Study on distribution law of geological disasters in karst mountainous area of east Yunnan
-
摘要: 文章是在1∶5万地质灾害详细调查、精细化调查与风险评价的基础上,针对滇东高原高山峡谷、岩溶石山区的特点,通过开展数据统计与定性分析相结合的方法,从地形地貌、斜坡结构类型、地质构造、工程地质岩组等方面,详细阐述研究区地质灾害分布特征及规律。结果表明:(1)研究区地质灾害分布特征呈由北向南逐渐递减的态势,北部高山峡谷—河谷斜坡区地质灾害最发育,是中部高原盆地地质灾害发育数量的2~3倍;(2)研究区地质灾害主要分布在坡向90°~135°、225°~270°以及270°~315°地段,总数4 249处,占地质灾害总数的39.88%,与北东—南西向、南北向的构造形迹具有一定相关性;(3)在断裂带交汇处或主断裂走向发生变化地段地质灾害最发育,且走滑型逆断裂上、下两盘地质灾害分布具有明显的“上盘效应”;(4)研究区含泥岩、页岩软弱夹层的顺层斜坡体中灾害最为发育,有2 995处,占灾害总数的31.94%;正交结构的斜坡体没有天然的介质分界面,不易形成贯通性的结构滑动面,地质灾害不发育,仅901处,占灾害总数的9.61%;(5)含软弱夹层的碳酸盐岩组,受地表(下)水影响强烈,易形成“上硬下软、头重脚轻”的易灾结构体,是研究区地质灾害最为发育的岩组。Abstract:
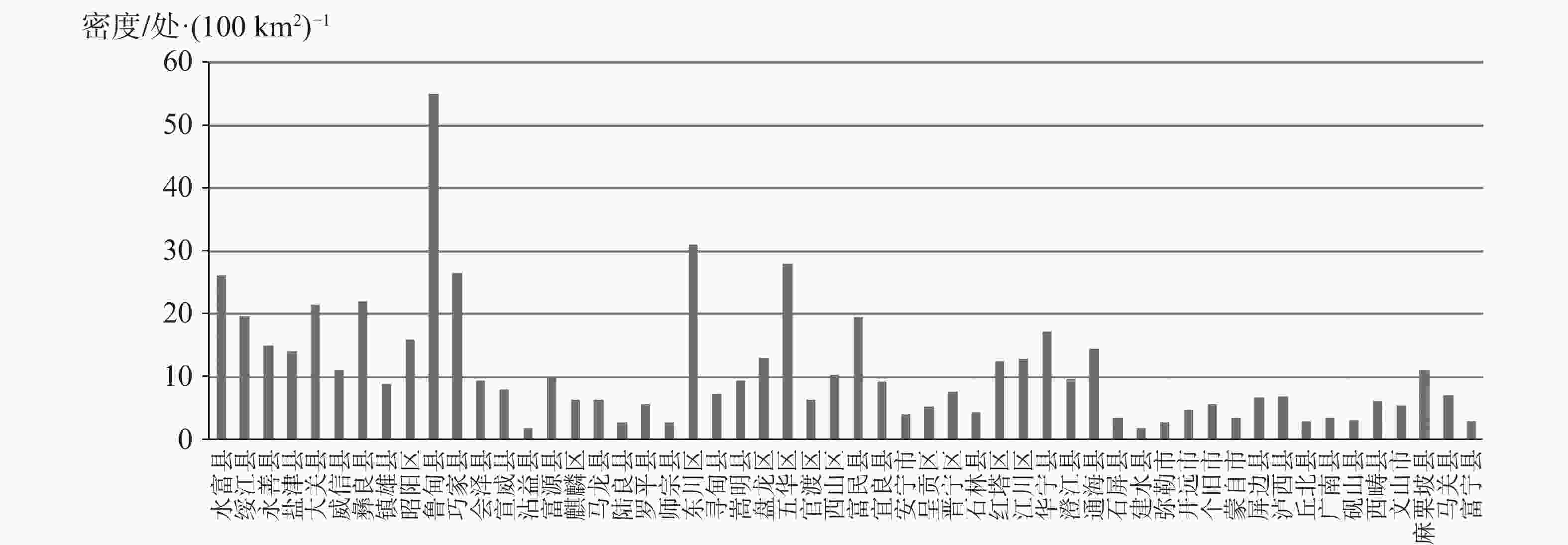
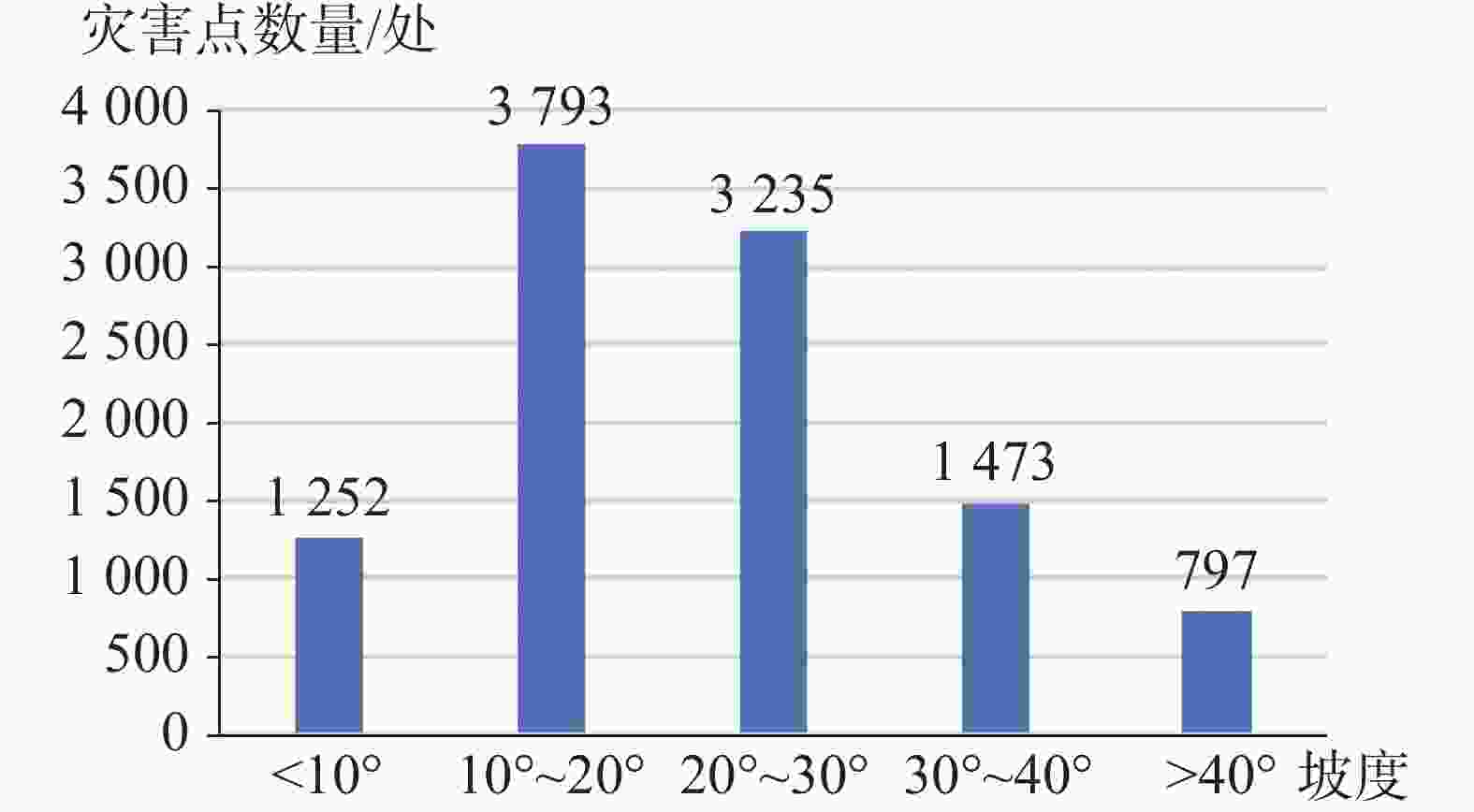
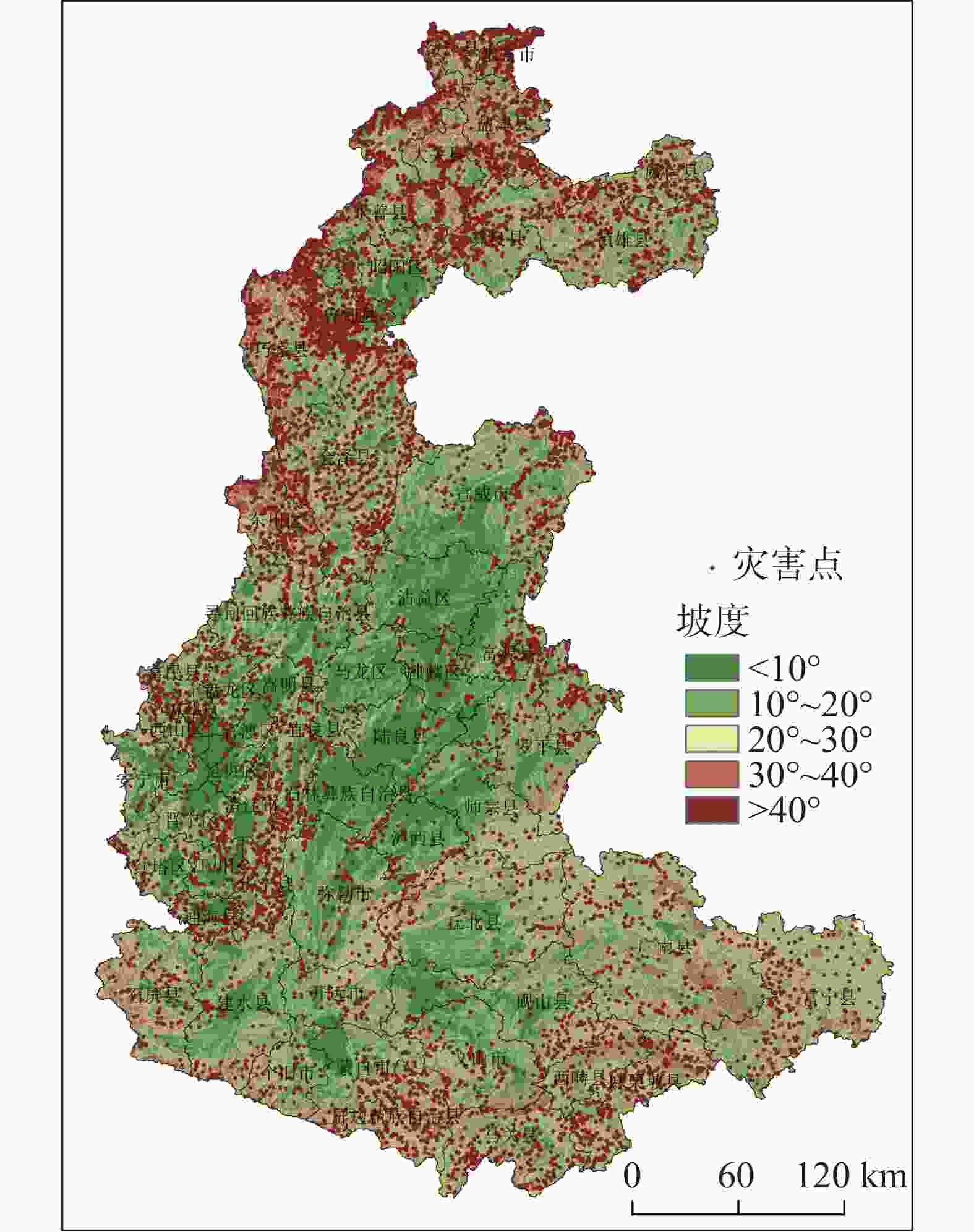
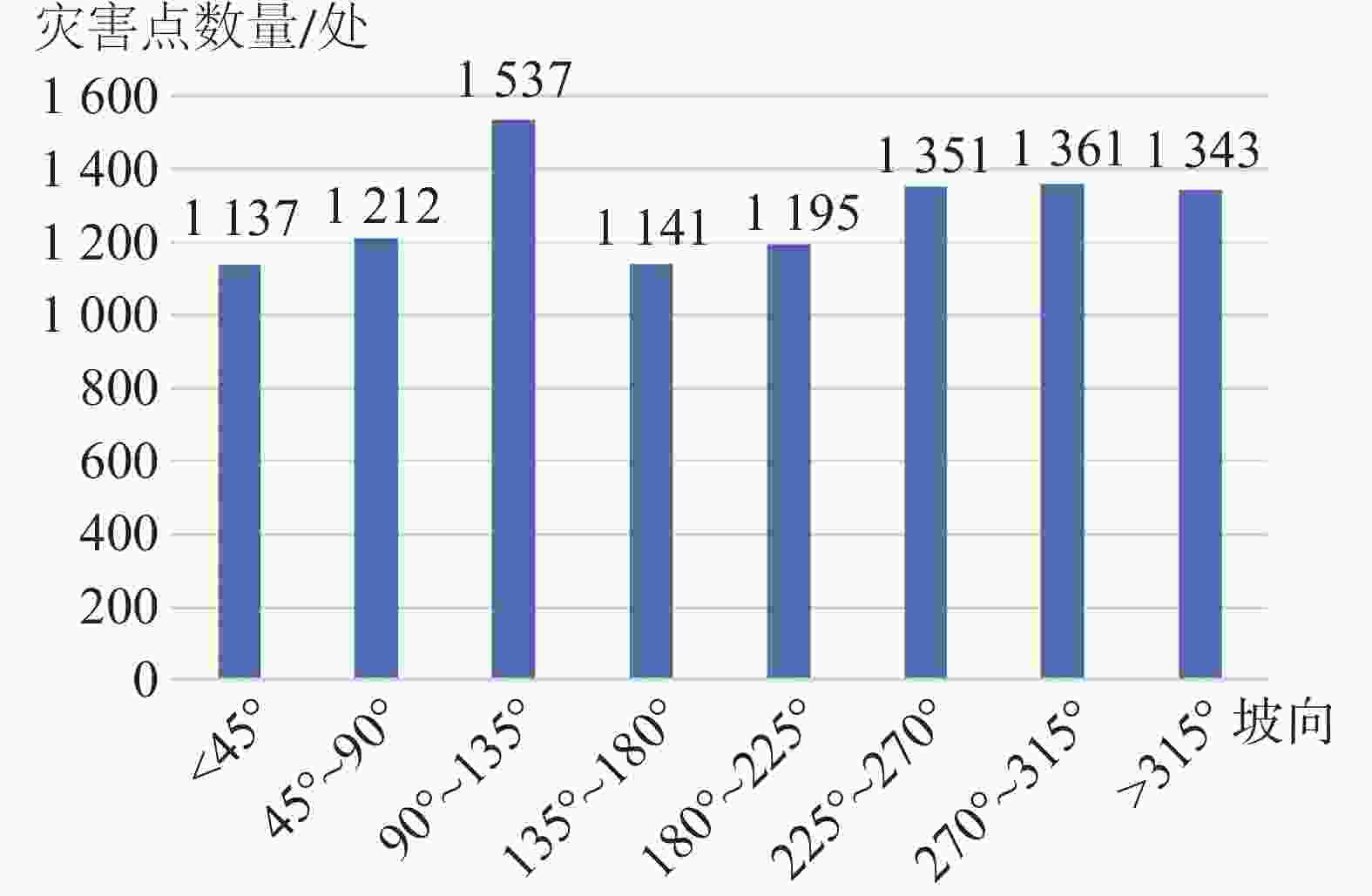
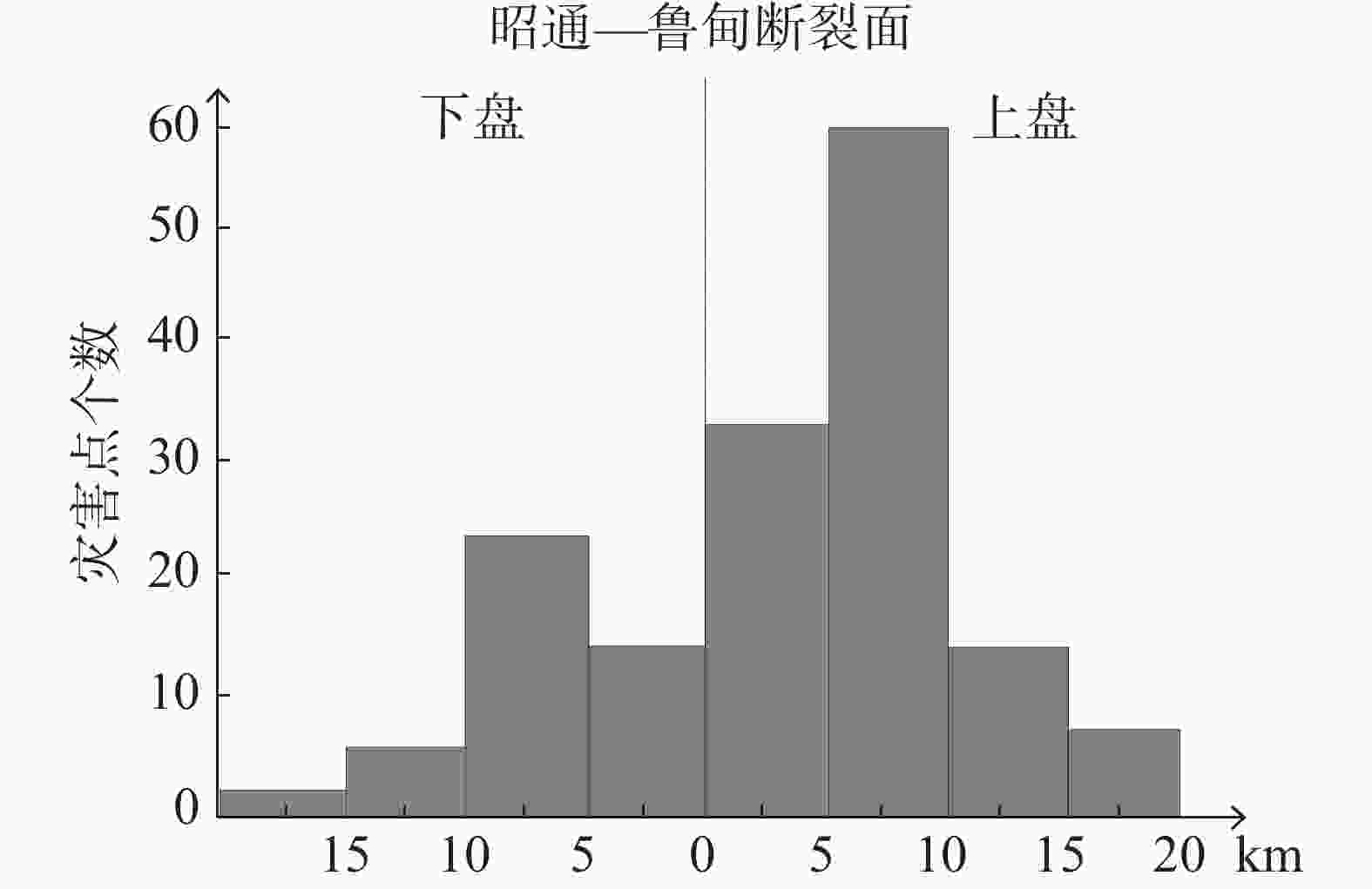
Based on a comprehensive and detailed investigation, coupled with a risk assessment of geological disasters at a scale of 1∶50,000 in the study area, this paper focuses on the unique characteristics of high mountain valleys and karst rock mountains prevalent within the region. Through a combination of data statistics and qualitative analysis, the distribution patterns and laws of geological disasters in the study area are meticulously elaborated in terms of landform, slope structure type, geological structure, geological engineering, and rock formation. The findings are listed as followings: (1) The terrain in northeast Yunnan is characterized by significant relief, with deep river valleys predominantly located along the plateau edges and valley slopes. Consequently, the distribution of geological disasters gradually diminishes from north to south, with a mean density of 8.62 per 100 km². The northern alpine valleys and valley slope areas exhibit the most developed geological disasters, which are approximately 2 to 3 times more numerous than those in the central plateau basin. (2) Geological disasters are more prevalent in the geomorphic units dominated by the edges of plateaus and slopes of river valleys, with a total of 3,161 occurrences, which accounts for 29.67% of all recorded disasters. The geological disasters are not developed in the plateau areas of central and east Yunnan, where the plateau morphology is relatively intact and the terrain is gentle, with only 87 occurrences, accounting for 0.82% of the total disasters. (3) The geological disasters in the study area are mainly distributed in sections with slopes of 10°–30°, totaling of 7,028 occurrences, which account for 66.62% of all geological disasters. In contrast, the sections with slopes greater than 40° exhibit the fewest geological disasters, with only 797 occurrences, representing 7.55% of the total. Additionally, geological disasters in the study area are primarily concentrated in slope sections with orientations of 90°–135°, 225°–270°, and 270°–315°, totaling 4,249 occurrences, which account for 39.88% of the overall. These disasters generally extend from north to south and west, demonstrating a correlation with the northeast-to-south and north structural patterns. (4) Geological disasters predominantly occur at the intersections of fault zones or in regions where the orientation of the primary faults changes. These disasters tend to be distributed in a linear or belt-like patterns. When faults remain continuously active, signs of multiple disasters events become apparent. The distribution of geological disasters correlates with structural features, including the orientation of faults, and the dip direction of slopes. Geological disasters are arranged in an imbricated pattern on both sides of the main controlling faults. In the case of strike-slip reverse faults, the distribution of geological disasters exhibits a notable "upper plate effect". Particularly, under seismic activities, the frequency of geological disasters on the upper plate is significantly greater than that on the lower plate. (5) In the study area, geological disasters are most prevalent in dip-slope formations that contain weak interlayers of mudstone and shale, with a total 2,995 occurrences, accounting for 31.94% of all recorded disasters. In contrast, slopes formations with orthogonal structures lack natural medium interfaces, which hinders the formation of continuous structural sliding surfaces. Consequently, geological disasters are less common in these areas, with only 901 occurrences, representing 9.61% of the total number of disasters. (6) The carbonate group containing weak interlayers is more susceptible to the development of joint fissures under tectonic forces. Surface water and groundwater can easily infiltrate these joint fissures, leading to the hydration and softening of the interlayers. Over time, this process may evolve into a slip zone for rock falls or landsides, resulting in a disaster-prone structural formation characterized by being solid and heavy on top, and soft and light below. This rock group is where geological disasters are most prevalent in the study area. The findings from this study can provide a geological foundation for comprehensive prevention and control of geological disasters, as well as a foundation for land use planning and regulation in the study area. -
Key words:
- karst plateau /
- geological disaster /
- distribution law /
- upper plate effect /
- disaster-prone structure
-
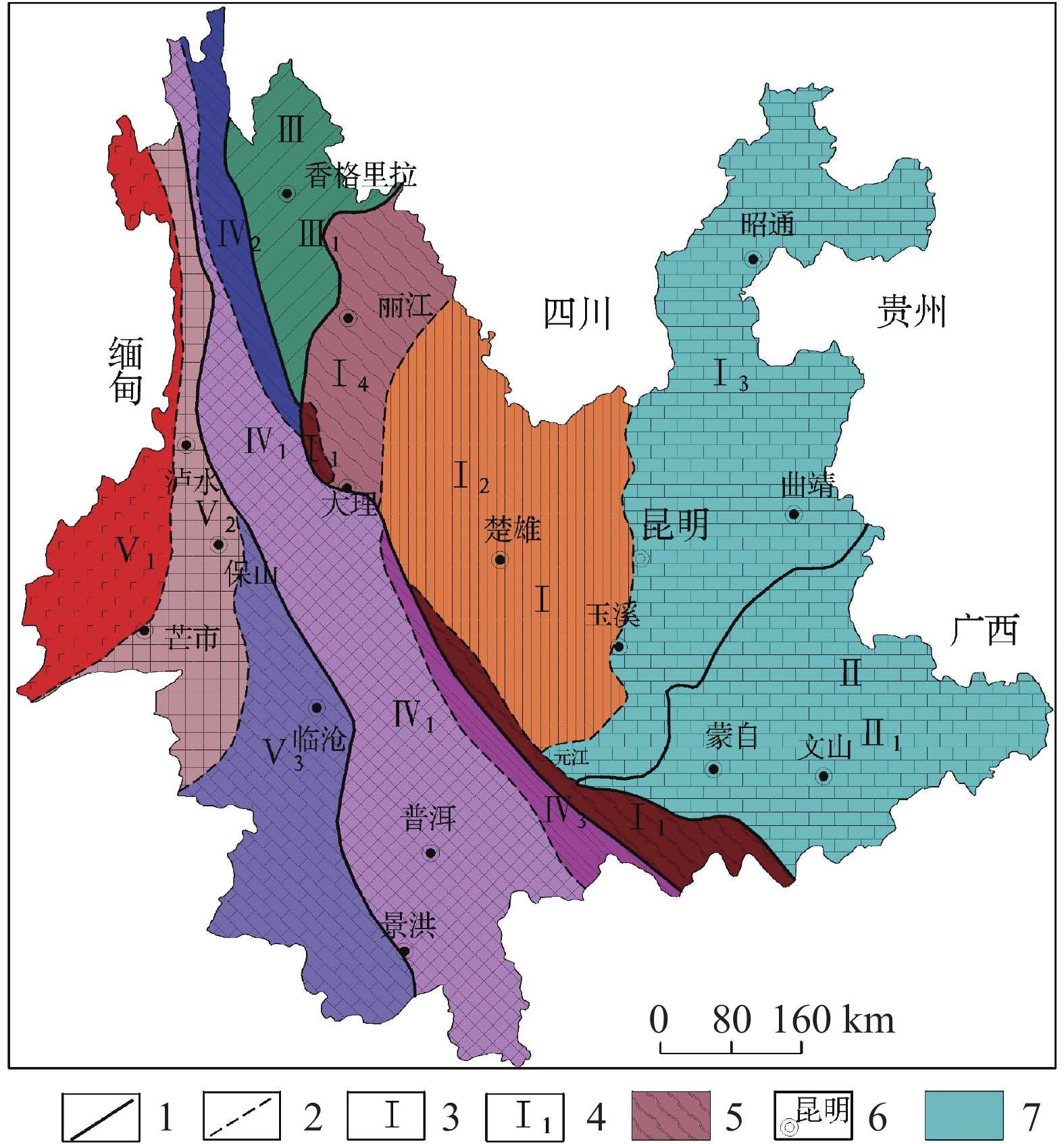
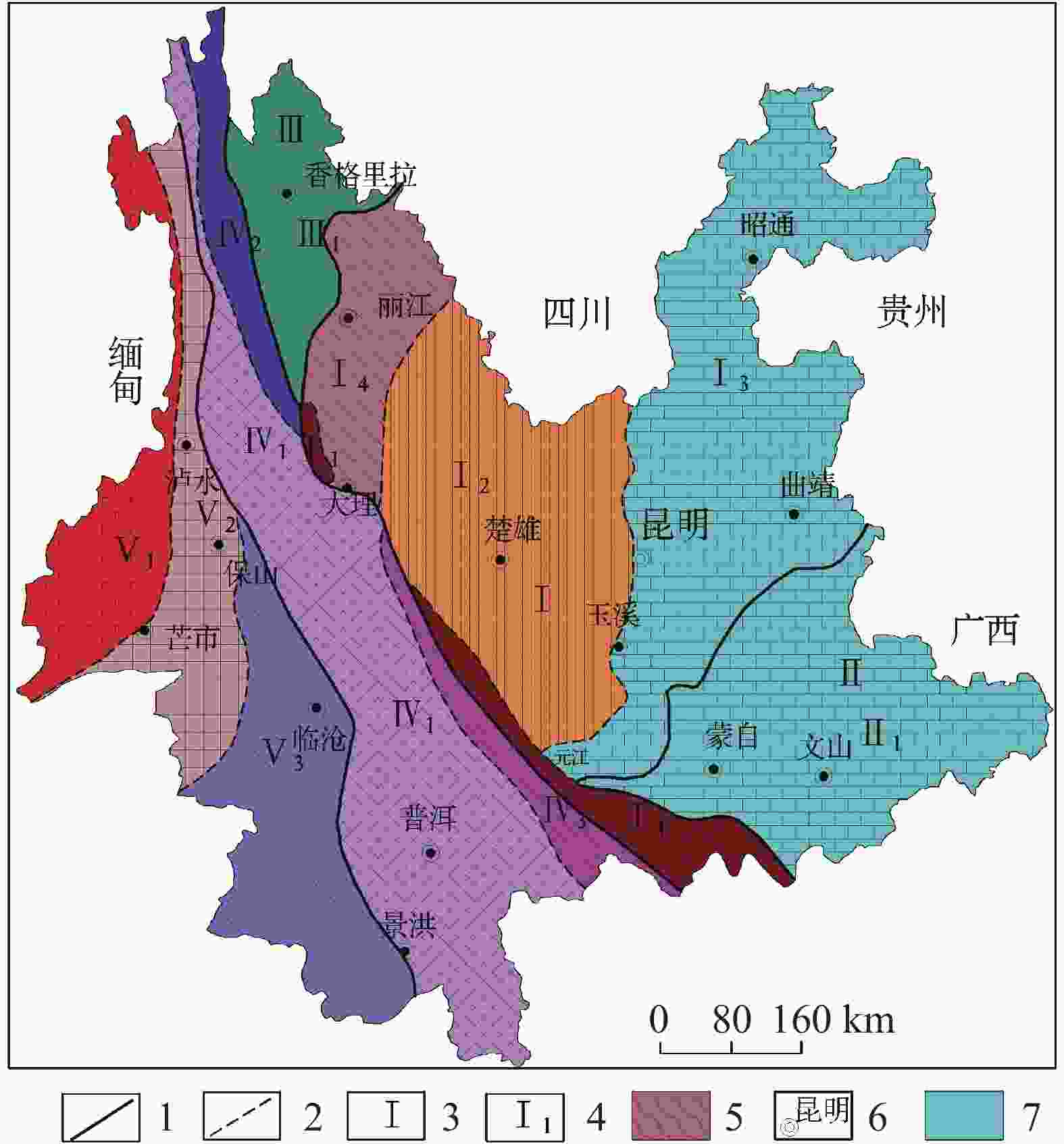
图 1 云南省大地构造分区图
1.一级构造单元界线 2.二级构造单元界线 3.一级构造单元代号 4.二级构造单元代号 5.哀牢山变质带 6.州市政府驻地 7.研究区(Ⅰ.扬子准地台构造单元;Ⅱ.华南褶皱系构造单元;Ⅲ.松潘—甘孜褶皱系构造单元;Ⅳ.唐古拉—昌都—兰坪—思茅褶皱系构造单元;Ⅴ.冈底斯—念青唐古拉褶皱系构造单元)
Figure 1. Geotectonic zoning of Yunnan Province
1. boundary of first-level tectonic unit 2. boundary of secondary tectonic unit 3. code of first-level tectonic unit 4. code of secondary tectonic unit 5. metamorphic belt of Ailao mountain 6. municipal governments of autonomous prefectures 7. the study area (Ⅰ. tectonic unit of the Yangtze platform; Ⅱ. tectonic unit of South China fold system; Ⅲ. tectonic unit of Songpan–Ganzi fold system; Ⅳ. tectonic unit of Tanggula–Changdu–Lanping–Simao fold system; V. tectonic unit of Gangdisi–Nyainqentanglha fold system)
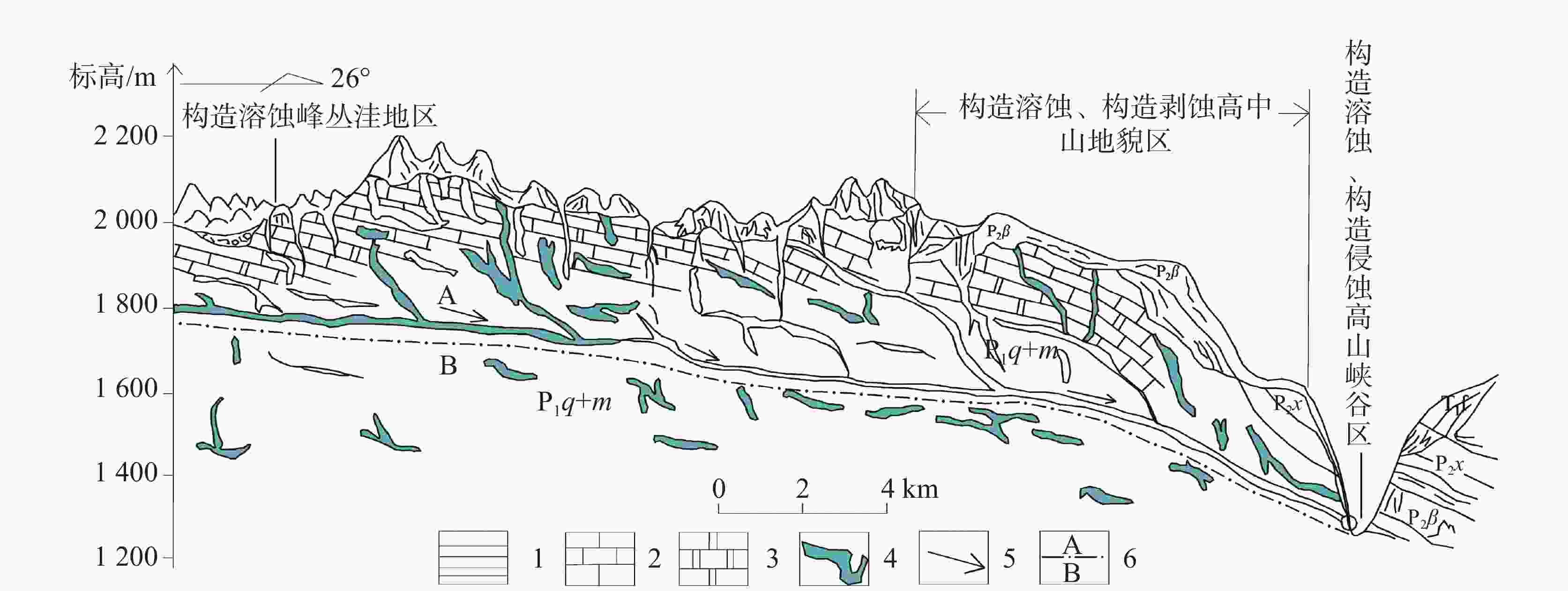
图 2 滇东北高原面边缘(河谷斜坡)示意图[5]
1.泥页岩 2.灰岩 3.白云岩 4.岩溶洞穴 5.地下水流向 6.岩溶分带界线(A.强岩溶发育带, B.弱岩溶发育带)
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the plateau edge (valley slope) in northeast Yunnan
1. mud shale 2. limestone 3. dolomite 4. karst cave 5. groundwater flow direction 6. karst zoning boundary (A. zone of strong karst development,B.zone of weak karst development)
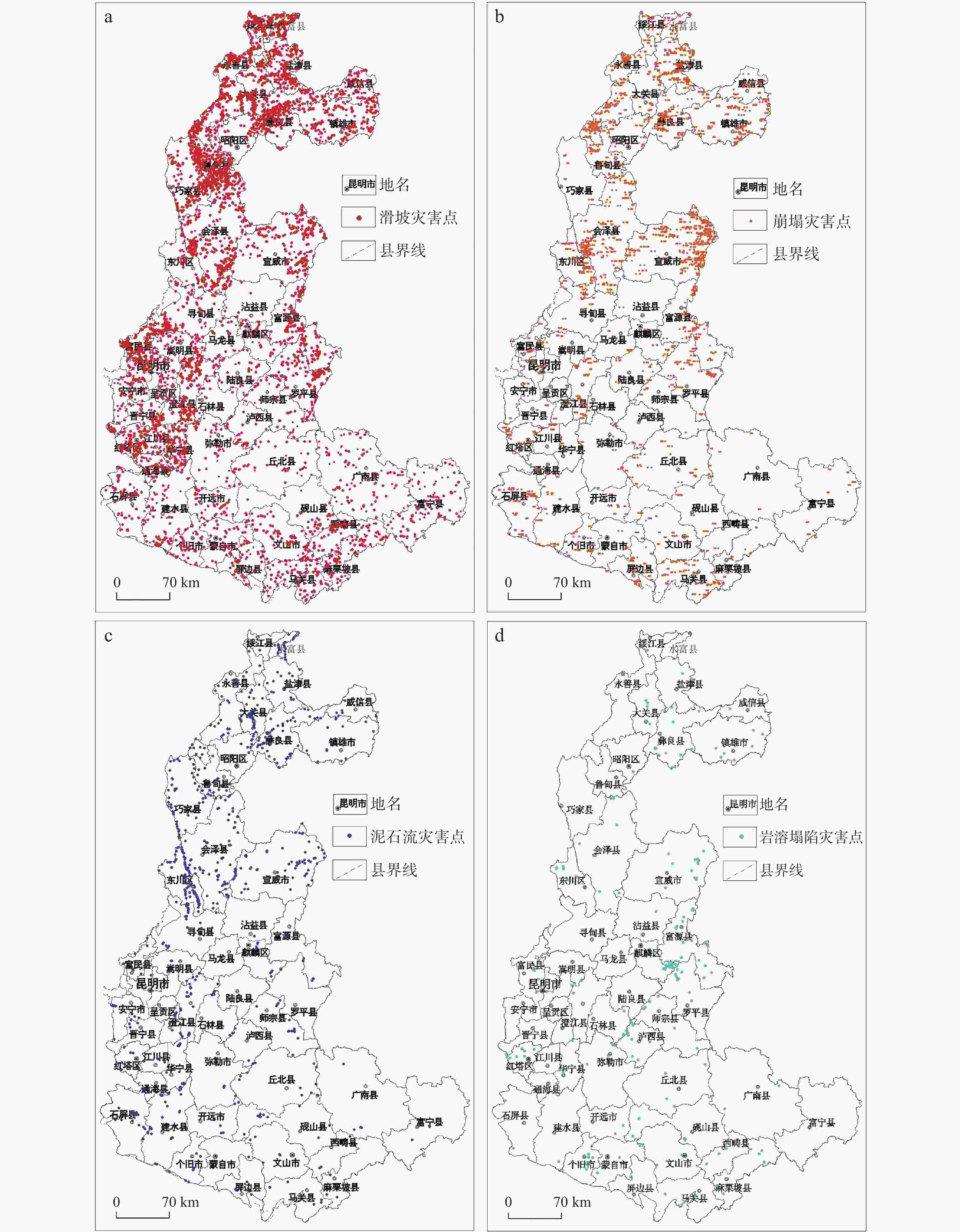
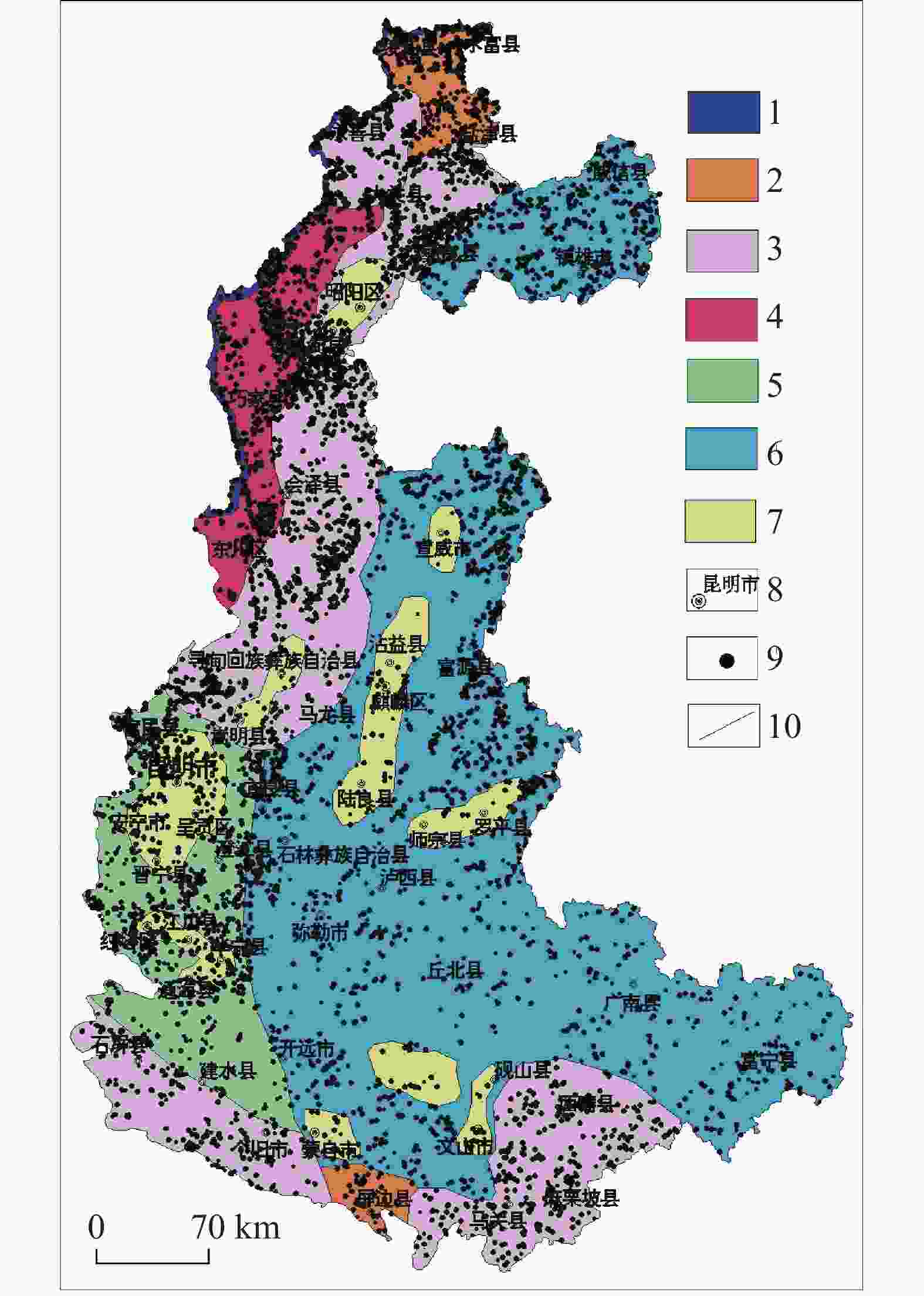
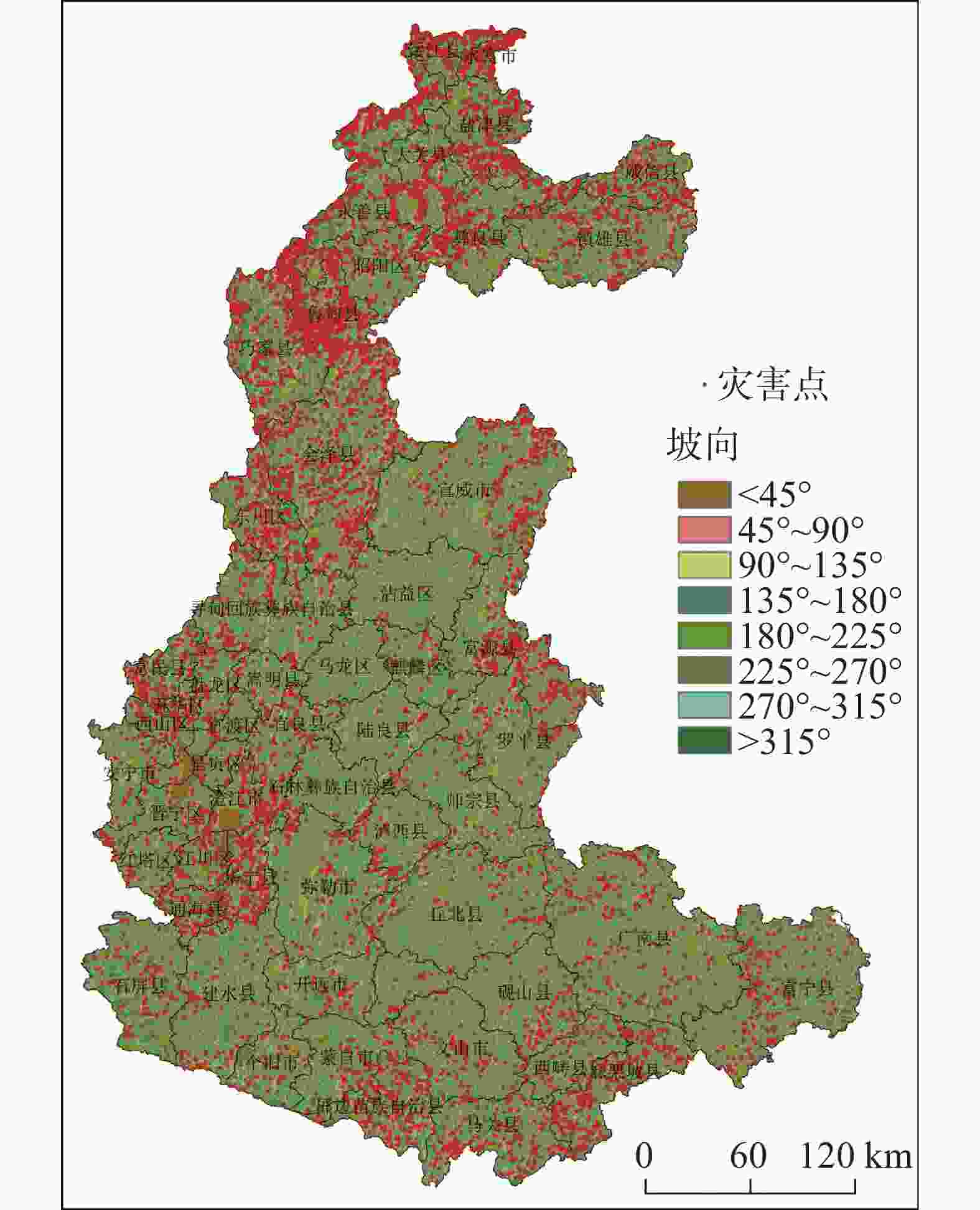
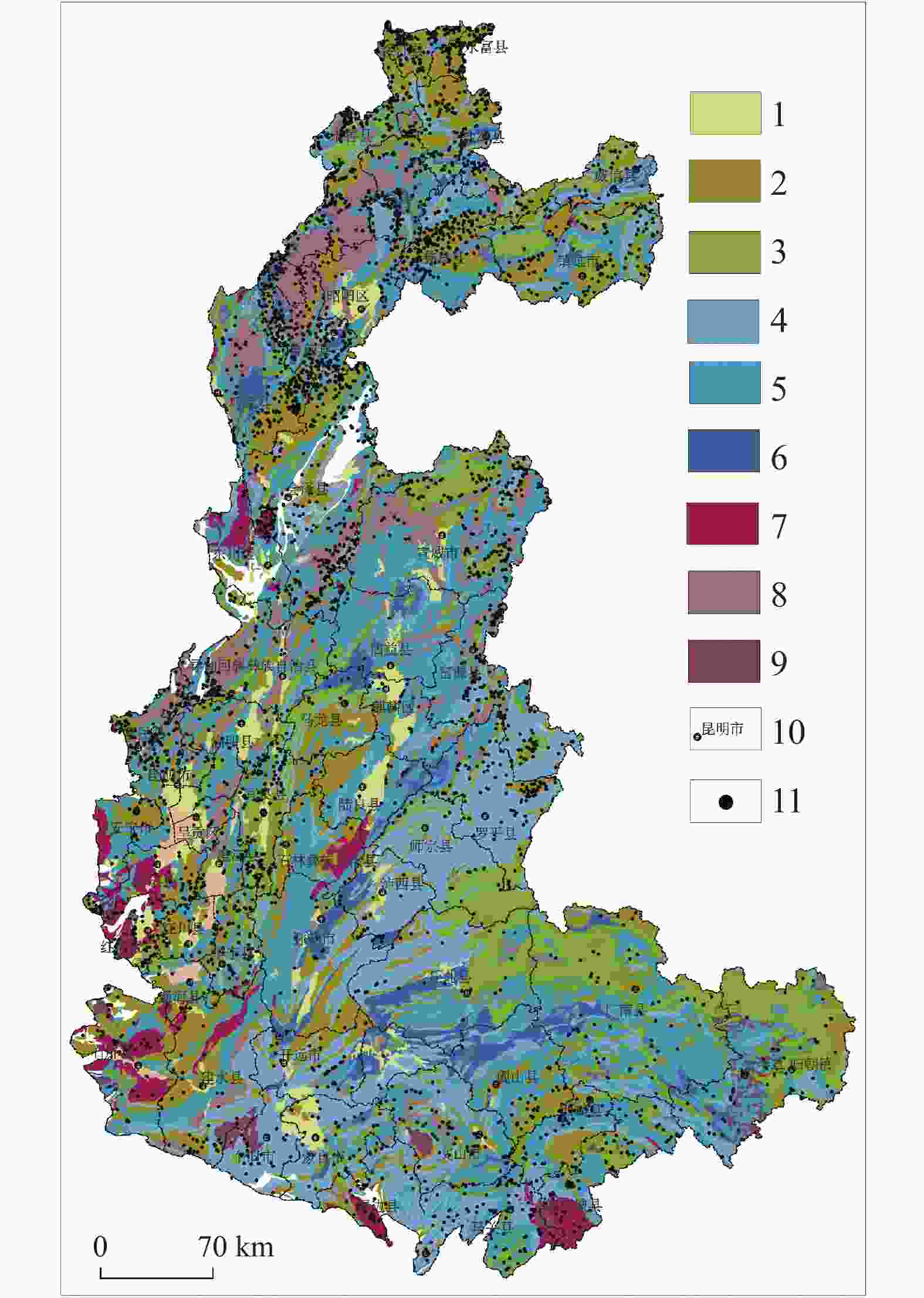
图 7 研究区各地貌区地质灾害分布图
1.构造溶蚀高山峡谷地貌区 2.构造侵蚀低中山地貌区 3.构造溶蚀高中山地貌区 4.构造剥蚀高中山地貌区 5.构造溶蚀低中山地貌区 6.构造溶蚀峰丛洼地地貌区 7.高原盆地地貌区 8.地名 9.灾害点 10.分区界线
Figure 7. Distribution of geological disasters in various landforms of the study area
1.geomorphic area of tectonic erosion alpine canyon 2.geomorphic area of tectonic erosion low-medium mountain 3.geomorphic area of tectonic erosion high-medium mountain 4.geomorphic area of tectonic denudation high-medium mountain 5.geomorphic area of tectonic dissolution low-medium mountain 6.area of tectonic dissolution peak-cluster depression 7.geomorphic area of plateau basin 8.geographical names 9.disaster sites 10.zoning boundaries
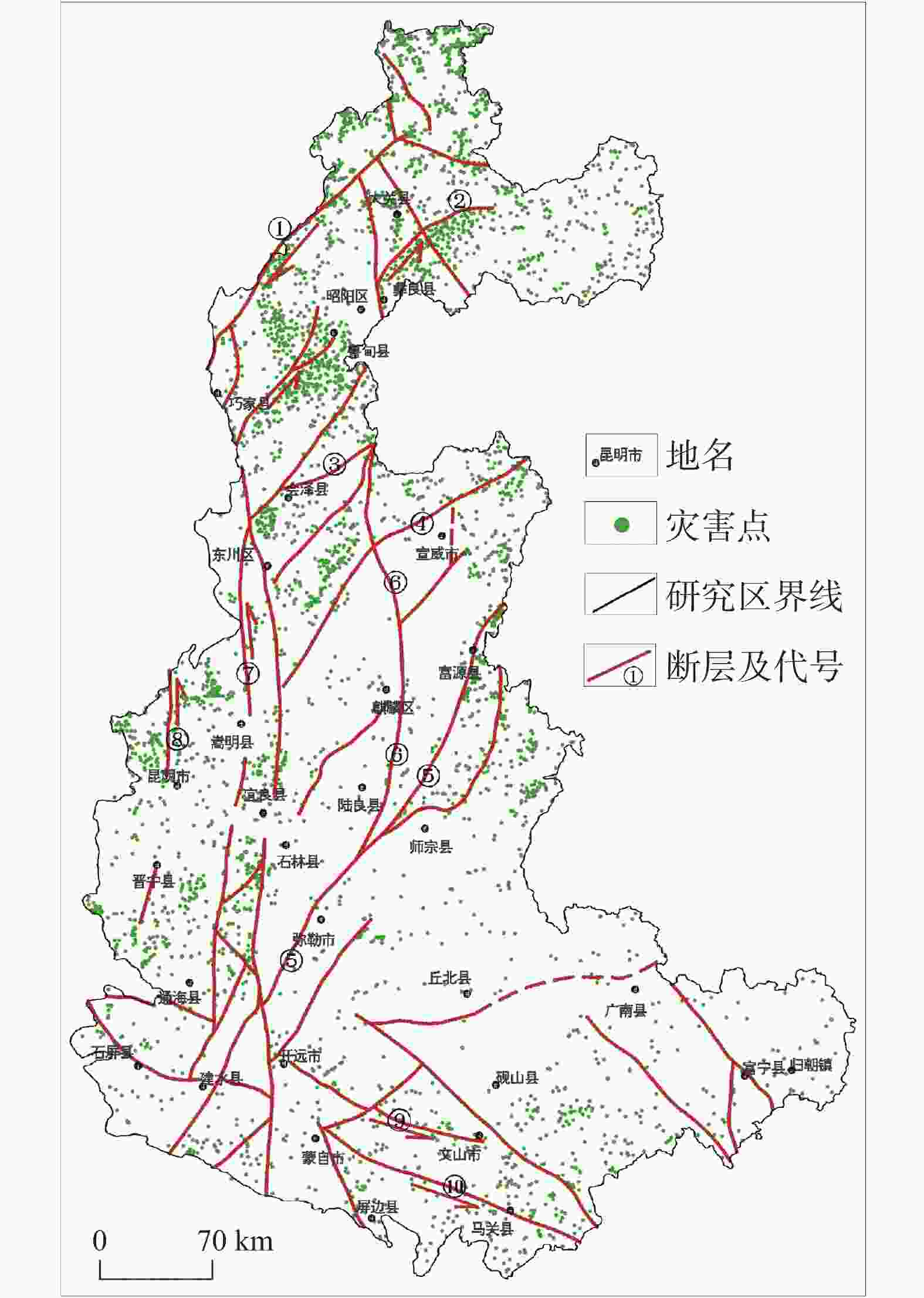
图 12 研究区地质灾害与地质构造关系分布图
①巧家—莲峰断裂 ②昭鲁断裂 ③会泽断裂 ④寻甸—来宾铺断裂 ⑤弥勒—富源断裂 ⑥曲靖—昭通断裂 ⑦小江断裂 ⑧普渡河断裂 ⑨文麻断裂 ⑩建水—蒙自断裂
Figure 12. Distribution of geological disasters and geological structures in the study area
① Qiaojia–Lianfeng fracture ② Zhaolu fracture ③ Huize fracture ④ Xundian–Laibinpu fracture ⑤ Mile–Fuyuan fracture ⑥ Qujing–Zhaotong fracture ⑦ Xiaojiang fracture ⑧ Puduhe fracture ⑨ Wenma fracture ⑩ Jianshui–Mengzi fracture
图 14 研究区地质灾害与工程地质岩组关系分布图
1.松散土体 2.层状碎屑岩岩组 3.层状碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩岩组 4.层状中等岩溶化碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 5.层状强岩溶化碳酸盐岩岩组 6.层状软硬相间的碳酸盐岩碎屑岩岩组 7.层状坚硬中等风化变质岩岩组 8.块状坚硬弱风化侵入岩岩组 9.碎裂状较坚硬中等风化喷出岩岩组 10.地名 11.地质灾害点
Figure 14. Relationship between geological disasters and engineering geological rock groups in the study area
1.loose soil 2.stratified clastic rock group 3.stratified rock group of clastic rocks interbedded with carbonate rocks 4.stratified and moderately karstified rock group of carbonate rocks interbedded with clastic rocks 5.stratified and strongly karstified carbonate rock group 6.stratified carbonate clastic rock group with alternating hard and soft layers 7.stratified hard metamorphic rock group weathered moderately 8.massive hard intrusive rock group weathered weakly 9.hard and moderately weathered extrusive rock group in the form of fragmentation 10.place names 11.geological disaster sites
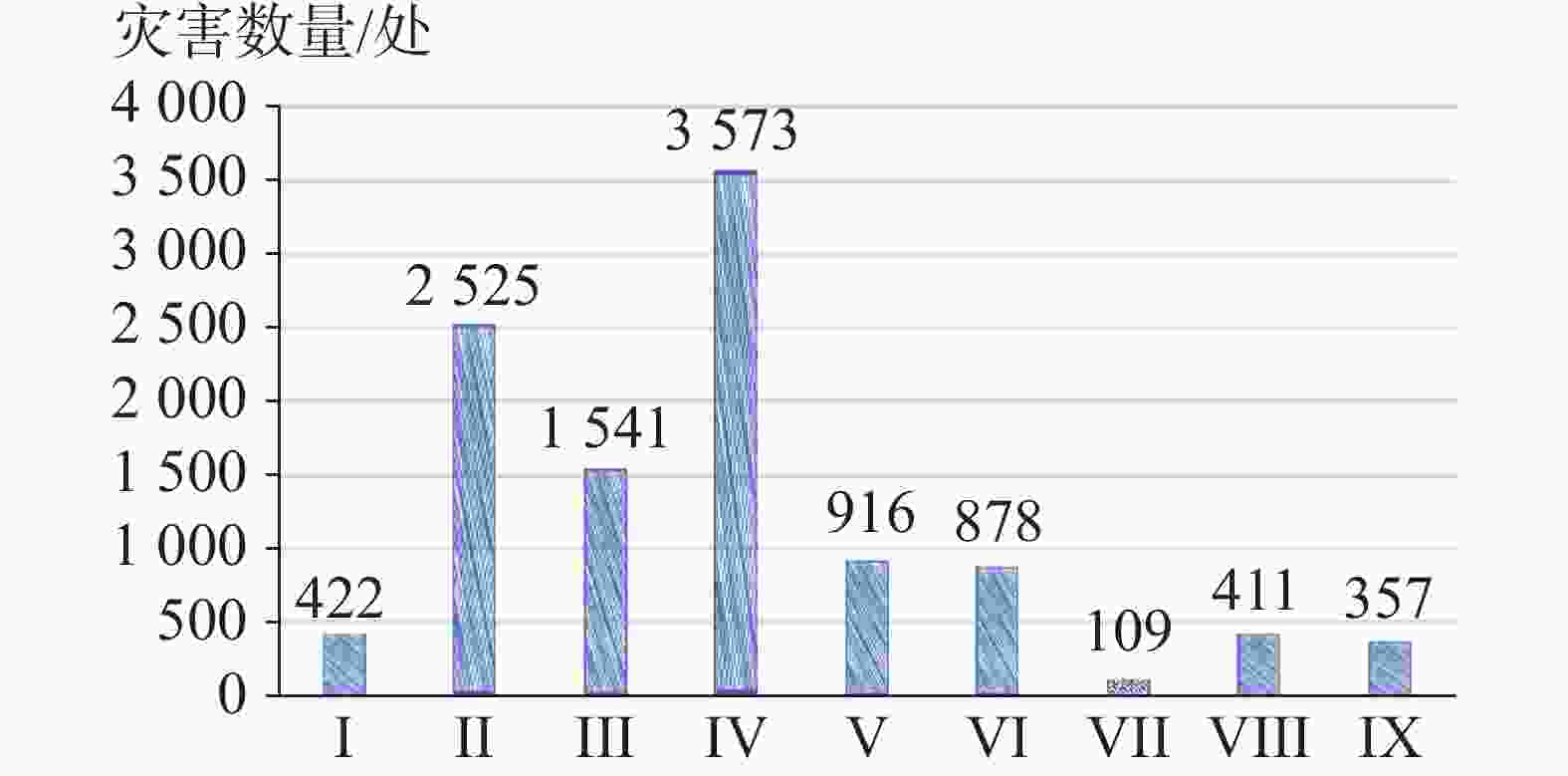
图 15 研究区各岩组灾害分布对比图
Ⅰ.松散土体 Ⅱ.层状碎屑岩岩组 Ⅲ.层状碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩岩组 Ⅳ.层状中等岩溶化碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 Ⅴ.层状强岩溶化碳酸盐岩岩组 Ⅵ.层状软硬相间的碳酸盐岩碎屑岩岩组 Ⅶ.层状坚硬中等风化变质岩岩组 Ⅷ.块状坚硬弱风化侵入岩岩组 Ⅸ.碎裂状较坚硬中等风化喷出岩岩组
Figure 15. Comparison of geological disaster distribution of different rock groups in the study area
Ⅰ.loose soil Ⅱ. stratified clastic rock group Ⅲ. stratified rock group of clastic rocks interbedded with carbonate rocks Ⅳ. stratified and moderately karstified rock group of carbonate rocks interbedded with clastic rocks V. stratified and strongly karstified carbonate rock group Ⅵ. stratified carbonate clastic rock group with alternating hard and soft layers Ⅶ. stratified hard metamorphic rock group weathered moderately Ⅷ. massive hard intrusive rock group weathered weakly Ⅸ. hard and moderately weathered extrusive rock group in the form of fragmentation
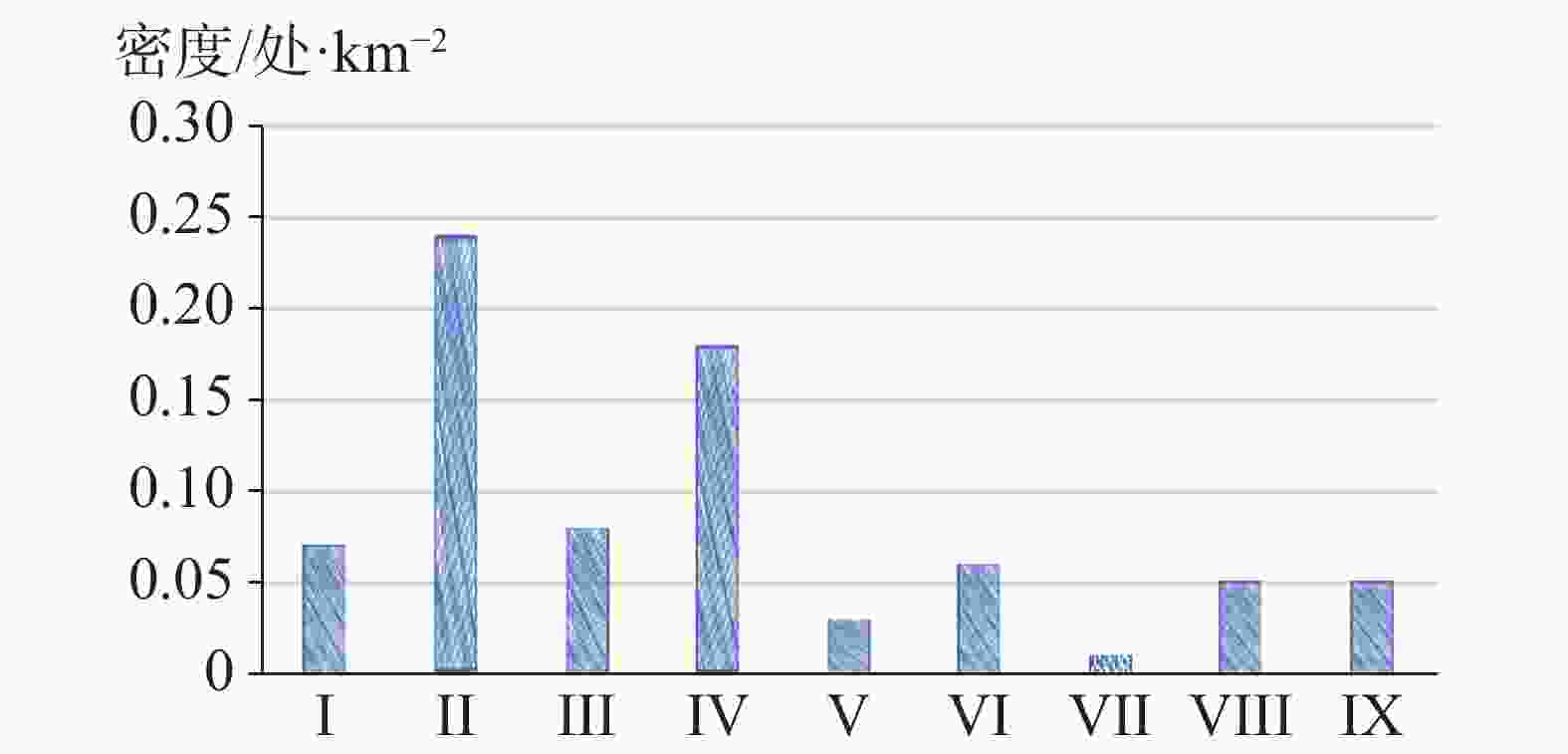
图 17 研究区各岩组灾害发育密度对比图
Ⅰ.松散土体 Ⅱ.层状碎屑岩岩组 Ⅲ.层状碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩岩组 Ⅳ.层状中等岩溶化碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 Ⅴ.层状强岩溶化碳酸盐岩岩组 Ⅵ.层状软硬相间的碳酸盐岩碎屑岩岩组 Ⅶ.层状坚硬中等风化变质岩岩组 Ⅷ.块状坚硬弱风化侵入岩岩组 Ⅸ.碎裂状较坚硬中等风化喷出岩岩组
Figure 17. Comparison of density of geological disaster development of different rock groups in the study area
Ⅰ.loose soil Ⅱ.stratified clastic rock group Ⅲ. stratified rock group of clastic rocks interbedded with carbonate rocks Ⅳ.stratified and moderately karstified rock group of carbonate rocks interbedded with clastic rocks V.stratified and strongly karstified carbonate rock group Ⅵ.stratified carbonate clastic rock group with alternating hard and soft layers Ⅶ.stratified hard metamorphic rock group weathered moderately Ⅷ.massive hard intrusive rock group weathered weakly Ⅸ.hard and moderately weathered extrusive rock group in the form of fragmentation
表 1 研究区不同地貌区地质灾害分布特征统计表
Table 1. Statistics of distribution characteristics of geological disasters in different landforms of the study area
分区及代号 面积/km2 灾害类型及数量/个 占灾害总数
/%灾害密度
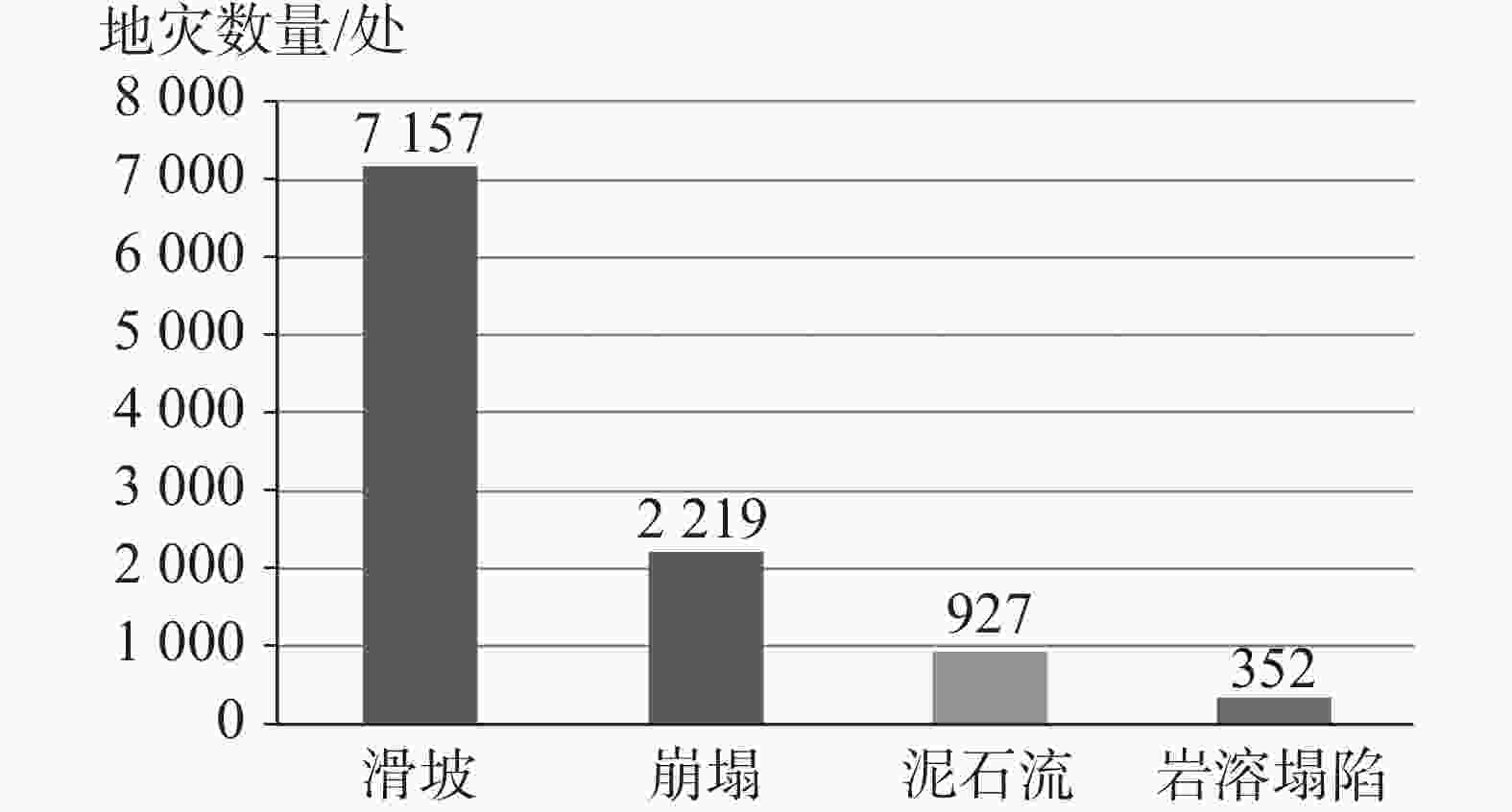
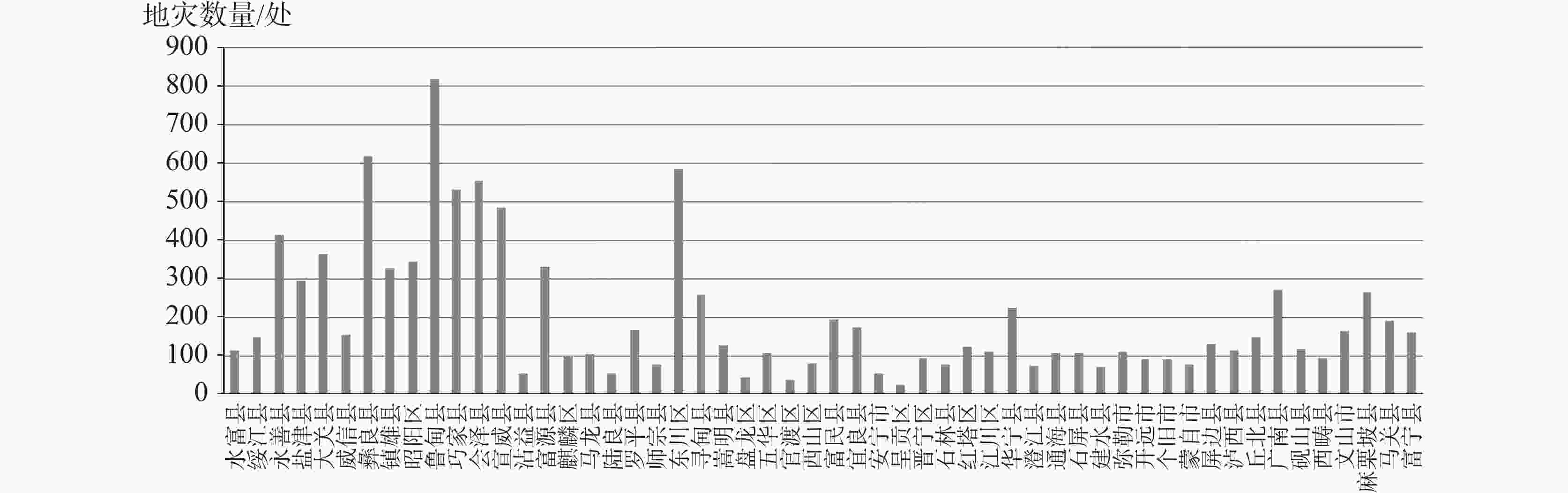
/个·km−2滑坡 崩塌 泥石流 岩溶塌陷 小计 构造溶蚀高山峡谷地貌区 3 581 356 214 237 0 807 7.57 0.23 构造侵蚀低中山地貌区 6 813 932 98 59 0 1 089 10.22 0.16 构造溶蚀高中山地貌区 15 937 1 894 841 287 139 3 161 29.67 0.2 构造剥蚀高中山地貌区 9 766 1 368 553 149 0 2 070 19.43 0.21 构造溶蚀低中山地貌区 9 275 984 379 54 98 1 515 14.22 0.16 构造溶蚀峰丛洼地地貌区 66 349 1 577 134 141 74 1 926 18.08 0.03 高原盆地地貌区 12 737 46 0 0 41 87 0.82 0.01 合计 124 458 7 157 2 219 927 352 10 655 100 0.09 表 2 研究区不同斜坡结构类型地质灾害数量对比表
Table 2. Comparison of quantity of geological disasters in different types of slope structures in the study area
斜坡结构类型 滑坡 崩塌 合计 数量 百分比 数量 百分比 数量 百分比 横向斜坡 845 11.81 78 3.52 923 9.84 顺向斜坡 1 638 22.89 1 357 61.15 2995 31.94 正交斜坡 847 11.83 54 2.43 901 9.61 斜交斜坡 2 264 31.63 689 31.05 2953 31.50 逆向斜坡 1 563 21.84 41 1.85 1604 17.11 合计 7 157 100.00 2 219 100.00 9376 100.00 -
[1] 段乔文, 俞富有, 张天柏, 何 伟, 段春林. 滇东高原罗平湾子水库岩溶渗漏机理及库外补漏设想[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(2):287-297. doi: 10.11932/karst20220209DUAN Qiaowen, YU Fuyou, ZHANG Tianbai, HE Wei, DUAN Chunlin. Karst leakage and its sealing at Wanzi reservoir in Luoping county on the plateau of eastern Yunnan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(2): 287-297. doi: 10.11932/karst20220209 [2] 王虎, 冉勇康, 李彦宝, 陈立春. 川西地区安宁河断层古地震行为及其与则木河断层的比较[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3):706-717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.013WANG Hu, RAN Yongkang, LI Yanbao, CHEN Lichun. Paleoseismic behavior of the Anninghe fault and its comparison with the Zemuhe fault in western Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(3): 706-717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.013 [3] 王宇, 黄兴章, 谭继中. 云南省岩溶水有效开发利用规划建议报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质矿产厅、云南省计划委员会,1997. [4] 王宇, 张贵, 柴金龙, 王波, 何绕生, 彭淑惠, 康晓波, 周翠琼. 云南岩溶石山地区重大环境地质问题及对策[M]. 昆明:云南科技出版社,2013:17-27.WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, CHAI Jinlong, WANG Bo, HE Raosheng, PENG Shuhui, KANG Xiaobo, ZHOU Cuiqiong. The serious environmental geoligical problems and countermeasures in karst area of Yunnan Province[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2013: 17-27. [5] 王宇, 张贵, 何绕生. 云南岩溶石山地区地下水资源勘查与生态环境地质调查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质调查院, 2002. [6] 张超, 陈艳, 张宇飞, 孙秀娟. 基于多元线性回归模型的云南昭通地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2016, 43(3):159-163.ZHANG Chao, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Yufei, SUN Xiujuan. Geohazard susceptibility evaluation in Zhaotong of Yunnan based on the multivariate linear regression model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(3): 159-163. [7] 张杰, 黄成, 晏祥省, 王裕琴. 云南“9 · 07”地震彝良水泥厂危岩体破坏模式分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2013, 24(Suppl.1):129-132. [8] 张华, 康晓波, 王波, 柴金龙, 周翠琼, 蔡双乐, 侯旭涛, 黄晨晖, 潘晓东. 滇东南高原斜坡区某拟建铁路岩溶水文地质问题及对策建议[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(5):718-727. doi: 10.11932/karst20220506ZHANG Hua, KANG Xiaobo, WANG Bo, CHAI Jinlong, ZHOU Cuiqiong, CAI Shuangle, HOU Xutao, HUANG Chenhui, PAN Xiaodong. Karst hydrogeological problems and countermeasures of a proposed railway in plateau slope area of southeast Yunnan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(5): 718-727. doi: 10.11932/karst20220506 [9] 邓国仕, 岑鑫雨, 唐业旗, 钟金先. 乌蒙山以礼河流域岩溶地下水富集特征及供水意义研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4):685-698. doi: 10.11932/karst20230405DENG Guoshi, CEN Xinyu, TANG Yeqi, ZHONG Jinxian. Study on the enrichment characteristics and water supply significance of karst groundwater in the Yili river basin, Wumeng mountain area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 685-698. doi: 10.11932/karst20230405 [10] 裴向军, 黄润秋. “4·20”芦山地震地质灾害特征分析[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(3):257-262.PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu. Analysis of characteristics of geological harzards by "4·20" Lushan earthquake in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(3): 257-262. [11] 殷志强, 赵无忌, 褚宏亮, 孙伟. “4·20”芦山地震诱发地质灾害基本特征及与“5·12”汶川地震对比分析[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(6):1145-1156.YIN Zhiqiang, ZHAO Wuji, CHU Hongliang, SUN Wei. Basic characteristics of geohazards induced by Lushan earthquake and compare to them of Wenchuan eathquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(6): 1145-1156. [12] 罗一鸣, 成建梅, 徐文杰, 巴净慧, 黄盛财, 段天宇. 西南岩溶区深埋隧洞涌水条件分析及涌水量预测:以滇中引水工程大坡子隧洞为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(6):1224-1236. doi: 10.11932/karst20230608LUO Yiming, CHENG Jianmei, XU Wenjie, BA Jinghui, HUANG Shengcai, DUAN Tianyu. Analysis of water inflow conditions and prediction for water inflow of deep-buried tunnels in the karst area of Southwest China: Taking Dapozi tunnel of central Yunnan Water Diversion Project as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(6): 1224-1236. doi: 10.11932/karst20230608 [13] 张杰, 王宇, 张红兵, 朱春林, 李俊东, 晏祥省. 云南彝良9·07地震次生地质灾害特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(2):280-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.019ZHANG Jie, WANG Yu, ZHANG Hongbing, ZHU Chunlin, LI Jundong, YAN Xiangsheng. Characteristics of secondary geological hazards induced by Yiliang 9·07 earthquakes in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(2): 280-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.019 [14] 黄润秋, 李为乐. 汶川大地震触发地质灾害的断层效应分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1):19-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.003HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Fault effect analysis of geo-hazard triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1): 19-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.003 [15] Abrahamson N A, Somerville P G. Effects of the hanging wall and footwall on ground motions recorded during the Northridge earthquake[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1996, 86(1B): S93-S99. doi: 10.1785/BSSA08601B0S93 [16] 俞言祥, 高孟潭. 台湾集集地震长地震动的上盘效应[J]. 地震学报, 2001, 23(6):615-621.YU Yanxiang, GAO Mengtan. Effects of the hanging wall and footwall on peak acceleration during the Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2001, 23(6): 615-621. [17] 黄润秋, 李为乐. “5.12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[C]//汶川大地震工程震害调查分析与研究. 成都理工大学地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室, 2009:159-167. [18] 刘春玲, 祁生文, 童立强, 安国英, 李小慧. 喜马拉雅山地区重大滑坡灾害及其与地层岩性的关系研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(5):669-676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.010LIU Chunling, QI Shengwen, TONG Liqiang, AN Guoying, LI Xiaohui. Great landslides in Himalaya Mountain area and their occurrence with lithology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(5): 669-676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.010 [19] 李成芳, 王忠诚, 李振炜, 徐宪立. 西南喀斯特区土壤侵蚀研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(6):962-974. doi: 10.11932/karst20220608LI Chengfang, WANG Zhongcheng, LI Zhenwei, XU Xianli. Research progress of soil erosion in karst areas of Southwest China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(6): 962-974. doi: 10.11932/karst20220608 -




 下载:
下载: