Flood hydrological process and its effective control measures in the high-altitude depressions of peak-cluster areas in Lijiang River
-
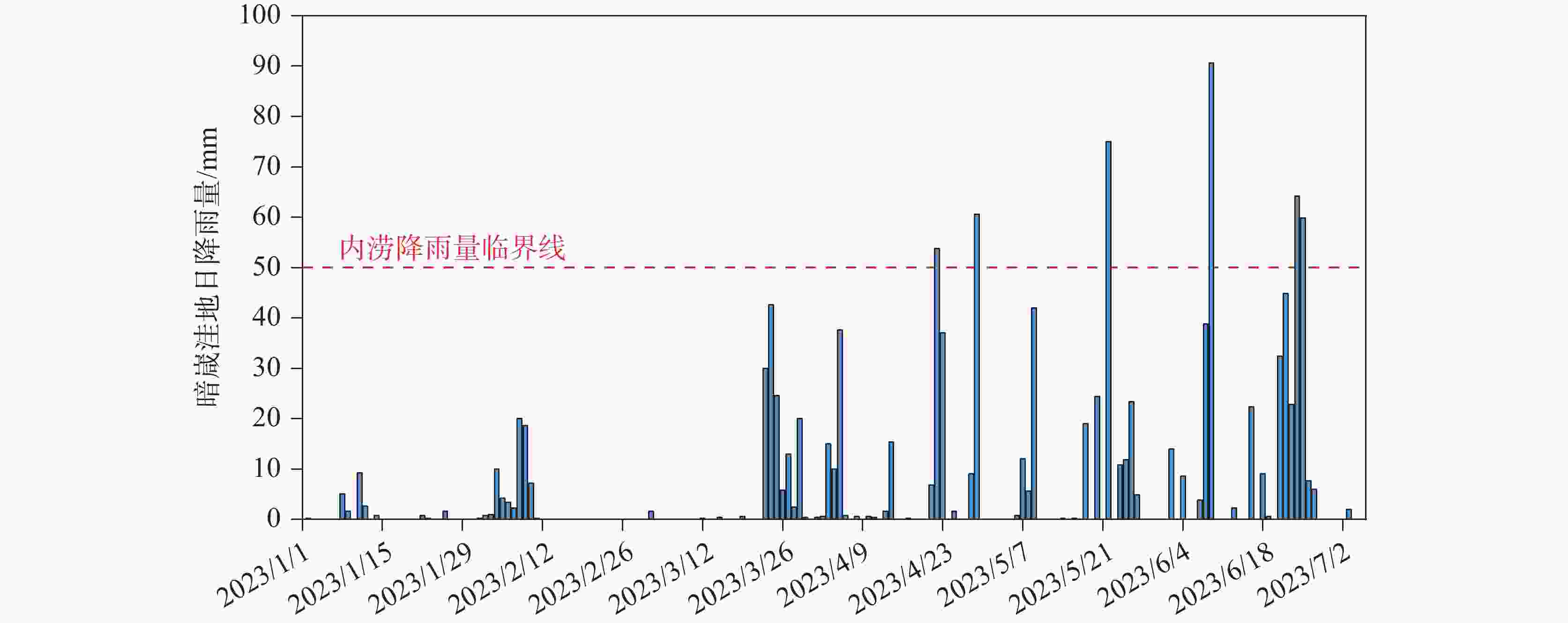
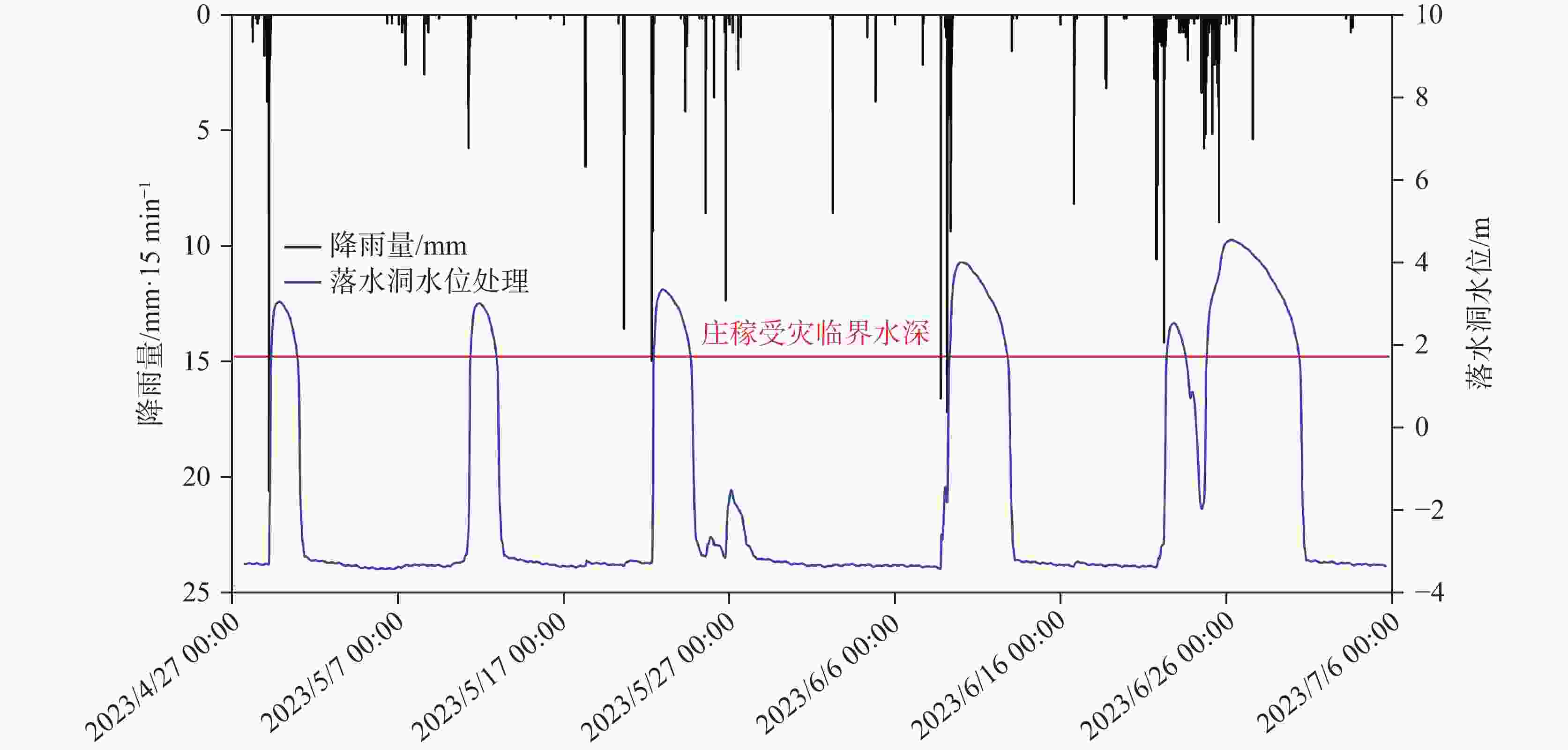
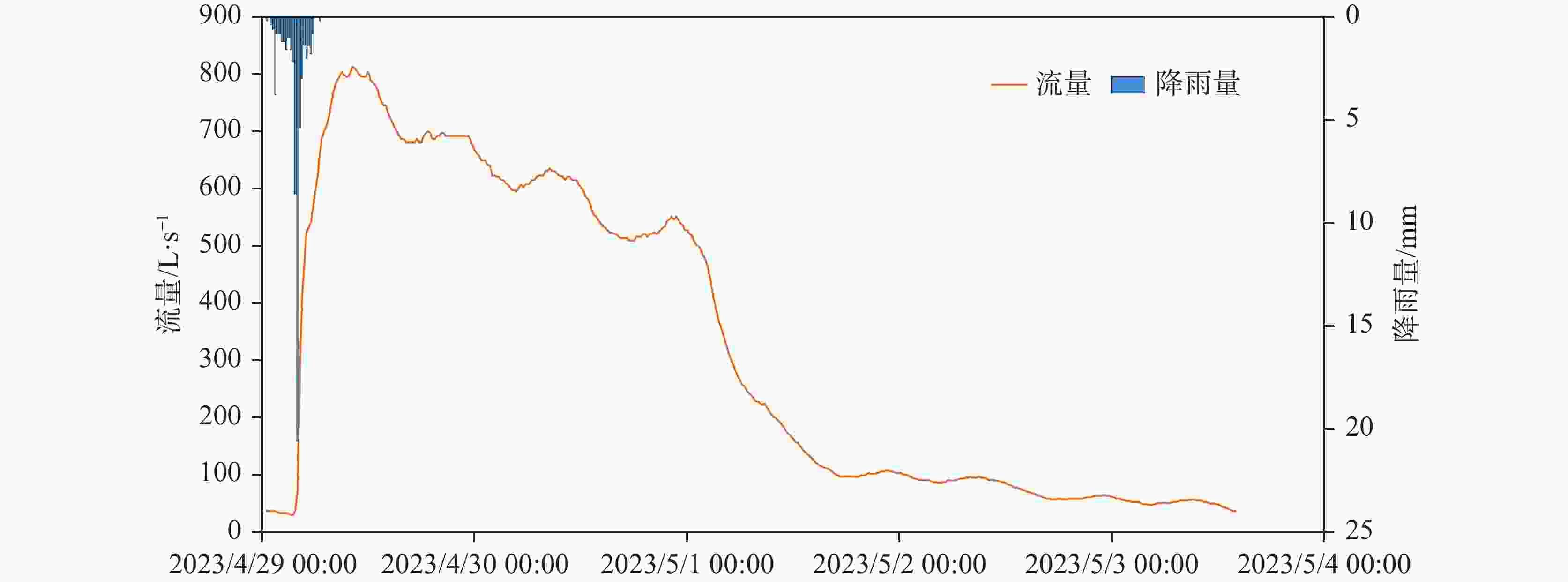
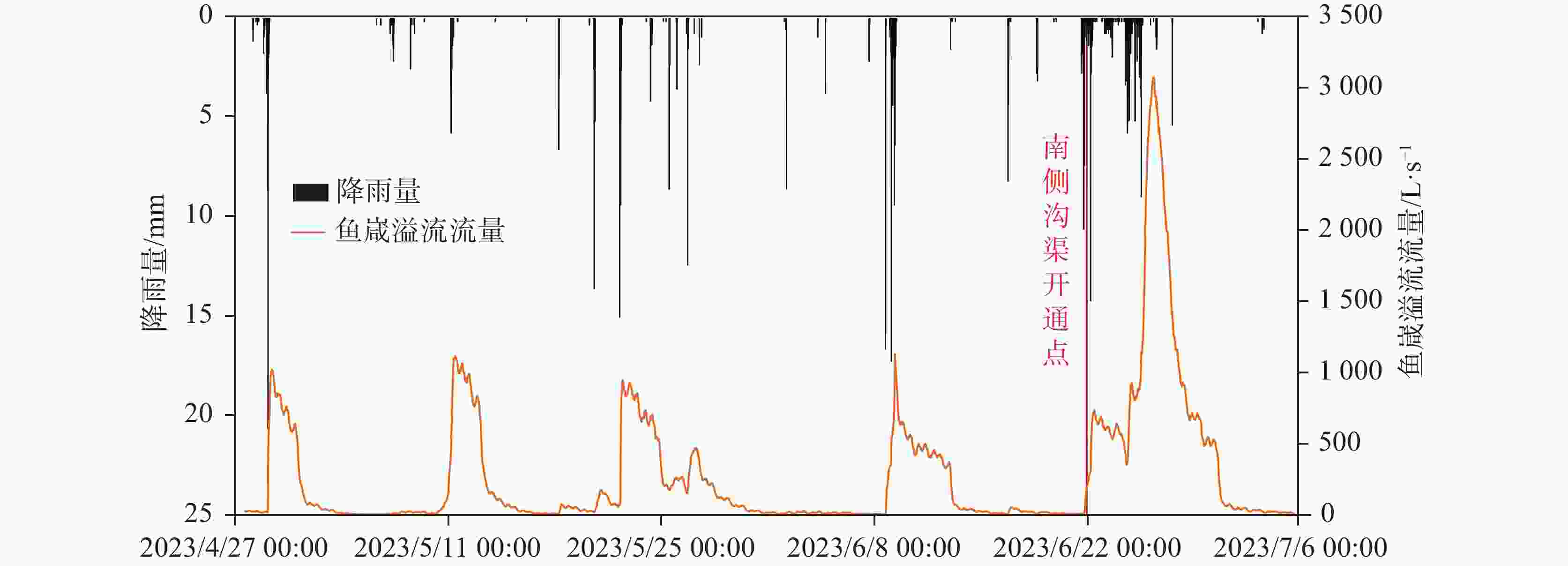
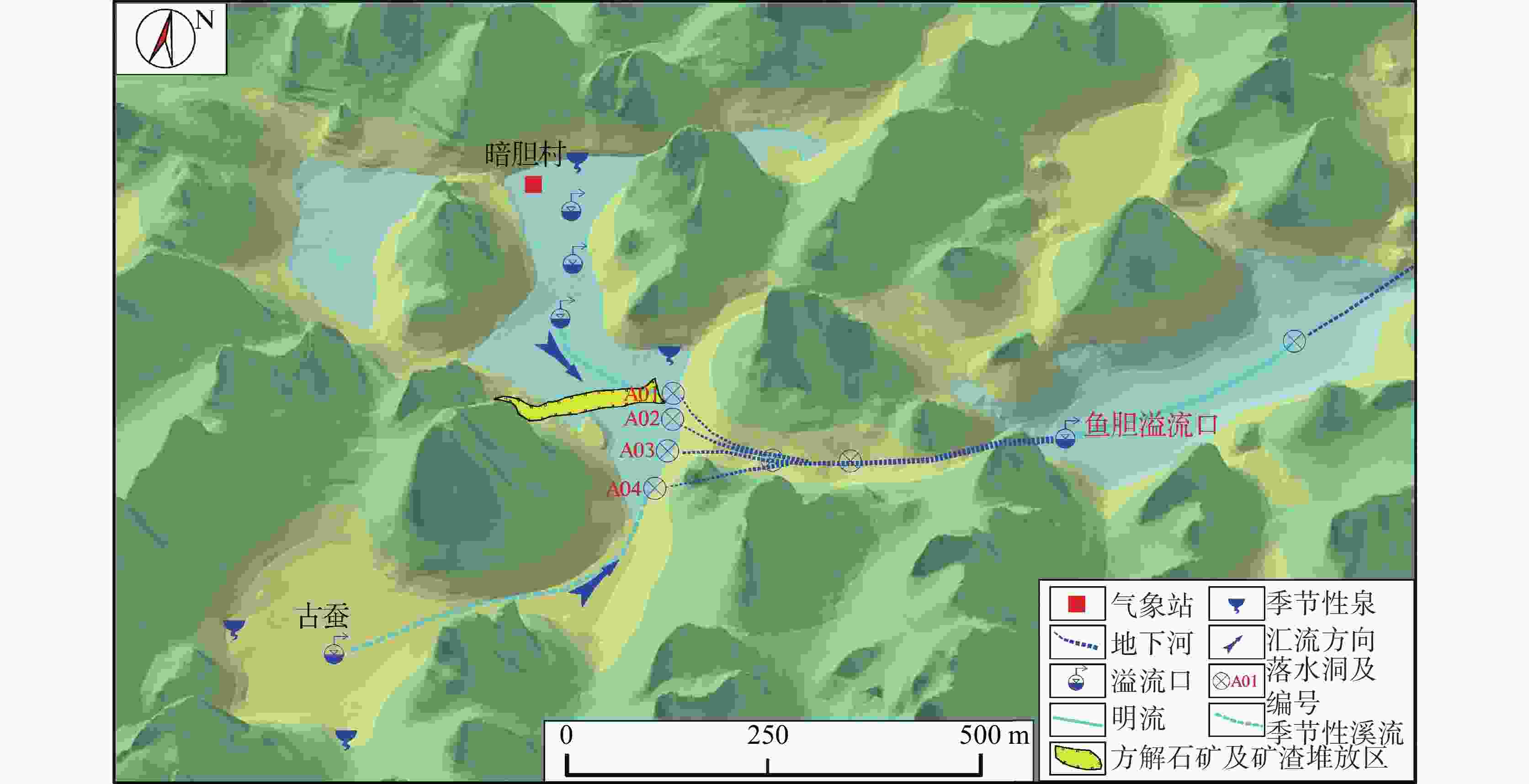
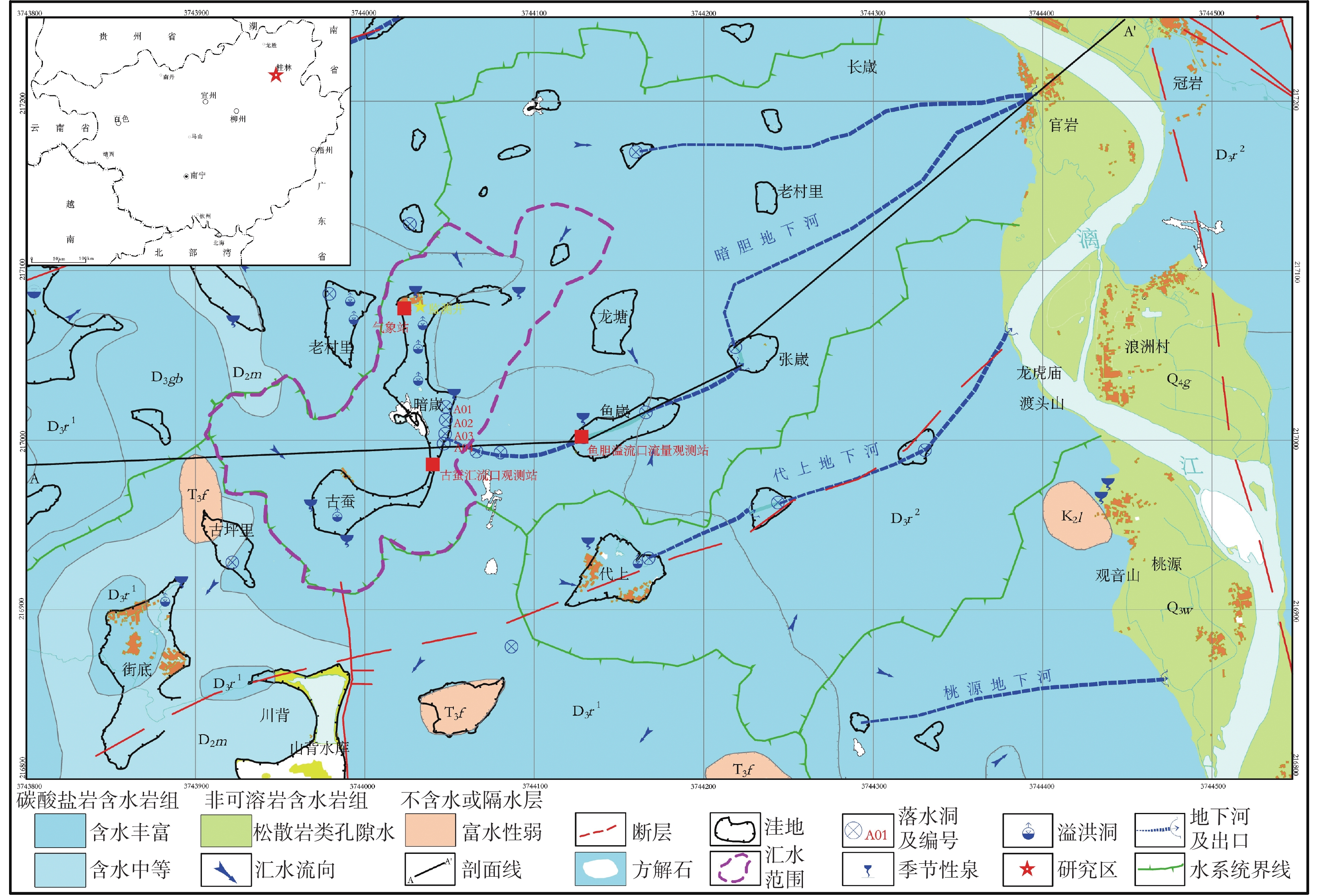
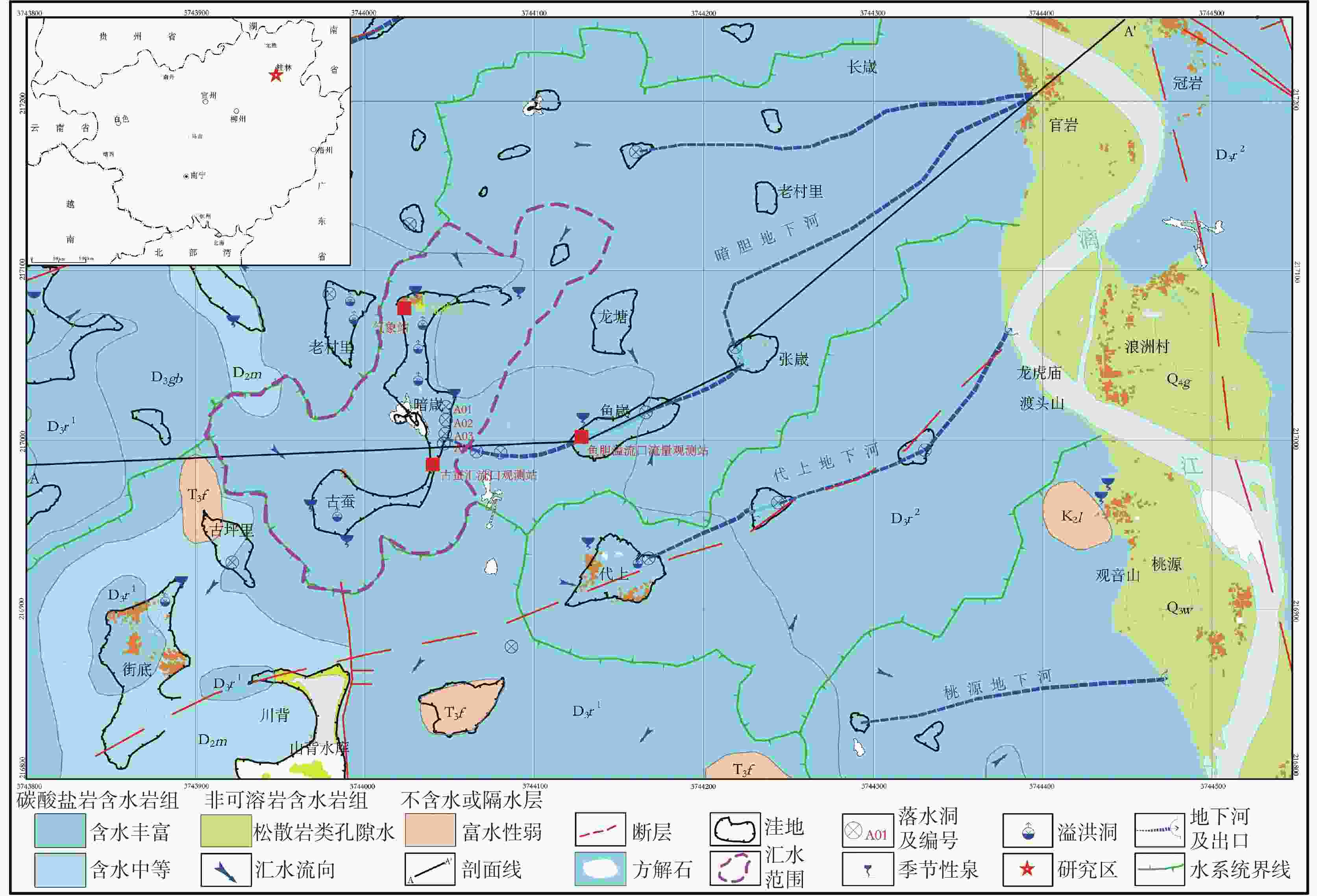
摘要: 漓江峰丛片区高位岩溶洼地洪涝频发,严重影响该地区农村经济发展和自然景观资源开发与保护。本研究选择在漓江峰丛片区暗嵅高位洼地开展洪涝水循环过程研究,对洼地内主要消水口(A01、A03落水洞)进行扩宽和疏通,加大过水能力,使洪涝水害得到有效治理。结果表明:洼地积水成涝对降雨响应迅速,降雨结束后,12~24 h内洼地积水深度就能达到最大,日降雨量超过50 mm或72 h累计降雨量超过90 mm,洼地就容易积水成涝。2023年4-7月共造成了8次洪涝灾害,洪涝总时长达417.5 h(18.6 d)。鱼嵅地下河出口排泄量达到大气降雨补给量的77.77%和87.32%,为暗嵅洼地地下水总排泄口,主要通过中部A01、A02、A03、A04 4个消水洞排水,4个消水洞不同的消水速度造成了出口流量的4个峰值。A01消水洞水力坡度小,下部管道受方解石矿渣堵塞,消水速度较慢,现仅对A01洞口进行整治,未能有效解决洼地洪涝问题。A03、A04消水洞位于方解石脉矿的南侧,未受到方解石尾矿渣的影响,岩溶管道过水通畅。通过疏通A04消水洞,并将南侧古蚕洼地的洪流引至A03消水洞,缩短洪涝时间66.71 h(2.8 d)。因此,修建好南部排水沟系统,使南部古蚕洼地的水全部通过A03、A04消水洞快速向鱼嵅地下河出口排泄,是进一步减轻暗嵅洼地洪涝受灾程度的重要措施。Abstract:
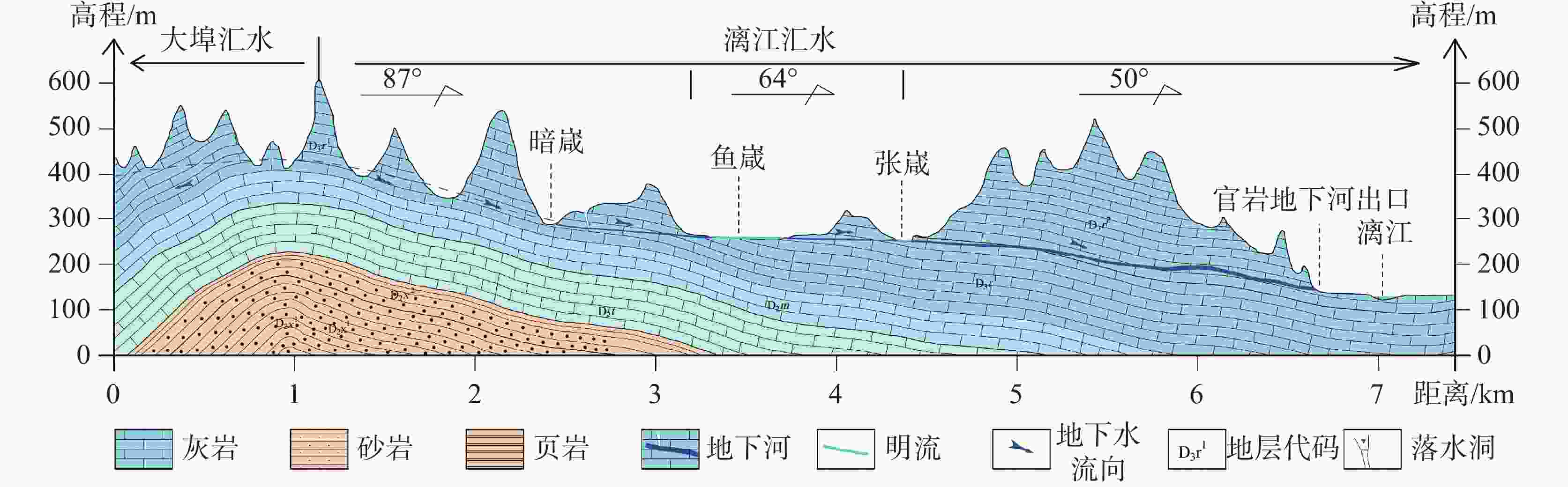
With a length of 83 km and an area of about 624 km2, the high-altitude karst depressions in peak-cluster areas are mainly distributed in the middle reaches of the Lijiang River from Daxu town to Yangshuo county, Guilin. There are thousands of depressions in this area, with sufficient nutrients in soil. Large depressions with flat terrain are concentrated with villages, but land resources are scarce. The frequent alternation of droughts and floods has seriously affected not only the local economic development and rural revitalization but also the improvement of landscape resources, which is the main bottleneck restricting the development and protection of natural landscape resources in these depressions. Previous studies mainly focused on the geomorphological origins and geological structures of depressions, but there is little research on the flood formation conditions and hydrological processes. In this study, the Andang depression in the peak-cluster area of Lijiang River basin was selected as a study area in the analysis of flood water cycle, About 3.5 km away from the Lijiang river, the study area is located on the west bank of the Lijiang River, with a catchment area of 2.3 km2. Rainfall mainly recharges the karst underground river channels through A01, A02, A03 and A04 sinkholes in north-south alignment in the central part of the depression, then discharges to the surface at Guanyan village on the west bank of the Lijiang river, and finally flows into the Lijiang River. The elevation of the Andang depression (150 m) is higher than that of the Lijiang river (130 m). A calcite vein about 20 m wide developed in the middle of the depression was mined in the early years. The slag was piled up in Sinkhole A01, resulting in the blockage of underground channels and limited water discharge capacity. Consequently, floods are likely to occur due to the poor drainage system when it rains heavily. With flooding depths of 3–10 m, floods take place 3 or 4 times every year in the depressions, lasting 5–10 days each time, even one month for the longest. A large area of cultivated land in the depression has been deserted due to years of waterlogging. This study established real-time monitoring stations for atmospheric rainfall, surface water level, groundwater level, and outlet flow in the depression to analyze the conditions and causes of floods. The main drainage outlets (A01 and A03 sinkholes) in the depressions were widened and dredged to increase their drainage capacity, which was effective for the control of flood and waterlogging. The results showed that the depression were highly subject to flooding after rainfall. The water depth in the depression could reach the maximum within 12–24 h after the rainfall. If the daily rainfall exceeded 50 mm or the cumulative rainfall exceeded 90 mm in 72 h, the depression was prone to flood. A total of 8 floods occurred in the depression area from April to July, 2023, with a flooding time of 417.5 h (18.6 d). The discharge at the outlet of the Yudang underground river reached 77.77% and 87.32% of the rainfall recharge, which was the total groundwater discharge outlet of the Andang depression. The four sinkholes A01, A02, A03 and A04 were discharge outlets for the central section of the underground river. The water discharge rates of these four sinkholes formed four flow peaks at the outlets. Because the hydraulic gradient in Sinkhole A01 was small, and the karst channels of the lower section were blocked by calcite slag, the water discharge speed was slow. Renovating Sinkhole A01 is not an effective way to control flooding in the depressions. Located on the south side of the calcite lode, Sinkhole A03 and Sinkhole A04 were not affected by the blockage of calcite slag; therefore, groundwater discharged smoothly. The dredging of Sinkhole A04 and water diversion from the south of Gucan depression to Sinkhole A03 reduced the flooding time to 66.71 h (2.8 d). Therefore, constructing the south drainage system, diverting water from the south Gucan depression to Sinkhole A03, and discharging water from Sinkhole A04 to the outlet of the Yudang underground river are crucial for further control of flood hazards in the Andang depression. -
表 1 2023年4月到6月洼地洪涝时间统计
Table 1. Flooding time in depressions from April to June, 2023
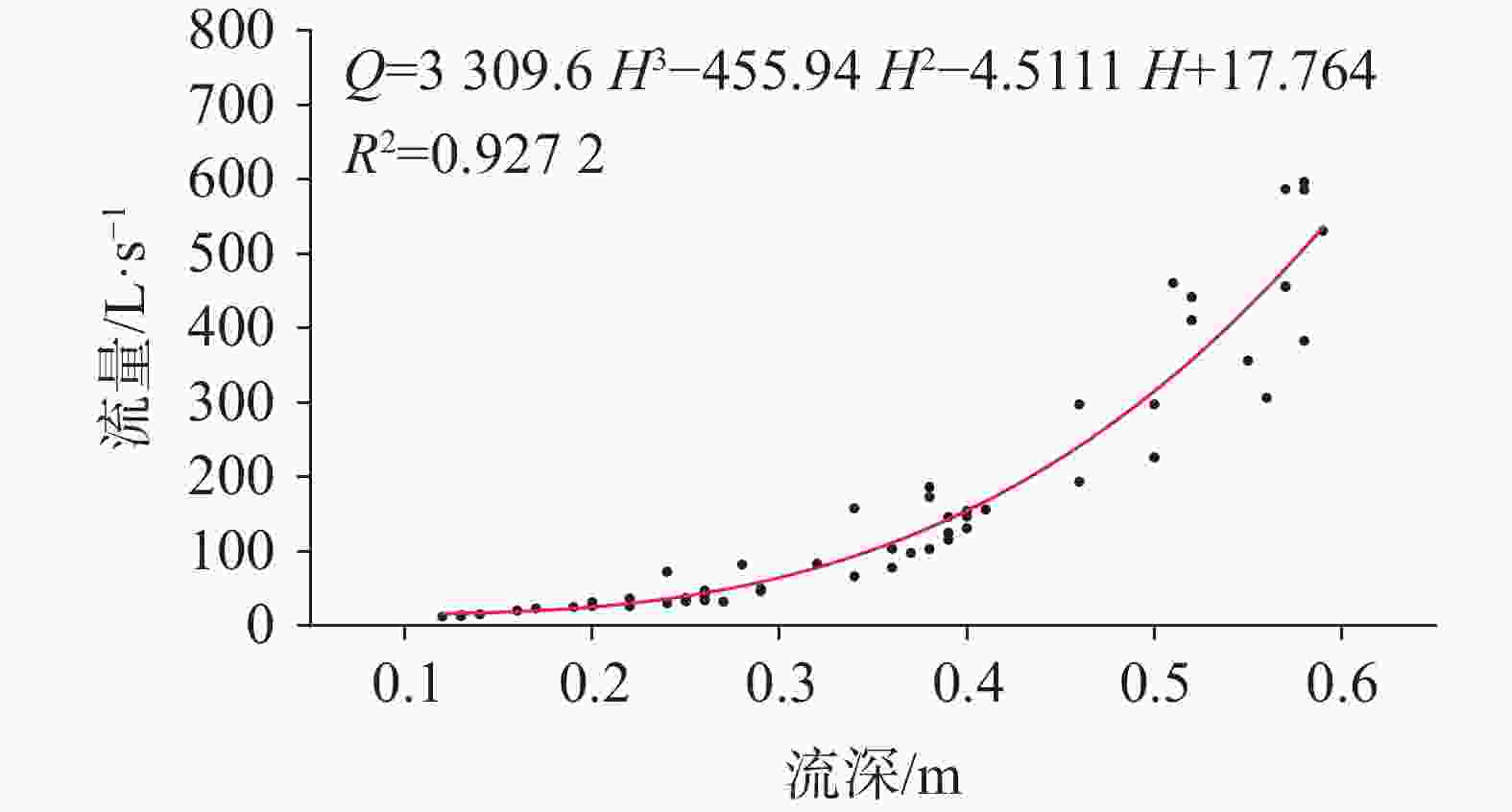
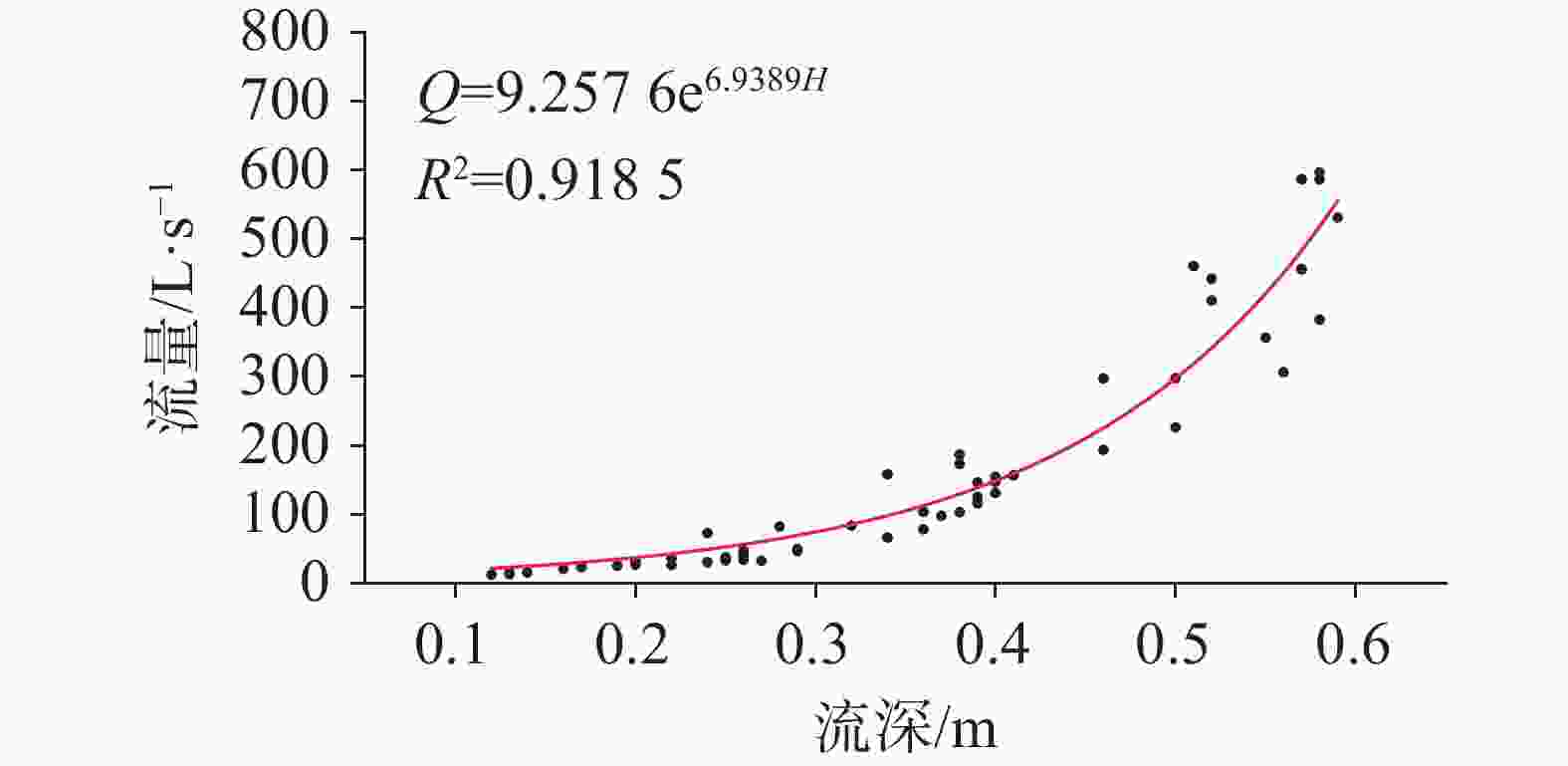
降雨时间 场雨降雨量 淹水时段 淹水时间/h 最大积水 mm 深度/m 时刻 4月3日-4月5日 62.6 4月05日08:00—4月06日01:30 17.5 0.457 4月5日14:00 4月22日-4月23日 90.8 4月23日15:00—4月24日15:30 24.5 0.815 4月24日0:15 4月29日 60 4月29日07:00—4月30日20:30 37.5 1.299 4月29日18:30 5月7日-5月9日 59.6 5月11日08:30—5月12日22:00 37.5 1.269 5月11日20:30 5月20日-5月22日 99.4 5月22日10:00—5月24日15:00 53 1.609 5月22日23:30 6月8日-6月9日 129.4 6月09日07:30—6月12日19:00 84 2.265 6月10日0:00 6月21日-6月22日 77.2 6月22日10:00—6月23日13:30 27.5 0.792 6月22日19:30 6月23日-6月25日 146.8 6月24日20:00—6月30日10:00 136 2.808 6月26日7:30 表 2 古蚕洼地汇水沟水深和A01三角堰口水深最大值对比
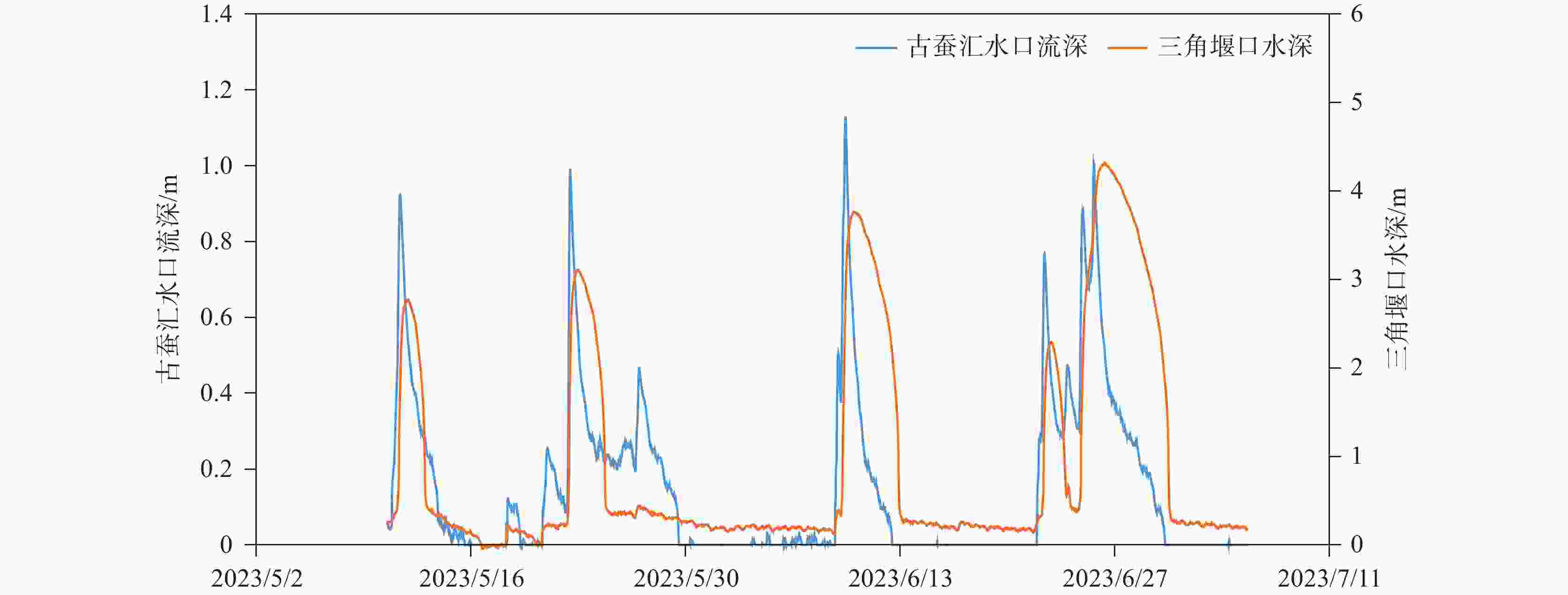
Table 2. Comparison of the maximum water depth of the catchment ditch in Gucan depression and water depth curve of the triangular weir mouth of A01
古蚕洼地排水沟 A01消水洞三角堰口 间隔 时间 深度/m 时间 深度/m 小时/h 5月11日09:00 时 0.924 5月11日20:30 时 1.269 11.5 5月22日11:15 时 0.993 5月22日23:30 时 1.609 12.09 6月09日10:30 时 1.122 6月10日0:00 时 2.265 13.5 6月22日10:00 时 0.768 6月22日19:30 时 0.792 9.5 6月25日15:15 时 1.006 6月26日7:30 时 2.808 16.5 -
[1] 袁道先. 岩溶地区的地质环境和水文生态问题[J]. 南方国土资源, 2003(1):22-25 [2] 李阳兵, 侯建筠, 谢德体. 中国西南岩溶生态研究进展[J]. 地理科学, 2002(3):365-370.LI Yangbing, HOU Jianyun, XIE Deti. The recent development of research on karst ecology in Southwest China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2002(3): 365-370. [3] 黎廷宇, 王世杰. 贵州省岩溶洼地洪涝灾害加重的原因分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2001, 21(3):1-4.LI Tingyu, WANG Shijie. Analysis of flood aggravation in Guizhou karst depression[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 21(3): 1-4. [4] 苏维词. 西南岩溶山区生态系统基本特征及其调控措施研究:以贵州省为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2004, 24(2):55-59.SU Weici. Characteristics and its regulation of karst ecosystem in Southwest China: In the case of Guizhu Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004, 24(2): 55-59. [5] 罗贵荣, 李兆林, 梁小平. 广西岩溶石山区洪涝灾害成因与防治对策研究:以马山岩溶地下河流域为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2010, 17(1):6-9.LUO Guirong, LI Zhaolin, LIANG Xiaoping. Research on the causes and countermeasures of flood disaster in Guangxi karst rock areas: A case study of karst underground river area in Mashan[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2010, 17(1): 6-9. [6] Fleury P, Maréchal J C, Ladouche B. Karst flash-flood forecasting in the city of Nîmes (Southern France)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 164: 26-35. [7] 姜光辉, 郭芳. 我国西南岩溶区表层岩溶带的水文动态分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2009, 36(5):89-93.JIANG Guanghui, GUO Fang. Hydrological character of epikarst in Southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2009, 36(5): 89-93. [8] Maréchal J C, Ladouche B, Dörfliger N. 地中海喀斯特山洪暴发:以尼姆喷泉为例[J]. 工程地质, 2008, 99(3-4):138-146.Maréchal J C, Ladouche B, Dörfliger N. Karst flash flooding in a Mediterranean karst, the example of Fontaine de Nîmes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 99(3-4): 138-146. [9] 郭纯青. 岩溶浸没内涝灾害风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2005(Suppl.1):337-342.GUO Chunqing. The evaluation of karst immersion-waterlogging hazards' risk[J]. Earth and Environment, 2005(Suppl.1): 337-342. [10] 郭纯青, 胡君春, 潘林艳. 中国西南典型岩溶洼地旱涝灾害演变规律:以西南块所岩溶区为例[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2013(11):160-164.GUO Chunqing, HU Junchun, PAN Linyan. Evolvement rules of drought and karst depression in Southwest China: A case study of Kuaisuo karst depression in Yunnan[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2013(11): 160-164. [11] 蒋忠诚. 中国南方表层岩溶带的特征及形成机理[J]. 热带地理, 1998(4):322-326.JIANG Zhongcheng. Features of epikarst zone in South China and formation mechanism[J]. Tropical Geography, 1998 (4): 322-326. [12] 李庆松, 李兆林, 裴建国, 覃小群, 易连兴, 梁茂珍. 马山东部岩溶洼地谷地内涝特征与治理规划[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(4):359-365.LI Qingsong, LI Zhaolin, PEI Jianguo, QIN Xiaoqun, YI Lianxing, LIANG Maozhen. Characteristics of waterlogging and management planning in karst depressions and valley in the east Mashan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(4): 359-365. [13] 罗锦珠. 桂林漓江洪旱灾害成因分析及综合治理刍议[J]. 人民珠江, 2006(4):77-79. [14] 肖攀, 万军伟, 曹雪琴, 黄小琴. 湖北宣恩岩底河流域洪涝灾害成因分析及防治对策[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2012, 32(4):500-504.XIAO Pan, WAN Junwei, CAO Xueqin, HUANG Xiaoqin. Formation and flood prevention in Yandi river in Xuanen of Hubei[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2012, 32(4): 500-504. [15] 李远强, 李中蔚. 岩溶山区洪涝灾害成因分析及对策[J]. 长江水利教育, 1995, 12(4):64-65. [16] 蒋忠诚, 罗为群, 邓艳, 曹建华, 覃星铭, 李衍青, 杨奇勇. 岩溶峰丛洼地水土漏失及防治研究[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(5):535-542.JIANG Zhongcheng, LUO Weiqun, DENG Yan, CAO Jianhua, QIN Xingming, LI Yanqing, YANG Qiyong. The Leakage of water and soil in the karst peak cluster depression and its prevention and treatment[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(5): 535-542. [17] 苏昌, 陈海波, 董炳维. 岩溶洪涝灾害成因机制分析及防治建议[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2008, 22(2):193-196.SU Chang, CHEN Haibo, DONG Bingwei. Genetic mechanism anaslysis and controlling suggestions on flood disaster in karst area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2008, 22(2): 193-196. [18] 裴建国, 李庆松. 生态环境破坏对岩溶洼地内涝的影响:以马山古寨乡为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2001, 20(4):297-300.PEI Jianguo, LI Qingsong. The effect of ecological environment change on waterlogging of karst depressions: A case study in Guzhai, Mashan county[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2001, 20(4): 297-300. [19] 裴建国. 广西溶洼系统结构特征及其对岩溶内涝的影响[J]. 广西科学, 2002(3):193-197.PEI Jianguo. The structure characteristic of karst depression system and its effect on karst depression waterlogging[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2002(3): 193-197. [20] 罗锦珠, 黄联锋. 广西北部地区“85·5”特大暴雨洪水分析[J]. 广西水利水电, 2001(4):42-45.LUO Jinzhu, HUANG Lianfeng. Analysis of "85·5" extreme storm flood in northern Guangxi[J]. GX Water Resources & Hydropower Engineering, 2001(4): 42-45. [21] 王恒松, 熊康宁, 刘云. 西南岩溶区地下水土流失浅析[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2008, 18(32):144-146.WANG Hengsong, XIONG Kangning, LIU Yun. Analysis on the belowground water and soil loss in karst area[J]. Sci-tech Information Development & Economy, 2008, 18(32): 144-146. [22] 黄琨, 武亚遵, 万军伟, 肖攀. 落马洞暗河发育特征及其洪涝成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(4):385-388.HUANG Kun, WU Yazun, WAN Junwei, XIAO Pan. Analysis on the development characteristic of the Luoma cave underground river and the origin of the flood[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(4): 385-388. [23] 黄秀凤. 下牙谷地岩溶内涝成因分析与治理工程方案设计[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(4):52-57.HUANG Xiufeng. Cause analysis of karst waterlogging and scheme design of the control project in Xiaya karst valley[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(4): 52-57. [24] Chen Weike, Dong Jing, Yan Chaohua, Dong Hui, Liu Ping. What causes waterlogging?—Explore the urban waterlogging control scheme through system dynamics simulation[J]. Sustainability (Switzerland), 2021, 13(15): 8546. [25] Ow L F, Chan E. Deferring waterlogging through stormwater control and channelling of runoff[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2021, 65: 127351. [26] 罗书文, 杨桃, 邓亚东, 吕勇, 吴克华, 孟庆鑫. 桂林岩溶地貌发育演化过程地文期的解析[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(10):1652-1665.LUO Shuwen, YANG Tao, DENG Yadong, LYU Yong, WU Kehua, MENG Qingxin. Analysis of the physiographic stages of the development and evolution process of karst geomorphology in Guilin, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(10): 1652-1665. [27] 罗书文, 吕勇, 吴克华, 邓亚东, 杨桃, 潘明, 傅良同. 桂林峰林平原、峰丛洼地残留中生代地层空间展布形成机制探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):805-814.LUO Shuwen, LYU Yong, WU Kehua, DENG Yadong, YANG Tao, PAN Ming, FU Liangtong. Formation mechanism of the spatial distribution of Mesozoic strata in Guilin peak-forest plain and peak-cluster depression[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5): 805-814. [28] 邓自强, 林玉石, 刘功余, 张美良. 岩溶发育过程中的改造与建造作用分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 1993, 12(1):23-32.DENG Ziqiang, LIN Yushi, LIU Gongyu, ZHANG Meiliang. Analysis on reformation and formation processes in the course of karst development[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1993, 12(1): 23-32. [29] 缪钟灵. 漓江发育演化及与相邻流域关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 1998, 17(4):385-391.MIAO Zhongling. The development and evolution of Lijiang river and its relations to its adjacent basins[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1998, 17(4): 385-391. -




 下载:
下载: