Flow attenuation analysis and inorganic carbon flux estimation of surface karst spring in rocky desertification control area: A case study at Laoquan spring in the Longtan trough valley, Youyang county, Chongqing City, China
-
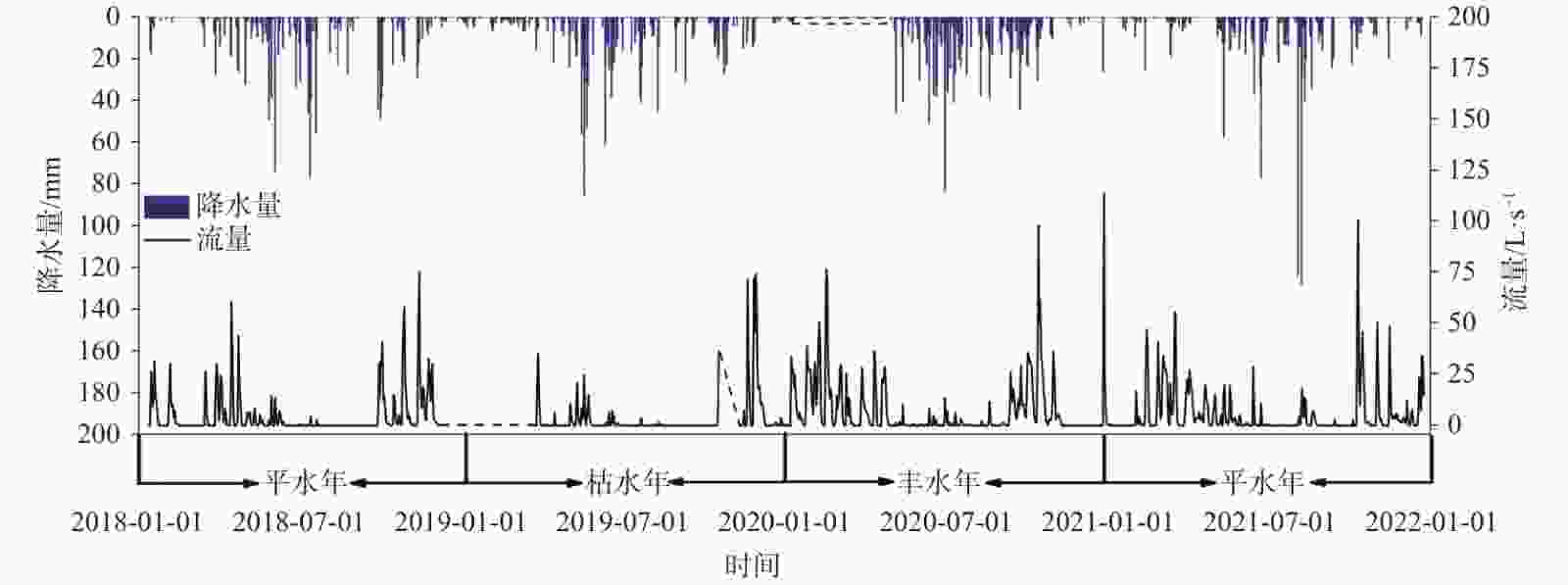
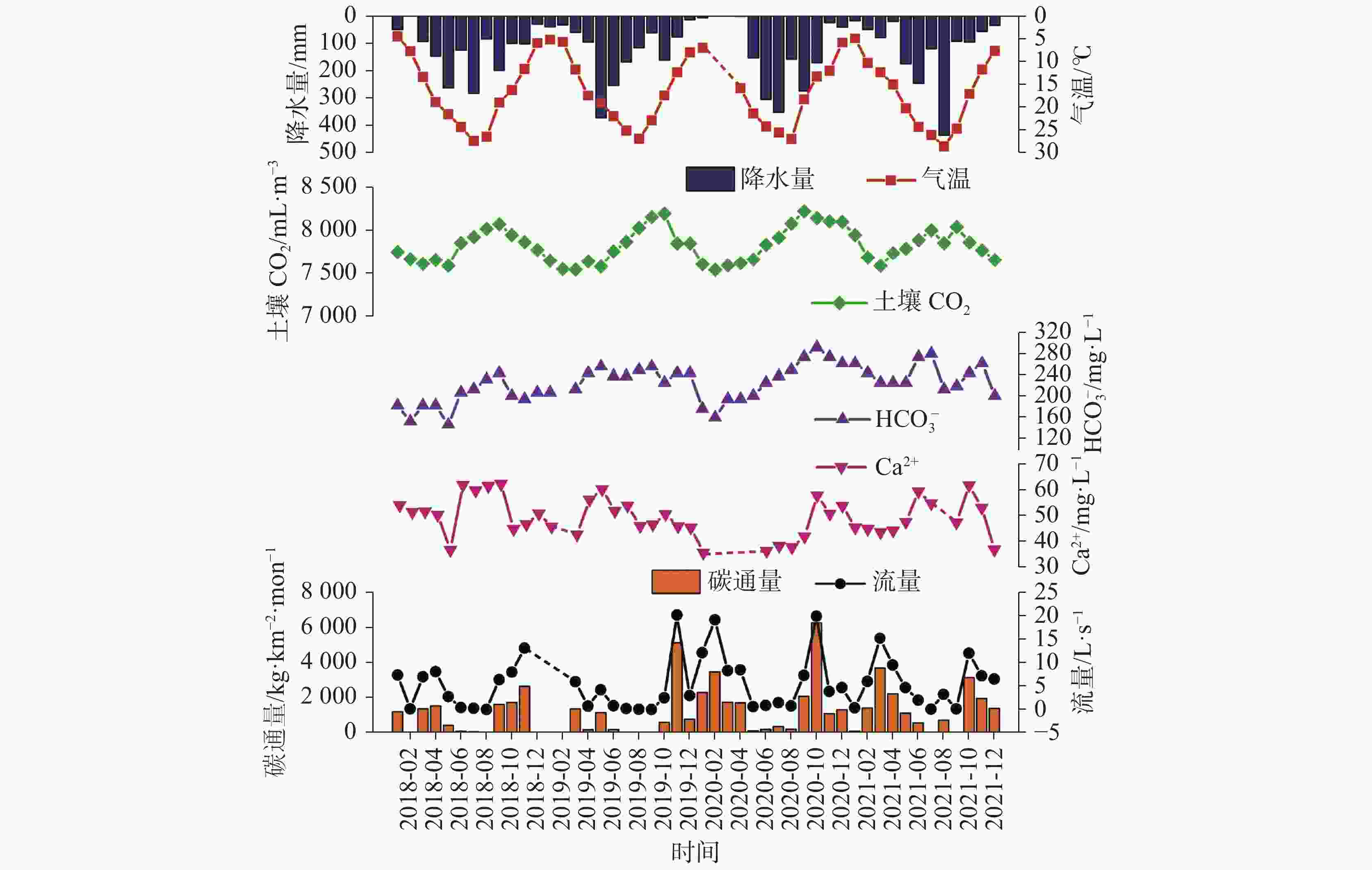
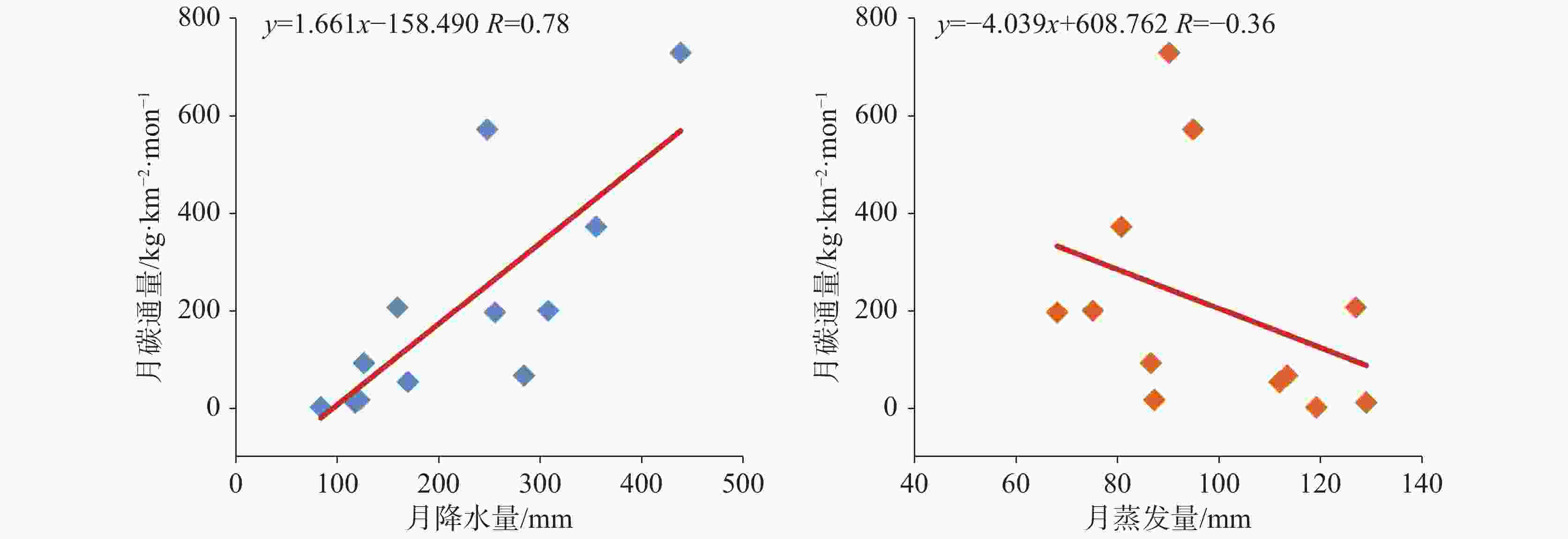
摘要: 应对“双碳”目标,加强岩溶石漠化综合治理工作,地下水是关键。为探究重庆市酉阳县龙潭槽谷石漠化治理区岩溶泉的流量衰减及无机碳通量变化特征,采用流量衰减方程与水化学径流法对研究点老泉进行模拟与分析。结果表明:(1)老泉的流量衰减分为两个亚动态,衰减系数分别为0.089 2、0.019 6,其具有双重性含水介质特征。(2)暴雨期老泉的碳通量随流量变化的特征明显;而伏旱期(7月底-8月底)老泉的碳通量与土壤CO2、泉水CO2均具有明显的昼夜变化特征,表现为夜间低、日间高。(3)老泉夏季的碳通量与降水量呈正相关(R=0.78),与蒸发量呈负相关(R=−0.36),气候的不稳定性变化对碳通量影响显著。老泉的月
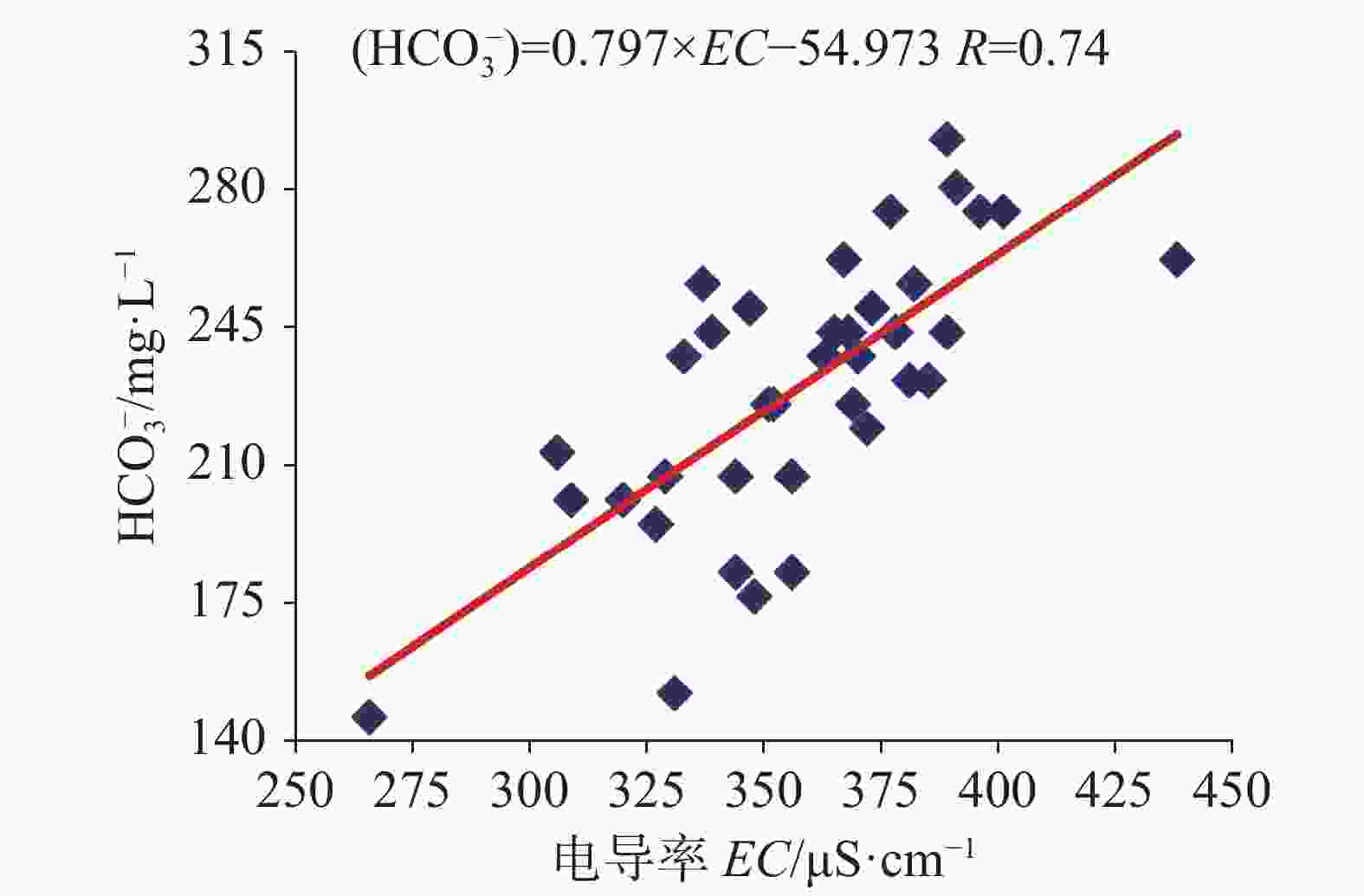
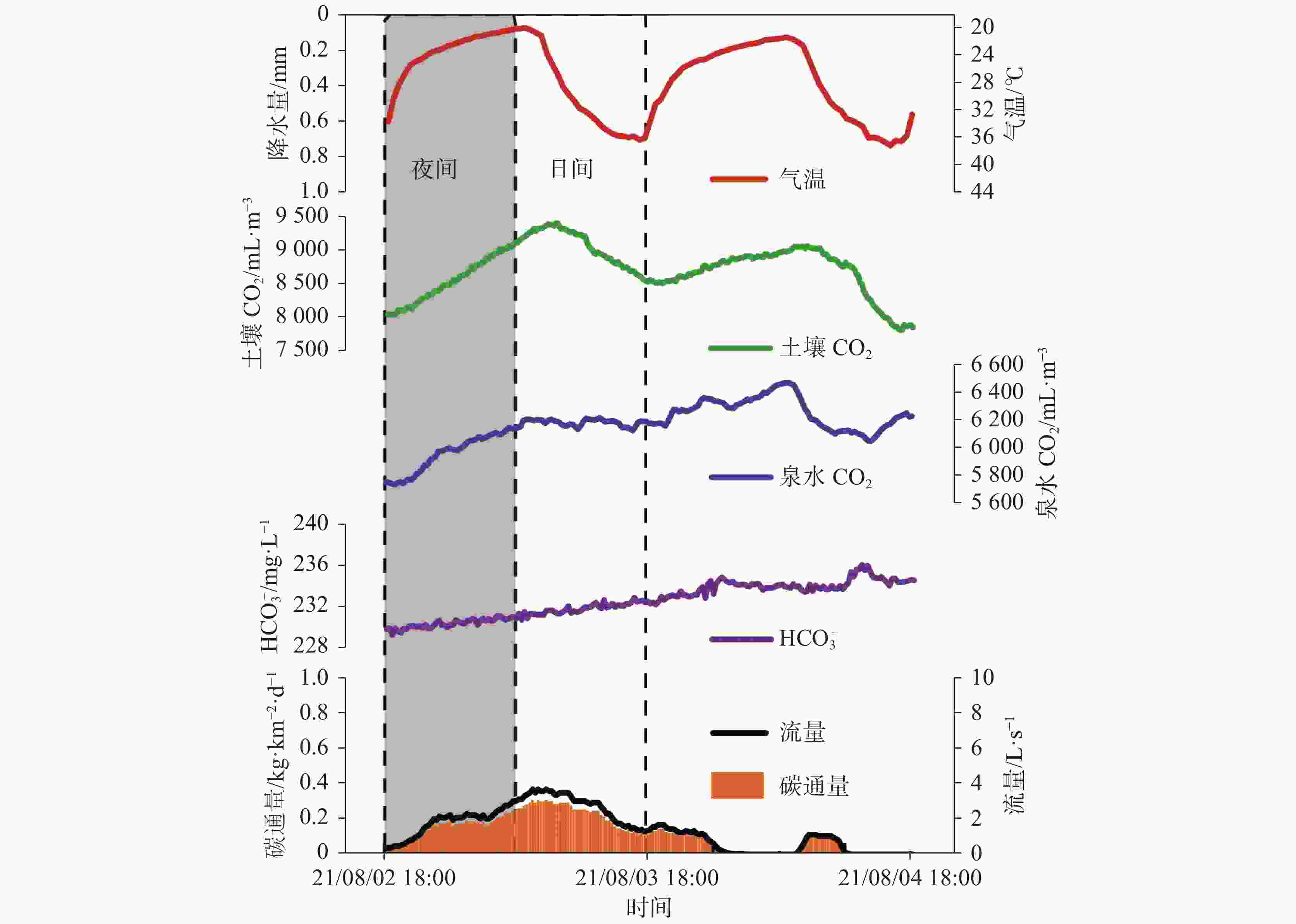
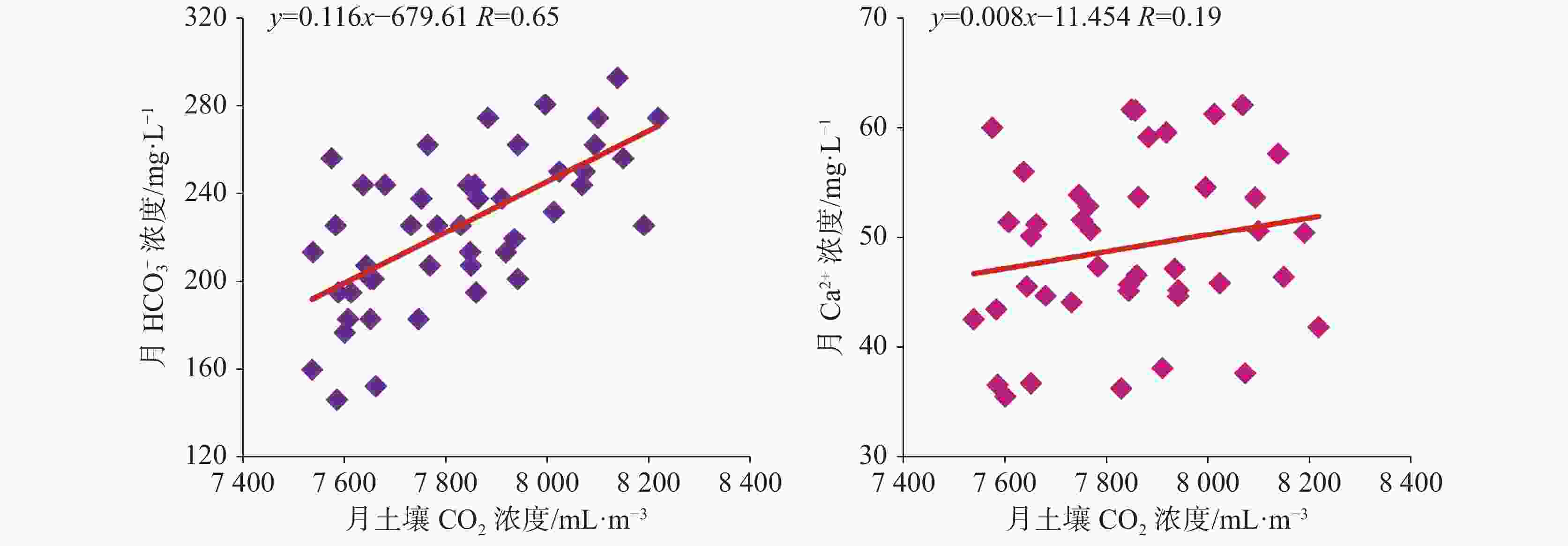
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 浓度与月土壤CO2浓度的相关系数为0.64,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 敏感地响应土壤CO2的变化;而老泉年碳通量与年土壤CO2浓度的相关系数为0.90,且年均δ13CDIC呈偏负趋势,土地利用变化(植被恢复)有利于土壤CO2及老泉碳通量的增加。(4)老泉2018-2021年的碳通量呈波动上升趋势,年均无机碳通量为15.05 t·km−2·a−1。研究结果能为石漠化生态恢复治理工作提供参考。Abstract:The rational utilization of groundwater resources is the key to achieving the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals, strengthening the comprehensive control of karst rock desertification and soil erosion in the ecological environment. On the southern wing of Tongmaling anticline in southeast Chongqing, Longtan trough valley—a part of Wuling Mountain area—is located in Youyang county, Chongqing City, China. The karst development is strong in the trough valley area, and the distribution of groundwater is extensive. At the same time, the problem of rocky desertification is severe in this area, so the efficient utilization of water resources and ecological restoration are especially important. The objective of this study is to explore the flow characteristics of karst spring and structure types of aquifer medium, and to further analyze the variation characteristics of inorganic carbon flux in the ecological restoration area of rock desertification control. In this study, the flow attenuation equation and hydrochemical runoff method are used to estimate and analyze attenuation process and inorganic carbon flux of Laoquan spring based on the re-vegetation in a karst rocky desertification area in Longtan trough valley in Youyang county, Chongqing City, Southwest China. The results show that: (1) The flow attenuation process of Laoquan spring is divided into two sub-dynamics with attenuation coefficients of 0.0892 and 0.0196, respectively. The attenuation process of this spring mainly occurs on the first sub-dynamics. In the aquifer medium of groundwater system, the ratio of pipeline to fissure is significant. The strong water conduction effect of aquifer medium leads to the weak capacity of Laoquan spring to regulate and store rainfall infiltration water. (2) The variation process of the carbon flux of Laoquan spring during the rainstorm period is divided into four stages, and the carbon flux has obvious variation characteristics with the flow. The carbon flux during the rainstorm period is 97.64 kg·km−2·d−1. In the summer drought period (from the end of July to the end of August), the carbon flux of Laoquan spring has obvious diurnal variation characteristics, low at night and high in the day. The soil CO2 concentration, water CO2 concentration and carbon flux of Laoquan spring are synchronized in the diurnal variation, and the carbon flux in the summer drought period is 18.23 kg·km−2·d−1. (3) The climate instability can affect the carbon flux of Laoquan spring. The precipitation of this spring in summer is positively correlated with the carbon flux (R=0.78), and the evaporation is negatively correlated with the carbon flux (R=−0.36). The change of land use mode has a significant effect on the carbon flux of Laoquan spring. The correlation coefficient between ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ concentration and soil CO2 concentration based on the monthly mean value of Laoquan spring is 0.64, indicating that${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ in Laoquan spring sensitively responds to the change of soil CO2. The correlation coefficient between the annual spring carbon flux and the annual soil CO2 concentration is 0.90, and the average annual δ13CDIC shows an obvious negative trend, indicating that land use change (Vegetation Restoration) is conducive to the increasing of soil CO2 concentration and carbon flux. (4) From 2018 to 2021, the carbon flux in Laoquan spring was 11.66, 10.33, 21.31 and 16.9 t·km−2·a−1, respectively, showing an increasing trend with fluctuation. The annual inorganic carbon flux is 15.05 t·km−2·a−1(CO2). The carbon sink capacity should be enhanced by the improvement of comprehensive control measures of rocky desertification. Therefore, in the process of rocky desertification control, it is necessary to make scientific use of karst water resources and heighten the awareness of karst environment protection, especially the scientific use and management of water resources in summer rainstorm and summer drought. In addition, it is necessary to boost regional carbon sink capacity by restoring natural dominant vegetation in rocky desertification control areas. -
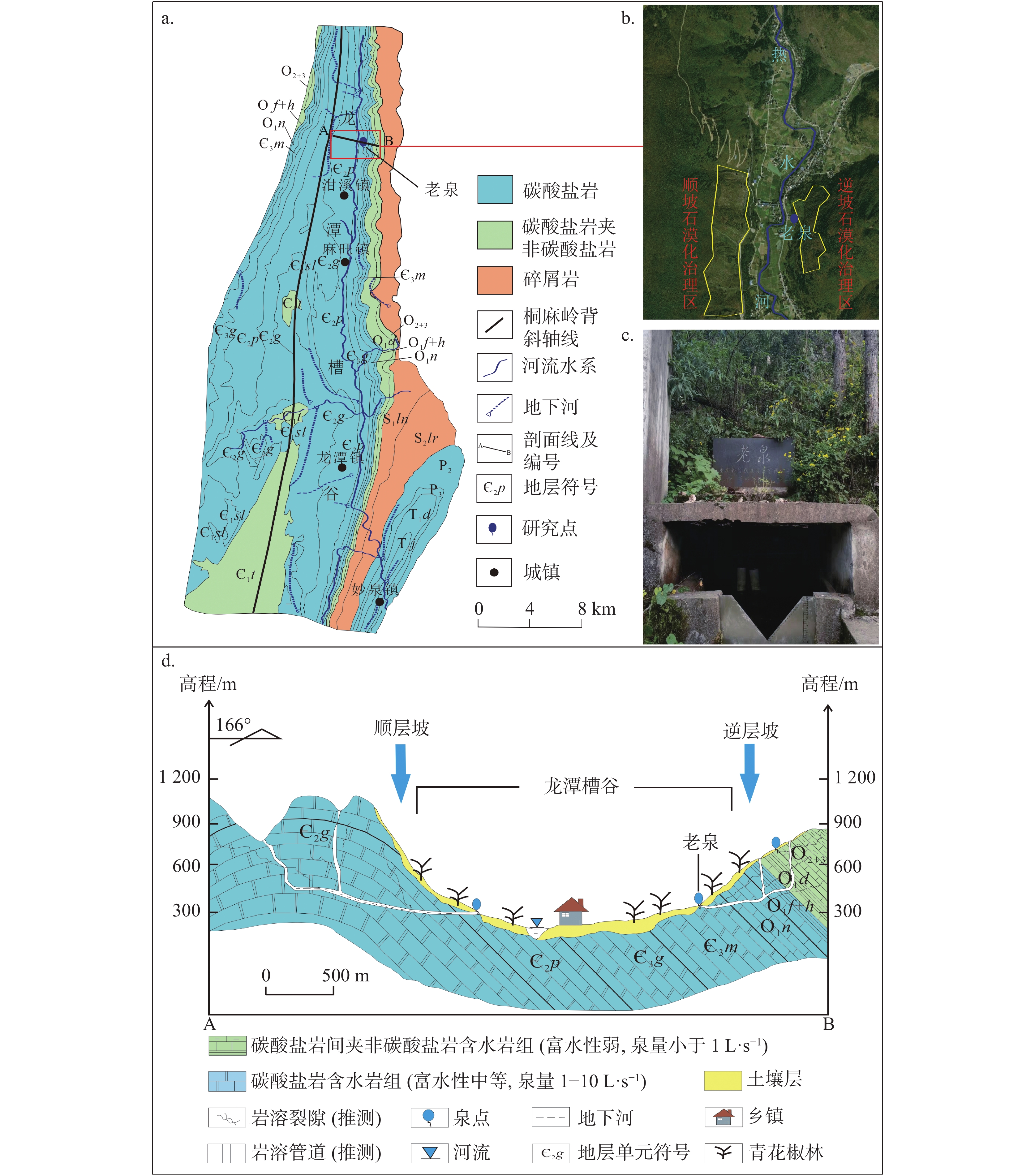
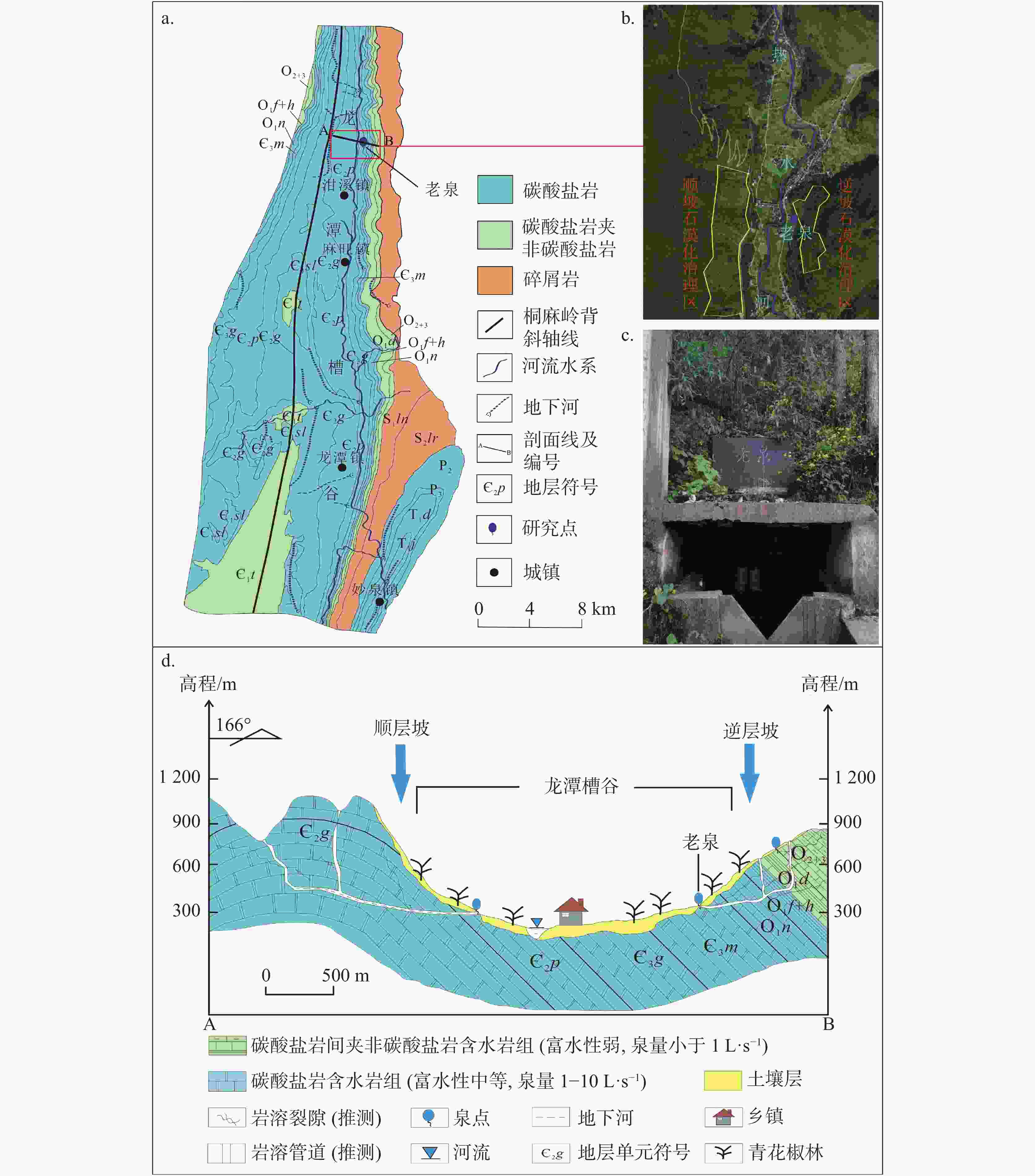
图 1 龙潭槽谷水文地质概况图(a-水文地质平面图,b-石漠化治理区卫星图(据Google Earth),c-老泉实景图,d-水文地质剖面图(修改自参考文献[25]))
Figure 1. Hydrogeological survey of Longtan trough valley (a- Hydrogeological map, b- Satellite map of rocky desertification control area (based on Google Earth), c- Map of Laoquan spring, d- Hydrogeological profile [25])
表 1 2018-2021年伏旱期(7月21日-8月31日)老泉的气候与流量情况
Table 1. Climate and discharge of Laoquan spring during the drought period (from July 21 to August 31) from 2018 to 2021
时间/年 2018 2019 2020 2021 多年平均值 降水总量/mm 1 485.2 1 461.6 1 500.2 1 429.8 1 470.0 伏旱期降水量/mm 103.8 139.6 216.8 491.2 237.9 伏旱期蒸发量/mm 166.9 178.7 178.7 226.9 187.8 伏旱期干旱天数/天 29 31 29 19 27 伏旱期降水天数/天 13 11 13 23 15 伏旱期高温天数(大于35 ℃)/天 27 29 23 25 26 伏旱期断流天数/天 37 34 18 23 28 伏旱期流量/L·s−1 0 0.03 0.65 2.38 0.76 表 2 老泉200506号暴雨的流量衰减参数
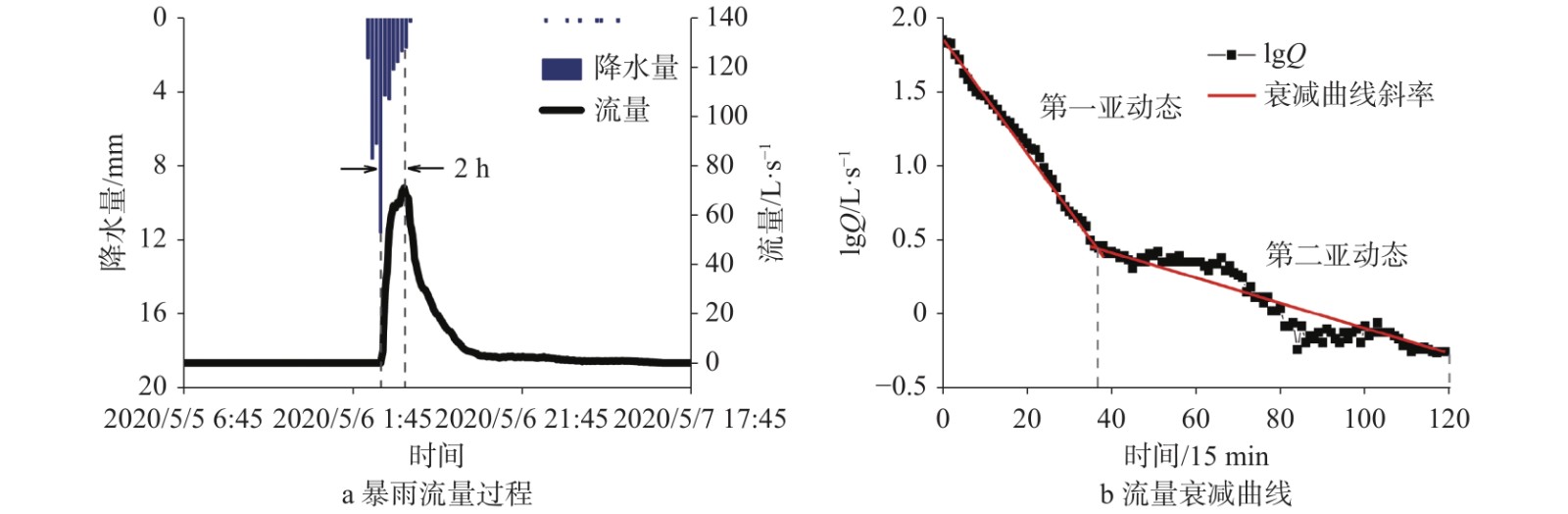
Table 2. Flow attenuation parameters of Rainstorm No. 200506 in Laoquan spring
岩溶水系统 亚动态 衰减系数/15 min 持续时间/h 含水介质储水量/m3 亚动态占总储水量之比/% 总储水量/m3 老泉 一 0.089 2 9 620.43 84 739.26 二 0.019 6 21 118.83 16 表 3 老泉210628号暴雨期间流量与碳通量参数
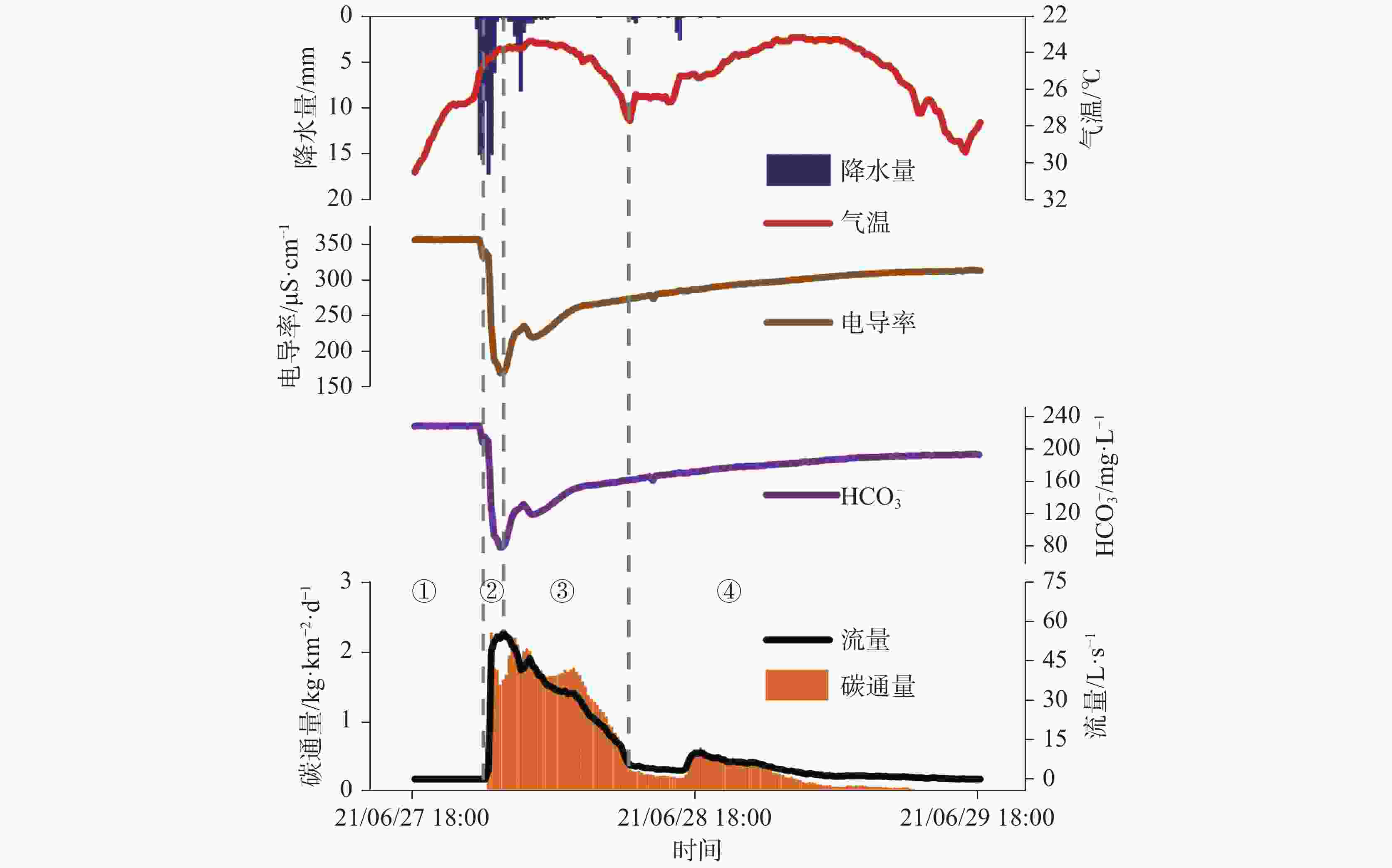
Table 3. Flow and carbon flux parameters during Rainstorm No.210628 in Laoquan spring
阶段 平均流量/L·s−1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$平均浓度/mg·L−1 持续时间/h 各阶段累计的碳通量/kg·km−2·d−1 累计碳通量/kg·km−2·d−1 ① 0 227.53 6 0 97.64 ② 38.52 127.49 1.5 9.25 ③ 31.75 140.30 10.5 64.43 ④ 3.25 181.78 29 23.96 表 4 老泉2018-2021年的水文水化学与碳通量参数
Table 4. Hydrochemical features and carbon sink flux of Laoquan spring from 2018 to 2021
时间/年 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$浓度/mg·L−1 CO2消耗量/mg·L−1 年均流量/L·s−1 无机碳通量/t·km−2·a−1 2018年 197.23 71.13 4.68 11.66 2019年 234.85 84.70 3.48 10.33 2020年 231.03 83.32 7.30 21.31 2021年 239.64 86.43 5.58 16.90 平均值 225.69 81.40 5.26 15.05 表 5 老泉2018-2021年碳通量与土壤CO2浓度的相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis between carbon flux and soil CO2 concentration of Laoquan spring from 2018 to 2021
年平均土壤CO2浓度/mL·m−3 年碳通量/t·km−2·a−1 Pearson 相关性 0.903 显著性(双侧) 0.097 N 4 表 6 2018-2021年老泉δ13CDIC的变化趋势
Table 6. Variation trend of δ13CDIC of Laoquan spring from 2018 to 2021
时间(年/月) 2018年 2019年 2020年 2021年 实测值/‰ 实测值/‰ 实测值/‰ 实测值/‰ 1月 − −10.13 −10.90 −10.56 2月 − −8.58 − −10.30 3月 − − − −10.62 4月 − −9.63 − −10.29 5月 −11.62 −10.37 − −11.47 6月 −11.72 −8.92 −11.26 −10.23 7月 −11.19 −9.45 −11.99 −12.10 8月 −11.17 −8.46 −11.91 − 9月 −11.03 −11.74 −12.25 −12.22 10月 −10.06 −9.84 −12.36 −11.58 11月 −10.59 −10.46 −11.35 −11.11 12月 −9.89 −10.82 −11.41 −11.36 年平均值/‰ −10.91 −9.85 −11.68 −11.08 注:−代表数据缺失。 -
[1] Zeng S B, Liu Z H, Goldscheider N, Frank S, Goeppert N, Kaufmann G, Zeng C, Zeng Q R, Sun H L. Comparisons on the effects of temperature, runoff, and land-cover on carbonate weathering in different karst catchments: Insights into the future global carbon cycle[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2021, 29:331-345. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02252-5 [2] 张彩云, 蒋勇军, 马丽娜, 汪啟容. 岩溶槽谷区不同土地利用方式下的坡地产流产沙规律[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(1):49-55.ZHANG Caiyun, JIANG Yongjun, MA Lina, WANG Qirong. Characteristics of runoff and sediment on slope land with different land use in karst trough valley area[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(1):49-55. [3] 伏文兵, 严友进, 李华林, 林梽桓, 胡刚, 黄朝海. 岩溶槽谷石漠化综合治理区治理生态效益评价[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(7):146-156. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2021.07.019FU Wenbin, YAN Youjin, LI Hualin, LIN Zhihuan, HU Gang, HUANG Chaohai. Evaluation of ecological benefits of comprehensive management of rocky desertification in karst trough valleys[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(7):146-156. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2021.07.019 [4] 蒋勇军, 刘秀明, 何师意, 何丙辉, 谢建平, 罗维均, 白晓永, 肖琼. 喀斯特槽谷区土地石漠化与综合治理技术研发[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(22):7092-7097.JIANG Yongjun, LIU Xiuming, HE Shiyi, HE Binghui, XIE Jianping, LUO Weijun, BAI Xiaoyong, XIAO Qiong. Research and development of comprehensive rehabilitation measures for land rocky desertification in karst trough valley area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(22):7092-7097. [5] 王明章. 西南岩溶石山区地下水开发在石漠化防治中的地位[J]. 贵州地质, 2006(4):261-265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2006.04.003WANG Mingzhang. Status on exploitation of undergroundwater in prevention and control of rocky desertification in the areas of karst rocky mountain, Southwestern China[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2006(4):261-265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2006.04.003 [6] 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 蒲俊兵, 肖琼. 现代岩溶学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 292-305.YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Yongjun, SHEN Licheng, PU Junbin, XIAO Qiong. Modern Karstology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 292-305. [7] Fiorillo F, Leone G, Pagnozzi M, Esposito L. Long-term trends in karst spring discharge and relation to climate factors and changes[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2021, 29:347-377. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02265-0 [8] Worthington S. R. H. Characteristics of channel networks in unconfined carbonate aquifers[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2015, 127(5-6):759-769. doi: 10.1130/B31098.1 [9] 吴平, 葛勤, 张卫民, 李荐华, 刘海燕, 王洋, 王振, 陈家鸿. 基于水化学和同位素示踪岩溶含水系统的水力联系: 以宜春市四方井副坝区为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(28):12058-12065. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.28.019WU Ping, GE Qin, ZHANG Weimin, LI Jianhua, LIU Haiyan, WANG Yang, WANG Zhen, CHEN Jiahong. Tracing hydraulic connection of a karst aquifer system based on hydrochemistry and isotopes: A case study of the auxiliary dam of Sifangjing in Yichun City[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(28):12058-12065. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.28.019 [10] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 潘晓东, 夏日元, 曹建文. 西南岩溶山区地下水资源评价方法对比研究: 以寨底地下河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1):111-123.YANG Yang, ZHAO Liangjie, PAN Xiaodong, XIA Riyuan, CAO Jianwen. Comparative study on evaluation methods of groundwater resources in karst area of Southwest China: Taking Zhaidi underground river basin as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1):111-123. [11] 张程鹏, 张凤娥, 耿新新, 冀俊杰, 陈永康. 岩溶地下河在SWAT中的概化方法: 以毕节倒天河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(5):665-672.ZHANG Chengpeng, ZHANG Fenge, GENG Xinxin, JI Junjie, CHEN Yongkang. Generalization method of karst underground river in SWAT: An example of the Daotian river watershed in Bijie, Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(5):665-672. [12] 常勇, 吴吉春, 刘玲, 罗跃. 岩溶泉流量衰减曲线分析[J]. 水文, 2016, 36(1):15-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2016.01.003CHANG Yong, WU Jichun, LIU Ling, LUO Yue. On recession curve of karst spring[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2016, 36(1):15-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2016.01.003 [13] 梁日胜, 曾成, 闫志为, 石彪, 何师意, 樊宇虹, 灌瑾. 贵州印江朗溪岩溶槽谷龙洞湾泉流量衰减分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(1):10-18.LIANG Risheng, ZENG Cheng, YAN Zhiwei, SHI Biao, HE Shiyi, FAN Yuhong, GUAN Jin. Recession flow analysis for Longdongwan spring at Langxi karst valley in Yinjiang county, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(1):10-18. [14] 吕玉香, 胡伟, 杨琰. 岩溶关键带水循环过程研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2019, 30(1):123-138.LV Yuxiang, HU Wei, YANG Yan. Research progress of hydrological cycle in karst critical zone[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2019, 30(1):123-138. [15] 孙平安, 肖琼, 郭永丽, 苗迎, 王奇岗, 章程. 混合岩溶流域碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率与岩溶碳汇: 以漓江流域上游为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):825-834.SUN Pingan, XIAO Qiong, GUO Yongli, MIAO Ying, WANG Qigang, ZHANG Cheng. Carbonate dissolution rate and karst carbon sink in mixed carbonate and silicate terrain: Take the upper reaches of the Lijiang river basin as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5):825-834. [16] LI H W, WANG S J, BAI X Y, CAO Y, WU L H. Spatiotemporal evolution of carbon sequestration of limestone weathering in China[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2019, 62(6):974-991. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9324-2 [17] 马明国, 汤旭光, 韩旭军, 时伟宇, 宋立生, 黄静. 西南岩溶地区碳循环观测与模拟研究进展和展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(8):1196-1205. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.08.008MA Mingguo, TANG Xuguang, HAN Xujun, SHI Weiyu, SONG Lisheng, HUANG Jing. Research progress and prospect of observation and simulation of carbon cycle in the karst areas of Southwest China[J]. Progress in Geography, 2019, 38(8):1196-1205. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.08.008 [18] 郭静芸, 毕鑫涛, 方然可, 李守定. 可溶岩化学溶蚀试验方法研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(4):24-34.GUO Jingyun, BI Xintao, FANG Ranke, LI Shouding. Advances in the chemical dissolution methods of soluble rocks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4):24-34. [19] 曹星星, 吴攀, 杨诗笛, 刘闪, 廖家豪. 贵州威宁草海流域地下水水化学特征及无机碳通量估算[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4):1761-1771.CAO Xingxing, WU Pan, YANG Shidi, LIU Shan, LIAO Jiahao. Hydrochemistry characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Caohai lake wetland catchment of Guizhou Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4):1761-1771. [20] 曾成, 赵敏, 杨睿, 刘再华. 岩溶作用碳汇强度计算的溶蚀试片法和水化学径流法比较: 以陈旗岩溶泉域为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1):106-111.ZENG Cheng, ZHAO Min, YANG Rui, LIU Zaihua. Comparison of karst processes-related carbon sink intensity calculated by carbonate rock tablet test and solute load method: A case study in the Chenqi karst spring system[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1):106-111. [21] 刘再华, 曾庆睿, 陈波, 贺海波. 碳酸盐风化碳汇研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021: 1-10.LIU Zaihua, ZENG Qingrui, CHEN Bo, HE Haibo. Study on carbonate weathering carbon sink[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021: 1-10. [22] Tong X W, Brandt M, Yue Y M, Ciais P, Rudbeck J M, Penuelas J, Wigneron J P, Xiao X M, Song X P, Horion S, Rasmussen K, Saatchi S, Fan L, Wang K L, Zhang B, Chen Z C, Wang Y H, Li X J, Fensholt R. Forest management in Southern China generates short term extensive carbon sequestration[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1):129. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13798-8 [23] Wang Y H, Li X B, Xin L J, Tan M H. Farmland marginalization and its drivers in mountainous areas of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719:135132. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135132 [24] 邹晓岗, 杨琰, 徐刚, 田宁, 游贤慧, 何志立, 田洪明, 曾朱周. 岩溶槽谷石漠化治理区表层泉水化学特征研究: 以重庆酉阳泔溪花椒基地老泉为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(6):524-533.ZOU Xiaogang, YANG Yan, XU Gang, TIAN Ning, YOU Xianhui, HE Zhili, TIAN Hongming, ZENG Zhuzhou. Chemical characteristics of surface spring in the rehabilitation area of karst rock desertification: A case study at Laoquan in the pepper planting base of Ganxi town, Youyang county, Chongqing City, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(6):524-533. [25] Xiao W J, Yang Y, Jiang X Y, He Z L, Zou X G, You X H, Yang Y Y, Zeng Z Z, Shi W Y. Different responses of ecohydrological processes in the re-vegetation area between the dip and anti-dip slope in a karst rocky desertification area in Southwestern China[J]. Plant and Soil, 2022, 475:25-43. doi: 10.1007/s11104-020-04821-9 [26] SL 551-2012, 土石坝安全监测技术规范[S]. 中华人民共和国水利部, 2012: 108-109.SL 551-2012, Technical specification for earth-rockfill dam safety monitoring[S]. Ministry of Water Resources of the PRC, 2012: 108-109. [27] 他金城, 谭立新, 张宗孝. 黄池沟配水枢纽分水池侧槽退水道水力特性试验研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2021, 32(2):141-145.TA Jincheng, TAN Lixin, ZHANG Zongxiao. Experiments on the hydraulic characteristics of the side channel spillway of the water allocation pool in Huangchigou Water Distribution Hub[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2021, 32(2):141-145. [28] 徐玲君, 陈刚, 李国栋, 薛阳. 薄壁堰泄流能力的数值模型计算及模拟自由水面的评价[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(1):225-230. doi: 10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2010.01.006XU Lingjun, CHEN Gang, LI Guodong, XUE Yang. Numerical simulation about Rectangle Sharp-crested Weir and evaluation of free-surface[J]. Journal of Northwest A& F University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(1):225-230. doi: 10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2010.01.006 [29] Cerino A E, Taddia G, Gizzi M, Lo R S. Reliability of spring recession curve analysis as a function of the temporal resolution of the monitoring dataset[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(7):249. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09529-2 [30] 张春来, 黄芬, 蒲俊兵, 曹建华. 中国岩溶碳汇通量估算与人工干预增汇途径[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4):40-52.ZHANG Chunlai, HUANG Fen, PU Junbing, CAO Jianhua. Estimation of karst carbon sink fluxes and manual intervention to increase carbon sinks in China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(4):40-52. [31] 康志强, 陈骏, 袁道先, 何师意, 邓艳, 陈旸, 刘媛媛, 姜光辉, 张勤军. 岩溶关键带植被对水循环过程的影响作用研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(3):391-396. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.080201KANG Zhiqiang, CHEN Jun, YUAN Daoxian, HE Shiyi, DENG Yan, CHEN Yang, LIU Yuanyuan, JIANG Guanghui, ZHANG Qinjun. The effect of vegetation on groundwater cycle in the critical zone of the karst area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(3):391-396. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.080201 [32] Chang W, Wan J W, Tan J H, Wang Z X, Jiang C, Huang K. Responses of spring discharge to different rainfall events for single-conduit karst aquifers in western Hunan Province, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(11):5775-5775. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115775 [33] Luo M M, Chen Z H, Yin D C, Jakada H, Huang H, Zhou H, Wang T. Surface flood and underground flood in Xiangxi River Karst Basin: Characteristics, models, and comparisons[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 27(1):15-21. doi: 10.1007/s12583-016-0624-5 [34] 万豪杰, 赵骏, 张松松, 张茹星. 永顺隧道岩溶涌水风险性评价及地下水流量衰减过程分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(5):1-7, 16.WAN Haojie, ZHAO Jun, ZHANG Songsong, ZHANG Ruxing. Analysis of water flow and risk assessment of karst water gushing in Yongshun Tunnel[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 26(5):1-7, 16. [35] Gan F L, He B H, Qin Z Y, Li W B. Role of rock dip angle in runoff and soil erosion processes on dip/anti-dip slopes in a karst trough valley[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020:588. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125093 [36] Zeng C, Liu Z H, Zhao M, Yang R. Hydrologically-driven variations in the karst-related carbon sink fluxes: Insights from high-resolution monitoring of three karst catchments in Southwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 533:74-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.049 [37] Zhang C, Yan J, Pei J G, Jiang Y J. Hydrochemical variations of epikarst springs in vertical climate zones: A case study in Jinfo Mountain National Nature Reserve of China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 63(2):375-381. doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0708-y [38] Liu Z H, Li Q, Sun H L, Wang J L. Seasonal, diurnal and storm-scale hydrochemical variations of typical epikarst springs in subtropical karst areas of SW China: Soil CO2 and dilution effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337(1-2):207-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.01.034 [39] 刘朋雨, 张连凯, 黄奇波, 覃小群. 外源水和外源酸对万华岩地下河系统岩溶碳汇效应的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(1):17-23.LIU Pengyu, ZHANG Liankai, HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun. Effect of exogenous water and acid on karst carbon sink in the Wanhuayan underground river system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1):17-23. [40] 任坤, 潘晓东, 曾洁, 焦友军, 彭聪, 梁嘉鹏. 岩溶区不同土地利用下地下水碳同位素地球化学特征及生态意义[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(10):4523-4531.REN Kun, PAN Xiaodong, ZENG Jie, JIAO Youjun, PENG Cong, LIANG Jiapeng. Geochemical characteristics and ecological significance of carbon isotopes in groundwater under the influence of different land use types in karst areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(10):4523-4531. [41] 李汇文, 王世杰, 白晓永, 操玥, 田义超, 罗光杰, 陈飞, 李琴, 吴路华, 王金凤, 王明明, 田诗琪, 邓元红, 胡泽银, 杨钰杰, 李朝君, 路茜, 习慧鹏, 陈欢, 冉晨, 罗旭玲. 气候变化及生态恢复对喀斯特槽谷碳酸盐岩风化碳汇的影响评估[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16):6158-6172.LI Huiwen, WANG Shijie, BAI Xiaoyong, CAO Yue, TIAN Yichao, LUO Guangjie, CHEN Fei, LI Qin, WU Luhua, WANG Jinfeng, WANG Mingming, TIAN Shiqi, DENG Yuanhong, HU Zeyin, YANG Yujie, LI Chaojun, LU Xi, XI Huipeng, CHEN Huan, RAN Chen, LUO Xuling. Effects of climate change and ecological restoration on carbonate rock weathering carbon sequestration in the karst valley of Southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16):6158-6172. [42] 孙亚卿, 李春, 石剑. 长江流域夏季极端高温的年代际变化特征及其与大西洋多年代际振荡的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(2):13-22. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20210079SUN Yaqing, LI Chun, SHI Jian. Interdecadal variation of Summer Extreme High Temperature in the Yangtze River and its relationship with Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2022, 52(2):13-22. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20210079 [43] Zhang C. Carbonate rock dissolution rates in different landuses and their carbon sink effect[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(35):3759-3765. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4404-4 [44] Zhao M, Liu Z, Li H C, Zeng C, Yang R, Chen B, Yan H. Response of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and δ13CDIC to changes in climate and land cover in SW China karst catchments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 165:123-136. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.041 -






 下载:
下载: