Research on remote sensing identification of dolines with dense vegetation cover based on point cloud principal component analysis point cloud principal component analysis
-
摘要: 岩溶渗漏是碳酸盐岩发育地区建设抽水蓄能电站面临最主要的工程地质问题之一,岩溶漏斗主要受构造影响,一般发育在断层附近,水沿着岩溶漏斗的孔道与地下暗河相通就可能导致水库渗漏,受限于岩溶漏斗隐蔽性强的特点,传统调查手段难以高效实现岩溶漏斗准确排查,为解决传统岩溶漏斗调查手段效率低下的问题,文章以某抽水蓄能电站库区作为研究对象,提出一种基于点云主成分分析的岩溶漏斗自动识别方法,以快速识别并提取库区的岩溶漏斗。其方法首先利用机载LiDAR技术获取研究区滤除植被后的地面三维点云数据,再针对岩溶漏斗下凹形态方向性强的特点,通过K-D树最邻近算法及主成分分析,提出一种指标特征值比值完成岩溶漏斗的初步提取,最后采用基于密度聚类算法的漏斗频数、长度、方向3种滤波算法对初提取结果进行背景滤噪。该方法采用受试者工作特征曲线检验AUC值可达0.854,F-score为0.859,其能适用于高植被覆盖下岩溶地貌发育地区的岩溶漏斗的识别与调查。Abstract:
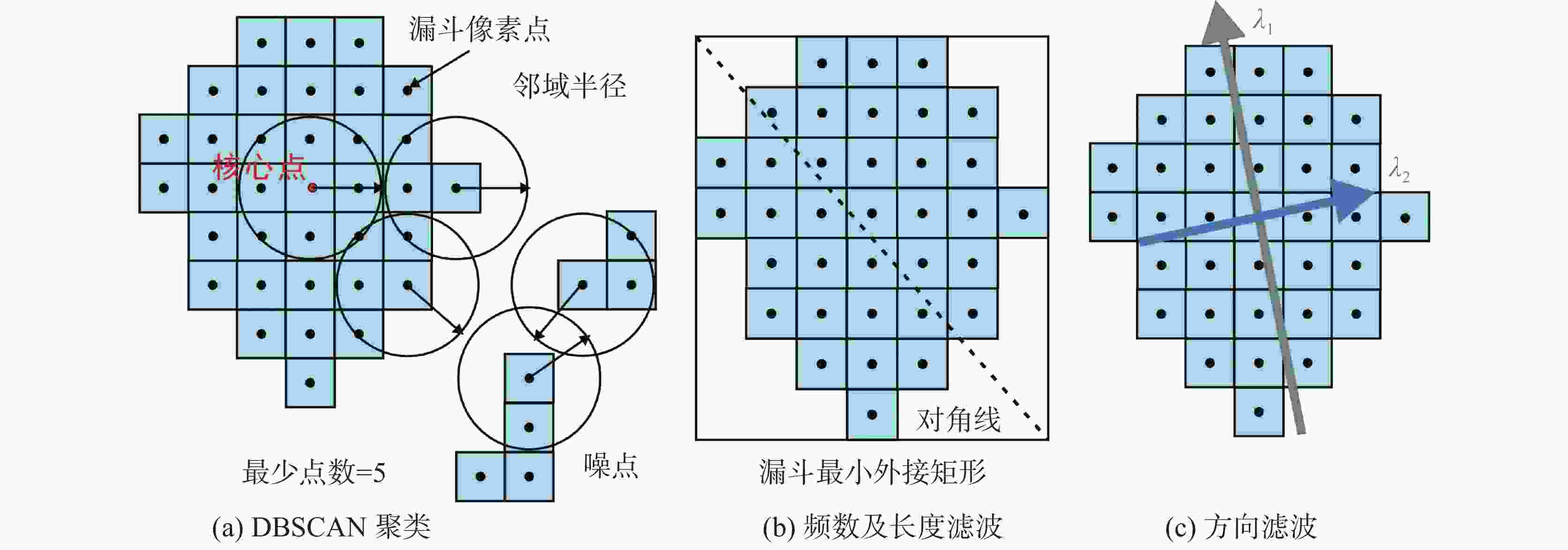
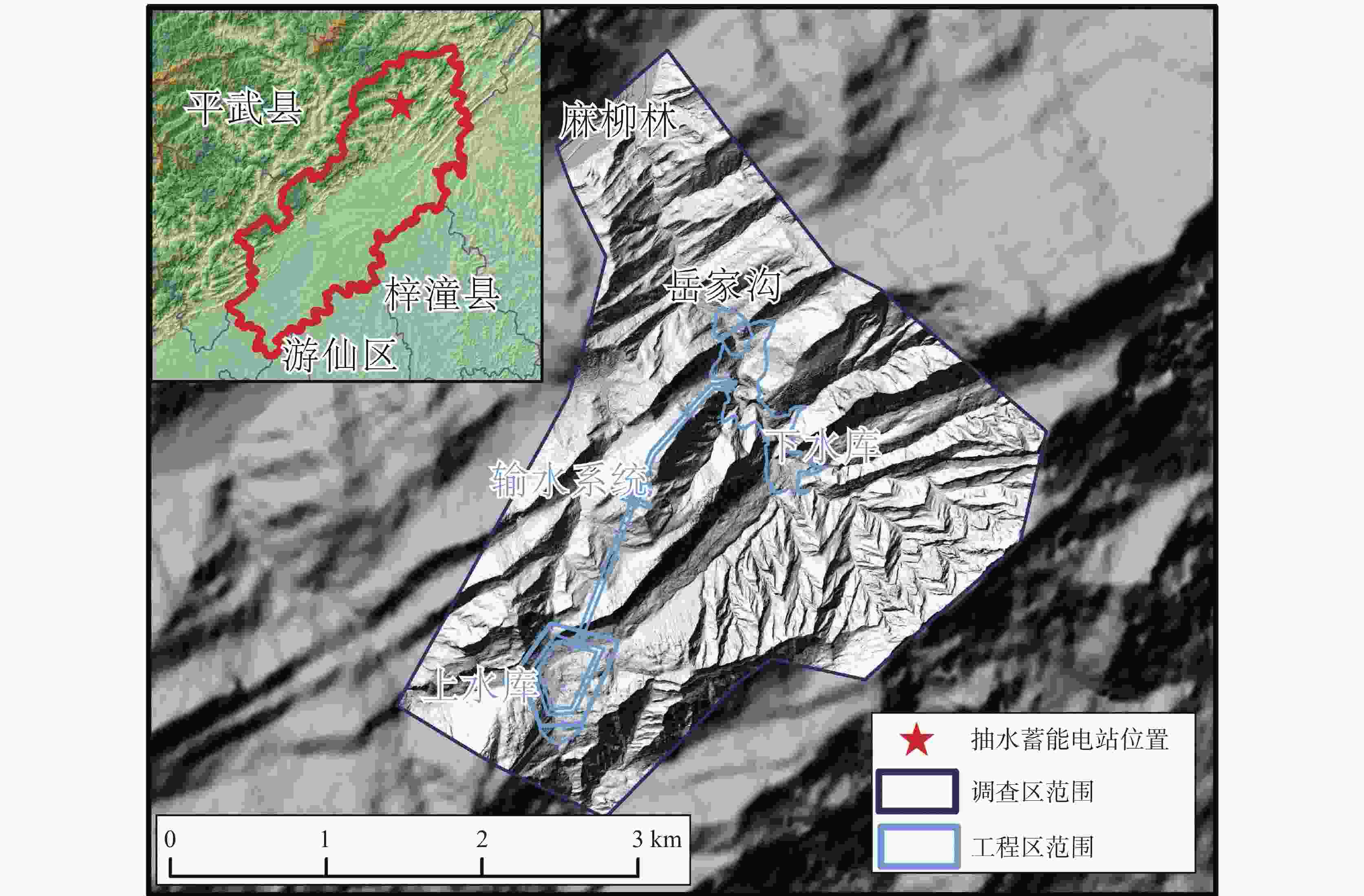
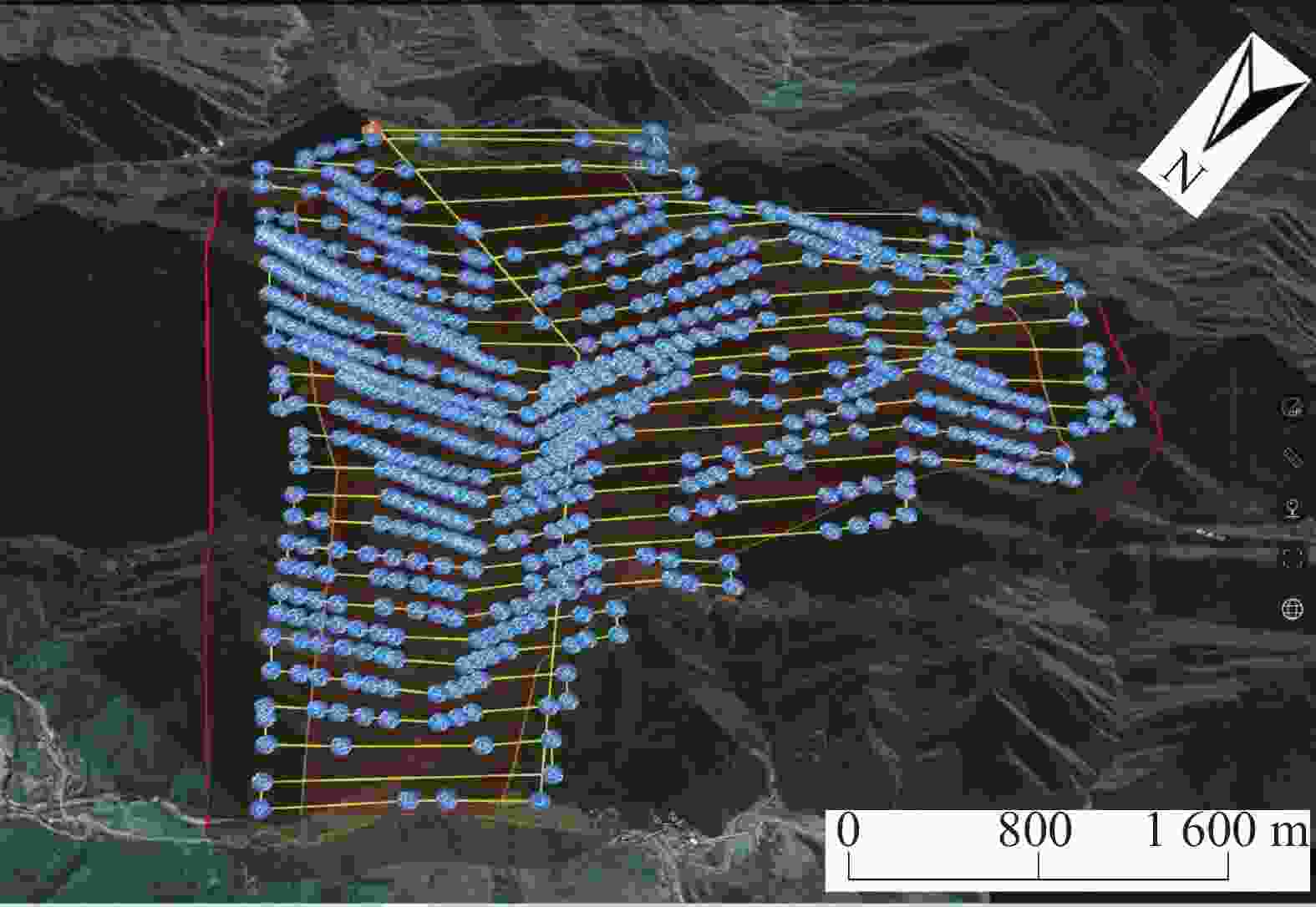
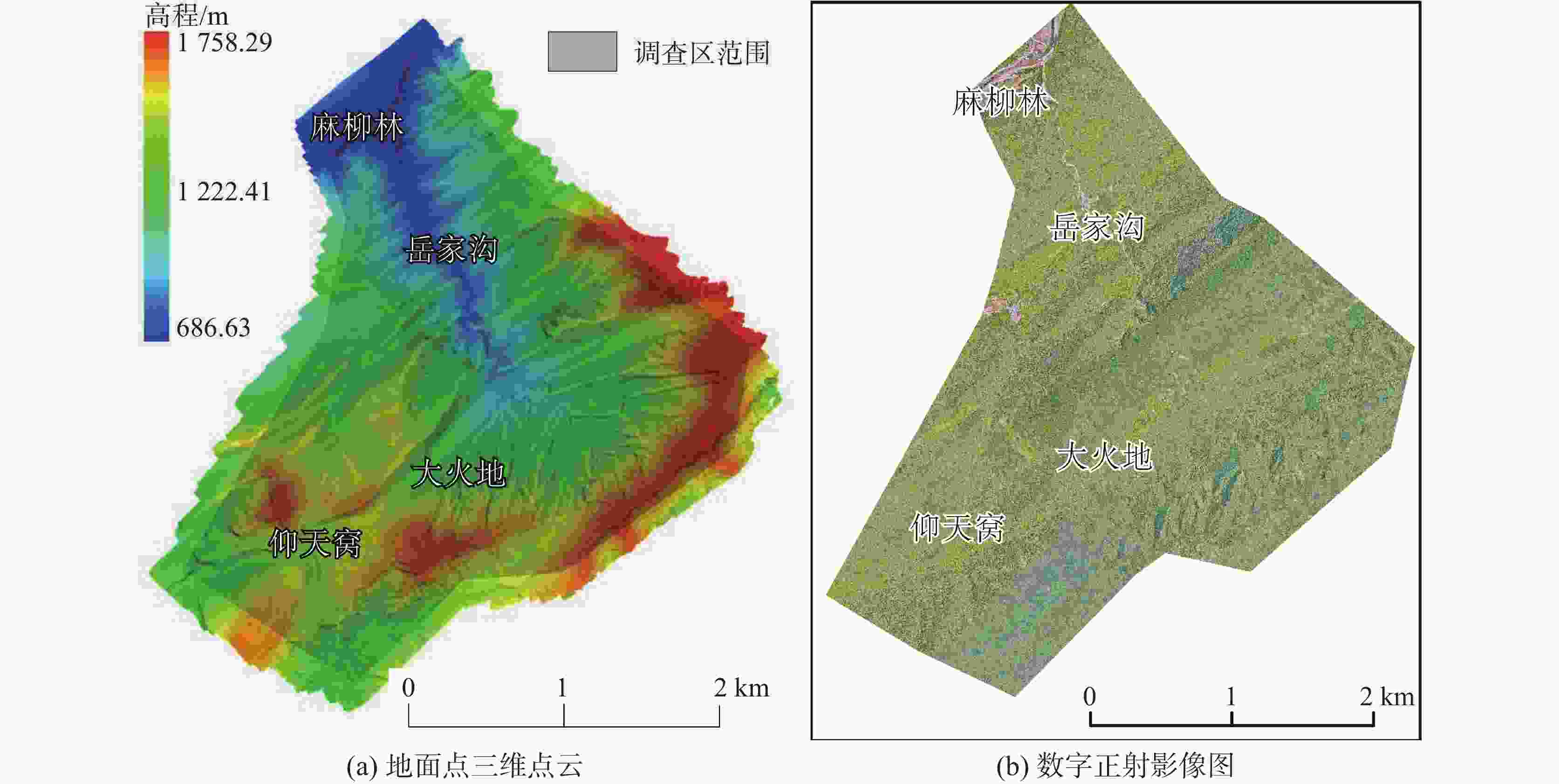
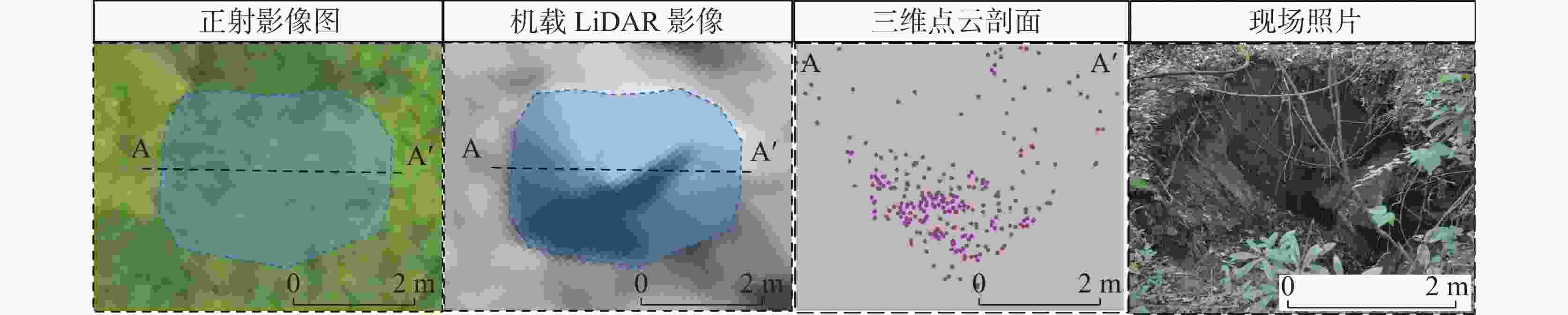
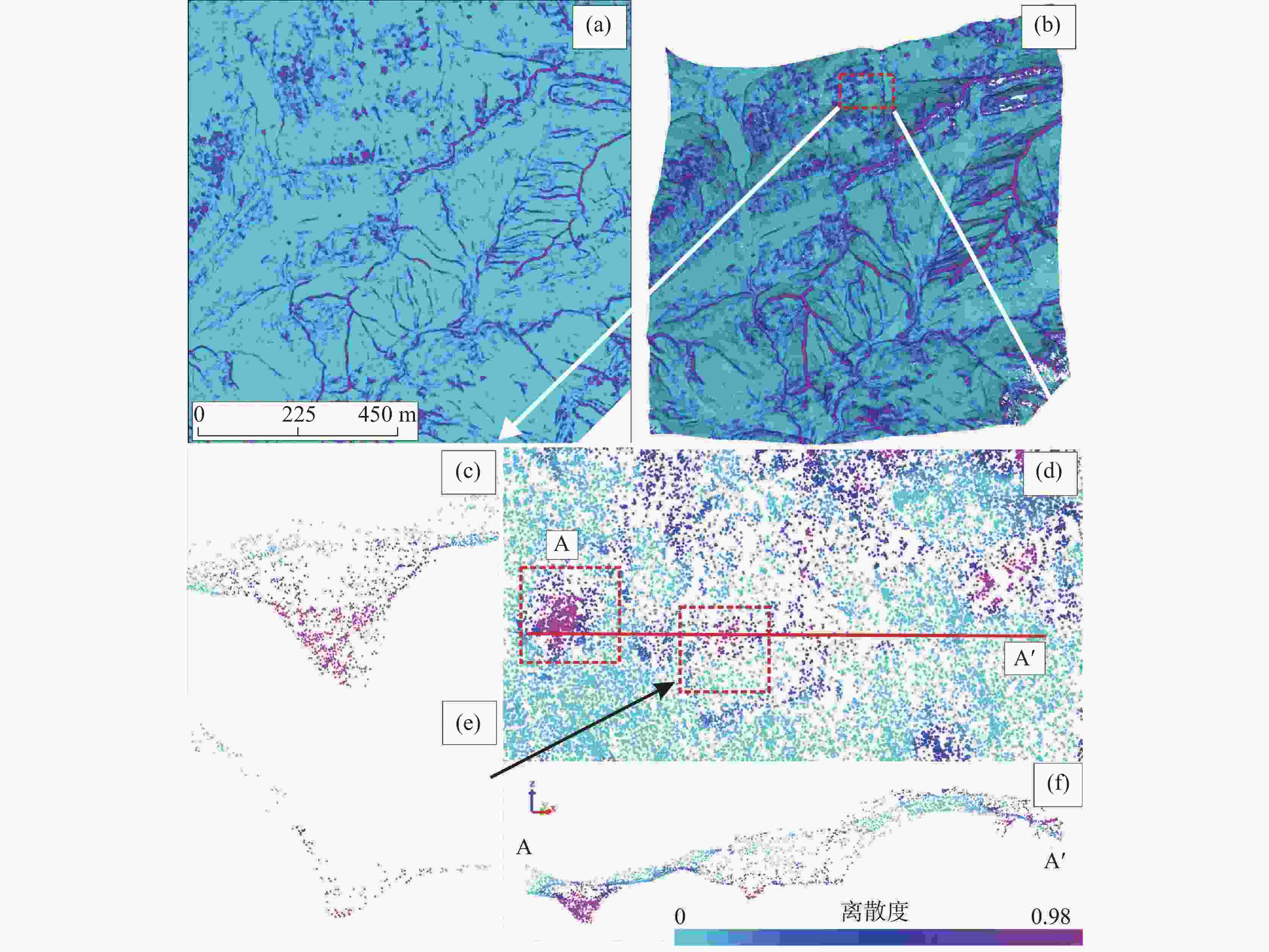
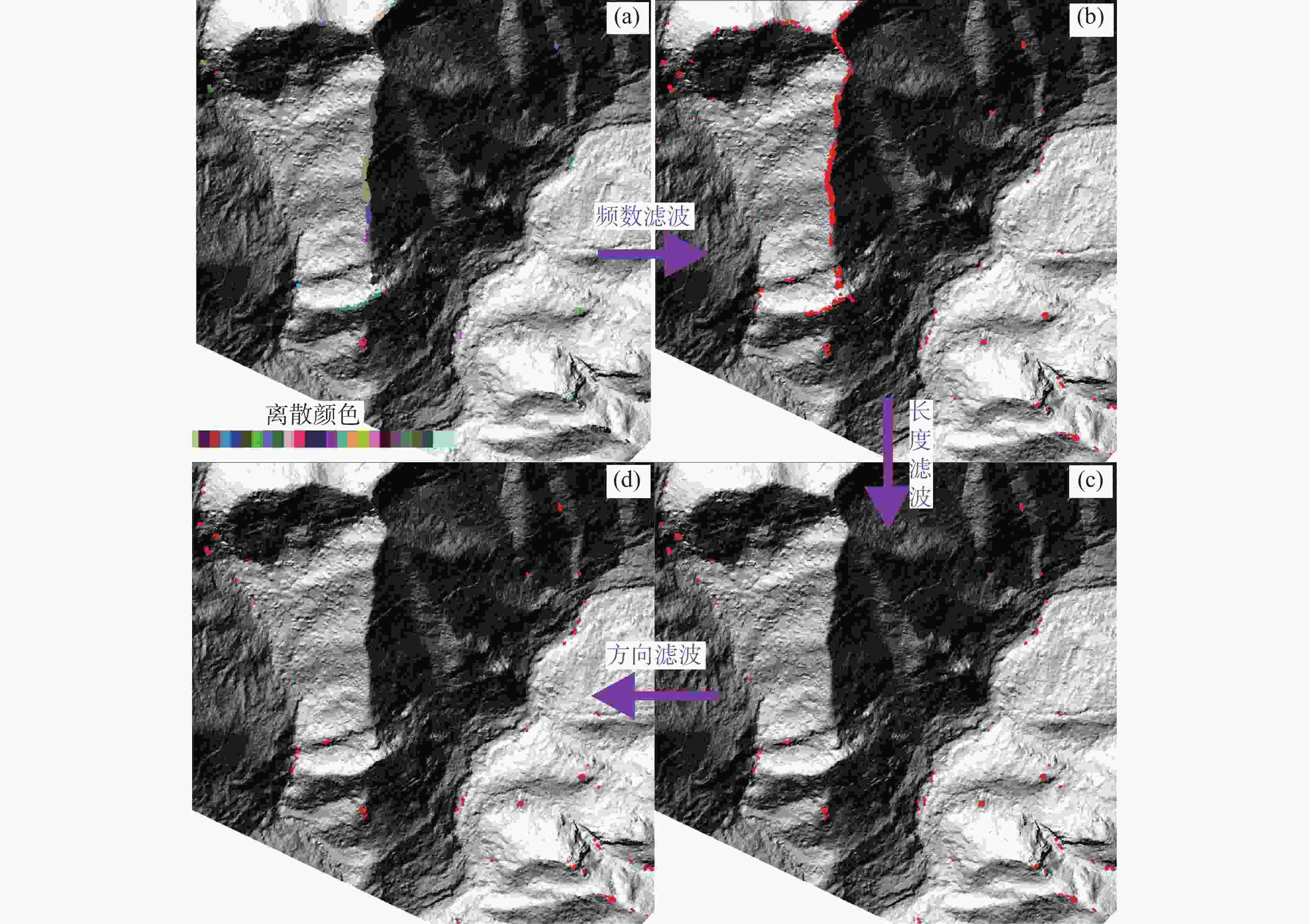
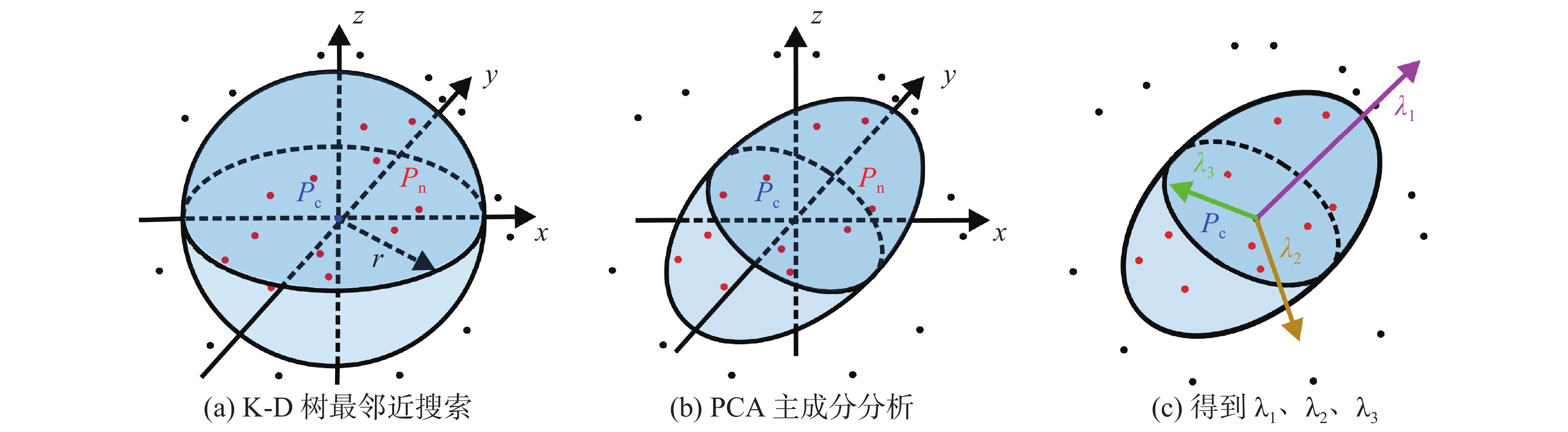
China's karst areas are widely distributed, with a total area of over 3.4 million square kilometers, accounting for one-third of the country's total land area. Karst engineering geological problems are widespread and difficult issues in the development of water conservancy and hydropower in Southwest China. In order to achieve the goals of "carbon peak" and "carbon neutrality", China is currently accelerating the construction of pumped storage power stations. However, karst leakage is one of the most important engineering geological problems faced by the construction of pumped storage power stations in areas with carbonate rock development. Therefore, in order to avoid reservoir leakage, it is of great significance to comprehensively, quickly, and accurately identify locations of dolines in reservoir and dam areas for water conservancy and hydropower engineering construction. The traditional investigation of dolines in reservoirs mainly uses the method of manual ground investigation and drilling. However, in the mountainous areas with dense vegetation cover in Southwest China, manual investigation is often very inefficient and limited by the strong concealment of dolines, making it difficult to achieve accurate and efficient investigation of large-scale dolines. To solve the problem of low efficiency in the investigation of dolines in dense vegetation areas, this article takes a reservoir area of pumped storage power station as a study area and proposes an automatic identification method for dolines based on point cloud principal component analysis to quickly identify and extract dolines in the reservoir area. The study area is located in the northeast of Sichuan Province, with an area of 10 km2. It is situated at the junction of the Qianlongmen mountains and the northwest of the Sichuan basin, in the tilted core of the Yangtianwo area. The terrain slope is generally above 30°, and the maximum relative height difference in the area is 1,070 m. The main vegetation in the area is forest, consisting of evergreen broad-leaved secondary forests and shrubs. In the study area, carbonate rock formations, such as the Upper Devonian Maoba Formation (D3m), Shawozi Formation (D3s), and Middle Devonian Guanwushan Formation (D2g), are mainly exposed with strong karst development. Firstly, airborne LiDAR technology was used to obtain ground 3D point cloud data in the study area after vegetation was filtered out. Then, in response to the strong directional characteristics of the concave shape of dolines, a preliminary extraction of dolines was achieved by the K-D tree nearest neighbor algorithm and principal component analysis, and an indicator eigenvalue ratio p was proposed. Finally, three filtering algorithms based on density clustering algorithm, namely, funnel frequency, length, and direction, were used to filter the background noise of the initial extraction results. The method used Receiver Operating Curve (ROC) to test the AUC value which was 0.854, and F-score is 0.859. This method is suitable for identifying and investigating dolines in karst areas with dense vegetation cover. -
Key words:
- airborne LiDAR /
- doline /
- point cloud /
- automatic identification /
- principal component analysis
-
表 1 机载LiDAR系统与光学相机各项参数
Table 1. Parameters of airborne LiDAR system and optical camera
雷达型号 RIEGL VUX-1 LR激光雷达系统 激光发射频率 750000 点/秒尺寸 227×180×125 mm 扫描速度 200次扫描/秒 重量 3.5 kg 相机型号 SONY A7RII 测量精度 15 mm 相机焦距 24 mm 最大测量范围 1350 m相机像素 4240MP 表 2 各采样半径提取漏斗模型评价结果
Table 2. Evaluation results of the funnel model extracted by each sampling radius
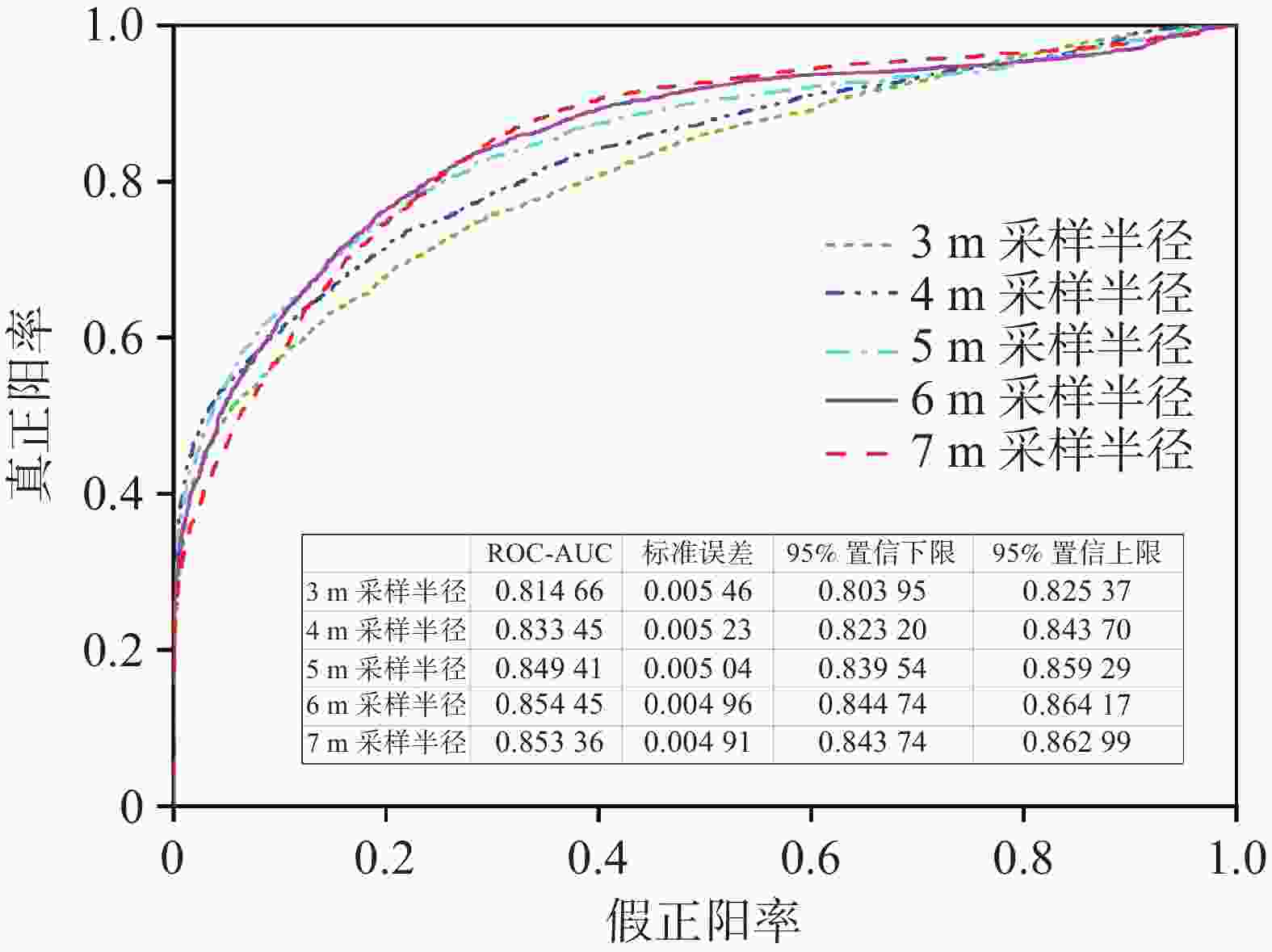
类型 真正阳率 假正阳率 准确率 F-score 3 m采样半径 81.03% 14.88% 82.14% 0.816 4 m采样半径 81.97% 15.31% 83.47% 0.827 5 m采样半径 82.55% 14.85% 84.53% 0.835 6 m采样半径 83.99% 11.33% 87.96% 0.859 7 m采样半径 83.35% 13.49% 85.38% 0.844 表 3 自动提取岩溶漏斗结果
Table 3. Results of automatic extraction of dolines
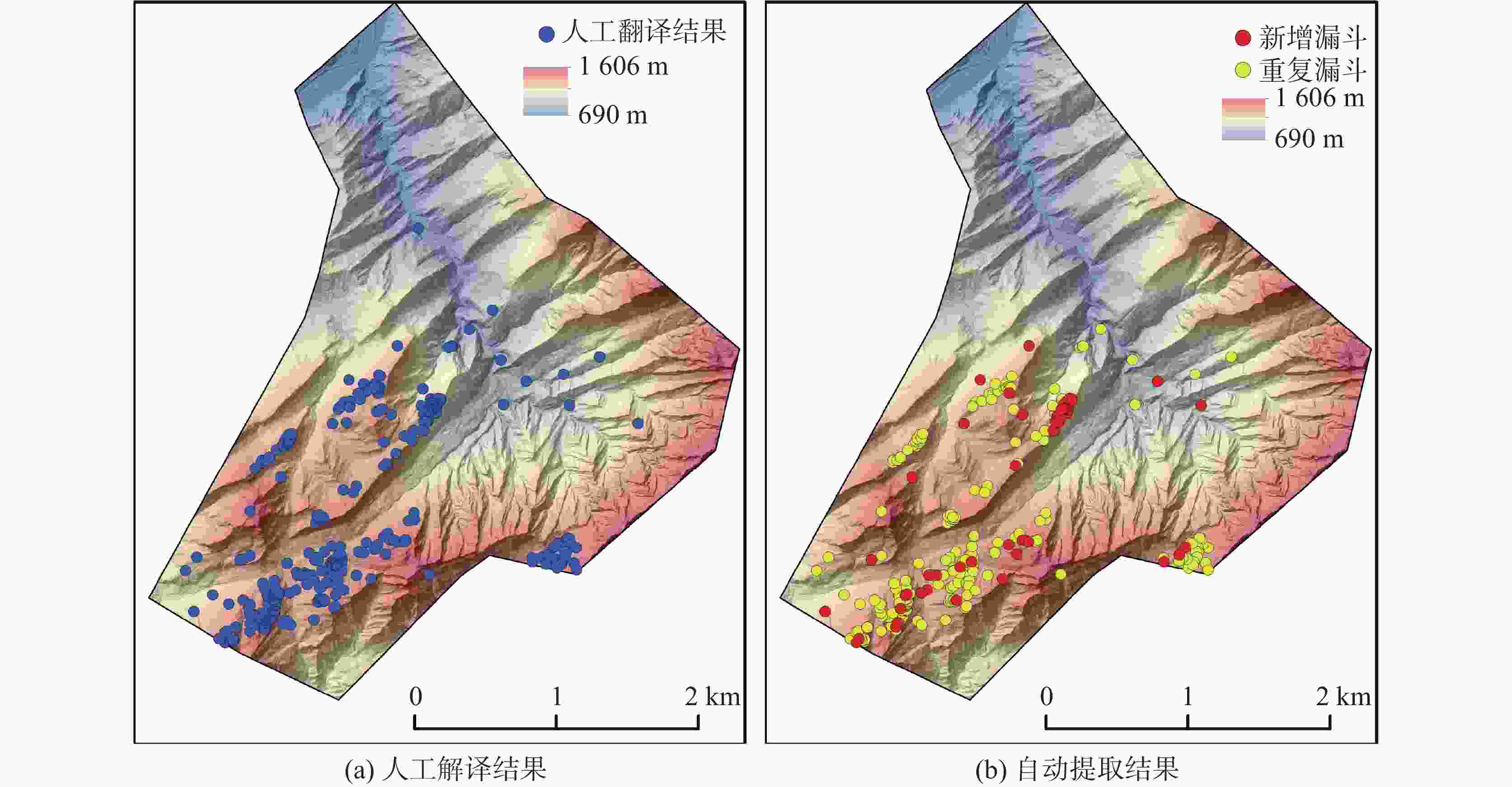
总数量 重叠数量 未发现数量 新增数量 重叠率 自动提取/个 305 243 16 46 93.8% -
[1] 曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 夏日元, 章程. 岩溶动力系统与全球变化研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5):874-900. doi: 10.12029/gc20170504CAO Jianhua, JIANG Zhongcheng, YUAN Daoxian, XIA Riyuan, ZHANG Cheng. The progress in the study of the karst dynamic system and global changes in the past 30 years[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 874-900. doi: 10.12029/gc20170504 [2] 曾洁, 潘晓东, 任坤, 刘伟, 彭聪, 郑智杰. 贵州省碧云湖岩溶渗漏水文地质条件与渗漏管道位置识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(1):201-208. doi: 10.11932/karst20240101ZENG Jie, PAN Xiaodong, REN Kun, LIU Wei, PENG Cong, ZHENG Zhijie. Hydrogeological conditions of karst leakage and locating of leakage channels in Biyun lake, Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(1): 201-208. doi: 10.11932/karst20240101 [3] 冯志刚, 韦国建, 张汉猛, 许国. 西南某水电站断裂构造和层间溶蚀带组合岩溶渗漏研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(5):728-735. doi: 10.11932/karst2021y33FENG Zhigang, WEI Guojian, ZHANG Hanmeng, XU Guo. Study on karst leakage caused by the combination of fault structure and interlayer corrosion zone of a hydropower station in Southwest China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(5): 728-735. doi: 10.11932/karst2021y33 [4] 袁道先, 蔡桂鸿. 岩溶环境学[M]. 重庆:重庆出版社, 1988. [5] 蒋小珍, 冯涛, 郑志文, 雷明堂, 张伟, 马骁, 伊小娟. 岩溶塌陷机理研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3):517-527. doi: 10.11932/karst20230304JIANG Xiaozhen, FENG Tao, ZHENG Zhiwen, LEI Mingtang, ZHANG Wei, MA Xiao, YI Xiaojuan. A review of karst collapse mechanisms[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 517-527. doi: 10.11932/karst20230304 [6] 袁道先. 现代岩溶学[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2016. [7] 伍法权. 西部水利水电开发与岩溶水文工程地质学术研讨会学术总结报告[J]. 工程地质学报, 2004, 12(4):441-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.04.020WU Faquan. Academic summary on the western conference of hydro-power development and karst hydro-engineering geology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004, 12(4): 441-444 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.04.020 [8] 卢耀如. 岩溶地区水利水电建设中一些环境地质问题的探讨[C]//喀斯特与环境地学——卢耀如院士80华诞祝寿论文选集, 2011:98-104. [9] 李芳涛, 李华明, 胡志平, 陈南南, 晏长根. 峨汉高速廖山隧道岩溶发育规律及其工程效应浅析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4):592-603.LI Fangtao, LI Huaming, HU Zhiping, CHEN Nannan, YAN Changgen. Features of karst development and geotechnical effects in the Liaoshan tunnel on the E-Han expressway[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 592-603. [10] 谭先亮. 拉浪水电站左岸绕坝渗漏问题的探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 1986, 5(1):25-34.TAN Xianliang. Discussion on bypassing leakage problem at left abutment of Lalang hydroelectric power atation[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1986, 5(1): 25-34. [11] 姚臣良. 大龙洞水库漏水量测验初析[J]. 广西水利水电, 1991(1):46-50. [12] 肖万春, 王占元. 猫跳河四级水电站坝肩及坝基渗漏稳定分析[J]. 贵州水力发电, 1999(2):20-24.XIAO Wanchun, WANG Zhanyuan. Analysis on seepage and stability of dam abutments and foundation in Cascade IV hydropower station on Maotiaohe river[J]. Guizhou Water Power, 1999(2): 20-24. [13] 吴宗信, 梁纪信, 王德成. 桃曲坡水库灰岩库区的漏水情况及治理措施[J]. 水利水电技术, 1990(12):49-52. [14] 曹建文, 杨海洋, 王喆, 赵良杰, 林玉山, 栾崧, 李录娟. 湖北某抽水蓄能电站建设中地下河系统多元信息综合分析评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4):699-710. doi: 10.11932/karst20230406CAO Jianwen, YANG Haiyang, WANG Zhe, ZHAO Liangjie, LIN Yushan, LUAN Song, LI Lujuan. Comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the multi-information on the underground river system in construction of a pumped-storage hydropower station in Hubei[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 699-710. doi: 10.11932/karst20230406 [15] 任启磊. 岩溶地区工程地质勘察方法技术应用[J]. 资源信息与工程, 2018, 33(3):12-13, 15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5391.2018.03.006 [16] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天—空—地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(7):957-966.XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space–air–ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. [17] Chen Weitao, Li Xianju, Wang Yanxin, Chen Gang, Liu Shengwei. Forested landslide detection using LiDAR data and the random forest algorithm: A case study of the Three Gorges, China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 152: 291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.07.004 [18] Meirman Syzdykbayev, Bobak Karimi, Hassan A Karimi. Persistent homology on LiDAR data to detect landslides[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 246: 111816. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111816 [19] 姜丙波, 柳忠伟, 彭云, 徐生望, 邓勇. 无人机机载激光雷达在抽水蓄能电站大比例尺地形图测绘中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2021(Suppl.1):248-251.JIANG Bingbo, LIU Zhongwei, PENG Yun, XU Shengwang, DENG Yong. Application of UAV airborne LiDAR in large scale topographic mapping of pumped storage power stations[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2021(Suppl.1): 248-251. [20] 徐晓臣, 谢津平. 机载激光雷达技术在乌龙山抽水蓄能电站工程测量中的应用[J]. 水利水电技术, 2017, 48(10):136-141.XU Xiaochen, XIE Jinping. Application of airborne-LiDAR technique to engineering survey for Wulongshan pumped storage hydropower station[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2017, 48(10): 136-141. [21] 郑鹏, 魏星灿, 李宁, 李强, 陈江攀. 无人机机载LiDAR技术在抽水蓄能电站库区岩溶识别中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(4):121-127.ZHENG Peng, WEI Xingcan, LI Ning, LI Qiang, CHEN Jiangpan. Application of UAV airborne LiDAR technology in karst identification of pumped storage power station reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(4): 121-127. [22] 刘汉湖, 杨武年, 夏涛. 高精度遥感三维可视化在岩溶地区工程初勘调查中的应用:以云南小哨机场为例[J]. 测绘科学, 2007,32(5):111-113, 205. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2007.05.041LIU Hanhu, YANG Wunian, XIA Tao. Application of high-accuracy remote 3D visualization in engineering exploration of karst: A case study of Yunnan Xiaoshao airport[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2007,32(5): 111-113, 205. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2007.05.041 [23] 夏涛, 杨武年, 马安青. 遥感影像三维可视化在岩溶漏斗解译中的应用[J]. 测绘科学, 2009, 34(6):266-267, 167.XIA Tao, YANG Wunian, MA Anqing. Application of 3D visualization of remote sensing images in doline interpretation[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2009, 34(6): 266-267, 167. [24] 尹盛虎, 米德才, 成功, 骆俊晖, 叶琼瑶. 无人机三维遥感在岩溶隧址区构造解译中的应用研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2021, 44(3):60-63.YIN Shenghu, MI Decai, CHENG Gong, LUO Junhui, YE Qiongyao. Research on application of unmanned aerial vehicle 3D remote sensing in structural interpretation of karst tunnel site[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2021, 44(3): 60-63. [25] Chen Yewang, Zhou Lida, Tang Yi, Jai Puneet Singh, Nizar Bouguila, Wang Cheng, Wang Huazhen, Du Jixiang. Fast neighbor search by using revised k-d tree[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 472: 145-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.012 [26] Abdulla Al Rawabdeh, Fangning He, Adel Moussa, Naser El Sheimy, Ayman Habib. Using an unmanned aerial vehicle-based digital imaging system to derive a 3D point cloud for landslide scarp recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(2): 95. [27] 邓博, 许强, 董秀军, 巨袁臻, 胡武婷. 点云与数字图像数据融合的斜坡变形裂缝自动检测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2023, 48(8):1296-1311.DENG Bo, XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, JU Yuanzhen, HU Wuting. Automatic detection of deformation cracks in slopes fused with point cloud and digital image[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(8): 1296-1311. [28] Hajian Tilaki Karimollah. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation[J]. Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine, 2013, 4(2): 627-635. -




 下载:
下载: