Modelling karst spring flow in Southwest China based on machine learning
-
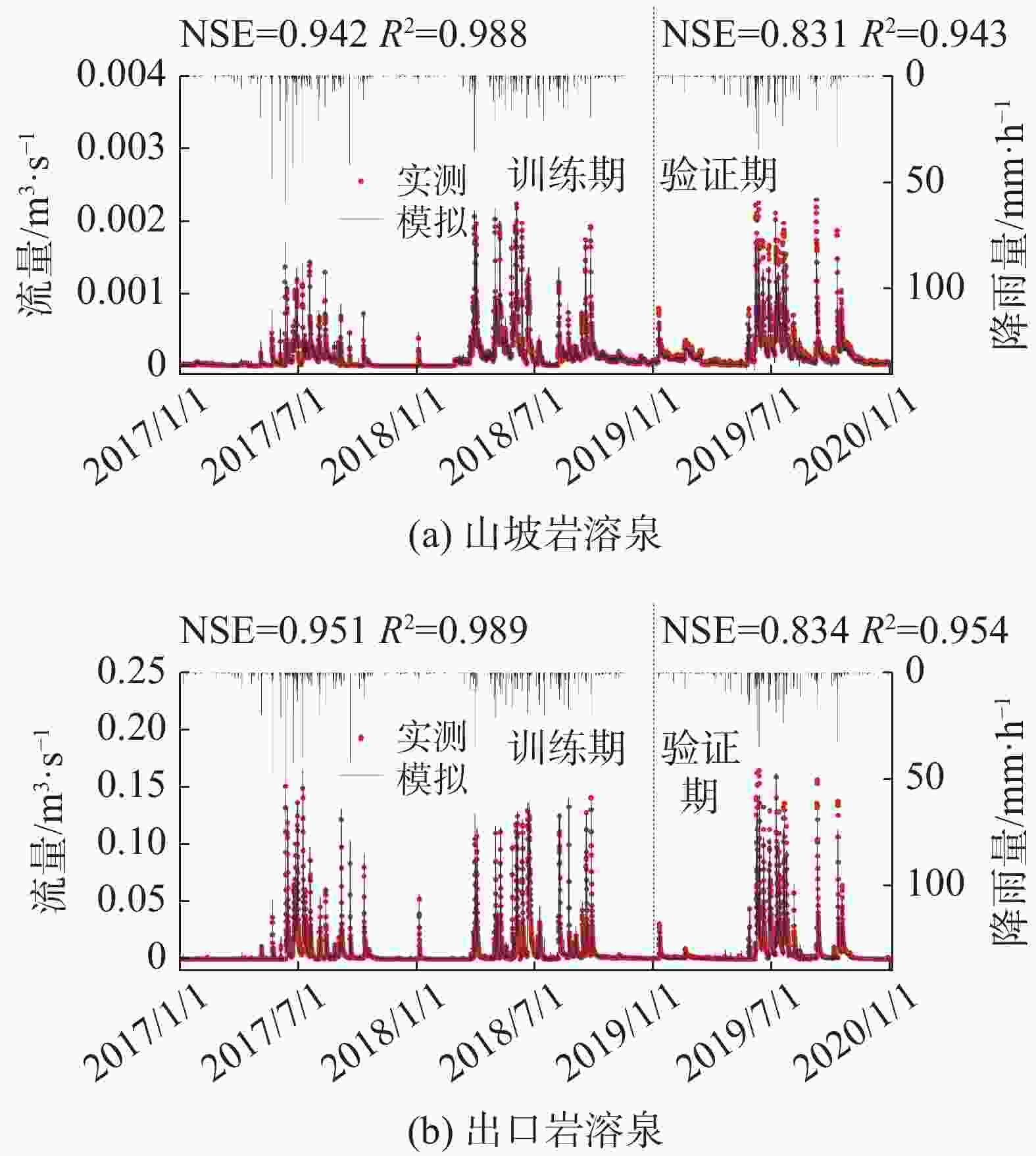
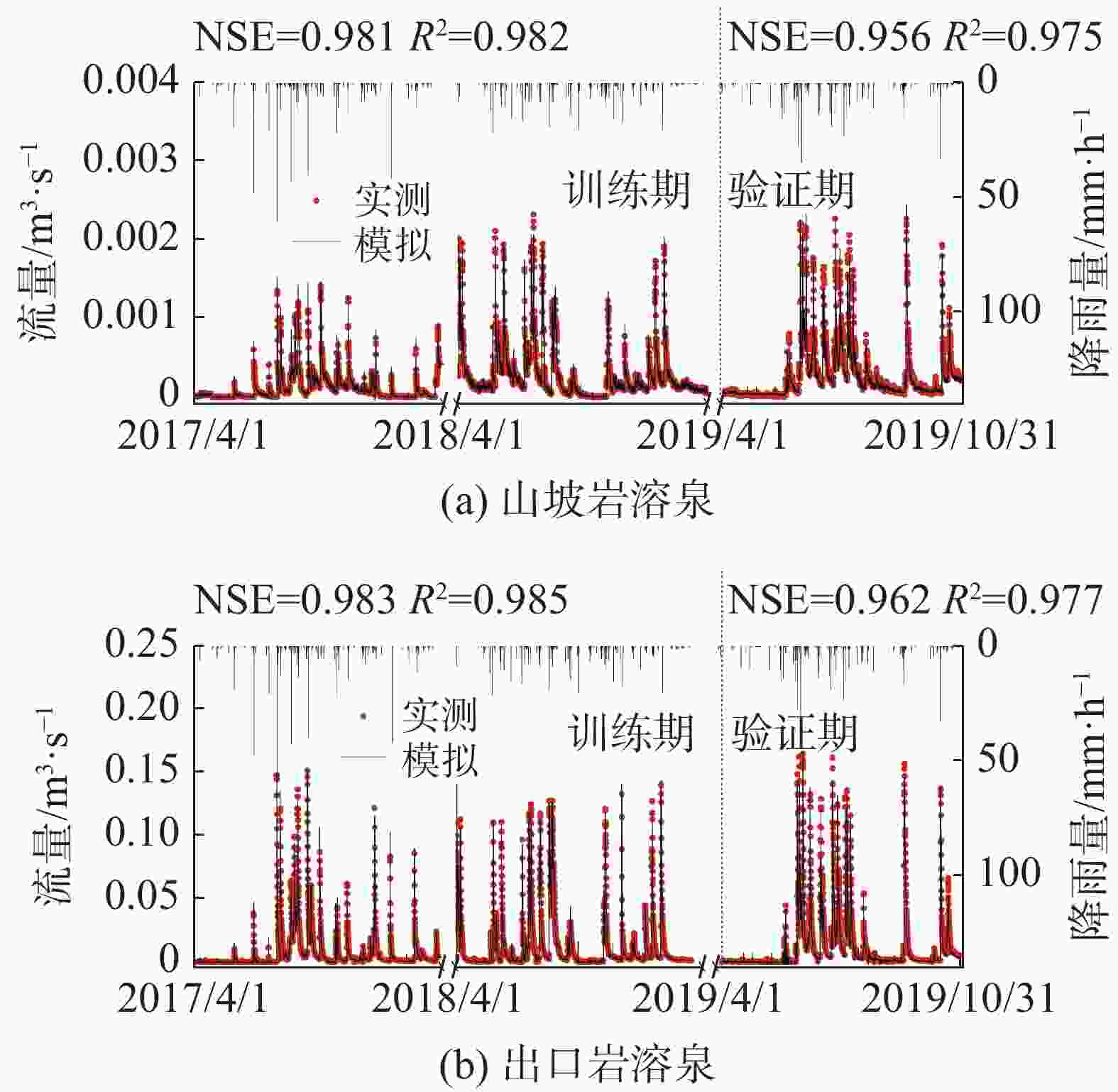
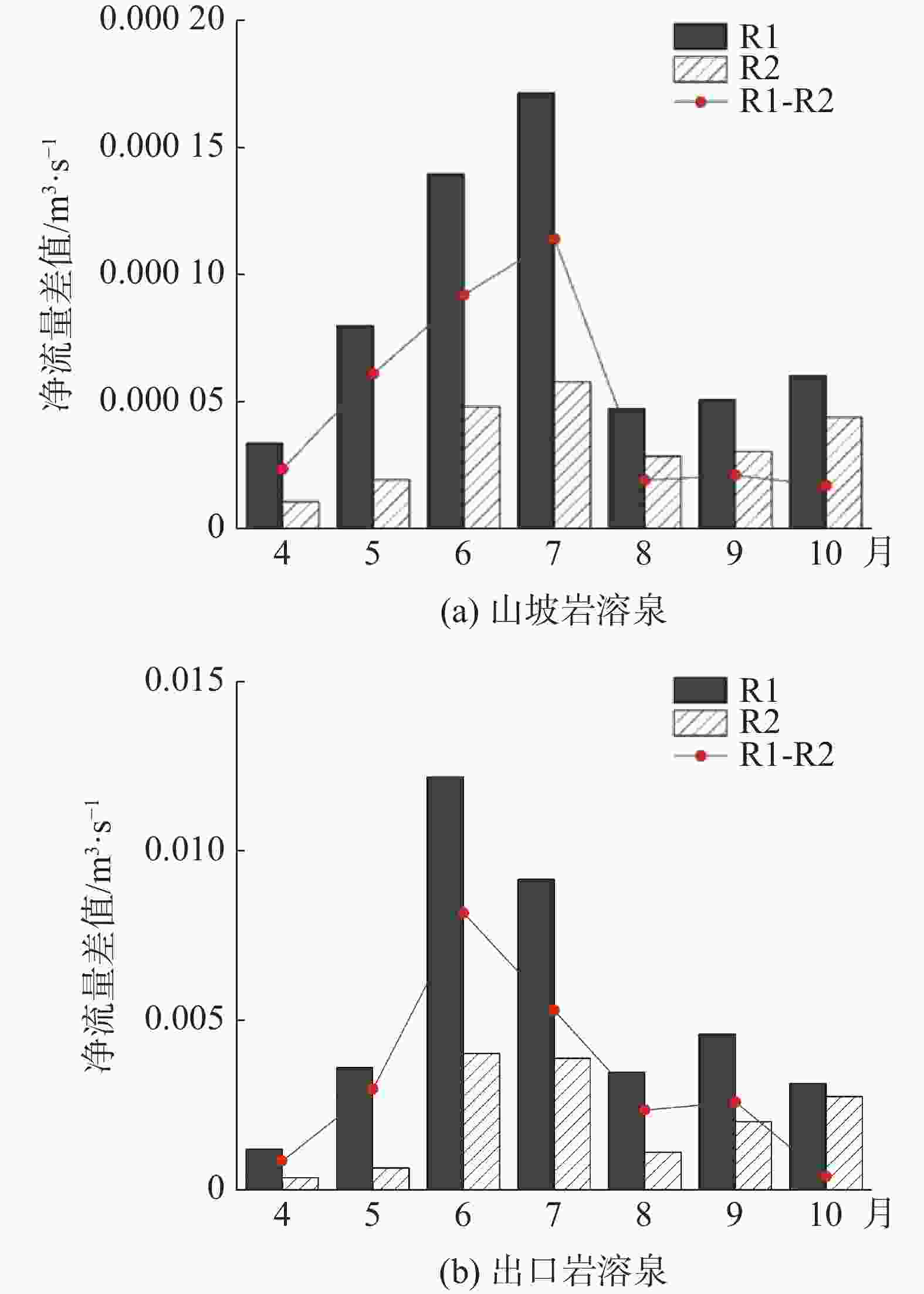
摘要: 岩溶泉对西南岩溶区生态系统稳定和经济社会发展具有重要意义。受岩溶区独特水文地质结构与多重水流过程控制,岩溶泉流量具有复杂的动态变化特征,机器学习模型为其模拟和预测提供了有效手段。然而,岩溶泉域降雨−泉流量过程及其时空变异特征对机器学习模型结构与模拟精度的影响仍不明晰。本文选取西南典型岩溶泉,基于长短期记忆网络(LSTM)建立岩溶泉流量模拟模型,利用泉域实测逐小时降雨与泉流量序列进行模型训练与验证。在此基础上,分析了不同降雨−泉流量过程对岩溶泉流量模拟精度的影响,以及岩溶水文地质结构对降雨−泉流量响应滞时的控制作用。研究结果显示,山坡岩溶泉与流域出口岩溶泉训练期纳什效率系数(NSE)分别为0.942与0.951,验证期分别为0.831与0.834。对于山坡岩溶泉与流域出口岩溶泉,利用全年实测序列训练的模型预测雨季泉流量存在较大偏差,NSE分别为0.793与0.798,而利用雨季实测序列训练的模型预测雨季泉流量,精度显著提升,NSE分别为0.956与0.962,且此差异在暴雨频繁的5、6、7月尤为显著。受浅薄土壤与表层岩溶带分布影响,山坡岩溶泉LSTM模型时序步长显著小于流域出口岩溶泉。
-
关键词:
- 机器学习 /
- LSTM /
- 岩溶泉流量 /
- 响应滞时 /
- 岩溶降雨−泉流量过程
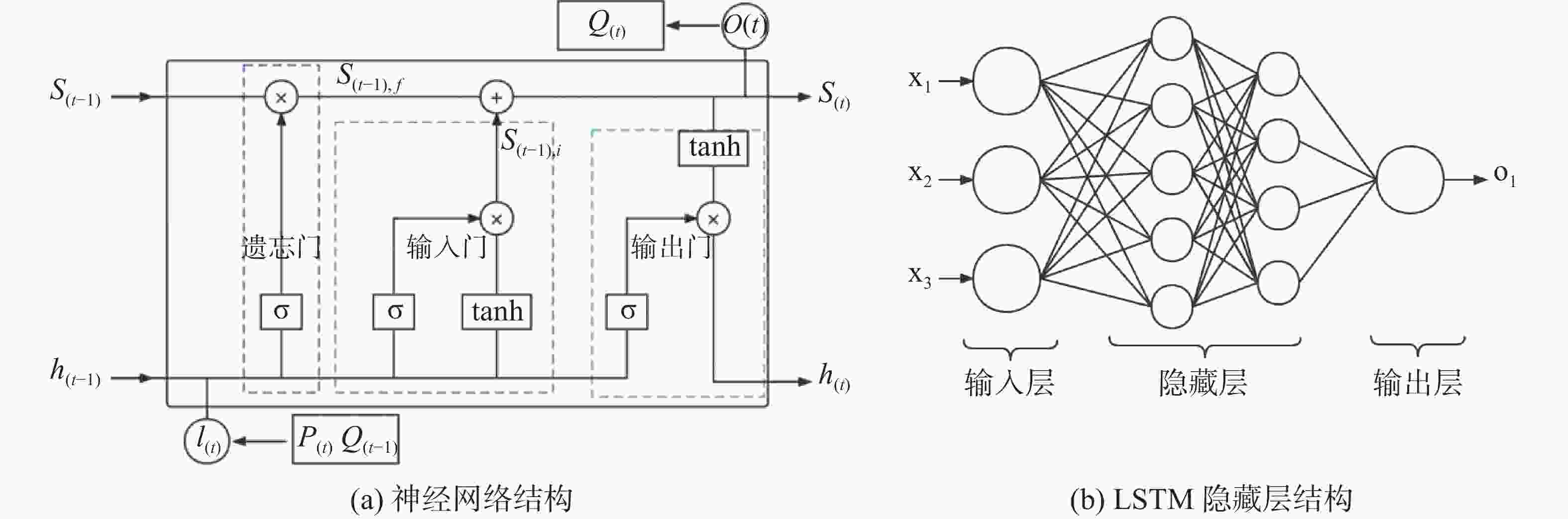
Abstract:Karst springs are important for ecosystem and economic development in Southwest China. Controlled by the unique karst hydrogeological structure and multiple water flow processes, the karst spring flow has complex dynamic characteristics, thus posting a great challenge to simulate and predict the dynamic process of karst spring flow which can reflect the characteristics of rainfall–spring flow in the karst basin. As a data-driven model, the machine learning model omits the necessity of considering complex physical processes, showing its significant advantages in the simulation and prediction of nonlinear system variables. Therefore, it provides an effective approach for simulation and prediction of karst spring discharge. However, the influence of the flow processes and hydrogeological conditions on the structure and simulation accuracy of machine learning model is still unclear. Among the machine learning algorithms, LSTM, as the most popular algorithm in recent years, is widely used in the simulation and prediction of various long-time series data. LSTM adds a cell state similar to "conveyor belt" in the hidden layer, and the cell state is adjusted by forgetting gate, input gate and output gate. This structure can effectively solve the long-term transportation and memory problems of time series data, and is more suitable for runoff simulation and prediction than the traditional neural network algorithm. In this study, for the processes of rainfall–spring flow in karst areas, two typical karst springs (hillside karst spring and outlet karst spring) representing different geomorphic units in Southwest China are selected. Through hyper parameter optimization, a double hidden layer and double input LSTM model are adopted to build a machine learning model of typical karst spring flow. The measured meteorological and hydrological data from 0:00 on January 1, 2017 to 24:00 on December 31, 2019 are used. 2017–2018 is the training period and 2019 is the validation period. The model has been trained and verified. Based on the simulation results, the influence of different rainfall–spring flow forming processes on the simulation accuracy of karst spring flow and the influence of karst hydrogeological structure on the response time lag of rainfall–spring flow are compared and analyzed. The results show that the Nash efficiency coefficients (NSE) for the hillside karst spring and the outlet karst spring were 0.942 and 0.951 in the training period, and 0.831 and 0.834 in the validation period, respectively. The model can well simulate the whole dynamic process of karst spring discharge in different geomorphic units, but there are significant errors in the simulation of flood peak in the rainy season. The formation process and variation of rainfall–spring discharge in the karst spring area have an important influence on the simulation accuracy of machine learning model. Compared with the model trained by the annual measured sequence, the model trained by the measured sequence in the rainy season can significantly improve the simulation accuracy of the karst spring flow in this season. The NSE of the hillside karst spring increases from 0.793 to 0.956, and the outlet karst spring increases from 0.798 to 0.962. The difference is most significant in May, June and July when rainstorms and flood are concentrated. Under the same precision of simulating spring flow, the time step of LSTM model of hillside karst spring is obviously smaller than that of outlet karst spring. When the simulation precision of the two types of spring flow is the highest, the time step of the model is 15 h and 28 h, respectively. This result can be combined with the actual geological structure. In karst areas, the development degree of the epikarst zone is closely related to the terrain, and its thickness usually decreases with the increase of the slope. Generally, the thickness of the epikarst zone on steep hillsides is less than that in flat depressions, and gradually increases from top to bottom along the hillsides. Compared with the water flow in the depression, the water flow in the aquifer of the hillside unit is rapid because it is controlled by the shallow epikarst zone, and it is easier to form the fast water flow with the large fissure as the channel, which may further show the rapid flow and rainfall response characteristics of the hillside karst spring. Therefore, affected by the development characteristics of the epikarst zone, the response lag time of rainfall–spring flow in the hillside karst spring area is less than that in the depression, and the time step of LSTM model of hillside karst spring flow is significantly smaller than that of the karst spring at the outlet of the basin. -
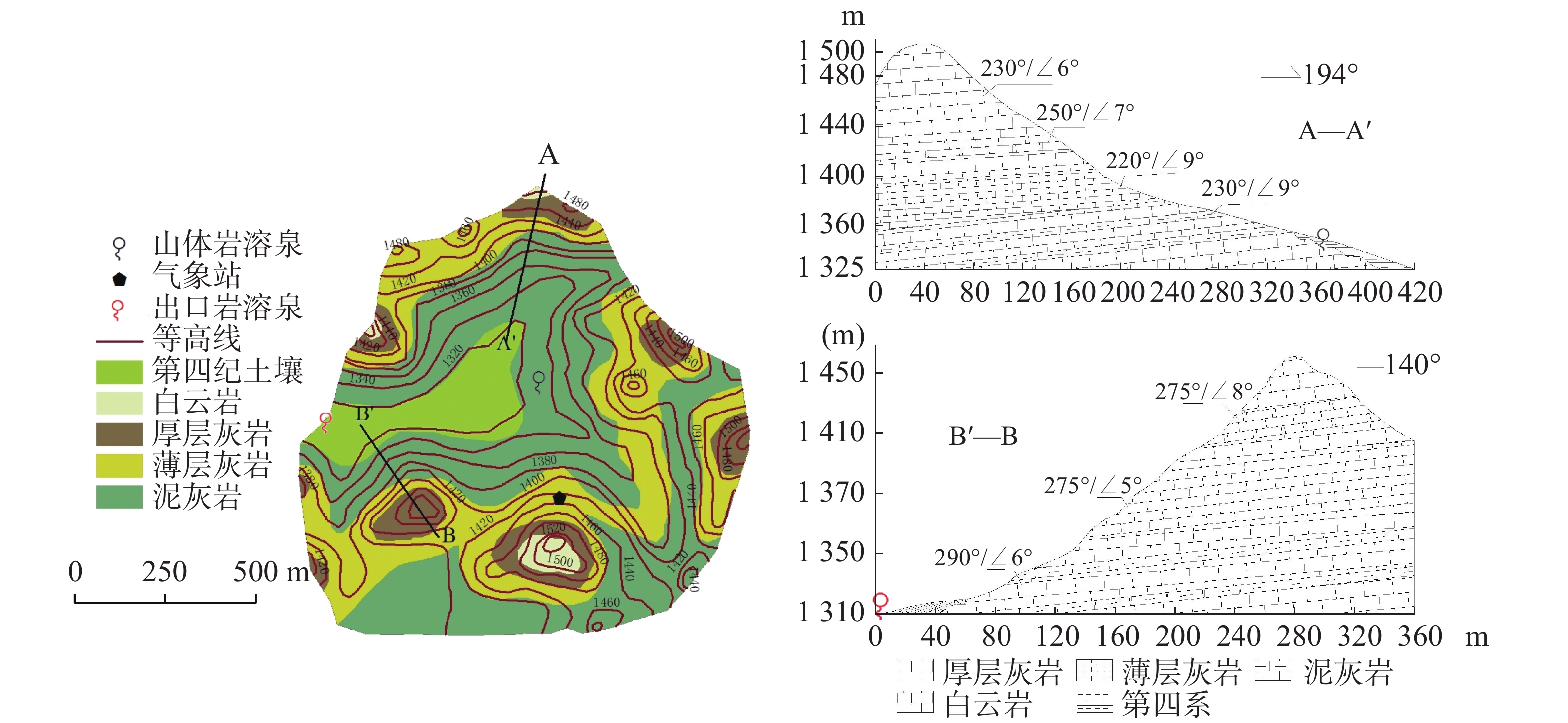
表 1 研究期降雨、泉流量统计特征
Table 1. Statistical characteristics of rainfall and spring flow during the study period
站点 降雨量 泉流量/m3·s−1 时段总量/mm 最大值/mm·h−1 最大值 最小值 均值 山坡岩溶泉 3 584.2 59.9 0.002 3 0 0.000 2 出口岩溶泉 0.164 6 0 0.006 8 表 2 超参数取值
Table 2. Hyperparameter values
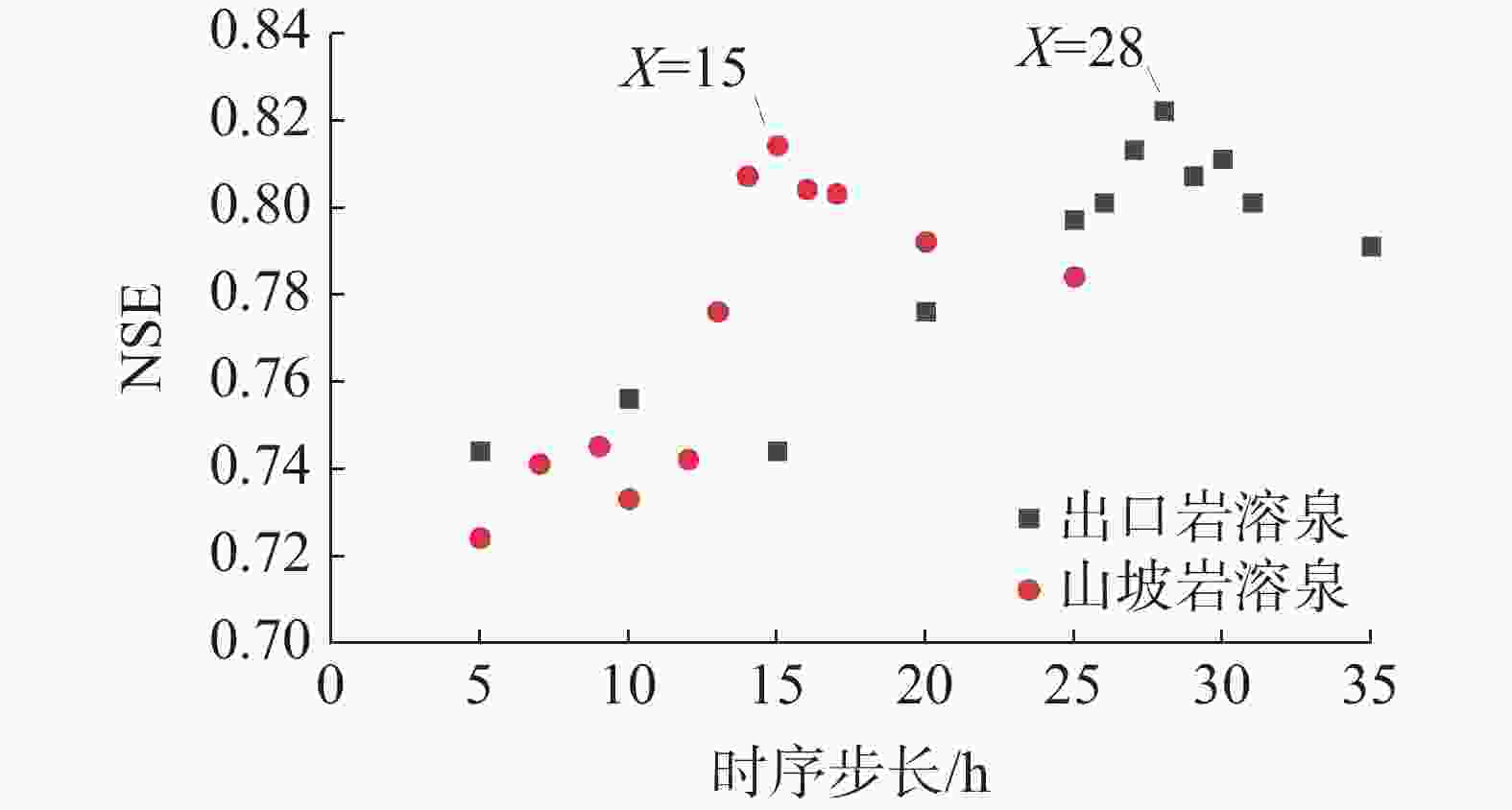
超参数名称 含义 取值 隐藏层数(layer) 神经网络结构层数 2 单个隐藏层神经元数(hidden size) 隐藏层节点的数量 10 训练轮数(epoch) 模型进行完整训练的次数 100 批量大小(batch size) 一次训练所选取的样本数 32 学习率(learning rate) 神经网络的学习速度 0.001 时序步长(time step) 山坡岩溶泉 数据传递时长大小 15 出口岩溶泉 28 表 3 基于全年数据训练的验证期雨、枯季LSTM模拟结果
Table 3. LSTM simulation results for the rainy and dry seasons in validation period trained based on annual data
时间 山坡岩溶泉 出口岩溶泉 NSE R2 NSE R2 训练期 0.942 0.988 0.951 0.989 验证期 枯季 0.973 0.987 0.982 0.993 雨季 0.793 0.942 0.798 0.935 -
[1] Hartmann A, Goldscheider N, Wagener T, Lange J, Weiler M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2014, 52(3): 218-242. doi: 10.1002/2013RG000443 [2] 李潇, 漆继红, 许模. 西南典型紧窄褶皱小尺度浅层岩溶水系统特征及隧道涌水分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):375-383.LI Xiao, QI Jihong, XU Mo. Analysis on the characteristics of small-scale shallow karst water systems in typical tight-narrow folds and tunnel water inrush in Southwestern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 375-383. [3] Zhang Zhicai, Chen Xi, Soulsby Chris. Catchment-scale conceptual modelling of water and solute transport in the dual flow system of the karst critical zone[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2017, 31(19): 3421-3436. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11268. [4] 蒙海花, 王腊春, 苏维词, 霍雨. 基于落水洞的岩溶半分布式水文模型的构建及其应用[J]. 地理科学, 2009, 29(4):550-554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2009.04.014MENG Haihua, WANG Lachun, SU Weici, HUO Yu. Development of a karst sinkhole-based semi-distributed hydrological model and its application[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2009, 29(4): 550-554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2009.04.014 [5] 王宇. 西南岩溶区岩溶水系统分类、特征及勘查评价要点[J]. 中国岩溶, 2002, 21(2):114-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.008WANG Yu. Classification, features of karst water system and key point for the evaluation to karst water exploration in Southwest China karst area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2002, 21(2): 114-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.008 [6] 王宇. 岩溶高原地下水径流系统垂向分带[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):1-8.WANG Yu. Vertical zoning of groundwater runoff system in karst plateau[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1): 1-8. [7] 王在高, 徐萍莉. 浅析喀斯特流域水文地貌过程—响应系统[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 20(1):36-39.WANG Zaigao, XU Pingli. An elementary analysis of hydro-geomorphological process—response system[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2002, 20(1): 36-39. [8] Hu Caihong, Wu Qiang, Li Hui, Jian Shengqi, Li Nan, Lou Zhengzheng. Deep learning with a long short-term memory networks approach for rainfall-runoff simulation[J]. Water, 2018, 10(11): 1543. doi: 10.3390/w10111543 [9] Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge, USA: The MIT Press, 2016. [10] Kratzert F, Klotz D, Brenner C, Schulz K. Rainfall-runoff modelling using Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) networks[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2018, 22(11): 6005-6022. doi: 10.5194/hess-22-6005-2018 [11] 党池恒, 张洪波, 陈克宇, 支童, 卫星辰. 长短期记忆神经网络在季节性融雪流域降水-径流模拟中的应用[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(5):10-18, 33. doi: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2020057DANG Chiheng, ZHANG Hongbo, CHEN Keyu, ZHI Tong, WEI Xingchen. Application of the long-short-term memory neural network for rainfall-runoff simulation in seasonal snowmelt basin[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(5): 10-18, 33. doi: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2020057 [12] Y Bengio, P Simard, P Frasconi. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1994, 5(2): 157-166. doi: 10.1109/72.279181 [13] Hochreiter S. The vanishing gradient problem during learning recurrent neural nets and problem solutions[J]. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, 1998, 6(2): 107-116. doi: 10.1142/S0218488598000094 [14] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [15] Gao Shuai, Huang Yuefei, Zhang Shuo, Han Jingcheng, Wang Guangqian, Zhang Meixin, Lin Qingsheng. Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 589: 125188. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125188 [16] Zhang Di, Lin Junqiang, Peng Qidong, Wang Dongsheng, Yang Tiantian, Soroosh Sorooshian, Liu Xuefei, Zhuang Jiangbo. Modeling and simulating of reservoir operation using the artificial neural network, support vector regression, deep learning algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 565: 720-736. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.08.050 [17] Tennant C, Larsen L, Bellugi D, Moges E, Zhang Liang, Ma Hongxu. The utility of information flow in formulating discharge forecast models: A case study from an arid snow-dominated catchment[J]. Water Resources Research, 2020, 56(8): e2019WR024908. [18] 顾逸. 基于长短期记忆循环神经网络及其结构约减变体的中长期径流预报研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018.GU Yi. Research on mid-long-term runoff forecasting based on long-short-term memory recurrent networks and its structural reduction variant[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018. [19] Cho K, Kim Y. Improving streamflow prediction in the WRF-Hydro model with LSTM networks[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 605: 127297. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127297 [20] Lu Dan, Goutam Konapala, Scott L Painter, Shih Chieh Kao, Sudershan Gangrade. Streamflow simulation in data-scarce basins using bayesian and physics-Informed machine learning models[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2021, 22(6): 1421-1438. [21] 张志才, 陈喜, 刘金涛, 彭韬, 石朋, 严小龙. 喀斯特山体地形对表层岩溶带发育的影响:以陈旗小流域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(2):137-143.ZHANG Zhicai, CHEN Xi, LIU Jintao, PENG Tao, SHI Peng, YAN Xiaolong. Influence of topography on epikarst in karst mountain areas: A case study of Chenqi catchment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(2): 137-143. [22] Zhang Zhicai, Chen Xi, Cheng Qinbo, Soulsby Chris. Using Storage Selection(SAS) functions to understand flow paths and age distributions in contrasting karst groundwater systems[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 602: 126785 [23] Zhang Zhicai, Chen Xi, Cheng Qinbo, Soulsby Chris. Storage dynamics, hydrological connectivity and flux ages in a karst catchment: Conceptual modelling using stable isotopes[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2019, 23(1): 51-71. doi: 10.5194/hess-23-51-2019 [24] Cai Lianbin, Chen Xi, Huang Richao, Keith Smettem. Runoff change induced by vegetation recovery and climate change over carbonate and non-carbonate areas in the karst region of South-west China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 604: 127231. [25] 侯怡萍. 流域生态水文敏感度及其影响因子分析[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019.HOU Yiping. Research on ecohydrological sensitivity of watershed and its influencing factors analysis[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. [26] 刘炜, 焦树林, 李银久, 莫跃爽, 赵宗权, 张洁, 赵梦. 喀斯特地表植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子相关性分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(3):203-215. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.03.024LIU Wei, JIAO Shulin, LI Yinjiu, MO Yueshuang, ZHAO Zongquan, ZHANG Jie, ZHAO Meng. Analysis on the correlation between vegetation cover of land surface and climatic factors in karst area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2021, 28(3): 203-215. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2021.03.024 [27] 李林立. 西南典型岩溶区生态环境对表层岩溶水调蓄功能的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2009.LI Linli. Study of effects of ecological environment on regulated function of epikarst water in typical karst area of Southwest, China[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2009. [28] Zhang Zhicai, Chen Xi, Chen Xunhong, Shi Peng. Quantifying time lag of epikarst-spring hydrograph response to rainfall using correlation and spectral analyses[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2013, 21(7): 1619-1631. doi: 10.1007/s10040-013-1041-9 -




 下载:
下载: