Spatiotemporal patterns of CO2 efflux fluxes from the outflow of karst underground river: A case study of the Panyang river in Bama, Guangxi
-
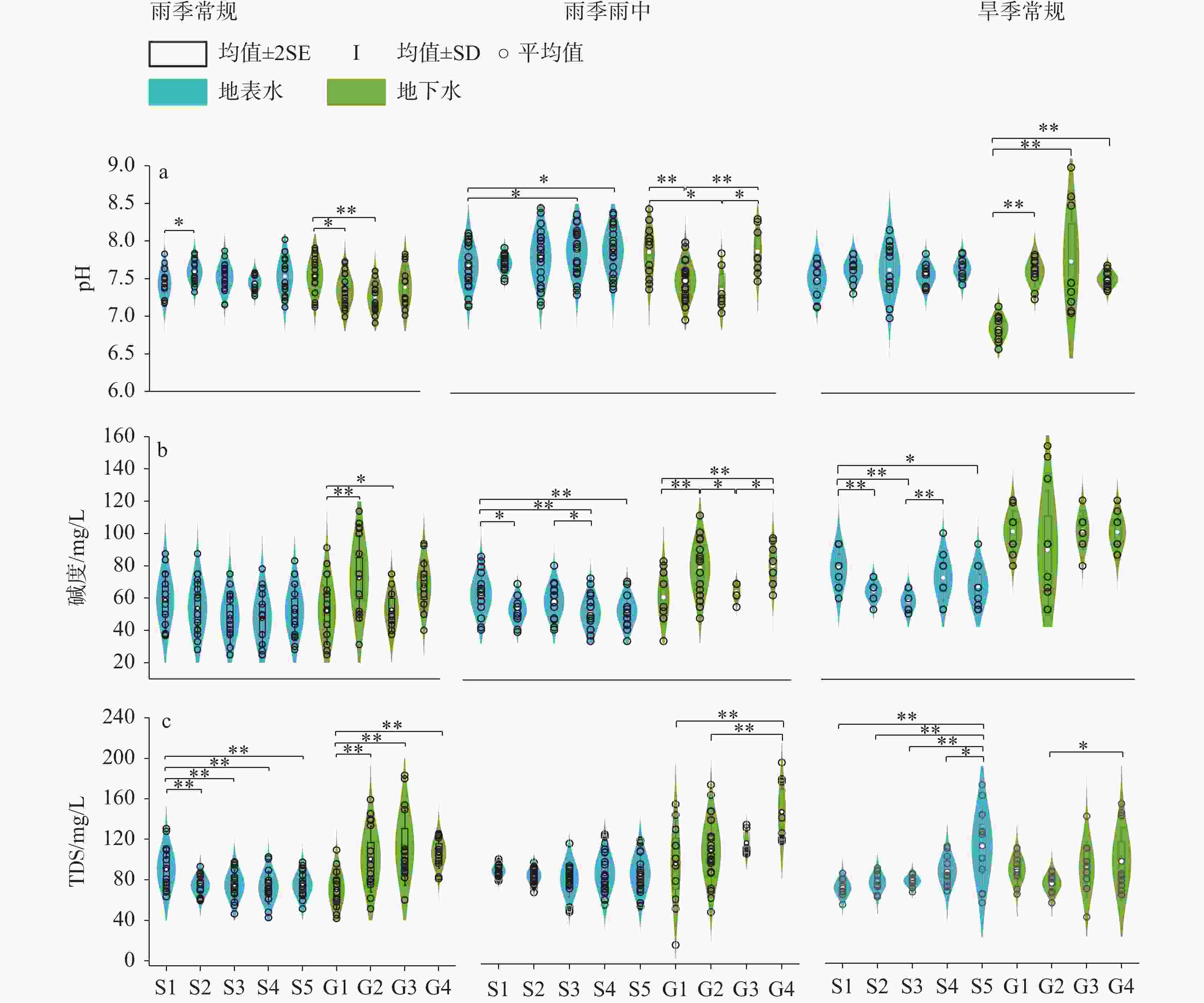
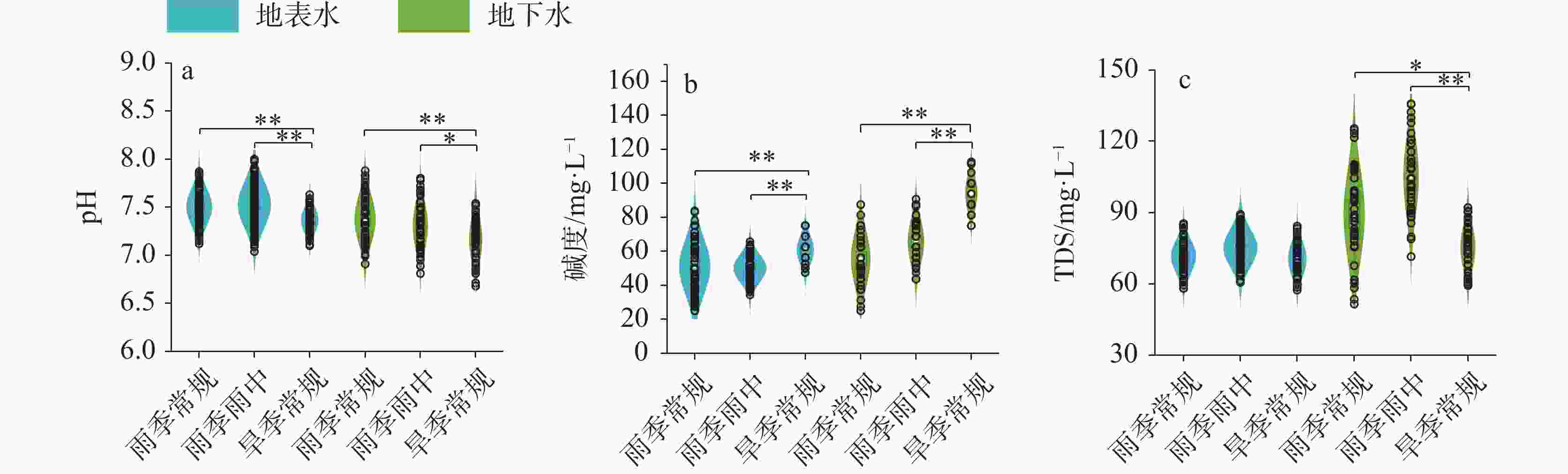
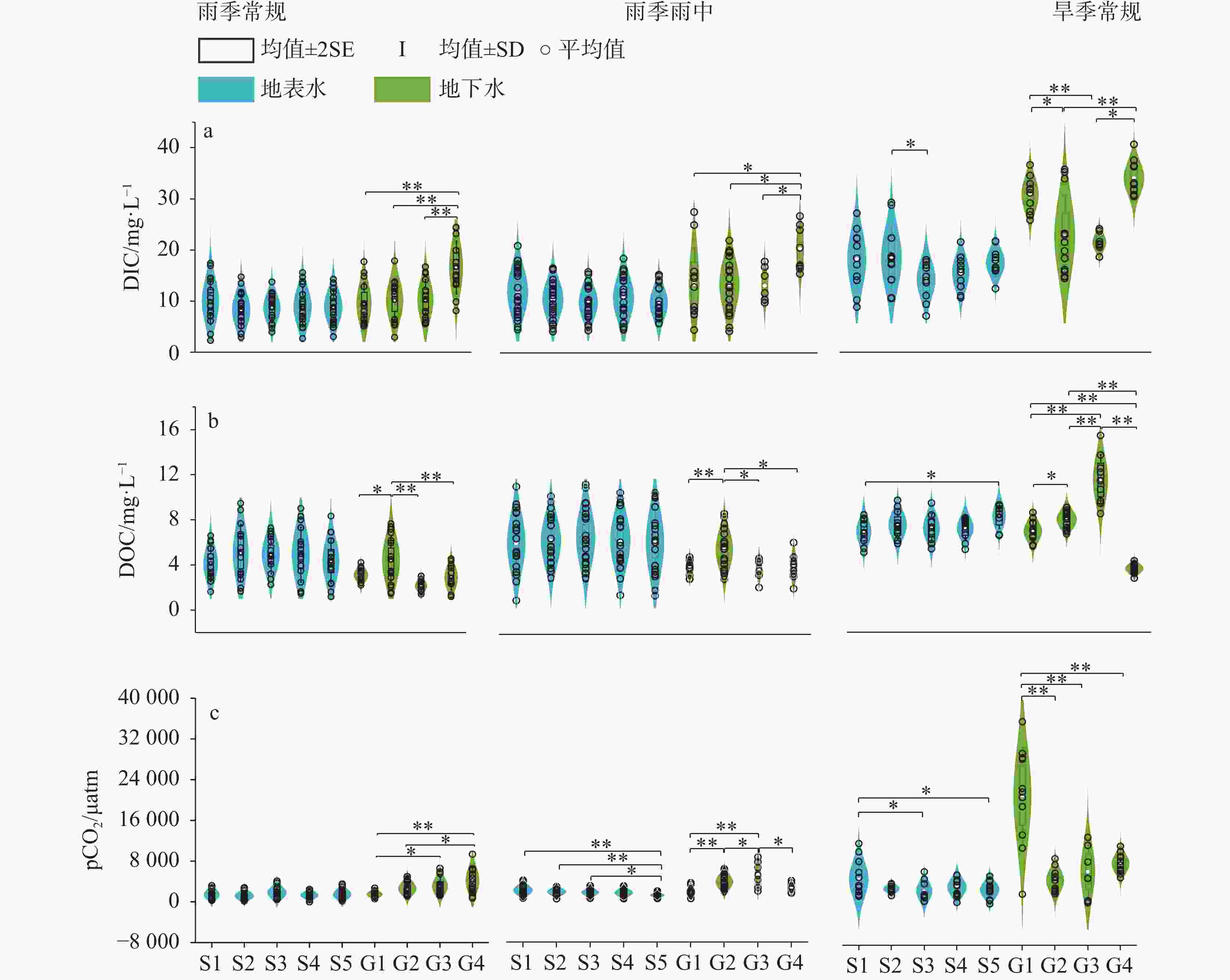
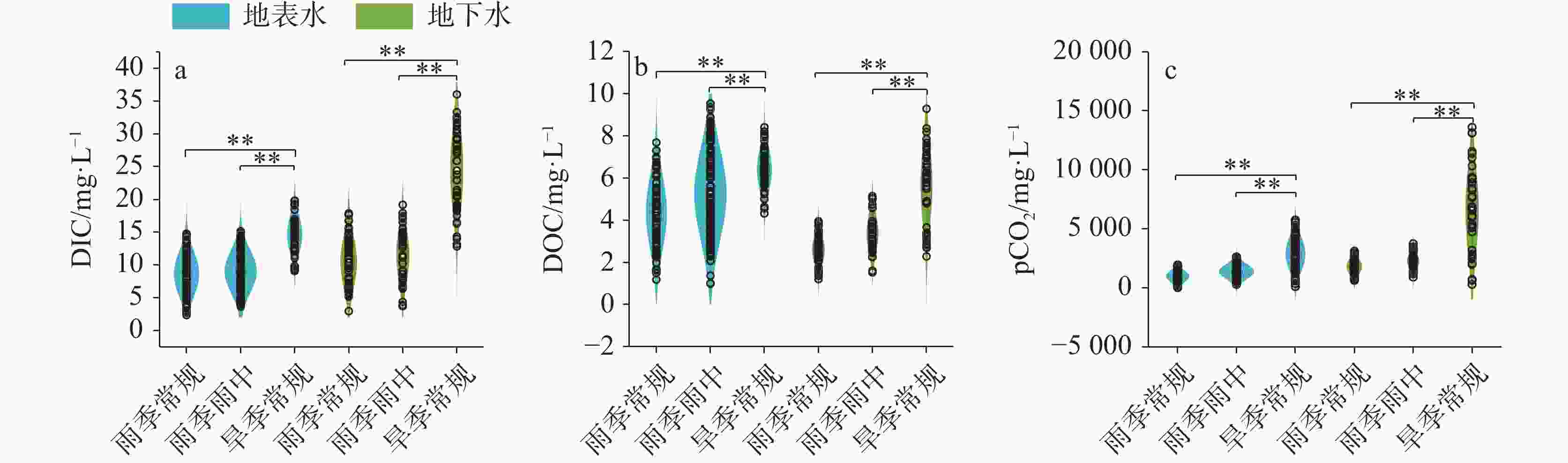
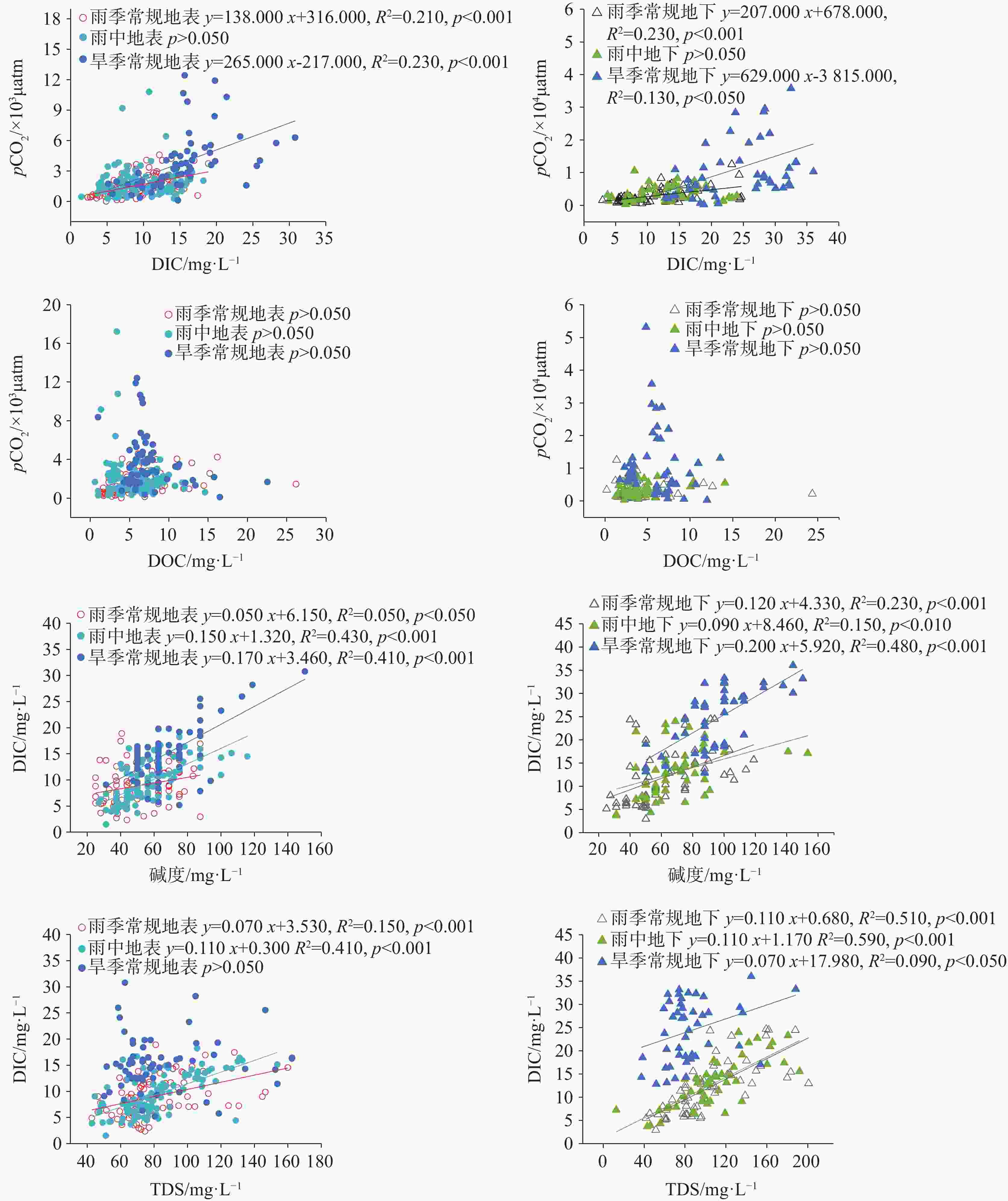
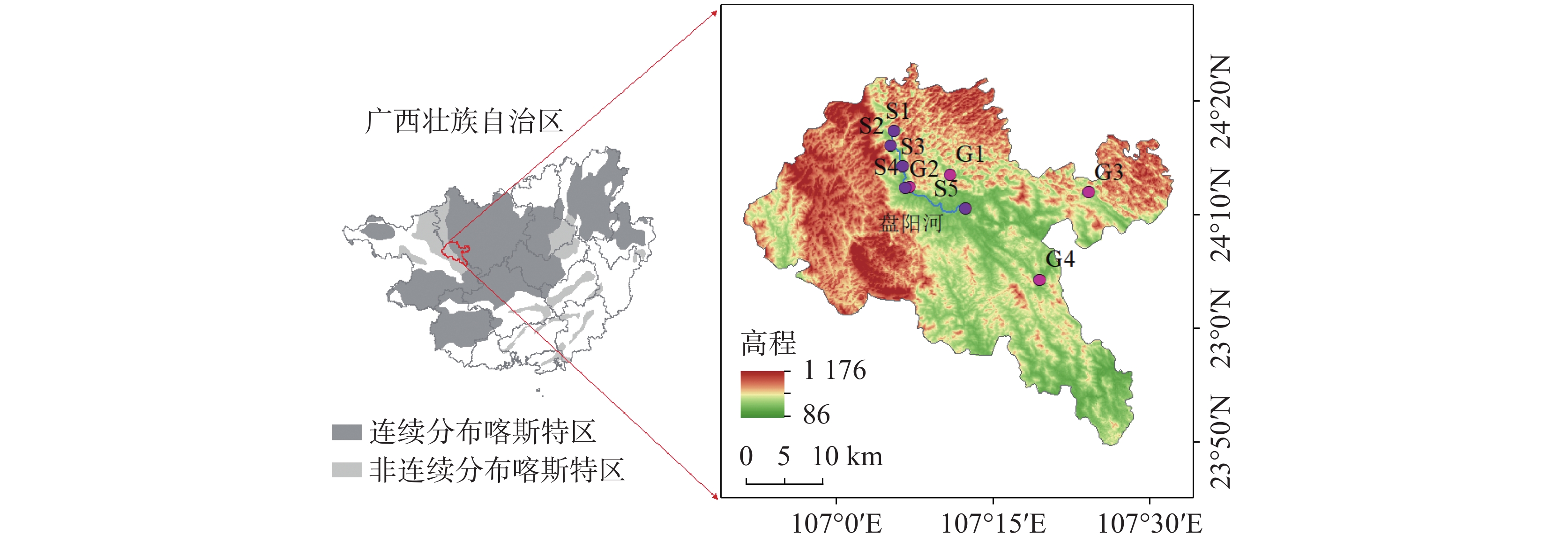
摘要: 喀斯特流域是岩石风化碳汇的关键区域,同时也是CO2逸散研究的热点区域。为探究喀斯特地下河涌出后CO2分压(pCO2)及其逸散通量的时空变化格局,选择喀斯特流域巴马盘阳河为对象,分析水体的pH、碱度、总溶解性固体(TDS)、溶解无机碳(DIC)、溶解有机碳(DOC)、pCO2的时空变化特征,探讨pCO2的调控因素并估算了CO2逸散通量。结果表明,流域内地下水碱度、TDS、DIC和pCO2显著高于地表水,表明喀斯特碳酸盐风化释放大量DIC进入地下水,地下水涌出后产生CO2逸散降低了地表水DIC含量和pCO2。在时间尺度上,旱季常规地表、地下水的碱度、TDS、DIC、pCO2、CO2逸散通量均显著高于雨季,主要归结于雨季雨水的稀释效应。然而次降雨事件下地表、地下水的pH、碱度、TDS、DIC、DOC、pCO2无显著性差异,可能由于降雨量不足或降雨持续时间短。研究期间,巴马盘阳河流域地表水、地下水CO2逸散通量范围分别为−0.10~9.20 kg C m−2 year−1,−0.12~17.28 kg C m−2 year−1,平均CO2逸散通量分别为1.06±1.46 kg C m−2 year−1和2.40±3.14 kg C m−2 year−1,远高于全球主要大型流域的平均CO2逸散通量(0.64 kg C m−2 year−1)。阐明喀斯特流域的CO2逸散通量及其时空变化特征对准确评估河流碳收支状况与评估岩石风化碳汇具有重要意义。Abstract:
Karst basins are key regions for rock weathering and carbon sinks. Because water bodies in karst basins contain high concentrations of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), and can affect carbon cycle through both lateral migration of DIC and vertical efflux of CO2, they become research hotspots for CO2 efflux. Although there have been many studies on CO2 efflux fluxes in karst rivers, our understanding is still limited in terms of the spatiotemporal variations in CO2 efflux fluxes of water bodies from the outflow of karst underground rivers. In order to explore the spatiotemporal patterns of partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2) and CO2 efflux flux from the outflow of karst underground rivers, this study focused on the Panyang river in Bama in the karst area of Southwest China. Monthly routine sampling of surface water and groundwater as well as sampling based on rainfall events was conducted from July 2022 to April 2023. The spatiotemporal variations of pH, alkalinity, total dissolved solids (TDS), DIC, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and pCO2 in both the surface water and underground water were explored. The relationships between DIC, DOC and pCO2, as well as the relationships between TDS, alkalinity, and DIC, were also analyzed. The controlling factors of pCO2 were discussed, and the CO2 efflux flux was estimated. The results showed that alkalinity, TDS, DIC and pCO2 of groundwater in the basin were significantly higher than those of surface water, indicating that karst carbonate weathering released a large amount of DIC into groundwater, and the outflow of groundwater resulted in the CO2 efflux, reducing the DIC content and pCO2 of surface water. There was no significant difference in DIC concentrations and pCO2 of surface water from upstream to downstream, indicating that groundwater could release CO2 into the atmosphere in a short time and quickly reached equilibrium. During the rainy season, DIC and pCO2 of groundwater showed an increasing trend from upstream to downstream, while during the dry season, they showed a decreasing trend, indicating that rock weathering during groundwater recharge is an important source of inorganic carbon in groundwater. Alkalinity, TDS, DIC, pCO2 and CO2 efflux flux of surface water and groundwater during the dry season were significantly higher than those during the rainy season, mainly due to the dilution effect of rainwater during the rainy season. In addition, there were high DOC concentrations during the dry season, and the mineralization of DOC contributed directly to CO2 production, which also led to higher pCO2 in the dry season compared to the rainy season. Overall, there were no significant differences in pH, alkalinity, TDS, DIC, DOC and pCO2 of surface water and groundwater under rainfall events, possibly due to insufficient rainfall or its short duration. However, several samples during rainfall events showed significantly higher pCO2 than in the regular rainy seasons, because the continuous heavy rainfall likely raised the water level of underground rivers and supplied high CO2 concentrations from groundwater to surface rivers. There was no significant correlation between DOC and pCO2, possibly because the carbon input from other sources disrupted the coupling relationship between DOC and pCO2. These sources include soil CO2, organic carbon synthesized by CO2 that was absorbed by photosynthesis of plants, and human activities. A large amount of carbonate and other salt-based ions released from carbonate rocks into groundwater through dissolution increased DIC content, TDS and alkalinity, which contributed to a significantly positive correlation between DIC and indicators such as alkalinity and TDS. The CO2 efflux flux of surface water in the Panyang river basin during the dry season (2.05 ± 1.89 kg C m−2 year−1) was significantly higher than that during the rainy season (0.40 ± 0.30 kg C m−2 year−1), and the CO2 efflux flux of groundwater during the dry season (4.72 ± 4.15 kg C m−2 year−1) was about 4.6 times higher than that during the rainy season (1.03 ± 0.74 kg C m−2 year−1). During the study period, the CO2 efflux fluxes of surface water and groundwater in the Panyang river basin ranged from -0.10 to 9.20 kg C m−2 year−1 and -0.12 to 17.28 kg C m−2 year−1, with average CO2 efflux fluxes of 1.06 ± 1.46 kg C m−2 year−1 and 2.40 ± 3.14 kg C m−2 year−1, respectively, which were much higher than the average CO2 efflux fluxes of major global river basins (0.64 kg C m−2 year−1). Understanding the CO2 efflux flux and its spatiotemporal variations in karst basins is of great significance for us to accurately assess the carbon budget of rivers and to evaluate the role of rock weathering as a carbon sink. -
Key words:
- karst spring /
- dissolved inorganic carbon /
- river CO2 partial pressure /
- CO2 efflux flux.
-
表 1 盘阳河流域各个采样点的CO2逸散通量
Table 1. Dissolved CO2 efflux flux at various sampling points in the Panyang river basin
采样点 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 G1 G2 G3 G4 旱季常规 3.08±2.98 1.74±0.86 1.83±1.72 1.99±1.47 1.59±1.18 9.55±4.94 3.42±2.66 2.15±2.24 4.76±2.50 雨季常规 0.41±0.36 0.23±0.0.25 0.58±0.44 0.37±0.27 0.51±0.44 0.41±0.25 0.89±0.48 1.29±0.84 1.39±0.80 雨季雨中 0.58±0.38 0.47±0.22 0.43±0.26 0.46±0.34 0.18±0.13 0.47±0.33 1.34±0.66 1.85±1.06 0.93±0.50 全年平均 1.52±2.34 0.82±0.93 1.03±1.24 0.99±1.23 0.90±0.95 4.07±5.46 1.76±2.00 1.60±1.56 2.74±2.37 注: CO2逸散通量单位为kg C m−2 year−1
Note: CO2 efflux flux unit: kg C m−2 year−1 -
[1] Ding Shengjun, Zhou Zhongfa, Dong Hui, Yan Lihui, Shi Liangxing, Huang Jing, Zhang Heng. Spatiotemporal variations of riverine CO2 partial pressure and its effect on CO2 flux at the water−air interface in a small karst river[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 2022, 28(3-4): 135-154. doi: 10.1007/s10498-022-09406-9 [2] Sun Huiguo, Han Jingtai, Zhang Shurong, Lu Xixi. Carbon isotopic evidence for transformation of DIC to POC in the lower Xijiang river, SE China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380-381: 288-296. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.01.018 [3] Hope Diane, Palmer Sheila M, Billett Michael F, Dawson Julian J C. Variations in dissolved CO2 and CH4 in a first-order stream and catchment: An investigation of soil-stream linkages[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2004, 18(17): 3255-3275. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5657 [4] Peter Hannes, Singer Gabriel A, Preiler Christian, Chifflard Peter, Steniczka Gertraud, Battin Tom J. Scales and drivers of temporal pCO2 dynamics in an Alpine stream[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2014, 119(6): 1078-1091. doi: 10.1002/2013JG002552 [5] Lynch Janet K, Beatty Cory M, Seidel Matthew P, Jungst Laura J, DeGrandpre Michael D. Controls of riverine CO2 over an annual cycle determined using direct, high temporal resolution pCO2 measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2010, 115(G3). [6] 章程, 肖琼, 孙平安, 高旭波, 郭永丽, 苗迎, 汪进良. 岩溶碳循环及碳汇效应研究与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5):190-198.ZHANG Cheng, XIAO Qiong, SUN Ping'an, GAO Xubo, GUO Yongli, MIAO Ying, WANG Jinliang. Progress on karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effect study and perspective[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 190-198. [7] Zeng Sibo, Liu Zaihua, Chris Groves. Large-scale CO2 removal by enhanced carbonate weathering from changes in land-use practices[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 225: 103915. [8] Lee Kern Y, van Geldernb Robert, Barth Johannes A C. Extreme gradients in CO2 losses downstream of karstic springs[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 778: 146099. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146099 [9] Lee Kern Y, van Geldern Robert, Barth Johannes A C. A high-resolution carbon balance in a small temperate catchment: Insights from the Schwabach River, Germany[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 85: 86-96. [10] Van Geldern Robert, Schulte Peter, Mader Michael, Baier Alfons, Barth Johannes A C. Spatial and temporal variations of pCO2, dissolved inorganic carbon and stable isotopes along a temperate karstic watercourse[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2015, 29(15): 3423-3440. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10457 [11] Brunet F, Dubois K, Veizer J, Nkoue Ndondo G R, Ndam Ngoupayou J R, Boeglin J L, Probst J L. Terrestrial and fluvial carbon fluxes in a tropical watershed: Nyong basin, Cameroon[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 265(3-4): 563-572. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.020 [12] Richey Jeffrey E, Melack John M, Aufdenkampe Anthony K, Ballester Victoria M, Hess Laura L. Outgassing from Amazonian rivers and wetlands as a large tropical source of atmospheric CO2[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6881): 617-620. doi: 10.1038/416617a [13] Dubois Kristal D, Lee Dongho, Veizer Ján. Isotopic constraints on alkalinity, dissolved organic carbon, and atmospheric carbon dioxide fluxes in the Mississippi River[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2010, 115: G02018. [14] Marx A, Dusek J, Jankovec J, Sanda M, Vogel T, van Geldern R, Hartmann J, Barth J A C. A review of CO2 and associated carbon dynamics in headwater streams: A global perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2017, 55(2): 560-585. doi: 10.1002/2016RG000547 [15] Schelker Jakob, Singer Gabriel A, Ulseth Amber J, Hengsberger Sabrina, Battin Tom J. CO2 evasion from a steep, high gradient stream network: Importance of seasonal and diurnal variation in aquatic pCO2 and gas transfer[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2016, 61(5): 1826-1838. doi: 10.1002/lno.10339 [16] Marx Anne, Conrad Marcus, Aizinger Vadym, Prechtel Alexander, van Geldern Robert, Barth Johannes A C. Groundwater data improve modelling of headwater stream CO2 outgassing with a stable DIC isotope approach[J]. Biogeosciences, 2018, 15(10): 3093-3106. doi: 10.5194/bg-15-3093-2018 [17] Xiong Ying, Hou Zhengmeng, Tan Xiucheng, Luo Jiashun, Yue Ye, Wu Kunyu. Constraining fluid-rock interactions during eogenetic karst and their impacts on carbonate reservoirs: Insights from reactive transport modeling[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 131: 105050. [18] Ni Maofei, Li Siyue. Dynamics and internal links of dissolved carbon in a karst river system: Implications for composition, origin and fate[J]. Water Research, 2022, 226: 119289. [19] 覃蔡清, 李思亮, 岳甫均, 丁虎, 徐胜, 刘丛强. 喀斯特关键带溶解性碳的迁移转化过程及其对降雨事件的响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(4):1128-1139.QIN Caiqing, LI Siliang, YUE Fujun, DING Hu, XU Sheng, LIU Congqiang. Biogeochemical processes of dissolved carbon in the karst critical zone and its response to rainstorms[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(4): 1128-1139. [20] 丁虎, 郎赟超, 刘文景, 刘丛强. 桂西北峰丛洼地泉水和溪流在降雨过程中的水化学动态变化特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 39(1):48-55.DING Hu, LANG Yunchao, LIU Wenjing, LIU Congqiang. Variations in chemical composition of spring and stream water during rain events in a karst peak cluster-depression catchment, northwest Guangxi, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(1): 48-55. [21] 罗维均, 王世杰, 刘秀明. 喀斯特洞穴系统碳循环的烟囱效应研究现状及展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(12):1333-1340.LUO Weijun, WANG Shijie, LIU Xiuming. Research progresses and prospect of chimney effect about carbon cycle in the karst cave system[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(12): 1333-1340. [22] 李丽, 蒲俊兵, 李建鸿, 于奭, 肖琼, 张陶. 亚热带典型岩溶溪流水气界面CO2交换通量变化过程及其环境影响[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(7):2487-2495.LI Li, PU Junbing, LI Jianhong, YU Shi, XIAO Qiong, ZHANG Tao. Variations of CO2 exchange fluxes across water-air interface and environmental meaning in a surface stream in subtropical karst area, SW China[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(7): 2487-2495. [23] 邹晨曦. 巴马瑶族自治县盘阳河沿岸风景林改造规划[J]. 绿色科技, 2020, 9(9):111-112, 117.ZOU Chenxi. Transformation planning of Panyang river scenic forest in Bama Yao Autonomous County[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2020, 9(9): 111-112, 117. [24] 覃小群, 蒙荣国, 莫日生. 土地覆盖对岩溶地下河碳汇的影响:以广西打狗河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):372-378.QIN Xiaoqun, MENG Rongguo, MO Risheng. Influence of land covers on carbon sink of underground river: A case in the Dagouhe basin in Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. [25] 李丹阳, 张连凯, 李灿锋, 王晓宇, 王兴荣, 杨镇飞, 钱龙藤. 泸江流域水体溶解无机碳来源定量解析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(1):92-104.LI Danyang, ZHANG Liankai, LI Canfeng, WANG Xiaoyu, WANG Xingrong, YANG Zhenfei, QIAN Longteng. Quantitative analysis of dissolved inorganic carbon sources in water bodies in the Lujiang river basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(1): 92-104. [26] 王克林, 岳跃民, 陈洪松, 吴协保, 肖峻, 祁向坤, 张伟, 杜虎. 喀斯特石漠化综合治理及其区域恢复效应[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20):7432-7440.WANG Kelin, YUE Yuemin, CHEN Hongsong, WU Xiebao, XIAO Jun, QI Xiangkun, ZHANG Wei, DU Hu. The comprehensive treatment of karst rocky desertification and its regional restoration effects[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7432-7440. [27] Liu Zaihua, Li Qiang, Sun Hailong, Wang Jinliang. Seasonal, diurnal and storm-scale hydrochemical variations of typical epikarst springs in subtropical karst areas of SW China: Soil CO2 and dilution effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337(1-2): 207-223. [28] 倪茂飞, 李思悦. 典型喀斯特河流二氧化碳分压及交换通量季节变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2023, 43(2):412-424.NI Maofei, LI Siyue. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide and its water-air exchange in a typical karst river[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2023, 43(2): 412-424. [29] Ni Maofei, Li Siyue, Isaac Santos, Zhang Jing, Luo Jiachen. Linking riverine partial pressure of carbon dioxide to dissolved organic matter optical properties in a dry-hot valley region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135353. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135353 [30] 张勇, 吴福, 刘振宇, 于奭, 张婉军, 黄桂强, 岳志升, 翟国军. 西江流域化学风化过程及其CO2消耗通量[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(4):425-437.ZHANG Yong, WU Fu, LIU Zhenyu, YU Shi, ZHANG Wanjun, HUANG Guiqiang, YUE Zhisheng, ZHAI Guojun. Chemical weathering process and its CO2 consumption flux in the Xijiang river basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 425-437. [31] 王文欣, 庄义琳, 庄家尧, 吕晓宁, 吴胡强. 不同降雨强度下坡地覆盖对土壤有机碳流失的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(4):62-66.WANG Wenxin, ZHUANG Yilin, ZHUANG Jiayao, LV Xiaoning, WU Huqiang. Effects of downhill coverage on soil organic carbon loss under different rainfall intensities[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(4): 62-66. [32] Ni Maofei, Li Siyue, Luo Jiachen, Lu Xixi. CO2 partial pressure and CO2 degassing in the Daning river of the upper Yangtze River, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 569: 483-494. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.017 [33] Luo Jiachen, Li Siyue, Ni Maofei, Zhang Jing. Large spatiotemporal shifts of CO2 partial pressure and CO2 degassing in a monsoonal headwater stream[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 579: 124135. [34] 罗佳宸, 毛瑢, 李思悦. 三峡库区主要河流秋季pCO2及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7):3134-3141.LUO Jiachen, MAO Rong, LI Siyue. pCO2 in the main rivers of the Three Gorges Reservoir and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(7): 3134-3141. [35] 周苗, 李思亮, 丁虎, 覃蔡清, 岳甫均. 地表流域有机碳地球化学研究进展[J]. 生态学杂质, 2018, 37(1):255-264.ZHOU Miao, LI Siliang, DING Hu, QIN Caiqing, YUE Fujun. Advances in study on organic carbon characteristics in the riverine systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(1): 255-264. [36] Raymond Peter A, Hartmann Jens, Lauerwald Ronny, Sobek Sebastian, McDonald Cory, Hoover Mark, Butman David, Striegl Robert, Mayorga Emilio, Humborg Christoph, Kortelainen Pirkko, Dürr Hans, Meybeck Michel, Ciais Philippe, Guth Peter. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters[J]. Nature, 2013, 503(7476): 355-359. doi: 10.1038/nature12760 [37] Liu Jinke, Han Guilin. Controlling factors of seasonal and spatial variation of riverine CO2 partial pressure and its implication for riverine carbon flux[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 786: 147332. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147332 [38] Liu Zaihua, Macpherson G L, Groves Chris, Martin Jonathan B, Yuan Daoxian, Zeng Sibo. Large and active CO2 uptake by coupled carbonate weathering[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.007 [39] 蒋忠诚, 章程, 罗为群, 肖琼, 吴泽燕. 我国岩溶地区碳汇研究进展与展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(3):345-355.JIANG Zhongcheng, ZHANG Cheng, LUO Weiqun, XIAO Qiong, WU Zeyan. Research progress and prospect of carbon sink in karst region of China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(3): 345-355. [40] 梁顺田, 王雨春, 胡明明, 王启文. 夏季朱衣河二氧化碳分压分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2017, 15(2):153-160.LIANG Shuntian, WANG Yuchun, HU Mingming, WANG Qiwen. Distributions of partial pressure of carbon dioxide and its affecting factors in the Zhuyi river in summer[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2017, 15(2): 153-160. [41] Zeng Fanwei, Masiello Caroline A, Hockaday William C. Controls on the origin and cycling of riverine dissolved inorganic carbon in the Brazos river, Texas[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 104(1-3): 275-291. [42] Li Mingxu, Peng Changhui, Zhang Kerou, Xu Li, Wang Jianming, Yang Yan, Li Peng, Liu Zelin, He Nianpeng. Headwater stream ecosystem: An important source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere[J]. Water Research, 2021, 190: 116738. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116738 [43] Crawford John T, Dornblaser Mark M, Stanley Emily H, Clow David W, Striegl Robert G. Source limitation of carbon gas emissions in high-elevation mountain streams and lakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2015, 120(5): 952-964. doi: 10.1002/2014JG002861 [44] 史红岩, 冉立山, 岳荣, 于瑞宏, 赵艳霞, 吕喜玺. 窟野河水-气界面CO2交换通量变化特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(2):369-379.SHI Hongyan, RAN Lishan, YUE Rong, YU Ruihong, ZHAO Yanxia, LV Xixi. Variations of CO2 exchange in the Kuye river basin and its influencing factors[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(2): 369-379. [45] 刘睿, 张静, 陈祖胜, 倪茂飞, 刘文胜. 典型喀斯特河流水-气界面二氧化碳交换特性及其营养调控因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2):740-748.LIU Rui, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Zusheng, NI Maofei, LIU Wensheng. Water-air carbon dioxide exchange and nutritional controls in a typical karst river[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 740-748. [46] Gaillardet J, Dupre B, Louvat P, Allegre C J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large river[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1-4): 3-30. [47] Cole J J, Prairie Y T, Caraco N F, McDowell W H, Tranvik L J, Striegl R G, Duarte C M, Kortelainen P, Downing J A, Middelburg J J, Melack J. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget[J]. Ecosystems, 2007, 10(1): 172-185. doi: 10.1007/s10021-006-9013-8 -




 下载:
下载: