Spectral characteristics and indication of dissolved organic matter in the karst water system of Jinan
-
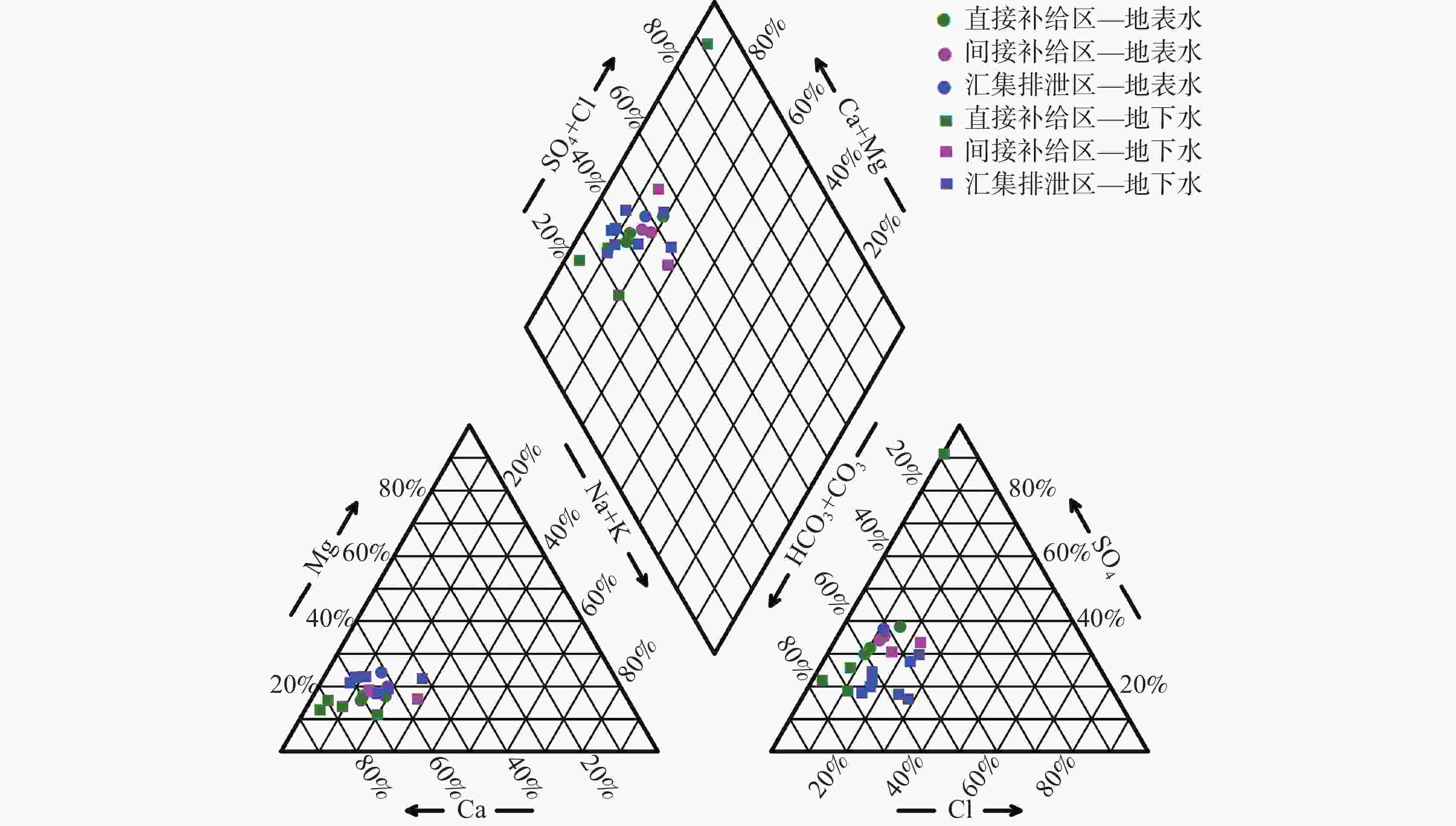
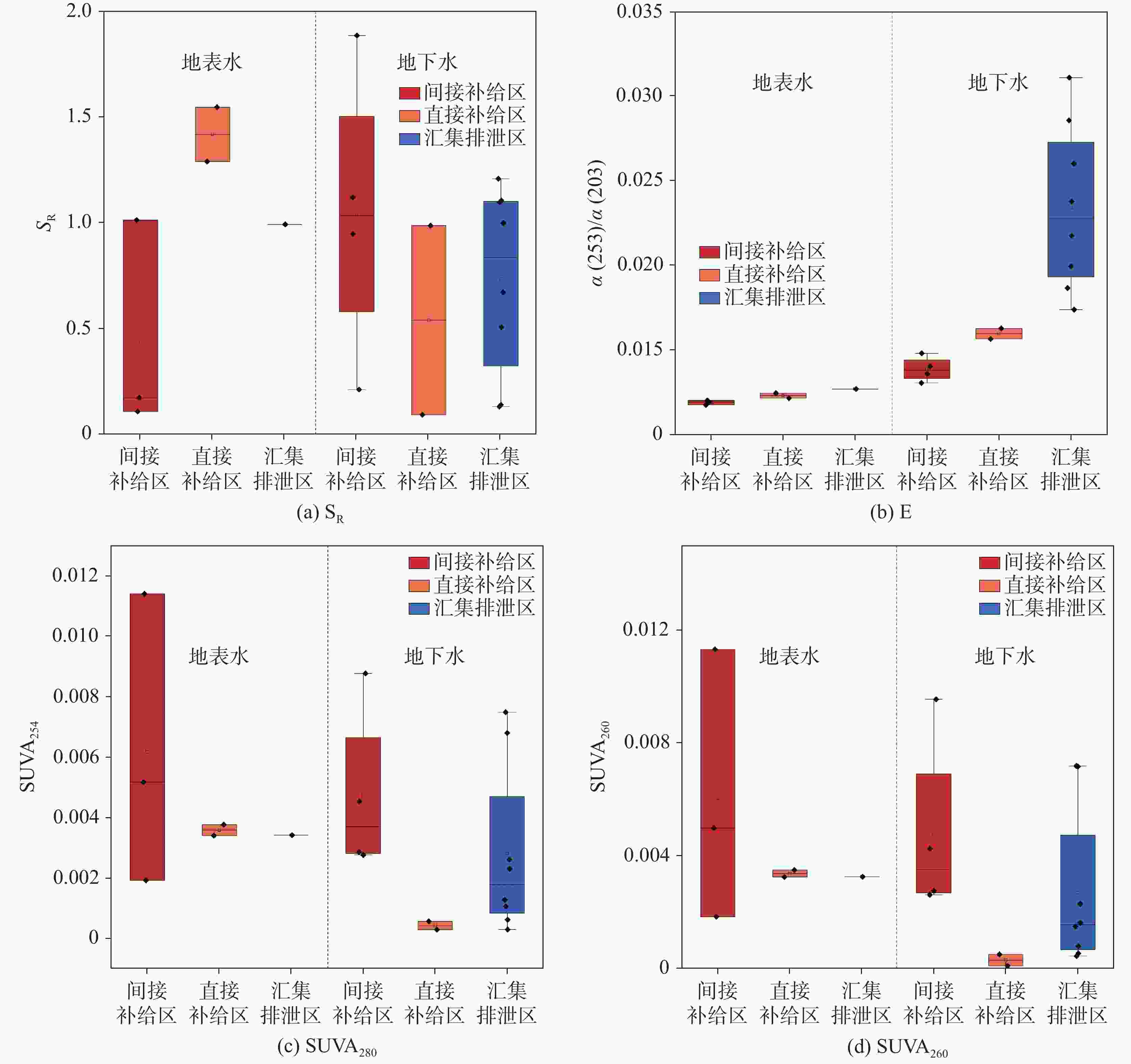
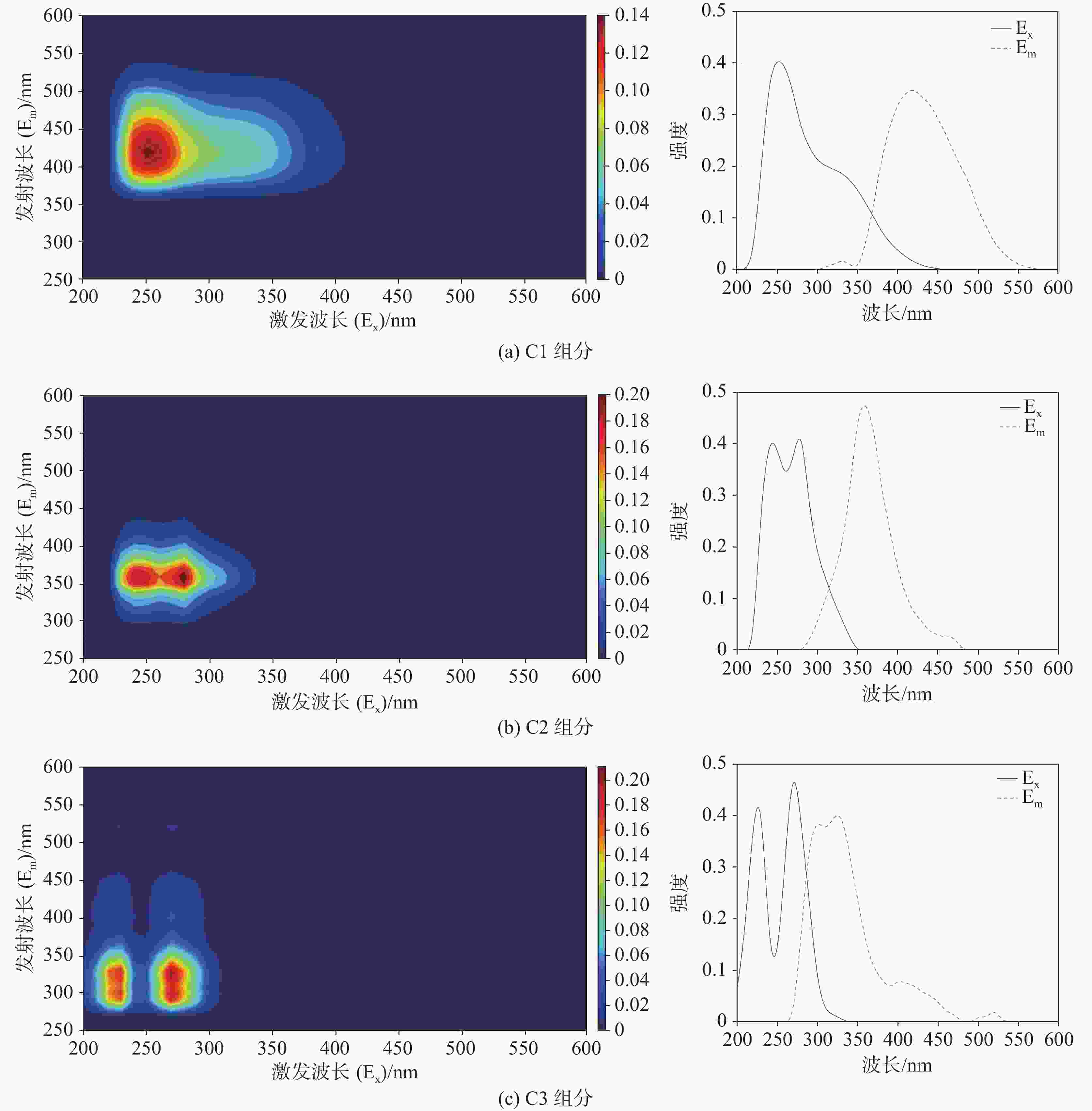
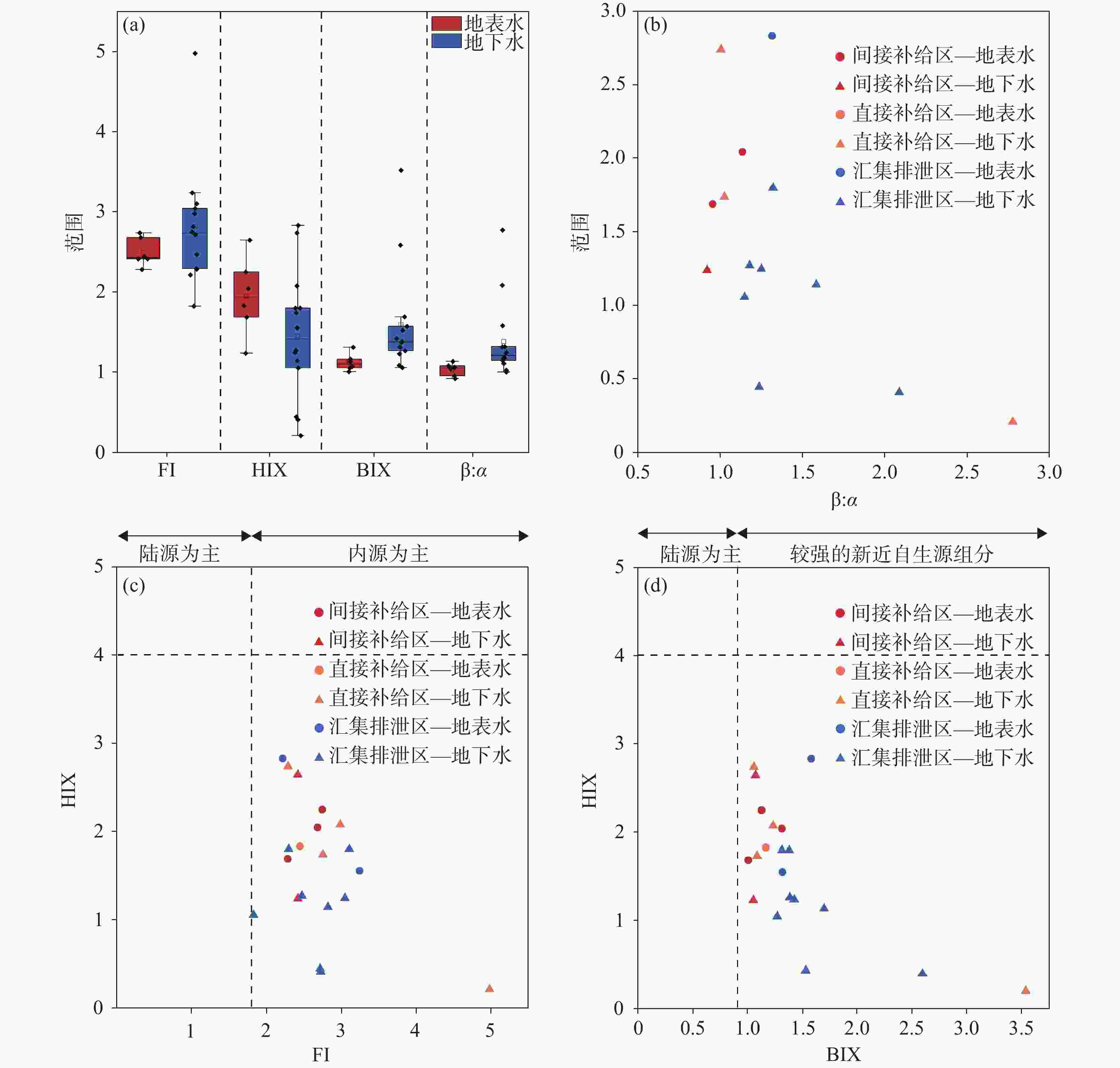
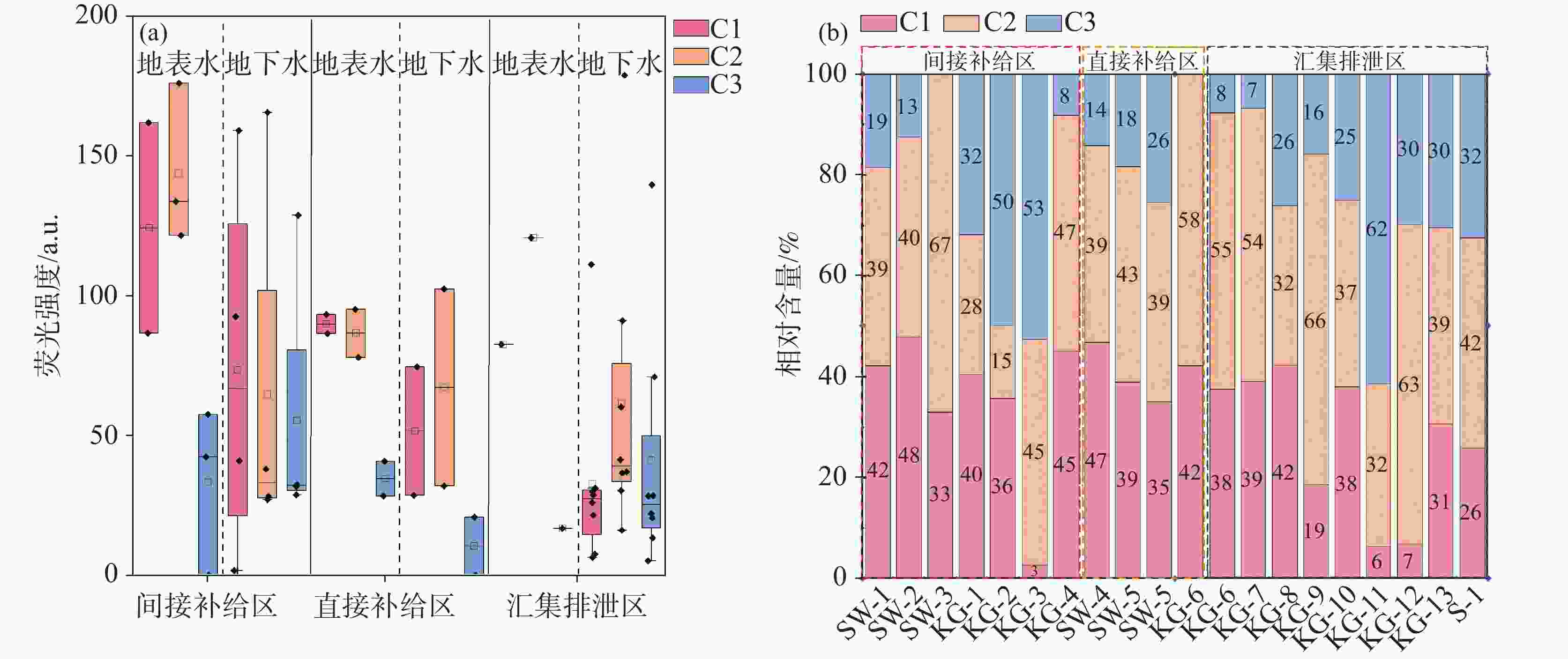
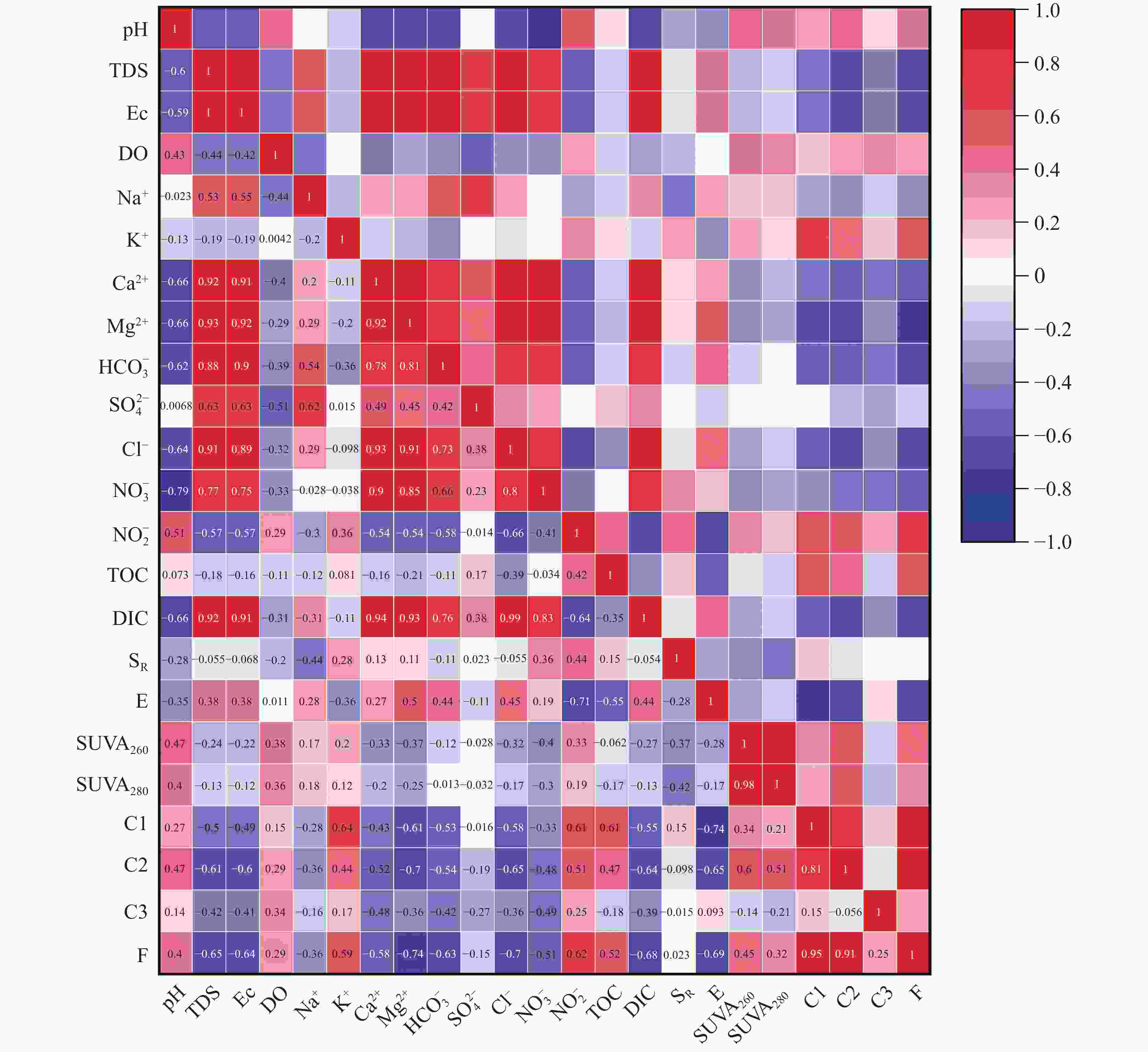
摘要: 选取济南泉域岩溶水系统为研究对象,在分析水化学特征的基础上,采用紫外—可见光光谱、三维荧光光谱和平行因子分析方法,识别岩溶水系统中溶解性有机质(DOM)的组分、来源及其空间分布特征,探讨影响DOM分布特征的控制因素及其指示作用。结果表明:识别出的岩溶水系统中3种主要荧光组分分别为腐殖质物质、类蛋白色氨酸和类蛋白酪氨酸,间接补给区以腐殖质物质组分为主(31%),直接补给区和汇集排泄区以类蛋白色氨酸物质为主(48.5%和45.6%)。岩溶地下水DOM处于弱腐殖化水平,在微生物活动影响下以内源输入为主。腐殖质物质与TDS、Ec、K+、Mg2+等水化学指标显著相关;类蛋白色氨酸、类蛋白酪氨酸与微生物作用关系密切,可作为评价岩溶水系统生态及脆弱性的指标。Abstract:
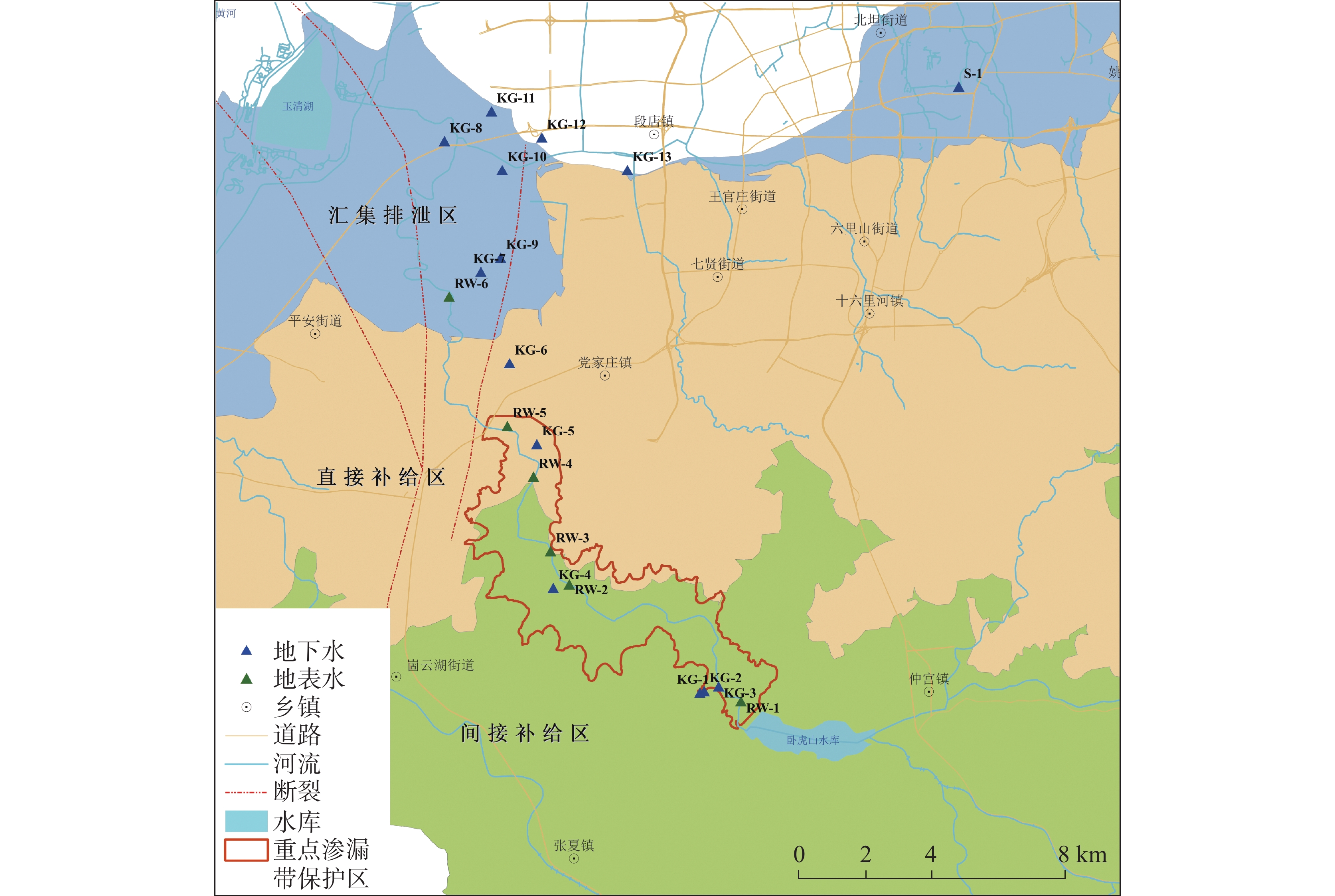
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in the biochemical cycle of karst water systems. In this paper, the karst water system of Jinan spring, a typical karst area in North China as well as an important source of drinking water in Jinan, was selected as the research area. In the southern part of the area, the metamorphic rocks of the Taishan Group of Archean Eonothem are exposed. The carbonate rock strata of the Cambrian and Ordovician, which incline toward the north with monoclinic structures and are hidden under the Quaternary in the north part, are located above the metamorphic rocks. The regional groundwater flows from south to north under the control of topography. The main aquifers in the sampling area of this study are the middle Cambrian Zhangxia Formation, the upper Cambrian Fengshan Formation and the Ordovician aquifers, which contain carbonate fissure water with lithology mainly composed of limestone, dolomite limestone and argillaceous limestone. According to the hydrogeological conditions in the source area and the formation process of the source, the study area was successively divided into the indirect recharge area (IRA), direct recharge area (DRA) and discharge area (DA) from south to north. The direct recharge area can directly be recharged by surface water leakage. In the indirect recharge area, recharged by atmospheric precipitation, surface water and groundwater flows into the direct recharge area in the form of surface and subsurface runoffs. Groundwater was blocked by magmatic rocks in the north, and fissures were developed in the contact zone between aquifers and the magmatic rocks, where karst groundwater rose and was exposed, and springs came into being. This study aims to investigate the spectral characteristics, spatial distribution and indicator of DOM in karst groundwater in recharge, runoff and discharge areas at a spring-area scale. The composition, source and spatial distribution in the karst water system of Jinan spring were analyzed by absorption spectrum, fluorescence spectrum and PARAFAC, combined with water chemical index and correlation analysis. In this study, three main fluorescence components have been identified in the Jinan spring area, namely, C1, C2 and C3, which are humus, protein-like tryptophan and protein-like tyrosine, respectively. Groundwater in the indirect recharge area is dominated by humic substances in low molecular weight, while groundwater in the direct recharge area and the confluence and discharge area are dominated by protein-like substances. In these two areas, the change in protein-like substances caused by microbial activities is the main driving force for the change in geochemical characteristics of DOM. The order of endogenous contributions is DA>DRA>IRA, which is consistent with the order of water circulation quantity in the karst water system. In this karst water system, aromatic substances are mainly present in hydrophobic components. The humus component C1 is an exogenous input, and is significantly positively correlated with the protein-like tryptophan component C2. These two components from different sources are subject to the same factors. The protein-like tyrosine component C3 has no obvious correlation with all indices. The humus component C1 and the total fluorescence intensity can be used as natural indicators to trace the karst water cycle. Besides, the protein-like tryptophan C2 and the protein-like tyrosine C3 may provide important biogeochemical information to evaluate the vulnerability of karst aquifers. -
表 1 主要现场理化指标和DOC浓度
Table 1. Main on-site physical and chemical indicators and DOC concentrations
类型 编号 pH TDS/mg·L−1 Ec/μs·cm−1 DO/mg·L−1 DOC/mg·L−1 地表水 间接补给区 SW-1 7.95 298 588 6.99 5.67 SW-2 8.02 279 550 7.63 11.20 SW-3 8.28 283 553 7.76 4.56 直接补给区 SW-4 8.07 272 540 7.02 4.90 SW-5 8.06 233 458 6.91 8.45 汇集排泄区 SW-6 8.05 197 396 7.02 10.30 地下水 间接补给区 KG-1 7.50 420 813 7.31 5.51 KG-2 7.92 270 539 7.38 4.90 KG-3 7.86 2421 4137 7.79 2.67 KG-4 7.63 175 342 6.44 7.31 直接补给区 KG-5 7.93 401 786 5.45 5.52 KG-6 7.72 446 872 5.08 10.40 汇集排泄区 KG-7 7.38 496 992 7.11 7.32 KG -8 7.71 369 688 6.18 4.09 KG-9 7.89 319 628 6.69 3.59 KG-10 7.52 506 972 6.20 3.78 KG-11 7.78 266 524 7.23 2.76 KG-12 8.01 266 526 7.52 4.62 KG-13 7.87 427 846 7.14 4.50 S-1 7.86 703 1239 6.79 2.46 -
[1] Beck A J, Jones K C, Hayes M B H, Mingelgrin U. Organic substances in soil and water: Natural constituents and their influence on contaminant behavior[M]. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry, 1993. [2] 徐长栋. 台湾绿岛热泉和钱塘江水体溶解性有机物的三维荧光特性与时空变化研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017.XU Changdong. The study on three-dimensional fluorescent characteristics and temporal/spatial variations of dissolved organic matter in the hot spring in Green island, Taiwan and Qiantang River[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. [3] 洪晨飞, 崔正国, 白莹, 江涛, 胡清静, 周明莹, 李玉, 曲克明. 莱州湾荧光溶解有机物的时空分布[J]. 海洋科学, 2022, 46(6):15-31.HONG Chenfei, CUI Zhengguo, BAI Ying, JIANG Tao, HU Qingjing, ZHOU Mingying, LI Yu, QU Keming. Spatial and temporal distribution of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in Laizhou bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2022, 46(6): 15-31. [4] 陈雪霜. 三峡库区内陆腹地典型水库型湖泊:长寿湖水体溶解性有机质(DOM)的光谱学特征[D]. 重庆:西南大学, 2017.CHEN Xueshuang. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in Changshou lake: A typical inland reservoir of Three Gorges Region[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017. [5] Patel Sorrentino N, Mounier S, Benaim J Y. Excitation-emission fluorescence matrix to study pH influence on organic matter fluorescence in the Amazon basin rivers[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(10): 2571-2581. [6] 陈永娟, 胡玮璇, 庞树江, 王晓燕. 北运河水体中荧光溶解性有机物空间分布特征及来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(8):3017-3025.CHEN Yongjuan, HU Weixuan, PANG Shujiang, WANG Xiaoyan. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of dissolved organic matter in Beiyun river[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(8): 3017-3025. [7] 张连凯, 刘朋雨, 覃小群, 单晓静, 刘文, 赵振华, 姚昕, 邵明玉. 溶解性有机质在岩溶水系统中的迁移转化及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(5):2104-2116.ZHANG Liankai, LIU Pengyu, QIN Xiaoqun, SHAN Xiaojing, LIU Wen, ZHAO Zhenhua, YAO Xin, SHAO Mingyu. Migration and transformation of dissolved organic matter in karst water system and an analysis of their influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(5): 2104-2116. [8] 傅平青, 刘丛强, 吴丰昌. 三维荧光光谱研究溶解有机质与汞的相互作用[J]. 环境科学, 2004, 25(6):140-144.FU Pingqing, LIU Congqiang, WU Fengchang. Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of the complexation between mercury (Ⅱ) and dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(6): 140-144. [9] Coble P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325-346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3 [10] Liang Y P, Gao X B, Zhao C H, Tang C L, Shen H Y, Wang Z H, Wang Y X. Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(5): 1371-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1792-4 [11] 邢立亭, 周娟, 宋广增, 邢学睿. 济南四大泉群泉水补给来源混合比探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(3):260-272.XING Liting, ZHOU Juan, SONG Guangzeng, XING Xuerui. Mixing ratios of recharging water sources for the four largest spring groups in Jinan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(3): 260-272. [12] Mahler B, Massei N. Anthropogenic contaminants as tracers in an urbanizing karst aquifer[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2007, 91(1): 81-106. [13] Jiang Y J, Yan J. Effects of land use on hydrochemistry and contamination of karst groundwater from Nandong underground river system, China[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2010, 210: 123-141. doi: 10.1007/s11270-009-0229-z [14] 刘丹, 陈学群, 田婵娟, 张文静, 管清花. 岩溶地下水环境微生物信息技术应用研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(2):185-192.LIU Dan, CHEN Xuequn, TIAN Chanjuan, ZHANG Wenjing, GUAN Qinghua. Research review on the application of microbial information technology to karst groundwater environment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(2): 185-192. [15] Lapworth D J, Gooddy D C, Allen D, Old G H. Understanding groundwater, surface water, and hyporheic zone biogeochemical processes in a Chalk catchment using fluorescence properties of dissolved and colloidal organic matter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 2009, 114: 1-10. [16] 何伟, 白泽琳, 李一龙, 刘文秀, 何玘霜, 杨晨, 杨斌, 孔祥臻, 徐福留. 溶解性有机质特性分析与来源解析的研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2):359-372.HE Wei, BAI Zelin, LI Yilong, LIU Wenxiu, HE Qishuang, YANG Chen, YANG Bin, KONG Xiangzhen, XU Fuliu. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 359-372. [17] Baker A, Lamont Black J. Fluorescence of dissolved organic matter as a natural tracer of ground water[J]. Groundwater, 2001, 39(5): 745-750. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2001.tb02365.x [18] Lapworth D J, Gooddy D C, Allen D, Old G H. Understanding groundwater, surface water, and hyporheic zone biogeochemical processes in a Chalk catchment using fluorescence properties of dissolved and colloidal organic matter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2009, 114: G00F02. [19] Cruz F W, Karmann I, Magdaleno G B, Coichev N, Viana O. Influence of hydrological and climatic parameters on spatial-temporal variability of fluorescence intensity and DOC of karst percolation waters in the Santana Cave System, Southeastern Brazil[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 302(1-4): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.012 [20] 姚昕, 邹胜章, 夏日元, 许丹丹, 姚敏. 典型岩溶水系统中溶解性有机质的运移特征[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(5):1766-1772.YAO Xin, ZOU Shengzhang, XIA Riyuan, XU Dandan, YAO Min. Dissolved organic matter (DOM) dynamics in karst aquifer systems[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(5): 1766-1772. [21] 刘渝港, 贺秋芳, 沈立成, 范佳鑫. 洞穴溶解有机质组分和循环过程的季节变化特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3):456-471.LIU Yugang, HE Qiufang, SHEN Licheng, FAN Jiaxin. Seasonal variation characteristics of dissolved organic matter composition and cycle process in caves[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 456-471. [22] Quiers M, Batiot Guilhe C, Bicalho C, Perrette Y, Seidel J L, Van Exter S. Characterisation of rapid infiltration flows and vulnerability in a karst aquifer using a decomposed fluorescence signal of dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(2): 553-561. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2731-2 [23] Hartland A, Fairchild I J, Lead J R, Baker A. Fluorescent properties of organic carbon in cave dripwaters: Effects of filtration, temperature and pH[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(23): 5940-5950. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.040 [24] Wu X C, Li C S, Sun B, Geng F Q, Lv M H, Ma X Y, Li H, Xing L T. Groundwater hydrogeochemical formation and evolution in a karst aquifer system affected by anthropogenic impacts[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42: 2609-2626. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00450-z [25] 王开然, 吴振, 傅世东, 仇钰婷, 陈华伟. 济南泉域岩溶水系统水化学演化及成因分析[J]. 地球化学, 2023, 52(5):547-558.WANG Kairan, WU Zhen, FU Shidong, QIU Yuting, CHEN Huawei. Hydrochemical evolution and genesis analysis of karst water system in Jinan spring basin[J]. Geochimica, 2023, 52(5): 547-558. [26] 管清花, 李福林, 王爱芹, 冯平, 田婵娟, 陈学群, 刘丹. 济南市岩溶泉域地下水化学特征与水环境演化[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):653-662.GUAN Qinghua, LI Fulin, WANG Aiqin, FENG Ping, TIAN Chanjuan, CHEN Xuequn, LIU Dan. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of karst spring groundwater system in Jinan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 653-662. [27] Chen X Q, Guan Q H, Li F L, Liu D, Han C H, Zhang W J. Study on the ecological control line in the major leakage area of Baotu spring in Shandong Province, Eastern China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 133: 108467. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108467 [28] 管清花, 汪玉静, 陈学群, 曾桂华, 辛光明. 济南玉符河重点渗漏带岩溶地下水补给特征与保护[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(2):233-244.GUAN Qinghua, WANG Yujing, CHEN Xuequn, ZENG Guihua, XIN Guangming. Recharge characteristics and protection of karst groundwater in major leakage area of Yufu river in Jinan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(2): 233-244. [29] 荣倩. 玉符河强渗漏带黄河水回灌过程中含水层堵塞研究[D]. 济南:济南大学, 2017.RONG Qian. Study on the aquifer clogging along with the groundwater recharge by the Yellow River water in the strong leakage area of the Yufu river[D]. Jinan: Jinan University, 2017. [30] Stedmon C A, Markager S. Resolving the variability in dissolved organic matter fluorescence in a temperate estuary and its catchment using PARAFAC analysis[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2005, 50(2): 686-697. [31] 高洁, 江韬, 李璐璐, 陈雪霜, 魏世强, 王定勇, 闫金龙, 赵铮. 三峡库区消落带土壤中溶解性有机质(DOM)吸收及荧光光谱特征[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1):151-162.GAO Jie, JIANG Tao, LI Lulu, CHEN Xueshuang, WEI Shiqiang, WANG Dingyong, YAN Jinlong, ZHAO Zheng. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) and fluorescence spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soils of water-level fluctuation zones of the Three Gorges Reservior region[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1): 151-162. [32] Murphy K R, Hambly A, Singh S, Henderson R K, Baker A, Stuetz R, Khan S J. Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: Kard a unified PARAFAC model[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(7): 2909-2916. [33] Song K S, Shang Y X, Wen Z D, Jacinthe P A, Liu G, Lyu L L, Fang C. Characterization of CDOM in saline and freshwater lakes across China using spectroscopic analysis[J]. Water Research, 2019, 150: 403-417. [34] 朱裕强. 西安市典型时期水体中DOM的组成特征、紫外荧光光谱特性及来源分析[D]. 西安:西安建筑科技大学, 2022.ZHU Yuqiang. Analysis of DOM composition characteristics, spectral characteristics and source analysis of water bodies in Xi'an during the typical period[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2022. [35] Zhou L, Zhou Y Q, Hu Y, Cai J, Liu X, Bai C R, Tang X M, Zhang Y L, Jang K S, Spencer R G M. Microbial production and consumption of dissolved organic matter in glacial ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.048 [36] 白梅, 刘志彬, 詹良通, 范占煌, 元妙新, 刘朱. 氧气微纳米气泡曝气异位修复渗滤液污染地下水效果研究[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版, 2023, 56(1):18-26.BAI Mei, LIU Zhibin, ZHAN Liangtong, FAN Zhanhuang, YUAN Miaoxin, LIU Zhu. Ex-situ remediation of landfill leachate contaminated groundwater by oxygen Micro-Nano-Bubble aeration[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2023, 56(1): 18-26. [37] 谢理, 杨浩, 渠晓霞, 朱元荣, 张明礼, 吴丰昌. 滇池典型陆生和水生植物溶解性有机质组分的光谱分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(1):72-79.XIE Li, YANG Hao, QU Xiaoxia, ZHU Yuanrong, ZHANG Mingli, WU Fengchang. Characterization of water extractable organic matters from the dominant plants in Lake Dianchi by multiple spectroscopic techniques[J]. Research of Environment Science, 2013, 26(1): 72-79. [38] Hudson N, Baker A, Reynolds D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters: A review[J]. River Research and Applications, 2007, 23(6): 631-649. doi: 10.1002/rra.1005 [39] Frank S, Goeppert N, Goldscheider N. Fluorescence-based multi-parameter approach to characterize dynamics of organic carbon, faecal bacteria and particles at alpine karst springs[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615: 1446-1459. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.095 [40] Fellman J B, Hood E, Spencer R G M. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2010, 55(6): 2452-2462. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2452 [41] Simon K S, Pipan T, Ohno T, Culver D C. Spatial and temporal patterns in abundance and character of dissolved organic matter in two karst aquifers[J]. Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 2010, 177(2): 81-92. doi: 10.1127/1863-9135/2010/0177-0081 [42] Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond J M, Parlanti E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(6): 706-719. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002 [43] 姚振兴, 孙韶华, 李昂臻, 王明泉, 董露露, 赵清华, 贾瑞宝. 济南玉符河人工补源地表水和周边地下水的水质特征[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(9):2908-2918.YAO Zhenxing, SUN Shaohua, LI Angzhen, WANG Mingquan, DONG Lulu, ZHAO Qinghua, JIA Ruibao. Study on quality characteristics of artificial supplementary surface water and surrounding groundwater in Yufuhe river Jinan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(9): 2908-2918. -




 下载:
下载: