Formation and evolution of the karst pastoral landscape in Puzhehei
-
摘要: 文章根据大量的地质遗迹从地球系统科学的角度讨论了普者黑岩溶山水田园生态景观的形成过程,认为其经历了数亿年缓慢发展演化,泥盆纪到三叠纪末是研究区岩石圈形成时期,侏罗纪至白垩纪是研究区构造和地形基础形成时期。古近纪至今,喜玛拉雅运动继承和发展了原有构造和地形,为地表水、地下水的发育提供了地形条件,为岩溶的发育提供了运移空间,并推动了研究区气候条件的演变;气候演变为岩溶的发育提供了水、温度等有利的外部环境条件,并控制了生物圈演化;生物圈的演化助推了研究区岩溶发育进程,并在人类活动影响和改造下最终形成了今天普者黑岩溶山水田园生态景观。本文根据其演化过程初步预测了山水田园景观和湖泊水质的变化趋势,并提出了保护建议:一是开展资源承载力调查,规范旅游管控;二是加强基础设施建设,完善排污系统;三是建立科学监测体系,定期跟踪监测;四是提升科普宣传力度,增强环保意识。Abstract:
Traditional karstology examines karst geomorphic landscapes as geological processes occurring at the interface of lithosphere and hydrosphere. It concludes with a discussion on how factors such as structure, stratigraphy, hydrology, climatic conditions and neotectonic movements influence karst development. The emergence of theories in Earth system science has opened up new avenues for the advancement of karstology. Based on a substantial collection of geological relics, this study examines the formation process of the karst ecological pastoral landscape in Puzhehei from the perspective of Earth system science. It is posited that this evolution occurred gradually over hundreds of millions of years. From the Devonian period to the end of the Triassic period, a set of strata dominated by carbonate rocks with shallow marine and platform facies were deposited, which established a favorable lithospheric foundation for the karst development in the study area. The Indosinian movement and Yanshan movement from the Jurassic to the Cretaceous laid an important structural and topographic foundation for the study area. The period from the Paleogene to the present marks the formation of the karst ecological pastoral landscape in Puzhehei, which can be further divided into four stages. In the first act of the Himalayan movement, the northwest fault of the study area was reactivated, forming a topography characterized by high elevations in the south and low elevations in the north, as well as high terrain on the eastern and western sides and a low area in the center. This represents the initial stage of karst development. In the second act of the Himalayan movement, the northern plate of the Yangqi fault rose, creating a low-lying center around Luoshuidong lake. This led to the formation of fault depression lake basin in Puzhehei, marking an important stage in karst development. In the third act of the Himalayan movement, the uplift of the northern panel of the Yangqi fault intensified, leading to the gradual disappearance of surface water outlets. Consequently, the lake surface rapidly expanded southward, reaching the vicinity of Qiubei county. During this process, triangular fault basins were fully formed, and karst was further developed. Since the Late Pleistocene, the uplift of the crust and the headward erosion of the Beimen river have created a new water outlet in the surrounding area. Consequently, the lake water rapidly drained, resulting in the formation of a karst landscape. Since the Holocene, under the influence and transformation of human activities, today's pastoral landscape has come into being. According to the evolutionary process, this study preliminarily predicts the changing trends of landscape and lake water quality, and proposes several protective suggestions. First, conducting a survey on resource carrying capacity and standardizing tourism management. Second, strengthening infrastructure development and improving the sewage system. Third, establishing a scientific monitoring system for regular tracking and monitoring. Fourth, enhancing public awareness of environmental protection through effective science communication. -
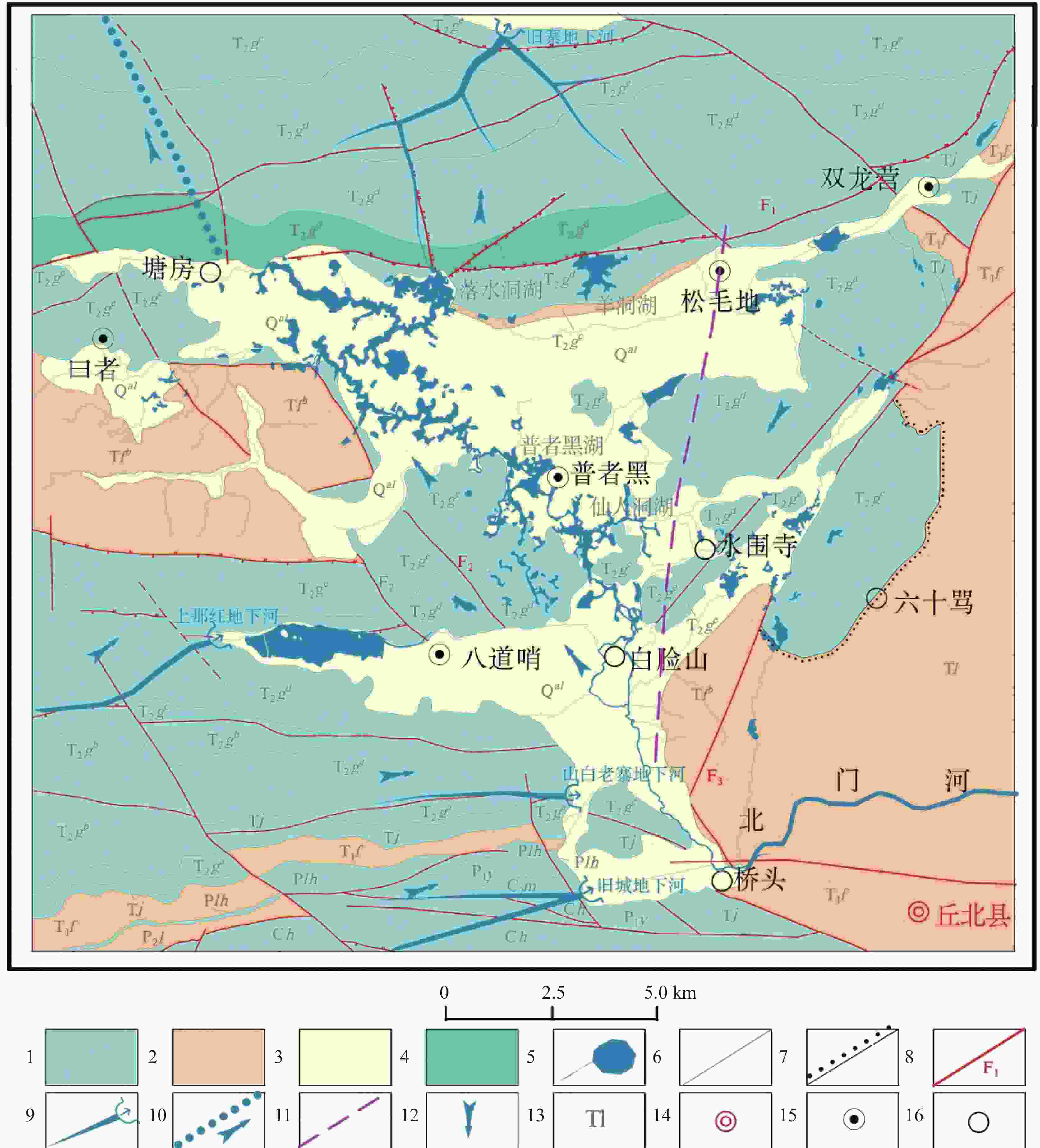
图 3 普者黑盆地水文地质图
1.岩溶含水层 2.裂隙含水层 3.孔隙含水层 4.碎裂状白云岩 5.水系湖泊湿地 6.地层界线 7.相变界线 8.断层及编号 9.地下河管道及出口 10.盆地原地表水系出流位置及流向 11.湖群分界线 12.地下水流向 13.地层代号 14.县城驻地 15.乡镇驻地 16.村驻地
Figure 3. Hydrogeological map of the Puzhehei basin
1. karst aquifer; 2. fractured aquifer; 3. pore aquifer; 4. cataclastic dolomite; 5. drainage lake wetland; 6. stratigraphic boundary; 7. phase change boundary; 8. faults and numbering; 9. pipeline and outlet of the underground river; 10. outflow location and direction of the original surface water system in the basin; 11. boundary lines of lake group; 12. direction of groundwater flow; 13. stratigraphic code; 14. county site; 15. township site; 16. village site
表 1 普者黑峰林展布特征一览表
Table 1. Distribution characteristics of peak forest in Puzhehei
展布
方向平均直
径/m高度/m 直径/
高度比例(%,
总个数28)北东 695.75 162.50 4.28 35.7 东西 460.50 121.28 4.05 32.2 北西 605.42 153.70 4.54 21.4 南北 423.33 109.31 4.58 10.7 表 2 普者黑盆地地层岩性简表
Table 2. Stratigraphic lithology in the Puzhehei basin

-
[1] 王宇, 李燕, 谭继中, 张贵, 何绕生. 断陷盆地岩溶水赋存规律[M]. 昆明:云南科技出版社, 2003. [2] 马铭嘉, 张兵, 赵晶晶. 丘北普者黑岩溶地貌景观特征[J]. 四川地质学报, 2010, 30(3):312-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2010.03.016MA Mingjia, ZHANG Bing, ZHAO Jingjing. Karst landscape in Puzhehei, Qiubei, Yunnan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2010, 30(3): 312-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2010.03.016 [3] 毛转梅, 刘青, 彭尔瑞, 陈劲松, 吴培军. 云南普者黑湿地流域水域面积变化及其影响因素[J]. 江西农业学报, 2021, 33(5):109-114.MAO Zhuanmei, LIU Qing, PENG Errui, CHEN Jinsong, WU Peijun. Dynamic changes of water area in Yunnan Puzhehei wetland river basin and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2021, 33(5): 109-114. [4] 张金凤. 旅游活动对普者黑景区水环境的影响分析[J]. 唐山学院学报, 2011, 24(3):37-39.ZHANG Jinfeng. Study on the influence of tourist activities on water environment of Puzhehei scenic spot[J]. Journal of Tangshan College, 2011, 24 (3): 37-39. [5] 张锐敏. 普者黑湖水质现状评价及富营养化变化趋势分析[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2022, 41(1):63-65, 84.ZHANG Ruimin. Water quality evaluation and eutrophication trend analysis of Puzhehei lake[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2022, 41 (1): 63-65, 84. [6] 张兵, 马铭嘉. 云南普者黑岩溶地貌特征及形成研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(理工版), 2010, 35(5):1-6.ZHANG Bing, MA Mingjia. A study on the characteristics and evolution of the Puzhehei karst, Yunnan[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Science and Technology), 2010, 35(5): 1-6. [7] 马铭嘉, 张兵, 赵晶晶. 云南普者黑成景水文地质条件及岩溶特征[J]. 云南地质, 2010, 29(1):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2010.01.017MA Mingjia, ZHANG Bing, ZHAO Jingjing. The Puzhehei karst characteristics and scenery-forming hydrogeologic condition, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2010, 29(1): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2010.01.017 [8] 袁道先, 朱德浩, 翁金桃, 等. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1994. [9] 张华, 王波, 高瑜, 康晓莉, 王宇, 刘绍华, 康晓波, 罗为群, 赵勇. 岩溶断陷盆地湿地成因类型及水流系统特征研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4):672-684. doi: 10.11932/karst20230404ZHANG Hua, WANG Bo, GAO Yu, KANG Xiaoli, WANG Yu, LIU Shaohua, KANG Xiaobo, LUO Weiqun, ZHAO Yong. Research on genetic types and flow system characteristics of wetland in karst fault basin, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 672-684. doi: 10.11932/karst20230404 [10] 袁道先. 碳循环与全球岩溶[J]. 第四纪研究, 1993(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001YUAN Daoxian. Carbon cycle and global karst[J]. Quaternary Research, 1993(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001 [11] 魏泽昳, 李向东. 云南省昭通市昭阳区地质遗迹分布特征及成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(1):188-200. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y038WEI Zeyi, LI Xiangdong. Distribution characteristics and genesis analysis of geological relics in Zhaoyang district, Zhaotong City, Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(1): 188-200. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y038 [12] 任世川, 杨颖彬, 李文丛, 宋子德, 刘海峰. 云南重点岩溶流域(北门河流域)水文地质环境地质调查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质环境监测院, 2014. [13] 王宇, 张华, 张贵, 王波, 彭淑惠, 何绕生, 周翠琼. 喀斯特断陷盆地环境地质分区及功能[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3):283-295. doi: 10.11932/karst20170316WANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, ZHANG Gui, WANG Bo, PENG Shuhui, HE Raosheng, ZHOU Cuiqiong. Zoning of environmental geology and functions in karst fault-depression basins[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3): 283-295. doi: 10.11932/karst20170316 [14] 王宇, 王梓溦. 岩溶地下水富集的地貌组合形态[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4):314-324.WANG Yu, WANG Ziwei. Patterns of karst geomorphologic combinations in areas with rich groundwater[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 314-324. [15] 赵祥华, 王志芸. 普者黑湖滨带恢复与管理对策[J]. 云南环境科学, 2005, 24(Suppl.1):82-85.ZHAO Xianghua, WANG Zhiyun. Management countermeasures and recovery of lakeside areas in Puzhehei lake[J]. Yunnan Environmental Science, 2005, 24(Suppl.1): 82-85. [16] 云南省丘北县地方志编篡委员会. 丘北县志[M]. 北京:中华书局, 1999. [17] 刘鹏, 张紫霞, 王研, 刘云根. 普者黑流域土地利用及“源―汇”景观的氮磷输出响应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(6):1332-1341.LIU Peng, ZHANG Zixia, WANG Yan, LIU Yungen. Effect of land use and the source–sink landscape on nitrogen and phosphorus export in the Puzhehei watershed[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(6): 1332-1341. [18] 沈其韩, 耿元生, 刘国惠, 高吉凤. 中国地层典[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1996. [19] 云南省地质矿产局. 云南省岩石地层[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996. [20] 毛志芳. 滇东南丘北地区晚二叠世吴家坪早期岩相古地理研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学, 2012. [21] 云南省地质局水文工程地质公司. 丘北幅区域水文地质普查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质局, 1981. [22] 云南省地质局地质调查大队. 丘北幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质局, 1980. [23] 云南省地质矿产局. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1990. [24] 赵锡文. 古气候学概论[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1992. [25] 黄晓园, 区智, 彭建松, 王松菘, 张卓亚. 普者黑省级自然保护区土地利用及景观格局变化研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 2019, 48(4):27-32, 38.HUANG Xiaoyuan, QU Zhi, PENG Jiansong, WANG Songsong, ZHANG Zhuoya. Land use and landscape patterns dynamics of Puzhehei provincial nature reserve in Yunnan[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2019, 48(4): 27-32, 38. [26] 何娴娴, 杨智谋, 赵宇鸾, 张蒙. 基于典型村落的山―坝系统土地利用演化时空分异特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(2):326-335. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y006HE Xianxian, YANG Zhimou, ZHAO Yuluan, ZHANG Meng. Spatial-temporal pattern of land use evolution in mountain–basin systems based on three typical villages[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(2): 326-335. doi: 10.11932/karst2024y006 -




 下载:
下载: