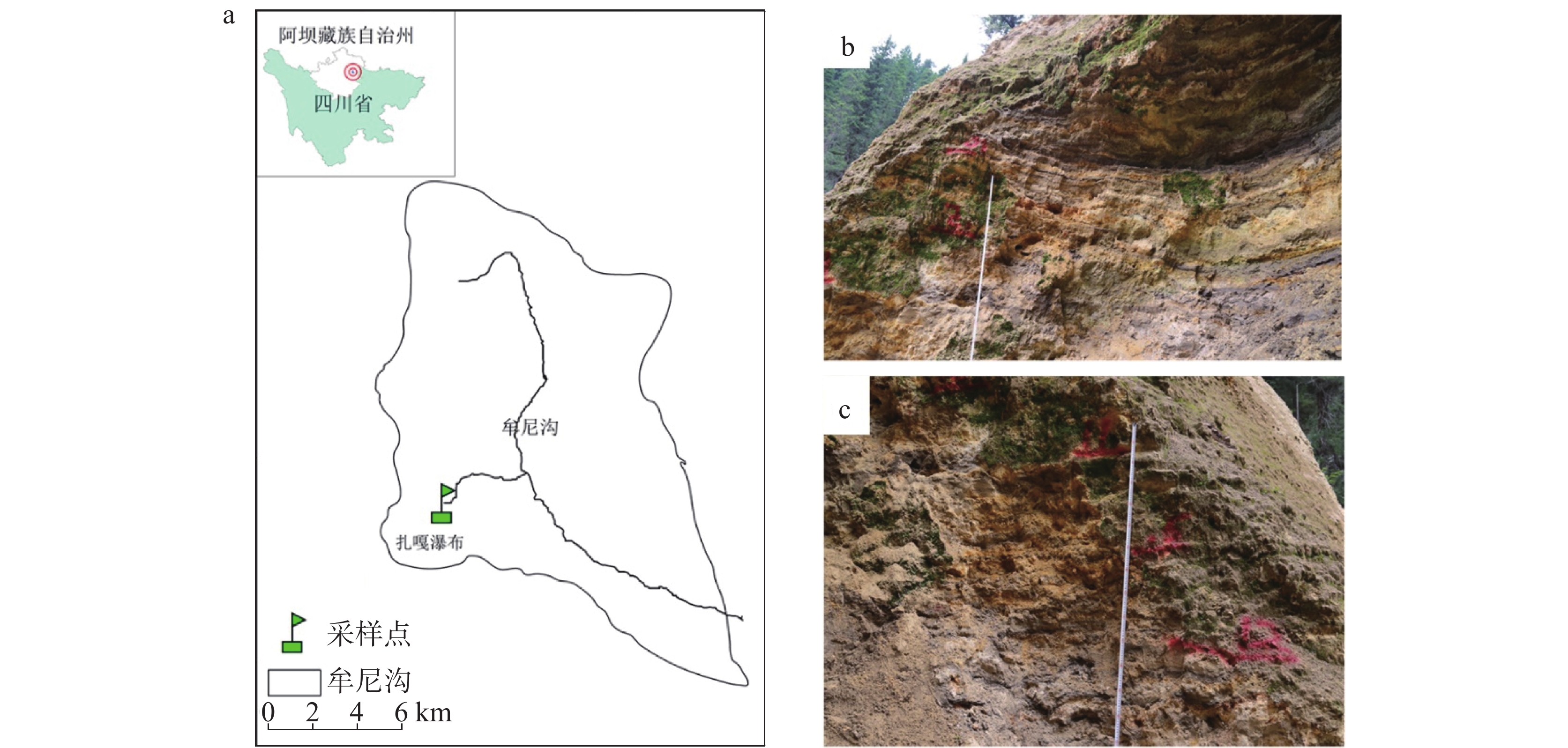
Characteristics of travertine profiles and their environmental indications in Munigou, Sichuan, China
-
摘要: 钙华沉积物记录着重要物理、化学和生物信息,被认为是指示环境变化的重要信息载体。文章选择四川牟尼沟钙华剖面为研究对象,测定钙华沉积物中的有机质、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)和其他化学元素,综合分析牟尼沟钙华剖面特征和环境指示意义。结果表明:有机质、TN、TP含量为294.66~
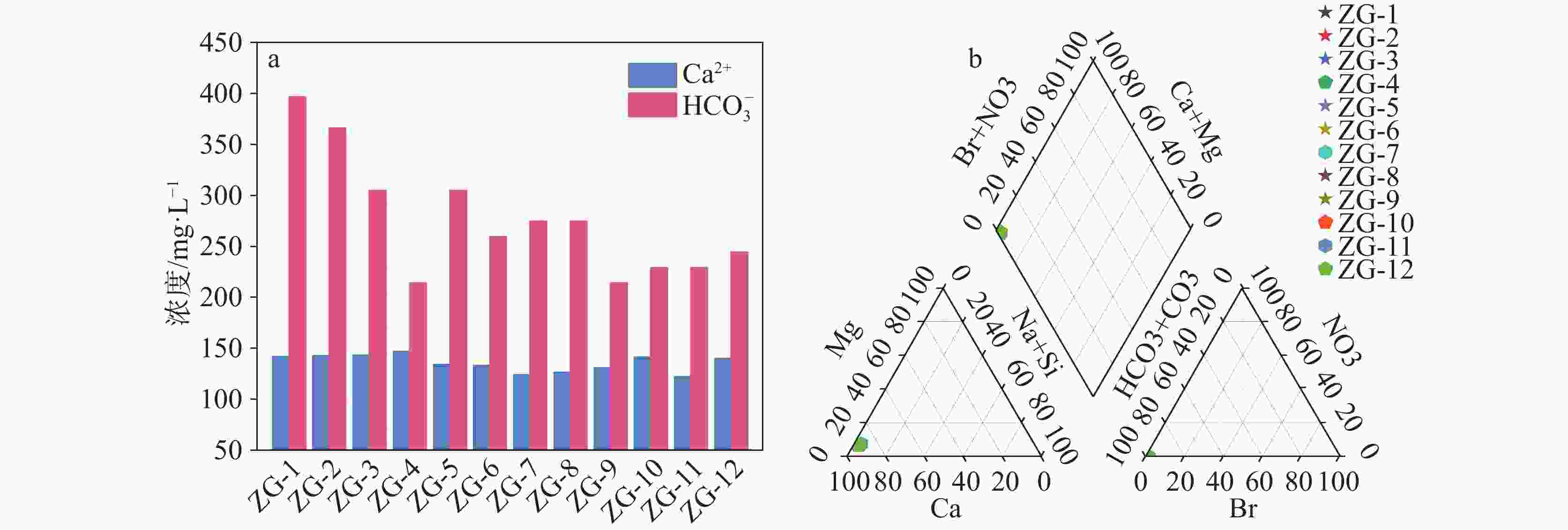
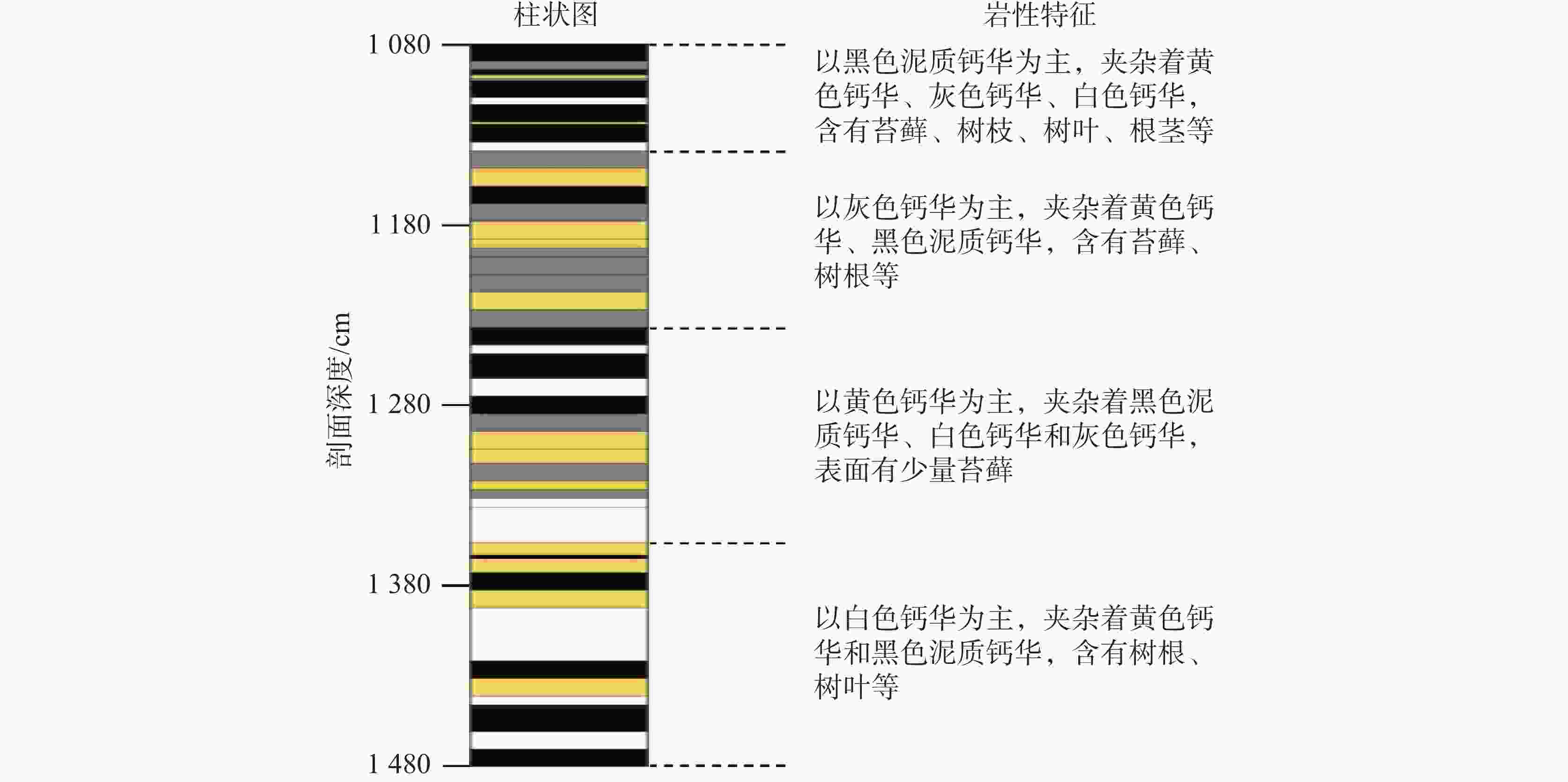
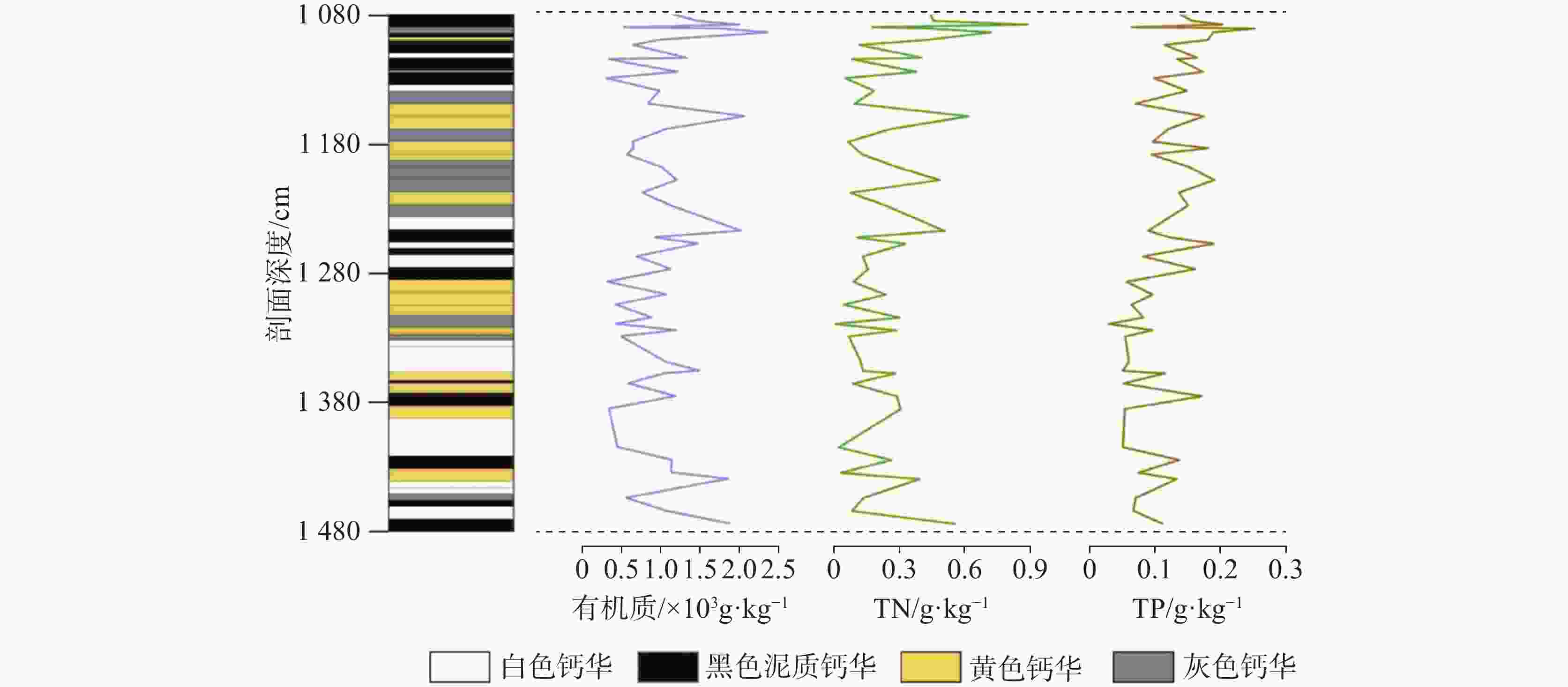
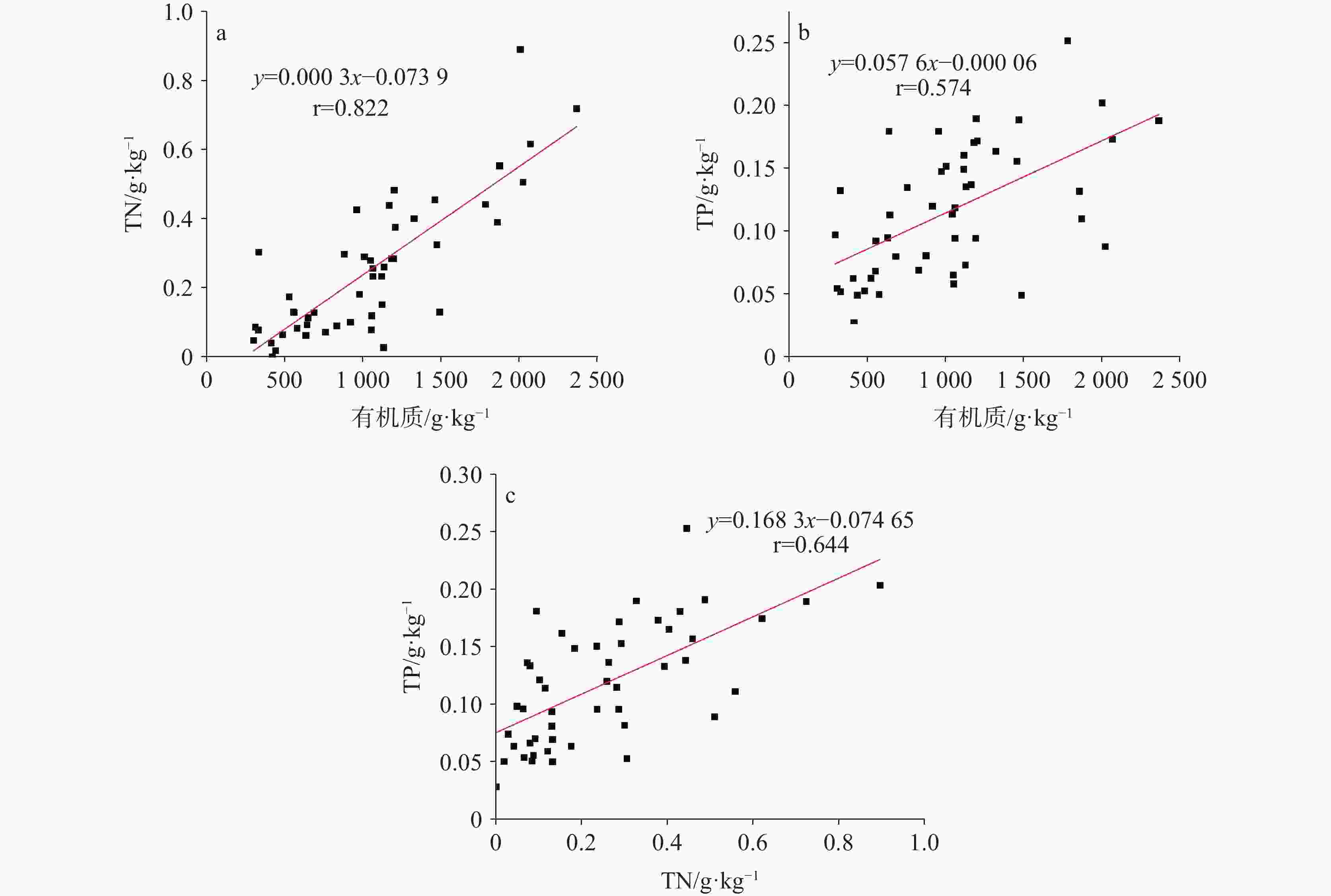
2 366.52 g·kg−1,0~0.89 g·kg−1,0.03~0.25 g·kg−1,在元素含量方面,黑色泥质钙华以SiO2为主,白色钙华、黄色钙华、灰色钙华均以CaO为主,推测黑色泥质钙华沉积于雨季,降水充沛,气候较湿润,而灰色钙华、白色钙华和黄色钙华形成于旱季,降水较少,气候较干冷。Abstract:The travertine profiles are located in the Zhaga waterfall in Munigou, Sichuan Province, where the highest altitude ranges from 4,070 m to 2,800 m, and the average annual temperature is 7℃. The study area is situated in the Minjiang fracture zone, with Paleozoic carbonate construction on the east side of the fracture, and shallow metamorphic rocks and slates of the Middle and Upper Triassic Xikang Group on the west side. Travertine is deposited by the stream fed by karst springs, and the mouth of the spring is located on the left bank of the hook upstream of Zhaga waterfall. The travertine deposits are distributed from the mouth of the spring down to the mouth of the gully. Their depositional patterns fall into striated travertine, clastic travertine, etc., and the type of depositional phase is a dam. The overall travertine profile is about 30-meter thick with horizontal sedimentary construction. In this study, the travertine profiles were investigated in terms of mineralogy and isotope geochemistry. UV spectrophotometry and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy were used to determine the organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and chemical elements in travertine profile sediments so as to comprehensively analyze the characteristics of the travertine profiles and their significance of environmental indications. The results show that the travertine profiles can be divided into four stages based on sedimentary features such as sediment color, texture and inclusions. Stage 1: 1,080–1130 cm, overall dominated by a black muddy travertine layer interspersed with yellow travertine, grey travertine, and white travertine, containing twigs, leaves, and roots; Stage 2: 1,130–1,230 cm, overall dominated by a grey travertine layer interspersed with yellow travertine and black muddy travertine layers containing tree roots; Stage 3: 1,230–1,353 cm, overall dominated by yellow travertine layers interspersed with black muddy travertine, white travertine and grey travertine; Stage 4: 1,353–1,480 cm, overall dominated by a white travertine layer interspersed with yellow travertine and black muddy travertine layers containing roots and leaves. The testing and analysis of the sediments from the travertine profile in Munigou revealed that the overall organic matter content of travertine sediments ranged from 294.66 g·kg−1 to 2,366.52 g·kg−1 with a mean value of 1,031.93 g·kg−1; the TN content ranged from 0 g·kg−1 to 0.89 g·kg−1 with a mean value of 0.25 g·kg−1; the TP content ranged from 0.03 g·kg−1 to 0.25 g·kg−1 with a mean value of 0.12 g·kg−1. In order to fully understand the relationship between organic matter, TN and TP, and to better reveal the environmental characteristics when the travertine was deposited, we carried out Pearson correlation analyses of organic matter, TN and TP, which showed that the organic matter and TN content exhibited a significant correlation (r=0.822, n=48, P<0.01); the organic matter and TP content were positively correlated (r=0.574, n=48, P<0.01); there was a good correlation between TN and TP contents (r=0.644, n=48, P<0.01). Travertine sediments with four different colors at different depths were selected for elemental analysis, and the results showed that the main chemical compositions of the travertine profile were CaO and SiO2, followed by Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, Na2O, and TiO2. The CaO content ranged from 97.79% to 27.51%, with an average value of 70.25%. The SiO2 content ranged from 50.10% to 0.76%, with an average value of 19.52%. CaO is chemically active and easy to migrate. The high CaO activity indicates that it is easily lost under warm and humid conditions, making its content relatively low, and under dry and cold conditions, the weak surface chemical action enriches CaO, making its content high. SiO2 is chemically stable and difficult to migrate; therefore, its high content can indicate much precipitation, warm and wet climate, and its relatively high enrichment, and vice versa. The travertine profiles at 1,080–1,130 cm, 1,250–1,280 cm and 1,460–1,480 cm were dominated by black muddy travertine, with high content of organic matter, TN and TP, and their chemical elements were dominated by SiO2. The environment at the time of travertine deposition is presumed to be of wet climate during the rainy season with abundant precipitation. The travertine profiles at 1,130–1,250 cm and 1,280–1,460 cm were dominated by grey travertine, white travertine and yellow travertine, with low levels of organic matter, TN, TP, and their chemical elements were dominated by CaO. The environment at the time of deposition is presumed to be of a dry season with little precipitation and dry and cold climate. The above conclusions are intended to reveal the environmental conditions of Munigou at the time when travertine was deposited and to lay the foundation for an in-depth study of the ancient environment of Munigou. -
Key words:
- Munigou /
- travertine profile /
- environmental indicators /
- sedimentary environment /
- precipitation
-
表 1 钙华剖面有机质、TN、TP测试结果(g·kg−1)
Table 1. Testing results of organic matter, TN and TP in travertine profiles (g·kg−1)
名称 有机质 TN TP 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 黑色泥质钙华 551.67~ 2 366.52 1 432.37 0.13~0.89 0.43 0.07~0.20 0.15 灰色钙华 306.69~ 1 782.51 1 047.66 0.08~0.48 0.29 0.06~0.25 0.14 黄色钙华 325.57~ 1 487.85 700.50 0.00~0.03 0.11 0.03~0.18 0.08 白色钙华 294.66~ 1 858.73 824.06 0.04~0.39 0.12 0.05~0.13 0.09 表 2 钙华沉积剖面元素测试结果(%)
Table 2. Testing results of elements from travertine deposition profiles (%)
深度/cm CaO SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O TiO2 P2O5 1 094 27.51 50.10 13.18 3.45 1.79 1.42 1.15 0.84 0.22 1 125 33.60 45.80 11.74 3.48 1.78 1.17 1.07 0.83 0.20 1 130 90.66 4.94 1.84 1.53 0.24 0.25 0.15 0.11 0.04 1 220 81.88 10.17 3.98 2.39 0.32 0.40 0.28 0.26 0.08 1 230 71.25 18.98 5.99 1.72 0.74 0.36 0.19 0.49 0.06 1 390 97.27 1.08 0.46 0.81 0.05 0.11 / / 0.02 1 420 97.79 0.76 0.35 0.71 0.03 0.12 / / 0.02 1 440 62.05 24.33 8.06 2.40 1.00 0.61 0.51 0.61 0.11 深度/cm SO3 BaO MnO ZrO2 SrO ZnO Rb2O Y2O3 Cl 烧失量 1 094 0.13 0.08 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 / 17.78 1 125 0.12 0.08 0.05 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 / / 16.59 1 130 0.12 0.06 / 0.01 / / / / / 43.47 1 220 0.13 0.04 / 0.01 0.03 / / / 0.03 31.77 1 230 0.09 0.05 / 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 / 0.01 34.52 1 390 0.11 0.06 / / 0.04 / / / / 23.45 1 420 0.10 0.06 / / 0.04 / / / 0.01 45.25 1 440 0.13 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.04 0.02 0.01 / 0.02 19.20 -
[1] 蒋忠诚, 代群威, 董发勤, 张强, 党政, 汪智军, 刘凡. 国内外钙华岩溶景观的研究进展与展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(1):4-10. doi: 10.11932/karst20210101JIANG Zhongcheng, DAI Qunwei, DONG Faqin, ZHANG Qiang, DANG Zheng, WANG Zhijun, LIU Fan. Review of research progress and prospect of tufa/travertine karst landscape at home and abroad[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(1): 4-10. doi: 10.11932/karst20210101 [2] 胡欣欣, 黄成敏. 钙华成因及其在古环境与古气候重建中的应用[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2008(3):331-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2008.03.025HU Xinxin, HUANG Chengmin. Tufa formation and its application in paleoenvironment and paleoclimate reconstruction[J]. World Science and Technology Research and Development, 2008(3): 331-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2008.03.025 [3] Dabkowski J, Limondin Lozouet N, Antoine P, Andrews J, Marca Bell A, Robert V. Climatic variations in MIS 11 recorded by stable isotopes and trace elements in a French tufa (La Celle, Seine Valley)[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2012, 27(8): 790-799. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2567 [4] Guo Yongqiang, Ge Yonggang, Cui Peng, Chen Xiaoqing, Mao Peini, Liu Tao, Zhou Liang. Early and mid-Holocene hydroclimate change recorded in tufa deposits in the Jiuzhaigou gully, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 104834. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104834 [5] 王华, 覃嘉铭, 安德军, 杨琰, 孙海龙, 林玉山, 杨勋林, 应启和, 张清明. 黄龙钙华210Pb计年与现代沉积的环境变化研究[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(2):216-222.WANG Hua, QIN Jiaming, AN Dejun, YANG Yan, SUN Hailong, LIN Yushan, YANG Xunlin, YING Qihe, ZHANG Qingming. A study of 210pb dating and climatic changes of modern sediments from tufa in Huanglong, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(2): 216-222. [6] Lyu Congcong, Zhao Xueqin, Jiang Yaoxi, Zhu Heyan, Zhang Hongmin, Wang Fudong, Li Qiongfang, Hou Keli. Insights into alpine-karst-type tufa deposits in geological environmental records: A case study of the calcareous tufa profile of the Jiuzhaigou Natural Reserve on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Minerals, 2023, 13(1): 120. doi: 10.3390/min13010120 [7] Andrews J E, Brasier A T. Seasonal records of climatic change in annually laminated tufas: Short review and future prospects[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2005, 20(5): 411-421. doi: 10.1002/jqs.942 [8] 崔杰, 代群威, 王富东, 董发勤, 宋韬, 党政. 四川黄龙地区鲕状钙华包壳粒的发现及其特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(1):125-132. doi: 10.11932/karst20210113CUI Jie, DAI Qunwei, WANG Fudong, DONG Faqin, SONG Tao, DANG Zheng. Discovery and feature of oolitic coated grains of travertine in the Huanglong area, Sichuan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(1): 125-132. doi: 10.11932/karst20210113 [9] 杜磊, 文华国, 罗连超, 董俊玲, 温龙斌, 游雅贤, 王启宇. 陆地热泉钙华:重建古气候历史信息重要载体[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(3):802-821. doi: 10.12029/gc20220309DU Lei, WEN Huaguo, LUO Lianchao, DONG Junling, WEN Longbin, YOU Yaxian, WANG Qiyu. Terrestrial hot-spring travertine: An important window into paleoclimate reconstruction[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(3): 802-821. doi: 10.12029/gc20220309 [10] 周荣军, 蒲晓虹, 何玉林, 黎小刚, 戈天勇. 四川岷江断裂带北段的新活动、岷山断块的隆起及其与地震活动的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(3):285-294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.009ZHOU Rongjun, PU Xiaohong, HE Yulin, LI Xiaogang, GE Tianyong. Recent activity of Minjiang fault zone, uplift of Minshan block and their relations with seismicity of Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2000, 22(3): 285-294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.009 [11] 杨农, 张岳桥, 孟辉, 张会平. 川西高原岷江上游河流阶地初步研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2003, 9(4):363-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2003.04.008YANG Nong, ZHANG Yueqiao, MENG Hui, ZHANG Huiping. Study of the Minjiang river terraces in the western Sichuan plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2003, 9(4): 363-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2003.04.008 [12] 韩建恩, 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 任三绍, 胥彪, 杨志华. 川西岷江松潘段第四纪与新构造运动特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(6):864-881.HAN Jian'en, GUO Changbao, WU Ruian, REN Sanshao, XU Biao, YANG Zhihua. Characteristics analysis of Quaternary and Neotectonic movements from Songpan section, Minjiang upper reaches, western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(6): 864-881. [13] 吴小平, 胡建中. 岷江源地区新构造运动特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(3):430-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.03.007WU Xiaoping, HU Jianzhong. Features of Neotectionic movement in the source area of Minjiang river[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(3): 430-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.03.007 [14] 钱君龙, 张连弟, 乐美麟. 过硫酸盐消化法测定土壤全氮全磷[J]. 土壤, 1990, 1990(5):258-262. [15] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京:中国农业科技出版社, 2000. [16] 魏复盛. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [17] Ford T D, Pedley H M. A review of tufa and travertine deposits of the world[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1996, 41(3-4): 117-175. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(96)00030-X [18] 徐洪飞, 周训, 王蒙蒙, 刘宇, 吴艳秋, 桌琳杨. 云南泸水登埂与玛布温泉形成特征及成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1739-1754. doi: 10.12029/gc20200611XU Hongfei, ZHOU Xun, WANG Mengmeng, LIU Yu, WU Yanqiu, ZHUO Linyang. Characteristics and origin of the Denggeng and Mabu hot spring in Lushui county, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1739-1754. doi: 10.12029/gc20200611 [19] 辜寄蓉, 范晓, 范立学. 黄龙钙华景观影响因素分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(32):10319-10322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2007.32.096GU Jirong, FAN Xiao, FAN Lixue. Analysis on influencing factors of travertine landscape in Huanglong[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(32): 10319-10322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2007.32.096 [20] 刘海生, 周训, 张彧齐, 海阔, 余鸣潇, 谭梦如, 尚子琦. 温泉钙华沉积的影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(1):11-16. doi: 10.11932/karst20200101LIU Haisheng, ZHOU Xun, ZHANG Yuqi, HAI kuo, YU Mingxiao, TAN Mengru, SHANG Ziqi. A brief review on the factors affecting deposition of travertines in hot springs[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1): 11-16. doi: 10.11932/karst20200101 [21] 杨俊义. 九寨沟黄龙地区景观钙华的特征与成因探讨[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2004.YANG Junyi. Characteristics and formation of the travertine in Jiuzhaigou-Huanglong area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2004. [22] 吴泓辰, 王敬富, 杨小红, 陈敬安. 云贵高原湖泊有机碳、氮沉积记录对环境变化和人类活动的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2022, 41(5):1014-1022.WU Hongchen, WANG Jingfu, YANG Xiaohong, CHEN Jing'an. Sediment records of organic carbon and nitrogen in Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau lakes: Implications of environmental changes and anthropogenic activities[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2022, 41(5): 1014-1022. [23] 秦伯强, 张运林, 高光, 朱广伟, 龚志军, 董百丽. 湖泊生态恢复的关键因子分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(7):918-924. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.07.006QIN Boqiang, ZHANG Yunlin, GAO Guang, ZHU Guangwei, GONG Zhijun, DONG Baili. Key factors affecting lake ecological restoration[J]. Progress in Geography, 2014, 33(7): 918-924. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.07.006 [24] 雷能忠, 蒋锦刚, 黄大鹏. 杭埠河流域土壤全氮和有机质的空间变异特征[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2008(2):300-304.LEI Nengzhong, JIANG Jingang, HUANG Dapeng. Spatial variance of total nitrogen and organic matter of soil in Hangbu river watershed[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2008(2): 300-304. [25] 张慧东, 尤文忠, 魏文俊, 周梅. 辽东山区原始红松林土壤理化性质及其与土壤有机碳的相关性分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(1): 76-82.ZHANG Huidong, YOU Wenzhong, WEI Wenjun, ZHOU Mei. Soil physical and chemical properties and correlation with organic carbon in original Korean pine forest in Eastern Liaoning mountainous area[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(1): 76-82. [26] 吴敬禄, 林琳, 刘建军, 高光. 太湖沉积物碳氮同位素组成特征与环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(2):25-30.WU Jinglu, LIN Lin, LIU Jianjun, GAO Guang. Environmental significance and stable isotope signatures from sedimented organic matter in Lake Taihu[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(2): 25-30. [27] 冯晨旭, 董发勤, 代群威, 霍婷婷, Nelson Belzile. 黄龙钙华纹层石特征与成因分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(1):55-63.FENG Chenxu, DONG Faqin, DAI Qunwei, HUO Tingting, Nelson Belzile. Characteristics and genesis of lamina travertine at Huanglong in Sichuan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinca, 2019, 39(1): 55-63. [28] 李玉辉, 郑绵平, 赵小庆, 王海雷. 柴达木盆地达布逊湖北雅丹剖面沉积特征及其环境意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(6):787-794. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.06.009LI Yuhui, ZHENG Mianping, ZHAO Xiaoqing, WANG Hailei. Sedimentary characteristics and environmental significance of Yadan profile in the northern Dabsun lake of Qaidam basin, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2017, 39(6): 787-794. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.06.009 [29] 胡砚泊, Bernd Winnemann, 张永战, 晏达达. 14 ka以来苦海沉积物地球化学记录及其古环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(1):104-114.HU Yanbo, Bernd Winnemann, ZHANG Yongzhan, YAN Dada. Geochemistry record and their environmental implications during the past 14 ka in Kuhai lake, NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(1): 104-114. [30] 金院, 汪勇, 胡洁, 韩瑞超, 项超生. 升金湖沉积物1 000年以来的元素地球化学记录及其水文意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(1):219-232.JIN Yuan, WANG Yong, HU Jie, HAN Ruichao, XIANG Chaosheng. Geochemical element records and hydrological significance of Lake Shengin sediments during the past millennium[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(1): 219-232. [31] Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1-4): 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X [32] 张红敏, 赵学钦, 王富东, 吴昌达, 李松. 四川九寨沟诺日朗瀑布钙华大坝放射性及沉积环境意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(1):157-165. doi: 10.11932/karst20210117ZHANG Hongmin, ZHAO Xueqin, WANG Fudong, WU Changda, LI Song. Radioactivity of Nuorilang waterfall travertine dam in Jiuzhaigou valley, Sichuan Province and its implication for the sedimentary environment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(1): 157-165. doi: 10.11932/karst20210117 -




 下载:
下载: