Genetic models and influence factors of karst collapses in Loudi City of central Hunan, China
-
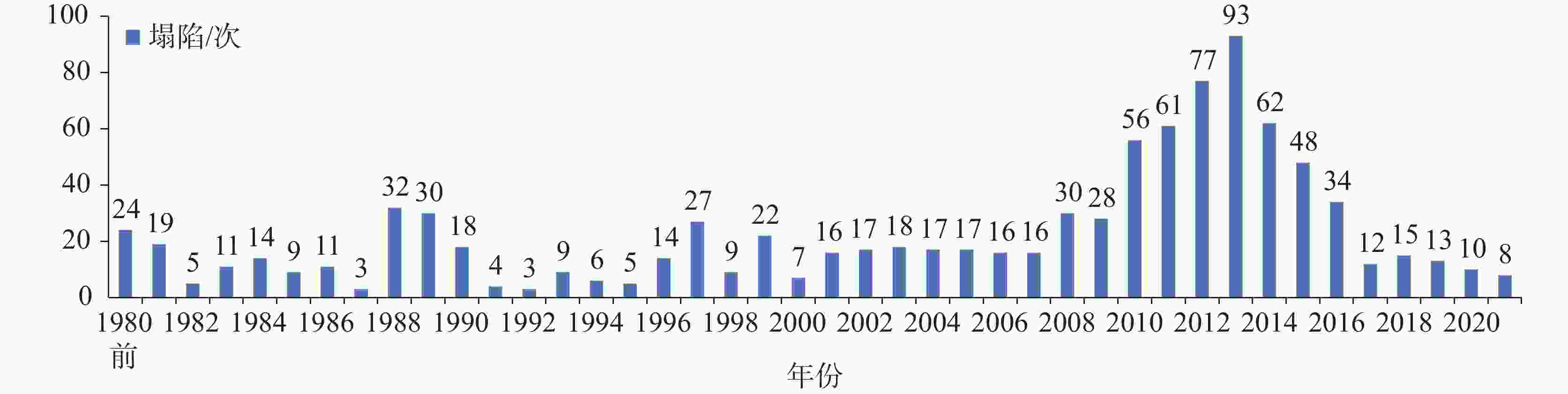
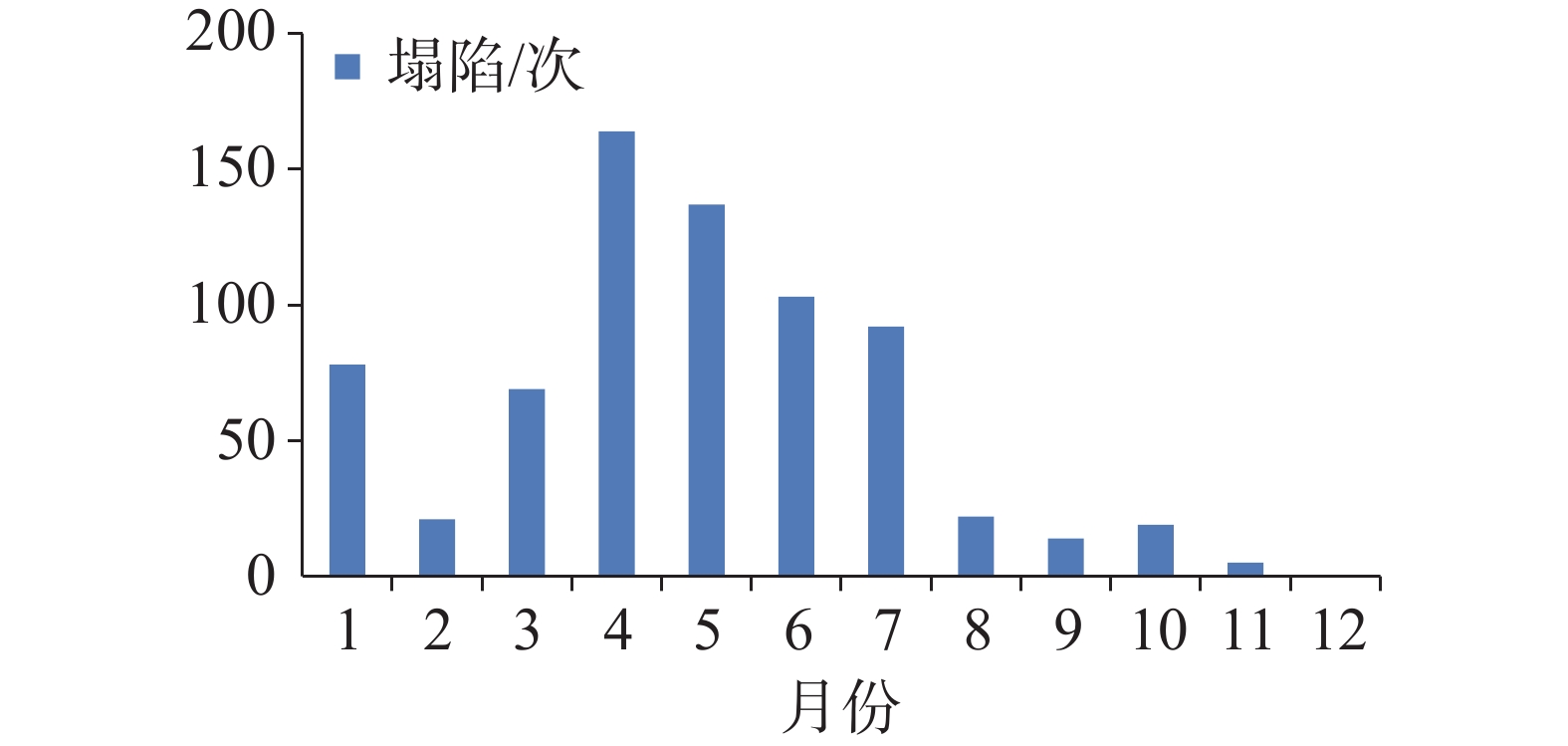
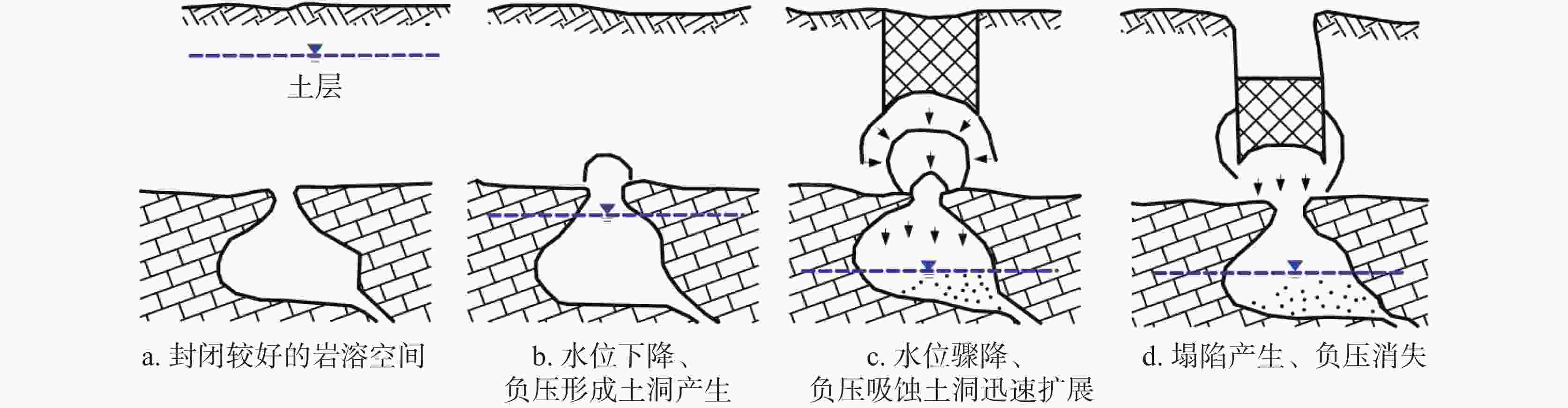
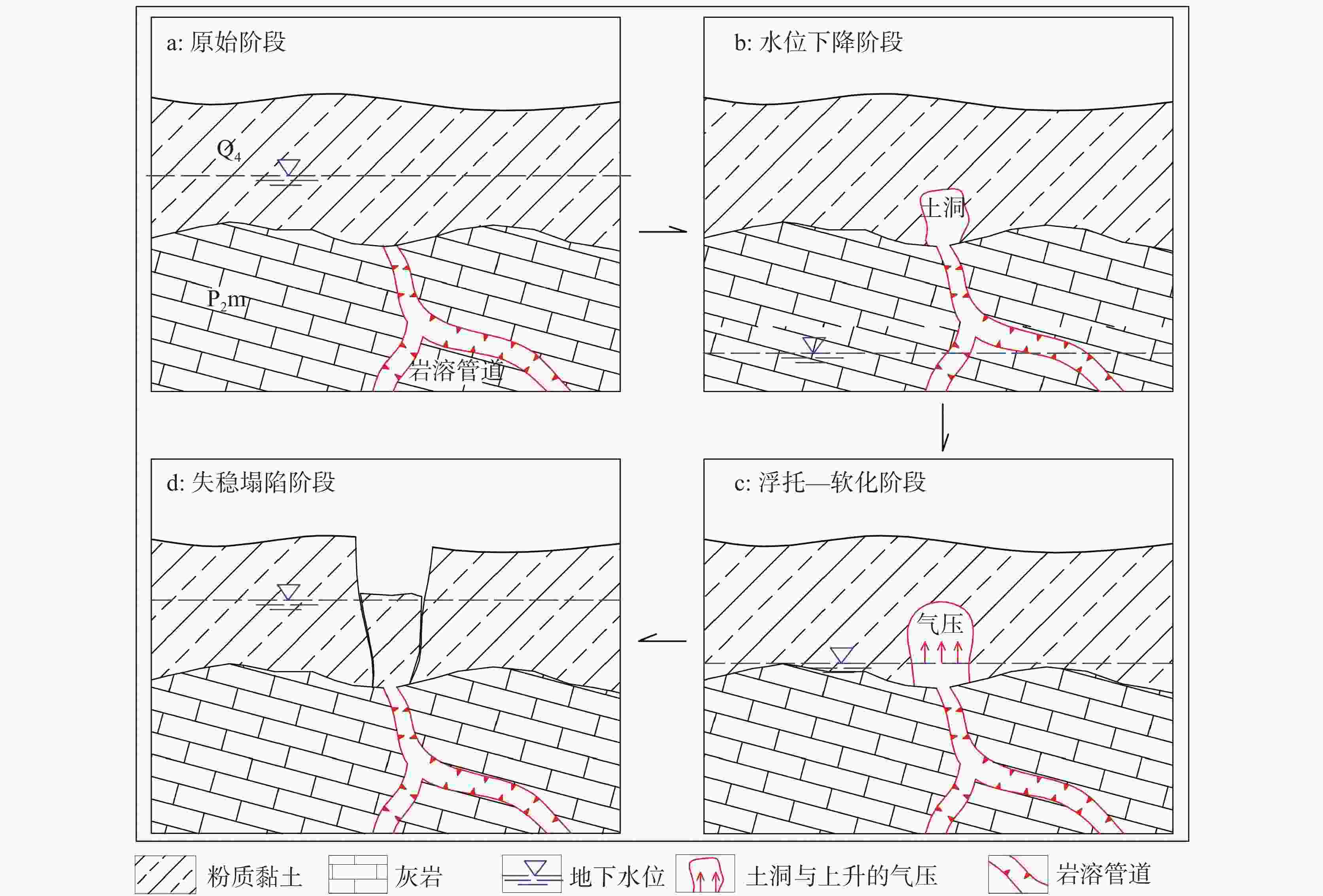
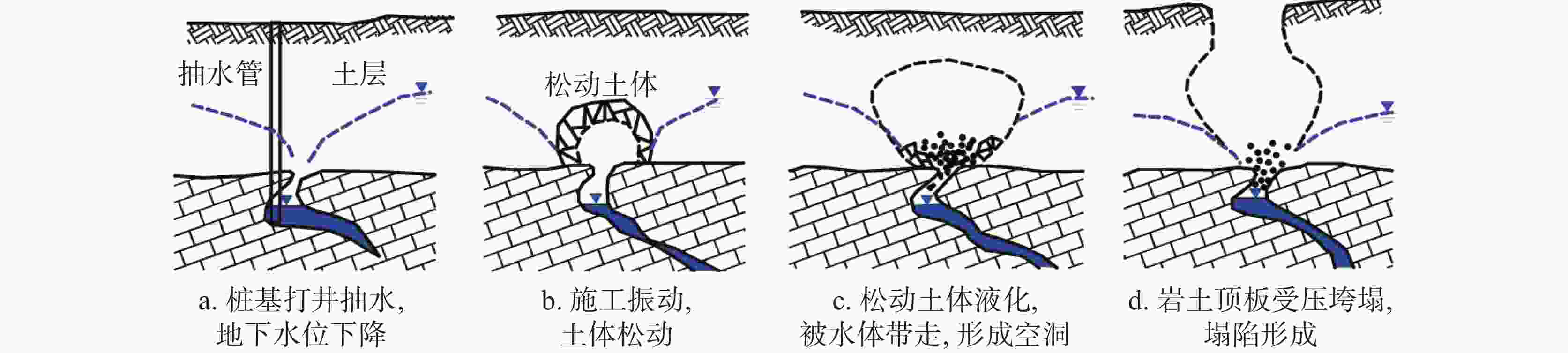
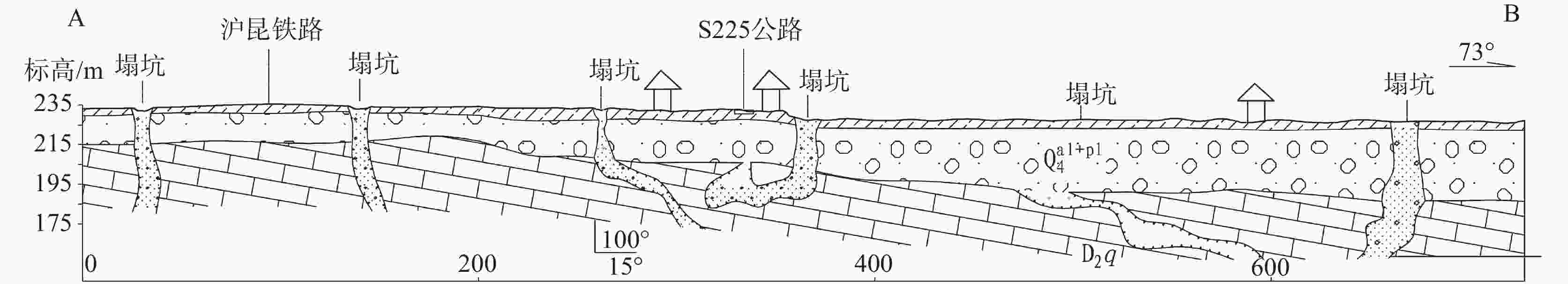
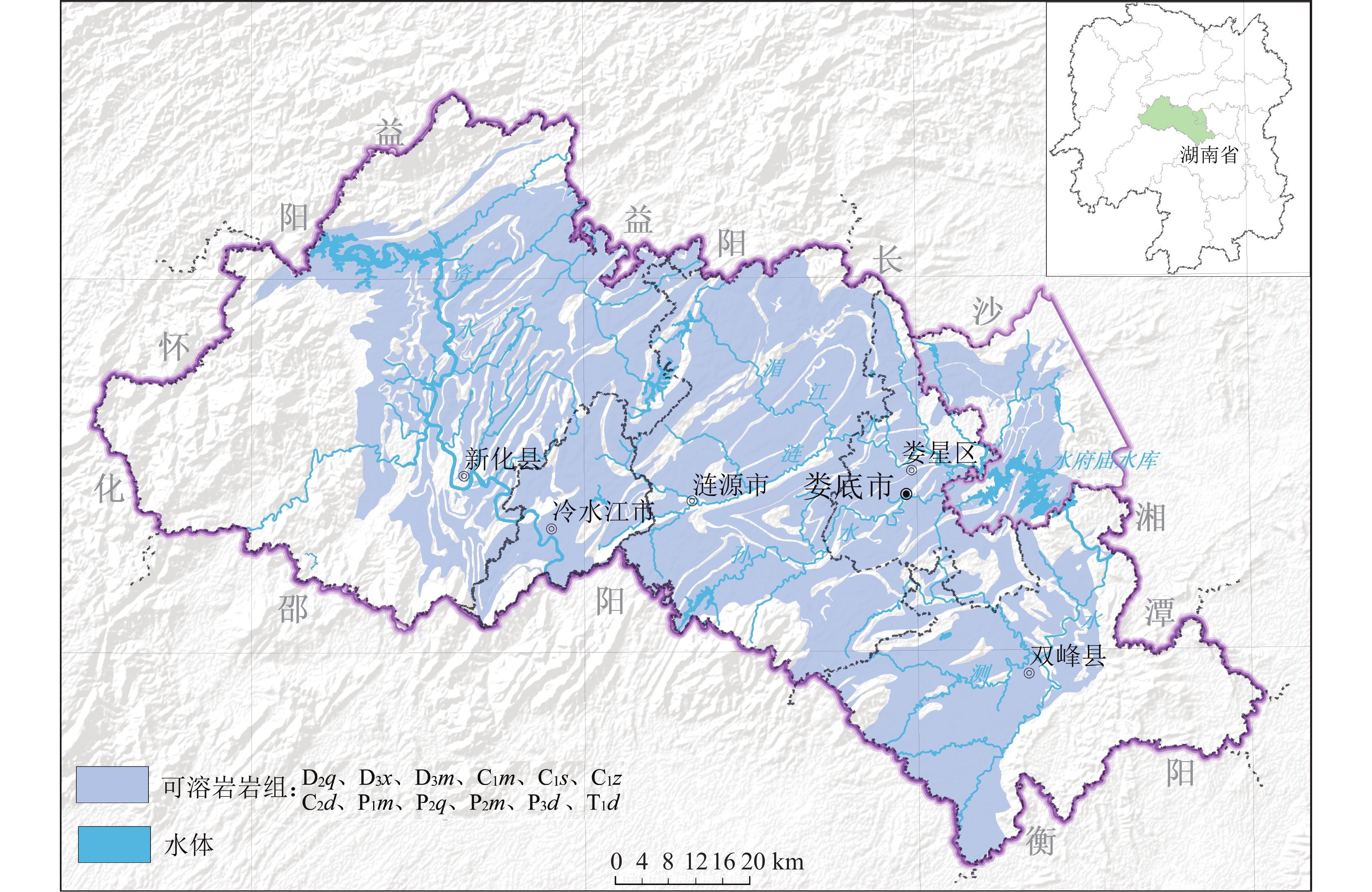
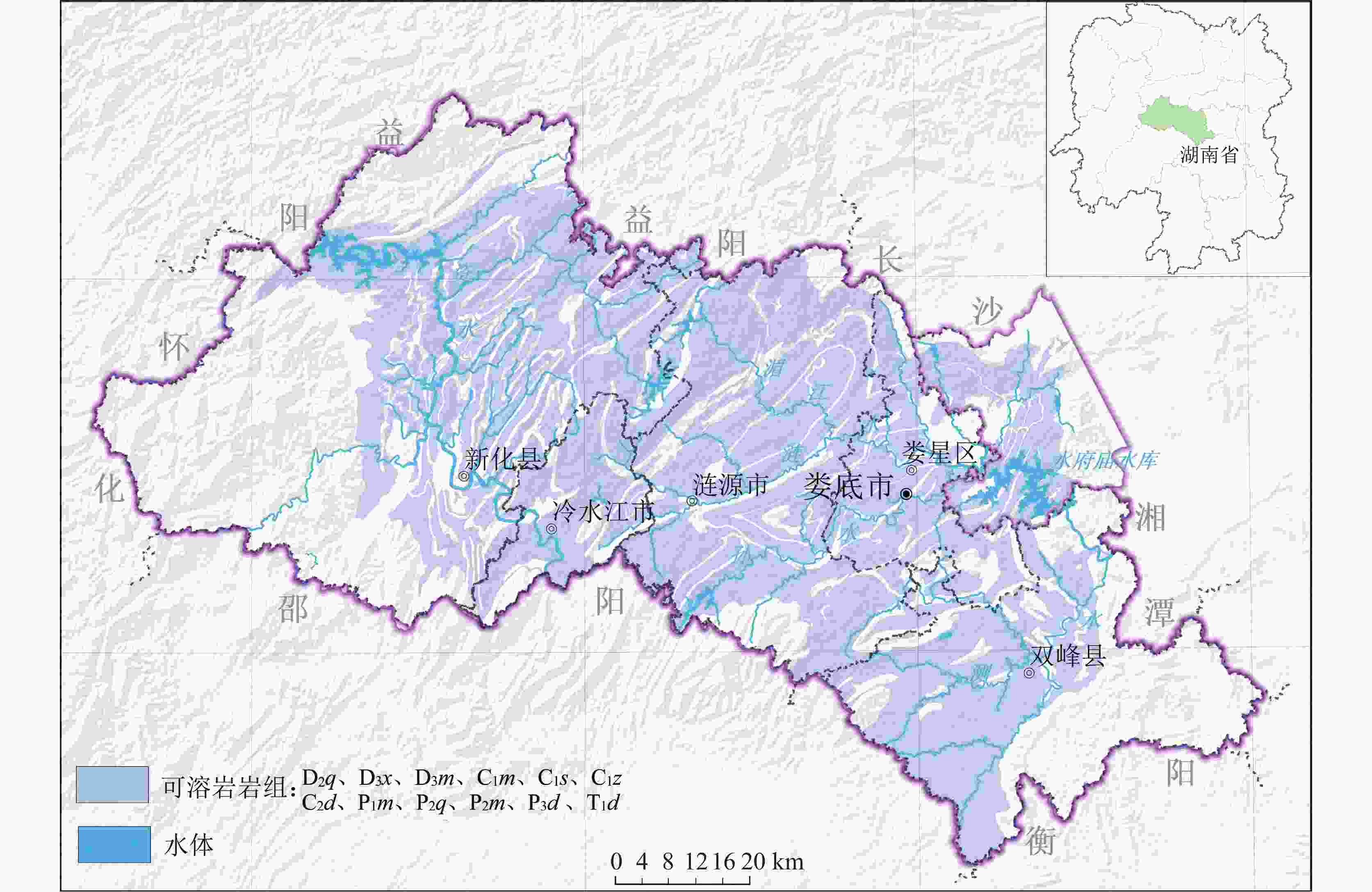
摘要: 湘中娄底市记录有281起岩溶塌陷事件以及上万个塌陷坑,是我国岩溶塌陷非常严重的城市之一。所有岩溶塌陷中,矿区岩溶塌陷有222起,占总数的79%,此外,还有地基工程造成的岩溶塌陷和降雨渗透潜蚀造成的岩溶塌陷。由此总结出娄底市具有真空吸蚀、浮托软化、荷载振动、渗透潜蚀4种岩溶塌陷发生模式,各模式均有4个致塌过程。其中,真空吸蚀塌陷和浮托软化塌陷主要为矿山活动所致,分别因矿区抽排水和矿区闭坑后回水所诱发;荷载振动塌陷主要为桩基施工等荷载外动力作用诱发,渗透潜蚀塌陷多为强降雨诱发的自然塌陷。岩溶塌陷的影响因素包括基础因素和诱发因素两个方面,基础因素有地层岩性、岩溶地貌、岩溶水富水性、与矿区相关性等,构成岩溶塌陷易发区的关键影响因素;诱发因素主要有矿区抽排水、闭坑矿区回水、工程振动、降雨过程等,其强度影响岩溶塌陷发生的时间、区域范围和规模。娄底市岩溶塌陷频发、突发,建议构建岩溶塌陷监测预警系统,科学编制岩溶塌陷防治规划和灾害应急预案,强化岩溶塌陷风险管理,保持岩-土-洞-水-气间的动态平衡。Abstract:
Loudi City in central Hunan has recorded 281 karst collapse incidents and tens of thousands of collapse pits, which made it one of the cities in China experiencing the most serious karst collapses. Among all these karst collapses, 222 karst collapses occurred in mining areas, accounting for 79% of the total. In addition, some karst collapses were caused by foundation engineering or by rainfall infiltration and erosion. By sorting out the temporal and spatial relationship between karst collapse events, karst collapses and collapse pits, it is concluded that karst collapses in Loudi City can fall into four occurrence modes, namely, vacuum erosion, floating–softening, load vibration and seepage erosion, and each mode has four collapse processes. Among them, vacuum erosion collapses and floating–softening collapses are mainly caused by mining activities, which are induced by drainage from the mining area and backwater after the mine has been closed; load vibration collapses are mainly induced by external dynamic loads such as pile foundation construction; seepage erosion collapses are natural collapses mostly induced by heavy rainfall. The influencing factors of karst collapses include basic factors and inducing factors. The basic factors include stratum lithology, karst landform, karst water abundance, correlation with mining areas, etc., which constitute the key influencing factors in karst collapse-prone areas; the inducing factors mainly include drainage in mining areas, backwatering in closed mines, engineering vibration, rainfall, etc., and the intensities of these factors can affect the time, scope and scale of karst collapses. In order to strengthen the risk management of karst collapses, it is recommended to establish a monitoring and early warning system for karst collapses, and scientifically develop risk assessment, prevention and control plans and disaster emergency response plans for karst collapses. Besides, controlling the area, method and intensity of engineering construction, prohibiting or limiting the mining of coal, gypsum, groundwater, etc. in karst areas, and maintaining the dynamic balance between rock, soil, cave, water and air are effective measures to prevent and control karst collapses. In this paper, the distinction between the basic factors and inducing factors of karst collapses can provide a scientific basis for their effective prevention and control in karst areas, and can provide a reference for the construction of harmonious and beautiful villages. -
Key words:
- karst collapse /
- genetic model /
- influence factors /
- mining activity /
- Loudi City of central Hunan
-
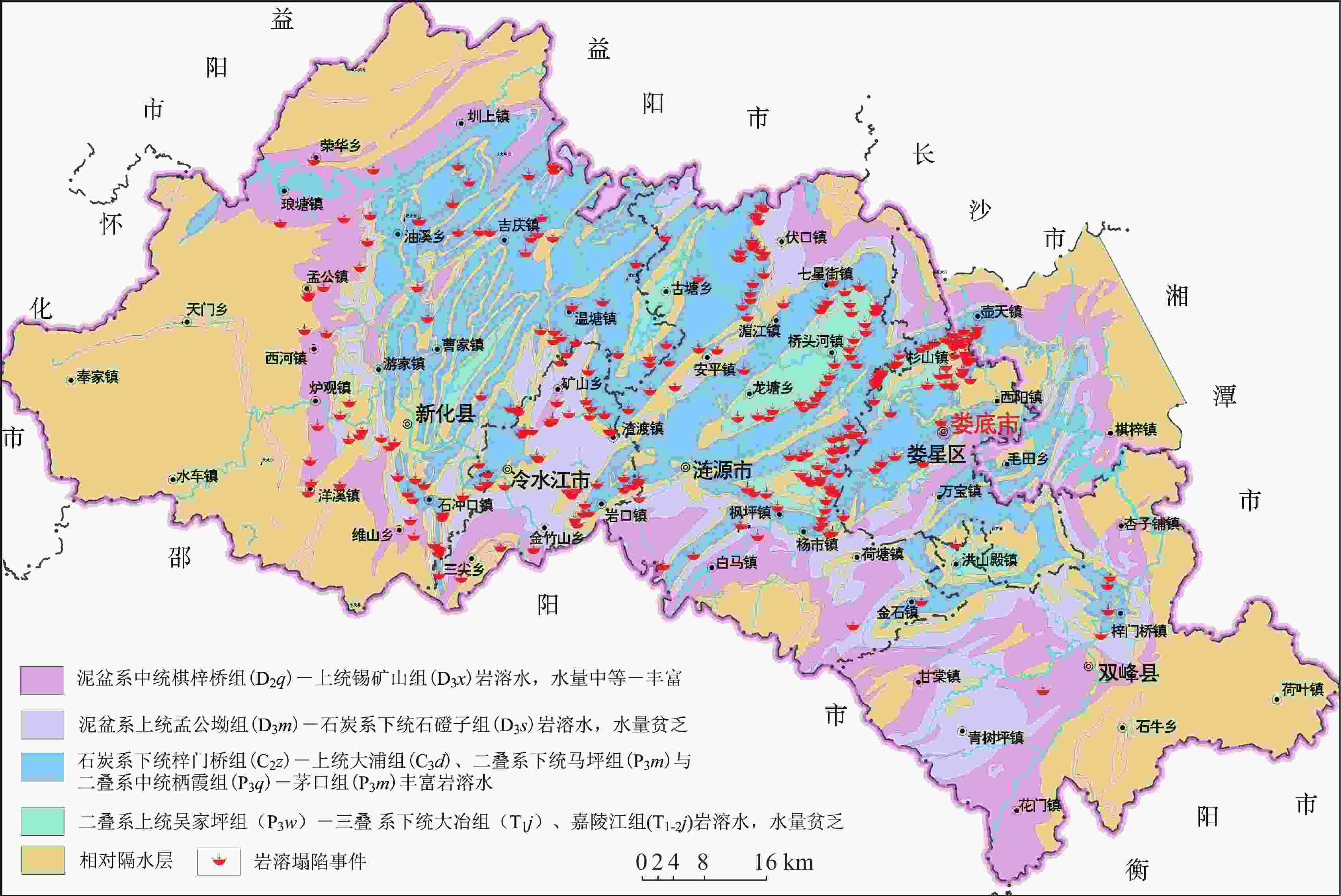
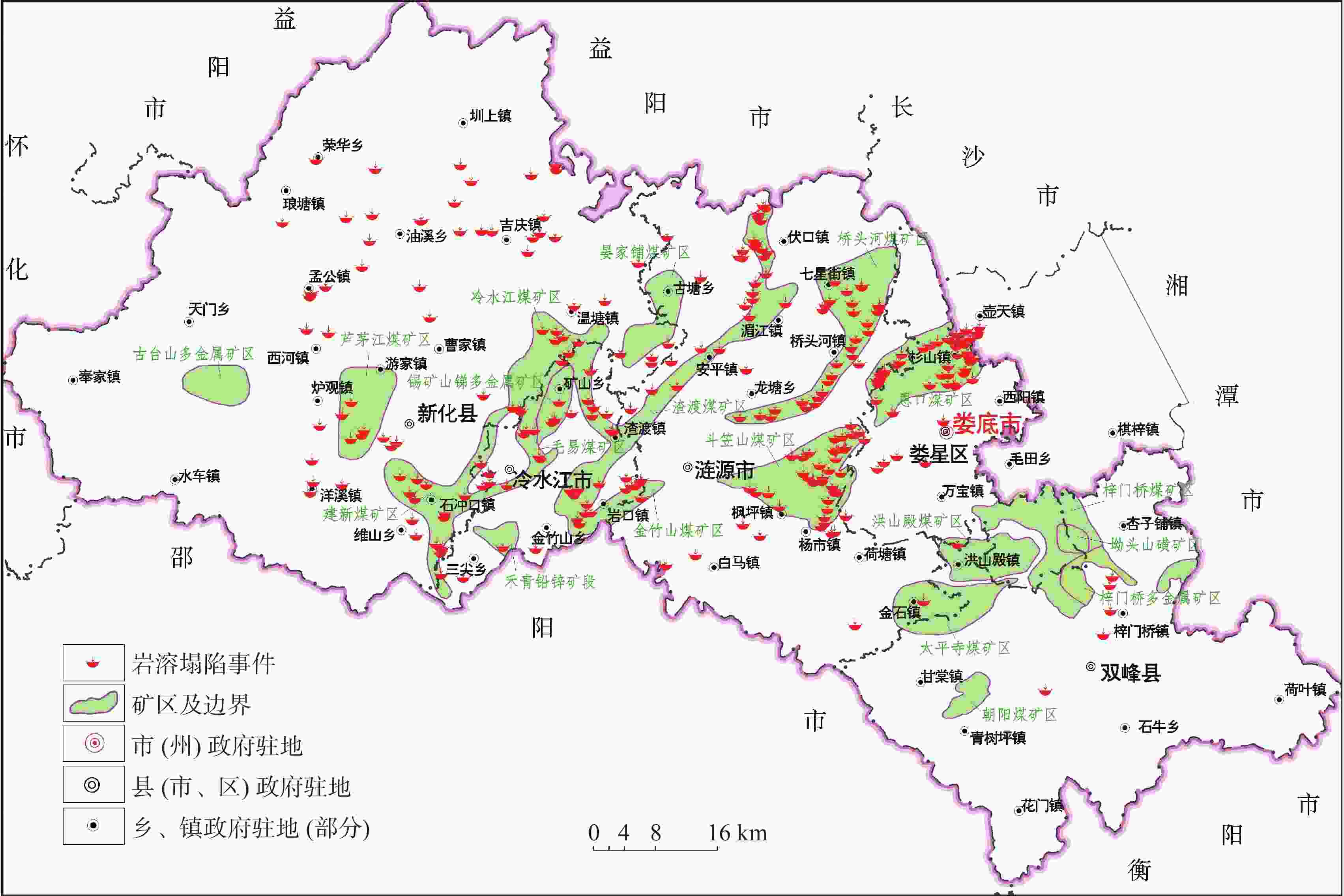
表 1 娄底各县市区岩溶塌陷情况统计
Table 1. Situation of karst collapses in each county of Loudi City
县市区 岩溶塌陷事件/起 百分比/% 面积/km2 面积密度/起/100 km2 娄星区 33 11.74 429 7.69 涟源市 121 43.06 1 912 6.33 冷水江市 40 14.23 439 9.11 新化县 75 26.69 3 620 2.07 双峰县 5 1.78 1 711 0.29 湘乡市壶天镇 7 2.49 144.7 4.84 合计 281 100 8 255.7 3.40 表 2 岩溶塌陷地层的特点及塌陷坑数量
Table 2. Features of karst collapse strata and numbers of collapse pits
发育地层 分布面积
/km2地层特点 岩溶塌陷坑 岩性 富水性 矿山面积
/km2数量/个 百分比 面积密度
/个/100 km2C2d 779.5 灰岩夹白云质灰岩 丰富 73.43 979 35.69 125.59 P2m 534.2 灰岩、生物屑灰岩 丰富 8.13 829 30.22 155.19 T1d 260.0 薄层状灰岩 贫乏 39.69 159 5.80 61.15 P1m 410.4 灰岩、白云质灰岩、白云岩 丰富 4.69 284 10.35 69.20 C1z 265.7 灰岩、泥灰岩、白云岩夹膏盐 中等丰富 6.08 247 9.00 92.96 P2q 176.7 生物屑灰岩 中等丰富 0 80 2.92 45.27 D3x 213.0 灰岩夹泥灰岩 中等丰富 7.34 38 1.39 17.84 D2q 320.9 灰岩夹白云质灰岩 丰富 0.12 71 2.59 22.13 K2d 154.1 砂岩、泥质砂岩,底部为灰质砾岩 贫乏 3.03 20 0.73 12.98 D3ql 158.8 灰岩、泥灰岩、砂岩、页岩互层 中等丰富 1.87 25 0.91 15.74 C1s 355.8 灰岩夹泥灰岩 中等丰富 8.51 4 0.15 1.12 C1m 251.3 灰岩 中等丰富 0 6 0.22 2.39 P3d 69.6 硅质灰岩夹硅质页岩 贫乏 1.30 1 0.04 1.44 合计 3 950 154.19 2 743 100 -
[1] 郭维君, 崔晓艳, 陈学军. 泗顶铅锌矿区岩溶塌陷成因及治理对策分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2009, 39(12):41-43.GUO Weijun, CUI Xiaoyan, CHEN Xuejun. Causes of karstic collapse in Lead-zinc mining area and its countermeasures[J]. Metal Mine, 2009, 39(12): 41-43. [2] Hosseini S T, Arefi S L, Bitarafan M, Abazarlou S, Zavadskas E K. Evaluation types of exterior walls to reconstruct Iran earthquake areas (Ahar Heris Varzeqan) by using AHP and fuzzy methods[J]. International Journal of Strategic Property Management, 2016, 20(3): 328-340. doi: 10.3846/1648715X.2016.1190794 [3] Liebermann J, Pelts E J, Matthews J M, Sanchez S R, Rapisarda J, Lederer K. Does artificial collpase of human day 6 blastocysts prior to the cooling steps of vitrification improve their probability of increased outcome?[J]. Fertility and Sterility, 2012, 98(3): S127. [4] 陈菊艳, 朱斌, 彭三曦, 单慧媚. 基于AHP 和 GIS 的矿区岩溶塌陷易发性评估:以贵州林歹岩溶矿区为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2021, 30(5): 226-236.CHEN Juyan, ZHU Bin, PENG Sanxi, SHAN Huimei. Assessment of susceptibility to karst collapse in mining area based on AHP and GIS: A case study in Lindai karst mining area in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(5): 226-236. [5] 项式均, 康彦仁, 刘志云, 谢代兴, 陈健, 阎志为. 长江流域的岩溶塌陷[J]. 中国岩溶, 1986, 5(4):255-272.XIANG Shijun, KANG Yanren, LIU Zhiyun, XIE Daixing, CHEN Jian, YAN Zhiwei. Karst collapse in Yangtze River Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1986, 5(4): 255-272. [6] 康彦仁. 试论岩溶地面塌陷的类型划分[J]. 中国岩溶, 1984, 3(2):146-155.KANG Yanren. Classification of land collapses in karst regions[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1984, 3(2): 146-155. [7] 张丽芬, 曾夏生, 姚运生, 廖武林. 我国岩溶塌陷研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2007, 18(3):126-130.ZHANG Lifen, ZENG Xiasheng, YAO Yunsheng, LIAO Wulin. Review on karst collapse in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2007, 18(3): 126-130. [8] 张宝柱, 陈振东. 矿山岩溶塌陷形成机理及综合治理[J]. 中国地质, 1997(3):27-29. [9] 谭克龙, 周春光. 湘中恩口—斗笠山矿区岩溶塌陷研究[J]. 西安矿业学院学报, 1996, 16(2):130-134.TAN Kelong, ZHOU Chunguang. Research on karst collapse in Enkou-Doulishan mine district of middle Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Xi'an of Mining Institute, 1996, 16(2): 130-134. [10] 戴长华, 何卫平, 邱猛. 湖南省娄底市矿山地质环境调查评价报告[R]. 湖南省地质环境监测总站, 2008. [11] 石益盛. 恩口煤矿区及周边地区地质环境调查报告[R]. 湖南省地勘局四一八队, 1998. [12] 贾龙, 吴远斌, 潘宗源, 殷仁朝, 蒙彦, 管振德. 我国红层岩溶与红层岩溶塌陷刍议[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(1):67-73. doi: 10.11932/karst20160110JIA Long, WU Yuanbin, PAN Zongyuan, YIN Renchao, MENG Yan, GUAN Zhende. A review of the research on karst and sinkhole of red beds in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(1): 67-73. doi: 10.11932/karst20160110 [13] 陈朝贵. 隐伏岩溶区地面塌陷机理分析与建筑物地基基础处理[J]. 中国岩溶, 1988, 7(4):349-355.CHEN Chaogui. The analysis of the mechanism of the surface collapse in regions of concealed karst and case studies of the foundation treatment for buildings[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1988, 7(4): 349-355. [14] 徐红星. 浅谈隧道施工释能降压法对环境的影响[J]. 铁道勘察, 2013, 39(2):27-30.XU Hongxing. Brief talk of the impact of tunnel construction energy-releasing voltage drop method on environment[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 2013, 39(2): 27-30. [15] 史栾生, 陈敬德. 广花盆地地面塌陷成因与防治[J]. 中国岩溶, 1996, 15(3):278-283.SHI Luansheng, CHEN Jingde. Genesis and preventive measure of surface collapse in Guanghua basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1996, 15(3): 278-283. [16] 刘新建, 郭杰华, 陈英姿. 疏干排水矿区闭坑后岩溶塌陷形成机理探索:以湘中地区恩口煤矿为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(6):842-850.LIU Xinjian, GUO Jiehua, CHEN Yingzi. Formation mechanism of karst collapse after mine closure: A case study of Enkou coal mine in central Hu'nan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(6): 842-850. [17] 周果, 等. 湖南省娄底市矿山地质环境调查评价报告[R]. 湖南省地勘局四一八队, 2020.ZHOU Guo, etc. Investigation and Evaluation Report on Mine Geological Environment in Loudi City, Southern Province [R], Bureau of Geology And Mineral Exploration And Development of Hunan Province, 418 Geological Brigade, 2020. [18] 戴长华, 何卫平, 邱猛. 湖南省娄底市矿山地质环境调查评价报告[R], 湖南省地质环境监测总站, 2008.DAI Changhua, HE Weiping, QIU Meng. Survey and Evaluation Report on Mine Geological Environment in Loudi City, Hunan Province[R], Hunan Provincial Geological Environment Monitoring Station, 2008. [19] 石益盛. 恩口煤矿区及周边地区地质环境调查报告[R]. 湖南省地勘局四一八队, 1998.7.SHI Yisheng. Geological Environmental Investigation Report of Enkou Coal Mine Area and Surrounding Areas [R], Bureau of Geology And Mineral Exploration and Development of Hunan Province , 418 Geological Brigade, 1998.7 -




 下载:
下载: