Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal water in northern Zhangqiu
-
摘要: 济南市章丘北部地区发育有厚度巨大的晚古生代至新生代沉积地层,断裂构造和岩浆岩也较为发育,区内地热资源丰富,目前有地热井3口,均位于断裂带附近。文章利用水化学和同位素数据,分析区内地热流体的水化学特征、水—岩作用过程、补给来源、形成年龄,估算补给区高程、热储温度、热水循环深度。结果表明:研究区地热流体水化学类型为Cl·SO4-Na·Ca型或SO4·Cl-Ca·Na型;水化学组分主要来源于水—岩溶解作用,且具有相似的水文地球化学过程;大气降水补给,补给区高程为+563~+616 m,14C表观年龄在5.55~29.71 ka之间,均是现代水与古水的混合水;利用玉髓温标计算的热储温度为41.9~52.4 ℃,相应循环深度为622~1 565 m;研究区为深循环—弱开放型岩溶热储,其地热水经深循环加热而形成,形成和富集受断裂构造控制明显,其为层状兼带状热储,属中低温地热资源。Abstract:
The northern part of Zhangqiu district in Jinnan City has developed a thick sedimentary formation from the late Paleozoic to the Cenozoic. In this district, relatively well-developed fault structures and magmatic rocks provide good geothermal conditions. Abundant geothermal resources have been discovered in the study area, with three geothermal wells located near the fault zone. Therefore, establishing the genesis model of geothermal resources is significant for their future sustainable development and utilization. Based on hydrochemical and isotopic data of the study area, hydrochemical characteristics, water-rock interaction process, recharge source and formation age of geothermal water have been analyzed in this study. Besides, the elevation of the recharge area, thermal reservoir temperature, and depth of hot water circulation have also been calculated. Research findings show that geothermal water in the study area is composed of Cl·SO4-Na·Ca or SO4·Cl-Ca·Na, whose hydrochemical components mainly come from water-rock dissolution in the similar hydrogeochemical process. The source of water recharge is supplied by atmospheric precipitation, at an elevation from +563 m to +616 m. The 14C apparent age ranges from 5.55 ka to 29.71 ka. The geothermal water is mixed with modern water and ancient water. The chalcedony temperature scale shows that the temperature of geothermal reservoir is at 41.9–52.4 ℃, with the circulation depth of geothermal water at 622–1,565 m. The study area is a small-opened karst hot reservoir with deep circulation, during which geothermal water is heated up. Formation and enrichment of geothermal water are significantly controlled by fault structures. The geothermal reservoir is of stratified and banded type, belonging to geothermal resources at medium-low temperature. -
Key words:
- Zhangqiu district /
- geothermal water /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- isotope /
- genesis model
-
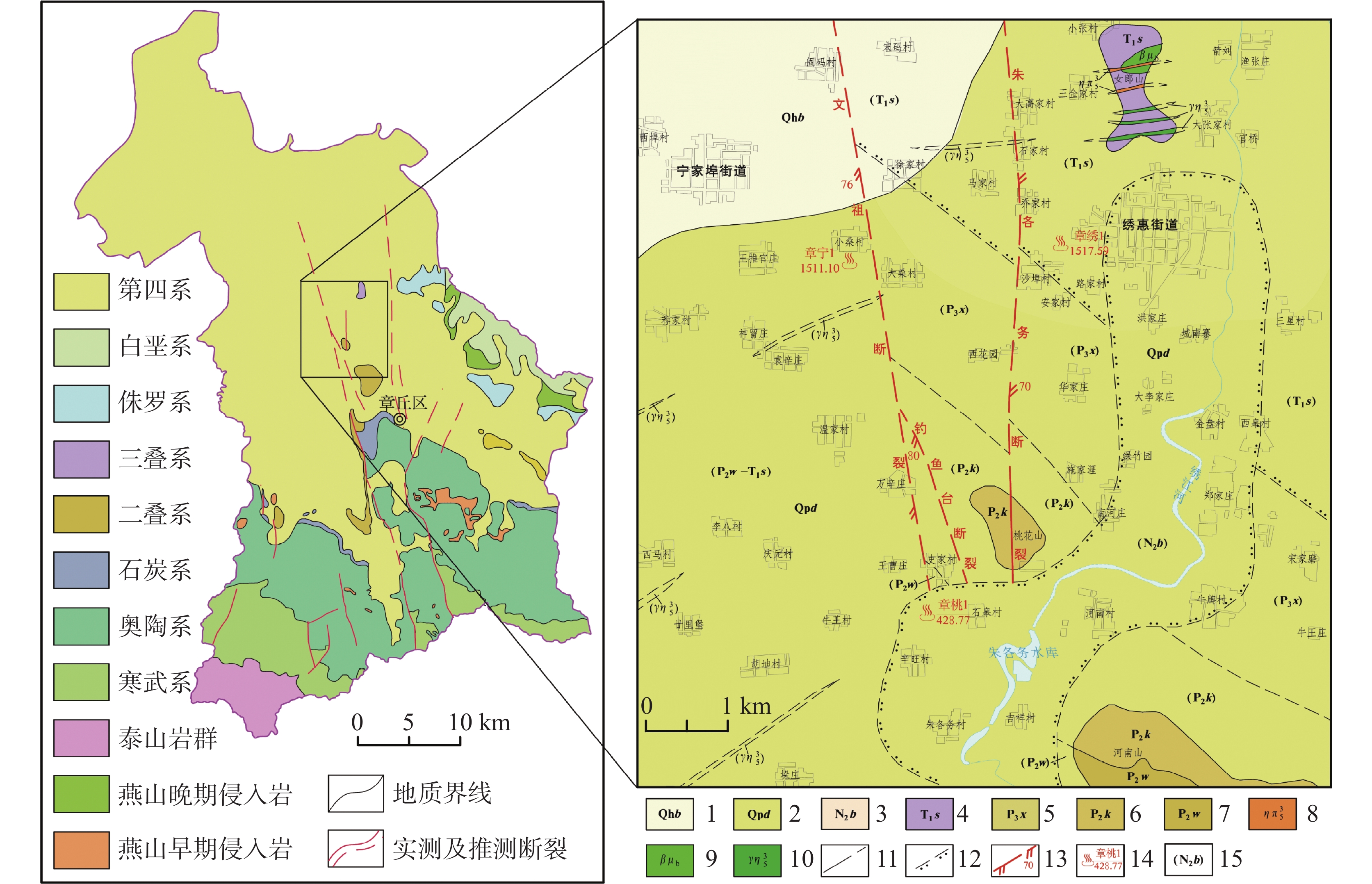
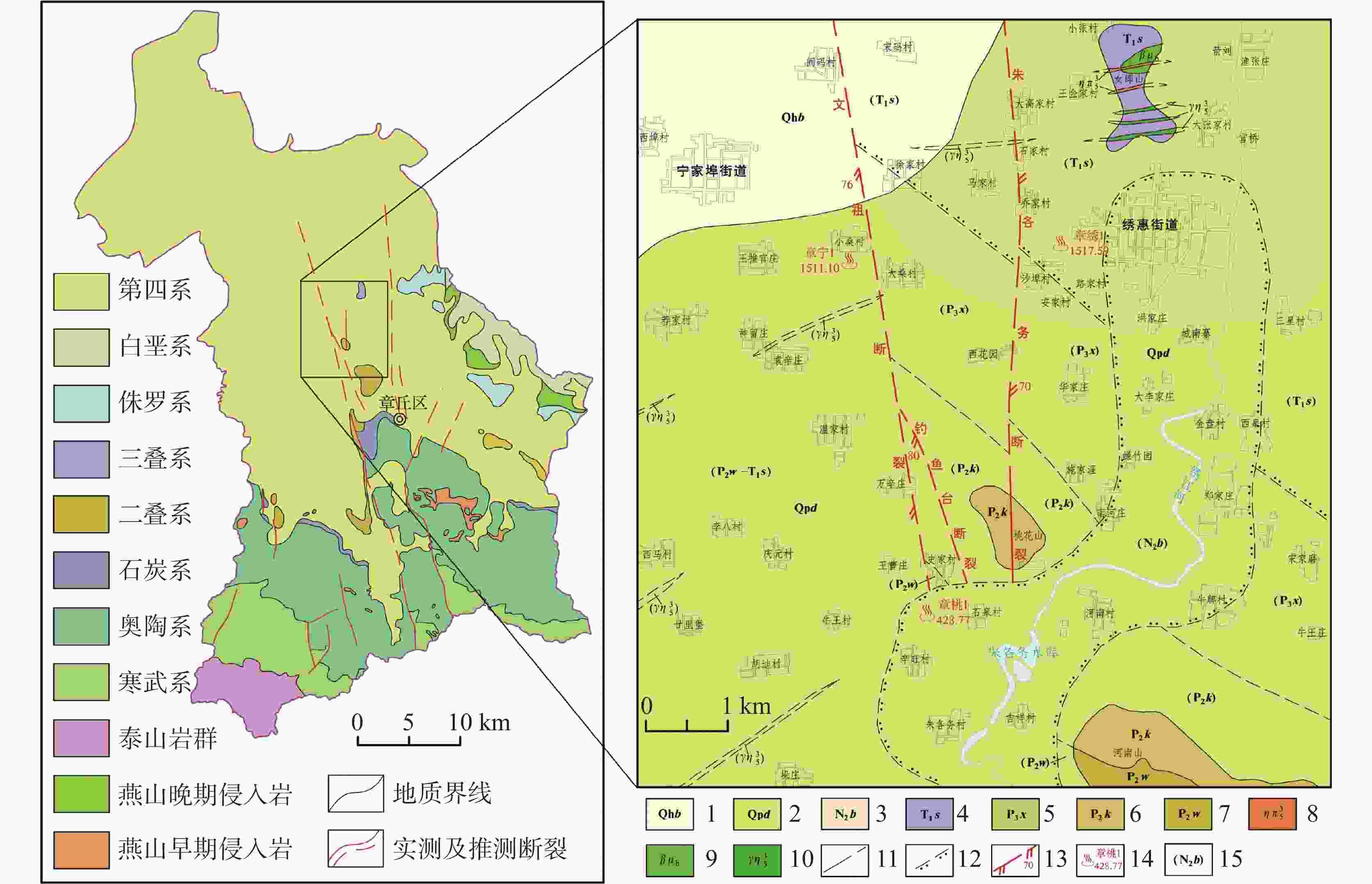
图 1 研究区地质及地热井位置分布图
1.第四系白云湖组 2.第四系大站组 3.新近系巴漏河组 4.三叠系孙家沟组 5.二叠系石盒子群孝妇河组 6.二叠系石盒子群奎山组 7.二叠系石盒子群万山组 8.中粗粒二长岩 9.辉绿玢岩 10.辉长玢岩 11.实测及推测地质界线 12.推测角度不整合界线 13.推测及实测张扭性断裂及产状(齿向示斜落盘方向) 14.地热井编号及深度/m 15.隐伏地层
Figure 1. Geology and distribution of geothermal wells in the study area
1. Quaternary Baiyunhu Formation 2. Quaternary Dazhan Formation 3. Neogene Baluohe Formation 4. Triassic Sunjiagou Formation 5. Xiaofuhe Formation of Permian Shihezi Group 6. Kuishan Formation of Permian Shihezi Group 7. Wanshan Formation of Permian Shihezi Group 8. medium-coarse monzonite 9. sillite 10. gabbroporphyrite 11. measured and extrapolated geological boundaries 12. extrapolated angular unconformity boundary 13. measured and extrapolated tension-torsion fracture and its occurrence (The tooth trace shows the direction of the inclined falling disc.) 14. number and depth of geothermal wells/m 15. buried stratum
表 1 研究区地热井信息表
Table 1. Information of geothermal wells in the study area
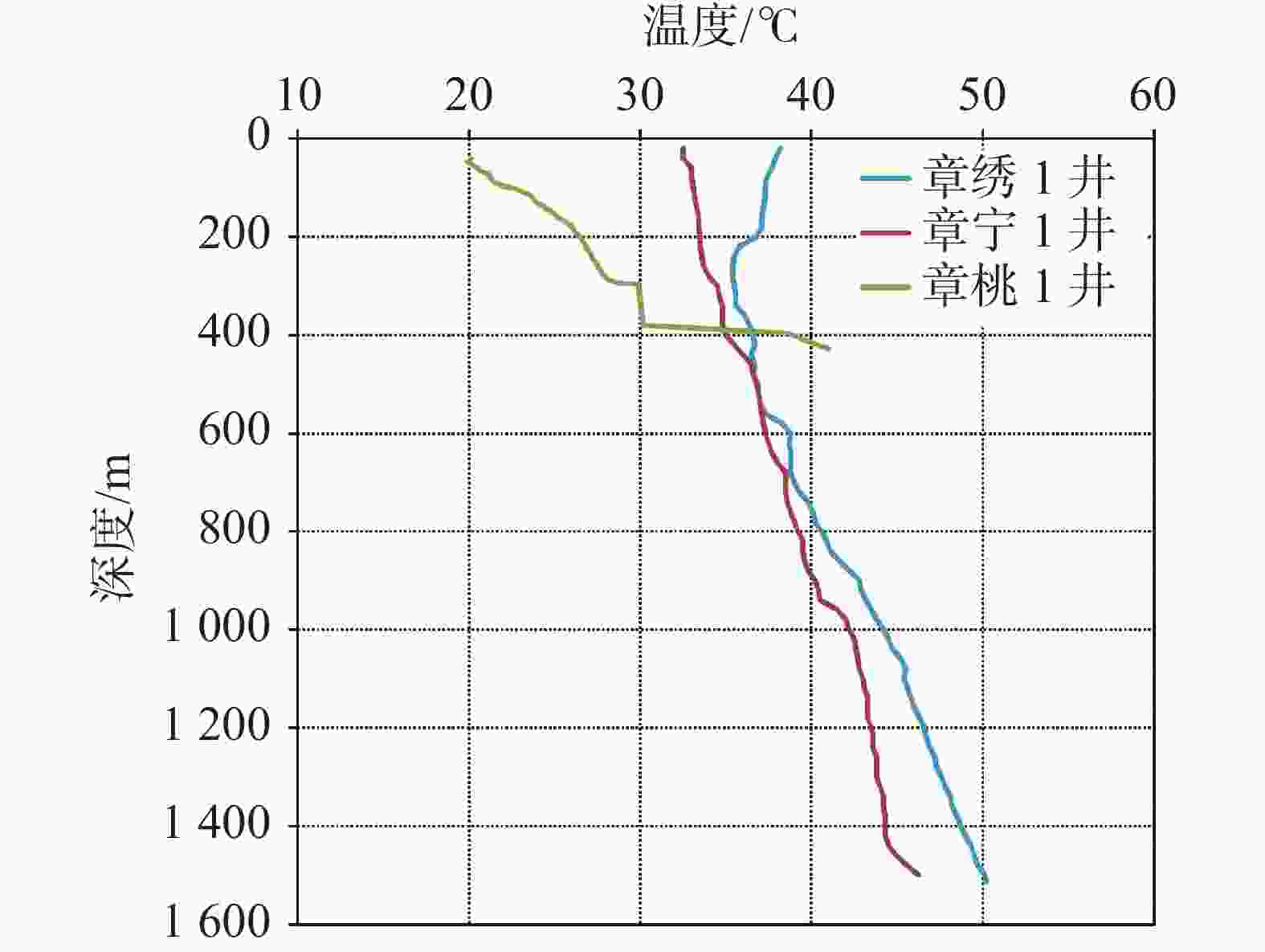
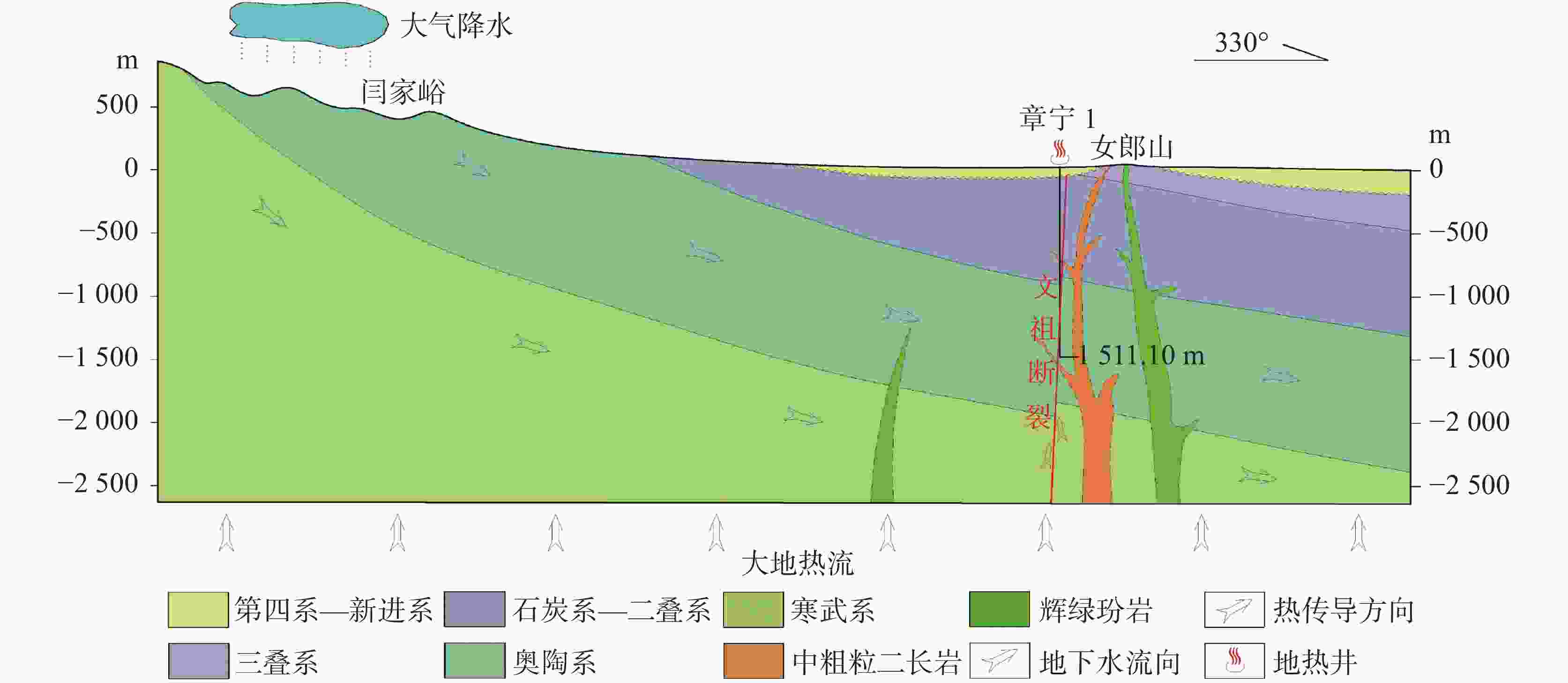
井编号 位置 井深/m 盖层时代 盖层厚度/m 热储层时代 揭露热储厚度/m 孔底温度/℃ 地温梯度/℃·100 m−1 水温/℃ 章桃1 枣园史家村南 428.77 Q,P,C 378.31 O2-3M 50.46 41.00 6.46 41.0 章宁1 宁家埠小桑村南 1 511.10 Q,T,P,C 954.00 O2-3M 557.10 46.24 2.09 45.5 章绣1 绣惠沙埠村北 1 517.59 Q,T,P,C 975.00 O2-3M 542.59 50.20 2.35 40.0 表 2 章绣1地热勘探井大地热流计算结果
Table 2. Results of terrestrial heat flow of Zhangxiu No.1 geothermal exploration well
岩性 深度范围/m 厚度/m 地温梯度/ ℃·km−1 热导率/W·(m ℃)−1 热流值/mW·m−2 平均热流值/ mW·m−2 灰岩 975~1 170 195 21.03 2.99 62.9 45.5 蚀变岩 1 170~1 200 30 16.67 3.29 54.8 灰岩 1 200~1 517 317 11.36 2.99 34.0 表 3 研究区地热水主要水化学组成
Table 3. Main hydrochemical composition of geothermal water in the study area
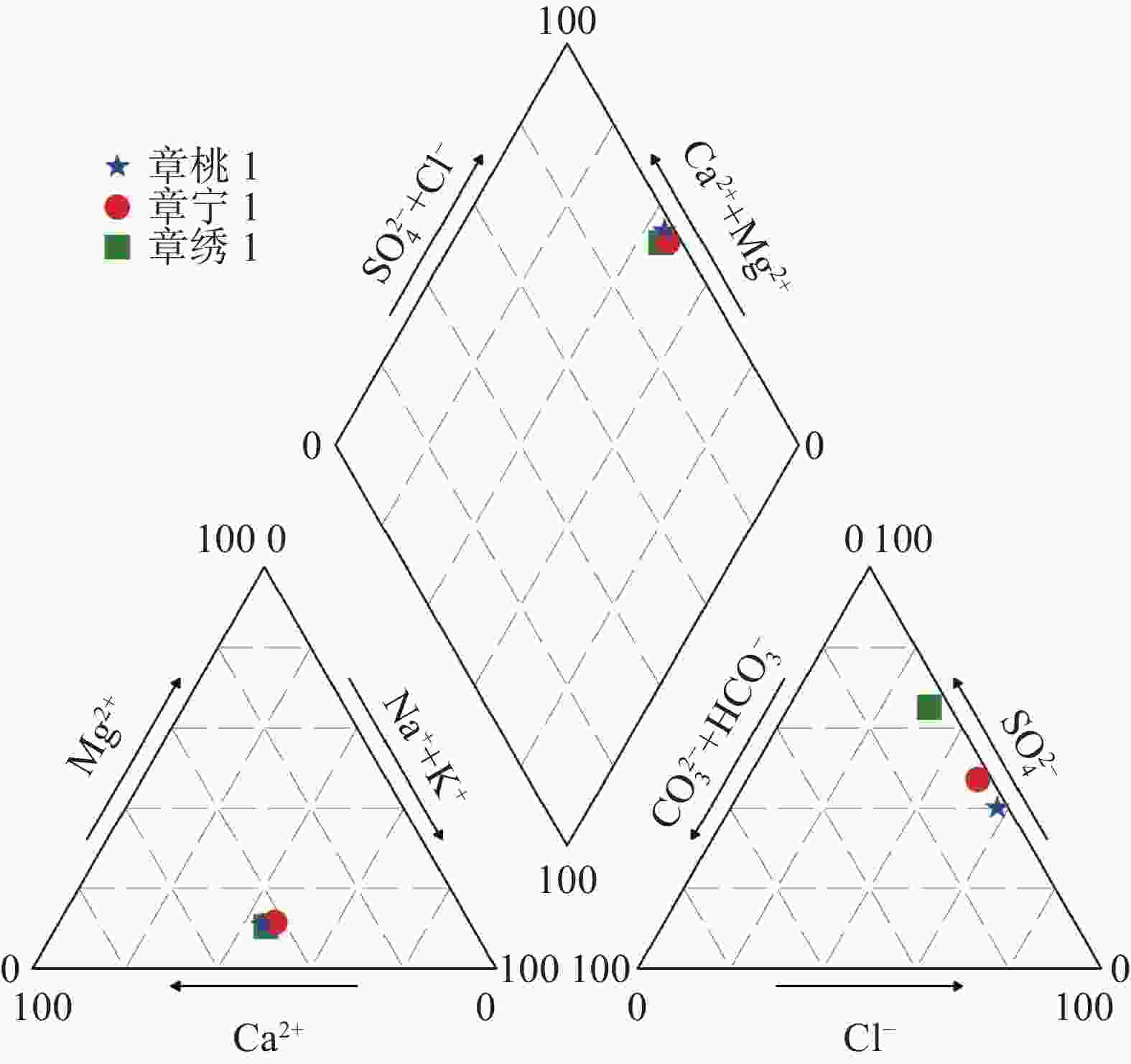
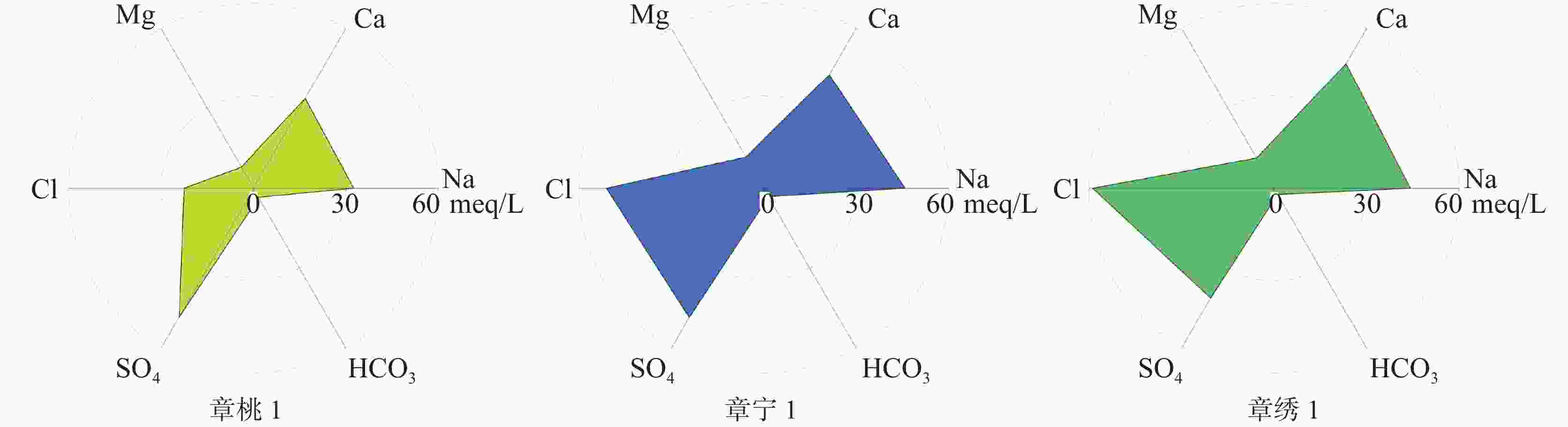
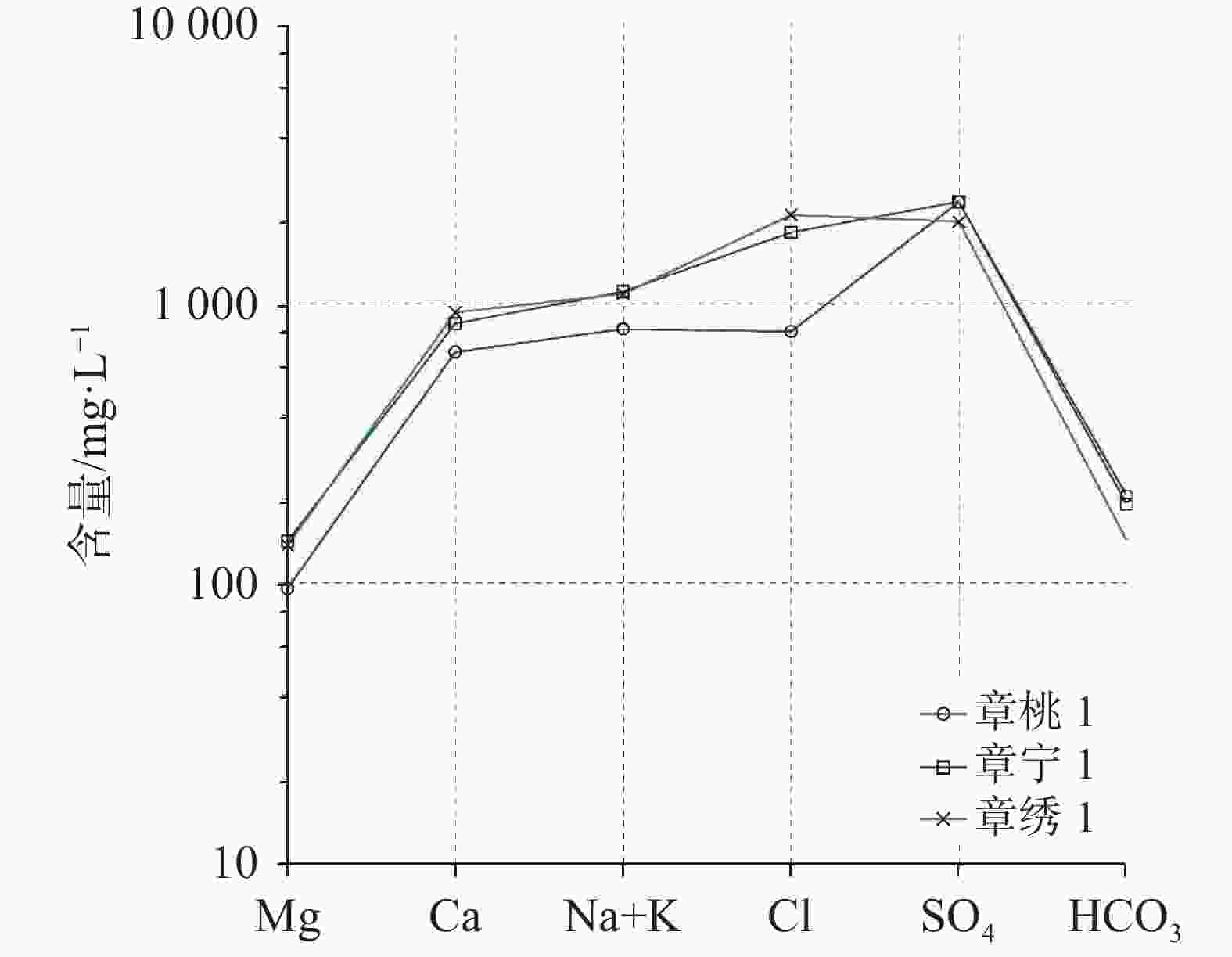
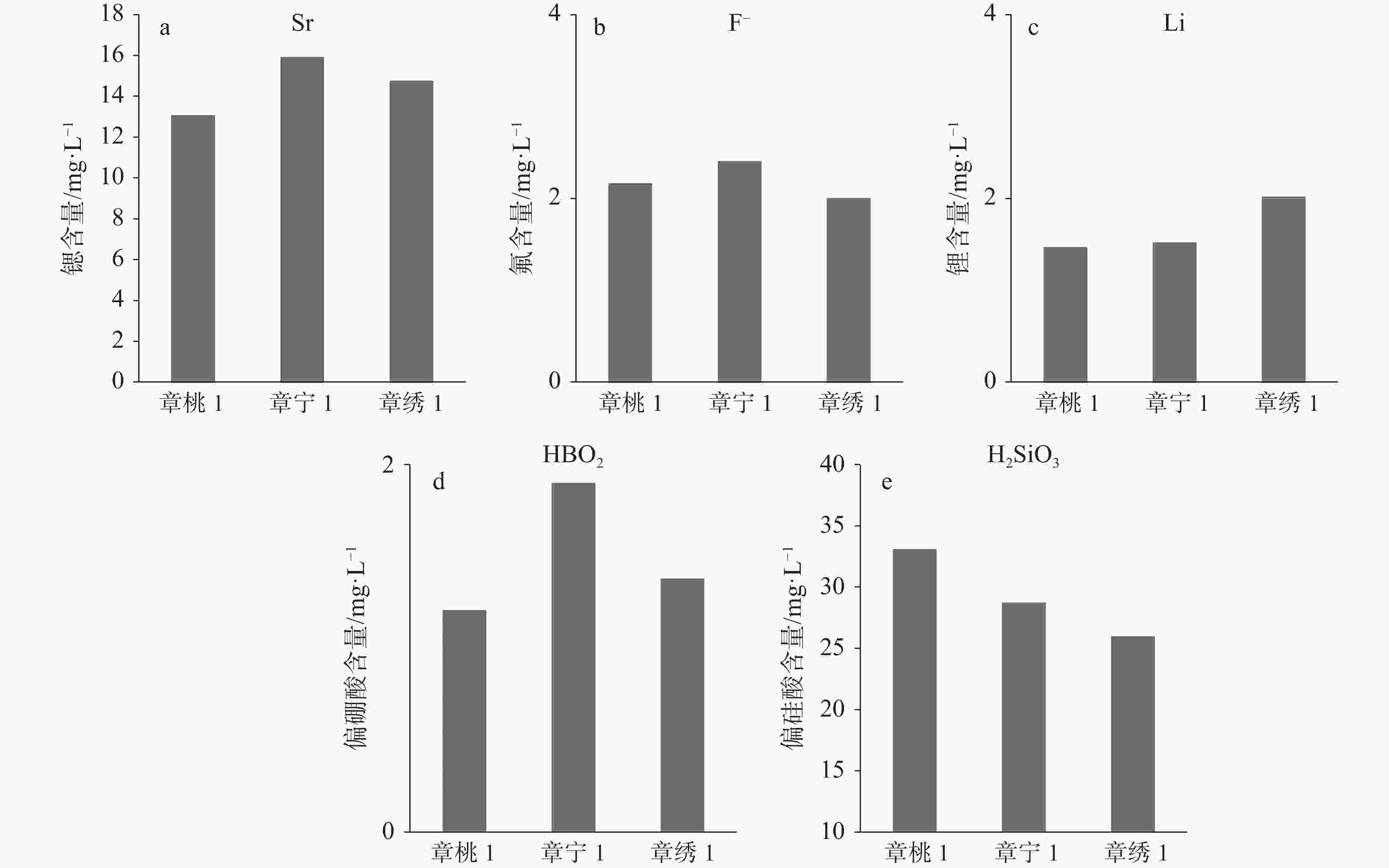
井编号 水温/ ℃ pH 水化学组分/mg·L−1 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 章桃1 41.0 7.59 67.28 747.51 673.82 95.83 798.63 2 320.04 205.88 章宁1 45.5 7.05 55.84 1 054.00 852.83 141.65 1 809.72 2 324.72 191.71 章绣1 40.0 7.04 73.57 1 015.59 935.10 137.03 2 087.18 1 975.38 142.30 井编号 水化学组分/mg·L−1 F− Br− 总硬度 TDS H2SiO3 HBO2 Li Sr 章桃1 2.17 1.45 2 122.28 4 830.00 33.10 1.21 1.48 13.09 章宁1 2.41 3.10 2 766.27 6 602.05 28.74 1.90 1.53 15.93 章绣1 2.01 2.64 3 183.41 6 311.00 25.99 1.38 2.03 14.77 表 4 补给、径流、排泄区主要水化学组成
Table 4. Main hydrochemical compositions of groundwater in recharge, runoff and discharge areas
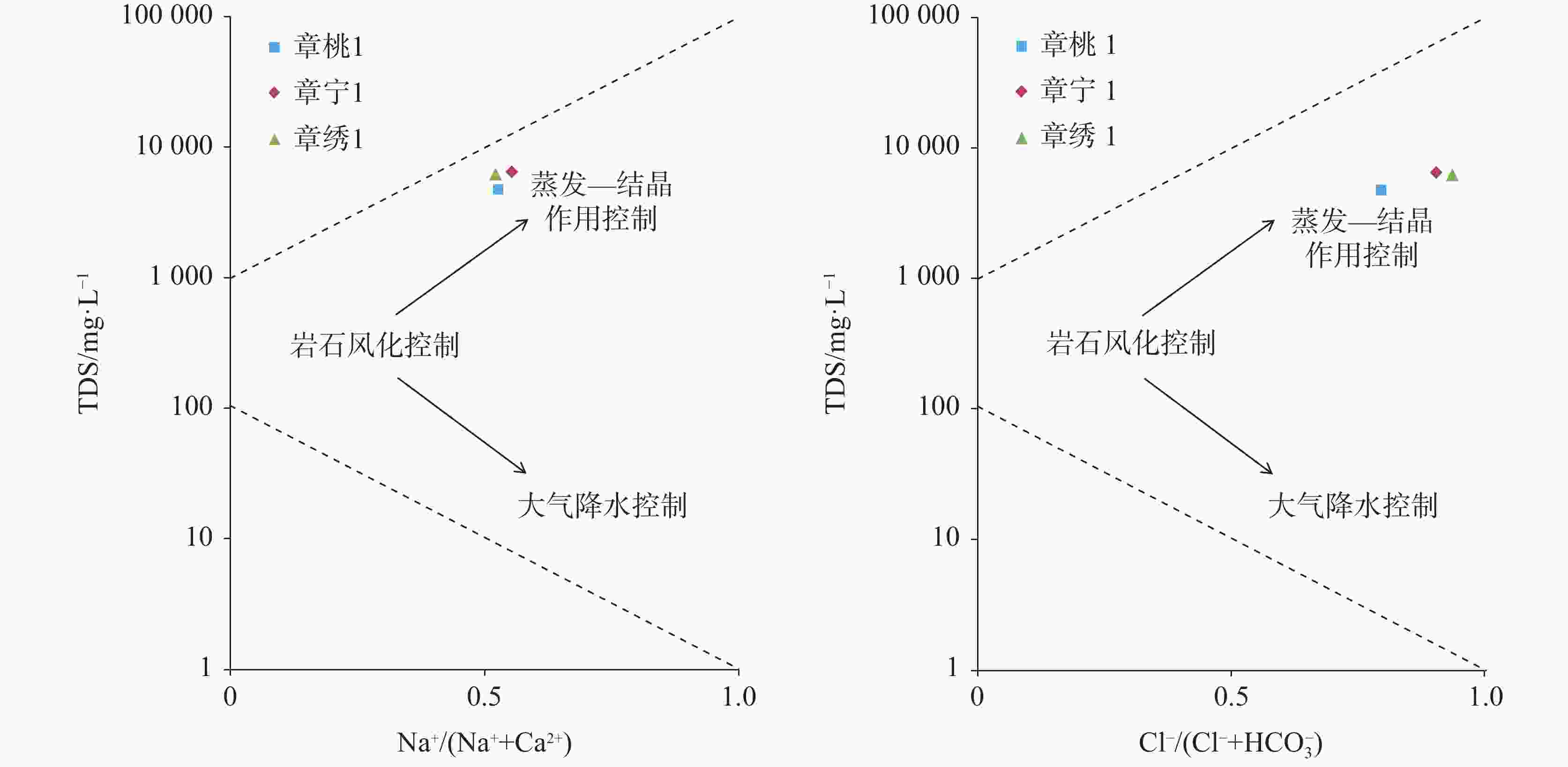
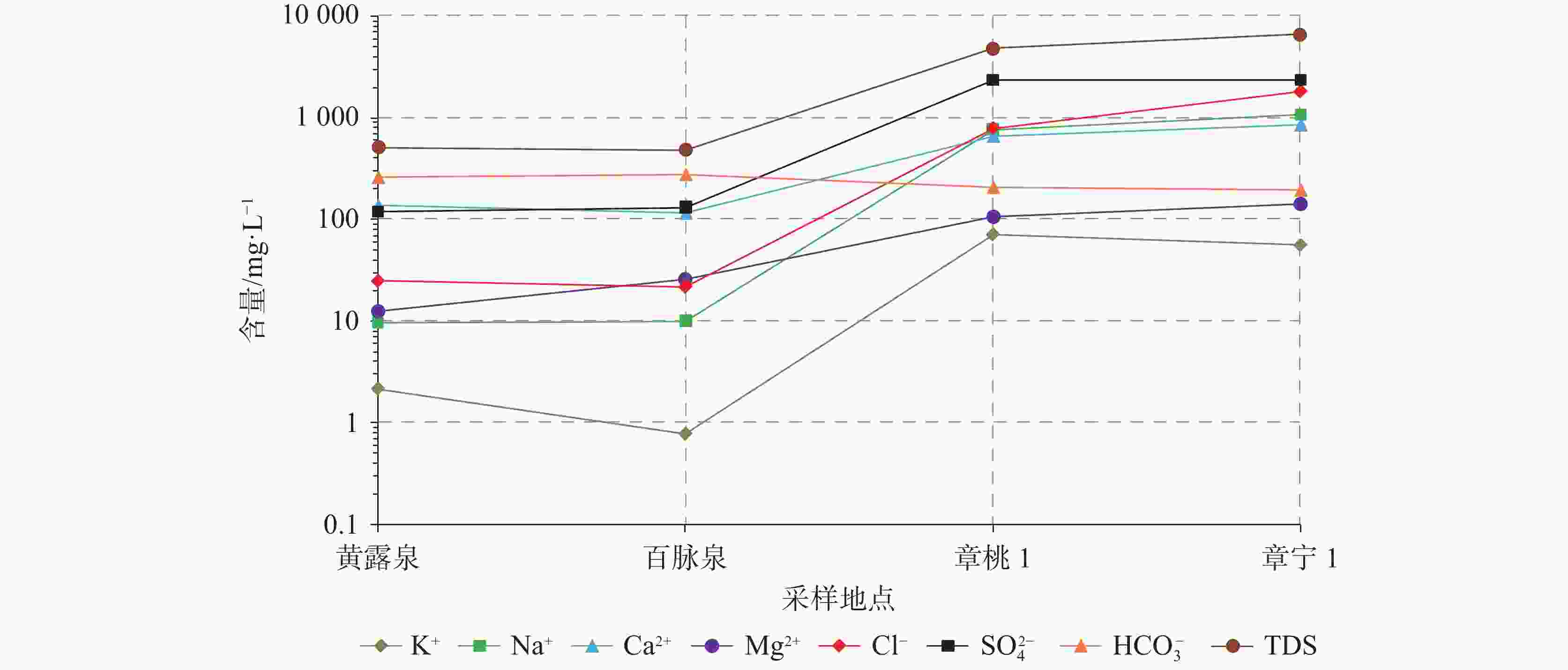
分区 采样地点 水化学组分/mg·L−1 水化学类型 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ TDS 补给区 黄露泉 2.17 9.58 136.33 12.49 24.31 117.84 256.19 502.17 HCO3·SO4-Ca 径流区 百脉泉 0.78 10.00 115.73 25.58 21.27 129.63 273.66 479.24 HCO3·SO4-Ca·Mg 径流—排泄区 章桃1 70.92 756.09 661.64 106.09 788.00 2 334.48 204.02 4 844.50 SO4·Cl-Ca·Na 章宁1 55.84 1 054.00 852.83 141.65 1 809.72 2 324.72 191.71 6 602.05 Cl·SO4-Na·Ca 表 5 研究区及周边代表性水样同位素组成
Table 5. Isotopic compositions of representative water samples in and around the study area
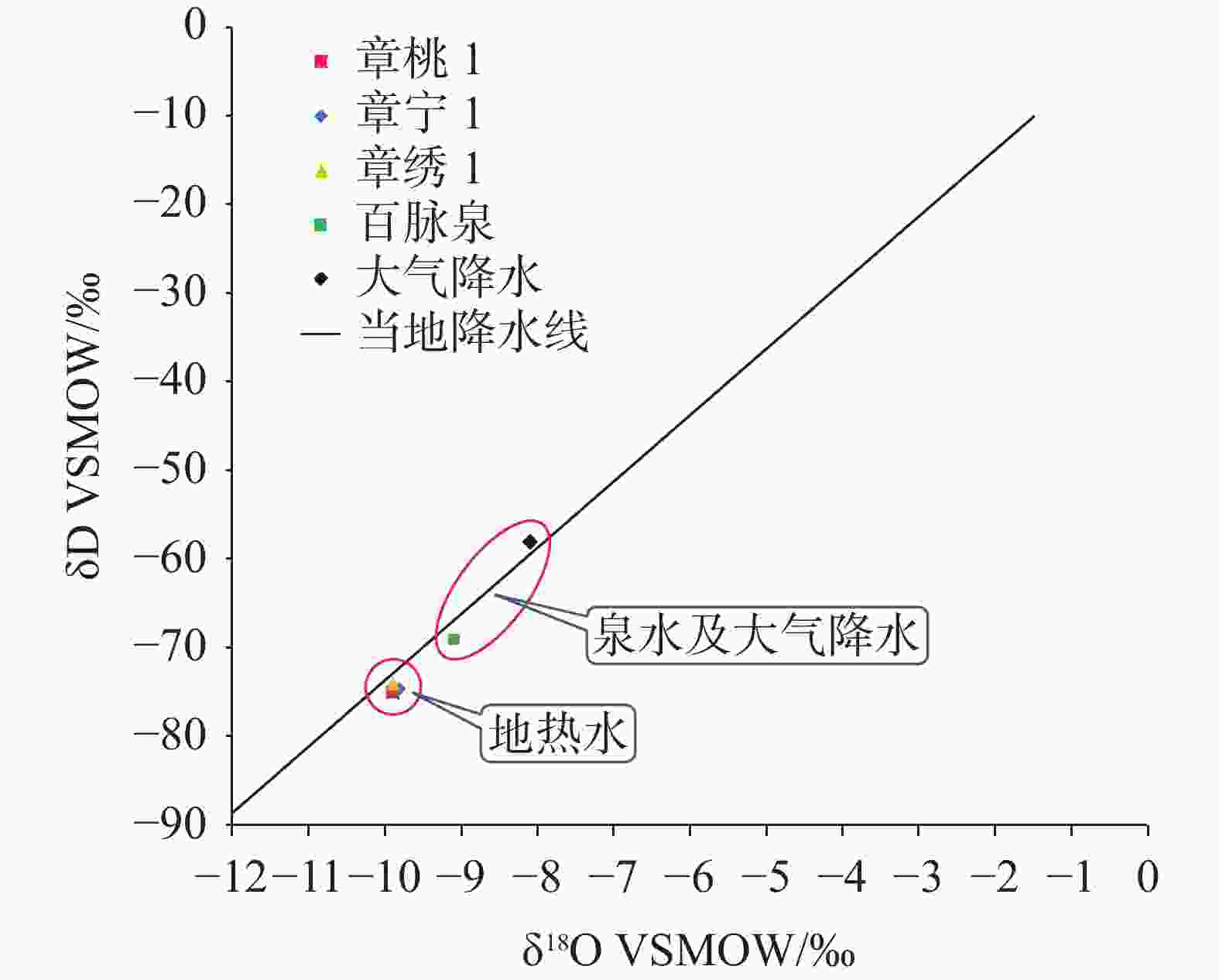
样品编号 样品类型 δD VSMOW/‰ δ18O VSMOW/‰ 现代碳百分数/% 14C表观年龄/ka 章桃1* 地热水 −75.00 −9.9 12.85±1.55 16.96±1.0.00 章宁1 地热水 −74.58 −9.8 51.10±0.80 5.55±0.08 章绣1 地热水 −74.00 −9.9 2.75±1.29 29.71±3.87 百脉泉* 常温泉水 −69.00 −9.1 大气降水* 大气降水 −58.00 −8.1 注:表中*数据来源于文献[16]、[27]。
Note: Data marked with "*" in above table is derived from literatures of [16] and [27].表 6 研究区地热水水化学特征系数
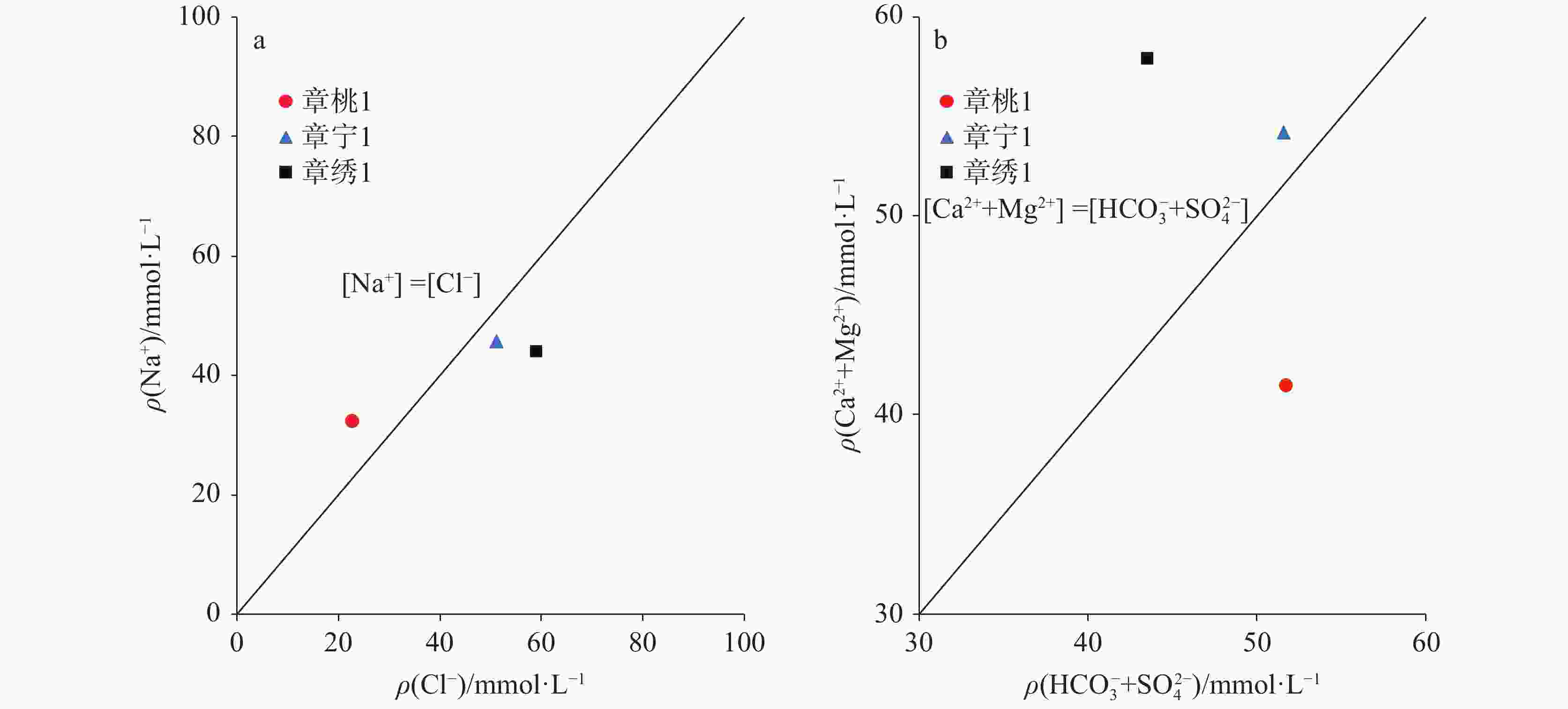
Table 6. Hydrochemical characteristic coefficient of geothermal water in the study area
井编号 γCl−/γCa2+ γCl−/(γ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$+γ${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-}$) 章桃1 0.67 6.67 章宁1 1.20 16.22 章绣1 1.26 25.20 表 7 二氧化硅地热温标计算结果
Table 7. Calculation results of silica geothermometer
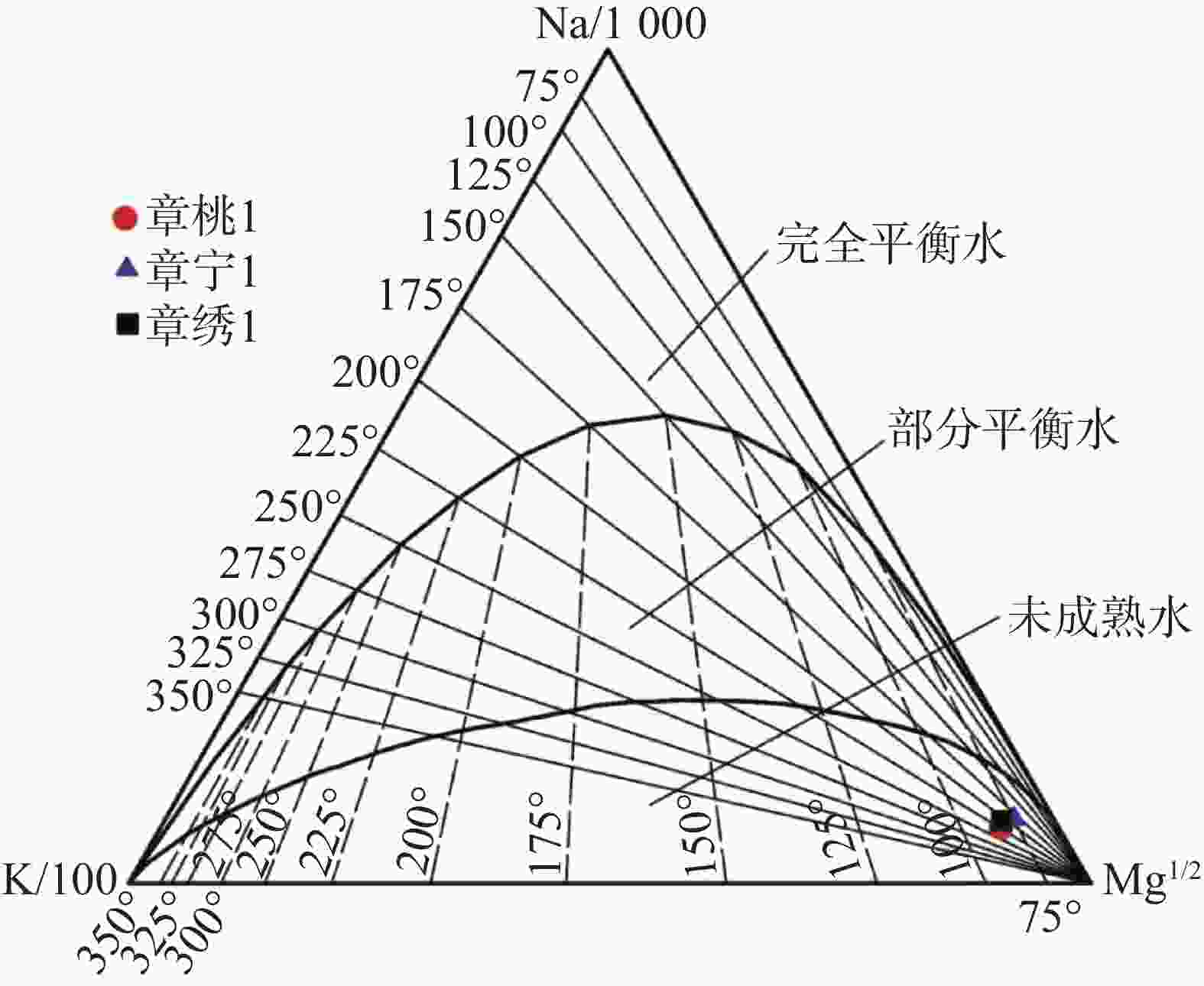
井编号 SiO2/mg·L−1 热储温度/ ℃ 玉髓温标 石英温标 章桃1 33.10 52.4 83.5 章宁1 28.74 46.2 77.6 章绣1 25.99 41.9 73.6 表 8 研究区地热水循环深度估算结果
Table 8. Estimation results of geothermal water circulation depth in the study area
井编号 热储温度/ ℃ 平均气温/ ℃ 地温梯度/ ℃·100 m−1 常温带深度/m 循环深度/m 章桃1 52.4 14.1 6.46 30 622 章宁1 46.2 14.1 2.09 30 1 565 章绣1 41.9 14.1 2.35 30 1 212 -
[1] 徐雪球, 杜建国, 王素娟. 江苏省地热资源开发利用现状与建议[C]//中国地热能:成就与展望——李四光倡导中国地热能开发利用40周年纪念大会暨中国地热发展研讨会论文集, 2010: 346-349.XU Xueqiu, DU Jianguo, WANG Sujuan. Current situation and suggestions on the development and utilization of geothermal resources in Jiangsu Province[C]//Geothermal Energy in China: Achievements and Prospects—Proceedings of the 40th Anniversary Conference of Li Siguang's Advocacy for the Development and Utilization of Geothermal Energy in China and the Symposium on Geothermal Energy Development in China, 2010: 346-349. [2] 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4):449-459. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02WANG Guiling, ZHANG Wei, LIANG Jiyun, LIN Wenjing, LIU Zhiming, WANG Wanli. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 449-459. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02 [3] 王奎峰, 李文平, 韩代成, 赵辉. 山东省临清地热田地热水化学特征及热水起源研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2014, 37(3):230-236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2014.03.012WANG Kuifeng, LI Wenping, HAN Daicheng, ZHAO Hui. Hydrochemistry and origin of the Linqing geothermal field in Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2014, 37(3): 230-236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2014.03.012 [4] 张保建. 鲁西北地区地下热水的水文地球化学特征及形成条件研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2011.ZHANG Baojian. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation conditions of the geothermal water in northwestern Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011. [5] 张保建, 沈照理, 乔增宝, 亓麟. 聊城市东部岩溶地热田地下热水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2009, 28(3):263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.03.006ZHANG Baojian, SHEN Zhaoli, QIAO Zengbao, QI Lin. Analysis on hydro-chemical features and origin of the hot spring in karst geothermal field, east Liaocheng City[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2009, 28(3): 263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.03.006 [6] 卞跃跃, 赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(4):491-497. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.060401BIAN Yueyue, ZHAO Dan. Genesis of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(4): 491-497. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.060401 [7] 谭梦如, 周训, 张彧齐, 刘海生, 余鸣潇, 海阔. 云南勐海县勐阿街温泉水化学和同位素特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(3):70-80.TAN Mengru, ZHOU Xun, ZHANG Yuqi, LIU Haisheng, YU Mingxiao, HAI Kuo. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics and formation of the Mengajie hot spring in Menghai county of Yunnan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(3): 70-80. [8] 徐刚, 伍坤宇, 王鹏, 陈永东, 李兴彦, 胡林, 刘子畅, 李海. 藏北温泉盆地地热田水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):299-310. doi: 10.11932/karst20200301XU Gang, WU Kunyu, WANG Peng, CHEN Yongdong, LI Xingyan, HU Lin, LIU Zichang, LI Hai. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the geothermal field in Wenquan basin, northern Tibet[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 299-310. doi: 10.11932/karst20200301 [9] 徐成华, 于丹丹, 骆祖江. 南京汤泉地下热水化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(28):11472-11478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.28.011XU Chenghua, YU Dandan, LUO Zujiang. Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal water from the Tangquan in Nanjing and its indicating significance[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(28): 11472-11478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.28.011 [10] 廖昕, 蒋翰, 徐正宣, 宋章, 欧阳吉, 张云辉, 巫锡勇. 西藏东部阿旺地下热水化学特征及其成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(4):916-924.LIAO Xin, JIANG Han, XU Zhengxuan, SONG Zhang, OUYANG Ji, ZHANG Yunhui, WU Xiyong. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis mechanism of geothermal water in Awang, eastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(4): 916-924. [11] 卢兆群, 彭明章, 董妍, 亓协全, 朱光骥, 孟祥鑫. 山东平阴地热水水文地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2022, 9(1):104-114.LU Zhaoqun, PENG Mingzhang, DONG Yan, QI Xiequan, ZHU Guangji, MENG Xiangxin. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of geothermal water in Pingyin of Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(1): 104-114. [12] 尚敏, 易武, 张兰新. 济南北部地区地热资源形成条件研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2008(4):22-25.SHANG Min, YI Wu, ZHANG Lanxin. Research on forming condition of geothermal resources in north region of Jinan[J]. Journal of Three Gorges University (Natural Science), 2008(4): 22-25. [13] 张中祥, 张海林. 济南北部地热田开发与保护建议[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2008, 31(3):264-269.ZHANG Zhongxiang, ZHANG Hailin. Development and protection suggestion for geothermal field in northern Jinan, Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2008, 31(3): 264-269. [14] 隋海波, 康凤新, 李常锁, 韩建江, 邢立亭. 水化学特征揭示的济北地热水与济南泉水关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(1):49-58. doi: 10.11932/karst20170106SUI Haibo, KANG Fengxin, LI Changsuo, HAN Jianjiang, XING Liting. Relationship between north Ji'nan geothermal water and Ji'nan spring water revealed by hydrogeochemical characteristics[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(1): 49-58. doi: 10.11932/karst20170106 [15] 蒙永辉, 王集宁, 于得芹. 章丘市枣园桃花山地热田地质特征分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 2010, 26(11):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2010.11.005MENG Yonghui, WANG Jining, YU Deqin. Analysis on geological characteristics of Taohuashan geothermal field in Zaoyuan of Zhangqiu City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2010, 26(11): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2010.11.005 [16] 蒙永辉, 于得芹. 章丘枣园桃花山地热水与百脉泉水力联系浅析[C]//地质调查环境保障实现找矿新突破-2012年华东六省一市地学科技论坛文集, 2012:285-289.MENG Yonghui, YU Deqin. Hydraulic connection analysis on geothermal water and Baimai springs located on Zaoyuan peach blossom mountain in Zhangqiu City[C]//Geological survey, environmental protection and new breakthroughs in ore prospecting-collected papers of the 2012 Geological Science and Technology Forum of Six Provinces and One City in East China, 2012: 285-289. [17] 程洪柱. 济南东部宁家埠地区地热资源特征与开发利用探讨[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2018, 30(Suppl.1):72-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.S1.14CHENG Hongzhu. Probing into geothermal resource features, exploitation and utilization in Ningjiabu area to the east of Jinan[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2018, 30(Suppl.1): 72-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.S1.14 [18] 程洪柱, 成世才, 王振涛. 基于水化学特征的“奥灰”地热流体水文地球化学演化机制研究:以济南东部章宁1地热井为例[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(8):20-25.CHENG Hongzhu, CHENG Shicai, WANG Zhentao. Study on hydrogeochemical evolution mechanism of "Ordovician limestone" geothermal fluid based on hydrochemical characteristics: Setting No. 1 Zhangning geothermal well in eastern Ji'nan as an example[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(8): 20-25. [19] 张元培, 牛俊强, 王炜. 湖北京山地区地热田地球化学特征及热源分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(6):806-809, 813.ZHANG Yuanpei, NIU Junqiang, WANG Wei. Geochemical characteristics and heat source of the geothermal field in Jingshan area, Hubei Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(6): 806-809, 813. [20] 潘明, 郝彦珍, 吕勇, 李波. 云南昌宁橄榄河热泉水化学特征及复合成因机制研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(2):281-289. doi: 10.11932/karst20210208PAN Ming, HAO Yanzhen, LYU Yong, LI Bo. Hydrochemical characteristics and composite genesis of a geothermal spring in Ganlanhe, Changning, Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(2): 281-289. doi: 10.11932/karst20210208 [21] 闫晓雪, 甘浩男, 岳高凡. 广东惠州—从化典型地热田水文地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(3):743-754.YAN Xiaoxue, GAN Haonan, YUE Gaofan. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of typical geothermal fields from Huangshandong to Conghua in Guangdong[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(3): 743-754. [22] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170: 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [23] 刘伟坡, 沙娜, 程旭学, 王文祥, 王雨山, 李海学, 张梦南. 海原县山前地下水化学特征分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(8):82-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.08.016LIU Weipo, SHA Na, CHENG Xuxue, WANG Wenxiang, WANG Yushan, LI Haixue, ZHANG Mengnan. Study on hydro-geochemical characteristics in piedmont of Haiyuan county[J]. Yellow River, 2019, 41(8): 82-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.08.016 [24] 王瑞, 李潇瀚. 百泉泉域岩溶地下水水化学演化特征及成因[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):398-408WANG Rui, LI Xiaohan. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of karst groundwater in the Baiquan spring catchment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3): 398-408. [25] 尚英男. 环境同位素示踪技术在地热地球化学研究中的应用[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2006,23(1):21-26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2006.01.005SHANG Yingnan. Application of environmental isotope tracing technology to geothermal geochemistry[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2006,23(1): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2006.01.005 [26] 柳鉴容, 宋献方, 袁国富, 孙晓敏, 刘鑫, 王仕琴. 中国东部季风区大气降水δ18O的特征及水汽来源[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(22):3521-3531. doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-22-3521LIU Jianrong, SONG Xianfang, YUAN Guofu, SUN Xiaomin, LIU Xin, WANG Shiqin. Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over Eastern Monsoon China and the water vapor sources[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(22): 3521-3531. doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-22-3521 [27] 薛磊, 申中华, 张佰康. 济南市东部地区地热流体的化学特征研究[J]. 地下水, 2020, 42(4):10-15.XUE Lei, SHEN Zhonghua, ZHANG Baikang. The brief analysis of the chemical characteristics of geothermal fluid in east Jinan[J]. Ground Water, 2020, 42(4): 10-15. [28] 阮云峰, 赵良菊, 肖洪浪, 周茅先, 程国栋. 黑河流域地下水同位素年龄及可更新能力研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2015, 37(3):767-782.RUAN Yunfeng, ZHAO Liangju, XIAO Honglang, ZHOU Maoxian, CHENG Guodong. The groundwater in the Heihe river basin: Isotope age and renewability[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2015, 37(3): 767-782. [29] 卢兆群, 成世才, 陈刚, 陈纪平, 徐健. 山东平阴氡温泉水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2020, 32(11):65-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2020.11.13LU Zhaoqun, CHENG Shicai, CHEN Gang, CHEN Jiping, XU Jian. Radon hot spring hydrochemical features and genetic analysis in Pingyin, Shandong[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2020, 32(11): 65-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2020.11.13 [30] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 张连凯, 程瑞瑞, 李腾芳. 山西柳林泉域岩溶地下水溶解无机碳特征及控制因素[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(4):961-972.HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun, LIU Pengyu, ZHANG Liankai, CHENG Ruirui, LI Tengfang. Characteristics and control factors of dissolved inorganic carbon in karst groundwater in Liuling spring catchment, Lvliang, Shanxi[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(4): 961-972. [31] 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 柳春晖, 周海燕. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4):605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003WANG Ying, ZHOU Xun, YU Yuan, LIU Chunhui, ZHOU Haiyan. Application of geothermometers to calculation of temperature of geothermal reservoirs[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(4): 605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003 [32] Giggenbach W F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52: 2749-2765. [33] 康凤新, 隋海波, 郑婷婷. 山前岩溶热储聚热与富水机理:以济南北岩溶热储为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5):1606-1624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.05.018KANG Fengxin, SUI Haibo, ZHENG Tingting. Heat accumulation and water enrichment mechanism of piedmont karstic geothermal reservoirs: A case study of northern Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(5): 1606-1624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.05.018 -




 下载:
下载: