Evaluation of groundwater pollution risk based on the optimized DRASTIC model: A case study of the areas along the route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project in Shandong Province
-
摘要: 基于南水北调工程对沿线区域提出的水质保障要求及生态可持续发展的需要,对地下水的污染防范和治理已成为研究重点。为查明山东省辖南水北调沿线地区的地下水污染风险,通过对地下水污染源荷载、生态脆弱性以及功能价值三个方面的评价构建地下水污染风险评价体系。通过污染物毒性、排放量及排放可能性对污染荷载进行定量、定性的分析;引入土地利用、土壤氧气含量等数据优化DRASTIC体系,构建DRASTOL模型;利用InVEST模拟的生境质量、夜间灯光系数以及研究区敏感的地下水F−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$等评价因子评估地下水功能价值。发现研究区地下水污染荷载结果整体较低,脆弱性中等偏高,功能价值中等偏低。叠加处理3个结果得到地下水污染风险数据分布状态,整体中等偏下。其中较高、高等级污染风险区域总面积约为
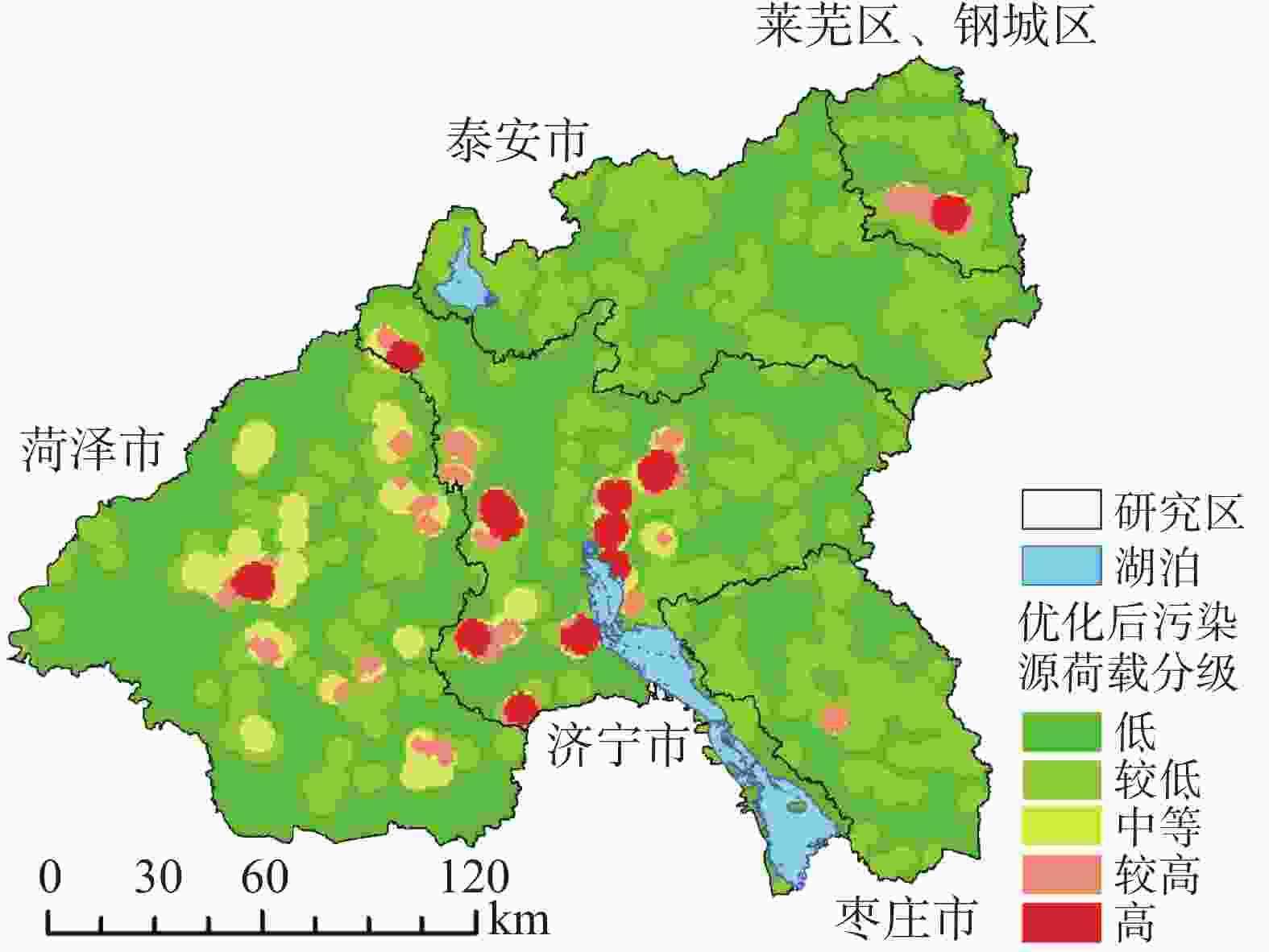
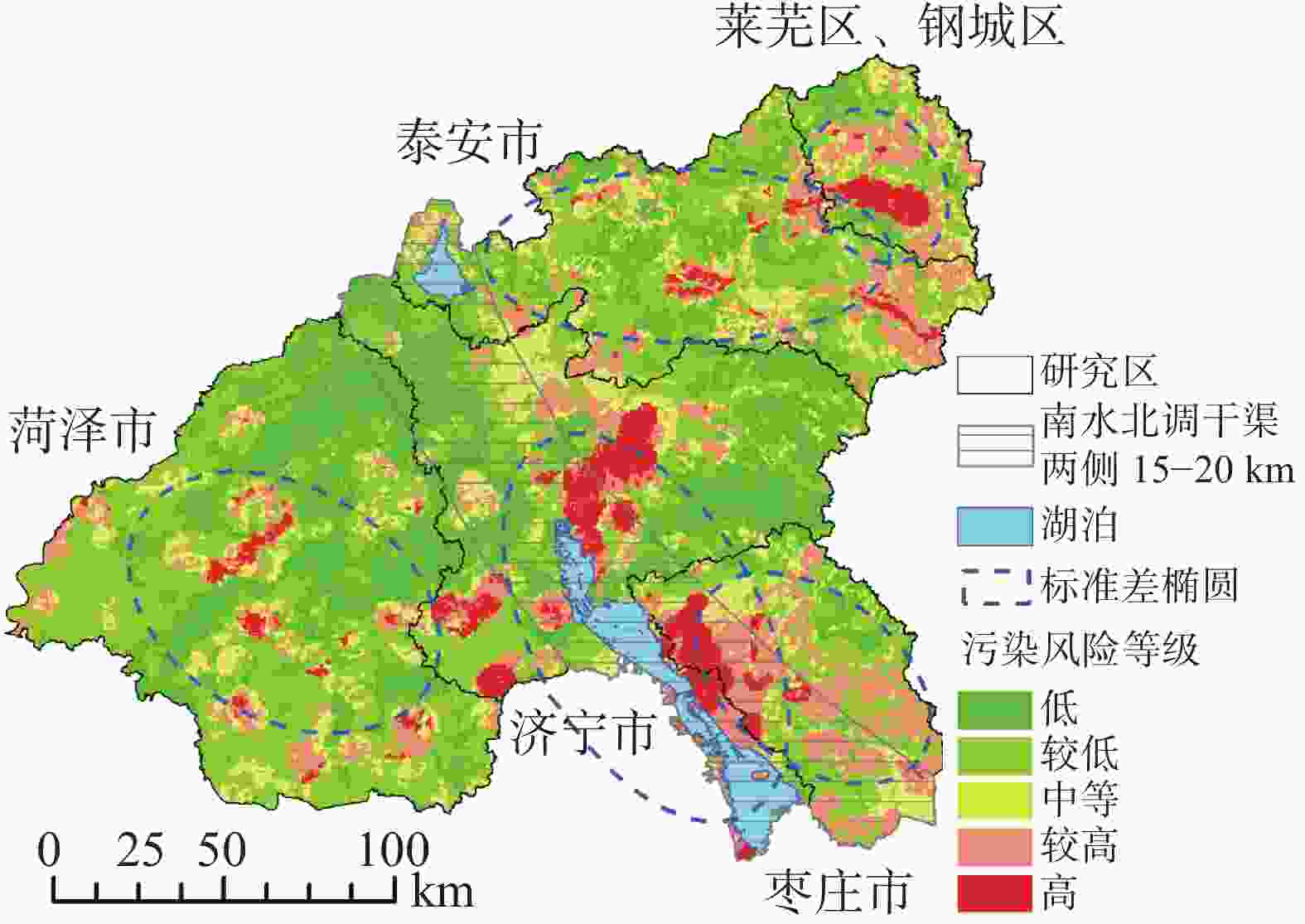
7 444.88 km2,占比约为20.17%,主要分布在菏泽市中部,济宁市中部、西南部,枣庄市西北部,泰安市中部、东部,钢城区南部,该区域地下水位埋深较浅,自然环境下较大的降水易携带地表污染物渗入地下;富水性强、工业及采矿用地密集且排放的污染物毒性较强;高强度的社会经济活动易产生较多污染物,多因素综合影响导致该区域地下水的污染风险指数较高。Abstract:Based on the requirements of guaranteeing water quality and sustainably developing ecology proposed by the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, the prevention and treatment of groundwater pollution has become a research focus. In this study, the prevention of shallow groundwater pollution along the route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project in Shandong Province was taken as an example, and the system of evaluating shallow groundwater pollution risk in the study area was constructed from the aspects of groundwater pollution source load, groundwater ecological vulnerability and groundwater functional value. The pollution load was quantitatively and qualitatively analyzed in terms of toxicity, emission and emission possibility of pollutants. Based on land use data and soil oxygen contents, an optimized DRASTOL model was constructed after the optimization of a traditional one. Habitat quality data and night light coefficients simulated by the InVEST model, and the sensitive F− and SO$_4^{2-}$ concentration distributions in groundwater in the study area were used as factors to evaluate the groundwater functional value. The results show low values in both shallow groundwater pollution loads and groundwater functions, and show medium values of groundwater vulnerability. Combined with groundwater pollution load, groundwater vulnerability and groundwater functional value, the distribution of groundwater pollution risk was obtained. The results show that the groundwater pollution risk in the study area is generally at a low or a medium level. The area with high pollution risk totals 7,444.88 km2, accounting for 20.17% of the whole study area, which is mainly distributed in central Heze City, the center and southwest of Jining City, the northwest Zaozhuang City, the center and east of Tai'an City, and the south of Gangcheng City. Reasons for groundwater pollution in these areas mentioned above are as follows. Because groundwater levels in these areas are relatively shallow, when much precipitation occurs in the natural environment, surface pollutants easily infiltrate into the ground, which can pose a threat to the groundwater quality. Besides, industrial and mining land is densely distributed in these areas whose strata are rich in water; consequently, a large number of strong toxic pollutants are likely to be emitted. At the same time, pollutants are also possibly generated by social and economic activities with high intensity. The combined influence of the above factors leads to high risk of groundwater pollution in the study area. The results obtained in this study provide a reference for the zoning of groundwater pollution risk in the areas along the route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project in Shandong Province. -
表 1 数据来源表
Table 1. Table of data sources
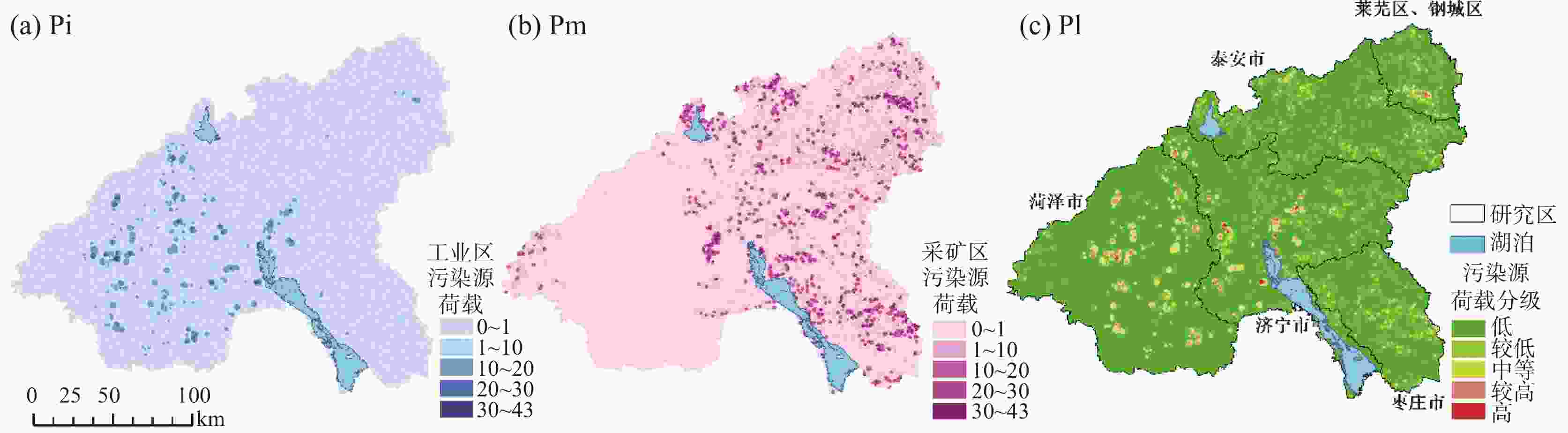
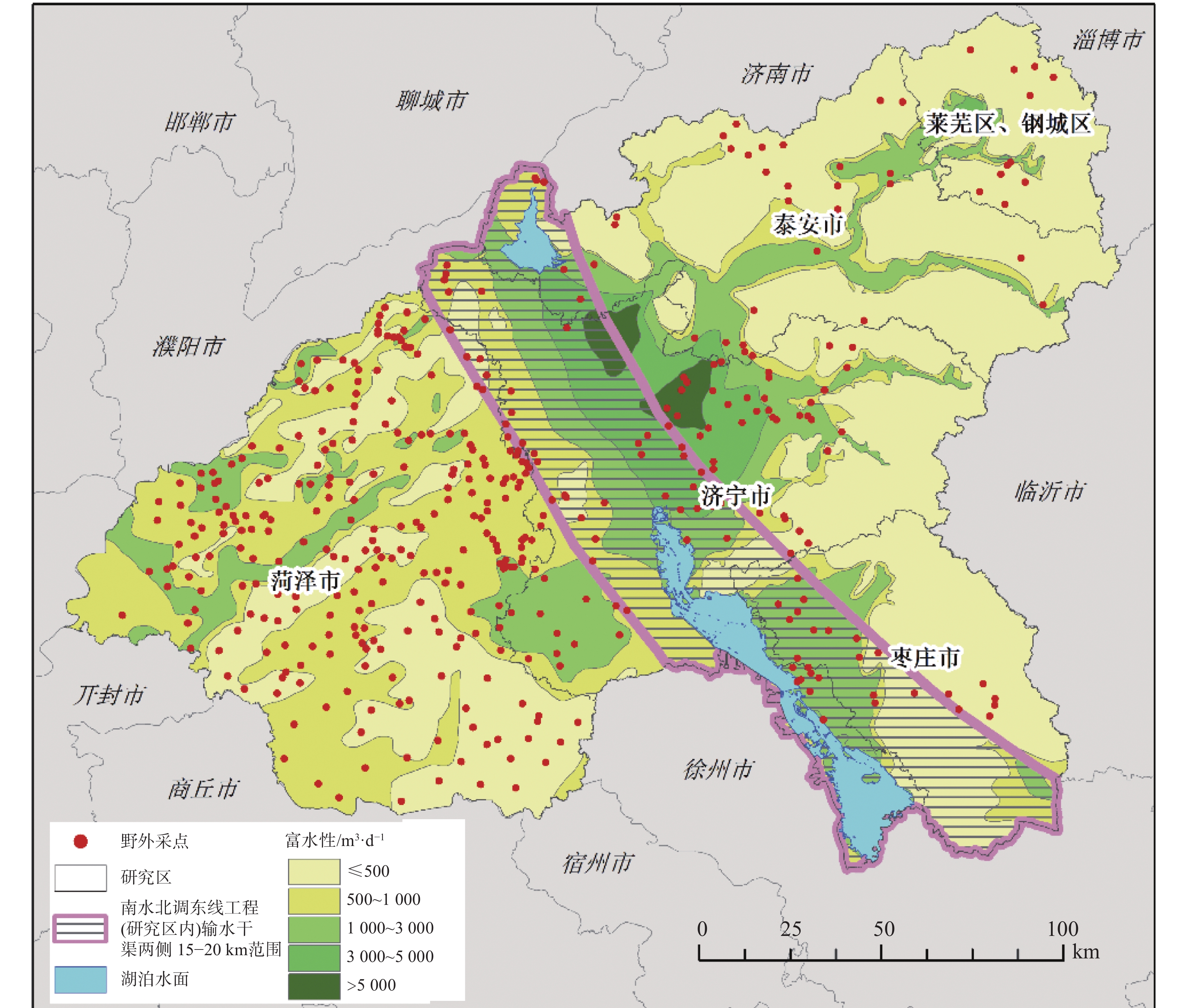
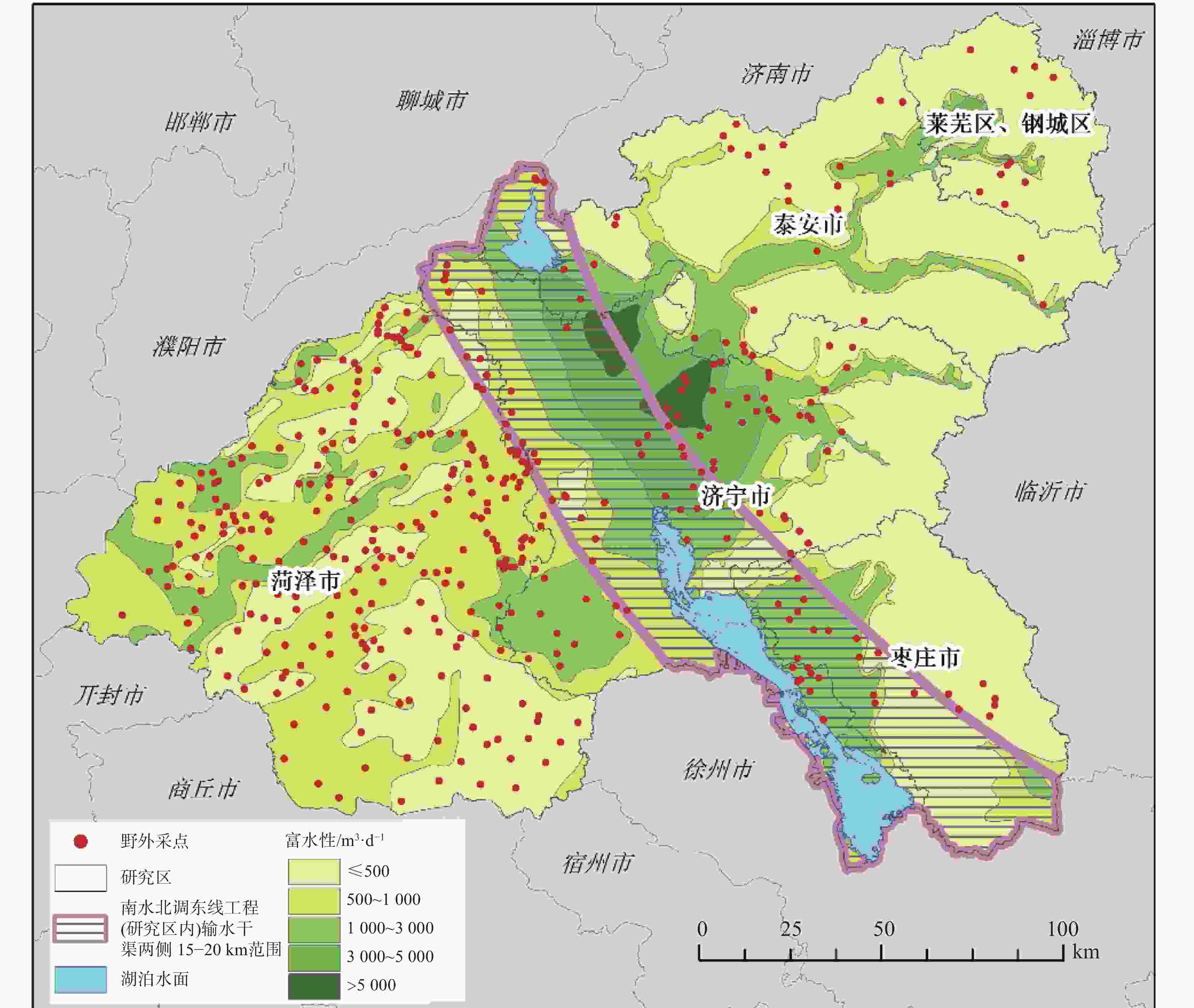
评价类型 数据名称 数据来源 地下水污染荷载评价(PI) 工业污染数据(Pi) 实地调研数据(545组信息) 采矿污染数据(Pm) 实地调研数据(545组信息)、2022年土地变更数据 地下水脆弱性评价(VI) 地下水埋深(D) 野外现场采样测量数据(2020年429组地下水位测量数据) 垂向净补给量(R) 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(年降水数据) 含水层渗透等级(A) 山东省水文地质图 土壤介质(S) 世界土壤数据库 地形坡度(T) 地理空间数据云(GDEMV3 30M 分辨率数字高程数据) 土壤氧气供应量(O) 世界土壤数据库 土地利用数据(L) 2022年土地变更数据 地下水功能价值评价(FI) 夜间灯光遥感(H) 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心 富水性(W) 野外现场采样测量统计数据 生境质量(E) 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心 地下水F离子浓度(F) 野外现场采样测量数据(2020年429组地下水F离子浓度测量数据) 地下水${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$离子浓度(Sw) 野外现场采样测量数据(2020年429组地下水${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$离子浓度测量数据) 表 2 地下水污染源荷载评价因子分级及评分表
Table 2. Grading and scoring of evaluation factors for groundwater pollution source load
污染源类型 毒性类别 Ti评分 缓冲区半径/km 工业污染源 石油加工、炼焦以及核燃料加工业 2.5 1.5 有色金属冶炼以及压延加工业 3 1 黑色金属冶炼以及压延加工业 2 1 化学原料及化学制品制造业 2.5 2 纺织业 1 2 皮革、毛皮、羽毛(绒)及其制品业 1 2 金属制品业 1.5 1 其他行业 0.2 1 矿区开采污染源 煤炭、石油以及天然气开采业 1.5 1.5 黑色金属矿采选业 2 1 污染源类型 释放可能性 Li评分 工业污染源 2011年之后建厂 0.2 1998—2011年间建厂 0.6 1998年之前建厂 1 矿区开采污染源 停产,矿井已回填 0.1 停产,矿井未回填 0.5 在产 0.7 污染源类型 污染物释放量 Qi评分 工业污染源/m3·a−1 ≤1 1 (1,50] 2 (50,100] 3 (100,300] 4 (300,500] 6 (500,1 000] 9 >1 000 12 矿区开采污染源 小型 3 中型 6 大型 9 表 3 地下水脆弱性评价因子分级及评分表
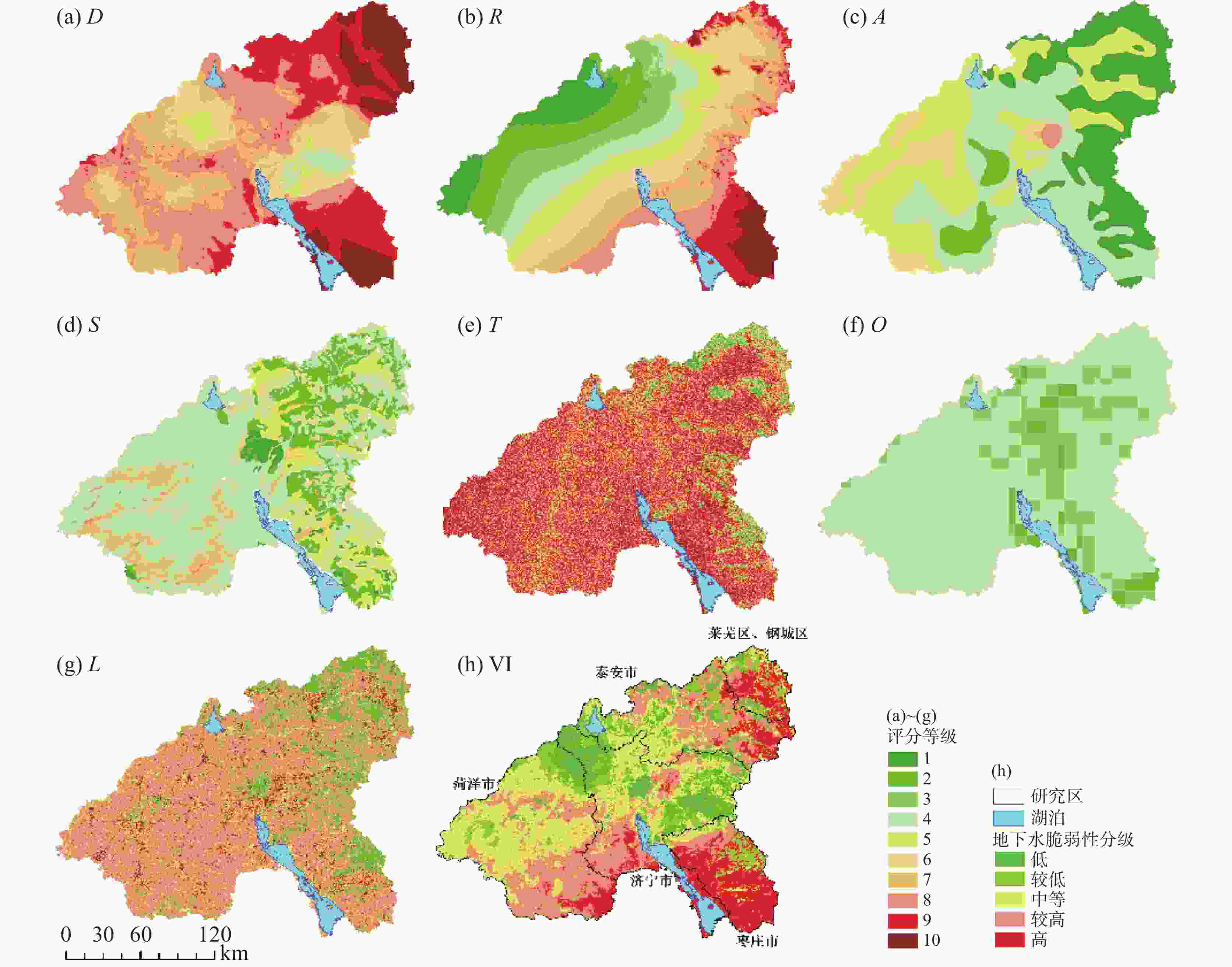
Table 3. Grading and scoring of evaluation factors for groundwater vulnerability
评分 D/m R/mm·a−1 A S T/° O L 1 >25 ≤575 1 黏土 >25 严重约束 戈壁、沙地等 2 20,25 575 600 2 黏壤土 (20,25] 较严重约束 林地、竹林地等 3 15,20 600 625 3 砂质黏土 (16,20] 中等约束 草地 4 12,15 625 650 4 − (12,16] 无/轻微约束 沼泽、滩涂 5 10,12 650 675 5 壤土 (10,12] − 河流、湖泊、坑塘等 6 8,10 675 700 6 砂质黏壤土 (8,10] − 农村居民点 7 6,8 700 725 7 砂质壤土 (6,8] − 城镇居民点 8 4,6 725 750 − − (4,6] − 旱地、水田、水浇地 9 2,4 750 800 − 壤质砂土 (2,4] − 其他建设用地 10 ≤ 2 >800 − 砂土 ≤ 2 − 工业用地、采矿用地 权重 0.307 0.164 0.124 0.086 0.049 0.043 0.227 表 4 生境质量威胁因子属性及敏感程度表
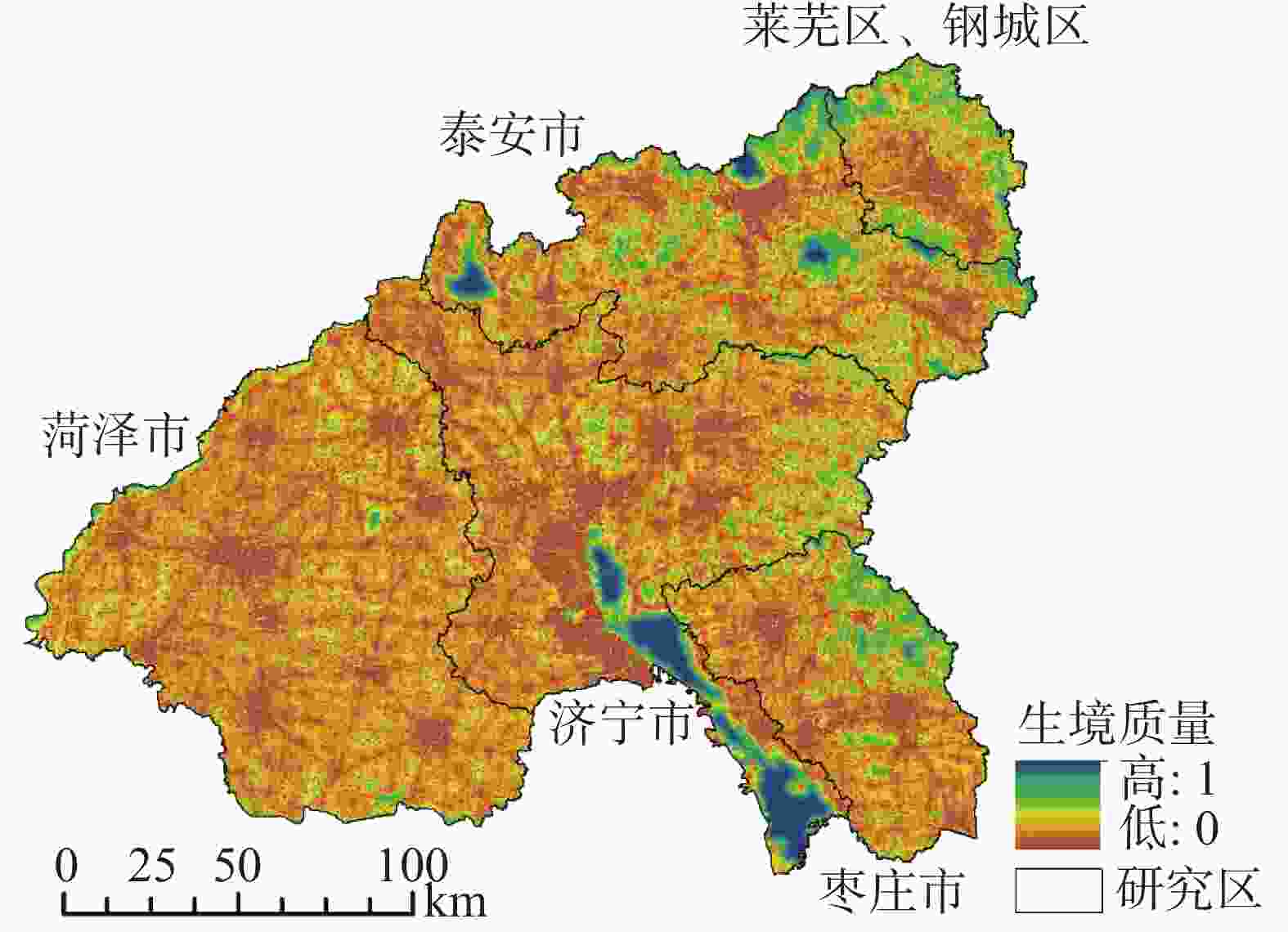
Table 4. Threat factor attributes and sensitivity in terms of habitat quality
威胁因子 耕地 道路用地 农村居民点 城镇居民点 其他建设用地 工业、采矿用地 最大威胁距离 4 3 5 6 8 10 权重 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.8 1 衰减性 linear linear exponential exponential exponential exponential 地类 生境 敏感性 旱地 0.6 0.3 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.6 水田 0.4 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.7 灌木林地 0.9 0.6 0.5 0.65 0.5 0.5 0.6 乔木林地 1 0.8 0.65 0.85 0.75 0.6 0.85 草地 0.7 0.55 0.35 0.5 0.6 0.3 0.7 河流水面 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.3 0.6 湖泊水面 0.9 0.65 0.6 0.65 0.65 0.4 0.75 坑塘水面 0.7 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 内陆滩涂 0.6 0.6 0.3 0.65 0.6 0.5 0.7 沼泽地 0.3 0.65 0.3 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.7 未利用地 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 农村居民点 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 城镇居民点 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 建设用地 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 5 地下水功能价值评价因子分级及评分表
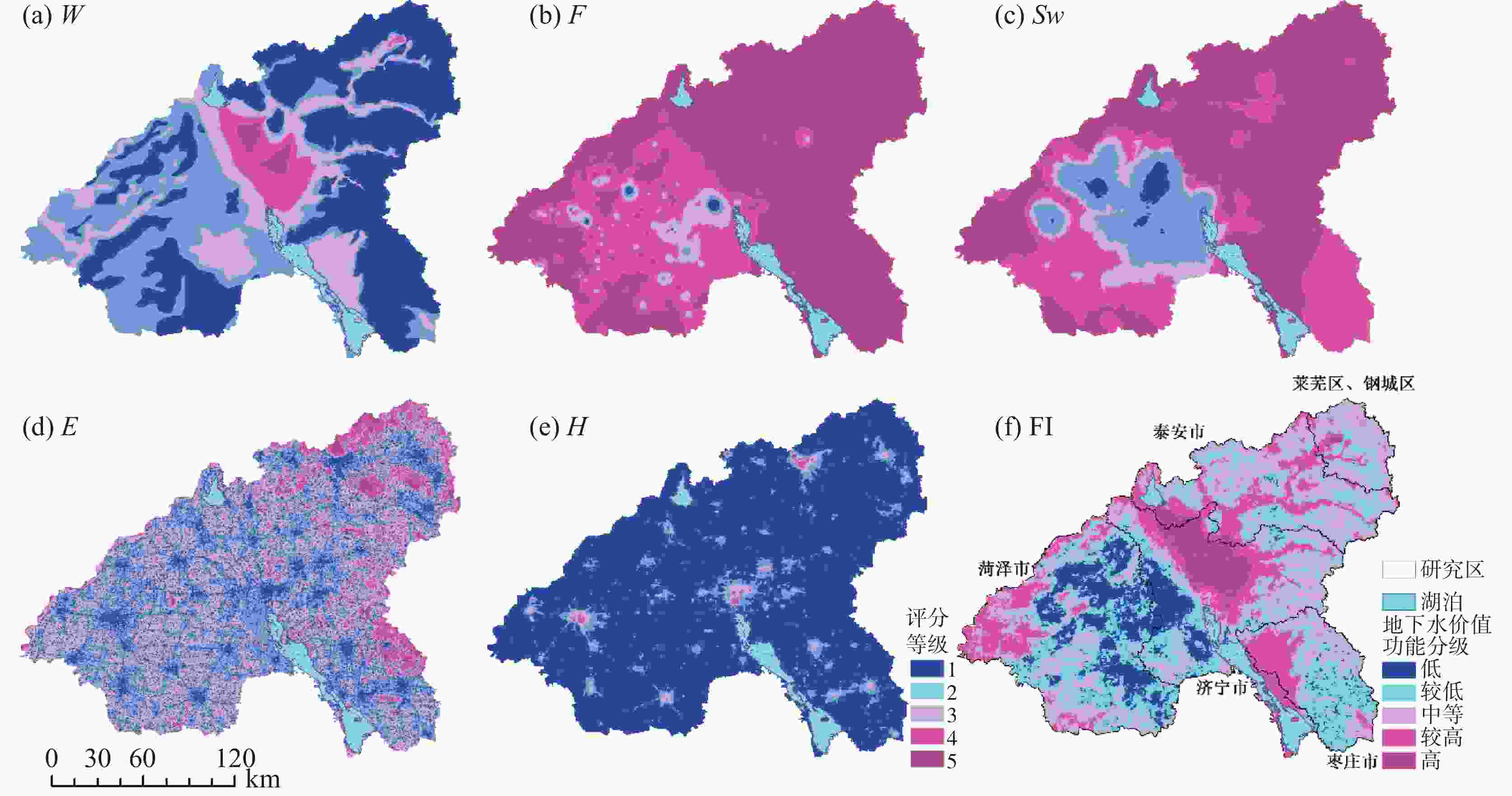
Table 5. Grading and scoring of evaluation factors for groundwater functional value
评分 W/m3·d−1 F/mg·L−1 Sw/ mg·L−1 E H 1 ≤500 >4 >1 000 [0,0.17] ≤4 2 500,1 000 (3,4] (500,1 000] (0.17,0.40] (4,16] 3 1 000 ,3 000(2,3] (350,500] (0.40,0.51] (16,40] 4 3 000,5 000 (1,2] (200,350] (0.51,0.69] (40,80] 5 > 5 000 ≤1 ≤200 (0.69,1.00] >80 权重 0.36 0.18 0.18 0.16 0.12 -
[1] 蒲生彦, 马晋, 杨庆, 马慧, 姜媛, 王嘉瑜, 何鹏. 地下水污染预警指标体系构建方法研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(3):191-197. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2019.03.027PU Shengyan, MA Jin, YANG Qing, MA Hui, JIANG Yuan, WANG Jiayu, HE Peng. A review on construction methods for index system of early warning of groundwater pollution[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(3): 191-197. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2019.03.027 [2] 张毅博, 赵剑斐, 黄涛, 安官平, 彭道平. 基于地统计分析的老旧工业园农田区域地下水重金属空间分布及风险评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(12):258-264. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.12.052ZHANG Yibo, ZHAO Jianfei, HUANG Tao, AN Guanping, PENG Daoping. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland area around old industrial park based on ground statistical analysis[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(12): 258-264. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.12.052 [3] 侯德义. 我国工业场地地下水污染防治十大科技难题[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(9):2015-2025. DOI: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.04.18HOU Deyi, Ten grand challenges for groundwater pollution prevention and remediation at contaminated sites in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(9): 2015-2025. [4] Wu J H, Li P Y, Wang D, Ren X F, Wei M J. Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2020, 26(6): 1603-1621. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2019.1594156 [5] 陈雳华, 张弛, 郑凌云, 付高平, 张蔚. 基于GMS软件的河谷盆地型工业园区地下水污染控制模拟[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(8):1025-1029. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.08.008CHEN Lihua, ZHANG Chi, ZHENG Lingyun, FU Gaoping, ZHANG Wei. Simulation of groundwater pollution control in a valley-basin industrial park based on GMS[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(8): 1025-1029. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.08.008 [6] Zhang Q, Li P, Lyu Q, Ren X F, He S. Groundwater contamination risk assessment using a modified DRATICL model and pollution loading: A case study in the Guanzhong basin of China[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(1): 1-12. [7] 刘治政, 李双, 刘柏含, 张学松, 刘华峰, 彭俊峰, 刘运德. 淄博市刘征水源地西张井群岩溶地下水硫酸盐溯源分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(5):1074-1084.LIU Zhizheng, LI Shuang, LIU Baihan, ZHANG Xuesong, LIU Huafeng, PENG Junfeng, LIU Yunde. Source-tracing of sulfate in groundwater of Xizhang Well Group in the Liuzheng water source area of Zibo City[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(5): 1074-1084. [8] Zwahlen F. Vulnerability and risk mapping for the protection of carbonate (karst) aquifers[M]. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, 2003. [9] Nobre R C M, Rotunno Filho O C, Mansur W J, Nobre M M M, Cosenza C A N. Groundwater vulnerability and risk mapping using GIS, modeling and a fuzzy logic tool[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2007, 94(3-4): 277-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.07.008 [10] 张文强, 滕跃, 唐飞, 王金晓, 许庆宇, 张海林. 山东省肥城断块岩溶水系统地下水水化学特征及演化分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(5):1047-1060, 1084.ZHANG Wenqiang, TENG Yue, TANG Fei, WANG Jinxiao, XU Qingyu, ZHANG Hailin. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of the karst water system in the Feicheng fault block in Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(5): 1047-1060, 1084. [11] 孙才志, 陈相涛, 陈雪姣, 郑德凤. 地下水污染风险评价研究进展[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2015, 35(5):152-161.SUN Caizhi, CHEN Xiangtao, CHEN Xuejiao, ZHENG Defeng, Recent advances in groundwater contamination risk assessment[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2015, 35(5): 152-161. [12] Zhao Y S, Zhang J W, Chen Z, Zhang W H. Groundwater contamination risk assessment based on intrinsic vulnerability, pollution source assessment, and groundwater function zoning[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 2019, 25(7): 1907-1923. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2018.1476965 [13] 高瑜, 张华, 康晓莉, 周俊蓉, 武红梅, 刘海峰, 叶咸. 云南省主要盆地地下水水质监测与变化趋势分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(4):542-552.GAO Yu, ZHANG Hua, KANG Xiaoli, ZHOU Junrong, WU Hongmei, LIU Haifeng, YE Xian. Trend analysis of groundwater quality in major basins of Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(4): 542-552. [14] 唐蕴, 王研, 唐克旺. 吐鲁番市浅层地下水功能区划分[J]. 水资源保护, 2017, 33(2):16-21, 78.TANG Yun, WANG Yan, TANG Kewang. Functional division of shallow groundwater in Turpan City[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(2): 16-21, 78. [15] 古兵华. 格尔木地区生态服务功能价值评估及其对地下水资源管理的意义[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2018.GU Binghua, Valuation of ecosystem services in Golmud area and its significance to groundwater resources management[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. [16] Zhang J J, Zhai Y Z, Xue P W, Huan H, Zhao X B, Teng Y G, Wang J S. A GIS-based LVF model for semiquantitative assessment of groundwater pollution risk: A case study in Shenyang, NE China[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 2017, 23(2): 276-298. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2016.1245099 [17] Huan H, Zhang B T, Kong H M, Li M X, Wang W, Xi B D, Wang G Q. Comprehensive assessment of groundwater pollution risk based on HVF model: A case study in Jilin City of Northeast China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 628-628: 1518-1530. [18] 闫志雲, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 孙英, 马常莲. 叶尔羌河流域平原区地下水污染风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6):3237-3246. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202207245YAN Zhiyun, ZENG Yanyan, ZHOU Jinlong, SUN Ying, MA Changlian. Groundwater pollution risk assessment in plain area of the Yarkant river basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(6): 3237-3246. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202207245 [19] Aller L, Thornhill J. DRASTIC: A standardized system for evaluating ground water pollution potential using hydrogeologic settings[M]. Washington, D.C.: Robert S. Kerr Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency, 1987. [20] 刘宇, 兰双双, 张永祥, 李芳春, 侯树楷. 基于空间自相关的地下水脆弱性时空演变[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10):4236-4244. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201704052LIU Yu, LAN Shuangshuang, ZHANG Yongxiang, LI Fangchun, HOU Shukai. Spatio-temporal evolution of groundwater vulnerability based on spatial autocorrelation[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4236-4244. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201704052 [21] 王涛, 徐明. 天山北坡经济带东段浅层地下水固有脆弱性评价[J]. 水资源保护, 2017, 33(1):41-45.WANG Tao, XU Ming. Vulnerability assessment of shallow groundwater in eastern section of Northern Tianshan Mountain Economic Belt[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(1): 41-45. [22] 吴建强, 王敏, 黄沈发, 龚静香, 郭晋川, 陈建国, 阮俊杰, 蔡卓尔, 鄢忠纯. 平原河网区地下水污染风险评价体系及其应用[J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(4):55-62.WU Jianqiang, WANG Min, HUANG Shenfa, GONG Jingxiang, GUO Jinchuan, CHEN Jianguo, RUAN Junjie, CAI Zhuoer, YAN Zhongchun. Risk assessment system of groundwater pollution in plain river network area and its application[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2019, 35(4): 55-62. [23] 孙才志, 奚旭, 董璐. 基于ArcGIS的下辽河平原地下水脆弱性评价及空间结构分析[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(20):6635-6646.SUN Caizhi, XI Xu, DONG Lu. An Arc GlS-based analysis of groundwater spatial structure and groundwater vulnerability in the lower reaches of the Liaohe river plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(20): 6635-6646. [24] 陈钰頔, 李妍颖, 叶忠, 聂宇晗, 覃杰, 刘国. 基于改进DRASTIC模型的冲洪积扇地下水脆弱性评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(12):194-202. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.1665.21.338CHEN Yudi, LI Yanying, YE Zhong, NIE Yuhan, QIN Jie, LIU Guo. Groundwater vulnerability assessment in alluvial-prouvial fan area based on the improved DRASTIC model[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(12): 194-202. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.1665.21.338 [25] 袁利, 李婷. 基于改进的DRASTIC方法对宿州市城区中深层承压水脆弱性评价[J]. 地质论评, 2023, 69(6):2195-2202. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2023.08.015YUAN Li, LI Ting. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability in urban district of Suzhou, northern Anhui, based on the improved DRASTIC[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69(6): 2195-2202. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2023.08.015 [26] 朱飞, 熊丽君, 吴建强, 赵诣, 黄静, 韦继雄, 林匡飞. 基于改进DRASTIC模型的平原河网地区地下水脆弱性评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(2):187-193. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.02.028ZHU Fei, XIONG Lijun, WU Jianqiang, ZHAO Yi, HUANG Jing, WEI Jixiong, LIN Kuangfei. Groundwater Vulnerability assessment in plain river network areas based on the improved DRASTIC model[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(2): 187-193. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.02.028 [27] 侯宇徽, 窦筱艳, 保善磊, 高海鹏, 杨悦锁, 文一, 王明铭. 基于DRASTIC模型优化的地下水污染风险评价研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2024, 44(2):227-236.HOU Yuhui, DOU Xiaoyan, BAO Shanlei, GAO Haipeng, YANG Yuesuo, WEN Yi, WANG Mingming. Assessment of groundwater contamination risk based on improved DRASTIC model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2024, 44(2): 227-236. [28] Wu W Y, Liao R K, Hu Y Q, Wang H, Liu H L, Yin S Y. Quantitative assessment of groundwater pollution risk in reclaimed water irrigation areas of Northern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 261: 114173. [29] 刘远书, 籍国东, 罗忠新, 罗敏. 南水北调东线治污对山东段的环境与经济影响:基于EKC曲线理论的实证分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(10):73-81.LIU Yuanshu, JI Guodong, LOU Zhongxin. LUO Min. Pollution control effects of the east route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on the environment and economy of Shandong: An empirical study based on the EKC curve[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2020, 30(10): 73-81. [30] 马越. 南水北调工程对山东省调蓄水库水质影响及风险控制技术研究[R]. 山东省调水工程运行维护中心棘洪滩水库管理站, 2021-09-23. [31] 杨戈芝, 袁卫宁, 马海珍, 朱世峰, 段磊, 闫姿呈, 靳博文. 白洋淀流域地下水质现状及主要影响因素[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 2021, 52(4):162-170. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2021.04.017YANG Gezhi, YUAN Weining, MA Haizhen, ZHU Shifeng, DUAN Lei, YAN Zicheng, JIN Bowen. Status quo of groundwater quality in Baiyangdian lake watershed and its main influencinc factors[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2021, 52(4): 162-170. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2021.04.017 [32] Li X Y, Wu H, Qian H. Groundwater contamination risk assessment using intrinsic vulnerability, pollution loading and groundwater value: A case study in Yinchuan plain, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(36): 45591-45604 doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10221-4 [33] Amiri V, Kamrani S, Ahmad A, Bhattacharya P, Mansoori J. Groundwater quality evaluation using Shannon information theory and human health risk assessment in Yazd Province, central plateau of Iran[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(1): 1108-1130. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10362-6 [34] 刘景超. 岩溶区地下水污染风险评价[D]. 北京:北京工业大学, 2022.LIU Jingchao. Risk assessment of groundwater pollution in karst area[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2022. [35] Yu S, Ding H H, Zeng Y F. Evaluating water-yield property of karst aquifer based on the AHP and CV[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 3308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07244-x [36] 吴泽华. 改进DRASTIC模型在平潭岛地下水脆弱性评价中的应用[J]. 水利科技, 2021(1):1-4.WU Zehua. Application of improved DRASTIC model to groundwater vulnerability assessment of Pingtan Island[J]. Hydraulic Science and Technology, 2021(1): 1-4. [37] 陈相涛. 下辽河平原浅层地下水污染风险评价及空间热点分析[D]. 大连:辽宁师范大学, 2016.CHEN Xiangtao. Evaluation and hotspots analysis of shallow groundwater contamination risk in the lower reach of the Liaohe river plain[D]. Dalian: Liaoning Normal University, 2016. [38] 张廷, 胡玉柱, 胡海辉, 雷婷婷. 基于PLUS-InVEST模型的哈尔滨市土地利用及生境质量预测[J/OL]. 环境科学, 1-20[2023-12-27]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202308212.ZHANG Ting, HU Yuzhu, HU Haihui, LEI Tingting. Prediction of land use and habitat quality in Harbin City based on the PLUS- InVEST mode[J/OL]. Environmental Science, 1-20[2023-12-27]. [39] 程飞飞, 李洪庆, 宋红艳, 陈明慧. 沿海城市陆海生态环境质量综合评价与耦合协调度分析[J/OL]. 生态学报, 2024(9):1-13[2023-12-27]. https://doi.org/10.20103/j.stxb.202307241580.CHENG Feifei, LI Hongqing, SONG Hongyan, CHEN Minghui. Comprehensive evaluation and coupling coordination analysis of land and sea ecological environment quality in coastal cities[J/OL]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024(9): 1-13. [40] 夏哲一, 刘黎明, 袁承程, 魏雪, 黄家嗣, 王怡. 基于社会-生态耦合视角的城市边缘区生境服务评估与分区[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(4):1501-1513.XIA Zheyi, LIU Liming, YUAN Chengcheng, WEI Xue, HUANG Jiashi, WANG Yi. Assessment and zoning of habitat services in urban fringe areas from the perspective of social-ecological coupling[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(4): 1501-1513. [41] 陈世莉, 陈浩辉, 李郇. 夜间灯光数据在不同尺度对社会经济活动的预测[J]. 地理科学, 2020, 40(9):1476-1483. doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.009CHEN Shili, CHEN Haohui, LI Xun. The ability of nighttime imagery in monitoring economic activity in different scales[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 1476-1483. doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.009 [42] 余柏蒗, 王丛笑, 宫文康, 陈佐旗, 施开放, 吴宾, 洪宇辰, 李乔玄, 吴健平. 夜间灯光遥感与城市问题研究:数据、方法、应用和展望[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1):342-364. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211018YU Bailang, WANG Congxiao, GONG Wenkang, CHEN Zuoqi, SHI Kaifang, WU Bin, HONG Yuchen, LI Qiaoxuan, WU Jianping. Nighttime light remote sensing and urban studies: Data, methods, applications, and prospects[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(1): 342-364. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211018 [43] 孟滢滢, 周思赜, 聂艳, 曾怀文, 于婧. POI和夜间灯光融合数据用于城乡结合部空间划定的研究:以武汉市为例[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 1-25[2023-12-27]. https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20220597MENG Yingying, ZHOU Size, NIE Yan, ZENG Huaiwen, YU Jing. Spatial delimitation of the urban-rural fringe based on POI and nighttime light data: A case study of Wuhan City[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 1-25. [44] 白凡, 周金龙, 周殷竹, 韩双宝, 孙英. 吐鲁番南盆地平原区地下水污染风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(8):4325-4333. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202210014BAI Fan, ZHOU Jinlong, ZHOU Yinzhu, HAN Shuangbao, SUN Ying. Assessment of groundwater contamination risk in the plain area of southern Turpan basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(8): 4325-4333. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202210014 [45] 刘钰, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 闫志雲, 白凡. 巴里坤-伊吾盆地平原区地下水污染风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(12):6778-6789.LIU Yu, ZENG Yanyan, ZHOU Jinlong, YAN Zhiyun, BAI Fan. Groundwater pollution risk assessment in plain area of Barkol-Yiwu basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(12): 6778-6789. [46] Li H J, Yu X P, Zhang W J, Huan Y, Yu J, Zhang Y. Risk assessment of groundwater organic pollution using hazard, intrinsic vulnerability, and groundwater value, Suzhou City in China[J]. Exposure and Health, 2018, 10(2): 99-115. doi: 10.1007/s12403-017-0248-8 [47] Wang J J, He J T, Chen H H. Assessment of groundwater contamination risk using hazard quantification, a modified DRASTIC model and groundwater value, Beijing Plain, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 432: 216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.005 [48] 贾晓青, 刘建, 罗明明, 周宏. 基于改进的DRASTIC模型对香溪河典型岩溶流域地下水脆弱性评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):255-261. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0427JIA Xiaoqing, LIU Jian, LUO Mingming, ZHOU Hong. Groundwater vulnerability assessment of Xiangxi river karst basin based on modified DRASTIC model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2019, 38(4): 255-261. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0427 -




 下载:
下载: