亚热带典型白云岩流域不同土地利用下的试片溶蚀速率及岩溶碳汇[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(5):529-538.YAN Wei, ZENG Cheng, XIAO Shizhen, LAN Jiacheng, DAl Linyu, TAl Zhiqin, HE Jianghu, HE Chun, Dl Yongning. Dissolution Rate and Karst Carbon Sink of Different Land Use in Typical Dolomite Watershed with Humid Subtropical Weather[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(5): 529-538. [7] 孙平安, 肖琼, 郭永丽, 苗迎, 王奇岗, 章程. 混合岩溶流域碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率与岩溶碳汇:以漓江流域上游为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):825-834. doi: 10.11932/karst20210509SUN Pingan, XIAO Qiong, GUO Yongli, MIAO Ying, WANG Qigang, ZHANG Cheng. Carbonate dissolution rate and karst carbon sink in mixed carbonate and silicate terrain: Take the upper reaches of the Lijiang river basin as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5): 825-834. doi: 10.11932/karst20210509 [8] 李瑞, 肖琼, 张陶, 李建鸿, 李丽. 人类活动影响下岩溶地下河水-岩作用强度时空差异分析[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(2):191-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.02.008LI Rui, XIAO Qiong, ZHANG Tao, LI Jianhong, LI li. Temporal and spatial variation patterns of water-rock interaction under the impact of human activity in karst underground water[J]. Geochimica, 2017, 46(2): 191-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.02.008 [9] 林云, 梁家乐, 武亚遵, 贾方建, 任华鑫. 许家沟泉域岩溶地下水δ13CDIC特征及碳汇效应[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(1):146-153.LIN Yun, LIANG Jiale, WU Yazun, JIA Fangjian, REN Huaxin. Characteristics of δ13CDIC of karst groundwater and carbon sink effect in Xujiagou spring area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(1): 146-153. [10] 曹建华, 杨慧, 康志强. 区域碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用碳汇通量估算初探: 以珠江流域为例[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(26):2181-2187. doi: 10.1360/csb2011-56-26-2181Cao Jianhua, Yang Hui, Kang Zhiqiang. Preliminary regional estimation of carbon sink flux by carbonate rock corrosion: A case study of the Pearl River Basin[J]. Chinese Sci Bull, 2011, 56(26): 2181-2187. doi: 10.1360/csb2011-56-26-2181 [11] LIU J, ZHONG J, CHEN S, XU S, LI S L. Hydrological and biogeochemical controls on temporal variations of dissolved carbon and solutes in a karst river, South China[J]. Environmental Sciences Europe, 2021, 33. [12] HAN X K, YAN Z L, LANG YC, DING H, GUO Q J, LI S L. Enhanced sulfide oxidation by monsoon rainfall in a small typical karstic catchment of Southwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 615: 128682. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128682 [13] ZNG S B, JIANG Y J, LIU Z H. Assessment of climate impacts on the karst-related carbon sink in SW China using MPD and GIS[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2016, 144: 171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.07.015 [14] LI Yu, GENG Huacai. Spatiotemporal trends in ecosystem carbon stock evolution and quantitative attribution in a karst watershed in southwest China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 153: 110429. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110429 [15] ZHANG J Y, BIAN Z H, DAI M H, WANG L C, ZENG C F, SU W C. Differences and influencing factors related to underground water carbon uptake by karsts in the Houzhai Basin, southwestern China[J]. Solid Earth, 2016, 7: 1259-1268. doi: 10.5194/se-7-1259-2016 [16] FENG H Y, Squires Victor. The temporal and spatial scales of arable land loss and its impact in Guangxi, China[J]. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal, 2022, 9(1): 76-84. doi: 10.14738/assrj.91.11512 [17] CHEN R S, YE C, CAI Y L, XING X S. Integrated Restoration of Small Watershed in Karst Regions of Southwest China[J]. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 2012, 41: 907-912. doi: 10.1007/s13280-012-0296-z [18] HUANG Q H, CAI Y L, XING X S. Rocky desertification, antidesertification, and sustainable development in the karst mountain region of Southwest China[J]. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 2008, 37(5): 390-392. doi: 10.1579/08-S-493.1 [19] GUO F, JIANG G H, YUAN D X, POLK J S. Evolution of major environmental geological problems in karst areas of Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 2427-2435. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-2070-8 [20] SUN H F, CHENG M, SU C X, LI H Y, ZHAO G D, SU M X, LI S C, ZHANG B, ZHANG L W, LI K. Characterization of shallow karst using electrical resistivity imaging in a limestone mining area[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76: 767. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-7112-9 [21] TANG Y M, CHEN L H, SHE S Y. Evaluation of instream ecological flow with consideration of ecological responses to hydrological variations in the downstream Hongshui River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 130: 108104. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108104 [22] HUANG Y, YI L, XIAO W H, HOU G B, ZHOU Y Y. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of extreme precipitation in the upper reaches of the Hongshui River Basin during 1959-2016[J]. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 2021, 12(6): 2378-2399. doi: 10.2166/wcc.2021.339 [23] 李俊, 杨德宏, 吴锋振, 陈如俊, 何万才. 基于PLUS与In VEST模型的昆明市土地利用变化动态模拟与碳储量评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(1):378-387.LI Jun, YANG Dehong, WU Fengzhen, CHEN Rujun, HE Wancai. Dynamic Simulation of Land Use Changes and Assessment of Carbon Storage in Kunming City Based on PLUS and InVEST Models[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 43(1): 378-387. [24] 李琛, 高彬嫔, 吴映梅, 郑可君, 武燕. 基于PLUS模型的山区城镇景观生态风险动态模拟[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(1):84-94.LI Sen, GAO Binpin, WU Yingmei, ZHENG Kejun, WU Yan. Dynamic simulation of landscape ecological risk in mountain towns based on PLUS model[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A& F University, 2022, 39(1): 84-94. [25] 陈曦. 广西土壤有机碳储量估算及与全国部分省区的比较研究[J]. 地理科学, 2014, 34(10):1247-1253.CHEN Xi. Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Reserves in Guangxi and Comparion Study with Some Provinces in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(10): 1247-1253. [26] 赵胤程, 覃盟琳, 庞雅月, 王政强, 史倩倩. 基于FLUS-InVEST模型的北部湾城市群生态空间碳汇演变模拟及驱动因素研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(03):345-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.3.stbctb202203043ZHAO Yincheng, QIN Menglin, PANG Yayue, Wang Zhengqiang, Shi Qianqian. Evolution Simulation and Driving Factors of Eco-spatial Carbon Sinks in Beibu Gulf Urban Agglomeration Based on FLUS-InVEST Model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(03): 345-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.3.stbctb202203043 [27] 丁岳, 王柳柱, 桂峰, 赵晟, 朱望远. 基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型的环杭州湾生态系统碳储量[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6):3343-3352.DING Yue, WANG Liuzhu, GUI Fng, ZHAO Sheng, ZHU Wangyuan. Ecosystem Carbon Storage in Hangzhou Bay Area Based on InVEST and PLUS Models[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(6): 3343-3352. [28] 任胤铭, 刘小平, 许晓聪, 孙嵩松, 赵林峰, 梁迅, 曾莉. 基于FLUS-InVEST模型的京津冀多情景土地利用变化模拟及其对生态系统服务功能的影响研究[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(11):4473-4487.REN Yinming, LIU Xiaoping, XU Xiaocong, SUN Songsong, ZHAO Linfeng, LIANG Xun, ZENG Li. Multi-scenario simulation of land use change and its impact on ecosystem services Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on the FLUS-InVEST Model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(11): 4473-4487. [29] LIANG X, GUAN Q F, Clarke K C, LIU S S, WANG B Y, YAO Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation(PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China[J]. Computers Environment and Urban Systems, 2021, 85: 101569. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2020.101569 [30] HU Z Y, WANG S J, BAI X Y, LUO G J, LI Q, WU L H, YANG Y J, TIAN S Q, LI C J, DENG Y H. Changes in ecosystem service values in karst areas of China[J]. Agriculture[J]. Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 30, 107026. [31] 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1):116-134.WANG Jinfeng, XU Chengdong. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 116-134. [32] LI Y H, YAO S, JIANG Z Z, JIANG H Z, WANG H R, RAN Q C, GAO X Y, DING X Y, GE D D. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Prediction of Carbon Storage: An Integrated Framework Based on the MOP-PLUS-InVEST Model and an Applied Case Study in Hangzhou, East China[J]. Land, 2022, 11(12): 2213. doi: 10.3390/land11122213 [33] 曾思博, 蒋勇军. 土地利用对岩溶作用碳汇的影响研究综述[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(2):153-163. doi: 10.11932/karst20160204ZENG Sibo, JIANG Yongjun. Impact of Land-Use and Land-Cover change on the carbon sink produced by karst processes: A review[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(2): 153-163. doi: 10.11932/karst20160204 [34] 蓝芙宁, 王文娟, 吴华英, 蒋忠诚, 覃小群, 安树青. 不同土地利用方式下土壤CO2时空分布特征及其影响因素:以湘西大龙洞地下河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(4):427-432.LAN Funing, WANG Wenjuan WU Huaying, JIANG Zhongcheng, QIN Xiaoqun, AN Shuqing. Temporal and spatial distributions of CO2 in soil and their influencing factors under different LUCC: A case study of the Dalongdong underground river drainage area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(4): 427-432. [35] 刘晓娟, 黎夏, 梁迅, 石洪, 欧金沛. 基于FLUS-InVEST模型的中国未来土地利用变化及其对碳储量影响的模拟[J]. 热带地理, 2019, 39(3):397-409.LIU Xiaojuan, LI Xia, LIANG Xu, Shi Hong, Ou Jinpei. Simulating the Change of Terrestrial Carbon Storage in China Based on the FLUS-InVEST Model[J]. Tropical Geography, 2019, 39(3): 397-409. [36] 孙婷, 邓飞艳, 焦树林. 土地利用空间差异对典型喀斯特泉域化学风化碳汇的影响[J]. 热带地理, 2017, 37(1):19-24.SUN Ting, DENG Feiyan, JIAO Shulin. Impact of Land-use Spatial Variability on the Atmospheric Carbon Sequestration of the Rock Weathering Process in Typical Karst Spring Catchments[J]. Tropical Geography, 2017, 37(1): 19-24. [37] LI C, Wu Y M, GAO B P, ZHENG K J, WU Y, LI C. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 132: 108328. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108328 [38] 朱志强, 马晓双, 胡洪. 基于耦合FLUS-InVEST模型的广州市生态系统碳储量时空演变与预测[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(2):222-229,239.ZHU Zhiqiang, MA Xiaoshuang, HU Hong. Spatio-temporal evolution and prediction of ecosystem carbon stocks in Guangzhou City by coupling FLUS-InVEST models[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(2): 222-229,239. [39] 史名杰, 武红旗, 贾宏涛, 朱磊, 董通, 何盘星, 杨强军. 基于MCE-CA-Markov和InVEST模型的伊犁谷地碳储量时空演变及预测[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(6):1010-1019.SHI Mingjie, WU Hongqi, JIA Hongtao, ZHU Lei, DONG Tong, HE Panxing, YANG Qiangjun. Temporal and spatial evolution and prediction of carbon stocks in Yili Valley based on MCE-CA-Markov and InVEST models[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(6): 1010-1019. -




 下载:
下载: