Study on ecological restoration countermeasures of abandoned mines in Yunnan Province
-
摘要: 实施历史遗留废弃矿山生态修复工作,是践行生态文明建设重要举措,对维护国家西南生态安全屏障及云南省生态文明排头兵建设具有重要意义。历史采矿遗留下的废弃矿山生态环境问题突出,生态难以修复,给当地村民的生产和生活带来困难。文章基于云南省历史遗留废弃矿山生态环境破坏现状、面临的形势和困难,结合矿区自然地理、生态修复规划、激励政策、国土空间用途管制要求等,聚焦自然资源要素保障,从修复方向、工程措施、投入机制、监督管理等方面,提出生态修复对策,以期为“山水林田湖草是生命共同体”新背景下的历史遗留废弃矿山生态修复工作提供技术支撑和新思路。Abstract:
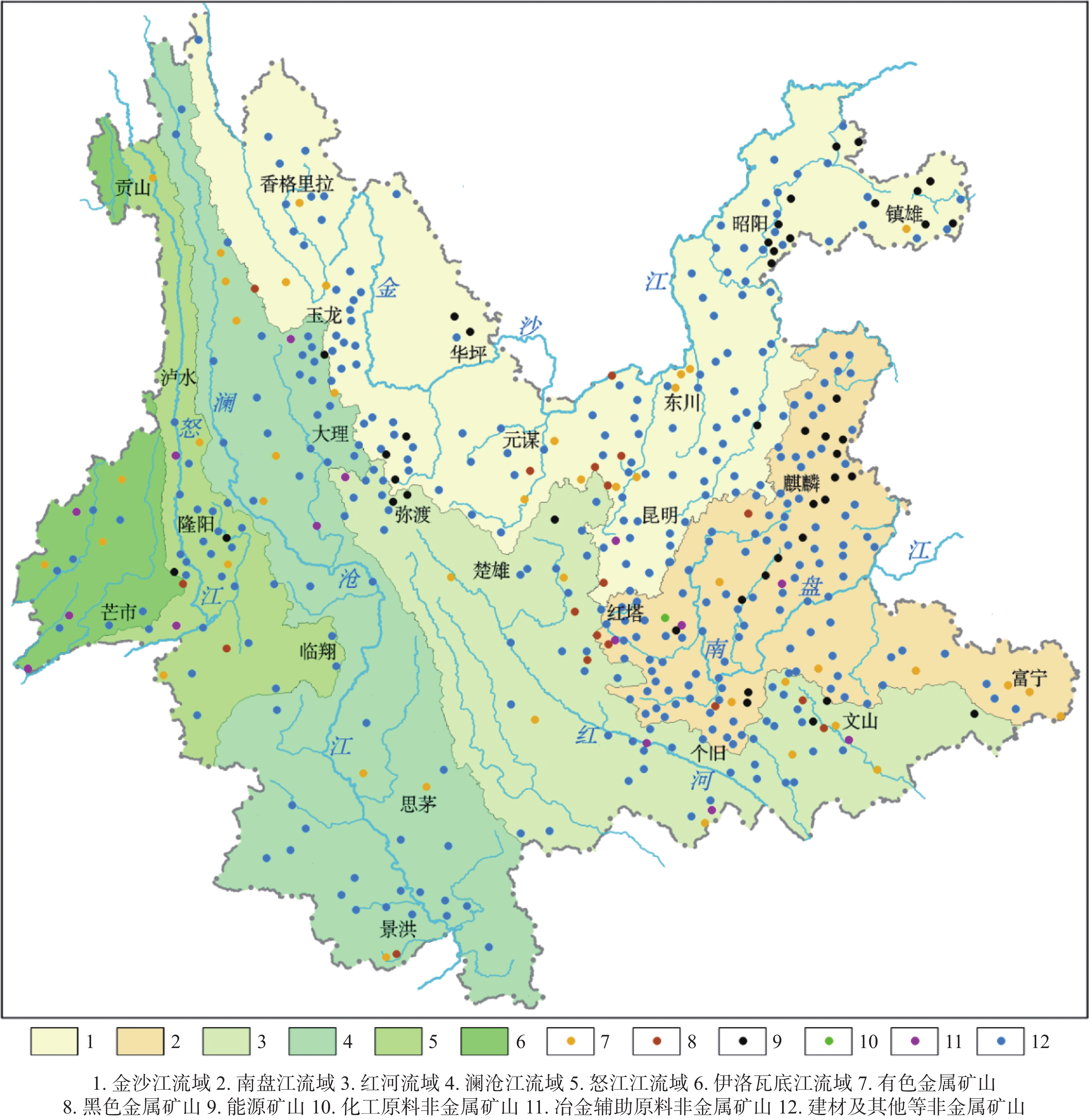
Ecological restoration of abandoned mines is an important step in practicing ecological civilization and is of great significance in maintaining ecological security in Southwest China. Yunnan Province is abundant in mineral resources and is often referred to as the "Kingdom of Non-ferrous Metals" and the "Province for Phosphorus Chemical Industry". Mining is one of the pillar industries in Yunnan, making significant contributions to the socio-economic development of Yunnan and the rest of China. However, the ecological and environmental issues carried over from mining activities of the past are prominent. The abandoned mines have, to some extent, hindered local socio-economic development; however, they also represent a natural resource that can be re-exploited. Mining activities in the past have excavated and occupied land resources, changed the original topography, destroyed forest and grassland vegetation, disrupted the connectivity of ecological corridors, caused damage or degradation to ecosystems, diminished water conservation functions, and aggravated rocky desertification and soil erosion. There are numerous abandoned mines in Yunnan Province, which are widely distributed and predominantly small in scale. These sites are burdened by significant debt, face complex ecological issues carried over from the past, and possess inadequate natural recovery capacity, resulting in a challenging remediation task. In recent years, there has been a focus on key watersheds and important ecological areas. This focus aligns with the overarching principles of respecting and adapting to nature, following the laws of natural ecosystem succession, prioritizing natural recovery while supplementing it with engineering solutions, and ensuring that all actions are suitable, technically feasible, and financially viable. As a result, ecological restoration methods and measures have been selected based on scientific criteria. Near-natural solutions have been implemented to fully embody the principles of comprehensive management and systematic restoration. These approaches have actively and systematically promoted the ecological restoration of abandoned mines, resulting in positive outcomes. However, the extensive number of abandoned mines and the funding shortfall for restoration efforts have resulted in a critical ecological restoration situation. Currently, over 100,000 acres of abandoned mines in Yunnan Province urgently require ecological restoration, posing significant challenges to the livelihoods and daily lives of local villagers. The diversity of Yunnan's climate presents varying requirements and challenges for environmental protection and ecological restoration. The northwestern cold climate zone of Yunnan experiences long winters with no summers and only short spring and autumn seasons, resulting in slow vegetation growth and significant challenges for ecological restoration. In contrast, the eastern and central temperate climate zones of Yunnan have indistinct seasons, characterized by moderate average annual temperatures and precipitation, which facilitate the recovery and growth of vegetation. The southern and southwestern tropical and subtropical climate zones of Yunnan are abundant in precipitation and biodiversity, creating favorable conditions for vegetation restoration and the protection of biodiversity. Dry and hot river valley regions of the Jinsha river and Yuanjiang river experience a scorching climate characterized by drought and limited rainfall. This results in an imbalance between water and heat, as well as low soil organic matter and nutrient content. Ecological restoration efforts in these areas should prioritize soil and water conservation, along with the protection of water sources. Based on the current situation of ecological and environment damage caused by abandoned mines in Yunnan Province, this paper analyzes the ecological problems of mines. Drawing on the experience gained in the ecological restoration of abandoned mines, it constructs restoration modes such as "natural restoration, ecological carbon sink, transformation and utilization, and ecological restoration+". Fully considering factors such as the natural geography of mining areas, the pattern of ecological restoration, incentive policies, and the requirements of controlling national land space use, it discusses countermeasures and suggestions for the ecological restoration of abandoned mines, focusing on aspects such as restoration direction, engineering measures, and investment mechanisms. The aim is to provide technical support and innovative ideas for the ecological restoration of abandoned mines in the context of the new paradigm of "mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, and grasslands as a community of life". In the next step of promoting the restoration of abandoned mines, it is necessary to redefine the concept of ecological restoration of mines. This involves accurately understanding the relationship between natural and artificial restoration. It is crucial to adhere to the principles of ensuring safety, restoring ecological balance, and considering the landscape. Additionally, it is important to scientifically select appropriate models for mine ecological restoration and engineering measures based on the potential value of abandoned land resources, while also complying with regulations of controlling national land space use. Taking into account the current situation of social and economic development in mining areas, as well as factors such as micro-landforms, surrounding vegetation, traffic conditions, and water and soil quality, the ecological restoration of mines has been carried out, and the restoration direction has been determined with careful consideration. Through policy incentives and the strategic allocation of financial funds, we will encourage social capital to engage in the ecological restoration of abandoned mines. Our goal is to revitalize these sites, and establish a new model of self-sustaining and self-cycling ecological restoration of abandoned mines. -
表 1 需修复治理历史遗留废弃矿山统计一览表
Table 1. Statistics of the abandoned mines for restoration
主要矿产类别 矿山数量占比/% 需治理面积占比/% 备注 有色金属 1.40 2.12 黑色金属 2.92 7.34 能源矿产 8.32 9.05 以煤矿为主 化工原料非金属 0.40 0.85 冶金辅助原料非金属 1.32 2.01 建材及其他等非金属 85.64 78.63 均为固体矿产 合 计 100.00 100.00 表 2 需修复治理历史遗留废弃矿山图斑规模统计一览表
Table 2. Statistics of the scales of abandoned mines for restoration
单图斑损毁土地规模/亩 数量占比/% 平均面积/亩 备注 小于10 46.81 4.49 10~20 21.50 14.30 20~50 20.72 31.56 50~100 7.58 68.80 100~200 2.67 134.20 大于200 0.72 300.38 合 计 100.00 100.00 -
[1] 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 陈利顶, 马克明, 李俊然. 中国生态区划方案[J]. 生态学报, 2001, 21(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.01.001FU Bojie, LIU Guohua, CHEN Liding, MA Keming, LI Junran. Scheme of ecological regionalization in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.01.001 [2] 张进德, 郗富瑞. 我国废弃矿山生态修复研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(21):7921-7930.ZHANG Jinde, XI Furui. Study on ecological restoration of abandoned mines in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(21): 7921-7930. [3] 白中科, 周伟, 王金满, 赵中秋, 曹银贵, 周妍. 再论矿区生态系统恢复重建[J]. 中国土地科学, 2018, 32(11):1-9. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20181107.162318BAI Zhongke, ZHOU Wei, WANG Jinman, ZHAO Zhongqiu, CAO Yingui, ZHOU Yan. Rethink on ecosystem restoration and rehabilitation of mining areas[J]. China Land Science, 2018, 32(11): 1-9. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20181107.162318 [4] 樊 彬. 历史遗留废弃矿山的生态环境问题及修复治理对策:以贵州省某历史遗留废弃矿山生态修复治理项目为例[J]. 四川有色金属, 2023(2):4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4079.2023.02.002FAN Bin. Ecological environment problems and remediation countermeasures of the historically abandoned mines: Take the ecological restoration and treatment project of a historical abandoned mine in Guizhou Province as an example[J]. Sichuan Nonferrous Metals, 2023(2): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4079.2023.02.002 [5] 姜丽丽, 李少飞, 徐洪伟. 历史遗留废弃矿山生态修复现状及治理对策研究[J]. 自然资源情报, 2023(1):22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2023.01.004JIANG Lili, LI Shaofei, XU Hongwei. Research of current situation and countermeasures of ecological restoration of abandoned mines left over by history[J]. Natural Resources Information, 2023(1): 22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2023.01.004 [6] 自然资源部办公厅. “十四五”历史遗留矿山生态修复行动计划[R]. 2022. [7] 云南省自然资源厅. 云南省国土空间生态修复规划(2021—2035年)[R]. 2023. [8] 段昌群, 李世玉, 温庆忠, 等. 基于云南实际的矿山生态修复模式选择研究[R]. 2022. [9] 张进德. 科学实施山水林田湖草生态保护与修复工程[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2018, 45(3):3. [10] TD/T 1070.1-2022. 矿山生态修复技术规范 第1部分: 通则[S].TD/T 1070.1-2022. Technical specifications for ecological restoration of mines—Part 1: General rule[S]. [11] 蔡保新, 杨晓艳, 刘涛, 等. 云南省矿山生态保护修复评估报告[R]. 2023.CAI Baoxin, YANG Xiaoyan, LIU Tao, et al. Evaluation report of mine ecological protection and restoration of Yunnan Province[R]. 2023. [12] 许庆良, 刘长伟. 废弃矿山生态修复综合技术[J]. 林业实用技术, 2010(12):15-16. -




 下载:
下载: