Heavy metal pollution of soil and its ecological risk evaluation in the phosphate mining area in central Guizhou
-
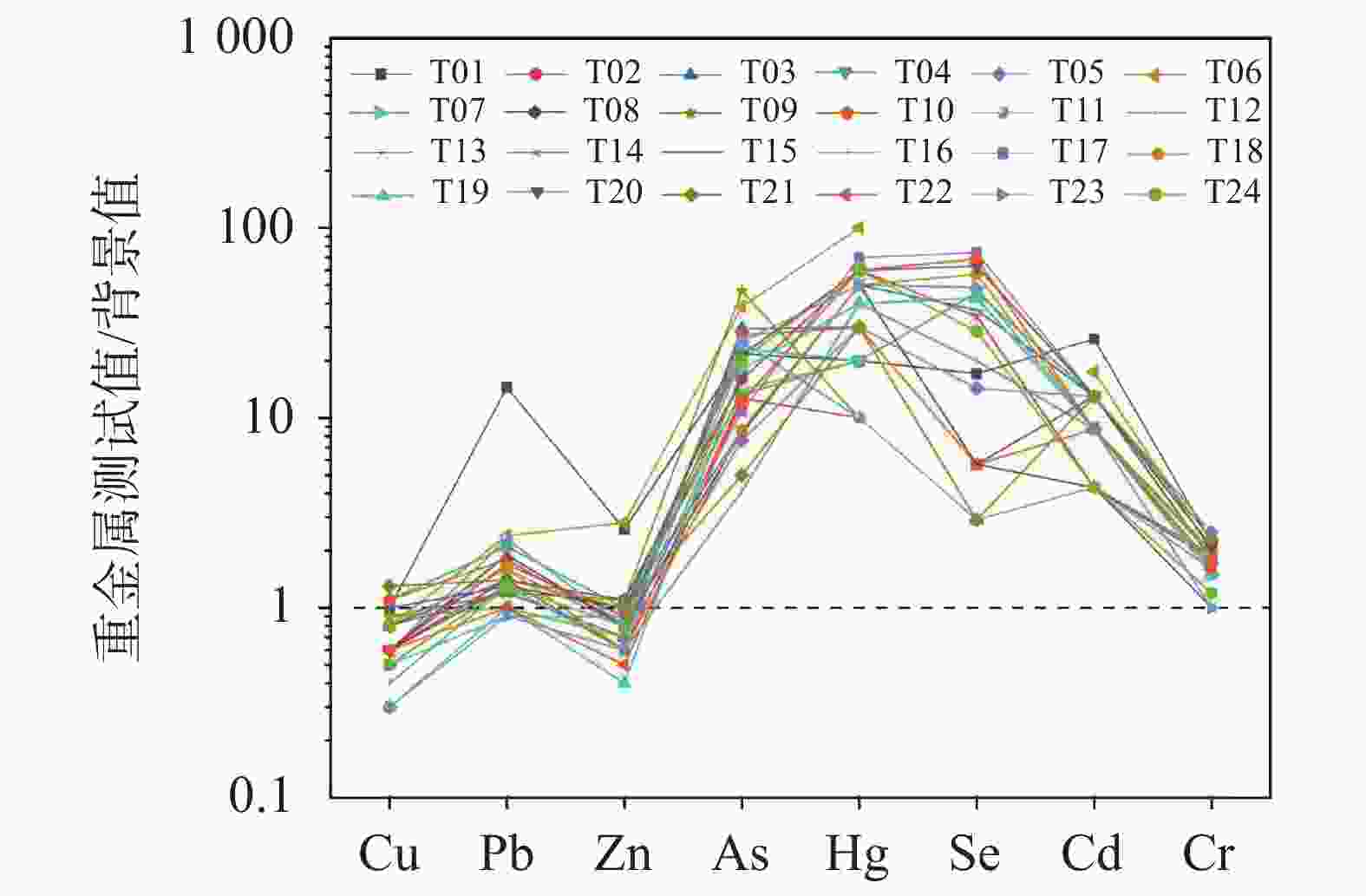
摘要: 为评价黔中磷矿区土壤重金属污染风险,采用梅花布点法在磷矿区周边区域和无矿区不同地层天然土壤采集24件表层土壤样品,测定Cu、Pb、Zn、As、Hg、Se、Cd、和Cr含量,并采用内梅罗综合污染指数(NPI)、地累积指数(Igeo)以及Hankanson潜在生态危害指数(RI)对磷矿区土壤重金属的污染程度和潜在生态风险进行评价。结果表明,黔中磷矿区土壤中Hg、Se、Cd、As、Pb、Zn和Cr等元素平均含量分别为贵州土壤背景值的37.58倍、24.40倍、19.26倍、18.09倍、2.67倍、2.17倍和1.78倍,各重金属富集特征明显,Cu元素平均含量未超过贵州省土壤背景值。研究区土壤中Hg、Se、Cd、As、Pb、Zn和Cr等元素NPI平均值介于4.59~69.32之间,处于重度污染水平,而Cr和Cu元素NPI平均值分别为1.89和1.21,处于轻度污染水平。研究区Hg元素Igeo平均值为4.45,处于严重至极重污染;As、Se和Cd元素Igeo平均值介于3.35~3.65之间,处于重度污染;Pb、Zn和Cr元素Igeo平均值0.21~0.44之间,处于未污染至中度污染水平,而Cu元素Igeo平均值为−0.83,显示其未受到污染。潜在生态风险评价结果表明,研究区土壤Hg元素处于极强生态风险水平,Cd处于强生态风险水平,Ad处于中等生态风险水平,而Cu、Pb、Zn和Cr均处于轻微风险水平。黔中磷矿区土壤RI平均值为2 285.50,显示出极强生态风险,Hg是最主要的生态风险元素,应引起高度重视。Abstract:
To investigate the current status of heavy metal pollution of soil in the phosphate mining area in central Guizhou and to comprehensively evaluate the potential pollution risks of eight heavy metal elements, a systematic sampling approach was employed in a plum blossom pattern. A total of 24 topsoil samples were collected from the surrounding areas of the phosphate mining area and from different strata in the non-mining area. The concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, As, Hg, Se, Cd, and Cr were determined. Based on the test results, comprehensive evaluations of the degree of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks in the topsoil of the mining area were conducted in terms of the Nemerow Pollution Index (NPI), Geo-accumulation Index (Igeo), and Hankanson Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI). The results indicate that the average concentrations of Hg, Se, Cd, As, Pb, Zn, and Cr in the topsoil of the phosphate mining area in central Guizhou were 3.83 mg·kg−1, 8.42 mg·kg−1, 2.29 mg·kg−1, 240.6 mg·kg−1, 65.83 mg·kg−1, 141.4 mg·kg−1, and 145.8 mg·kg−1, respectively. These values were 37.58, 24.40, 19.26, 18.09, 2.67, 2.17, and 1.78 times higher than the corresponding background values of soil in Guizhou, indicating significant enrichment of these heavy metals in the study area. In contrast, the average concentration of Cu did not exceed the background value of the surrounding soil. The evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the topsoil showed that NPI values for Hg, Se, Cd, As, Pb, Zn, and Cr ranged from 4.59 to 69.32, indicating a general level of heavy pollution. Specifically, NPI values for Hg, Se, As, Cd, and Pb were 75.73, 55.21, 35.36, 19.75, and 10.32, respectively, all demonstrating heavy pollution. NPI values of Cr and Zn were 2.17 and 2.11, respectively, suggesting moderate pollution. The lowest NPI values were observed in Cr and Cu, with averages of 1.89 and 1.21, respectively, indicating light pollution. The Igeo analysis revealed that the average Igeo value for Hg was 4.45, showing severe to extreme pollution. The average Igeo values for As, Se, and Cd ranged from 3.35 to 3.65, indicating heavy pollution. Igeo values of Pb, Zn, and Cr averaged between 0.21 and 0.44, suggesting a range from unpolluted to moderate levels of pollution. The average Igeo value for Cu was -0.83, indicating an unpolluted level. The evalution of potential ecological risk showed that the single-element RI for Hg in the topsoil was 1,533.33, indicating an extremely high ecological risk. The single-element RI value for Cd was 298.91, indicating a high ecological risk, while the value of As is 180.92, indicating a very high ecological risk. The values for Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cr were all below 10, suggesting minor risk levels. Overall, the average RI value for the topsoil in the phosphate mining area was 2,285.50, indicating an extremely high potential ecological risk. Hg was identified as the primary ecological risk element, followed by Cd and As, warranting significant attention and management measures. -
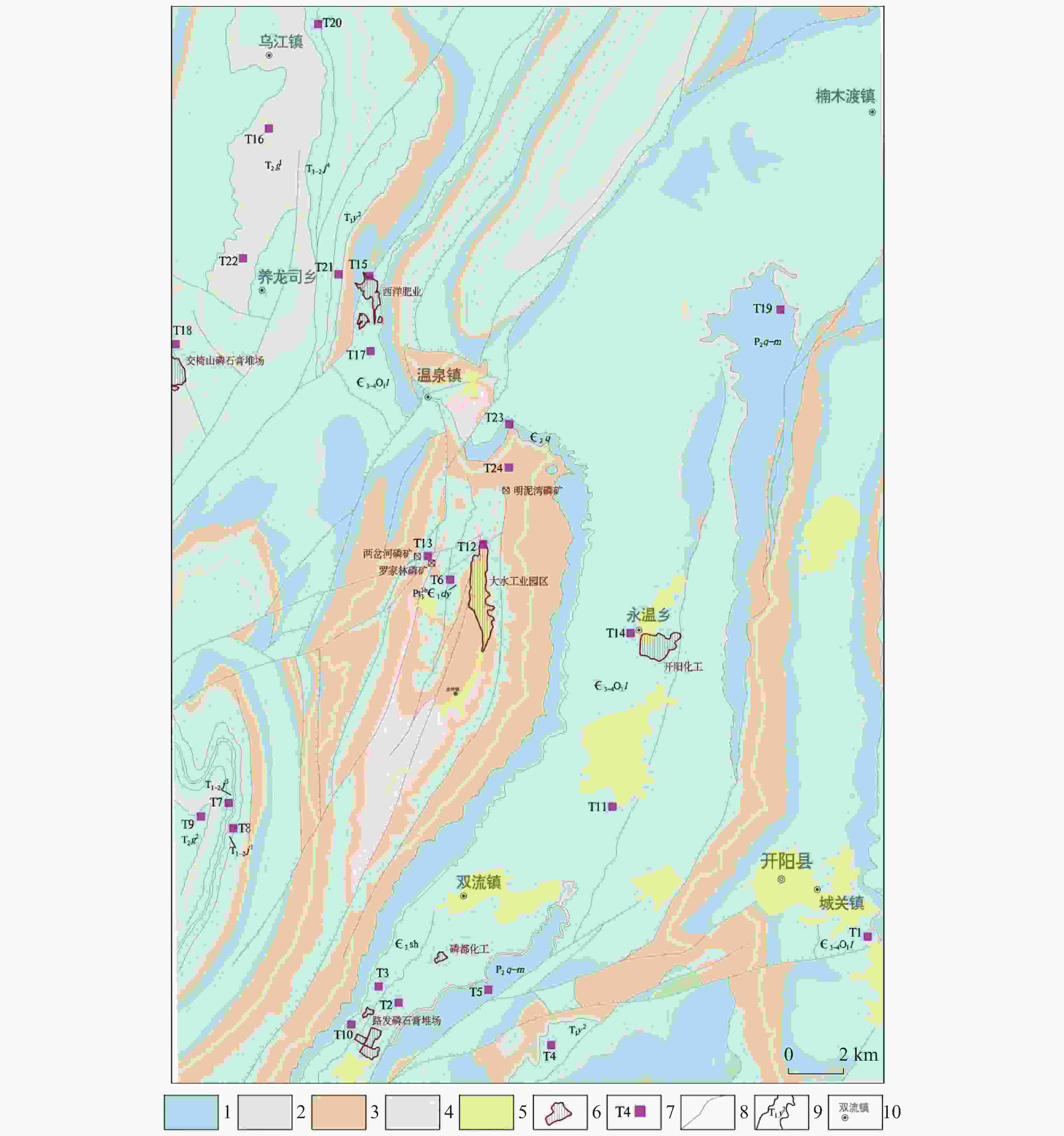
图 1 取样点分布图
1.碳酸盐岩含水岩组 2.碳酸盐岩夹非碳酸盐岩含水岩组 3.碎屑岩含水岩组 4.变质岩 5.第四系 6.磷化企业 7.取样点位置及编号 8.断层 9.地层界线
Figure 1. Distribution of sampling points
1.water-bearing rock formation comprised of carbonate rock; 2.water-bearing rock formation comprised of carbonate rock and non-carbonate rock; 3. water-bearing rock formation comprised of clastic rock; 4.metamorphic rock; 5.Quaternary; 6.phosphating enterprise; 7. locations and numbers of sampling points; 8.fault; 9.stratigraphic boundary
表 1 研究区土壤样品采集清单
Table 1. List of soil sample collection in the study area
序号
样品编号 备注 1 T1 寒武系中统清虚洞组∈2q 2 T2 寒武系苗岭统至芙蓉统奥陶系下统娄山关组∈3-4O1l 3 T3 寒武系苗岭统石冷水组∈3sh 4 T4 三叠系下统夜郎组第二段T1y2 5 T5 二叠系阳新统栖霞-茅口组P2q-m 6 T6 震旦系上统灯影组Pt33b∈1dy 7 T7 三叠系下统至中统嘉陵江组第三段T1-2j3 8 T8 三叠系下统至中统嘉陵江组第一段T1-2j1 9 T9 三叠系中统关岭组第二段T2g2 10 T10 路发磷石膏堆场下游 11 T11 川东化工下游 12 T12 大水工业园区下游 13 T13 磷矿开采区 14 T14 开阳化工下游 15 T15 西洋肥业下游 16 T16 采石场 17 T17 寒武系苗岭统至芙蓉统奥陶系下统娄山关组∈3-4O1l 18 T18 交椅山磷石膏堆场下游 19 T19 铝土矿开采区 20 T20 三叠系下统至中统嘉陵江组T1-2j 21 T21 三叠系下统夜郎组第二段T1y2 22 T22 三叠系中统关岭组第一段T2g1 23 T23 寒武系第二统清虚洞组∈2q 24 T24 明泥湾磷矿开采区 表 2 土壤样品检测方法仪器及其精度表
Table 2. Testing methods, instruments and their precision of testing soil samples
重金属元素 检测方法 仪器型号 精度/mg·kg−1 检出限/mg·kg−1
Cu LY/T 3129-2019 森林土壤铜、锌、铁、锰全量的测定电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 iCAP6300 2.0 0.7 Pb GB/T 39229-2020 肥料和土壤调理剂 砷、镉、铬、铅、汞含量的测定 iCAP6300 9 3.0 Zn LY/T 3129-2019 森林土壤铜、锌、铁、锰全量的测定电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 iCAP6300 15 5 As GB/T 39229-2020 肥料和土壤调理剂 砷、镉、铬、铅、汞含量的测定 iCAP6300 6 2 Hg GB/T 39229-2020 肥料和土壤调理剂 砷、镉、铬、铅、汞含量的测定 iCAP6300 6 2 Se GB/T 39356-2020 肥料中总镍、总钴、总硒、总钒、总锑、总铊含量的测定 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 iCAP6300 15 5 Cd GB/T 39229-2020 肥料和土壤调理剂 砷、镉、铬、铅、汞含量的测定 iCAP6300 6 2 Cr GB/T 39229-2020 肥料和土壤调理剂 砷、镉、铬、铅、汞含量的测定 iCAP6300 6 2.0 表 3 内梅罗综合污染指数法评价分级标准
Table 3. Grading criteria of Nemero comprehensive pollution index
等级 Pi分级标准 NPI分级标准 污染等级 污染评价 Ⅰ Pi≤0.7 NPI≤0.7 清洁 无污染 Ⅱ 0.7<Pi≤1.0 0.7<E≤1.0 轻微 基本无污染 Ⅲ 1.0<Pi≤2.0 1.0<RI≤2.0 轻度 轻度污染 Ⅳ 2.0<Pi≤3.0 2.0<RI≤3.0 中度 污染较严重 Ⅴ Pi>3.0 E>3.0 重度 污染非常严重 表 4 潜在生态风险指数法评价分级标准
Table 4. Grading criteria of potential ecological risk index
分级标准 等级 潜在生态风险 E≤40; RI≤150 Ⅰ 轻微 40<E≤80; 150<RI≤300 Ⅱ 中等 80<E≤160; 300<RI≤600 Ⅲ 较强 160<E≤320; 600<RI≤ 1200 Ⅳ 很强 E>320; RI> 1200 Ⅴ 极强 表 5 黔中磷矿区土壤重金属含量统计表
Table 5. Statistics of heavy metal contents in soil of the phosphate mine area in central Guizhou
重金属元素 样本数N 最小值/mg·kg−1 最大值/mg·kg−1 均值/mg·kg−1 变异系数 土壤背景值/mg·kg−1 Cu 24 11.00 45.00 25.33 0.36 35.97 Pb 24 30.00 484.00 65.83 1.37 33.47 Zn 24 58.00 420.00 141.40 0.61 148.67 As 24 54.00 620.00 240.60 0.58 13.30* Hg 24 0.00 10.00 3.83 0.61 0.10* Se 24 0.00 26.00 8.42 1.03 0.35* Cd 24 1.00 6.00 2.29 0.51 0.23 Cr 24 80.00 204.00 145.80 0.23 81.80* 注:*代表贵州省土壤背景值,来源于夏曾禄著《土壤元素背景值及其研究方法》[25],其余背景值来源于文献[11]。
Note: * represents soil background in Guizhou Province and it is derived from Xia Zenglu's "Background values of soil element and its research methods". Other background values are derived from an abstract [11].表 6 黔中磷矿区土壤重金属内梅罗综合污染指数法计算评价结果
Table 6. Calculation and evaluation results of Nemerow comprehensive pollution index for heavy metals in soil of the phosphate mine area in central Guizhou
重金属元素
内梅罗综合污染指数NPI 重金属污染评价结果 Cu 1.02 轻度污染 Pb 10.32 重污染 Zn 2.11 中度污染 As 35.36 重污染 Hg 75.73 重污染 Se 55.21 重污染 Cd 19.75 重污染 Cr 2.17 中度污染 表 7 黔中磷矿区土壤重金属地累积指数Igeo计算评价结果表
Table 7. Calculation and evaluation results of soil heavy metal geo-accumulation index Igeo in the phosphate mine area of central Guizhou
检测编号 地累积指数Igeo Cu Pb Zn As Hg Se Cd Cr 2019G-857 −0.62 3.27 0.80 3.85 3.74 3.54 4.12 0.54 2019G-858 −1.36 −0.13 −1.22 3.08 2.74 − 2.54 −0.03 2019G-859 −0.90 −0.36 −1.03 4.30 4.32 0.95 1.54 0.30 2019G-860 −0.51 0.48 −0.57 3.15 3.74 4.95 3.12 0.45 2019G-861 −2.29 −0.56 −1.06 2.34 4.32 3.27 3.12 0.73 2019G-862 −0.95 0.69 0.91 4.68 6.06 − 3.54 0.41 2019G-863 −1.51 −0.74 −0.76 3.95 3.74 − 2.54 −0.03 2019G-864 −1.00 −0.10 −0.42 3.44 − 1.95 3.12 0.27 2019G-865 −0.75 −0.29 −0.48 4.96 2.74 2.54 0.37 2019G-866 −0.51 0.26 −0.82 4.19 4.32 1.95 2.54 0.17 2019G-867 −1.36 0.64 −0.98 4.07 2.74 0.95 1.54 0.13 2019G-868 −0.67 −0.56 −1.13 3.24 3.74 1.54 −0.28 2019G-869 −1.43 0.33 −0.92 2.46 5.06 1.95 1.54 −0.53 2019G-870 −1.36 0.16 −0.76 3.41 5.32 4.54 1.54 0.32 2019G-881 −0.58 −0.26 −0.52 2.53 5.06 4.65 3.12 0.65 2019G-882 −1.75 −0.19 −1.34 1.44 4.74 3.76 2.54 0.17 2019G-883 −1.00 0.08 −0.94 2.84 5.54 5.65 3.12 0.59 2019G-884 −0.95 0.05 −1.37 2.51 5.06 5.27 2.54 0.42 2019G-885 −2.17 −0.65 −1.94 3.59 4.74 4.86 2.54 0.04 2019G-886 −1.36 −0.19 −0.65 3.83 5.32 5.41 3.12 0.45 2019G-887 −0.26 −0.13 −0.64 1.75 4.32 0.95 3.12 0.65 2019G-888 −1.43 −0.65 −1.59 3.02 5.32 5.54 2.54 0.08 2019G-889 −2.17 −0.74 −1.33 4.07 5.06 5.04 2.54 −0.62 2019G-890 −1.67 −0.26 −0.89 3.74 5.32 4.27 1.54 −0.30 avg. −1.19 0.01 −0.82 3.35 4.48 3.65 2.56 0.21 评价结果 无污染 未污染至中等
程度污染无污染 重污染 严重至极
重污染重污染 中度至
重污染未污染至中等
程度污染表 8 内梅罗综合污染指数法和地累积指数污染评价结果表
Table 8. Pollution evaluation results of Nemero comprehensive pollution index and geo-accumulation index
重金属元素 内梅罗综合污染指数NPI评价结果 地累积指数评价结果 Cu 轻度污染 无污染 Pb 重污染 未污染至中等程度污染 Zn 中度污染 无污染 As 重污染 重污染 Hg 重污染 严重至极重污染 Se 重污染 重污染 Cd 重污染 中度至重污染 Cr 中度污染 未污染至中等程度污染 表 9 土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价结果表
Table 9. Evaluation results of potential ecological risk of soil heavy metal
样品编号 单项潜在生态风险指数$ {\mathit{E}}_{\mathit{j}}^{\mathit{i}} $ 综合潜在生态风险指数
Cu Pb Zn As Hg Cd Cr RIj 2019G-857 4.87 72.30 2.62 216.54 800.00 782.61 4.38 1 883.31 2019G-858 2.92 6.87 0.65 127.07 400.00 260.87 2.93 801.31 2019G-859 4.03 5.83 0.73 295.49 1 200.00 130.43 3.69 1 640.21 2019G-860 5.28 10.46 1.01 133.08 800.00 391.30 4.11 1 345.24 2019G-861 1.53 5.08 0.72 75.94 1 200.00 391.30 4.99 1 679.56 2019G-862 3.89 12.10 2.83 385.71 4 000.00 521.74 3.99 4 930.26 2019G-863 2.64 4.48 0.89 231.58 800.00 260.87 2.93 1 303.39 2019G-864 3.75 7.02 1.12 162.41 0.00 391.30 3.62 569.23 2019G-865 4.45 6.12 1.08 466.17 400.00 260.87 3.89 1 142.57 2019G-866 5.28 8.96 0.85 272.93 1 200.00 260.87 3.37 1 752.27 2019G-867 2.92 11.65 0.76 252.63 400.00 130.43 3.28 801.67 2019G-868 4.73 5.08 0.69 141.35 800.00 130.43 2.47 1 084.75 2019G-869 2.78 9.41 0.79 82.71 2 000.00 130.43 2.08 2 228.21 2019G-870 2.92 8.37 0.89 159.40 2 400.00 130.43 3.74 2 705.75 2019G-881 5.00 6.27 1.05 86.47 2 000.00 391.30 4.69 2 494.79 2019G-882 2.22 6.57 0.59 40.60 1 600.00 260.87 3.37 1 914.23 2019G-883 3.75 7.92 0.78 107.52 2 800.00 391.30 4.52 3 315.80 2019G-884 3.89 7.77 0.58 85.71 2 000.00 260.87 4.01 2 362.83 2019G-885 1.67 4.78 0.39 180.45 1 600.00 260.87 3.08 2 051.24 2019G-886 2.92 6.57 0.96 213.53 2 400.00 391.30 4.11 3 019.39 2019G-887 6.26 6.87 0.96 50.38 1 200.00 391.30 4.69 1 660.46 2019G-888 2.78 4.78 0.50 121.80 2 400.00 260.87 3.18 2 793.91 2019G-889 1.67 4.48 0.60 251.88 2 000.00 260.87 1.96 2 521.45 2019G-890 2.36 6.27 0.81 200.75 2 400.00 130.43 2.44 2 743.08 AVG. $ {\mathit{E}}_{\mathit{j}}^{\mathit{i}} $ 3.52 9.83 0.95 180.92 1 533.33 298.91 3.56 2 031.04 生态风
险评价轻微生
态风险轻微生
态风险轻微生
态风险很强生
态风险极强生
态风险很强生
态风险轻微生
态风险极强生
态风险 -
[1] 刘品祯, 贾亚琪, 程志飞, 杨珍, 杜启露, 吴迪. 不同方法评价喀斯特煤矿区农田土壤重金属生态风险比较[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(3):371-378. doi: 10.11932/karst20180307LIU Pinzhen, JIA Yaqi, CHENG Zhifei, YANG Zhen, DU Qilu, WU Di. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around karst coal mining areas: A comparison of various methods[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 371-378. doi: 10.11932/karst20180307 [2] 张广映, 吴琳娜, 欧阳坤长, 吴攀. 都柳江上游沿岸喀斯特地区土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):495-503.ZHANG Guangying, WU Linna, OUYANG Kunchang, WU Pan. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils along the upper reaches of the Duliu river[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3): 495-503. [3] Lin Wenting, Wu Kangming, Lao Zhilang, Hu Wei, Lin Boji, Li Yanliang, Fan Hongbo, Hu Junjie. Assessment of trace metal contamination and ecological risk in the forest ecosystem of dexing mining area in northeast Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 167: 76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.001 [4] 余飞, 罗恺, 王佳彬, 李瑜 , 周皎, 王锐, 余亚伟, 张云逸. 重庆岩溶地质高背景区土壤-农作物系统重金属累积特征及影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(1):71-83.YU Fei, LUO Kai, WANG Jiabin, LI Yu, ZHOU Jiao, WANG Rui, YU Yawei, ZHANG Yunyi. Characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal accumulation in soil-crop system in the karst area with high geological background of Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(1): 71-83. doi: 10.11932/karst20230106 [5] 邬光海, 王晨昇, 陈鸿汉. 内蒙古废弃钨钼矿区周围土壤重金属污染生态环境评价及成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1838-1852. doi: 10.12029/gc20200619WU Guanghai, WANG Chensheng, CHEN Honghan. Eco-environmental assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal pollution in the soil around the abandoned tungsten-molybdenum mine area in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1838-1852. DOI: 10.12029/gc20200619 [6] 刘凯栋. 贵州崩塌灾害及其影响因素[J]. 贵州地质, 1993, 10(4):345-349.LIU Kaidong. Devolution disaster and its controlling factors in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 1993, 10(4): 345-349. [7] 丁坚平, 李扬, 褚学伟, 丁振超. 贵州开阳县龙井湾崩塌地质灾害评估及防治[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2006, 17(4):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.04.005DING Jianping, LI Yang, CHU Xuewei, DING Zhenchao. Evaluation and prevention of rock fall in Longjingwan‚ Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2006, 17(4): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.04.005 [8] 彭红明. 贵州省开阳磷矿洋水矿区崩塌形成机理研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2012.PENG Hongming. Research on formation mechanism of Yangshui mining area collapse of Kaiyang phosphate in Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012. [9] 杨勇. 贵州开阳磷矿洋水矿区环境地质问题分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2005(Suppl.1):624-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.z1.130YANG Yong. Evaluating environmental geology of Yangshui phosphorite deposit district in Kaiyang phosphorite mine[J]. Earth and Environment, 2005( Suppl.1): 624-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.z1.130 [10] 黄刚, 郑达. 贵州开阳磷矿山体崩塌形成机理与数值模拟[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2013, 24(1):46-50.HUANG Gang, ZHENG Da. Research on formation mechanism and numerical simulation of rockfall in Kaiyang phosphorite, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(1): 46-50. [11] 石振情, 毕陈权, 谭伟, 成剑波, 周鑫游, 王诗磊. 典型磷矿区表层土壤重金属空间分布特征研究[J]. 化工环保, 2020, 40(4):442-448.SHI Zhenqing, BI Chenquan, TAN Wei, CHENG Jianbo, ZHOU Xinyou, WANG Shilei. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface soil of typical phosphate mine area[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2020, 40(4): 442-448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2020.04.017 [12] 徐小蓉, 张习敏, 唐婧, 牛晓娟, 郝丽丽, 乙引. 瓮福磷矿矿渣和废水中元素成分分析[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 28(5):133-135.XU Xiaorong, ZHANG Ximin, TANG Jing, NIU Xiaojuan, HAO Lili, YI Yin. The elements analysis of slag and waste water in Wengfu phosphorite[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 28(5): 133-135. [13] 程馨, 施泽明, 张成江, 倪师军. 贵州开阳磷矿开采对洋水河水体重金属污染与评价[J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(2):78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.016CHENG Xin, SHI Zeming, ZHANG Chengjiang, NI Shijun. Evaluation of heavy metals pollution to Yangshui river in mining of phosphate rock of Kaiyang phosphate mine in Guizhou[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(2): 78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.016 [14] 程馨, 施泽明, 张成江, 倪师军. 开阳磷矿洋水矿区近地表大气降尘中重金属污染特征分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2013, 33(Suppl.2):690-691.CHENG Xin, SHI Zeming, ZHANG Chengjiang, NI Shijun. Analysis of heavy metal pollution characteristics in near-surface atmospheric dust in Kaiyang phosphate mine area[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2013, 33(Suppl.2): 690-691. DOI: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2013.s2.597 [15] Bouzekri Siham, El Hachimi Moulay Laarbi, Touach Noureddine, El Fadili Hamza, El Mahi Mohammed, Lotfi El Mostapha. The study of metal (As, Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu) contamination in superficial stream sediments around of Zaida mine (High Moulouya-Morocco)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2019, 154: 49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.03.014 [16] Howari F M, Banat K M. Assessment of Fe, Zn, Cd, Hg, and Pb in the Jordan and Yarmouk river sediments in relation to their physicochemical properties and sequential extraction characterization[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2001, 132: 43-59. [17] Li Xin, Yang Hong, Zhang Chang, Zeng Guangming, Liu Yunguo, Xu Weihua, Wu Youe, Lan Shiming. Spatial distribution and transport characteristics of heavy metals around an antimony mine area in Central China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 170: 17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.011 [18] Zhuang Qifan, Li Gang, Liu Zhiyong. Distribution, source and pollution level of heavy metals in river sediments from South China[J]. Catena, 2018, 170: 386-396. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.06.037 [19] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47: 1-16.BAO Liran, DENG Hai, JIA Zhongmin, LI Yu, DONG Jinxiu, YAN Mingshu, ZHANG Fenglei. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1625-1636. DOI: 10.12029/gc20200602 [20] 胡国成, 张丽娟, 齐剑英, 杨剑, 于云江, 郑海, 陈凤, 陈棉彪, 王程程, 黎华寿. 贵州万山汞矿周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(5):879-885.HU Guocheng, ZHANG Lijuan, QI Jianying, YANG Jian, YU Yunjiang, ZHENG Hai, CHEN Feng, CHEN Mianbiao, WANG Chengcheng, LI Huashou. Contaminant characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Wanshan mercury mine area, Guizhou Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(5): 879-885. [21] 吴健, 王敏, 张辉鹏, 黄宇驰, 徐志豪, 李青青, 陈昊, 黄沈发. 复垦工业场地土壤和周边河道沉积物重金属污染及潜在生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(12):5620-5627.WU Jian, WANG Min, ZHANG Huipeng, HUANG Yuchi, XU Zhihao, LI Qingqing, CHEN Hao, HUANG Shenfa. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk of soil from reclaimed industrial sites and surrounding river sediments[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(12): 5620-5627. [22] Hakanson Lars. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14: 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [23] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 万金忠, 张胜田, 龙涛, 李群, 林玉锁, 吴运金. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6):2884-2892.ZHOU Yan, CHEN Qiang, DENG Shaopo, WAN Jinzhong, ZHANG Shengtian, LONG Tao, LI Qun, LIN Yusuo, WU Yunjin. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine in Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. [24] 向龙, 刘平辉, 李欣. 基于GIS的华东某铀矿区水冶厂周边稻米中重金属的污染评价及分布差异[J]. 中国科技论文, 2017, 12(3):312-318, 326.XIANG Long, LIU Pinghui, LI Xin. GIS-based spatial variablity and pollution evaluation of heavy matal in surrounding of hydrometallurgy plant area of a uranium mining area, East China[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2017, 12(3): 312-318, 326. [25] 夏增禄. 土壤元素背景值及其研究方法[M]. 北京:气象出版社, 1987.XIA Zenglv. Background values of soil elements and their research methods[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1987. -




 下载:
下载: