Source characteristics and influencing factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in the karst areas of central Guizhou
-
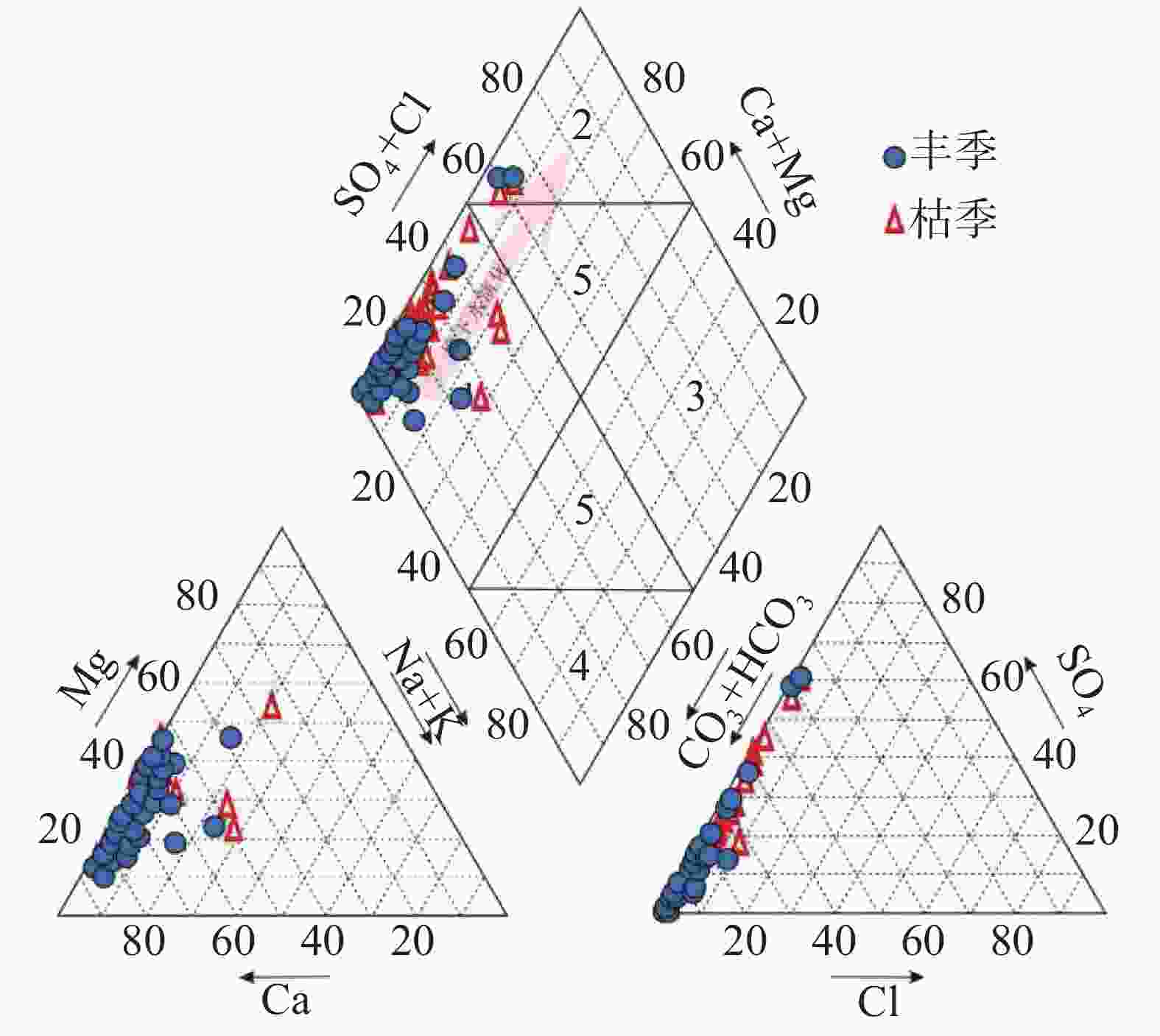
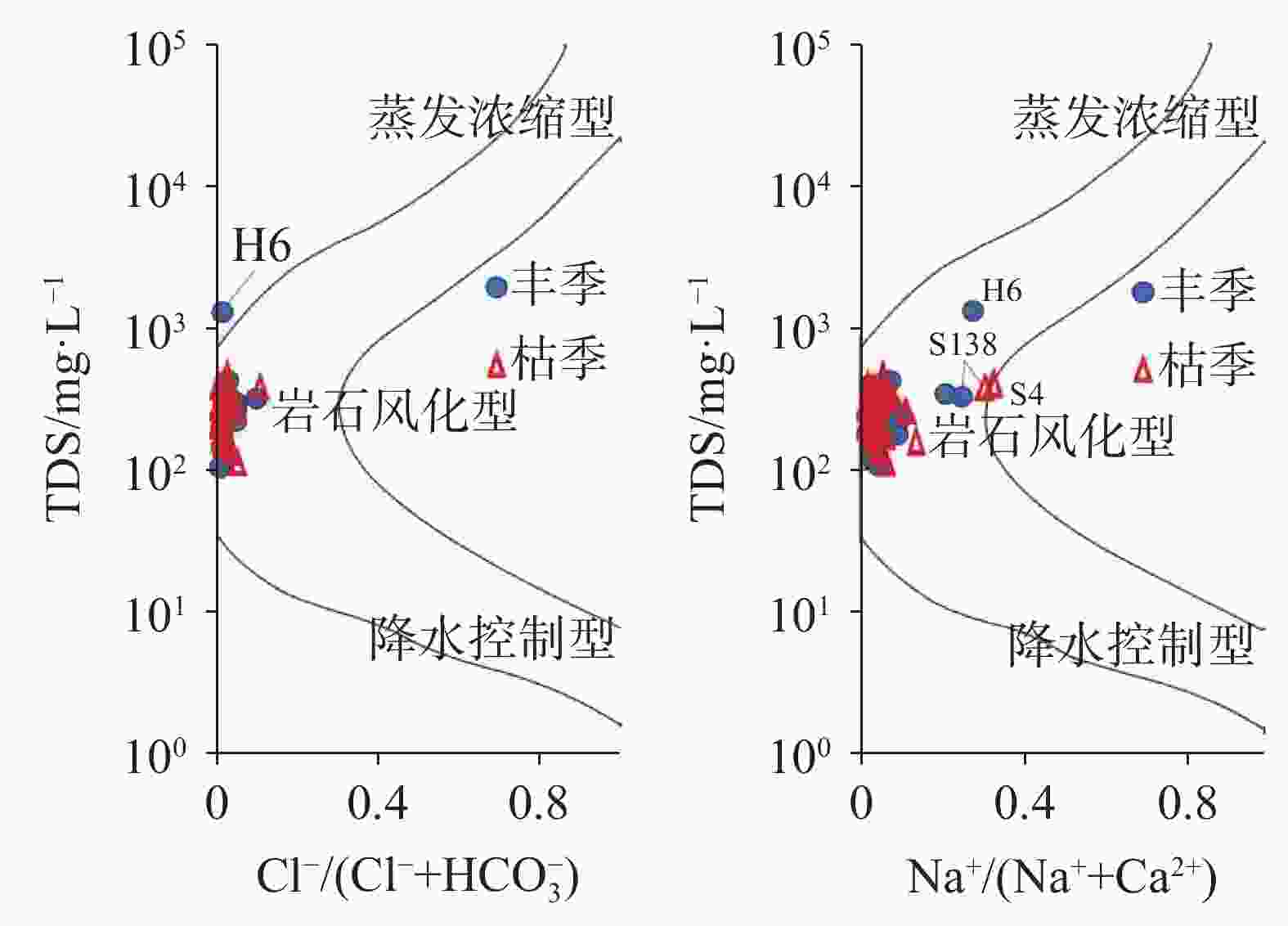
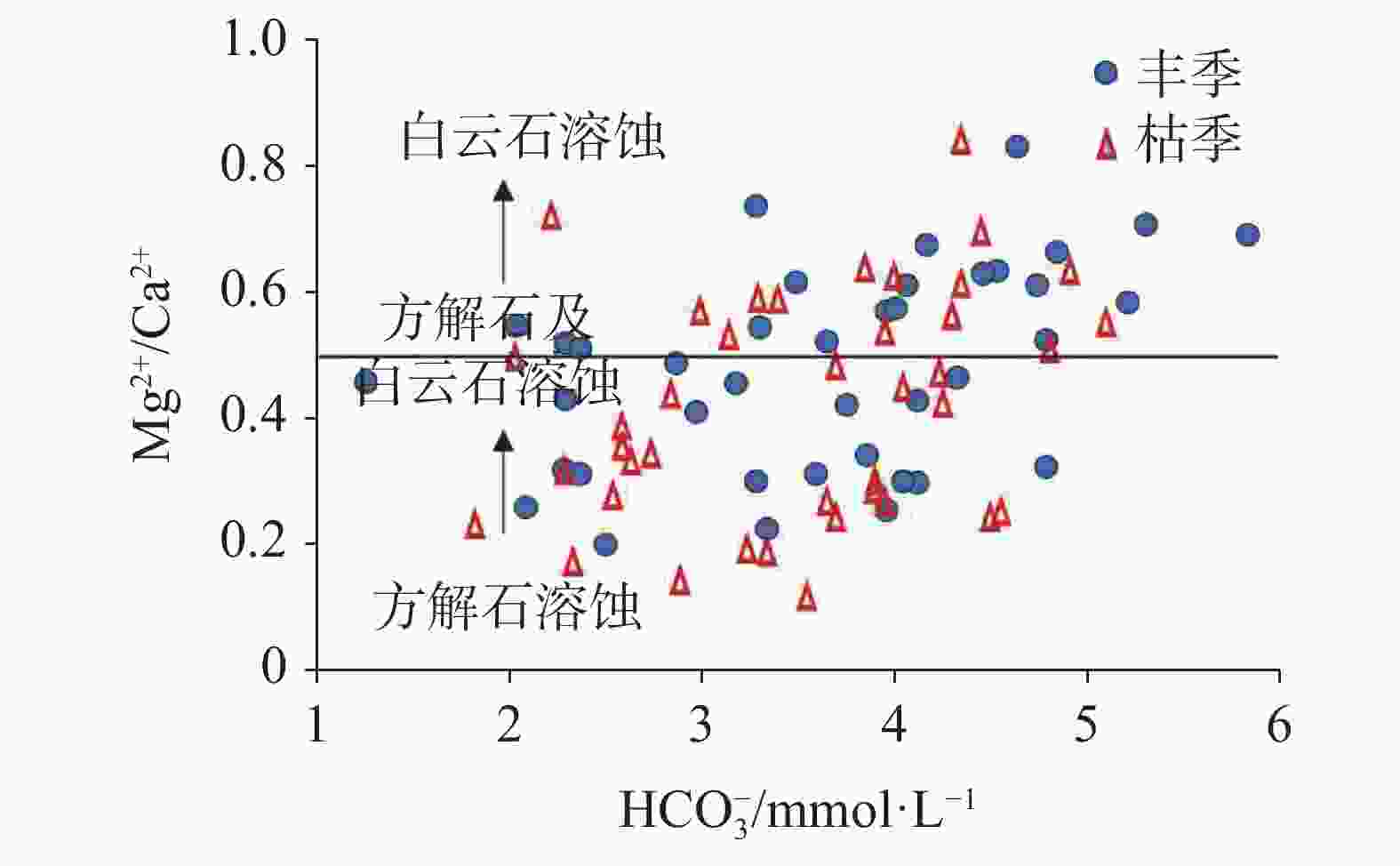
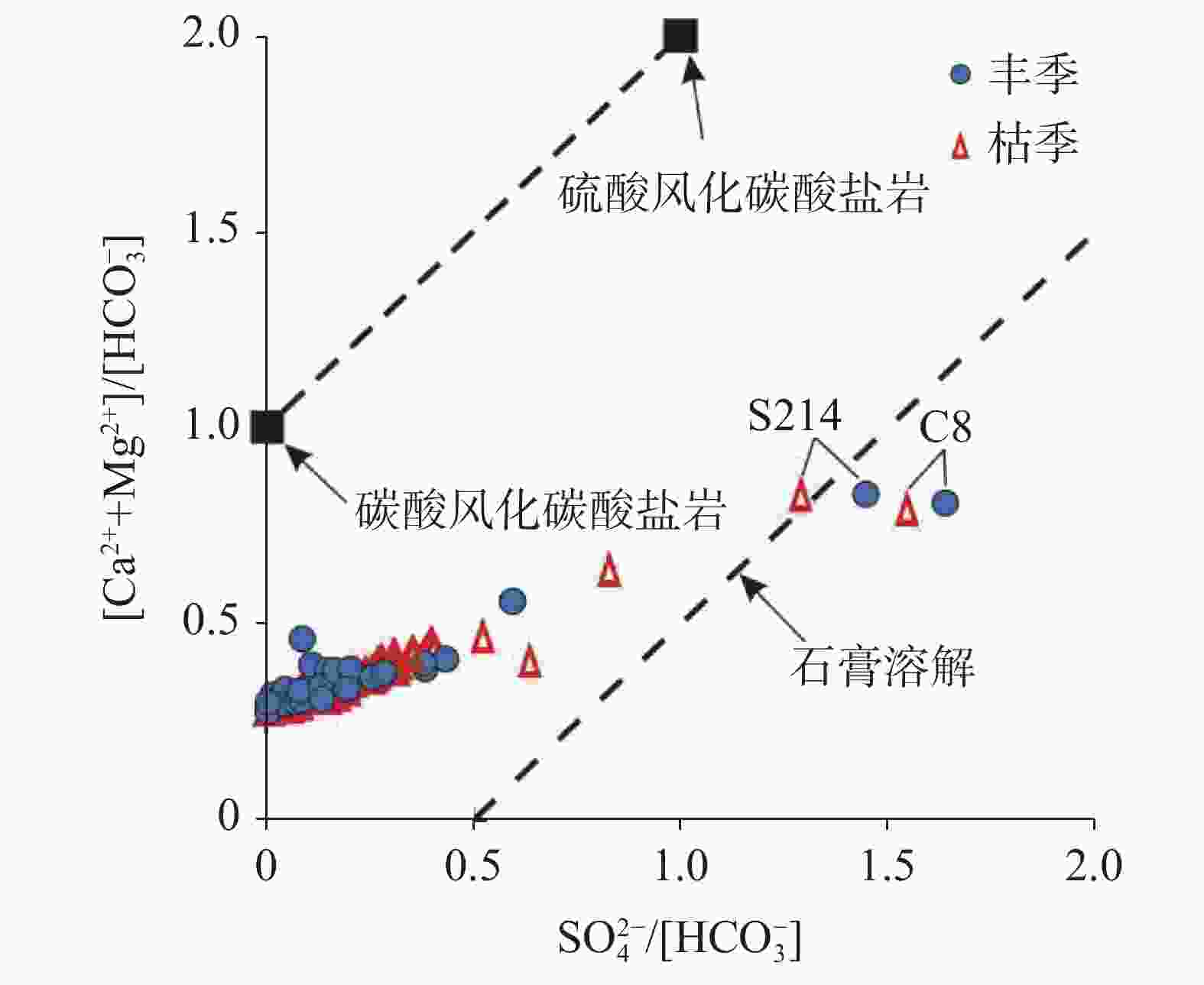
摘要: 文章基于区域水文地质、环境地质调查成果,对黔中岩溶区43个地下水点进行了枯水期和丰水期水样采集测试,利用地球化学图解及主成分分析(PCA)法,探讨该区枯水期和丰水期岩溶地下水水化学特征、离子来源及其影响因素。结果表明,该区地下水枯水期和丰水期的水化学特征及影响因素一致,水化学类型均以HCO3(SO4)-Ca(Mg)为主,吉布斯图解分析表明研究区岩溶地下水为岩石风化型,水化学组成主要来源于岩石风化淋滤溶解;[(Ca+Mg)/HCO3] - [ SO4/HCO3]图解分析认为研究区可溶性碳酸盐岩主要受碳酸的风化侵蚀作用控制,局部样品受石膏溶解影响显著;丰水期地下水主成分主要受水岩作用过程(PC1)、人类活动(PC2)及工业生产(PC3)等3类因素影响,这三个影响因素能够解释丰水期地下水水化学组分83.7%的特征;枯水期地下水主要受水岩作用过程(PC1*)和人类活动(PC2*)影响,这二类综合因子能够解释枯水期地下水化学组分85.1%的特征。水岩作用过程是该区地下水水化学组分最主要的影响因素。水岩作用主要影响K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$、TP、F−、SiO2等8项水质指标,人类活动主要影响NH$_4^{+}$、CODMn及Cl−等3项水质指标,而磷矿开采主要影响${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$。研究成果深化了对黔中地区岩溶地下水水化学特征的认识,揭示了地下水离子组分来源及影响因素,研究成果对黔中岩溶区地下水资源的合理开发利用与保护具有积极的指导意义。Abstract:
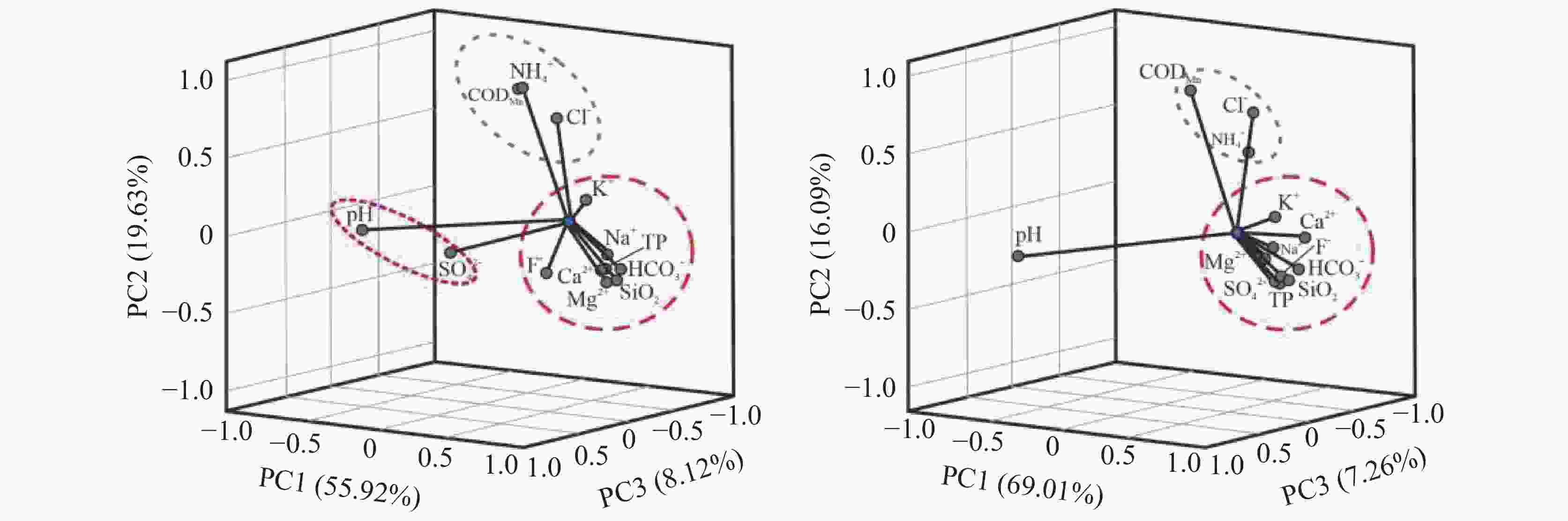
Based on the results of regional hydrogeological and environmental geological surveys, this study conducted comprehensive water sampling and testing at 43 groundwater points across the karst areas of central Guizhou during the dry and wet seasons. The study utilized three widely-used geochemical diagrams—Piper trilinear plots, Gibbs diagrams, and ion ratio diagrams (including relationships like HCO$_3^{-}$-(Mg2+/Ca2+ and [SO$_4^{2-}$/HCO$_3^{-}$]-[Ca2++Mg2+]/HCO$_3^{-}$) to identify the sources and characteristics of hydrochemical indicators of groundwater in the karst areas of central Guizhou. In addition to these geochemical methods, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed separately on the results of water quality tests completed from the dry and wet seasons to further clarify and verify the characteristics of groundwater sources during these two seasons, and to pinpoint specific water quality indicators influenced by various environment and human factors in the karst areas. The research findings reveal that the hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors of groundwater in the study area are relatively consistent during the dry and wet seasons. Hydrochemical types of groundwater in this area is predominantly characterized by HCO3(SO4)-Ca(Mg). The Gibbs diagrams show that the groundwater chemistry across the study area aligns closely with the rock weathering type, with only minor deviations of a single mine water sample (H6). A comprehensive analysis using Gibbs diagrams confirms that karst groundwater in the study area is primarily of a rock weathering type, with its hydrochemical composition predominantly derived from rock weathering and leaching dissolution processes. Further analysis using the [(Ca+Mg)/HCO3]-[SO4/HCO3] diagrams indicates that the molar ratio of [Ca2++Mg2+]/HCO$_3^{-}$ in groundwater during both the wet and dry seasons is largely below 0.5. This finding is particularly concentrated in the areas dominated by carbonate rocks, with some samples showing a trend towards gypsum dissolution. Particularly, certain samples, such as Spring S214 in Yongjing town of Xifeng county, and Spring C8 in Longyanpo village of Jinzhong town, Kaiyang county, are located either to the right or near the gypsum dissolution line. These positions indicate a significant influence of gypsum dissolution on groundwater chemistry, suggesting gypsum dissolution plays a crucial role in shaping the hydrochemical profile in parts of the areas. A comprehensive analysis of ion ratio correlations suggests that the soluble carbonate rocks in the study area are primarily affected by carbonate weathering and erosion processes. However, significant impacts from gypsum dissolution are also observed in some samples. This suggests that while the majority of the groundwater chemistry is shaped by carbonate dissolution, there are distinct pockets where gypsum dissolution contributes markedly to the groundwater composition. During the wet season, groundwater composition is mainly influenced by three principal factors: water-rock interactions (PC1), human activities (PC2), and industrial production (PC3). Together, these factors explain 83.7% of the variance in groundwater chemical composition. In contrast, during the dry season, groundwater is primarily influenced by water-rock interactions (PC1*) and human activities (PC2*), jointly accounting for 85.1% of the chemical composition variance. This seasonal variation highlights the dynamic nature of groundwater chemistry in response to both natural and human factors. Water-rock interactions emerge as the predominant factor influencing the hydrochemical composition of groundwater in the study area. These interactions significantly affect the concentrations of major ions such as potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate, total phosphorus, fluoride, and silica. Human activities, particularly agricultural and domestic activities, mainly influence the concentrations of ammonium, chemical oxygen demand (CODMn), and chloride. Additionally, the impact of phosphate mining is evident in its contribution to elevated sulfate ion concentrations, particularly in areas near mining operations. The research findings provide valuable insights into the complex hydrochemical dynamics of karst groundwater in central Guizhou. The consistent hydrochemical characteristics observed during the dry and wet seasons, alongside the predominant influence of rock weathering and dissolution processes, underscore the importance of geological factors in shaping groundwater chemistry in karst areas. However, the notable influence of gypsum dissolution in certain samples also highlights the need to consider localized geological variations when groundwater quality and developing management strategies are assessed. Moreover, the identification of human activities and industrial production as significant secondary influences on groundwater quality points to the need for targeted management interventions. These interventions should aim to mitigate the impacts of human activities on groundwater resources, particularly in the areas where agricultural runoff, domestic wastewater discharge, and industrial effluents contribute to the groundwater contamination. Overall, this study enhances our understanding of the hydrochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in central Guizhou, revealing the sources of groundwater ion components and their influencing factors. The findings have significant implications for the rational development and conservation of groundwater resources in karst areas. Effective management strategies should consider both natural geological processes and human influences identified in this study to ensure the sustainable use and protection of groundwater resources in the karst areas in central Guizhou. By integrating hydrogeological surveys with geochemical and statistical analyses, this study provides a comprehensive framework for understanding groundwater systems in karst environment, offering valuable guidance for future research and water resource management. -
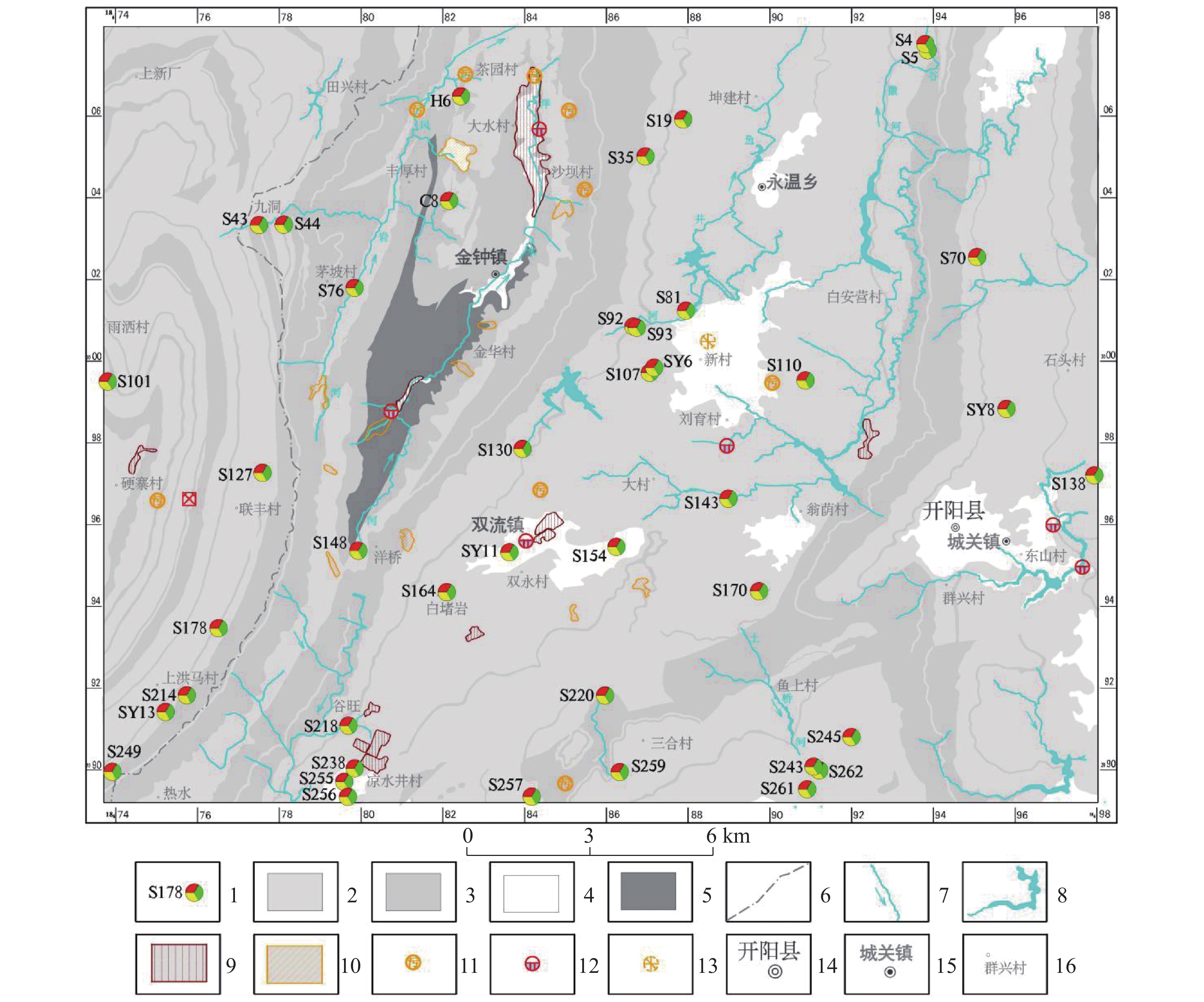
图 1 黔中岩溶地区水文地质简图及取样点分布位置图
1.取样点及编号 2.碳酸盐岩区 3.碎屑岩区 4.第四系区 5.变质岩区 6.县域界线 7.河流水系 8.水库水域 9.工矿企业 10.工业固废堆场(依比例尺) 11.工业固废堆场 12.污水处理厂 13.垃圾堆场 14.县政府驻地 15.乡镇驻地 16.村寨驻地
Figure 1. Hydrogeology map and distribution of sampling sites in the karst areas of cental Guizhou
1.sampling sites and numbers; 2. carbonate rock zone; 3. clastic rock zone; 4. Quaternary; 5. metamorphic rock zone; 6. the boundary of county; 7. river system; 8. water area of reservoir; 9. industrial and mining enterprises; 10. industrial solid waste dump (on a scale); 11. industrial solid waste dump; 12. sewage treatment plant; 13. dumping site; 14. county government site; 15. township site 16. village site
表 1 黔中岩溶区地下水描述性统计结果
Table 1. Descriptive statistical results of groundwater in the karst areas of central Guizhou
离子类别 季节 极小值/mg·L−1 极大值/mg·L−1 均值/mg·L−1 变异系数/% 峰度 Ca2+ 丰水期 28.58 239.50 56.07 56.40 28.00 枯水期 20.17 155.50 57.95 38.50 7.65 Mg2+ 丰水期 6.63 288.00 27.49 151.90 38.33 枯水期 8.66 326.20 33.72 139.30 38.05 NH$_4^{+}$ 丰水期 0.02 2.00 0.08 368.80 41.45 枯水期 0.02 0.48 0.04 204.30 17.29 K+ 丰水期 0.30 12.70 1.74 130.40 14.04 枯水期 0.40 20.60 1.87 175.30 27.03 Na+ 丰水期 0.50 90.00 5.02 275.30 36.16 枯水期 0.40 115.00 6.10 295.00 33.76 Cl− 丰水期 0.55 27.58 4.44 109.80 11.48 枯水期 1.47 30.89 5.55 91.70 14.39 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 丰水期 2.00 220.00 33.23 117.80 11.69 枯水期 2.00 883.00 74.60 176.80 35.61 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 丰水期 55.40 1 138.00 235.50 65.30 29.53 枯水期 34.80 1 295.00 246.50 72.70 29.03 pH 丰水期 6.63 8.37 7.60 4.30 1.76 枯水期 6.96 8.44 7.90 4.70 −0.74 COD 丰水期 0.02 4.77 0.50 149.80 26.34 枯水期 0.02 4.13 0.48 138.20 22.95 TP 丰水期 0.02 7.84 0.35 404.50 22.66 枯水期 0.02 25.50 0.64 603.40 42.97 SiO2 丰水期 0.21 12.90 3.13 53.20 28.81 枯水期 2.14 27.80 4.66 86.90 26.66 F− 丰水期 0.10 0.80 0.17 92.80 7.56 枯水期 0.00 0.84 0.13 92.80 27.00 表 2 KMO 和 Bartlett 检验结果表
Table 2. Test results of KMO and Bartlett
取样足够度的
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin 度量丰水期 0.67 枯水期 0.74 Bartlett 的球形度检验
近似卡方丰水期 746.67 枯水期 1 150.82 表 3 丰水期地下水特征值、方差百分数和累计方差百分数
Table 3. Eigen values, percentages of variance and cumulative percentages of groundwater in the wet season
成分 PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6 PC7 PC8 PC9 PC10 PC11 PC12 PC13 特征值 7.269 2.552 1.055 0.661 0.614 0.329 0.17 0.102 0.095 0.076 0.042 0.03 0.004 方差百分数/% 55.918 19.628 8.115 5.088 4.725 2.535 1.306 0.788 0.729 0.588 0.324 0.228 0.029 累计方差百分数/% 55.92 75.55 83.66 88.75 93.48 96.01 97.32 98.10 98.83 99.42 99.74 99.97 100.0 表 4 枯水期地下水特征值、方差百分数和累计方差百分数
Table 4. Eigen values, percentages of variance and cumulative percentages of groundwater in the dry season
成分 PC1* PC2* PC3* PC4* PC5* PC6* PC7* PC8* PC9* PC10* PC11* PC12* PC13* 特征值 8.971 2.092 0.944 0.407 0.194 0.139 0.080 0.069 0.044 0.035 0.016 0.009 0.000 方差百分数 69.01 16.09 7.263 3.129 1.492 1.067 0.617 0.531 0.339 0.266 0.126 0.068 0.003 累计方差百分数 69.01 85.10 92.36 95.49 96.98 98.05 98.67 99.20 99.54 99.80 99.93 99.99 100.0 -
[1] 袁道先. 我国西南岩溶石山的环境地质问题[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 1997, 19(5):41-43.YUAN Daoxian. On the environmental and geologic problems of karst mountains and rocks in the South-west China[J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 1997, 19(5): 41-43. [2] 杨平恒, 袁道先, 叶许春, 谢世友, 陈雪彬, 刘子琦. 降雨期间岩溶地下水化学组分的来源及运移路径[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(18): 1755-1763.YANG Pingheng, YUAN Daoxian, YE Xuchun, XIE Shiyou, CHEN Xuebin, LIU Ziqi. Sources and migration path of chemical compositions in a karst groundwater system during rainfall events[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(18): 1755-1763. [3] 张彦林, 李生永, 付东林, 崔旭东. 陇东盆地西部岩溶地下水形成机制研究[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1393-1399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.024ZHANG Yanlin, LI Shengyong, FU Donglin, CHUI Xudong. Formation mechanism of karst groundwater in the western Longdong basin, Northwestern China[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1393-1399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.024 [4] 袁道先, 薛禹群, 傅家谟. 防止我国西南岩溶地区地下河变成“下水道”的对策与建议[R]. 中国科学院院士建议, 2007, 4: 1-14. [5] 管清花, 李福林, 王爱芹, 冯平, 田婵娟, 陈学群, 刘丹. 济南市岩溶泉域地下水化学特征与水环境演化[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):653-662. doi: 10.11932/karst20190501GUAN Qinghua, LI Fulin, WANG Aiqin, FENG Ping, TIAN Chanjuan, CHEN Xuequn, LIU Dan. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of karst spring groundwater system in Jinan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 653-662. doi: 10.11932/karst20190501 [6] 鲁孟胜, 韩宝平, 武凡, 孙德全, 张兆民. 鲁西南地区高氟地下水特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1):294-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.024LU Mengsheng, HAN Baoping, WU Fan, SUN Dequan, ZHANG Zhaomin. Characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine groundwater in southwestern Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1): 294-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.024 [7] 朱琳, 苏小四. 吉林西部地区第四系潜水水质影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2006, 28(1):51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2006.01.011ZHU Lin, SU Xiaosi. Application of R-mode analysis in determining influencing factors of Quaternary unconfined groundwater quality in west area of Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2006, 28(1): 51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2006.01.011 [8] 董维红, 苏小四, 侯光才, 林学钰, 柳富田. 鄂尔多斯白垩系地下水盆地地下水水化学类型的分布规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(2): 288-292.DONG Weihong, SU Xiaosi, HOU Guangcai, LIN Xueyu, LIU Futian. Distribution law of groundwater hydrochemical type in the Ordos Cretaceous Artesian Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2006, 36(3): 391 398. [9] 任坤, 师阳, 李晓春, 蓝家程, 徐尚全. 典型岩溶槽谷区地下水化学特征及地球化学敏感性分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(1):15-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2014.01.003REN Kun, SHI Yang, LI Xiaochun, LAN Jiacheng, XU Shangquan. Study of the chemical features and geochemical susceptibility of the groundwater system in a typical karst trough valley[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(1): 15-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2014.01.003 [10] 冯亚伟, 陈洪年, 卜华, 贾德旺. 羊庄岩溶水系统水化学成因及同位素特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(3):394-403. doi: 10.11932/karst20190309FENG Yawei, CHEN Hongnian, BU Hua, JIA Dewang. Hydro-chemical genesis and isotope characteristics of Yangzhuang karst water system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(3): 394-403. doi: 10.11932/karst20190309 [11] 樊连杰, 裴建国, 邹胜章, 杜毓超, 卢丽. 重庆市南川区南部岩溶地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5):697-703.FAN Lianjie, PEI Jianguo, ZOU Shengzhang, DU Yuchao, LU Li. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in southern Nanchuan district of Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 697-703. [12] 杨秀丽, 罗维, 裴建国, 犹俊. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水质变化特征浅析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5):713-720.YANG Xiuli, LUO Wei, PEI Jianguo, YOU Jun. Analysis of variation characteristics of karst groundwater quality in Guiyang City[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 713-720. [13] 杨桂花, 潘晓东, 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 唐业旗. 黔西北裸露岩溶地区水文地球化学特征对土地利用方式的响应研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):535-544. doi: 10.11932/karst20180407YANG Guihua, PAN Xiaodong, YUAN Jianfei, DENG Guoshi, TANG Yeqi. Response of hydrogeochemical characteristics to land-use modes in exposed karst areas of northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4): 535-544. doi: 10.11932/karst20180407 [14] 张海月, 杨平恒, 王建力, 蓝家程, 詹兆君, 任娟, 张宇. 城市化对岩溶水系统化学组分演化的影响:以重庆市南山老龙洞地下河为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(4):541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416ZHANG Haiyue, YANG Pingheng, WANG Jianli, LAN Jiacheng, ZHAN Zhaojun, REN Juan, ZHANG Yu. Effect of urbanization on the hydrogeochemical evolution of karst groundwater system: A case of the Laolongdong watershed, Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(4): 541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416 [15] Chen K P, Jiao J J, Huang J M, Huang R Q. Multivariate statistical evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(3): 771-780. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.09.002 [16] Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, Savard M M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 353(3): 294-313. [17] 黄科云, 刘德深, 马祖陆, 许丹丹, 欧梦梦, 杨苗清. 云南鹤庆西山岩溶地下水主要离子雨季和旱季对比及来源分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(2):183-189.HUANG Keyun, LIU Deshen, MA Zhulu, XU Dandan, OU Mengmeng, YANG Miaoqing. Major ion chemistry and their source of karst groundwater from the Heqing west mountain, China during flood and dry seasons[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(2): 183-189. [18] 蒲俊兵, 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 苟鹏飞, 殷建军. 重庆岩溶地下河水文地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 水科学进展, 2010, 21(5):628-636.PU Junbing, YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Yongjun, GOU Pengfei, YIN Jianjun. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental meaning of Chongqing subterranean karst streams in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(5): 628-636. [19] 陈静生, 王飞越, 何大伟. 黄河水质地球化学[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(1): 58-73.CHEN Jingsheng, WANG Feiyue, HE Dawei. Geochemistry of water quality of the Yellow River basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(1): 58-73. [20] Jolliffe I. Principal component analysis[M]. New York, USA: Springer, 1986. [21] J Edward Jackson. A user's guide to principal components[M]. New York, USA: A Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1992. [22] Sun Jianguo. A note on principal component analysis for multi-dimensional data[J]. Statistics & Probability Letter, 2000, 46(1): 69-73. [23] 王松, 夏绍玮. 一种鲁棒主成分分析(PCA)算法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 1998, 18(l):9-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.1998.01.002WANG Song, XIA Shaowei. A robust principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 1998, 18(l): 9-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.1998.01.002 [24] Irie B, Miyake S. Capabilities of three-layered Perceptrons[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Inter Coof on Neural Networks, 1988(1): 641-648. [25] Hanson S. Knowledge representation in connectionist networks. Bell communications Research Technical Report[R]. 1987. [26] John I Marden. Some robust estimates of principal components[J]. Statistics & Probability Letter, 1999, 43: 349-359. [27] Mohamed N Nounou, Bhavik R Bakshi, Prem K Goel, Shen X T. Improving principal component analysis Bayesian estimation[R]. Proceedings of the American Control Conference Arlington, 2001: 25-27. [28] 孟生旺. 用主成份分析法进行多指标综合评价应注意的问题[J]. 统计研究, 1992(4):86-87. [29] 陈述云, 张崇莆. 对多指标综合评价的主成分分析方法的改进[J]. 统计研究, 1995(1):35-39. [30] 阎慈琳. 关于用主成分分析做综合评价的若干问题[J]. 数理统计与管理, 1998, 17(2):22-25.YAN Cilin. On composite evaluation by principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Applied Statistics and Management, 1998, 17(2): 22-25. [31] 姜旭平, 马宁辉. PCA方法及其在多准则评估模型中的应用[J]. 系统理论与实践, 1997, 17(4): 110-115.JIANG Xuping, MA Ninghui. Research on PCA and it's application in multicriteria evaluation[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 1997, 17(4): 110-115. [32] 冯慕华, 潘继征, 柯凡, 李文朝. 云南抚仙湖流域废弃磷矿区水污染现状[J]. 湖泊科学, 2008, 20(6):766-772. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.06.011FENG Muhua, PAN Jizheng, KE Fan, LI Wenchao. Water pollution of post-mined lands in Lake Fuxian watershed in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2008, 20(6): 766-772. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.06.011 [33] 朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 周长松, 李录娟, 谢浩. 不同城镇功能区岩溶地下水化学敏感因子识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):484-492. doi: 10.11932/karst20180402ZHU Danni, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHOU Changsong, LI Lujuan, XIE Hao. Identification of hydrochemical sensitive factors of karst groundwater in different functional urban areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4): 484-492. doi: 10.11932/karst20180402 [34] Lasaga A C, Soler J M, Ganor J, Burch T E, Nagy K L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(10): 2361-2386. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90016-7 [35] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [36] Feth J H, Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry: Evaporation-crystallization process[J]. Science, 1971, 172(3985): 870-872. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3985.870 [37] Kilham P. Mechanisms controlling the chemical composition of lakes and rivers: Data from Africa[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1990, 35(1): 80-83. doi: 10.4319/lo.1990.35.1.0080 [38] Négrel P. Geochemical study of a granitic area—the Margeride Mountains, France: Chemical element behavior and 87Sr/86Sr constraints[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 1999, 5(2): 125-165. doi: 10.1023/A:1009625412015 [39] 江峰, 李强, 吉勤克补子, 周亚男. 贵州省岩溶地区饮用天然矿泉水化学特征及其宏量组分来源分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2019, 36(2):173-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2019.02.010JIANG Feng, LI Qiang, JI Qinkebuzi, ZHOU Ya'nan. The chemical characteristics of the potable natural mineral water and its major components source analysis of the karst area in Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2019, 36(2): 173-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2019.02.010 [40] White W B. Geomorphology and hydrology of karst terrains[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988: 103-1481. [41] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 蓝芙宁, 张连凯, 苏春田. 乌江中上游段河水主要离子化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(5):1779-1787.HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun, LIU Pengyu, LAN Funing, ZHANG Liankai, SU Chuntian. Major ionic features and their controlling factors in the upper-middle reaches of Wujiang river[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(5): 1779-1787. [42] 李军, 刘丛强, 李龙波, 李思亮, 王宝利, B Chetelat. 硫酸侵蚀碳酸盐岩对长江河水DIC循环的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2010, 39(4):305-313.LI Jun, LIU Congqiang, LI Longbo, LI Siliang, WANG Baoli, B Chetelat. The impacts of chemical weathering of carbonate rock by sulfuric acid on the cycling of dissolved inorganic carbon in Changjiang River water[J]. Geochimica, 2010, 39(4): 305-313. [43] Barnes R T, Raymond P A. The contribution of agricultural and urban activities to inorganic carbon fluxes within temperate watersheds[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 266(3): 327-336. [44] Jiang Y. The contribution of human activities to dissolved inorganic carbon fluxes in a karst underground river system: Evidence from major elements and δ13CDIC in Nandong, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2013, 152(4): 1-11. [45] Perrin A S, Probst A, Probst J L. Impact of nitrogenous fertilizers on carbonate dissolution in small agricultural catchements: Implications for weathering CO2 uptake at regional and global scales[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(13): 3105-3123. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.011 [46] Semhi K, Suchet P A, Clauer N, Probst J L. Impact of nitrogen fertilizers on the natural weathering-erosion processes and fluvial transport in the Garonne basin[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(6): 865-878. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00076-1 [47] Cartwright I. The origins and behaviour of carbon in a major semiarid river, the Murray River, Australia, as constrained by carbon isotopes and hydrochemistry[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(11): 1734-1745. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.08.020 [48] Li S L, Calmels D, Han G, Gaillardet J R, Liu C Q. Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by δ13CDIC: Examples from Southwest China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 270(3): 189-199. [49] 刘丛强, 蒋颖魁, 陶发祥, 郎赟超, 李思亮. 西南喀斯特流域碳酸盐岩的硫酸侵蚀与碳循环[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(4): 404-414.LIU Congqiang, JIANG Yingkui, TAO Faxiang, LANG Yunchao, LI Siliang. Chemical weathering of carbonate rocks by sulfuric acid and the carbon cycling in Southwest China[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(4): 404-414. -




 下载:
下载: