Structure and application of SWAT-MODFLOW coupling model for surface-groundwater
-
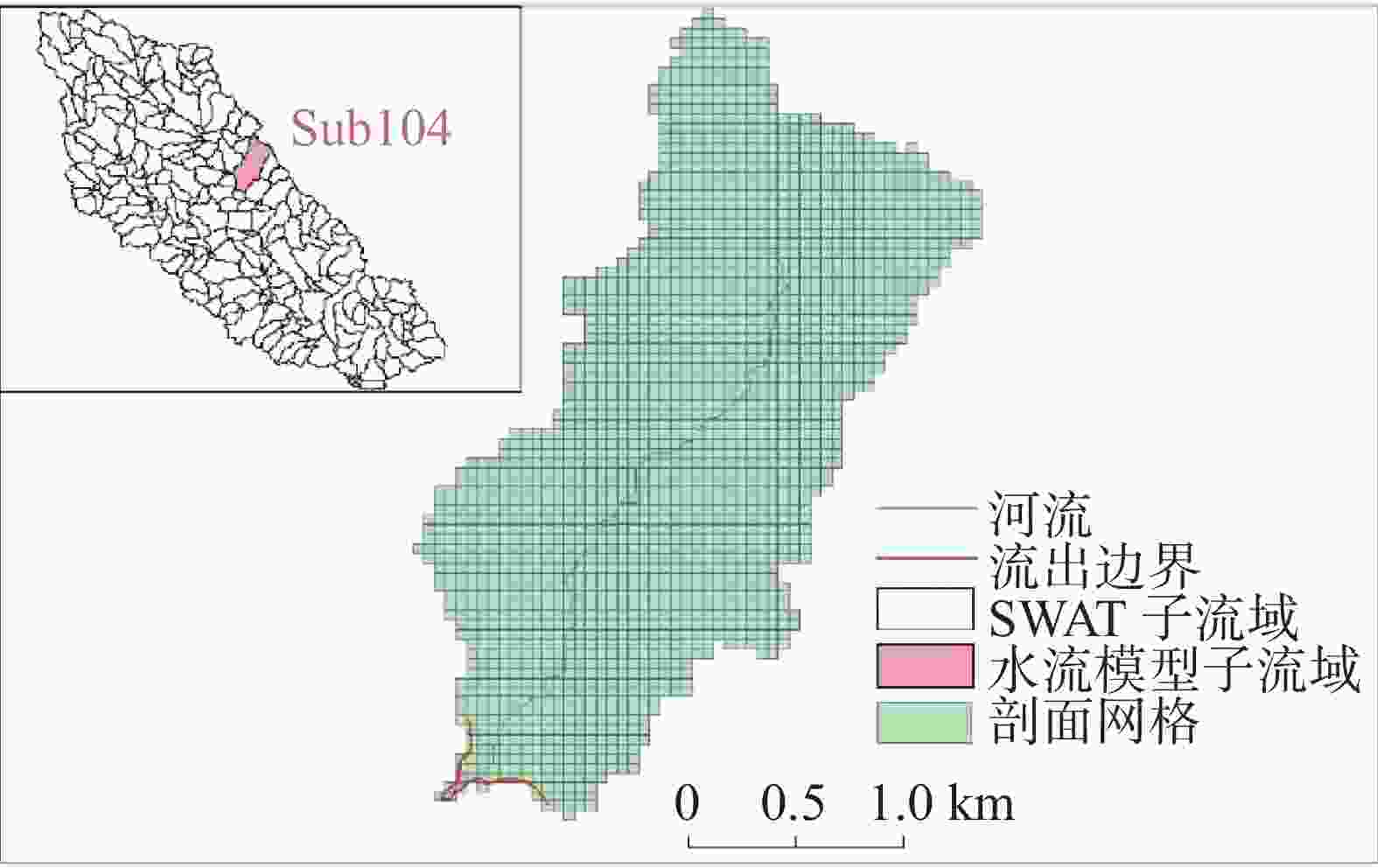
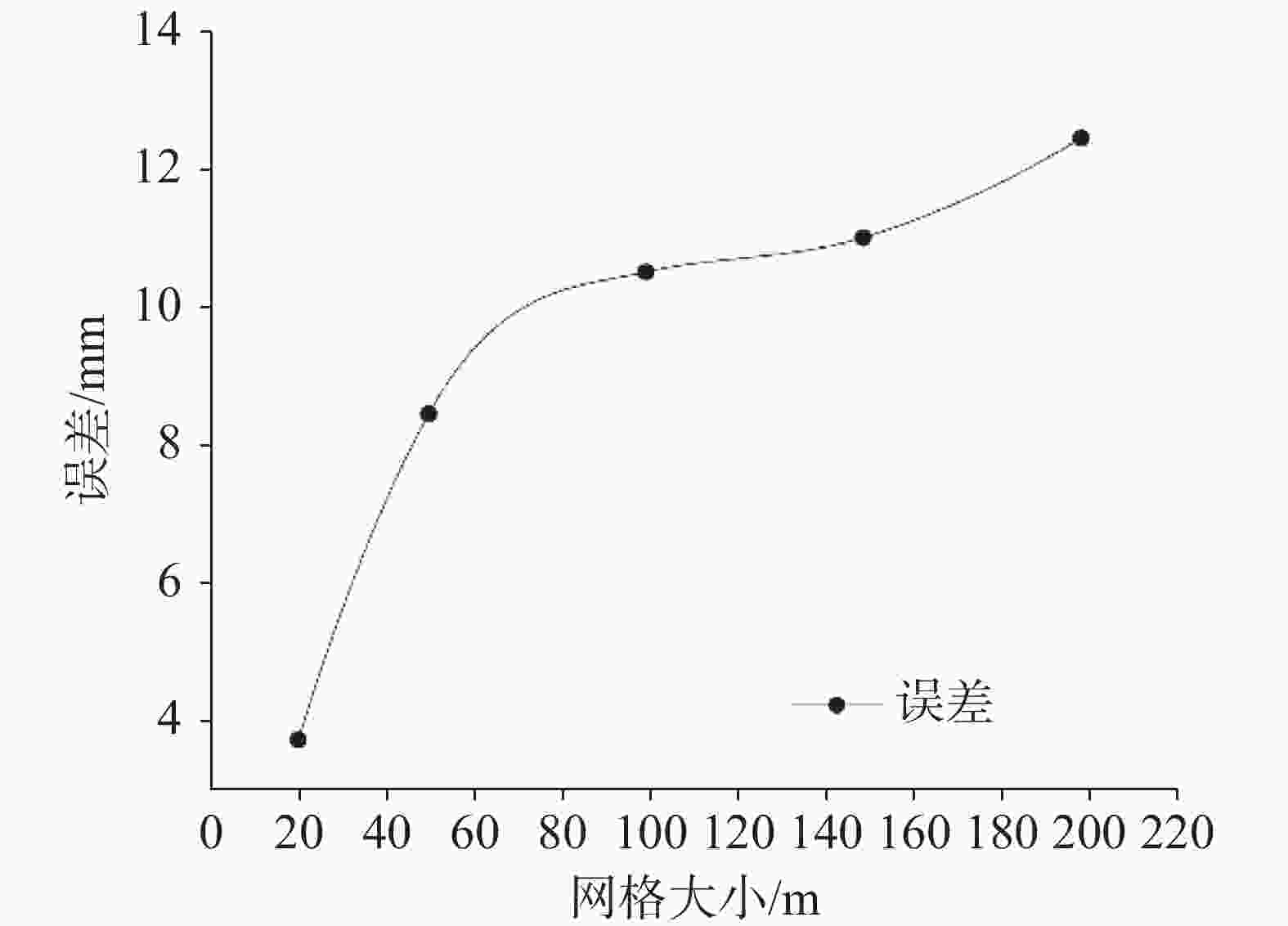
摘要: 为了利用Seonggyu Park和Ryan T.Bailey的SWAT-MODFLOW耦合程序实现地表、地下不同范围模型耦合,同时探究耦合程序输出的以SWAT计算的地下水补给量和以MODFLOW网格计算的补给量之间的差异,以及耦合程序在有关地表地下水研究上的优势。本文以该耦合程序示例模型美国佐治亚州南部小河流域(LRW)为例,选取模型中SWAT划分的104号子流域为边界,用GMS10.4建立地下水流模型,最后将地下水流模型和原SWAT模型进行耦合。研究结果表明:(1)耦合程序能实现以地表分水岭自然边界为范围的SWAT模型与以子流域为边界的小范围MODFLOW模型的耦合,但由于地下水流模型网格边界和子流域边界不能完全匹配,导致MODFLOW以网格计算的地下水降雨补给量和SWAT统计的地下水降雨补给量存在差异,误差随网格变小而变小;(2)耦合后各均衡项发生了变化,河道对地下水的总补给量变为耦合前的15.25%,地下水向河道的总排泄量比耦合前多19.29%,总降雨补给比耦合前多17.07%,总蒸发量是耦合前的3.08倍。经过研究发现耦合模型能更准确的模拟地表地下水文过程,反映降水与地下水、地表水与地下水转化关系。
-
关键词:
- SWAT-MODFLOW /
- 耦合模型 /
- 地表−地下水
Abstract:Surface water and ground water is a unified whole in the water circulation system, and there is a close relationship between them. Especially in the areas where karst surfaces such as drop holes and funnels are developed, surface water and groundwater can form a direct connection. The interactions between surface water and groundwater have been a hot topic in research. A great deal of research has been carried out both nationally and internationally. The SWAT-MODFLOW coupling procedure developed by Seonggyu park and Ryan T. Peley is a beneficial tool for studying surface-groundwater interactions. This coupling procedure establishes the link between the Hydrological Response Unit (HRUs) in SWAT model and the spatial grid in MODFLOW through the ARCGIS platform in order to achieve a loose coupling of the model. A number of applications of this program have been carried out abroad. However, no relevant studies have used this procedure to achieve model coupling in different ranges of surface and subsurface. As far as the actual situation is concerned, often the plains are the focus of extraction and their groundwater dynamic field needs to be detailed delineated. However, the scope of SWAT model covers the overall basin, which is not consistent with the scope of groundwater flow model. Considering the running time and the accuracy of the model, it is necessary to explore the model coupling process in different ranges of surface-groundwater. In this study, the SWAT-MODFLOW coupling program of Seonggyu park and Ryan T. Bailey was used to implement the coupling of models at different scales of the surface and subsurface, and to investigate the differences between the groundwater recharge calculated in SWAT and that calculated in the MODFLOW grid output of the coupling program. Then the advantages of the coupling program for relevant studies on surface water and groundwater were analyzed. Taking this coupling procedure model of the Little River Watershed (LRW) in southern Georgia, USA as an example, this study selected Sub-basin 104 divided by the SWAT in the model as the boundary, and built the groundwater flow model with GMS10.4 based on the data of the original example model. According to the coupling model manual, ARCGIS platform and EXCEL platform, four link files required by the coupling model were completed: swatmf_dhru2grid, swatmf_dhru2hru, swatmf_grid2dhru, and swatmf_river2grid. A coupling model of Sub-basin 104 water flow model and the overall SWAT model was further developed, and the format of the model output results was controlled through its link files. On the basis of calculation results of the model, its multi-year equilibrium condition was calculated in EXCEL to judge its rationality so that the model can be calibrated. After the calibration, the accuracy of each equilibrium item was compared between the coupling model and the independent groundwater flow model. Study results show as follows. (1) The coupling procedure enables the coupling of the SWAT model naturally bounded by the surface watershed with the small-scale MODFLOW model divided by the sub-basin boundary. However, because the grid boundary of the groundwater flow model and that of sub-basin cannot be completely matched, there is a difference between MODFLOW and SWAT in terms of the calculation of rainfall recharge for groundwater. In general, the calculation volume of SWAT is larger than that of MODFLOW grid. The calculations clearly indicate that the error margin becomes smaller as the grid gets smaller because the smaller the grid area is, the more exact the match between the grid and the boundary becomes. (2) Each equilibrium item has changed after coupling. Because the river depth in GMS is taken as the empirical value, and it is taken as the confluence evolution value in SWAT, calculations show that the groundwater recharge of the river before and after the model coupling is significantly different, and the total recharge from the river to the groundwater reduces to 15.25% of that before the coupling. On the other hand, the total discharge from groundwater to river increases 19.29% after coupling. The rainfall recharge of the model before coupling is calculated by infiltration coefficient method, and the groundwater recharge after coupling is the seepage of the soil bottom of the SWAT model. The calculations show that the total rainfall recharge increases 17.07% after coupling. The groundwater evaporation before model coupling is calculated by the Avyanov formula, and the groundwater evaporation after coupling was calculated according to the potential evapotranspiration and the actual evapotranspiration calculated by SWAT. The calculations show that the total evapotranspiration is 3.08 times larger than that before coupling. It is found that the coupling model can simulate the surface-subsurface hydrological process more accurately, and can reflect the relationship between precipitation and groundwater, surface water and groundwater transformation. -
Key words:
- SWAT-MODFLOW /
- coupling model /
- surface-groundwater
-
表 1 SWAT-MODFLOW传递变量说明表
Table 1. Variables passed by SWAT-MODFLOW
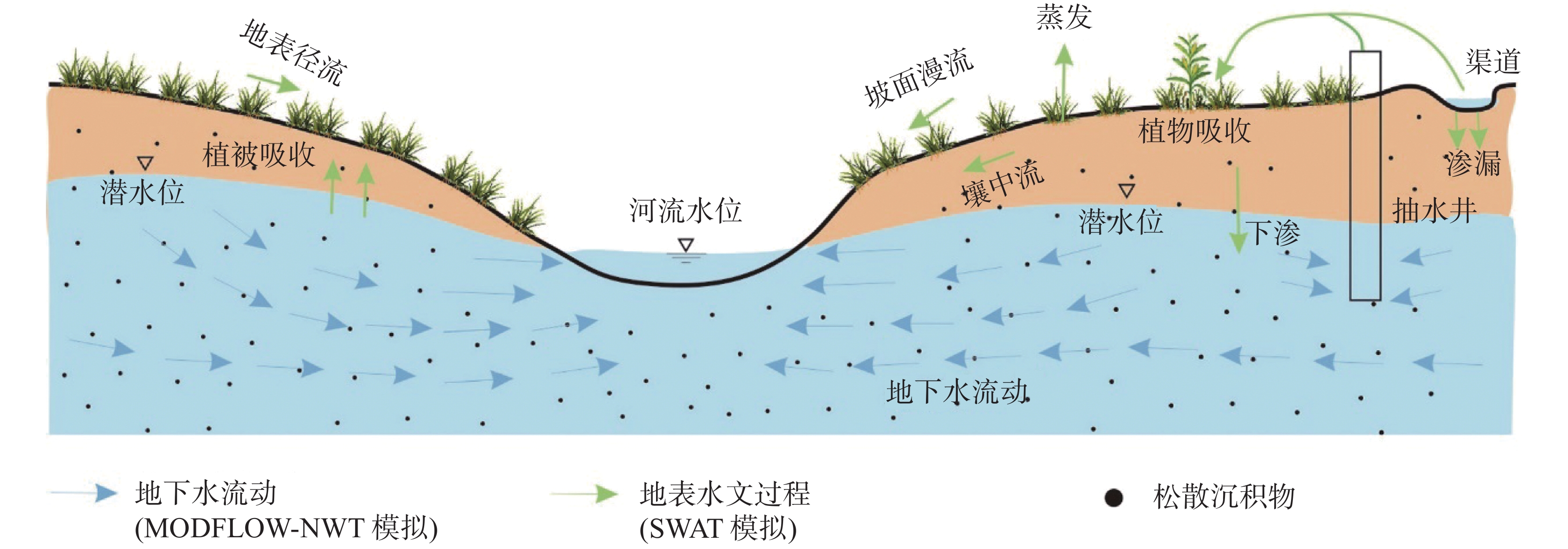
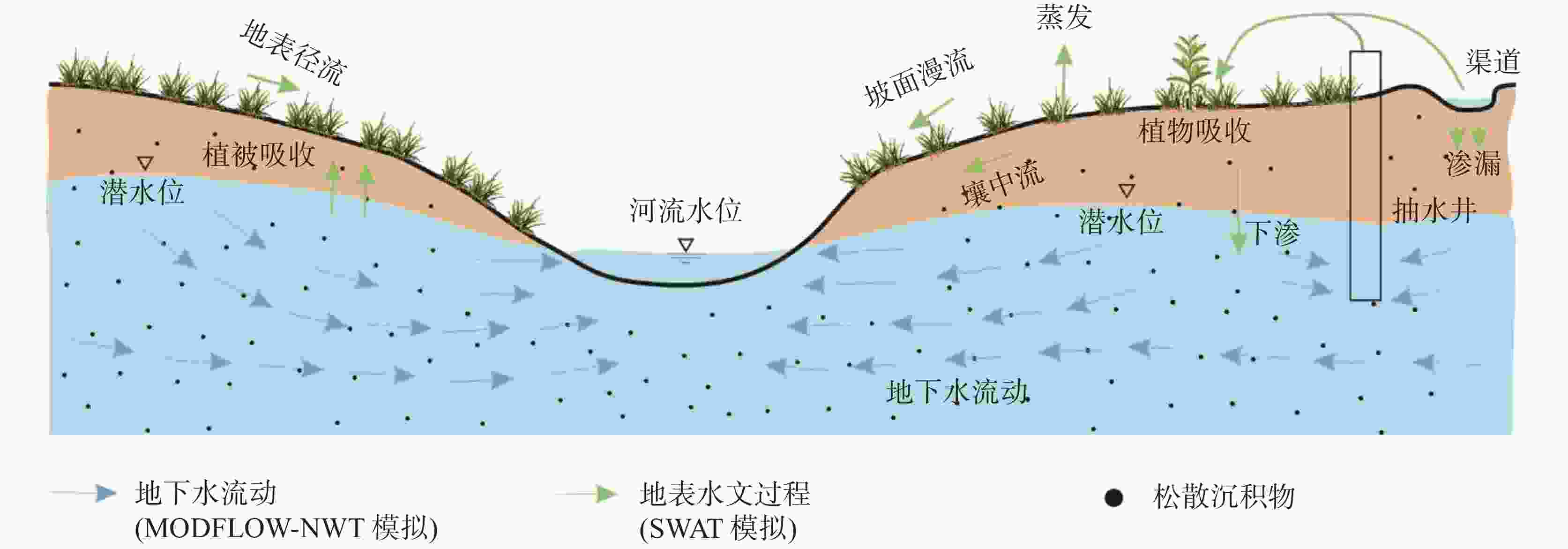
变量 传递方式 说明 潜水的补给量 水文响应单元到地下水流模型
对应活动网格地下水补给由SWAT计算 蒸发 水文响应单元到地下水流模型
对应活动网格SWAT计算的潜在蒸散发和实际蒸
散发的差值由潜水继续蒸发子流域河道的水位 SWAT计算的河道水位到地下
水流模型河流网格地下水流模型的河流网格水位由
SWAT计算的河道水位而定地下水和河流的交换量 地下水流模型河流网格计算结果到
SWAT子流域河道交换量由River包计算后传递给
SWAT模型河道表 2 小河流域土地利用类型
Table 2. Land use types in the small river basin
类型 森林 农田 牧场 湿地 其它 比例/% 65 30 2 2 1 表 3 地下水补给量误差分析列表(单位:mm)
Table 3. Error analysis of groundwater recharge (unit: mm)
组号 网格大小/m 项 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 平均 SWAT 281.92 417.84 148.54 160.65 322.96 229.36 103.80 254.44 231.60 239.01 1 20 MODFLOW 277.01 412.20 146.30 157.71 314.76 228.73 102.64 245.75 232.56 235.30 误差 4.90 5.64 2.24 2.94 8.20 0.64 1.16 8.69 −0.96 3.72 2 50 MODFLOW 271.41 403.84 143.32 154.49 308.43 224.15 100.54 240.94 227.76 230.54 误差 10.51 14.00 5.22 6.16 14.53 5.21 3.26 13.50 3.85 8.47 3 100 MODFLOW 269.05 400.40 142.06 152.90 305.76 222.08 99.51 238.67 225.79 228.47 误差 12.86 17.44 6.47 7.76 17.20 7.28 4.28 15.78 5.81 10.54 4 150 MODFLOW 268.40 399.20 141.52 153.27 304.61 221.38 99.67 238.34 225.41 227.98 误差 13.52 18.64 7.02 7.38 18.35 7.99 4.13 16.10 6.19 11.04 5 200 MODFLOW 266.75 396.80 141.05 152.21 302.59 220.05 99.17 235.66 224.41 226.52 误差 15.17 21.04 7.49 8.44 20.37 9.31 4.63 18.78 7.19 12.49 6 200 MODFLOW 283.49 418.63 150.37 158.93 320.69 236.38 104.96 238.88 241.06 239.27 误差 0.69 0.52 −0.14 0.86 1.37 −0.86 0.15 0.93 0.04 0.40 表 4 耦合前地下水流模型均衡表(单位:104 m3)
Table 4. Equalization table of groundwater flow model before coupling (unit: 104 m3)
项 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 流入 河流 6.00 5.39 5.42 3.96 4.46 4.47 4.05 4.44 5.06 4.90 4.19 5.15 5.28 4.61 降雨 95.51 106.89 99.73 132.19 105.53 109.14 141.48 80.55 94.97 119.34 105.56 77.89 105.85 101.00 总流入 101.51 112.28 105.15 136.15 109.99 113.61 145.53 84.99 100.03 124.24 109.76 83.04 111.14 105.60 流出 边界 36.60 36.50 36.5 36.50 36.60 36.50 36.50 36.50 36.60 36.50 36.50 36.50 36.50 36.50 河流 60.57 65.39 64.70 84.31 76.81 75.97 85.22 79.15 67.58 68.91 80.96 65.22 64.40 72.41 蒸发 0.34 0.37 0.36 0.49 0.44 0.43 0.49 0.45 0.37 0.38 0.46 0.36 0.36 0.41 总流出 97.51 102.26 101.57 121.30 113.85 112.90 122.21 116.10 104.55 105.80 117.92 102.08 101.36 109.32 均衡 4.00 10.02 3.58 14.85 −3.86 0.71 23.32 −31.11 −4.52 18.44 −8.16 −19.05 9.77 −3.71 总均衡 14.28 表 5 耦合后地下水流模型均衡表(单位:104m3)
Table 5. Equilibrium table of groundwater flow model after coupling (unit: 104m3)
项 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 流入 河流 0.75 0.99 0.76 0.70 0.57 0.65 0.64 0.43 0.70 0.93 0.54 0.72 1.11 0.78 降雨 102.80 109.61 87.05 214.65 135.54 141.00 209.76 74.45 80.33 160.17 116.36 52.15 125.39 118.29 总流入 103.54 110.59 87.82 215.35 136.12 141.65 210.39 74.88 81.02 161.1 116.90 52.87 126.50 119.07 流出 边界 36.60 36.5 36.50 36.50 36.60 36.50 36.50 36.50 36.60 36.50 36.50 36.50 36.60 36.50 河流 81.98 59.20 71.96 117.54 101.81 100.52 118.00 107.79 70.73 70.99 107.99 60.90 55.20 82.76 蒸发 1.05 0.66 1.10 1.92 1.50 1.57 1.61 1.83 0.99 0.89 1.82 0.81 0.68 1.23 总流出 119.62 96.36 109.57 155.96 139.91 138.58 156.11 146.12 108.32 108.38 145.73 98.21 92.49 120.49 均衡 −16.08 14.24 −21.75 59.39 −3.80 3.06 54.28 −71.24 −27.29 52.72 −28.82 −45.34 34.01 −1.42 总均衡 1.96 -
[1] 闫红飞, 王船海, 文鹏. 分布式水文模型研究综述[J]. 水电能源科学, 2008, 26(6):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2008.06.001YAN Hongfei, WANG Chuanhai, WEN Peng. Overview of studies on distributed hydrological model[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2008, 26(6):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2008.06.001 [2] 吕清华. SWAT模型对农业面源污染模拟的适用性分析[J]. 云南水力发电, 2022, 38(2):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3951.2022.02.013LV Qinghua. Applicability analysis of SWAT model to agricultural non-point source pollution simulation[J]. Yunnan Water Power, 2022, 38(2):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3951.2022.02.013 [3] Saha G K, Cibin R, Elliott H A, Elliott H A, Preisendanz H E. Toward a robust land suitability framework for manure management: Modeling impacts and evaluating biophysical characteristics[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2022, 58(3): 435-452. [4] 魏健, 潘兴瑶, 孔刚, 白涛, 黄强, 李波, 马盼盼. 基于生态补水的缺水河流生态修复研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2020, 31(1):64-69, 76.WEI Jian, PAN Xingyao, KONG Gang, BAI Tao, HUANG Qiang, LI Bo, MA Panpan. Study on ecological restoration of water-deficient rivers based on ecological water supplement method[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2020, 31(1):64-69, 76. [5] 陈栋, 梁敏, 仇春光, 王颖聪, 蒋坤. 基于水质模拟分析的生态补水方案研究[J]. 人民长江, 2018, 49(Suppl.1):34-37.CHEN Dong, LIANG Min, CHOU Chunguang, WANG Yingcong, JIANG Kun. Ecological water supplement solution based on water quality simulation[J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(Suppl.1):34-37. [6] 焦丽君, 刘瑞民, 王林芳, 党晋华, 肖艳艳, 夏星辉. 基于SWAT模型的汾河流域生态补水研究[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(14): 5778-5788JIAO Lijun, LIU Ruimin, WANG Linfang, DANG Jinhua, XIAO Yanyan, XIA Xinghui. Study on ecological water supplement in Fenhe river basin based on SWAT model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(14): 5778-5788. [7] 卜玉. 基于SWAT模型的中长期洪水径流预测研究[J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2022, 50(4): 165-168, 224.PU Yu. Study on medium and long term flood runoff prediction based on SWAT model[J]. Heilongjiang Hydraulic Science and Technology, 2022, 50(4): 165-168, 224. [8] Sushanth K, Sandeep H, Rao B K. Assessment of inflows to Rallapadu reservoir from catchment area using SWAT Model[J]. Indian Journal of Ecology, 2020, 47(11). [9] 刘家威, 蔡宏, 郑婷婷, 唐敏. 基于SWAT模型的赤水河流域径流年内分配特征及其对降水的响应研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(3):180-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.3.stbctb202203024LIU Jiawei, CAI Hong, ZHENG Tingting, TANG Min. Annual distribution characteristics of Chishui river watershed runoff and its response to precipitation based on SWAT model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(3):180-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.3.stbctb202203024 [10] 邰理想, 饶文波, 檀涛, 谭红兵, 姜三元, 张西营. 基于格尔木河流域的SWAT模型水文特征情景模拟研究[J]. 水文, 2023, 43(2): 46-51.TAI Lixiang, RAO Wenbo, TAN Tao, TAN Hongbin, JIANG Sanyuan, ZHANG Xiying. Scenario simulation research on hydrological characteristics of the Golmud river basin based on SWAT model[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2023, 43(2): 46-51. [11] Luo Z, Shao Q. A modified hydrologic model for examining the capability of global gridded PET products in improving hydrological simulation accuracy of surface runoff, streamflow and baseflow[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022:127960. [12] Khadka A. Runoff modeling using SWAT Model in Little Wabash river watershed, Illinois[D]. Edwardsville, USA: Southern Illinois University at Edwardsville, 2022. [13] 胡倩, 王军霞, 刘世强, 吴嘉铃, 唐仲华, 成建梅. 基于SWAT模型的洞庭湖平原水资源量计算[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(3):244-252. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20210444HU Qian, WANG Junxia, LIU Shiqiang, WU Jialing, TANG Zhonghua, CHENG Jianmei. Calculation of water resources in Dongting lake plain based on SWAT model[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(3):244-252. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20210444 [14] 陈沛源, 李金文, 俞巧. 基于 SWAT 模型的泾河流域地下水分布特征与水资源评价[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(12):102-109, 126.CHEN Peiyuan, LI Jinwen, YU Qiao. Evaluation groundwater resource and its distribution in Jinghe basin using the SWAT model[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(12):102-109, 126. [15] 孙振权, 魏涛, 洪梅. 基于SWAT模型的最佳管理措施对伊逊河流域水沙的影响研究[J]. 世界地质, 2022, 41(4): 914-925.SUN Zhenquan, WEI Tao, HONG Mei. Impact of best management practices on water and sediment in Yixun river basin based on SWAT model[J]. Global Geology, 2022, 41(4): 914-925. [16] 曹灿, 孙瑞, 吴志祥, 李茜. 基于SWAT模型的南渡江流域土地利用/覆被变化的径流响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(4):167-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2022.4.stbcyj202204024CAO Can, SUN Rui, WU Zhixiang, LI Xi. Responses of streamflow to land use/cover changes in Nandu river basin based on SWAT model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(4):167-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2022.4.stbcyj202204024 [17] 严芳芳. Visual Modflow在水资源论证中的应用探讨[J]. 山东水利, 2021(5):44-45.YAN Fangfang. The discussion on the application of Visual Modflow in water resources argumentation[J]. Shandong Water Resources, 2021(5):44-45. [18] 温海燕, 吕昊楠. 基于Visual MODFLOW的丰南区北刘堼水源地地下水位预测[J]. 河南科技, 2021, 40(20):13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2021.20.013WEN Haiyan, LV Haonan. Groundwater level prediction of the Beiliuheng water source area in Fengnan district based on Visual MODFLOW[J]. Henan Science Technology, 2021, 40(20):13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2021.20.013 [19] 于红梅, 张楠, 燕艳, 李莉莉. 基于ModFlow对地下水资源量的计算[J]. 内蒙古水利, 2018(5):50-51. [20] Mondal N C, Singh V S. Mass transport modeling of an industrial belt using Visual MODFLOW and MODPATH: A case study[J]. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 2009, 2(1):1-19. [21] 何浩, 张强, 张金林, 冯杰, 李威龙, 王志鹏. 基于Visual Modflow研究武隆–广杨深层岩溶水径流特征[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术, 2022, 58(2):22-27, 34. [22] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 邵景力, 易连兴, 王喆. 基于MODFLOW的岩溶管道水流模拟方法探讨与应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3):346-351. doi: 10.11932/karst20170308ZHAO Liangjie, XIA Riyuan, YANG Yang, SHAO Jingli, YI Lianxing, WANG Zhe. Discussion and application of simulation methods for karst conduit flow based on MODFLOW[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3):346-351. doi: 10.11932/karst20170308 [23] 杨杨, 唐建生, 苏春田, 潘晓东, 赵良杰. 岩溶区多重介质水流模型研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(4):419-424. doi: 10.11932/karst20140405YANG Yang, TANG Jiansheng, SU Chuntian, PAN Xiaodong, ZHAO Liangjie. Research advances on multi-medium flow model for karst aquifers[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(4):419-424. doi: 10.11932/karst20140405 [24] 杨郑秋, 杨杨, 邵景力, 苏春田, 崔亚莉, 罗飞. 基于MODFLOW-CFP的岩溶水模型降雨非线性入渗补给研究:以湖南省香花岭地区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):691-695.YANG Zhengqiu, YANG Yang, SHAO Jingli, SU Chuntian, CUI Yali, LUO Fei. Study on non-linear rainfall infiltration recharge of numerical karst water model based on MODFLOW-CFP: A case study of Xianghualing area, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5):691-695. [25] 李星宇, 南天, 王新娟, 李鹏, 谢振华, 邵景力. 数值模拟方法在隐伏岩溶水源地保护区划分及污染治理中的应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(3):280-287. doi: 10.11932/zgyr20140303LI Xingyu, NAN Tian, WANG Xinjuan, LI Peng, XIE Zhenhua, SHAO Jingli. Application of the numerical simulation method in concealed karst wellhead for protection area delimitation and contamination prevention[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(3):280-287. doi: 10.11932/zgyr20140303 [26] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 夏日元, 王莹. 珠江流域岩溶地下河分布特征与影响因素研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(4): 562-576.YANG Yang, ZHAO Liangjie, XIA Riyuan, WANG Ying. Distribution and influencing factors of karst underground rivers in the Pearl River Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(4): 562-576. [27] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 潘晓东, 夏日元, 曹建文. 西南岩溶山区地下水资源评价方法对比研究:以寨底地下河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1):111-123.YANG Yang, ZHAO Liangjie, PAN Xiaodong, XIA Riyuan, CAO Jianwen. Comparative study on evaluation methods of groundwater resources in karst area of Southwest China: Taking Zhaidi underground river basin as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1):111-123. [28] 徐中平, 周训, 崔相飞, 拓明明, 王昕昀, 张颖. 岩溶区地下水数值模拟研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):475-483.XU Zhongping, ZHOU Xun, CUI Xiangfei, TUO Mingming, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Ying. Research advances of numerical simulation of groundwater in karst areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4):475-483. [29] 姜光辉. 融合生态学和提升岩溶水数值模拟技术的国际前沿研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(1):1-4. doi: 10.11932/karst201601y01JIANG Guanghui. The research progress and developing tendency of karst water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(1):1-4. doi: 10.11932/karst201601y01 [30] 张琳琳, 崔亚莉, 梁桂星, 梁灵君, 王晓阳. SWAT-MODFLOW耦合模型在地下水量均衡分析中的应用[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2020, 18(6): 176-183.ZHANG Linlin, CUI Yali, LIANG Guixing, LIANG Lingjun, WANG Xiaoyang. Application of SWAT-MODFLOW coupling model in groundwater balance analysis[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2020, 18(6): 176-183. [31] Yifru B A, Chung I M, Kim M G, Chang S W. Assessing the effect of land/use land cover and climate change on water yield and groundwater recharge in East African Rift Valley using integrated model[J]. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 2021, 37:100926. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100926 [32] 王蕾. 基于SWAT-MODFLOW的变化环境下渠井结合灌区地下水循环特征研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017.WANG Lei. Study on characteristics of groundwater circulation in canal-well combined irrigation area under changing environment based on SWAT-MODFLOW model[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2017. [33] 吴德丰. 基于SWAT-MODFLOW的灌区土壤水与地下水转化特征研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2021.WU Defeng. Assessment of water exchange between soil water and groundwater in irrigation area based on SWAT-MODFLOW[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2021. [34] 周铮. 基于SWAT-MODFLOW模型的北山水库流域地表–地下水耦合模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021.ZHOU Zheng. Coupling simulation of surface water and groundwater in Beishan reservoir watershed based on SWAT-MODFLOW[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2021. [35] Jafari T, Kiem A S, Javadi S, Nakamura T, Nishida K. Using insights from water isotopes to improve simulation of surface water-groundwater interactions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 798:149253. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149253 [36] Bailey R T, Wible T C, Arabi M, Records R M, Ditty J. Assessing regional-scale spatio-temporal patterns of groundwater-surface water interactions using a coupled SWAT-MODFLOW model[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2016, 30(23):4420-4433. [37] 康燕楠. 基于SWAT-MODFLOW的多尺度干旱时段水资源优化配置[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021.KANG Yannan. Multi-scale optimal allocation of water resources in drought periods based on SWAT-MODFLOW[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021. [38] Petpongpan C, Ekkawatpanit C, Bailey R T, Kositgittiwong D. Improving integrated surface water-groundwater modelling with groundwater extraction for water management[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2021, 66(10):1513-1530. doi: 10.1080/02626667.2021.1948549 [39] 张洪波, 支童, 卫星辰, 党池恒, 夏岩, 高文冰. 基于SWAT-MODFLOW的黄河中游区径流过程模拟及对黄土高原变绿的响应[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(6):1-10.ZHANG Hongbo, ZHI Tong, WEI Xingchen, DANG Chiheng, XIA Yan, GAO Wenbing. Simulation of runoff process in the middle Yellow River based on SWAT-MODFLOW and its response to the greening of the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(6):1-10. [40] Frederiksen R R, Molina Navarro E. The importance of subsurface drainage on model performance and water balance in an agricultural catchment using SWAT and SWAT-MODFLOW[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 255:107058. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107058 [41] Bailey R, Rathjens H, Bieger K, Chaubey I, Arnold J. SWATMOD-Prep: Graphical user interface for preparing coupled SWAT-MODFLOW simulations[J]. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2017, 53(2):400-410. doi: 10.1111/1752-1688.12502 [42] Bosch D D, Sheridan J M, Lowrance R R, Hubbard R K, Strickland T C, Feyereisen G W, Sullivan D G. Little river experimental watershed database[J]. Water Resources Research, 2007, 43(9): W09470.1-W09470.6. -




 下载:
下载: