A study on multiple-model evaluation of landslide susceptibility
-
摘要: 滑坡是我国最常见的地质灾害之一,其突发性和不确定性给防灾减灾工作带来巨大的挑战。滑坡易发性评估是一个复杂的过程,常规手段是依赖于静态因子分析,难以实现滑坡易发性的动态评估。随着合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)技术的发展,可实现地表形变的动态监测,文章以双江县作为研究区,在常规地质灾害易发性评价中,引入地表形变表征性因子,并使用三种模型分别进行滑坡易发性评估,改善了滑坡地质灾害易发性评估的不确定性,提高了评估精度。综合考量研究区地形地貌、地质构造、水文环境、人类工程活动等静态地质环境条件因子,同时引入InSAR地表形变速率动态因子,共同构建多维度的评估指标体系,并使用信息量模型、确定性系数模型和频率比模型进行滑坡区域易发性评估比较。试验结果表明,CF模型在高易发区和较高易发区滑坡密度比值较高,为7.77、1.10,其准确值和AUC值最大,分别为0.822、0.879,均优于其他模型。基于InSAR技术获取地表形变因子,结合CF模型的滑坡易发性具有最好的评估精度。使用滑坡密度比值、ROC曲线和AUC评估绘制出的滑坡易发性图的精度更具有竞争优势。Abstract:
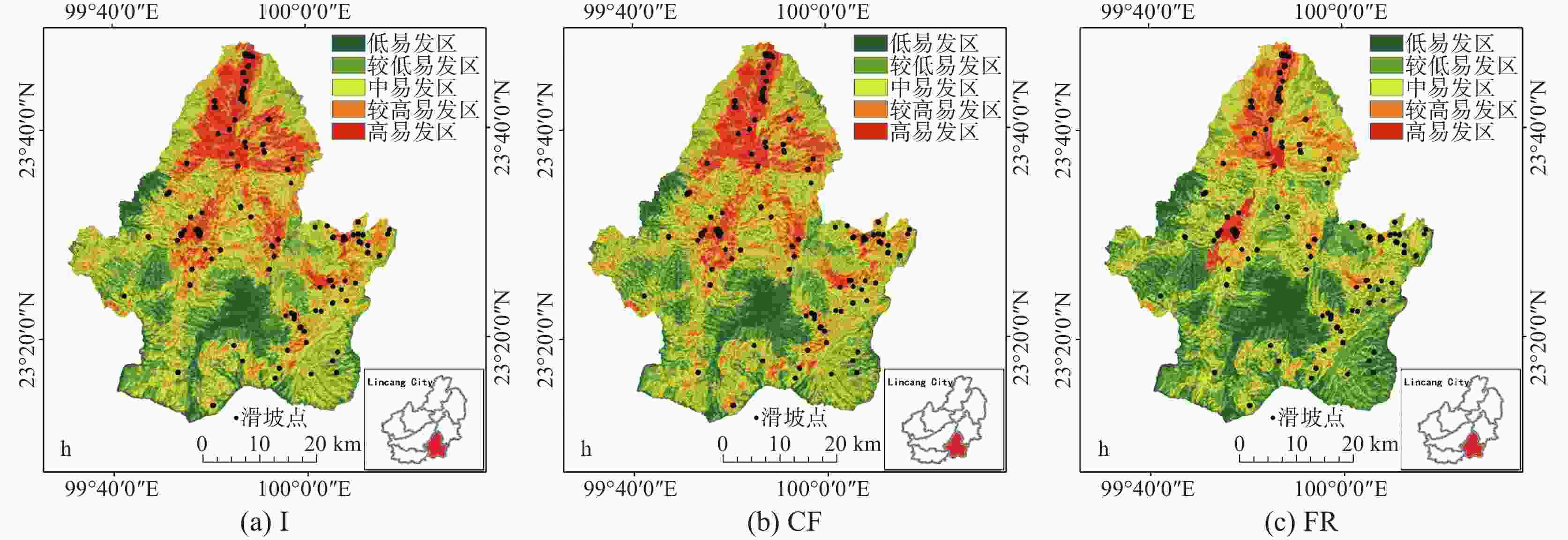
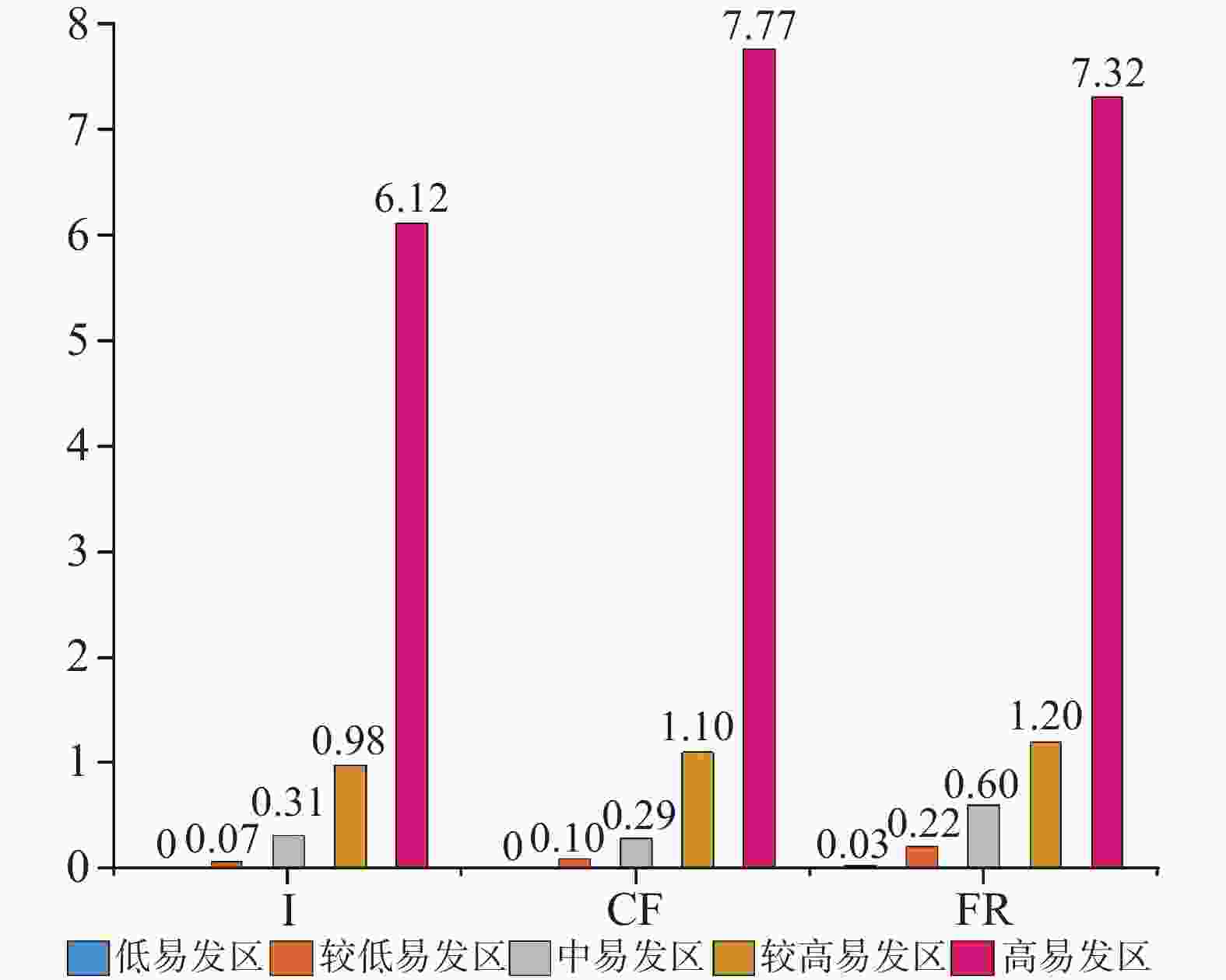
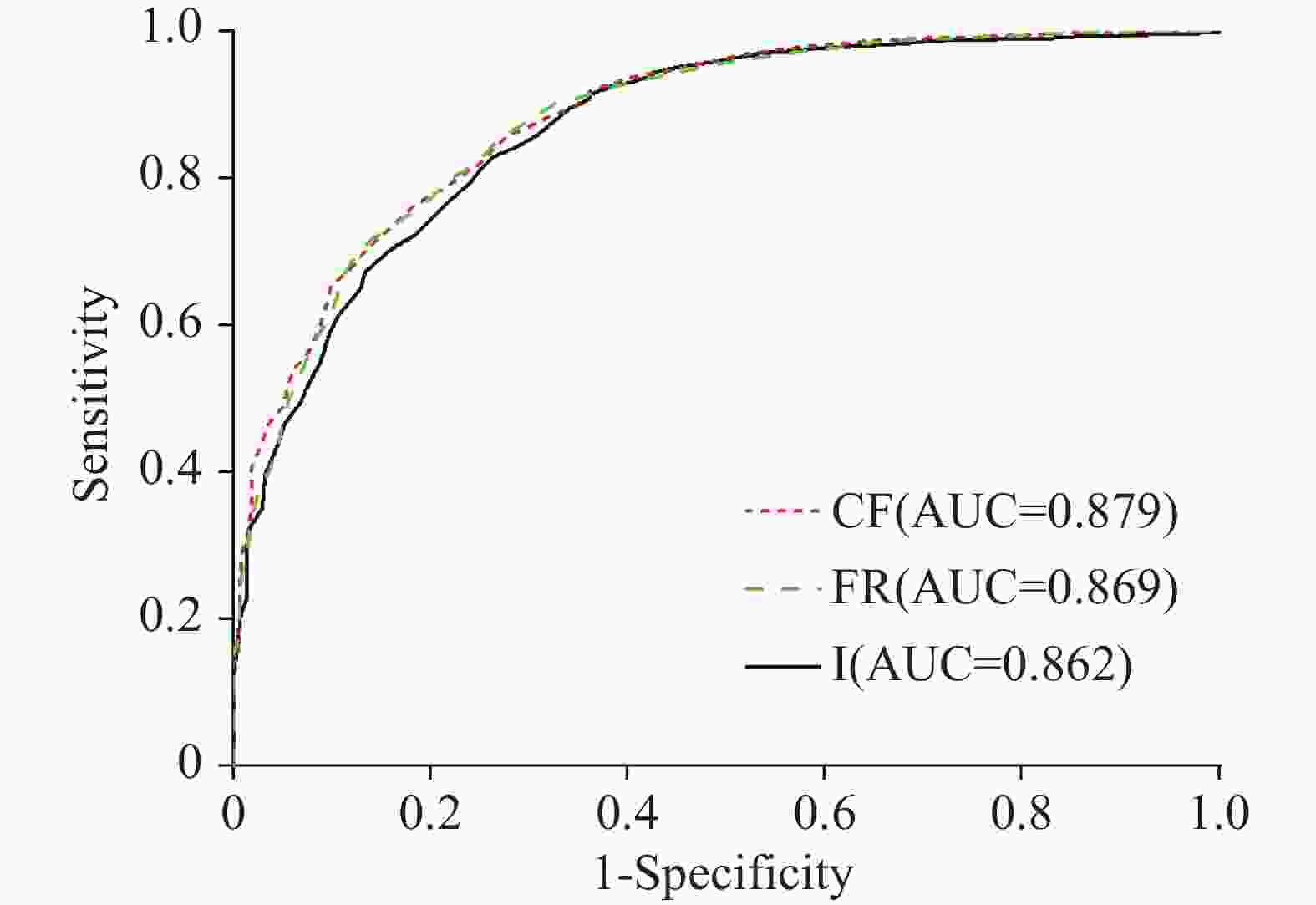
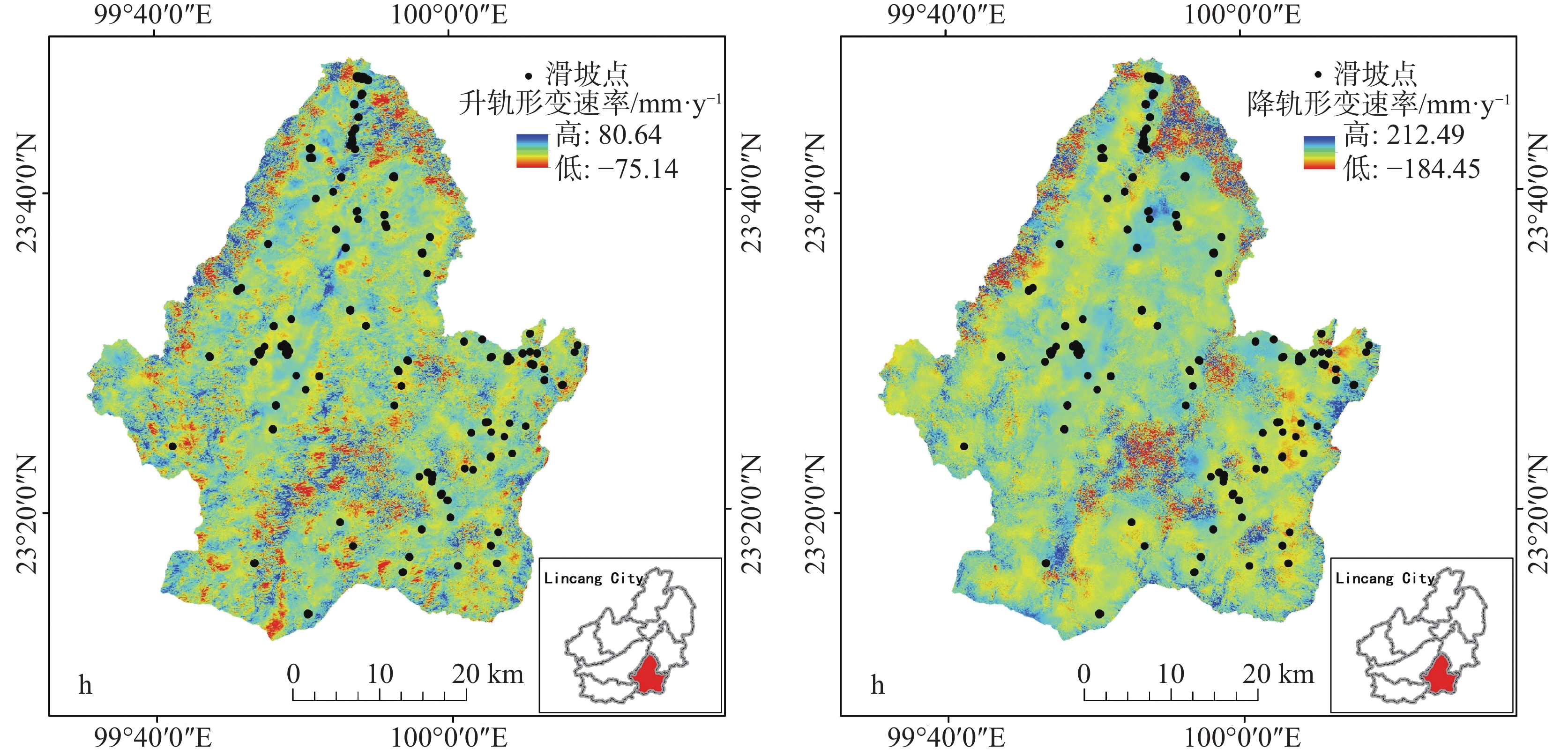
Landslides are one of the most common geological disasters in China, characterized by sudden occurrence and uncertainty. The evaluation of landslide susceptibility is a complex process. Conventional methods mainly use static factors, making it difficult to achieve dynamic assessment of landslide susceptibility. With the ongoing advancement of science and technology, interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) has been successively applied to the study of geological disasters. This technology is characterized by its all-weather capability, continuous operation, and extensive coverage, allowing for real-time monitoring of the Earth's surface under varying environmental conditions. InSAR enables a comprehensive understanding of the movement of the surface rocks and soil masses associated with landslide geological disasters. It effectively captures the dynamic deformation characteristics of landslides in the vertical direction, thereby enhancing the identification and dynamic monitoring of surface deformation and improving the accuracy of evaluating landslide susceptibility. In this study, the surface deformation representative factor has been introduced into the conventional evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility. This addition improves the reliability of the evaluation of landslide susceptibility and enhances the overall accuracy. This study focused on Shuangjiang county as the research area. It utilizes evaluation index factors such as Digital Elevation Model (DEM), slope gradients, aspects, curvatures, stratigraphic lithology, faults, land use, annual average rainfall, roads, and rivers. The representative factor of InSAR surface deformation was comprehensively considered to evaluate landslide susceptibility. Through an extensive analysis of InSAR deformation, a dataset of landslides was established, identifying a total of 116 landslide geological disasters. Among them, 56 landslide areas exhibited deformation, with some slopes showing significant signs of deformation. The information quantity, certainty factor, and frequency ratio models were employed to evaluate the susceptibility of areas to landslides. The accuracy of the generated landslide susceptibility was evaluated with the use of the landslide density ratio, curve of Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC), and the Area Under the Curve (AUC). In this study, 70% of the landslide events were randomly selected for spatial modeling training, while the remaining 30% were used for model verification. The segment set statistical tool in ArcGIS software was utilized to conduct the mutual independence test on the evaluation factors. Research findings indicate that all the correlation coefficients are less than 0.3, suggesting that the evaluation factors are independent of one another. According to the natural paragraph point method in Geographic Information System (GIS), the susceptibility can be categorized into five intervals: low susceptibility area, relatively low susceptibility area, medium susceptibility area, relatively high susceptibility area, and high susceptibility area. The high landslide susceptibility areas are mainly distributed in the northern part of Shuangjiang county; the low landslide susceptibility areas are mainly concentrated in its northwestern part. In the relatively high susceptibility area and the high susceptibility area, the raster of the inspection samples accounts for 88.69% of the total landslide inspection raster. The experimental results show that the Certainty Factor (CF) model exhibits a relatively high landslide density ratio in both the high susceptibility area and the relatively high susceptibility area, with ratios of 7.77 and 1.10, respectively. Additionally, the model demonstrates the highest accuracy and AUC values, which are 0.822 and 0.879, respectively. The accuracy of Frequency Ratio (FR) model is followed by CF model, and that of Information Quantity (I) model is the lowest. The landslide susceptibility map generated by the CF model provides a more accurate evaluation of slope instability in Shuangjiang county. Therefore, deriving the surface deformation factor based on InSAR technology and the CF model for evaluating landslide susceptibility yields the highest accuracy. -
Key words:
- landslide susceptibility /
- InSAR /
- information quantity /
- certainty factor /
- frequency ratio
-
表 1 评价因子相关系数矩阵
Table 1. Correlation coefficient matrix of evaluation factors
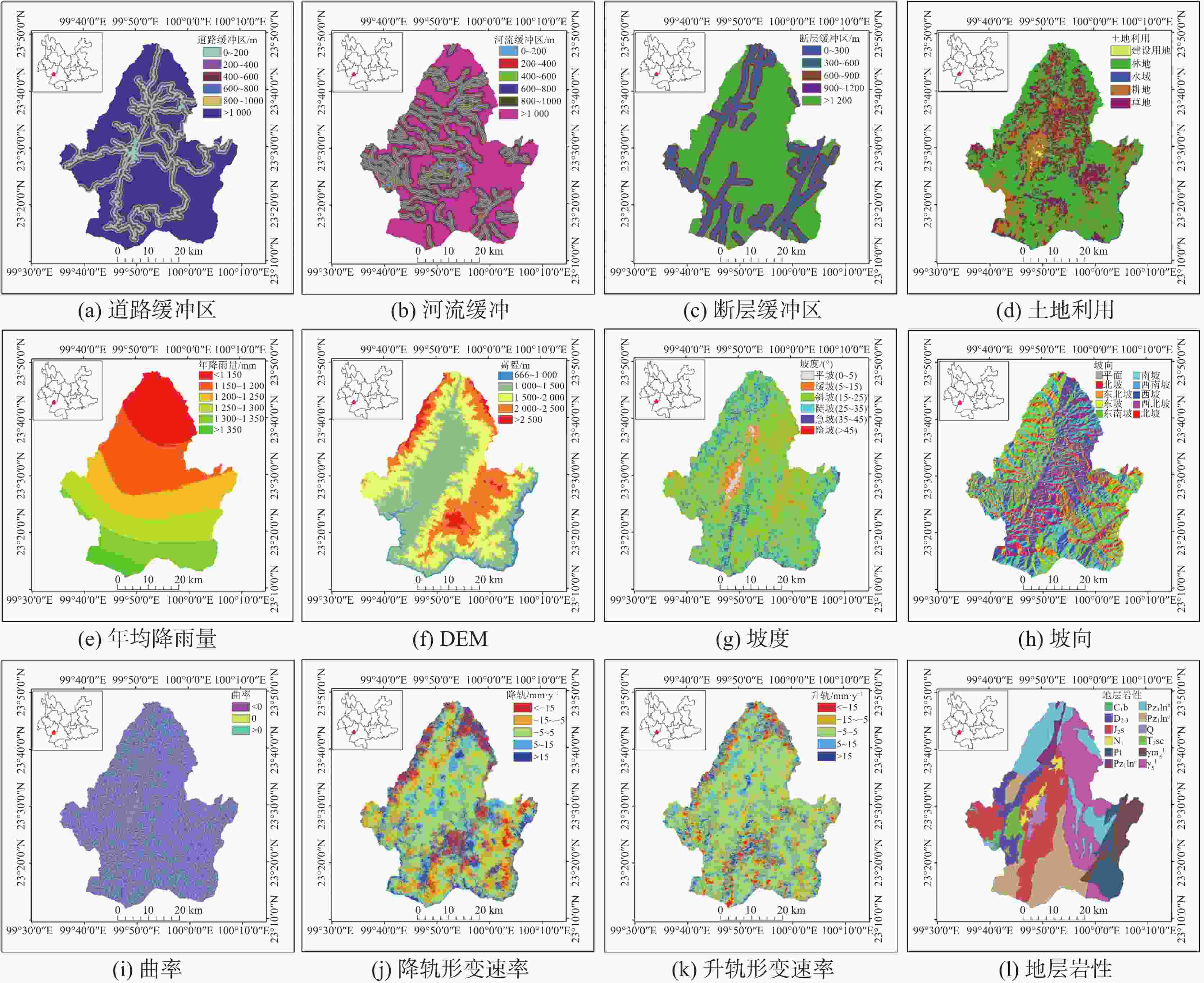
评价因子 a b c d e f g h i j k l a 1.000 b 0.048 1.000 c −0.044 −0.018 1.000 d −0.184 −0.025 0.028 1.000 e 0.148 0.082 −0.146 −0.103 1.000 f 0.152 0.182 0.109 −0.140 −0.224 1.000 g 0.201 0.014 −0.078 −0.143 0.116 0.034 1.000 h −0.043 −0.011 0.016 0.016 −0.018 −0.004 −0.038 1.000 i 0.002 0.012 0.002 0.004 −0.001 0.052 0.025 0.001 1.000 j −0.007 0.005 0.016 0.001 0.003 −0.096 0.044 0.067 −0.016 1.000 k −0.020 0.017 −0.017 −0.008 −0.004 0.014 0.036 −0.052 0.038 0.042 1.000 l 0.033 0.039 0.061 −0.030 0.111 −0.065 −0.039 0.003 −0.001 0.017 −0.021 1.000 注:a.道路 b.河流 c.断层 d.土地利用 e.降雨量 f.DEM g.坡度 h.坡向 i.曲率 j.降轨形变速率 k.升轨形变速率 l.地层岩性。
Note: a. road b. river c. fault d. land use e. rainfall f. DEM g. slope gradient h. aspect i.curvature j. orbital deformation rate k. rail lifting deformation rate l. stratigraphic lithology.表 2 评价因子分级计算
Table 2. Grading calculation of evaluation factors
评价因子 分类 I CF FR 断层缓冲区/m 900~1 200 0.723 7 0.515 3 2.053 6 降轨形变速率/mm·y−1 <−15 −1.419 0 −0.758 1 0.242 0 >1 200 −0.436 3 −0.353 7 0.664 9 −15~−5 −0.514 3 −0.402 2 0.597 9 河流缓冲区/m 0~200 −0.598 4 −0.450 4 0.528 5 −5~5 0.272 1 0.238 3 1.312 7 200~400 0.2139 0.1926 1.3107 5~15 0.474 8 0.378 1 1.607 6 400~600 0.2823 0.2460 1.3414 >15 −1.004 6 −0.633 9 0.366 2 600~800 − 1.2248 − 0.7063 0.3191 升轨形变速率/mm·y−1 <−15 −1.134 4 −0.678 5 0.321 6 800~ 1000 − 0.2825 − 0.2462 0.7612 −15~−5 −0.181 2 −0.165 8 0.834 3 > 1000 0.1779 0.1631 1.1695 −5~5 0.079 6 0.076 6 1.082 9 降雨量/mm < 1150 1.0940 0.6654 2.9087 5~15 0.290 7 0.252 3 1.337 3 1150 ~1200 0.1038 0.0986 1.1266 >15 −1.233 9 −0.708 9 0.291 1 1200 ~1250 − 0.6966 − 0.5018 0.5182 DEM/m < 1000 − 2.0000 − 1.0000 0.0000 1250 ~1300 − 1.1307 − 0.6773 0.3424 1000 ~1500 0.0387 0.0379 1.0414 1300 ~1350 − 1.5561 − 0.7891 0.2215 1500 ~20000.4885 0.3866 1.6270 > 1350 − 1.9933 − 0.8638 0.1430 2000~ 2500 − 1.7878 − 0.8327 0.1688 道路缓冲区/m 0~200 1.0529 0.6514 2.9438 > 2500 − 2.0000 − 1.0000 0.0000 200~400 0.2886 0.2508 1.3625 坡度/° 0~5 − 1.9420 − 0.8566 0.1405 400~600 0.3021 0.2608 1.3413 5~15 − 0.0195 − 0.0193 0.9383 600~800 0.9409 0.6100 2.5809 15~25 − 0.1405 − 0.1311 0.9131 800~ 1000 0.6058 0.4546 1.6748 25~35 0.2523 0.2231 1.2455 > 1000 − 0.9685 − 0.6204 0.3770 35~45 0.2097 0.1892 1.2594 土地利用 建设用地 − 1.3142 − 0.7314 0.1881 >45 0.2392 0.2128 1.3336 林地 − 0.5301 − 0.4115 0.5889 坡向/° 平面 − 2.0000 − 1.0000 0.0000 水域 − 0.4605 − 0.3691 0.5888 北坡 − 0.8777 − 0.5843 0.3920 耕地 0.6864 0.4968 1.9965 东北坡 − 1.3344 − 0.7368 0.2735 草地 0.1144 0.1081 1.1126 东坡 − 0.0745 − 0.0718 0.9857 地层岩性 Pz1lnb 1.0508 0.6506 2.7529 东南坡 0.5670 0.4330 1.7808 Pz1lna 1.0322 0.6441 2.8523 南坡 0.8518 0.5736 2.2895 J2s − 1.3024 − 0.7282 0.2976 西南坡 − 0.5084 − 0.3987 0.6242 N1 1.9544 0.8587 7.2381 西坡 − 0.7342 − 0.5202 0.4891 D2-3 − 2.1400 − 0.8824 0.1441 西北坡 − 0.4770 − 0.3795 0.5792 Pz1lnc − 1.6072 − 0.7996 0.2044 曲率 <0 0.0997 0.0949 1.0999 Q 0.2877 0.2501 1.3066 l 0.1511 0.1403 1.1598 Pt 0.0295 0.0290 0.9839 >0 − 0.1347 − 0.1261 0.8793 T3sc − 2.6868 − 0.9319 0.0953 断层缓冲区/m 0~300 0.2659 0.2336 1.3440 C1b − 0.6366 − 0.4710 0.3703 300~600 0.3696 0.3091 1.3927 γ$_5^{1}$ − 0.4582 − 0.3677 0.6640 600~900 0.4485 0.3616 1.4663 γ m$_5^{1}$ 0.0514 0.0502 1.0718 表 3 检验样本占比表
Table 3. Proportions of test samples
模型 易发性等级 I/% CF/% FR/% 检验样本占比 低 0.00 0.00 0.68 较低 1.81 2.49 7.47 中 9.50 8.60 16.97 较高 22.17 20.36 22.85 高 66.52 68.55 52.04 表 4 混淆矩阵
Table 4. Confusion matrix
是否滑坡(实际) 预测结果 准确值 是 否 I 是 1123 277 0.795 否 314 1160 FR 是 1166 289 0.806 否 271 1148 CF 是 1203 280 0.822 否 234 1157 -
[1] 唐亚明, 薛强, 李政国, 冯卫. 基于单体和区域尺度的黄土滑坡监测预警方法与实例[J]. 灾害学, 2015, 30(4):91-95, 106.TANG Yaming, XUE Qiang, LI Zhengguo, FENG Wei. Loess landslide monitoring and early-warning methods and practices on scale of single slope and regional scope[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2015, 30(4): 91-95, 106. [2] 王宇. 云南省地质灾害应急监测预警及处置措施研究[R]. 云南省地质调查局, 2019-03-12.Wang Yu. Research on Emergency Monitoring, Early Warning and Disposal Measures of Geological Disasters in Yunnan Province [R]. Yunnan Geological Survey Bureau, March 12, 2019. [3] 周超, 殷坤龙, 曹颖, 李远耀. 基于集成学习与径向基神经网络耦合模型的三峡库区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6):1865-1876.ZHOU Chao, YIN Kunlong, CAO Ying, LI Yuanyao. Landslide susceptibility assessment by applying the coupling method of radial basis neural network and adaboost: A case study from the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 1865-1876. [4] 王宇. 云南省崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害及防治[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 1998, 9(4):38-41, 47.WANG Yu. Hazards collapse landslide and debris flow in Yunnan and their control[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 1998, 9(4): 38-41, 47. [5] 李文彬, 范宣梅, 黄发明, 武雪玲, 殷坤龙, 常志璐. 不同环境因子联接和预测模型的滑坡易发性建模不确定性[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(10):3777-3795.LI Wenbin, FAN Xuanmei, HUANG Faming, WU Xueling, YIN Kunlong, CHANG Zhilu. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility modeling under different environmental factor connections and prediction models[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(10): 3777-3795. [6] 殷坤龙, 朱良峰. 滑坡灾害空间区划及GIS应用研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(2):279-284.YIN Kunlong, ZHU Liangfeng. Landslide hazard zonation and application of GIS[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(2): 279-284. [7] 张玘恺, 凌斯祥, 李晓宁, 孙春卫, 徐建祥, 黄涛. 九寨沟县滑坡灾害易发性快速评估模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(8):1595-1610.ZHANG Qikai, LING Sixiang, LI Xiaoning, SUN Chunwei, XU Jianxiang, HUANG Tao. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou county, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1595-1610. [8] 刘睿, 施婌娴, 孙德亮, 许嘉慧. 基于GIS与随机森林的巫山县滑坡易发性区划[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 37(3):86-96.LIU Rui, SHI Shuxian, SUN Deliang, XU Jiahui. Based on GIS and random forest model for landslide susceptibility mapping in Wushan county[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 2020, 37(3): 86-96. [9] 黄武彪, 丁明涛, 王栋, 蒋良文, 李振洪. 基于层数自适应加权卷积神经网络的川藏交通廊道沿线滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(6):2015-2030.HUANG Wubiao, DING Mingtao, WANG Dong, JIANG Liangwen, LI Zhenhong. Landslide susceptibility assessment along the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor based on layer adaptive weighted convolutional neural network[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(6): 2015-2030. [10] 吴雨辰, 周晗旭, 车爱兰. 基于粗糙集−神经网络的IBURI地震滑坡易发性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6):1226-1235.WU Yuchen, ZHOU Hanxu, CHE Ailan. Susceptibility of landslides caused by IBURI earthquake based on rough set-neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1226-1235. [11] 唐亚明, 程秀娟, 薛强, 毕俊擘. 基于层次分析法的黄土滑塌风险评价指标权重分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2012, 23(4):40-46.TANG Yaming, CHENG Xiujuan, XUE Qiang, BI Junbo. Weights analysis of Loess collapse risk assessing factors based on analytical hierarchy process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2012, 23(4): 40-46. [12] 黄立鑫, 郝君明, 李旺平, 周兆叶, 贾佩钱. 基于RBF神经网络-信息量耦合模型的滑坡易发性评价:以甘肃岷县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(6):116-126.HUANG Lixin, HAO Junming, LI Wangping, ZHOU Zhaoye, JIA Peiqian. Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value: A case study in Minxian, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6): 116-126. [13] 周萍, 邓辉, 张文江, 薛东剑, 吴先谭, 卓文浩. 基于信息量模型和机器学习方法的滑坡易发性评价研究: 以四川理县为例[J]. 地理科学, 2022, 42(9):1665-1675.ZHOU Ping, DENG Hui, ZHANG Wenjiang, XUE Dongjian, WU Xiantan, ZHUO Wenhao. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on information value model and machine learning method: A case study of Lixian county, Sichuan Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 1665-1675. [14] Bhagya S B, Sumi A S, Balaji S, Danumah J H, Costache R, Rajaneesh A, Gokul A, Chandrasenan C P, Quevedo R P, Johny A, Sajinkumar K S, Saha S, Ajin R S, Mammen P C, Abdelrahman K, Fnais M S, Abioui M. Landslide Susceptibility assessment of a part of the Western Ghats (India) employing the AHP and F-AHP models and comparison with existing susceptibility maps[J]. Land, 2023, 12(468). [15] Ikram R M A, Dehrashid A A, Zhang B Q, Chen, Z H, Le B N, Moayedi H. A novel swarm intelligence: Cuckoo optimization algorithm (COA) and SailFish optimizer (SFO) in landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2023, 37(5): 1-27. [16] Huang C, Li F, Wei L, Hu X D. Landslide susceptibility modeling using a deep random neural network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(24): 12887. [17] 王宇. 云南省地质灾害防治与研究历史评述[J]. 灾害学, 2019, 34(3):134-139.WANG Yu. Historical review of geological disaster prevention and research in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Jouranl of Catastrophology, 2019, 34(3): 134-139. [18] 陈立权, 赵超英, 任超锋, 王佩杰, 陈雪蓉, 陈恒祎. 光学遥感用于贵州发耳镇尖山营滑坡监测研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4):518-523.CHEN Liquan, ZHAO Chaoying, REN Chaofeng, WANG Peijie, CHEN Xuerong, CHEN Hengwei. Monitoring the Jianshanying landslide in a karst mountainous area of Guizhou by optical remote sensing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 518-523. [19] 杨辰, 邓飞, 史绪国. 利用2015-2019年Sentinel-1数据监测武汉白沙洲岩溶区地表沉降特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(3):558-564.YANG Chen, DENG Fei, SHI Xuguo. Monitoring subsidence characteristics of Baishazhou karst area in Wuhan with Sentinel-1 images from 2015 to 2019[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(3): 558-564. [20] 殷跃平, 王文沛. 高位远程滑坡动力侵蚀犁切计算模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(8):1513-1521.YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei. A dynamic erosion plowing model of long run-out landslides initialized at high locations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1513-1521. [21] 魏云杰, 王俊豪 , 胡爱国, 苟安田. 澜沧江拉金神谷滑坡成灾机理分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2022, 9(4):19-26.WEI Yunjie, WANG Junhao, HU Aiguo, GOU Antian. Analysis of formation mechanism of Lajinshengu landslide in Lancang river[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(4): 19-26. [22] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(7):957-966.XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. [23] 李梦华, 张路, 董杰, 蔡杰华, 廖明生. 四川茂县岷江河谷区段滑坡隐患雷达遥感识别与形变监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(10):1529-1537.LI Menghua, ZHANG Lu, DONG Jie, CAI Jiehua, LIAO Mingsheng. Detection and monitoring of potential landslides along Minjiang river valley in Maoxian county, Sichuan using radar remote sensing[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(10): 1529-1537. [24] Jiang Z, Zhao C Y, Yan M, Wang B H, Liu X J. The early identification and spatio-temporal characteristics of loess landslides with SENTINEL-1A datasets: A case of Dingbian county, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(23): 6009. doi: 10.3390/rs14236009 [25] 王志旺, 李端有, 王湘桂. 区域滑坡空间预测方法研究综述[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2012, 29(5):78-85, 94.WANG Zhiwang, LI Duanyou, WANG Xianggui. Review of researches on regional landslide susceptibility mapping model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2012, 29(5): 78-85, 94. [26] Shortliffe E H, Buchanan B G. A model of inexact reasoning in medicine[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 1975, 23(3-4): 351-379. [27] Heckerman D. Probabilistic interpretations for MYCIN's certainty factors[J]. Machine Intelligence and Pattern Recognition, 1986: 167-196. [28] 李文彦, 王喜乐. 频率比与信息量模型在黄土沟壑区滑坡易发性评价中的应用与比较[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2020, 29(4):213-220.LI Wenyan, WANG Xile. Application and comparison of frequency ratio and information value model for evaluating landslide susceptibility of loess gully region[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2020, 29(4): 213-220. [29] 丁永辉, 张勤, 杨成生, 王猛, 丁辉. 基于高分遥感的金沙江流域滑坡识别:以巴塘县王大龙村为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2022(4):51-55.DING Yonghui, ZHANG Qin, YANG Chengsheng, WANG Meng, DING Hui. Landslide identification in Jinsha river basin based on high-resolution remote sensing: Taking Wangdalong village of Batang county as an example[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2022(4): 51-55. [30] 杨旭东, 李媛, 佟彬, 闫金凯, 徐为, 李崇贵. 基于移动3S技术的地质灾害野外调查数据采集系统设计与实现[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治报, 2016, 27(4):93-96, 113.YANG Xudong, LI Yuan, TONG Bin, YAN Jinkai, XU Wei, LI Chonggui. Design and implementation of field data acquisition system for geo-hazards urvey based on mobile 3S technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2016, 27(4): 93-96, 113. [31] 王宇, 黄成, 周翠琼, 杨迎冬, 肖华宗, 晏祥省, 张令泽, 王裕琴. 山区地质灾害应急调查的内涵及方法分析评述[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4):492-499.WANG Yu, HUANG Cheng, ZHOU Cuixiong, YANG Yingdong, XIAO Huazong, YAN Xiangsheng, ZHANG Lingze, WANG Yuqin. Review on the connotation and methods of emergency investigations to geological hazards in mountainous area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 492-499. [32] 张钟远, 邓明国, 徐世光, 张云波, 付弘流, 李忠海. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(1):157-171.ZHANG Zhongyuan, DENG Mingguo, XU Shiguang, ZHANG Yunbo, FU Hongliu, LI Zhonghai. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang county, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(1): 157-171 . [33] Shano L, Raghuvanshi T K, Meten M. Landslide susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio model: The case of Gamo highland, South Ethiopia[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14(7): 1-18. [34] 赵占骜, 王继周, 毛曦, 马维军, 路文娟, 何毅, 高轩宇. 多维CNN耦合的滑坡易发性评价方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(8):1466-1481.ZHAO Zhan'ao, WANG Jizhou, MAO Xi, MA Weijun, LU Wenjuan, HE Yi, GAO Xuanyu. A multi-dimensional CNN coupled landslide susceptibility assessment method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1466-1481. [35] 罗路广, 裴向军, 黄润秋, 裴钻, 朱凌. GIS支持下CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的九寨沟景区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(2):526-535.LUO Luguang, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, FEI Zuan, ZHU Ling. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area with GIS based on certainty factor and logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(2): 526-535. -




 下载:
下载: