Effect of soil-rock structures on the characteristics of rainfall-runoff responses in epikarst zones
-
摘要: 碳酸盐岩在溶蚀作用下形成的表层岩溶带,其上层土壤特性和厚度以及下覆裂隙大小和分布控制降雨入渗、蒸散发和地下径流过程。而不同土岩结构对水文过程的影响尚不明晰。文章构建3种典型土岩结构(薄层石灰土—石灰岩块型、薄层石灰土—白云岩碎石型、厚层土壤—石灰岩碎石型)土柱试验装置并进行观测,通过对比分析,揭示不同土岩结构的产流能力和径流响应特征的差异。结果表明:土岩结构对水平衡有显著影响。厚层土壤(85 cm)极大增加了蒸发量,其产流能力较小,表现为形成地下径流所需的降雨阈值大和形成的径流总量小。相比之下,薄层土壤(20 cm)具有较大的产流能力。当薄层土壤下覆为白云岩碎石时,相比于下覆为石灰岩岩块,碎石表面滞留水分能力较强,导致蒸发损失增加和径流量减少。此外,土岩结构还显著影响降雨—径流响应特征:对于厚层土壤,其对径流的调蓄能力强,洪峰流量显著减小,初始径流和洪峰流量的响应时间延长,但这种延长的幅度随着降雨事件的雨量和强度的增加而减小;对于薄层土壤,其对径流的调蓄能力较弱,其中对于下覆石灰岩岩块结构,裂隙率低、导水性强,在小降雨下容易入渗并形成较大的洪峰;而下覆白云岩碎石结构储水能力较大,在大降雨下,有利于入渗水积蓄,从而形成较大的洪峰。Abstract:
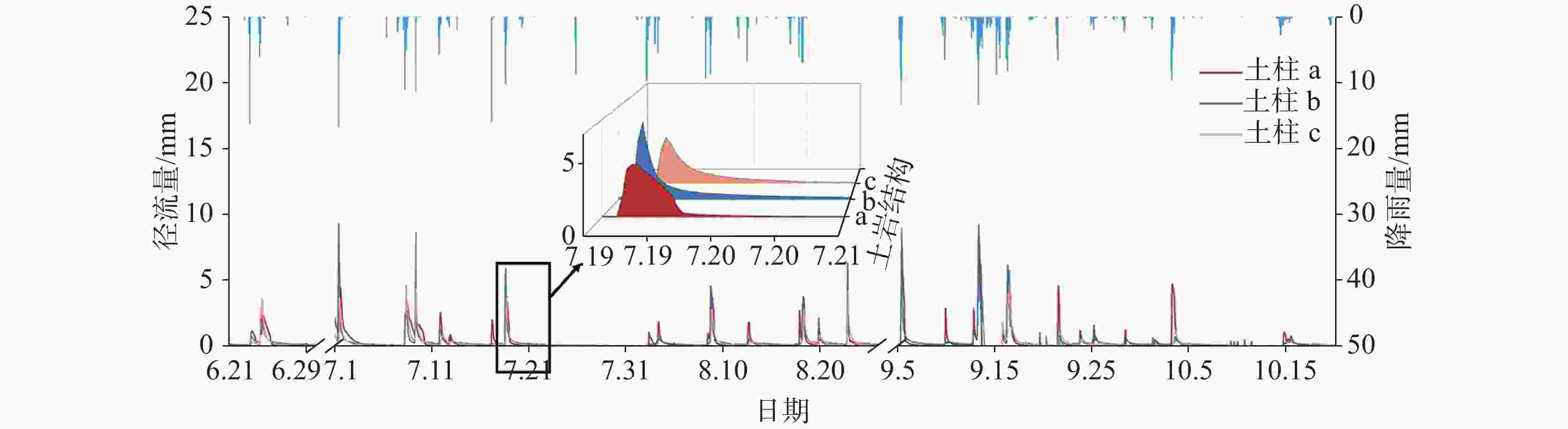
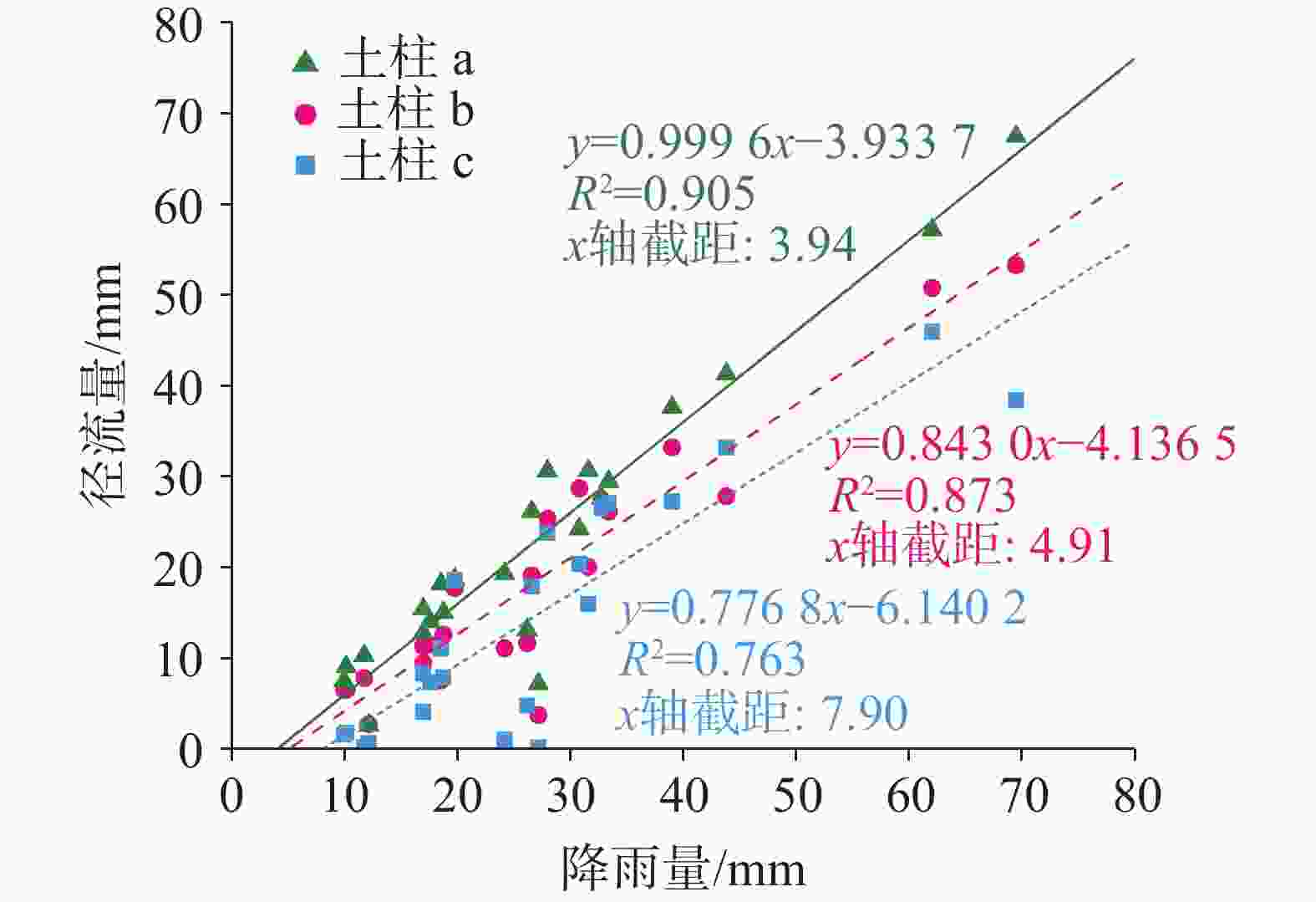
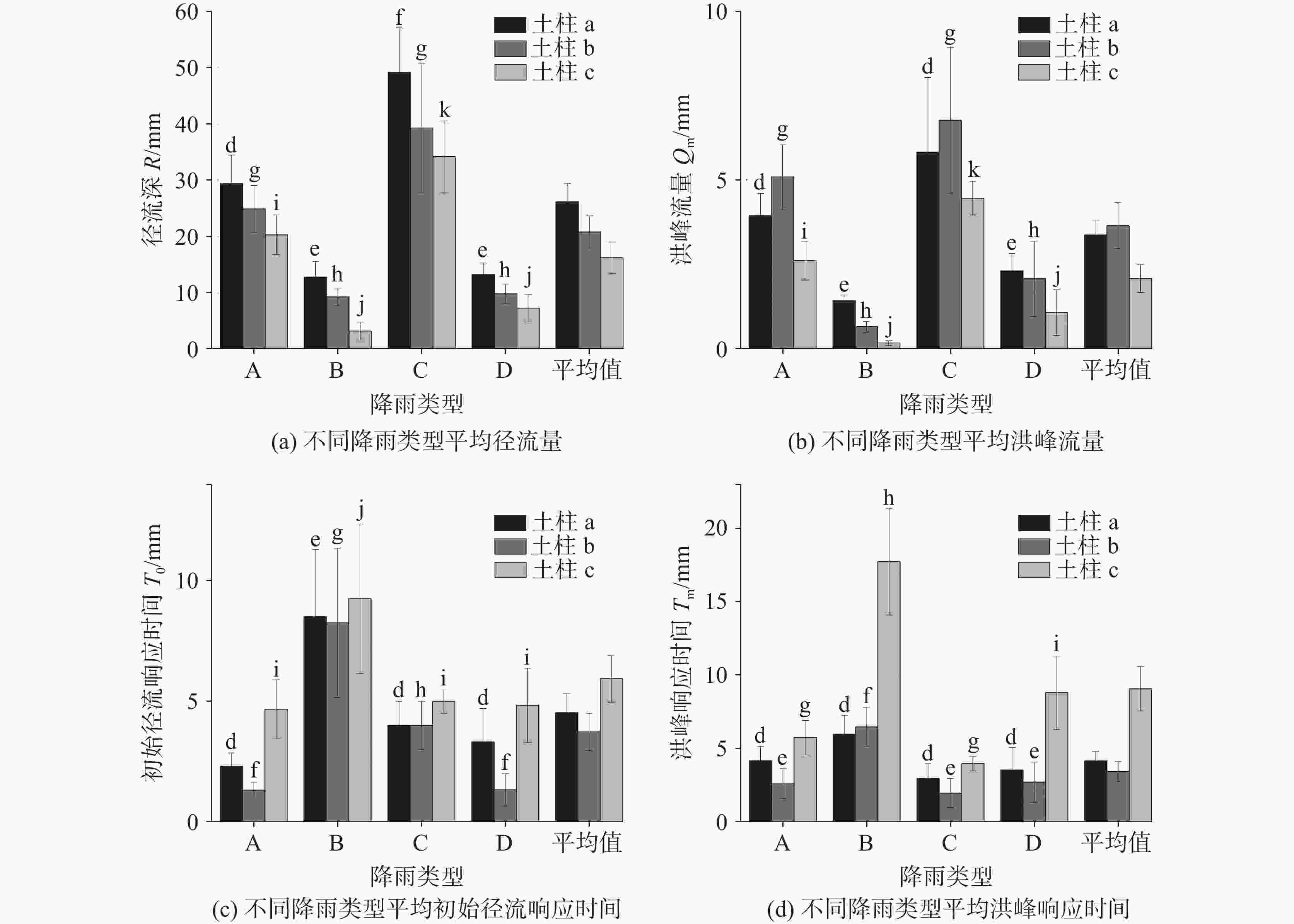
This study was conducted at the Puding Karst Ecosystem Research Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Three square columns were set up in the experiment to simulate different soil-rock structures. Each column has a cross-sectional area of 1 square meter and a height of 2 meters. The station is located in a warm, humid mid-subtropical monsoon climate zone, with an average annual rainfall of 1,315 mm and an average annual temperature of 15.1 ℃. The soil-rock structures in this area are diverse, mainly comprising limestone, dolomite, and associated soils. This study aims to reveal the impact of complex soil-rock structures on hydrological processes in the karst areas of Southwest China. In this study, physical models of three typical soil-rock structures (Column a: thin limestone soil over limestone blocks; Column b: thin limestone soil over dolomite gravel; Column c: thick soil over limestone gravel) were constructed, the underground runoff processes formed by natural rainfall were observed, and the water balance and runoff response characteristics under different soil-rock structures were compared. The research findings provide scientific insights into better understanding of the transformation and effective utilization of water resources in karst areas. Three square columns were used as experimental devices in this study to simulate different types of soil-rock structures (combinations of limestone, dolomite, overlying lime soil, and yellow soil). During natural rainfall events, evaporation and runoff of the soil columns with different soil-rock structures were compared and analyzed. Various methods of statistical analysis were employed to quantitatively assess the impact of these structures, revealing the hydrological processes of the complex soil-rock structures in epikarst zones. The main results are as follows. (1) Water Balance: As soil thickness increased (20 cm, 23 cm, 85 cm), evaporation increased and runoff decreased. Dolomite gravel (Column b) retained more water than limestone blocks (Column a), leading to higher evaporation and lower runoff. Seasonal runoff variability was significant in areas covered with thinner soil, in which flood and drought are prone to occur. (2) Rainfall-Runoff Relationship: Linear regression revealed a threshold-linear two-stage pattern. Runoff started after reaching a threshold, becoming linear beyond that. The increase of soil thickness raised the rainfall threshold for runoff formation. Column a had the highest runoff efficiency, while Column c had the lowest. The specific surface area of the gravel in Column b is larger, so its evaporation is twice as much as that of Column a, and the regression slope is lower. (3) Impact of Rainfall Patterns: Small-event rainfall (Patterns B and D) caused higher peaks in Column a, while large-event rainfall (Patterns A and C) caused higher peaks in Column b. Thicker soil in Column c delayed initial runoff and peak flow, especially in small events. Additionally, the initial runoff response time of soil-rock structures with thin soil layers depends on the rainfall process, while the initial runoff response time of soil-rock structures with thick soil layers is negatively correlated with soil moisture content. This study reveals the significant impact of different soil-rock structures on hydrological processes in the karst areas of Southwest China. The physical properties of soil-rock structures (e.g., soil thickness and characteristics of underlying rocks) not only affect the water balance but also determine the rainfall-runoff relationship and runoff characteristics under different rainfall patterns. Firstly, the soil layer thickness is a key factor influencing water balance and underground runoff response. Thicker soil can significantly delay the response time of underground runoff, reduce peak flow, and increase the rainfall threshold required for runoff generation. Additionally, the physical properties of rock fractures affect the water balance, with dolomite gravel under the soil having a higher water retention capacity than limestone blocks, leading to higher evaporation losses and lower runoff. Lastly, the response of water balance and underground runoff to different rainfall patterns varies significantly with soil-rock structures. Low-fracture limestone blocks beneath the soil (fracture porosity of 8%) have high water conductivity, allowing small rainfall to easily infiltrate and form substantial peak flows. In contrast, dolomite gravel beneath the soil, with a higher water storage capacity (fracture porosity of 40%), facilitates the accumulation of infiltrated water during heavy rainfall, leading to larger peak flows. -
Key words:
- karst /
- soil-rock structure /
- subsurface stormflow /
- water balance /
- runoff response characteristics
-
表 1 土柱中土壤质地
Table 1. Soil textures in soil columns
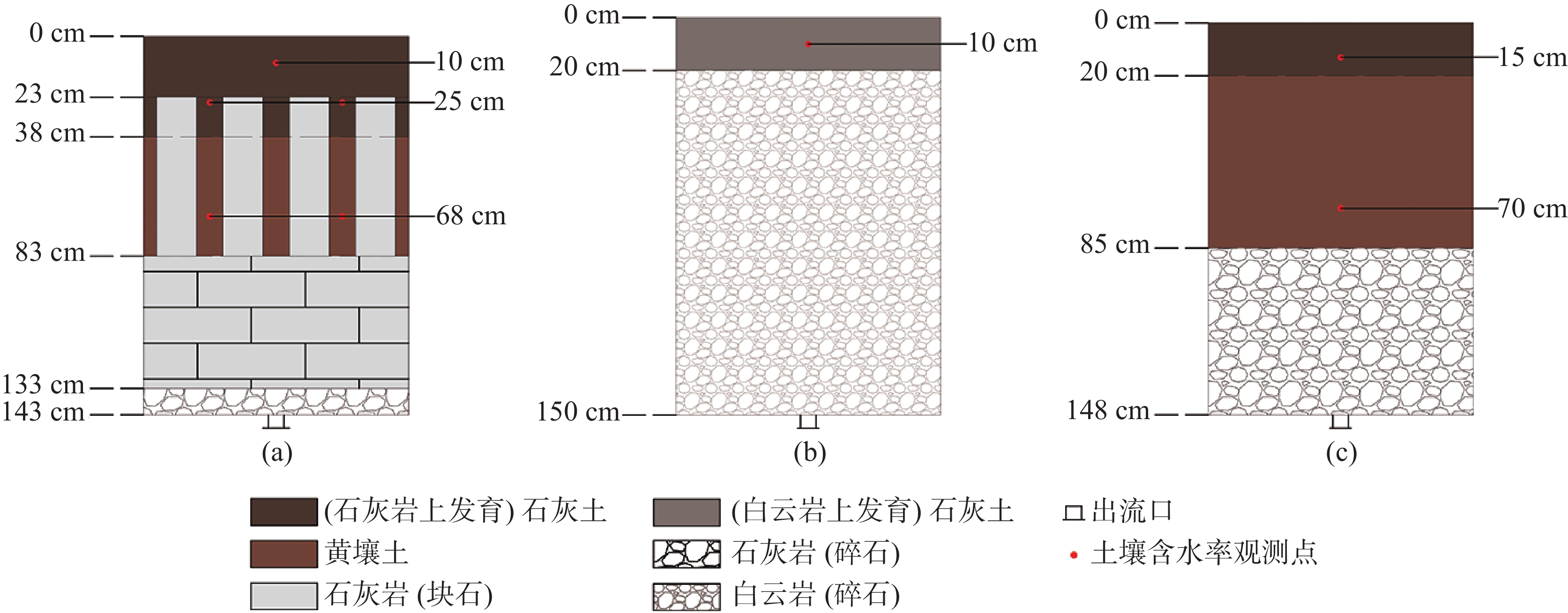
土壤类型 土壤质地 颗粒组成/% 砂粒 粉粒 黏粒 黄壤土 壤土 28.2 45.6 26.2 白云岩上发育石灰土 壤土 36.7 49.1 14.2 石灰岩上发育石灰土 粉壤土 26.1 57.6 16.3 注:砂、粉、黏粒粒径分别为0.05~2 mm、0.002~0.05 mm、<0.002 mm;土壤质地分类按照美国农业部(United States Department of Agriculture, USDA)的土壤质地分类标准进行。
Note: The particle sizes of sand, powder and clay are 0.05–2 mm, 0.002–0.05 mm and <0.002 mm, respectively. Soil textures are classified according to the soil texture classification standards of United States Department of Agriculture.表 2 土柱基本结构及特征参数
Table 2. Basic structures and physical properties of soil columns
土柱 分层特征 土壤占比/% 土壤容重/g·cm−3 岩石裂隙率/% 渗透系数(10−3) cm/·s−1 a ① 0~23 cm (石灰岩上发育)石灰土 100 1.34 − 0.815 ② 23~38 cm 石灰土—岩块 20 1.34 − 13.7* ③ 38~83 cm 黄壤土—岩块 20 1.25 − 13.7* ④ 83~133 cm 岩块 − − 8 18.9 ⑤ 133~143 cm 反滤层(碎石) − − 25 4.79 b ① 0~20 cm (白云岩上发育)石灰土 100 1.00 − 3.14 ② 20~150 cm 白云岩(碎石) − − 40 17.8 c ① 0~15 cm (石灰岩上发育)石灰土 100 1.34 − 0.815 ② 15~85 cm 黄壤土 100 1.25 − 0.0221 ③ 85~148 cm 石灰岩(碎石) − − 12.1 21.3 注:*23~83 cm层在注水实验中测出的渗透系数值。
Note: * Permeability coefficient of the layers from 23 cm to 83 cm measured in water injection experiment.表 3 次降雨、径流特征及变化范围
Table 3. Characteristics and variation range of rainfall and runoff
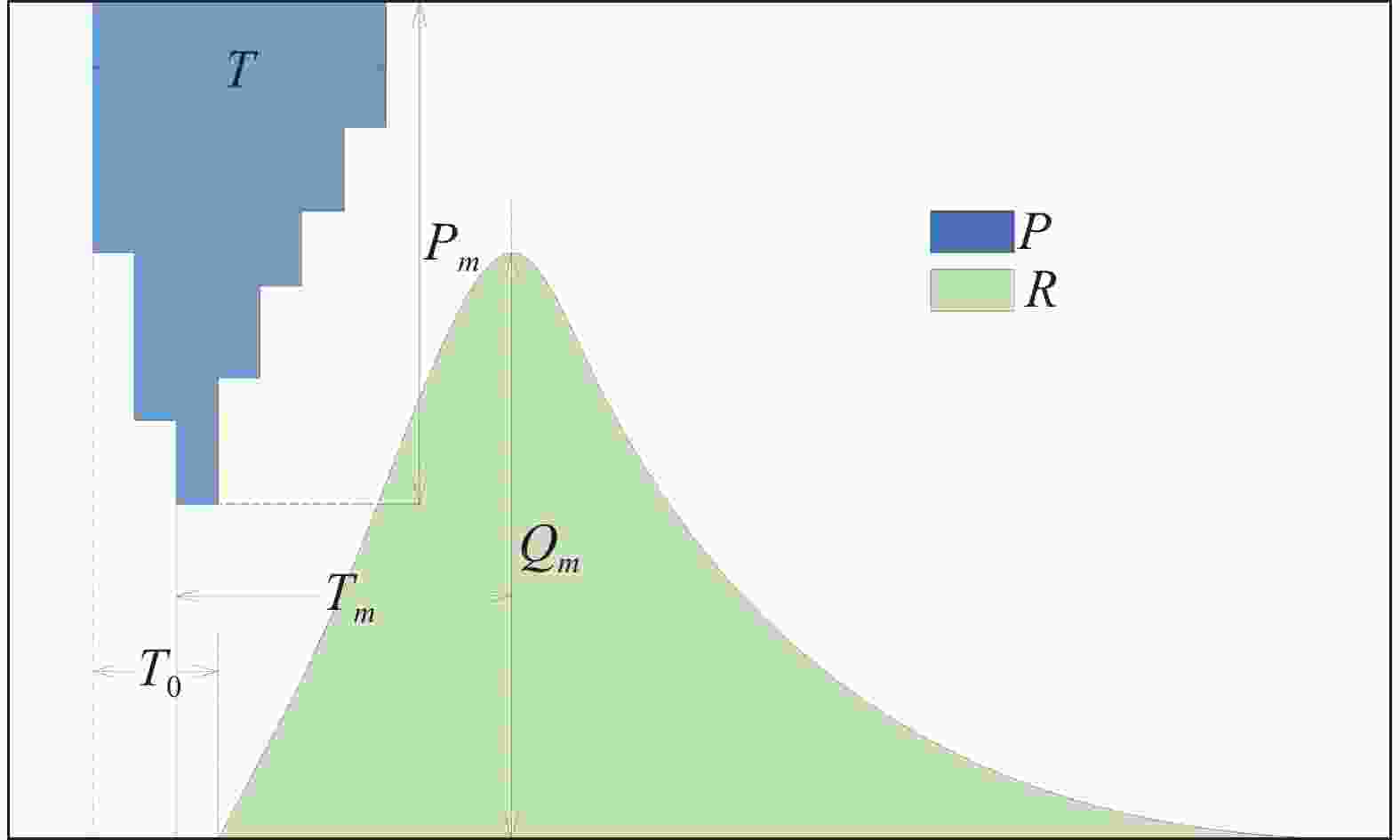
统计指标 指标符号 单位 变化范围 次降雨量 $ P $ mm 10.0~69.4 降雨历时 $ T $ h 2~40 降雨强度 $ I $ mmh−1 0.43~8.50 最大1 h雨量 $ {P}_{m} $ mm 0.6~16.8 土壤初始含水率 $ {S}_{w} $ − 0.178~0.365 径流深 $ R $ mm 0.33~67.37 洪峰流量 $ {Q}_{m} $ mm 0.04~9.26 初始径流响应时间 $ {T}_{0} $ h 0.1~18.0 洪峰响应时间 $ {T}_{m} $ h 0.1~25.0 表 4 不同降雨类型特征指标均值
Table 4. Average value of characteristic indexes under different rainfall types
降雨
类型次降雨量
$ P $/mm降雨历时
$ T $/h降雨强度
$ I $/mmh−11小时最大雨强
$ {P}_{m} $/mmA 34.5 11.8 3.2 10.8 B 15.8 28.0 0.6 2.9 C 52.9 31.0 1.7 12.3 D 16.3 6.3 3.6 8.7 表 5 水量平衡计算表
Table 5. Annual and rainy season water balance
土柱a 土柱b 土柱c 全年 雨季 全年 雨季 全年 雨季 降雨总量$ P $/mm 1294 850 1294 850 1294 850 径流总量$ R $/mm 1136 817 1016 771 717 499 土壤水蓄量差$ \Delta W $/mm 10.7 10.0 1.2 3.5 −32.0 8.3 实际蒸发量$ E $/mm 146.7 22.6 276.0 75.5 608.4 342.6 径流系数$ R/P $ 0.88 0.96 0.79 0.91 0.55 0.59 表 6 降雨径流特征统计量Spearman秩相关系数表
Table 6. Spearman correlation coefficient between rainfall and runoff statistical features
次径流深/mm 次洪峰流量/mm 次初始径流响应时间/h 次洪峰响应时间/h $ {R}_{a} $ $ {R}_{b} $ $ {R}_{c} $ $ {Q}_{m,a} $ $ {Q}_{m,b} $ $ {Q}_{m,c} $ $ {T}_{0,a} $ $ {T}_{0,b} $ $ {T}_{0,c} $ $ {T}_{m,a} $ $ {T}_{m,b} $ $ {T}_{m,c} $ $ P $ 0.873** 0.871** 0.817** 0.686** 0.683** 0.684** −0.201 −0.043 −0.115 −0.160 −0.324 −0.615** $ T $ 0.322 0.265 0.194 0.085 −0.009 −0.040 0.530** 0.690** 0.409 0.213 0.325 0.384 $ I $ 0.140 0.186 0.239 0.243 0.396 0.281 −0.676** −0.685** −0.318 −0.302 −0.484* −0.590** $ {P}_{m} $ 0.375 0.516* 0.458* 0.339 0.557* 0.378 −0.523** −0.438** −0.356 −0.334 −0.570* −0.794** $ {S}_{w,a} $ 0.283 0.558* −0.150 −0.137 $ {S}_{w,b} $ 0.118 0.355 0.083 0.072 $ {S}_{w,c} $ 0.247 0.447 −0.626* 0.004 注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。
Note: ** indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.01 (bilateral); * indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.05 (bilateral). -
[1] 曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 夏日元, 章程. 岩溶动力系统与全球变化研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5):874-900.CAO Jianhua, JIANG Zhongcheng, YUAN Daoxian, XIA Riyuan, ZHANG Cheng. The progress in the study of the karst dynamic system and global changes in the past 30 years[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 874-900. [2] Hartmann A, Goldscheider N, Wagener T, Lange J, Weiler M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2014, 52(3): 218-242. doi: 10.1002/2013RG000443 [3] 覃小群, 蒋忠诚. 表层岩溶带及其水循环的研究进展与发展方向[J]. 中国岩溶, 2005, 24(3):250-254.QIN Xiaoqun, JIANG Zhongcheng. A review on recent advances and perspective in epikarst water study[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2005, 24(3): 250-254. [4] Williams P W. The role of the epikarst in karst and cave hydrogeology: A review[J]. International Journal of Speleology, 2008, 37(1): 1-10. doi: 10.5038/1827-806X.37.1.1 [5] Williams P W. The role of the subcutaneous zone in karst hydrology[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1983, 61(1): 45-67. [6] 蒋忠诚, 王瑞江, 裴建国, 何师意. 我国南方表层岩溶带及其对岩溶水的调蓄功能[J]. 中国岩溶, 2001, 20(2):106-110.JIANG Zhongcheng, WANG Ruijiang, PEI Jianguo, HE Shiyi. Epikarst zone in South China and its regulation function to karst water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2001, 20(2): 106-110. [7] Sohrt J, Ries F, Sauter M, Lange J. Significance of preferential flow at the rock soil interface in a semi-arid karst environment[J]. Catena, 2014, 123(1): 1-10. [8] 张君, 付智勇, 陈洪松, 连晋姣, 覃常. 西南喀斯特白云岩坡地土壤:表层岩溶带结构及水文特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(6):2107-2118.ZHANG Jun, FU Zhiyong, CHEN Hongsong, LIAN Jinjiao, Qin Chang. Soil-epikarst structures and their hydrological characteristics on dolomite slopes in karst region of Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(6): 2107-2118. [9] 张信宝, 王世杰, 贺秀斌, 汪阳春, 何永彬. 碳酸盐岩风化壳中的土壤蠕滑与岩溶坡地的土壤地下漏失[J]. 地球与环境, 2007, 35(3):202-206.ZHANG Xinbao, WANG Shijie, HE Xiubin, WANG Yangchun, HE Yongbin. Soil creeping in weathering crusts of carbonate rocks and underground soil losses on karst slopes[J]. Earth and Environment, 2007, 35(3): 202-206. [10] 何江湖, 张科利. 西南喀斯特地区地下水土流失研究综述[J]. 泥沙研究, 2022, 47(5):1-8.HE Jianghu, ZHANG Keli. Spatial variation of soil steady-state infiltration rates in karst hillslopes[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2022, 47(5): 1-8. [11] 唐益群, 张晓晖, 周洁, 佘恬钰, 杨坪, 王建秀. 喀斯特石漠化地区土壤地下漏失的机理研究:以贵州普定县陈旗小流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(2):121-127.TANG Yiqun, ZHANG Xiaohui, ZHOU Jie, SHE Tianyu, YANG Ping, WANG Jianxiu. The mechanism of underground leakage of soil in karst rocky desertification areas: A case in Chenqi small watershed, Puding, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(2): 121-127. [12] 陈喜. 西南喀斯特地区水循环过程及其水文生态效应[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2014.CHEN Xi. Hydrological cycle and hydroecological effects in karst area of Southwest China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [13] 张兴, 王克林, 付智勇, 陈洪松, 张伟, 史志华. 桂西北白云岩坡地典型土体构型石灰土水文特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(7):2186-2196.ZHANG Xing, WANG Kelin, FU Zhiyong, CHEN Hongsong, ZHANG Wei, SHI Zhihua. Hydrological characteristics of calcareous soil with contrasting architecture on dolomite slope of northwest Guangxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(7): 2186-2196. [14] 张志才, 陈喜, 刘金涛, 彭韬, 石朋, 严小龙. 喀斯特山体地形对表层岩溶带发育的影响:以陈旗小流域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(2):137-143.ZHANG Zhicai, CHEN Xi, LIU Jintao, PENG Tao, SHI Peng, YAN Xiaolong. Influence of topography on epikarst in karst mountain areas: A case study of Chenqi catchment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(2): 137-143. [15] 张志才, 陈喜, 程勤波, 彭韬, 张艳芳, 纪忠华. 喀斯特山体表层岩溶带水文地质特征分析:以陈旗小流域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 39(1):19-25.ZHANG Zhicai, CHEN Xi, CHENG Qinbo, PENG Tao, ZHANG Yanfang, JI Zhonghua. Hydrogeology of epikarst in karst mountains: A case study of the Chenqi catchment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(1): 19-25. [16] 高强山, 彭韬, 付磊, 王世杰, 曹乐, 程倩云. 探地雷达技术对表层岩溶带典型剖面组构刻画与界面识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):759-765.GAO Qiangshan, PENG Tao, FU Lei, WANG Shijie, CAO Le, CHENG Qianyun. Structure description and interface recognition on epikarst typical profiles using GPR technology[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 759-765. [17] 程凭, 程勤波, 陈喜, 刘金涛, 张志才, 高满. 基于频域电磁法反演喀斯特表层土—岩结构研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(5):675-683. doi: 10.11932/karst20220501CHENG Ping, CHENG Qinbo, CHEN Xi, LIU Jintao, ZHANG Zhicai, GAO Man. Exploration of superficial soil-rock structure for karst area based on frequency domain electromagnetic method[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(5): 675-683. doi: 10.11932/karst20220501 [18] 李阳兵, 王世杰, 李瑞玲. 岩溶生态系统的土壤[J]. 生态环境, 2004, 13(3):434-438.LI Yangbing, WANG Shijie, LI Ruiling. Some soil features of karst ecosystem[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2004, 13(3): 434-438. [19] 刘鸿雁, 蒋子涵, 戴景钰, 吴秀臣, 彭建, 王红亚, Meersmans J, Green S M, Quine T A. 岩石裂隙决定喀斯特关键带地表木本与草本植物覆盖[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49(12):1974-1981.LIU Hongyan, JIANG Zihan, DAI Jingyu, WU Xiuchen, PENG Jian, WANG Hongya, Meersmans J, Green S M, Quine T A. Rock crevices determine woody and herbaceous plant cover in the karst critical zone[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2019, 49(12): 1974-1981. [20] 陈喜, 张志才. 喀斯特地区地球关键带科学与生态水文学发展综述[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(3):356-364.CHEN Xi, ZHANG Zhicai. An overview on the development of science and ecological hydrology of the earth critical zones in karst area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(3): 356-364. [21] 陈洪松, 杨静, 傅伟, 何菲, 王克林. 桂西北喀斯特峰丛不同土地利用方式坡面产流产沙特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(16):121-126.CHEN Hongsong, YANG Jing, FU Wei, HE Fei, WANG Kelin. Characteristics of slope runoff and sediment yield on karst hill-slope with different land-use types in northwest Guangxi[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(16): 121-126. [22] 彭韬, 王世杰, 张信宝, 容丽, 杨涛, 陈波, 汪进阳. 喀斯特坡地地表径流系数监测初报[J]. 地球与环境, 2008, 36(2):125-129.PENG Tao, WANG Shijie, ZHANG Xinbao, RONG Li, YANG Tao, CHEN Bo, WANG Jinyang. Results of preliminary monitoring of surface runoff coefficients for karst slopes[J]. Earth and Environment, 2008, 36(2): 125-129. [23] Rempe D M, Dietrich W E. Direct observations of rock moisture, a hidden component of the hydrologic cycle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(11): 2664-2669. [24] Wilcox B P, Taucer P I, Munster C L, Owens M K, Mohanty B P, Sorenson J R, Bazan R. Subsurface stormflow is important in semiarid karst shrublands[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(10): 1-6. [25] Tromp Van Meerveld H J, Mcdonnell J J. Threshold relations in subsurface stormflow: 1. A 147-storm analysis of the Panola hillslope[J]. Water Resources Research, 2006, 42(2): W02410. [26] Tromp Van Meerveld H J, Mcdonnell J J. Threshold relations in subsurface stormflow: 2. The fill and spill hypothesis[J]. Water Resources Research, 2006, 42(2): W02411. [27] Tromp Van Meerveld H J, Peters N E, Mcdonnell J J. Effect of bedrock permeability on subsurface stormflow and the water balance of a trenched hillslope at the Panola Mountain Research Watershed, Georgia, USA[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2007, 21(6): 750-769. doi: 10.1002/hyp.6265 [28] 张轶博, 王锦国, 刘芮彤. 岩溶包气带水流衰减过程与调蓄能力影响机制研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(6):1140-1148.ZHANG Yibo, WANG Jinguo, LIU Ruitong. Research on water flow attenuation process and regulating capacity in karst vadose zone[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(6): 1140-1148. [29] 马从文, 张志才, 陈喜, 程勤波, 彭韬, 张林. 基于机器学习的西南岩溶泉流量模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2024, 43(1):48-56.MA Congwen, ZHANG Zhicai, CHEN Xi, CHENG Qinbo, PENG Tao, ZHANG Lin. Modelling karst spring flow in Southwest China based on machine learning[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2024, 43(1): 48-56. [30] 王甲荣, 陈喜, 张志才, 张润润, 朱彪, 龚轶芳, 刘皓, 袁瞬飞. 喀斯特溶槽岩−土界面优势流及其对土壤水分动态的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(1):109-116.WANG Jiarong, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Zhicai, ZHANG Runrun, ZHU Biao, GONG Yifang, LIU Hao, YUAN Shunfei. Preference flow at rock-soil interface and its influence on soil water dynamics in the karst troughs[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(1): 109-116. [31] Gabrielli C P, Morgenstern U, Stewart M K, Mcdonnell J J. Contrasting groundwater and streamflow ages at the Maimai watershed[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(6): 3937-3957. doi: 10.1029/2017WR021825 [32] 闫钇全, 刘琦, 邓大鹏, 王涵. 表层岩溶裂隙带土壤地表流失/地下漏失室内模拟实验[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(2):240-248.YAN Yiquan, LIU Qi, DENG Dapeng, WANG Han. Laboratory simulation study on soil surface loss and underground leakage in the epikarst fissure zone[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(2): 240-248. [33] Fu Z Y, Chen H S, Zhang W, Xu Q X, Wang S, Wang K L. Subsurface flow in a soil-mantled subtropical dolomite karst slope: A field rainfall simulation study[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 250(1): 1-14. [34] 严友进, 戴全厚, 伏文兵, 杨智. 下垫面变化对喀斯特坡地地下产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1):67-73, 79.YAN Youjin, DAI Quanhou, FU Wenbing, YANG Zhi. Influences of underlying surface changes on underground runoff and sediment yield in karst slope land[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 67-73, 79. [35] 杨静, 王升, 丁亚丽, 陈洪松. 喀斯特白云岩地区不同土体构型土壤剖面持水导水性能研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(5):697-704.YANG Jing, WANG Sheng, DING Yali, CHEN Hongsong. Moisture-retaining and transmissibility properties of soil profiles with different architectures in dolomite karst areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(5): 697-704. [36] Fang Q, Zhao L S, Hou R, Fan C H, Zhang J X. Rainwater transformation to runoff and soil loss at the surface and belowground on soil-mantled karst slopes under rainfall simulation experiments[J]. Catena, 2022, 215: 106316. [37] Chen J, Luo W J, Zeng G N, Wang Y W, Lyu Y N, Cai X L, Zhang L, Cheng A Y, Zhang X B, Wang S J. Response of surface evaporation and subsurface leakage to precipitation for simulated epikarst with different rock-soil structures[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 610(4): 127850. [38] Zeng Q R, Liu Z H, Chen B, Hu Y D, Zeng S B, Zeng C, Yang R, He H B, Zhu H, Cai X L. Carbonate weathering-related carbon sink fluxes under different land uses: A case study from the Shawan simulation test site, Puding, Southwest China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 474: 58-71. [39] Fu Z Y, Chen H S, Zhang W, Xu Q X, Wang S, Wang K L. Subsurface flow in a soil-mantled subtropical dolomite karst slope: A field rainfall simulation study[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 250: 1-14. [40] Zhang J, Wang S, Fu Z Y, Chen H S, Wang K L. Soil thickness controls the rainfall-runoff relationship at the karst hillslope critical zone in Southwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 609: 127779. [41] Zhao M, Zeng C, Liu Z H, Wang S J. Effect of different land use/land cover on karst hydrogeochemistry: A paired catchment study of Chenqi and Dengzhanhe, Puding, Guizhou, SW China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 388(1): 121-130. [42] 张杨, 宁立波, 尹峰, 赵国红, 白冰珂, 朱晛亭. 岩体体裂隙率野外测量及计算方法的研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(1):10-18.ZHANG Yang, NING Libo, YIN Feng, ZHAO Guohong, BAI Bingke, ZHU Xianting. New method of field measurement and calculation for volumetric fracture rate of rock mass[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 10-18. [43] 霍丽娟, 李一菲, 钱天伟. 定水头法和降水头法测定黄土的饱和导水率[J]. 太原科技大学学报, 2010, 31(3):256-259.HUO Lijuan, LI Yifei, QIAN Tianwei. Determination of saturated hydraulic conductivity of loess soil by constant-head method and falling-head method[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2010, 31(3): 256-259. [44] 黄俊, 吴普特, 赵西宁. 多参数非线性降雨产流阈值模型试验研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2011, 33(1):84-89.HUANG Jun, WU Pute, ZHAO Xining. Experimental study on the nonlinear multi-parameter rainfall-runoff threshold model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2011, 33(1): 84-89. [45] Spearman C. The proof and measurement of association between two things[J]. American Journal of Psychology, 1987, 15(1): 72-101. [46] Wei W, Chen L D, Fu B J, Huang Z L, Wu D P, Gui L D. The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 335(3): 247-258. [47] 兰旻. 山坡尺度降雨产流过程宏观本构关系研究[D]. 北京:清华大学, 2014.LAN Min. Study on constitutive relationship of runoff generation at the hillslope scale[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2014. [48] 寇平浪, 许强, 王崔林, 徐建强, 袁爽. 基于逐5 min时间分辨率的降雨—径流关系研究[J]. 人民黄河, 2022, 44(6):34-37.KOU Pinglang, XU Qiang, WANG Cuilin, XU Jianqiang, YUAN Shuang. Research on rainfall-runoff relationship based on time resolution of five minutes[J]. Yellow River, 2022, 44(6): 34-37. [49] 方胜, 彭韬, 王世杰, 刘秀明, 孟凡德. 喀斯特坡地土壤稳渗率空间分布变化特征研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2014, 42(1):1-10.FANG Sheng, PENG Tao, WANG Shijie, LIU Xiuming, MENG Fande. Spatial variation of soil steady-state infiltration rates in karst hillslopes[J]. Earth and Environment, 2014, 42(1): 1-10. [50] 焦友军, 黄奇波, 于青春. 初始裂隙对岩溶水紊流形成的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(4):501-510.JIAO Youjun, HUANG Qibo, YU Qingchun. Influence of initial fractures on the occurrence of karst turbulent flow[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(4): 501-510. [51] 党宏宇, 陈洪松, 邵明安. 喀斯特地区不同层次土石混合介质对土壤水分入渗过程的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(8):38-43.DANG Hongyu, CHEN Hongsong, SHAO Ming'an. Effects of laminated rock fragments on soil infiltration processes in karst regions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(8): 38-43. -




 下载:
下载: