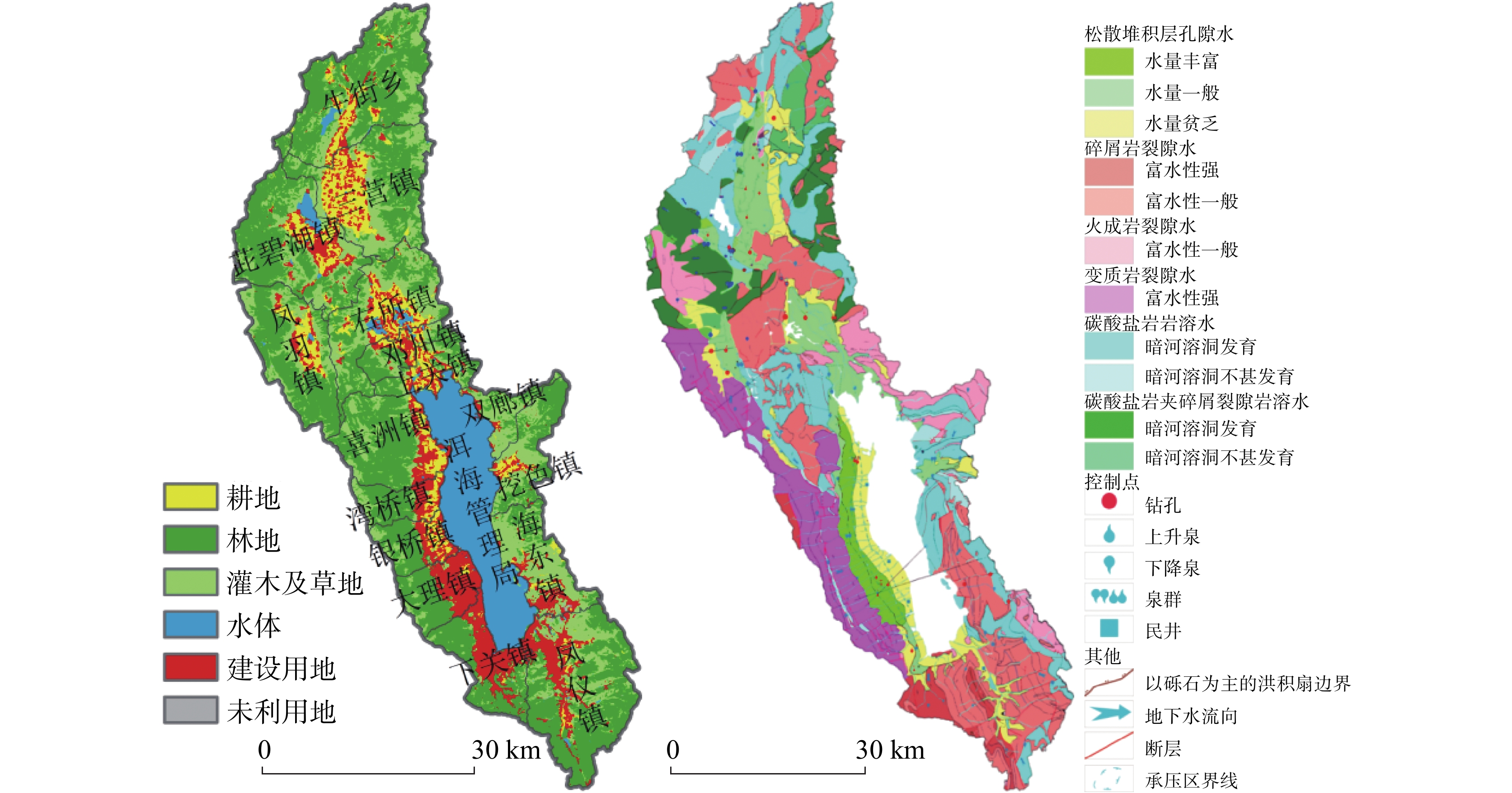
Research on water conservation in karst graben basin from the perspective of ecological restoration of territory space: A case study of the Erhai lake basin
-
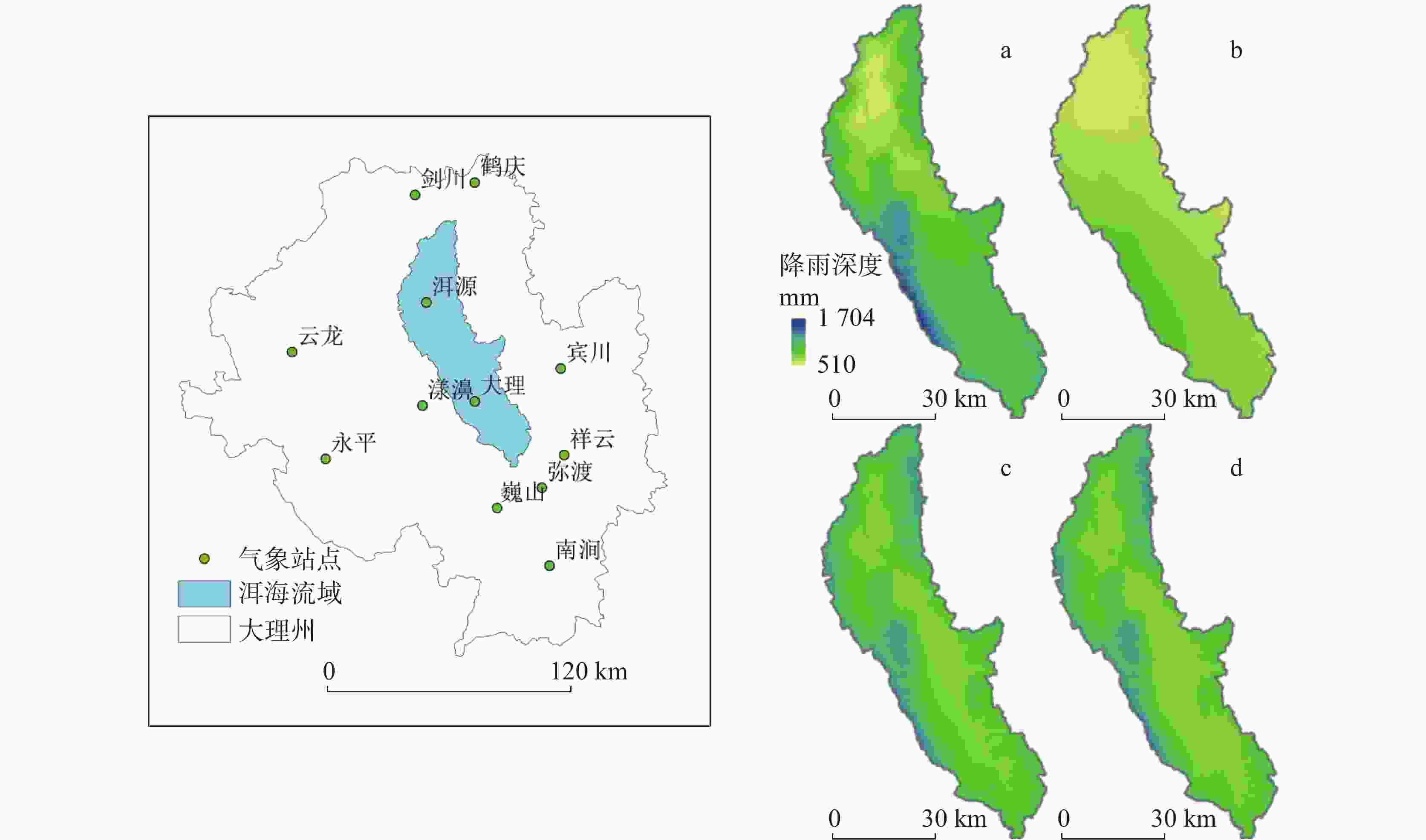
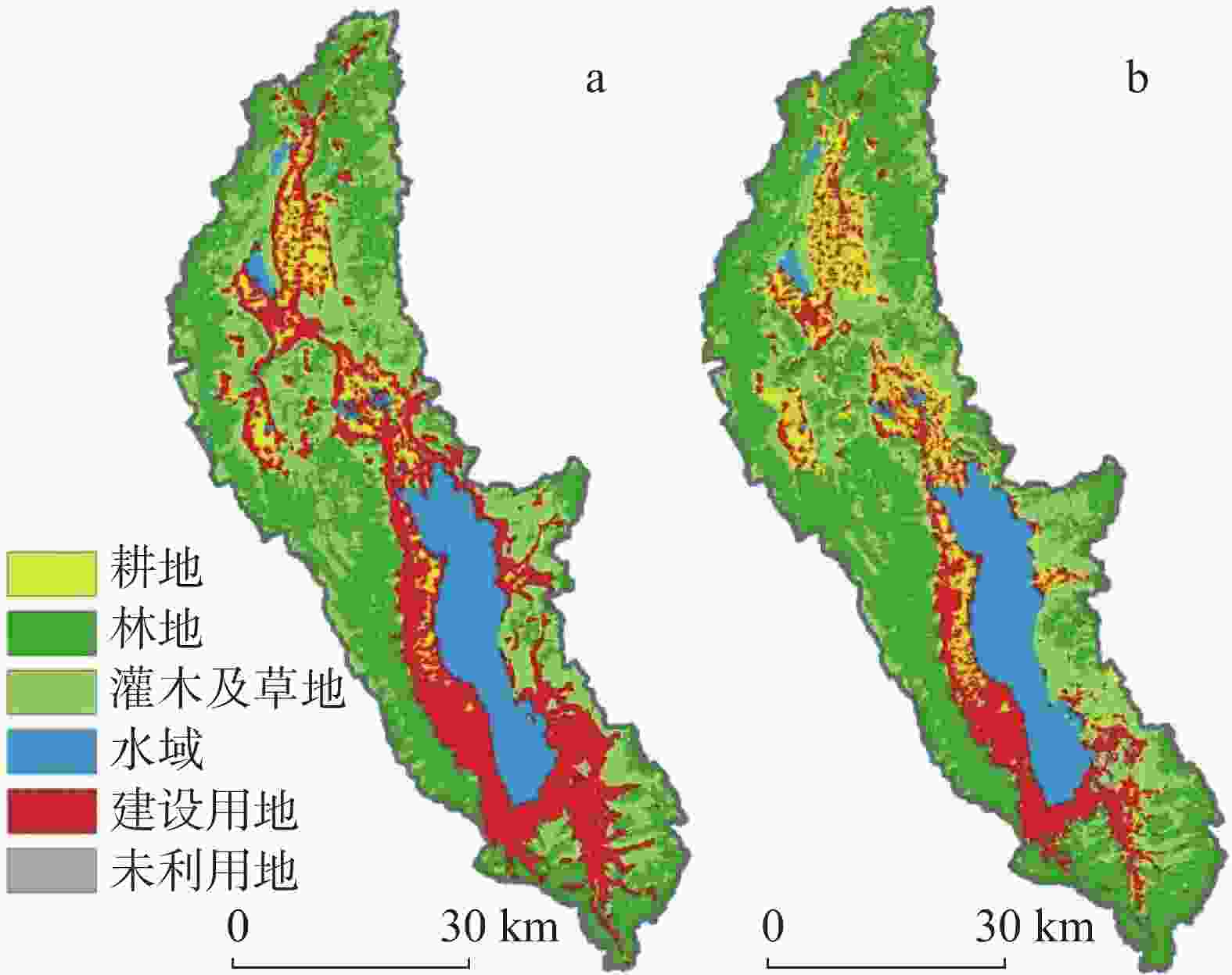
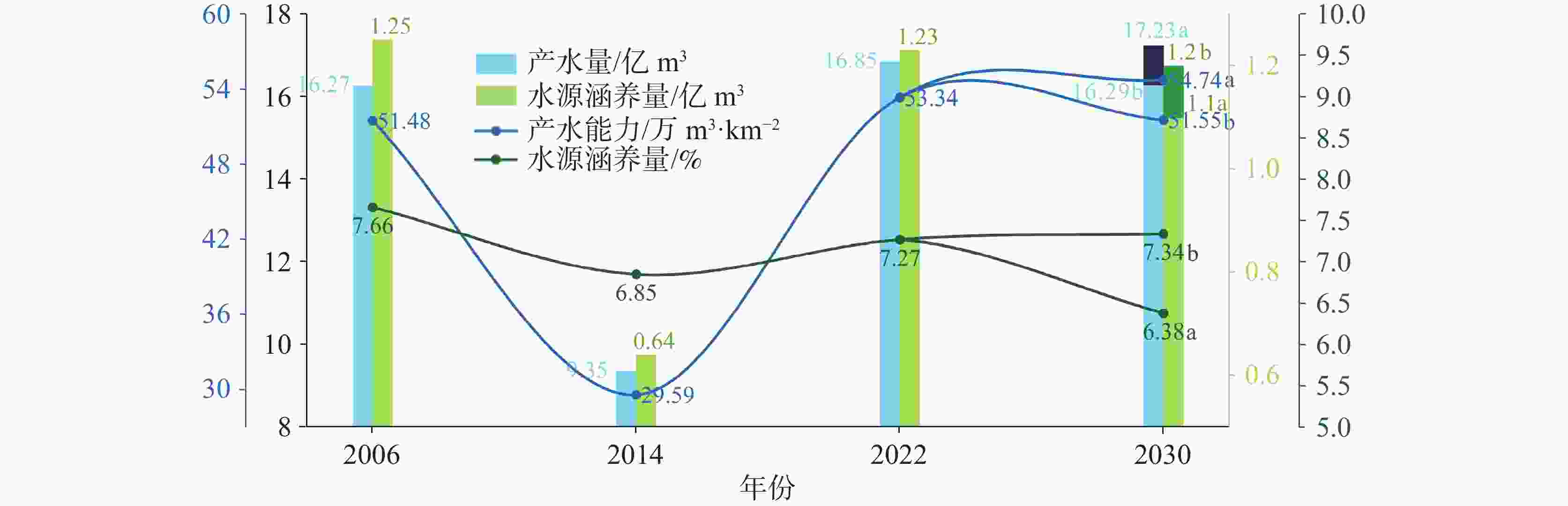
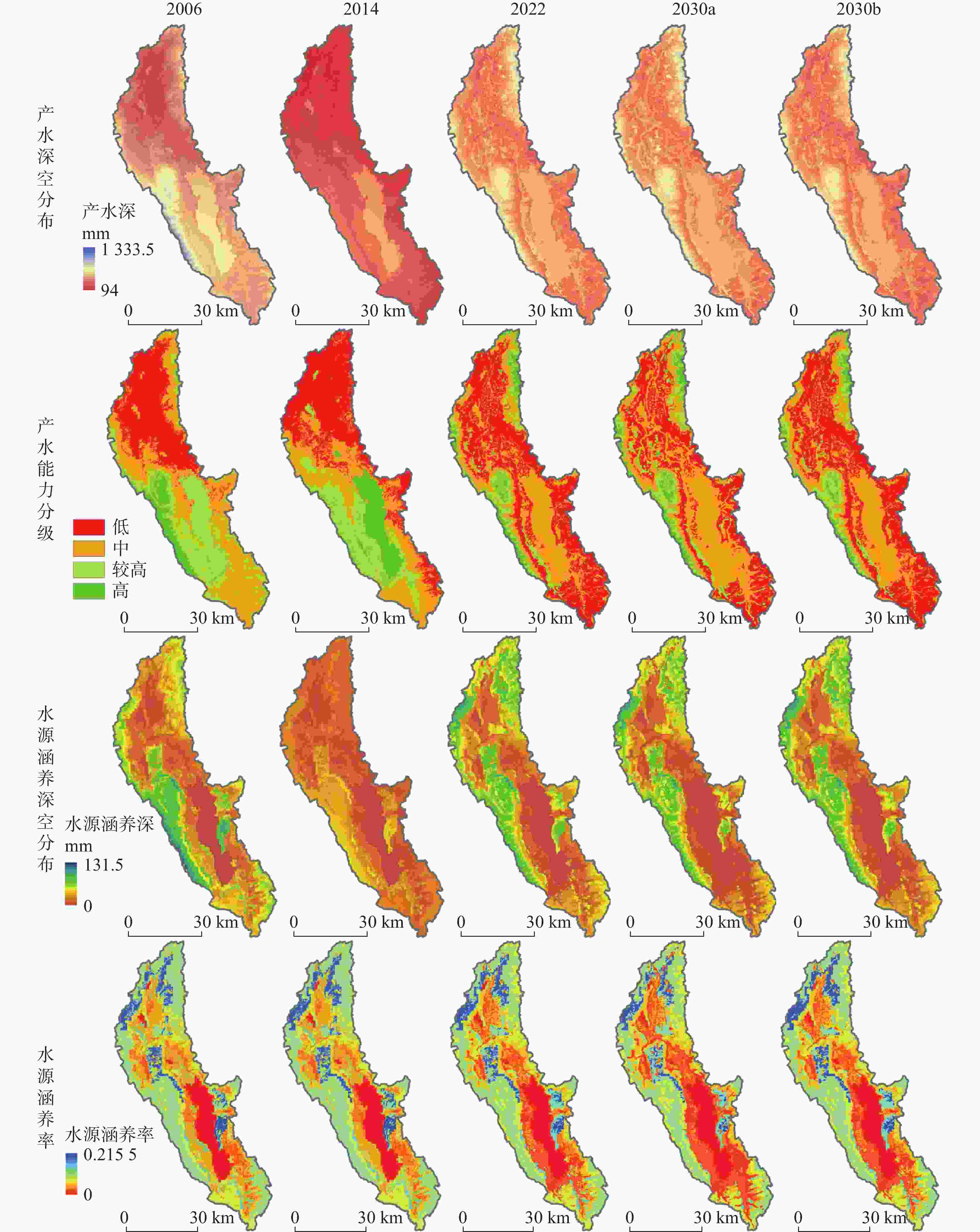
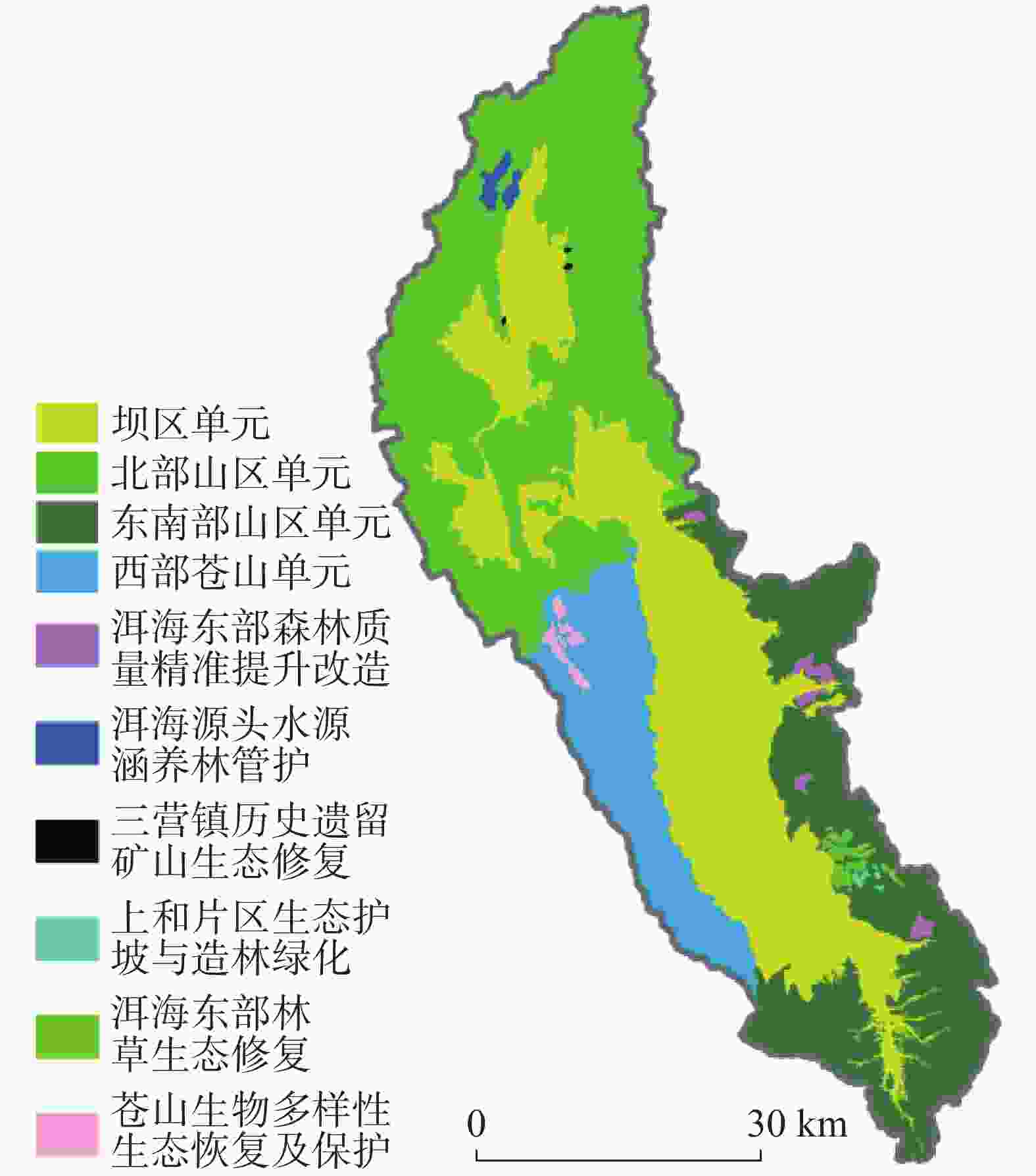
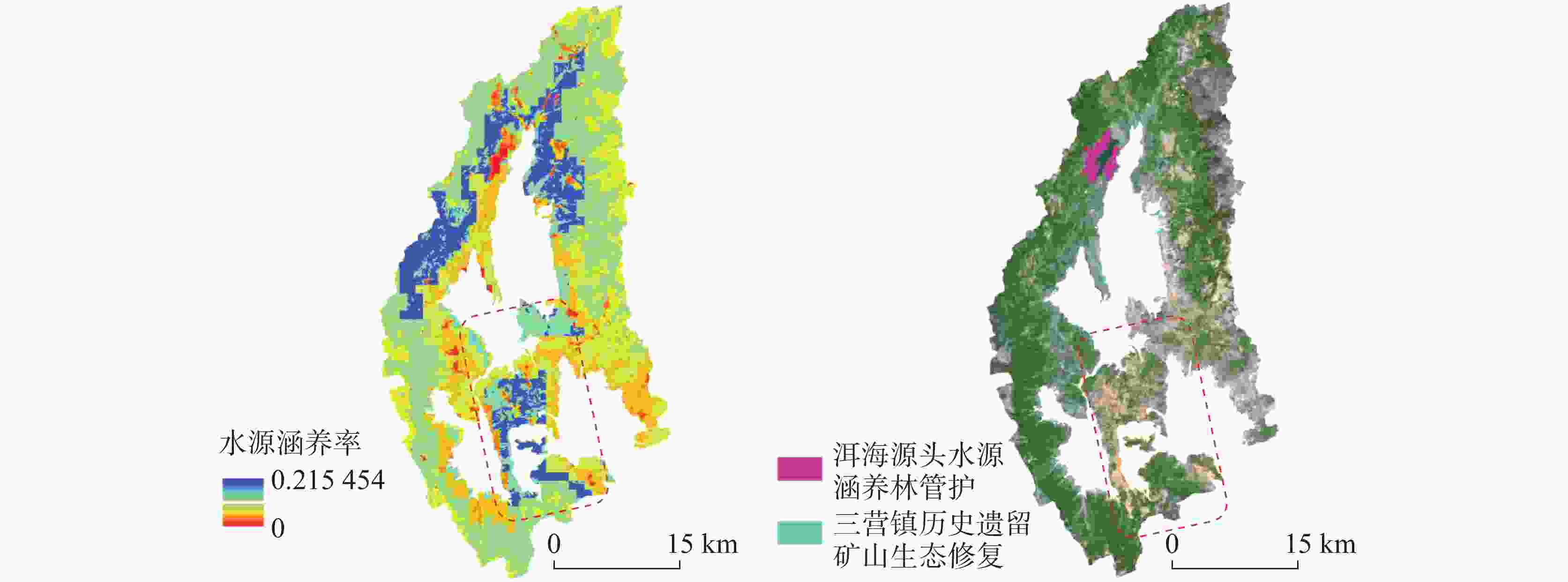
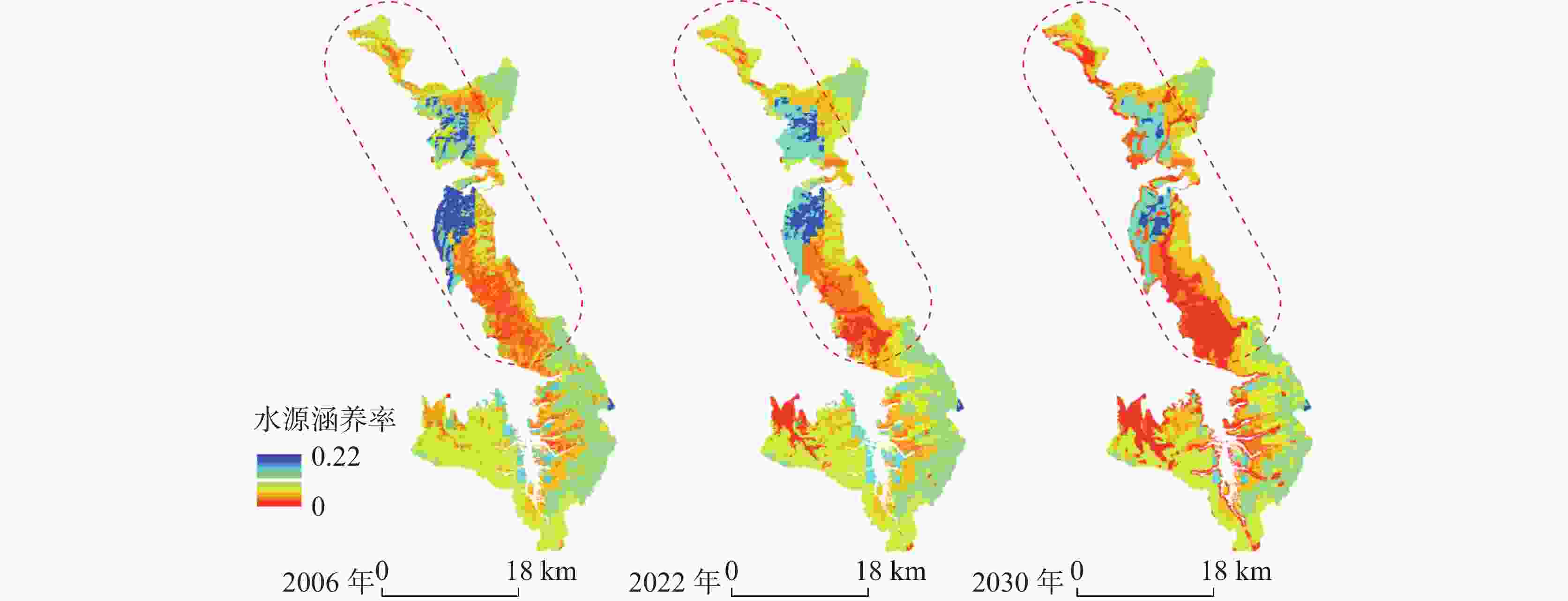
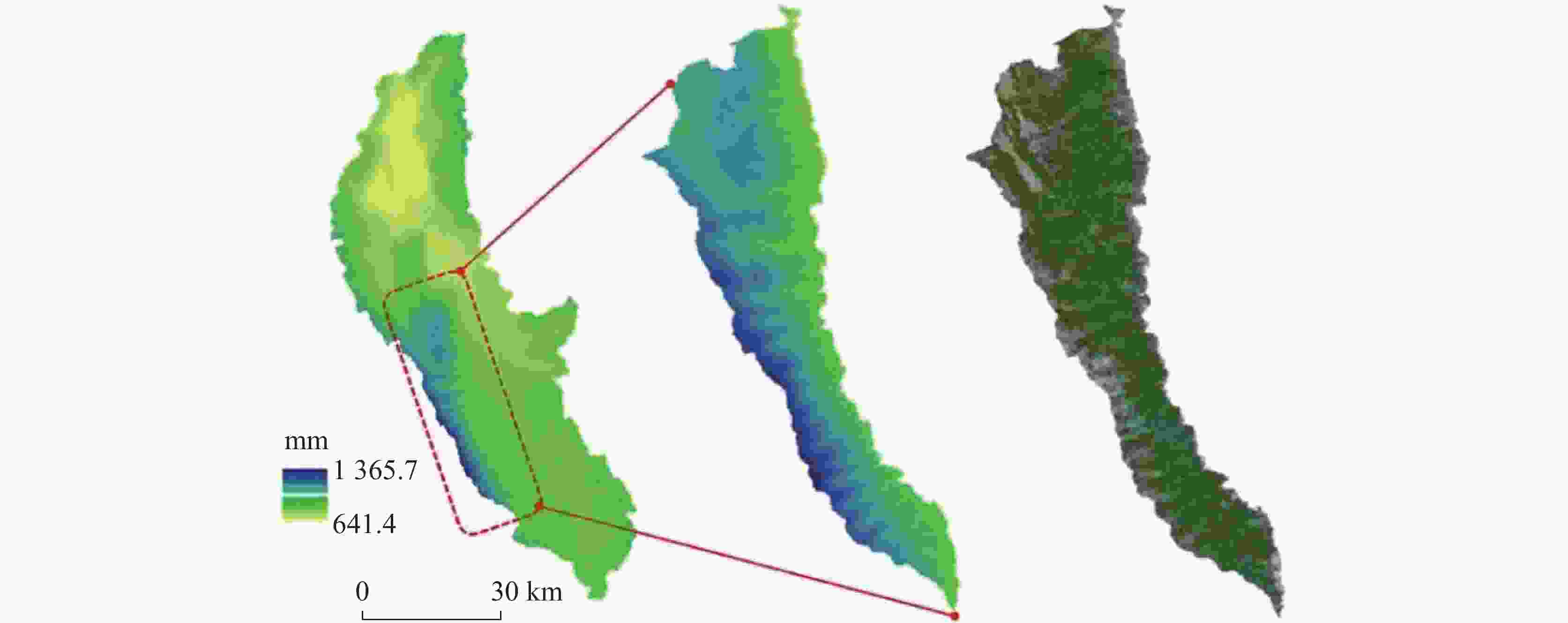
摘要: 洱海流域是“十四五”规划和“双重规划”的重要生态区,其水源涵养功能对保障水资源和生态平衡至关重要。为制订有效的保护和修复策略,通过ANUSPLIN气象插值、区域水文地质研判、InVEST产水计算等方法,对洱海流域产水及水源涵养功能进行评价和预测,结论如下:(1)经过水文地质评述,论证出洱海流域是一个相对完整的水文地质单元;受气候变迁和土地利用影响,2022年产水量较2006年增加3.60%,水源涵养量减少1.65%。高水源涵养区主要在苍山山脉及北部山区,平均水源涵养率超10%;低水源涵养区主要在坝区,平均水源涵养率仅2.89%;(2)未来预测结果显示,受降雨量减少的影响,自然惯性发展情景与生态保护修复情景均发生下降,而生态修复情景水源涵养量的减损量远低于自然惯性发展情景,且水源涵养率有所增加;自然惯性发展情景存在局部退化风险,生态保护修复情景通过措施可提升水源涵养量,降低退化风险;(3)洱海流域水源涵养时空分布与气候等自然因素及土地利用结构密切相关。针对洱海流域存在水源涵养功能退化的情况,研究评价了已有子工程,并特别关了注苍山山脉北部和东南部山区,提出生态现状评估、工程性补水等措施,以提升水源涵养功能,维护生态系统稳定,促进可持续发展。
-
关键词:
- 断陷盆地区 /
- 国土空间生态保护修复 /
- 水源涵养 /
- 土地利用情景模拟
Abstract:The Erhai lake basin is an important ecological area outlined in the "14th Five-Year Plan" and the Master Plan on Major Projects for the Conservation and Restoration of National Key Ecosystems (2021–2035). The water conservation function in the Erhai lake basin plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of water resources and ecology. To formulate effective protection and restoration strategies, methods such as ANUSPLIN meteorological interpolation, regional hydrogeological assessment, and InVEST water yield calculation have been employed to evaluate and predict the water yield and water conservation function of the Erhai lake basin. The research conclusions are as follows, (1) Through hydrological and geological assessments, it is confirmed that the Erhai basin constitutes a relatively complete hydrogeological unit. Influenced by climate change and land use, there was a 3.6% increase in water yield in 2022 compared to 2006, alongside a 1.65% decrease in water conservation. The areas with high water conservation rates are mainly located in the Cangshan mountain and northern mountainous regions, with an average water conservation rate exceeding 10%. In contrast, the areas with low water conservation rates are primarily found in the garben basin region, where the average water conservation rate is only 2.89%. (2) The prediction results indicate that, due to the decrease of precipitation, both the natural inertia development scenario and the ecological protection and restoration scenario will experience a decline in water source conservation. However, the reduction in water conservation under the ecological restoration scenario is significantly lower than that under the natural inertia development scenario, and the water conservation rate in ecological restoration has increased. There is a risk of local degradation in the natural inertia development scenario, while the ecological protection and restoration scenario can enhance the water conservation capacity through measures, and reduce the risk of degradation. (3)The spatial and temporal distribution of water conservation in the Erhai lake basin is closely related to natural factors such as climate and land use structure. In response to the degradation of water conservation function in the Erhai lake basin, existing sub-projects were studied and evaluated.Special attention was given to the northern Cangshan range and southeastern mountainous area, where measures such as ecological status assessment, and engineering water supplement were proposed to enhance water conservation, maintain ecosystem stability, and promote sustainable development. -
表 1 Kappa系数检验对照表
Table 1. Verification of Kappa coefficients
K 0.00~0.25 0.26~0.50 0.51~0.75 0.76~1.00 一致性程度 极低 低 中 高 表 2 数据来源表
Table 2. Data sources
数据类型 数据源 数据类型 土地利用 Annual China Land Cover Dataset[26]、Esri Sentinel-2 2006/2014/2022
年.jpg气象数据 国家气象数据中心、全球干旱指数和潜在蒸散
量数据库(第3版)2006—2020年
.txt、.jpg地形数据 中国地理数据云 .jpg 行政界线 中国科学院资源环境
科学与数据中心.shp 土壤数据 世界土壤数据库 .mbd 区域地质资料 全国地质资料馆 .png 水文数据 大理州水务局官网 .pdf 表 3 土地利用编码及相关参数
Table 3. Land use coding and related parameters
土地利用
类型土地利用
编码植物根系
深度/mm蒸散系数 流速系数 耕地 1 1500 0.65 800 林地 2 7000 1 200 灌木及草地 3 3000 0.65 400 水域 4 10 1 2012 建设用地 5 10 0.20 2012 裸地 6 10 0.20 1500 表 4 洱海流域各单元产水量、产水能力、水源涵养量及水源涵养率统计表
Table 4. Statistics of water yield, water yield capacity, water conservation and water conservation rate in each unit of the Erhai basin
流域面
积占比/%产水量/亿m3及占比/% 产水能力/万m3∙km−2 2006年 2014年 2022年 2030年生态
修复情景历史期
均值2006年 2014年 2022年 2030年生态
修复情景历史期
均值坝区单元 32.68 5.29/
32.493.97/
42.435.58/
33.105.35/
33.104.94/
34.9251.18 38.42 54.02 51.81 47.87 北部山区单元 34.83 4.59/
28.232.29/
24.445.94/
35.265.83/
35.264.27/
30.1841.72 20.76 53.99 52.97 38.82 东南部山区单元 20.98 3.55/
21.821.75/
18.683.00/
17.832.84/
17.832.77/
19.5553.54 26.35 45.31 42.78 41.73 西部苍山单元 11.50 2.84/
17.461.35/
14.442.33/
14.442.27/
13.952.17/
15.3578.14 37.15 64.07 62.51 59.79 流域面
积占比/%水源涵养量/亿m3及占比/% 水源涵养率/% 2006年 2014年 2022年 2030年生态
修复情景历史期
均值2006年 2014年 2022年 2030年生态
修复情景历史期
均值坝区单元 32.68 0.18/
14.080.12/
19.120.13/
10.300.12/
9.710.14/
13.633.32 3.09 2.26 2.17 2.89 北部山区单元 34.83 0.48/
38.300.23/
36.460.62/
50.490.62/
51.670.44/
42.7210.39 10.23 10.41 10.59 10.34 东南部山区单元 20.98 0.29/
23.580.14/
22.160.24/
18.980.23/
18.980.23/
21.848.28 8.13 8.12 8.00 8.18 西部苍山单元 11.50 0.30/
24.050.14/
22.250.24/
19.630.23/
19.630.23/
21.8110.55 10.56 10.16 10.33 10.42 -
[1] 生态环境部. 全国生态状况调查评估技术规范:生态系统服务功能评估 HJ 1173—2021[S]. 2021.Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Technical specification for investigation and assessment of national ecological status: Ecosystem services assessment HJ 1173—2021[S]. 2021. [2] 杨峰霁, 闫强, 王金满, 周治平, 刘彪. 国土空间生态修复中的水平衡研究进展[J/OL]. 生态学杂志, 1-10. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1148.Q.20240315.1057.007.YANG Fengji, YAN Qiang, WANG Jinman, ZHOU Zhiping, LIU Biao. Water balance analysis of territory spatial ecological restoration: A review[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-10. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1148.Q.20240315.1057.007. [3] 王云飞, 叶爱中, 乔飞, 李宗省, 缪驰远, 狄振华, 龚伟. 水源涵养内涵及估算方法综述[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2021, 19(6):1041-1071.WANG Yunfei, YE Aizhong, QIAO Fei, LI Zongxing, MIAO Chiyuan, DI Zhenhua, GONG Wei. Review on connotation and estimation method of water conservation[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2021, 19(6): 1041-1071. [4] 左其亭, 王娇阳, 杨峰, 宋全香. 水源涵养相关概念辨析及水源涵养能力计算方法[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2022, 42(2):13-19.ZUO Qiting, WANG Jiaoyang, YANG Feng, SONG Quanxiang. Concept analysis of water conservation and calculation methods of water conservation capacity[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2022, 42(2): 13-19. [5] 张乐开, 左其亭, 钟涛, 张羽, 吴青松. 基于SWAT的沁河流域水源涵养能力分析及预测[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2023, 21(5):862-872.ZHANG Lekai, ZUO Qiting, ZHONG Tao, ZHANG Yu, WU Qingsong. Analysis and prediction of water conservation capacity in Qinhe river basin based on SWAT[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2023, 21(5): 862-872. [6] Anand J, Gosain A K, Khosa R. Prediction of land use changes based on Land Change Modeler and attribution of changes in the water balance of Ganga basin to land use change using the SWAT model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644: 503-519. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.017 [7] Chen Y, Xu C Y, Chen X W, Xu Y P, Yin Y X, Gao L, Liu M B. Uncertainty in simulation of land-use change impacts on catchment runoff with multi-timescales based on the comparison of the HSPF and SWAT models[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 573: 486-500. [8] Marhaento H, Booij M J, Rientjes T H M, Hoekstra Arjen Y. Attribution of changes in the water balance of a tropical catchment to land use change using the SWAT model[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2017, 31(11): 2029-2040. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11167 [9] Belete M, Deng J S, Zhou M M, Wang K, You S X, Hong Y, Weston M. A new approach to modeling water balance in Nile river basin, Africa[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(3): 810. doi: 10.3390/su10030810 [10] 唐尧, 祝炜平, 张慧, 宋瑜. InVEST模型原理及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2015, 34(3):204-208.TANG Yao, ZHU Weiping, ZHANG Hui, SONG Yu. A review on principle and application of the InVEST model[J]. Ecological Science, 2015, 34(3): 204-208. [11] Bai Y, Ochuodho T O, Yang J. Impact of land use and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Kentucky, USA[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 51-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.01.079 [12] 刘友存, 邹杰平, 尹小玲, 孟丽红, 陈明, 曾金凤, 乔丽潘古丽·吐尔洪. HSPF模型在流域水文与水环境研究中的进展[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(1):225-232.LIU Youcun, ZOU Jieping, YIN Xiaoling, MENG Lihong, CHEN Ming, ZENG Jinfeng, Jolipanguli Turkhon. Review on HSPF model in watershed hydrology and water environment research[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2021, 43(1): 225-232. [13] 李芹, 王宇, 李笠, 张华, 王波. 喀斯特高原湖泊流域基于自然解决的生态修复方案:以云南九大高原湖泊为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3):391-401.LI Qin, WANG Yu, LI Li, ZHANG Hua, WANG Bo. Ecological restoration scheme of lake basins on the karst plateau based on natural solution: Take nine lakes on the Yunnan Plateau as example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 391-401. [14] Chen Z, Zhang C H, Raza S T. Evaluation of forest ecological security and its influencing factors in multi-climatic zones: A case study of Yunnan Province[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(22): 12345. doi: 10.3390/app132212345 [15] 刘佳, 肖玉, 张昌顺, 黄孟冬. 基于地表水与地下水分割校正的漓江流域水供给服务时空格局研究[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(15):6099-6116.LIU Jia, XIAO Yu, ZHANG Changshun, HUANG Mengdong. Spatio-temporal patterns of water supply service in the Li river basin based on correction method of surface water and groundwater partitioning[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(15): 6099-6116. [16] Qin H X, Li S, Sun J W, Cheng J H. Scale-dependent responses of ecosystem service trade-offs to urbanization in Erhai lake basin, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(57): 120663-120682. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-30885-y [17] 刘浩, 孙丽慧, 吕文魁, 舒昶, 张惠远. 基于土地利用变化的洱海流域生态系统服务价值评估与变化分析[J]. 生态经济, 2022, 38(1):147-152.LIU Hao, SUN Lihui, LYU Wenkui, SHU Chang, ZHANG Huiyuan. Evaluation and change analysis of ecosystem service value in Erhai lake basin based on land use change[J]. Ecological Economy, 2022, 38(1): 147-152. [18] 董亚坤, 郭羽鑫, 吴碧兰, 曾维军. 基于土地利用动态变化的洱海流域上游生态系统服务价值分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2023, 44(1):16-24.DONG Yakun, GUO Yuxin, WU Bilan, ZENG Weijun. Analysis of ecosystem service values in the upper Erhai lake basin based on dynamic changes in land-use[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2023, 44(1): 16-24. [19] 傅抱璞. 地形和海拔高度对降水的影响[J]. 地理学报, 1992, 47(4):302-314. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1992.04.003FO Baopu. The effects of topograpgy and elevation on precipitation[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1992, 47(4): 302-314. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1992.04.003 [20] 贾洋, 崔鹏. 高山区多时间尺度Anusplin气温插值精度对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(3): 757-766.JIA Yang, CUI Peng. Contrastive analysis of temperature interpolation at different time scales in the alpine region by Anusplin[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2018,37(3): 757-766. [21] 张仁平, 张云玲, 郭靖, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 新疆地区降水分布的空间插值方法比较[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(3):521-529. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0608ZHANG Renping, ZHANG Yunling, GUO Jing, FENG Qisheng, LIANG Tiangang. Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for precipitation distribution in Xinjiang region[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(3): 521-529. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2016-0608 [22] 石雅馨. 云南典型低丘缓坡项目区水源涵养功能变化研究[D]. 昆明:云南财经大学, 2020.SHI Yaxin. Study on the change of water conservation function in typical gentle hillside project area in Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, 2020. [23] 陈武, 张山江, 侯春华, 陈尘, 曾李晨. 二次指数平滑预测模型回归系数计算方法探讨[J]. 统计与决策, 2016(19):11-12. [24] 褚琳, 张欣然, 王天巍, 李朝霞, 蔡崇法. 基于CA-Markov和InVEST模型的城市景观格局与生境质量时空演变及预测[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(12):4106-4118.CHU Lin, ZHANG Xinran, WANG Tianwei, LI Zhaoxia, CAI Chongfa. Spatial-temporal evolution and prediction of urban landscape pattern and habitat quality based on CA-Markov and InVEST model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(12): 4106-4118. [25] 张学儒, 周杰, 李梦梅. 基于土地利用格局重建的区域生境质量时空变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(1):160-178.ZHANG Xueru, ZHOU Jie, LI Mengmei. Analysis on spatial and temporal changes of regional habitat quality based on the spatial pattern reconstruction of land use[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020, 75(1): 160-178. [26] Yang J, Huang X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(8): 3907-3925. doi: 10.5194/essd-13-3907-2021 [27] 赵兰兰, 闻童, 赵兵, 石朋. 西南地区近50年干旱趋势及特征分析[J]. 水文, 2021, 41(6):91-95, 59.ZHAO Lanlan, WEN Tong, ZHAO Bing, SHI Peng. Drought tendency and characteristic analysis in Southwest China during recent 50 years[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2021, 41(6): 91-95, 59. [28] 游智文, 李肖肖, 阳勇, 鲁梦格. 基于GRACE重力卫星与SPEI的云南干旱监测[J]. 节水灌溉, 2024(3):34-41, 49.YOU Zhiwen, LI Xiaoxiao, YANG Yong, LU Mengge. Drought monitoring in Yunnan Province based on GRACE gravity satellite and SPEI[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2024(3): 34-41, 49. [29] 荣艳淑, 巩琳, 卢寿德. 云南2009—2014年持续性气象水文干旱特征及成因分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2018, 34(3):22-29.RONG Yanshu, GONG Lin, LU Shoude. Analysis on characteristics and causes of persistent meteorological and hydrological drought in Yunnan from 2009 to 2014[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2018, 34(3): 22-29. [30] 张强, 邹旭恺, 陈鲜艳, 赵琳, 李婷婷, 钱忠华. 考虑多尺度和蒸散影响的新干旱指数研究:以云南为例[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 41(4):909-920.ZHANG Qiang, ZOU Xukai, CHEN Xianyan, ZHAO Lin, LI Tingting, QIAN Zhonghua. A new drought index study that takes into account a multi-timescale and the effects of evapotranspiration: Taking Yunnan as an example[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2022, 41(4): 909-920. [31] 吴绍洪, 潘韬, 曹杰, 何大明, 肖子牛. 西南纵向岭谷地形对季风的“通道—阻隔”作用[J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(1):1-13.WU Shaohong, PAN Tao, CAO Jie, HE Daming, XIAO Ziniu. Barrier-corridor effect of longitudinal range-gorge terrain on monsoons in Southwest China[J]. Geographical Research, 2012, 31(1): 1-13. [32] 张伟康. 孟加拉湾—青藏高原区域热力配置与云南五月雨量异常[D]. 昆明:云南大学, 2018.ZHANG Weikang. Thermal configuration of the Bay of Bengal–Tibetan Plateau region and the May precipitation anomaly in Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2018. [33] 包文, 段安民, 游庆龙, 胡蝶. 青藏高原气候变化及其对水资源影响的研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2):158-169.BAO Wen, DUAN Anming, YOU Qinglong, HU Die. Research progress on climate change and its impact on water resources over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 158-169. -




 下载:
下载: