Research progress of nitrate tracing in karst groundwater based on CiteSpace
-
摘要: 硝酸盐(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$)是地下水中主要的污染物之一,其浓度一旦超标,将会对水生态和人类健康产生不良影响。文章分析2003—2022年岩溶地下水硝酸盐来源的同位素示踪进展,在中国知网(CNKI)收录的全部期刊数据库检索,以“岩溶地下水”“岩溶含水层”“喀斯特地下水”“喀斯特含水层”“硝酸盐”“硝态氮”“氮同位素”“氧同位素”“MixSIAR”“硝酸盐源”“氮转化”“硝酸盐污染”“硝酸盐双同位素”为主题词,得到
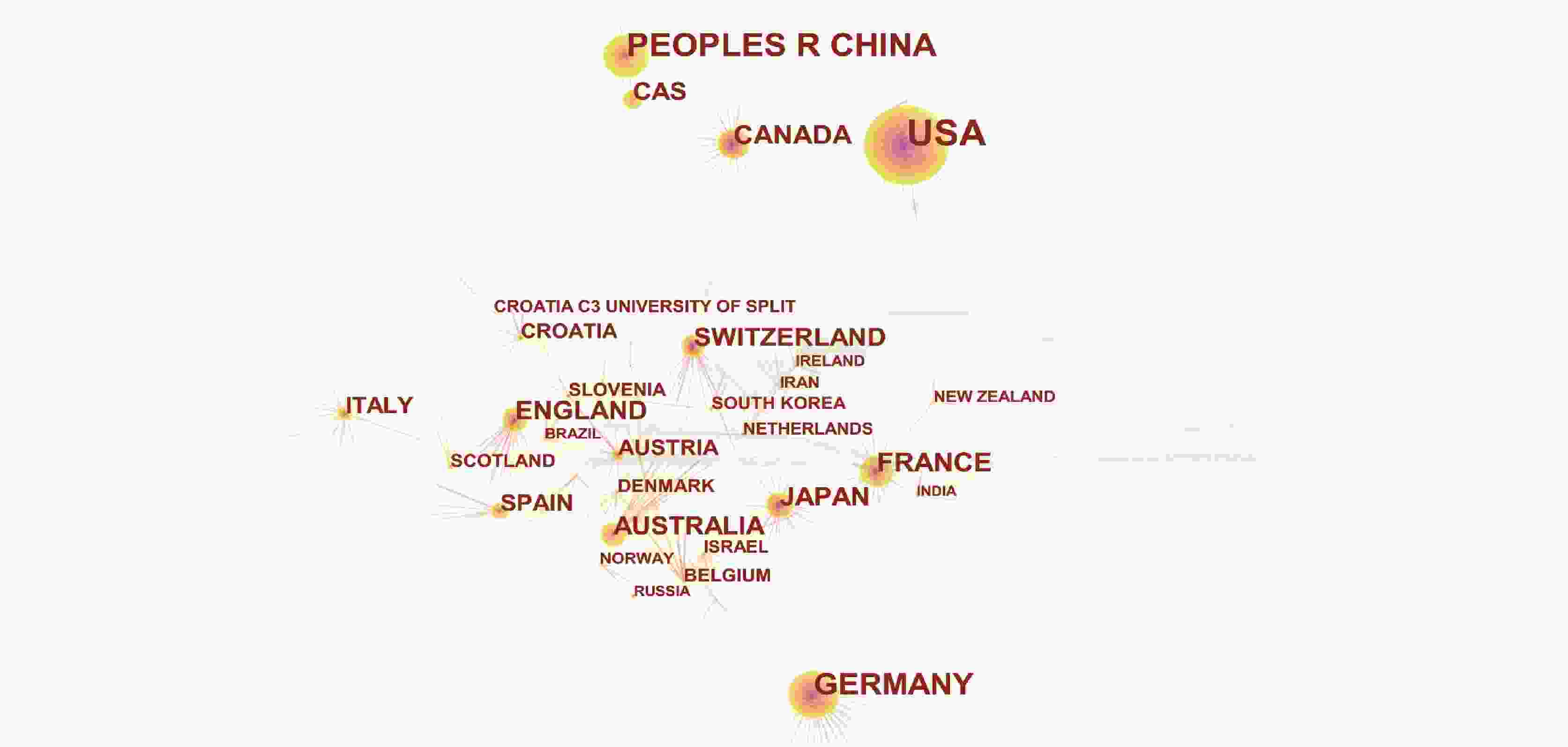
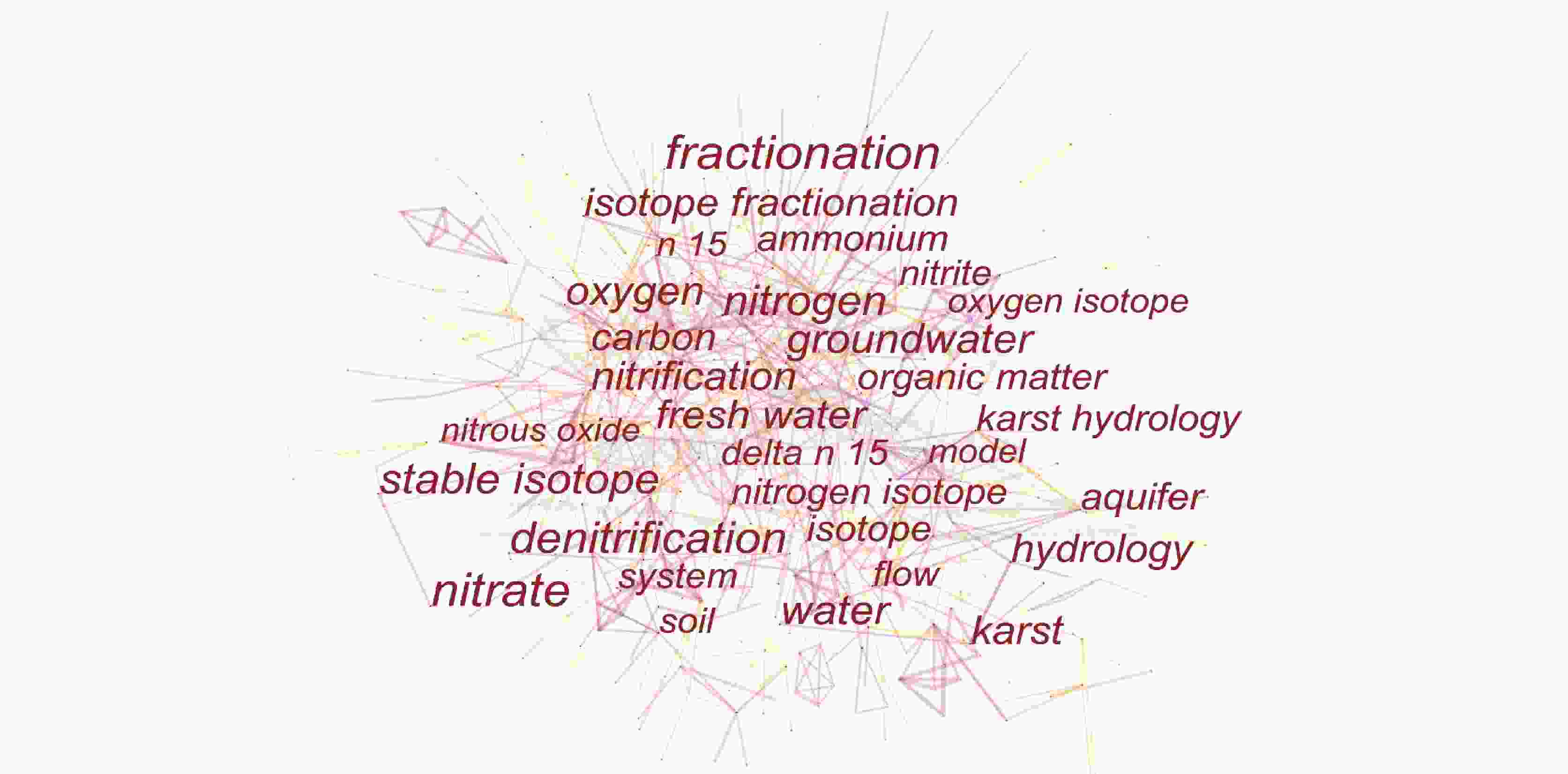
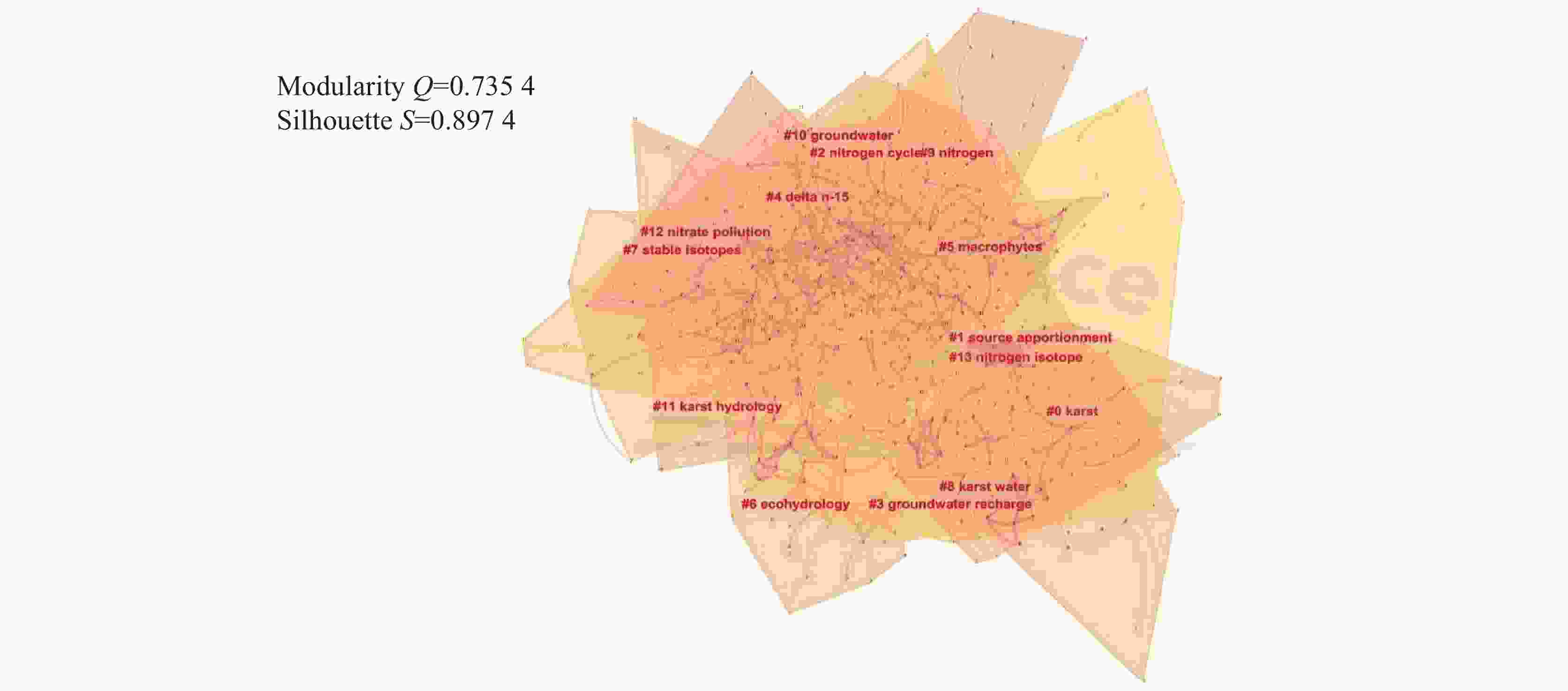
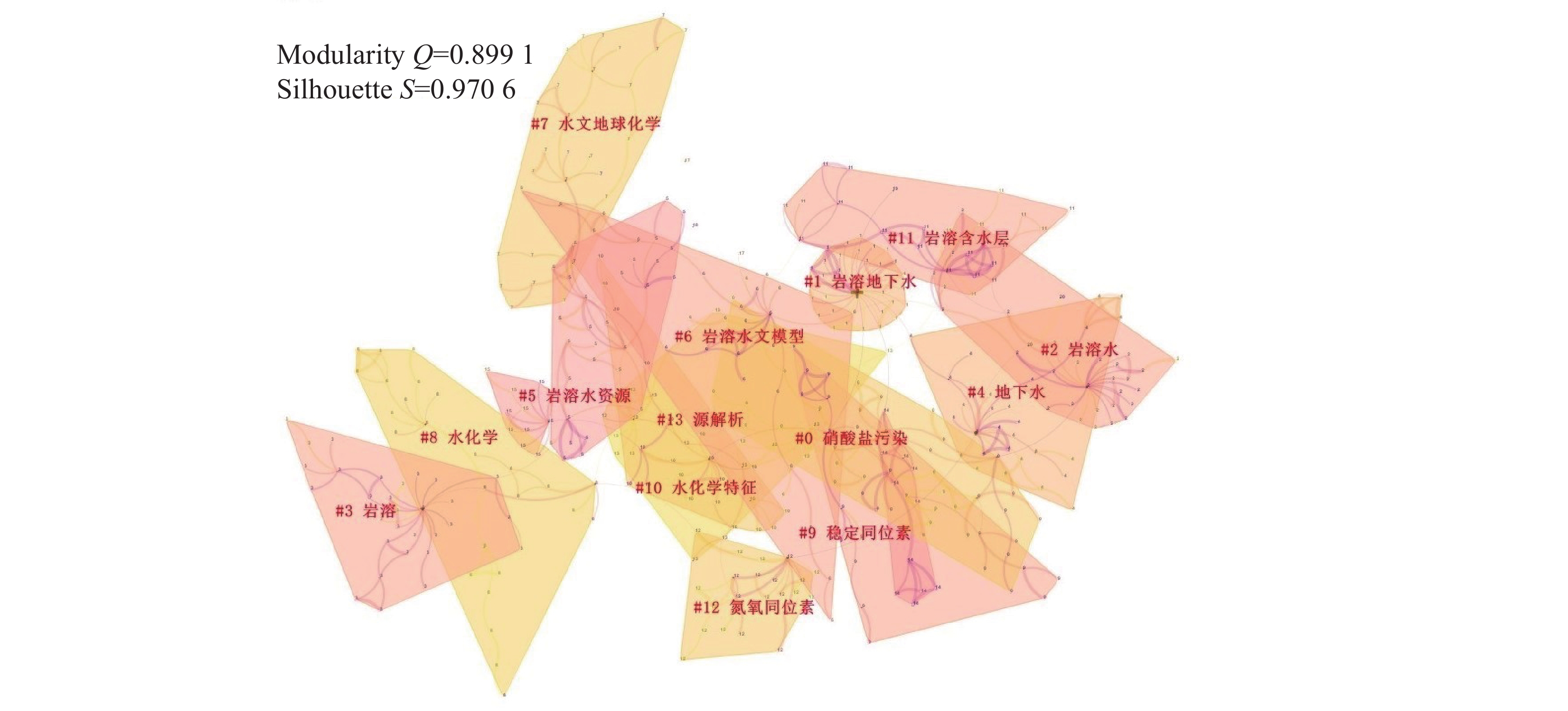
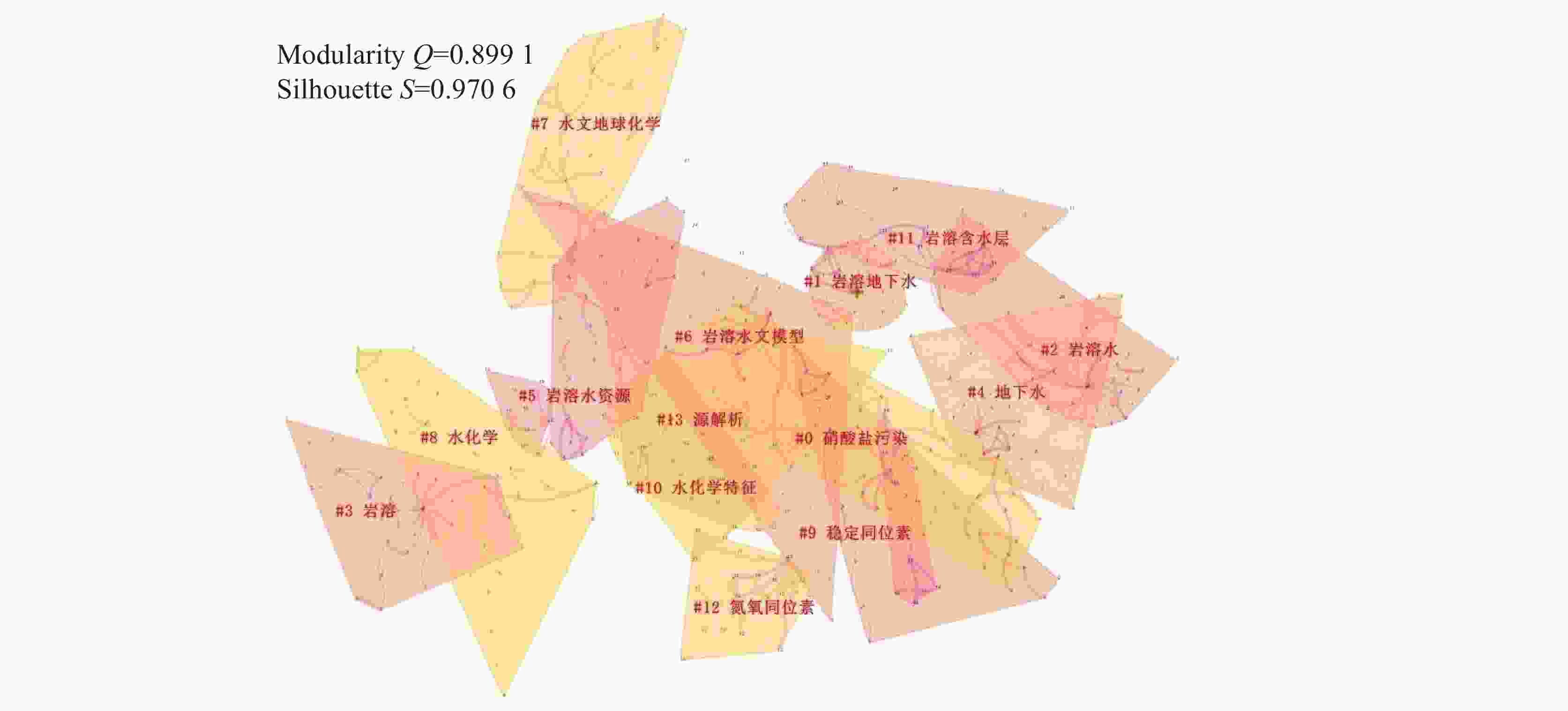
1191 篇论文;并在Web of Science(WOS)核心合集数据库中以“karst groundwater”“karst aquifer”“nitrate” “NOx-N”“nitrogen isotope”“oxygen isotope”“MixSIAR”“nitrate source”“nitrogen transformation”“nitrate contamination”和“dual nitrate isotopes”为主题词,得到2232 篇文献。利用知识网络分析软件CiteSpace,对检索到的文献进行统计和研究热点分析。结果表明:在中文文献方面,中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所在国内岩溶地下水硝酸盐研究领域优势巨大,中文文献发文量最多;关键词聚类知识图谱可概括为岩溶水文与水资源、水化学与水环境、岩溶地下水硝酸盐污染溯源3个研究热点;在英文文献方面,美国、中国和德国的发文数量最多,存在较为密切的合作关系。从研究单位来看,中国科学院的发文量最多;英文关键词聚类知识图谱可以概括为岩溶生态与水文、岩溶地下水硝酸盐的转化(氮循坏)、岩溶地下水硝酸盐污染溯源3个研究热点。硝酸盐氮氧同位素技术为岩溶地下水硝酸盐溯源与生物地球化学研究提供了强有力的支持;在定量溯源时,应考虑同位素分馏效应,以提高结果的准确性。Abstract:Nitrate (${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$) is one of the main pollutants in groundwater; therefore, once ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ concentrations exceed an acceptable level, it will have adverse effects on water ecology and human health. Identifying the sources and biogeochemical transformation process of nitrate in groundwater is of important theoretical and practical significance for pollution prevention and control. The karst groundwater system is characterized by high vulnerability. At present, studies on nitrate in karst groundwater based on nitrogen and oxygen isotope technology have made great progress but most of them were presented by case study, lacking a systematic summary of research progress. CiteSpace, the software of knowledge network analysis, uses bibliometrics and visualization methods, co-citation network, association rules, cluster analysis to analyze the research hotspots in a field in Chinese and foreign literature. CiteSpace enables readers to better understand the knowledge framework, research topics and future hot topics, and plays a very good role in promoting the analysis of research progress in different professional fields. To investigate the research progress of isotope tracing of nitrate sources in karst groundwater in recent years (from 2003 to 2022), and comprehensively analyze the research hotspots of nitrate in karst groundwater, "karst groundwater", "karst aquifer", "nitrate", "nitrate-nitrogen", "nitrogen isotope", "oxygen isotope", "MixSIAR", "nitrate sources", "nitrogen transformations", "nitrate pollution", and "dual nitrate isotopes" were selected as subject terms in CNKI, and 1,191 papers were retrieved after the unrelated subject terms had been excluded. Meanwhile, subject terms of "karst groundwater", "karst aquifer", "nitrate", "NOx-N", "nitrogen isotope", "oxygen isotope" "MixSIAR", "nitrate source", "nitrogen transformation", "nitrate contamination", and "dual nitrate isotopes" were searched in Web of Science (WOS) core collection database, and a total of2,232 papers were retrieved. CiteSpace was employed to analyze publishing institutions, authors, keywords and research hotspots, and co-citations of both the retrieved Chinese literature and English literature.The results show that the Institute of Karst Geology of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences had a great advantage in studies of nitrate in karst water system, because this institute has published the largest number of academic papers written in Chinese. The keyword clustering of "#1 karst groundwater", "#2 karst water", "#5 karst water resources", "#6 karst hydrological model" and "#11 karst aquifer" can be summarized as a research hotspot of karst hydrology and water resources. The keyword clustering of "#7 hydrogeochemistry", "#8 hydrochemistry" and "#10 hydrochemical characteristics" can be summarized as a research hotspot of karst hydrochemistry and water environment. The keyword clustering of "#0 nitrate pollution", "#3 karst", "#4 groundwater", "#9 stable isotope", "#12 nitrogen and oxygen isotope" and "#13 source analysis" can be summarized as a research hotspot of nitrate pollution tracing in karst groundwater. In terms of English literature, the United States, China and Germany had the largest number of publications, and there was a relatively close cooperative relationship between them. Academic papers published by the Chinese Academy of Sciences ranked top among the researching institutes. The keyword clustering of "#0 karst", "#5 macrophytes", "#6 ecohydrology", "#11 karst hydrology" and "#3 groundwater recharge" can be summarized as a research hotspot of karst ecology and hydrology research. The keyword clustering of "#10 groundwater", "#2 nitrogen cycle", "#9 nitrogen" and "#8 karst water" can be summarized as a research hotspot of nitrate transformation in karst groundwater (nitrogen cycle). The keyword clustering of "#1 source appointment", "#12 nitrate pollution", "#4 delta n15", "#7 stable isotope" and "#13 nitrogen isotope" can be summarized as a research hotspot of nitrate pollution tracing in karst groundwater. The technology of dual nitrate isotopes provides a strong technical support for the research of nitrate tracing and biogeochemistry in karst groundwater. Isotopic fractionation effect should be considered to improve the accuracy of nitrate pollution tracing results. This paper aims to provide reference for the source tracing and effective prevention of nitrate pollution in karst groundwater in the future. -
Key words:
- karst water /
- nitrate /
- trace /
- research progress /
- literature visualization analysis
-
表 1 中文文献主要发文机构信息
Table 1. Information of main publishing institutions of Chinese literature
序号 发文量 机构名称 1 94 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 2 44 中国地质大学(武汉)环境学院 3 43 西南大学地理科学学院 4 26 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所 5 23 联合国教科文组织国际岩溶研究中心 6 22 中国地质大学(北京)环境学院 7 22 贵州大学资源与环境工程学院 8 19 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所/自然资源部、广西岩溶动力学重点实验室 9 17 中国科学院地球化学研究所环境地球化学国家重点实验室 10 16 太原理工大学水利科学与工程学院 表 2 中文文献主要发文作者及所在单位信息
Table 2. Main authors and their affiliations of Chinese literature
序号 频次 作者 作者所在单位 1 38 梁永平 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 2 28 杨平恒 西南大学地理科学学院 3 24 申豪勇 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 4 22 赵春红 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 5 20 邹胜章 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 6 19 唐春雷 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 7 17 袁道先 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 8 16 潘晓东 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 9 14 姜光辉 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所 10 13 蒋勇军 西南大学地理科学学院 表 3 中文文献主要关键词信息
Table 3. Main keywords in Chinese literature
序号 频次 中心度 关键词 1 161 0.35 岩溶地下水 2 96 0.22 地下水 3 83 0.17 岩溶水 4 75 0.17 岩溶 5 60 0.17 硝酸盐 6 52 0.36 水化学特征 7 33 0.05 水化学 8 31 0.17 数值模拟 9 26 0.18 水文地质 10 24 0.11 氮氧同位素 表 4 英文文献的主要发文国家信息
Table 4. Main publishing countries of English literature
序号 频次 中心度 国家名称 1 693 0.45 The United States of America 2 326 0.23 The People’s Republic of China 3 226 0.33 Federal Republic of Germany 4 113 0.34 French Republic 5 105 0.77 Canada 6 99 0.21 Japan 7 93 0.32 England 8 88 0.32 Commonwealth of Australia 9 86 0.87 Switzerland 10 57 0.05 The Kingdom of Spain 表 5 英文文献主要发文机构、作者信息
Table 5. Main publishing institutions and authors of English literature
序号 机构 篇 作者 篇 1 Chinese Academy of Sciences 149 Baker A. 21 2 United States Geological Survey 58 Sigman D. M. 19 3 Princeton University 57 Casciotti K. L. 18 4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences 57 Liu C. Q. 17 5 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute 39 Yoshida N. 16 6 Tianjin University 36 Soler A. 15 7 Universidad de Barcelona 24 Michalskl G. 14 8 Stanford University 22 Fang Y. T. 12 9 University of Florida 22 Well R. 12 10 Tokyo Institute of Technology 21 Chen C. Q. 10 表 6 英文文献期刊共被引频次主要信息
Table 6. Co-citation frequencies of English journals
序号 共被引频次 中心度 期刊名 1 1125 0.03 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2 905 0.02 Journal of Hydrology 3 840 0.03 Nature 4 835 0 Science 5 788 0.02 Environmental Science & Technology 6 756 0.06 Analytical Chemistry 7 708 0.01 Limnology and Oceanography 8 653 0 Chemical Geology 9 577 0.13 Global Biogeochemical Cycles 10 566 0 Water Resources Research -
[1] 刘俊国, 孟莹, 张学静. IPCC AR6报告解读:地下水[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4):414-421.LIU Junguo, MENG Ying, ZHANG Xuejing. Interpretation of IPCC AR6 report: Groundwater[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(4): 414-421. [2] 曹建文, 夏日元. 西南岩溶石山地区不同类型地下河开发利用模式探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5):609-617.CAO Jianwen, XIA Riyuan. Exploitation models for different types of underground rivers in karst mountain areas of Southwestern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 609-617. [3] 覃小群, 宋开本, 黄奇波, 蓝芙宁, 黄春阳, 黄辉. 广西岩溶峰林区地下水赋存特征及钻探成井模式[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5):618-625.QIN Xiaoqun, SONG Kaiben, HUANG Qibo, LAN Funing, HUANG Chunyang, HUANG Hui. Groundwater occurrence characteristics and drilling well models in karst peak forest areas, Guangxi, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 618-625. [4] 袁道先, 薛禹群, 傅家谟, 郑度, 汪集旸, 林学玉, 陈梦熊. 防止我国西南岩溶地区地下河变成“下水道”的对策与建议[J]. 中国科学院院士建议, 2007(4):1-14. [5] Abascal E, Gomez Coma L, Ortiz I, Ortiz A. Global diagnosis of nitrate pollution in groundwater and review of removal technologies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 810: 152233. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152233 [6] 马宝强, 王潇, 汤超, 马建源. 全球地下水资源开发利用特点及主要环境问题概述[J]. 自然资源情报, 2022(8):1-6.MA Baoqiang, WANG Xiao, TANG Chao, MA Jianyuan. Overview of the characteristics of global groundwater resources development, utilization and the main environment problems[J]. Natural Resources Information, 2022(8): 1-6. [7] Davidson E A, David M B, Galloway J N, Goodale C L, Haeuber R, Harrison J A, Howarth R W, Jaynes D B, Lowrance R R, Thomas N B, Peel J L, Pinder R W, Porter E, Snyder C S, Townsend A R, Ward M H. Excess nitrogen in the U. S. environment: Trends, risks, and solutions[J]. Issues in Ecology, 2011(15): 1-16. [8] Fan A M, Steinberg V E. Health implications of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water: An update on methemoglobinemia occurrence and reproductive and developmental toxicity[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 1996, 23(1): 35-43. doi: 10.1006/rtph.1996.0006 [9] 孙亚乔, 王晓冬, 校康, 段磊, 吕梓昊. 淡水环境中氮污染同位素示踪的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(8):1693-1702.SUN Yaqiao, WANG Xiaodong, XIAO Kang, DUAN Lei, LYU Zihao. Research progress of nitrogen pollution isotope tracing in freshwater environment[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(8): 1693-1702. [10] Kendall C, Elliott E M, Wankel S D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems[J]. Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2007: 375-449. [11] Gutiérrez M, Biagioni R N, Alarcón Herrera M T, Rivas Lucero B A. An overview of nitrate sources and operating processes in arid and semiarid aquifer systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 624: 1513-1522. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.252 [12] Soto D X, Koehler G, Wassenaar L I, Hobson K A. Spatio-temporal variation of nitrate sources to Lake Winnipeg using N and O isotope (δ15N, δ18O) analyses[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 647: 486-493. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.346 [13] 金赞芳, 张文辽, 郑奇, 朱晨阳, 李非里. 氮氧同位素联合稳定同位素模型解析水源地氮源[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(5):2039-2047.JIN Zanfang, ZHANG Wenliao, ZHENG Qi, ZHU Chenyang, LI Feili. Contribution of nitrogen sources in water sources by combining nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and SIAR[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(5): 2039-2047. [14] Xue D, Botte J, De Baets B, Accoe F, Nestler A, Taylor P, Van Cleemput O, Berglund M, Boeckx P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface-and groundwater[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(5): 1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048 [15] Nikolenko O, Jurado A, Borges A V, Knӧller K, Brouyѐre S. Isotopic composition of nitrogen species in groundwater under agricultural areas: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621: 1415-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.086 [16] 于璐, 郑天元, 郑西来. 地下水硝酸盐污染源解析及氮同位素分馏效应研究进展[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2):563-573.YU Lu, ZHENG Tianyuan, ZHENG Xilai. Review of nitrate source apportionment and nitrogen isotope fractionation in groundwater[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(2): 563-573. [17] Choi W J, Lee S M, Ro H M. Evaluation of contamination sources of groundwater NO3– using nitrogen isotope data: A review[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2003, 7(1): 81-87. doi: 10.1007/BF02910268 [18] Richa A, Touil S, Fizir M. Recent advances in the source identification and remediation techniques of nitrate contaminated groundwater: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316: 115265. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115265 [19] Jung H, Koh D C, Kim Y S, Jeen S W, Lee J. Stable isotopes of water and nitrate for the identification of groundwater flowpaths: A review[J]. Water, 2020, 12(1): 138. doi: 10.3390/w12010138 [20] Parnell A C, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson A L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation[J]. Plos One, 2010, 5(3): e9672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009672 [21] Ming X X, Groves C, Wu X Y, Chang L R, Zheng Y L, Yang P H. Nitrate migration and transformations in groundwater quantified by dual nitrate isotopes and hydrochemistry in a karst World Heritage site[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 735: 138907. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138907 [22] Ren K, Pan X, Yuan D, Zeng J, Liang J, Peng C. Nitrate sources and nitrogen dynamics in a karst aquifer with mixed nitrogen inputs (Southwest China): Revealed by multiple stable isotopic and hydro-chemical proxies[J]. Water Research, 2022, 210: 118000. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.118000 [23] Husic A, Fox J, Adams E, Pollock E, Ford W, Agouridis C, Backus J. Quantification of nitrate fate in a karst conduit using stable isotopes and numerical modeling[J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115348. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115348 [24] Yang P H, Wang Y Y, Wu X Y, Chang L R, Ham B, Song L S, Groves C. Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 114835. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114835 [25] 李杰, 陈超美. Citespace:科技文本挖掘及可视化[M]. 北京:首都经济贸易大学出版社, 2016.LI Jie, CHEN Chaomei. Citespace: Text mining and visualization in scientific literature[M]. Beijing: Capital Economic and Trade University Press, 2016. [26] 许尔琪. 基于CiteSpace的喀斯特石漠化国际研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(4):728-738.XU Erqi. Progress of international research of karst rocky desertification based on CiteSpace[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(4): 728-738. [27] 童凌晨, 李强, 岳鹏鹏. 基于CiteSpace的喀斯特土壤有机碳研究进展[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(4):22-34.TONG Lingchen, LI Qiang, YUE Pengpeng. Research progress and prospects of karst soil organic carbon based on CiteSpace[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 40(4): 22-34. [28] 郭永丽, 章程, 吴庆, 全洗强. 基于文献计量学分析岩溶水文地质学研究热点[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):817-828.GUO Yongli, ZHANG Cheng, WU Qing, QUAN Xiqiang. Analysis of focused topics in karst hydrogeology research based on bibliometrics[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 817-828. [29] 杨平恒, 张宇, 田萍, 卢丙清, 谢世友, 况又莉. 川东平行岭谷典型岩溶含水介质特征的识别方法探讨:以重庆青木关地下水系统为例[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(2):90-97.YANG Pingheng, ZHANG Yu, TIAN Ping, LU Bingqing, XIE Shiyou, KUANG Youli. A methodological research on the identification of a typical karst aquifer media in the paralleled ridge-valley of east Sichuan: A case study of Qingmuguan karst groundwater system, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 38(2): 90-97. [30] 杨平恒, 罗鉴银, 彭稳, 夏凯生, 林玉石. 在线技术在岩溶地下水示踪试验中的应用:以青木关地下河系统岩口落水洞至姜家泉段为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(3):215-220.YANG Pingheng, LUO Jianyin, PENG Wen, XIA Kaisheng, LIN Yushi. Application of online technique in tracer test: A case in Qingmuguan subterranean river system, Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(3): 215-220. [31] 杨平恒, 詹兆君, 明晓星, 陈峰, 任娟, 邓书金, 洪爱花. 旅游酒店排污影响下的岩溶地下水水化学变化[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(2):416-428. doi: 10.18307/2019.0211YANG Pingheng, ZHAN Zhaojun, MING Xiaoxing, CHEN Feng, REN Juan, DENG Shujin, HONG Aihua. Hydrochemical variation of the karst groundwater impacted by the contaminant discharge from a tourism hotel[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(2): 416-428. doi: 10.18307/2019.0211 [32] 张珂, 周佳奇, 张企诺, 陈新宇, 晁丽君, 姚成, 李致家. 栅格岩溶分布式水文模型[J]. 水资源保护, 2022, 38(1):43-51.ZHANG Ke, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Qinuo, CHEN Xinyu, CHAO Lijun, YAO Cheng, LI Zhijia. Grid-based karst distributed hydrological model[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2022, 38(1): 43-51. [33] 梁桂星, 覃小群, 崔亚莉, 陈爽, 黄奇波. 分布式水文模型在岩溶地区的改进与应用研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(2):60-67.LIANG Guixing, QIN Xiaoqun, CUI Yali, CHEN Shuang, HUANG Qibo. Improvement and application of a distributed hydrological model in karst regions[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 60-67. [34] Liang Y P, Gao X B, Zhao C H, Tang C L, Shen H Y, Wang Z H, Wang Y X. Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(5): 1371-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1792-4 [35] 高帅, 李常锁, 贾超, 孙斌, 张海林, 逄伟. 济南趵突泉泉域岩溶水化学特征时空差异性研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(Suppl.1):61-70. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13937GAO Shuai, LI Changsuo, JIA Chao, SUN Bin, ZHANG Hailin, PANG Wei. Spatiotemporal difference study of karst hydrochemical characteristics in the Baotu Spring area of Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(Suppl.1): 61-70. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13937 [36] 刘莉. 济南泉域岩溶水水化学特征及其指示作用研究[D]. 济南:济南大学, 2010.LIU Li. Study on hydrochemical character of karst water and its indication in Jinan spring[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2010. [37] 马玉亮. 济南泉域岩溶水水文地球化学及其环境意义[D]. 青岛:青岛大学, 2017. [38] 李学先, 吴攀, 查学芳, 何守阳, 吴琳娜, 韩志伟. 基于水化学及稳定同位素的岩溶山区城镇水体硝酸盐来源示踪[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(4):1428-1439.LI Xuexian, WU Pan, ZHA Xuefang, HE Shouyang, WU Linna, HAN Zhiwei. Tracing nitrate sources in urban waters of karst mountainous area using hydrochemistry and stable isotope[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(4): 1428-1439. [39] 牛世伟, 安景文, 宫亮, 蔡广兴, 何志刚, 陈玥, 刘子琪, 隋世江. 辽河流域典型农区地下水硝酸盐时空变化特征[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(5):1147-1150, 1155.NIU Shiwei, AN Jingwen, GONG Liang, CAI Guangxing, HE Zhigang, CHEN Yue, LIU Ziqi, SUI Shijiang. Spatial-temporal change characteristics of nitrate in groundwater in typical agricultural areas of Liao river basin[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(5): 1147-1150, 1155. [40] 范祖金, 魏兴, 周育琳, 陈蒙恩, 申纪伟, 李佳文. 典型山地农业区浅层地下水硝酸盐来源及转化过程解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2023, 36(10):1946-1956.FAN Zujin, WEI Xing, ZHOU Yulin, CHEN Meng'en, SHEN Jiwei, LI Jiawen. Analysis of nitrate sources and transformation processes in shallow groundwater in typical mountainous agricultural area[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 36(10): 1946-1956. [41] 杨延梅, 张田, 郑明霞, 苏婧, 孙源媛, 傅雪梅. 基于水化学及当地稳定同位素的地下水硝酸盐污染空间分布特征及污染源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(9):2164-2172.YANG Yanmei, ZHANG Tian, ZHENG Mingxia, SU Jing, SUN Yuanyuan, FU Xuemei. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution source analysis of nitrate pollution in groundwater based on hydrochemistry and local stable isotopes[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(9): 2164-2172. [42] 张海林, 王重, 林广奇, 徐源, 马雪莹, 关琴. 济南趵突泉泉域岩溶水硝酸盐污染特征及其来源识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(6):998-1006.ZHANG Hailin, WANG Chong, LIN Guangqi, XU Yuan, MA Xueying, GUAN Qin. Nitrate pollution characteristics and identification of nitrate sources in Baotu Spring area of Jinan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(6): 998-1006. [43] Yang P H, Li Y, Groves C, Hong A H. Coupled hydrogeochemical evaluation of a vulnerable karst aquifer impacted by septic effluent in a protected natural area[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658: 1475-1484. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.172 [44] Dirnböck T, Kobler J, Kraus D, Grote R, Kiese R. Impacts of management and climate change on nitrate leaching in a forested karst area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 165: 243-252. [45] Chang L R, Ming X X, Groves C, Ham B, Wei C F, Yang P H. Nitrate fate and decadal shift impacted by land use change in a rural karst basin as revealed by dual nitrate isotopes[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 299: 118822. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118822 [46] Yoshimoto S, Tsuchihara T, Ishida S, Masumoto T, Imaizumi M. Groundwater flow and transport and potential sources of groundwater nitrates in the Ryukyu limestone as a mixed flow aquifer in Okinawa Island, Japan[J]. Paddy and Water Environment, 2011, 9(4): 367-384. doi: 10.1007/s10333-011-0252-8 [47] Zhang H, Xu Y, Cheng S Q, Li Q L, Yu H R. Application of the dual-isotope approach and Bayesian isotope mixing model to identify nitrate in groundwater of a multiple land-use area in Chengdu plain, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 717: 137134. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137134 [48] Ogrinc N, Tamše S, Zavadlav S, Vrzel J, Jin L. Evaluation of geochemical processes and nitrate pollution sources at the Ljubljansko polje aquifer (Slovenia): A stable isotope perspective[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 646: 1588-1600. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.245 [49] Han D M, Currell M J, Cao G L. Deep challenges for China's war on water pollution[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218: 1222-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.078 [50] Wells N S, Kappelmeyer U, Knöller K. Anoxic nitrogen cycling in a hydrocarbon and ammonium contaminated aquifer[J]. Water Research, 2018, 142: 373-382. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.005 [51] Musgrove M, Opsahl S P, Mahler B J, Herrington C, Sample T L, Banta J R. Source, variability, and transformation of nitrate in a regional karst aquifer: Edwards aquifer, central Texas[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 568: 457-469. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.201 [52] Husic A, Fox J, Al Aamery N, Ford W, Pollock E, Backus J. Seasonality of recharge drives spatial and temporal nitrate removal in a karst conduit as evidenced by nitrogen isotope modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2021, 126(10): e2021JG006454. doi: 10.1029/2021JG006454 [53] Einsiedl F, Mayer B. Hydrodynamic and microbial processes controlling nitrate in a fissured-porous karst aquifer of the Franconian Alb, Southern Germany[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(21): 6697-6702. [54] Frossard V, Aleya L, Vallet A, Henry P, Charlier J B. Impacts of nitrogen loads on the water and biota in a karst river (Loue river, France)[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2020, 847(11): 2433-2448. doi: 10.1007/s10750-020-04264-4 [55] Stock B C, Jackson A L, Ward E J, Parnell A C, Phillips D L, Semmens B X. Analyzing mixing systems using a new generation of Bayesian tracer mixing models [J]. PeerJ, 2018, 6: e5096. -




 下载:
下载: