Screening and isolation of carbonic anhydrase-producing microorganisms from rocky karst habitats
-
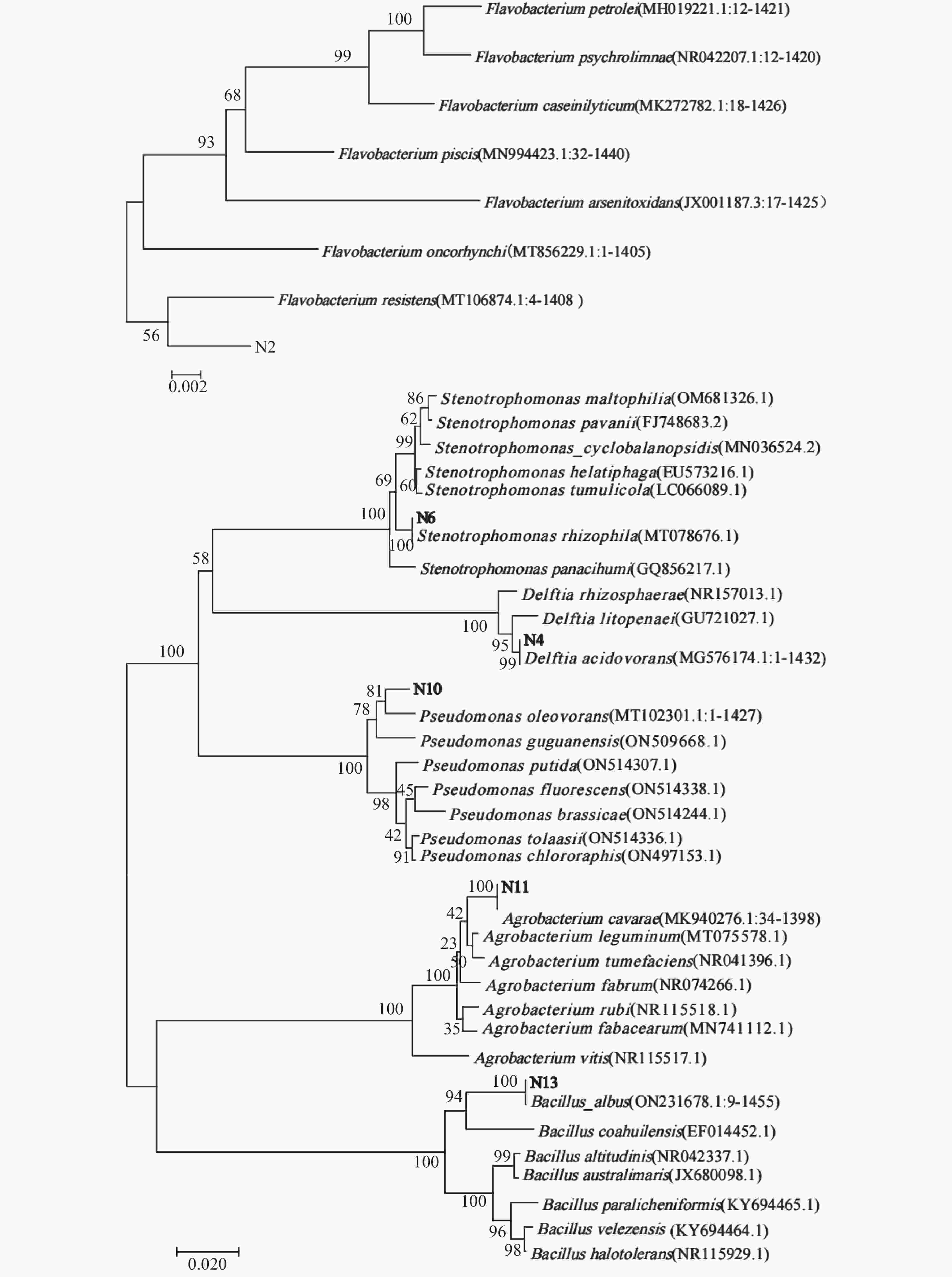
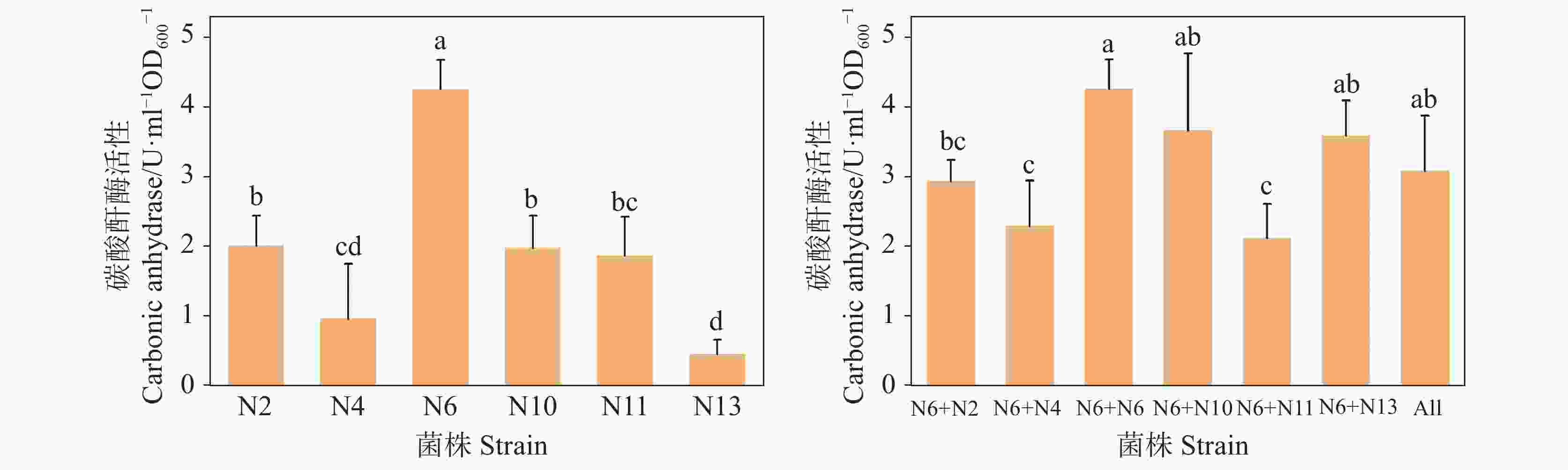
摘要: 喀斯特地区存在丰富的碳酸盐岩,是地球上最重要的碳库。碳酸酐酶(Carbonic anhydrase, CA)是地球上催化反应速率最快的几种酶之一,通过催化CO2的水合反应,不仅可以促进碳酸盐岩的风化,还可以通过吸收大气中的CO2来固定碳源。本研究目的是遴选喀斯特极度退化生境高CA活性菌株/菌群,探讨其用于喀斯特生态修复的可行性。利用碳酸钙培养基从喀斯特石质生境中分离筛选出产CA的菌株,并进行形态学观察、生理生化鉴定和分子生物学鉴定。通过CA活性的测定确定高CA活性的菌株,并比较单菌与多菌株组合群落的CA活性差异。利用碳酸钙培养基共分离得到产CA菌株6株,分别为耐药黄杆菌(Flavobacterium resistens)、食酸代尔夫特菌(Delftia acidovorans)、嗜根寡养单胞菌(Stenotrophomonas rhizophila)、食油假单胞菌(Pseudomonas oleovorans)、洞穴农杆菌(Agrobacterium cavarae)、白色杆菌(Bacillus albus),其中嗜根寡养单胞菌的CA活性最高,且其与其它菌株组合后CA活性均降低,说明产CA微生物的竞争作用可能大于协同作用,且在极度寡营养环境中,该嗜根寡养单胞菌具有较大的应用潜力。Abstract:
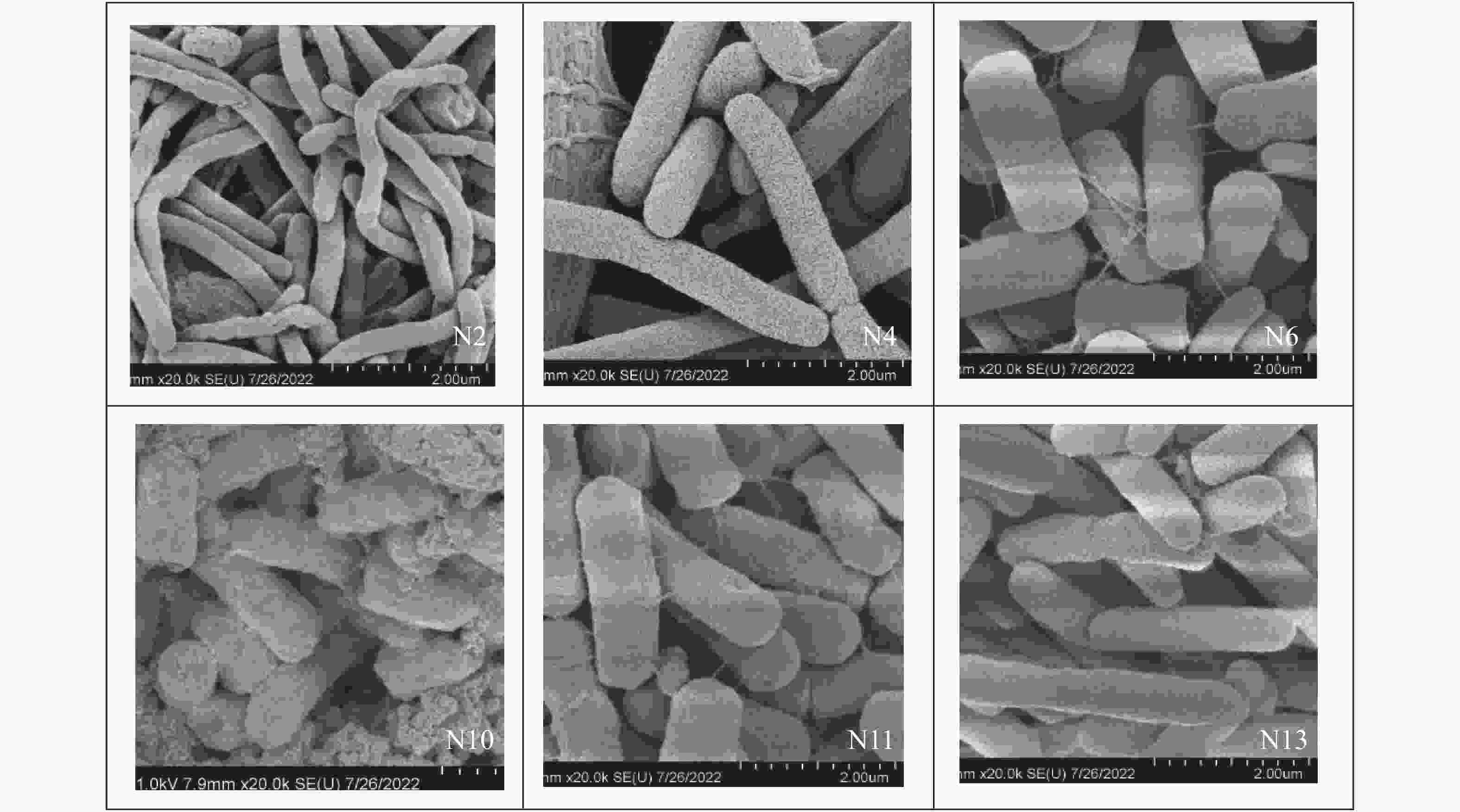
In China, the total area of rocky desertification covers 1.01×107 hm2, accounting for 22.3% of the karst area. Nowadays, rocky desertification has become one of the three major land degradation problems in our country, which has seriously affected our economic development and environmental governance. Naturally, rock weathering in the karst area is so long that it takes from a few decades to a hundred years to form a centimeter think of red soil. Because the karst area is rich in calcium and barren in soil, ecological restoration of this area is urgent in both rocky desertification control and karst carbon sink. Carbonic Anhydrase (CA), one of the fastest catalyzing enzymes, can promote the weathering of carbonate rocks by accelerating the hydration reaction of CO2, thus providing soil matrices for plant colonization. At the same time, CA can also be used to absorb CO2 in the atmosphere to fix the carbon source, thereby participating in the carbon cycle process of karst dynamic system. The CA-producing microorganisms are considered to have good application prospects in the restoration of degraded karst habitats. However, for the target strains isolated from favorable habitat, their weak adaptability to the extreme environment may constrain them from exerting their expected effects. In order to select the strain with high CA activity in the extremely degraded karst habitat, CA-producing strains were isolated from the samples of severely degraded rocky karst habitats in this study. The study area is located in Hechi City, Guangxi Zhuang (23°41'–25°37' N, 106°34'–109°09' E). It has a subtropical monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 16.9–21.5 ℃. The area is typically developed with karst, scattered with thin soil and highly exposed with rocks. From September to October 2021, four different habitat samples were collected, including lichen in the area with extreme rocky desertification weathered materials under moss, soil under moss, and weathered materials under moss in karst native forest. The source of isolation was a mixture of the four different habitat samples, 1g of each. CA-producing strains were isolated and screened from karst rocky habitats by inoculating suspension of isolation source in calcium carbonate medium with a sprayer. The field emission scanning electron microscope was used for morphological identification of the strain. The physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain were confirmed by carbohydrate decomposition test, V-P test, methyl red test, citrate utilization test, nitrate reduction test, starch hydrolysis test and contact enzyme test. Strains were identified by 16S rRNA sequence analysis. The CA activity of single strain and mixed strain was determined by electrode method. The sequence alignment was performed in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Database. In MEGA6, Neighbor-Joining method is used to construct the phylogenetic tree. SPSS software was used to analyze whether there were significant differences in CA activity among different strains/microflora. The results show that six CA-producing strains were isolated by calcium carbonate medium, namely, Flavobacterium resistens, Delftia acidovorans, Stenotrophomonas rhizophila, Pseudomonas oleovorans, Agrobacterium cavarae and Bacillus albus. The CA activity of Stenotrophomonas rhizophila was the highest, up to 4.27 U·mL−1·OD600−1, while that of Bacillus albus was only 0.46 U·mL−1·OD600−1, which indicated that although CA commonly existed in prokaryotes, the activity of different species of bacteria varied greatly. Mixed culturing of Stenotrophomonas rhizophila whose CA activity is high with other strains led to a decrease in CA activity, indicating the great potential application of Stenotrophomonas rhizophila in the extremely oligotrophic environment. The results provide a new bacterial source for ecological restoration of extremely degraded karst habitats. However, all the CA activity decreased when the isolated Stenotrophomonas rhizophila strain N6 with high CA activity is mixed with other 5 strains. Because of the complex living environment, the competition of indigenous microbial community will reduce the survival efficiency of the added microorganisms, make it difficult to form a stable community structure, and then reduce the repair effect. In restoration of degraded karst habitat, whether there is a kind of dominant bacteria that is symbiotic with Stenotrophomonas rhizophila N6 to jointly promote carbonate dissolution is a research focus. Therefore, future studies should identify the core species that drive the restoration of degraded habitats, and explore the relationship between the isolated and culturable CA dominant bacteria and the core species. These study focuses will promote the research and development of biological fertilizer for the rapid restoration of degraded karst habitats. -
Key words:
- karst /
- carbonic anhydrase /
- carbon cycle /
- extremely degraded habitat /
- rocky habitat /
- ecological restoration
-
表 1 培养基的成分
Table 1. Composition of the culture medium
培养基名称 成分 碳酸钙琼脂培养基 CaCO3 50 g、ZnSO4 1 μmol、琼脂15 g、蒸馏水1 000 mL LB培养基 胰蛋白胨10 g、酵母提取物5 g、NaCl 5 g、葡萄糖1 g、蒸馏水1 000 mL 葡萄糖发酵培养基 蛋白胨1 g、NaCl 0.5 g、0.2%溴百里香酚兰1.2 mL、葡萄糖1 g、蒸馏水100 mL V-P反应培养基 蛋白胨1.5 g、葡萄糖1.5 g、K2HPO4 1.5 g、蒸馏水300 mL 固体柠檬酸盐培养基 柠檬酸钠1 g、硫酸镁0.2 g、NaCl 5 g、NH4H2PO4 1 g、K2HPO4 1 g、琼脂20 g、
1%溴麝香草酚蓝酒精溶液10 mL、蒸馏水1 000 mL硝酸盐还原培养基 硝酸钾0.2 g、蛋白胨5 g、蒸馏水1 000 mL 淀粉水解培养基 牛肉膏0.5 g、蛋白胨1 g、NaCl 0.5 g、可溶性淀粉0.2 g、琼脂2 g、蒸馏水100 mL 表 2 不同菌种在LB固体培养基上的形态比较
Table 2. Comparison of different bacteria species on the LB solid culture medium
样品编号 菌落形态特征 菌落颜色 N2 表面光滑,边缘整齐 黄色 N4 表面光滑,中央凸起周围扁平,边缘不规则 白色 N6 表面光滑,边缘整齐 黄色 N10 表面光滑,边缘整齐 白色 N11 表面光滑饱满,边缘整齐 白色 N13 表面光滑,蜡状,边缘不规则 白色 表 3 菌株的生理生化特征
Table 3. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of strains
样品编号 N2 N4 N6 N10 N11 N13 糖类分解 + + + − + + V-P + + + + + + 甲基红 − − + − − + 硝酸盐还原 + + − + − − 淀粉水解 − − + − − + 柠檬酸盐利用 − + − − − − 接触酶 + + + − + − -
[1] 袁道先, 蔡桂鸿. 岩溶环境学[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988. [2] 王世杰, 季宏兵, 欧阳自远, 周德全, 郑乐平, 黎廷宇. 碳酸盐岩风化成土作用的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1999, 29(5):441-449. [3] 曹建华, 袁道先, 潘根兴. 岩溶生态系统中的土壤[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(1):37-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.01.006CAO Jianhua, YUAN Daoxian, PAN Genxing. Some soil features in karst ecosystem[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2003, 18(1):37-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.01.006 [4] 蒋忠诚, 杨德生, 曹建华. 中国水土流失防治与生态安全·西南岩溶卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. [5] WANG Chenwei, LI Wei, SHEN Taiming, CHENG Wenli, YAN Zhuang, YU Longjiang. Influence of soil bacteria and carbonic anhydrase on karstification intensity and regulatory factors in a typical karst area[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 313:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.016 [6] Mailloux Brian J, Alexandrova Ekaterina, Keimowitz Alison R, Wovkulich Karen, Freyer Greg A, Herron Michael, Stolz John F, Kenna Timothy C, Pichler Thomas, Polizzotto Matthew L, Dong Hailiang, Bishop Michael, Knappett Peter S K. Microbial mineral weathering for nutrient acquisition releases arsenic[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75:2558-2565. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02440-07 [7] 吴雁雯, 张金池. 微生物碳酸酐酶在岩溶系统碳循环中的作用与应用研究进展[J]. 生物学杂志, 2015, 32(3):78-83.WU Yanwen, ZHANG Jinchi. Microbial carbonic anhydrase action and application on carbon cycling in karst dynamic system: A review[J]. Journal of Biology, 2015, 32(3):78-83. [8] 蒋忠诚, 章程, 罗为群, 肖琼, 吴泽燕. 我国岩溶地区碳汇研究进展与展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(3):345-355.JIANG Zhongcheng, ZHANG Cheng, LUO Weiqun, XIAO Qiong, WU Zeyan. Research progress and prospect of carbon sink in karst region of China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(3):345-355. [9] 刘再华. 碳酸酐酶对碳酸盐岩溶解的催化作用及其在大气CO2沉降中的意义[J]. 地球学报, 2001, 22(5):477-480.LIU Zaihua. The role of carbonic anhydrase as an activator in carbonate rock dissolution and its significance in atmospheric CO2 precipitation[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2001, 22(5):477-480. [10] Li Wei, Yu Longjiang, Yuan Daoxian, Wu Yun, Zeng Xiandong. A study of the activity and ecological significance of carbonic anhydrase from soil and its microbes from different karst ecosystems of Southwest China[J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 272(1):133-141. [11] Li Wei, Yu Longjiang, Wu Yun, JIA Liping, Yuan Daoxian. Enhancement of Ca2+ release from limestone by microbial extracellular carbonic anhydrase[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(4):950-953. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.03.021 [12] 李永双, 范周周, 国辉, 周金星, 彭霞薇. 菌剂添加对不同树种根际土壤微生物及碳酸钙溶蚀的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):854-862.LI Yongshuang, FAN Zhouzhou, GUO Hui, ZHOU Jinxing, PENG Xiawei. Effects of microorganisms agent addition on soil microbes in different rhizosphere soils and calcium carbonate dissolution[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6):854-862. [13] 易哲, 叶姜瑜, 李大荣, 窦建军, 石玉竹. 喀斯特地貌中碳酸酐酶微生物鉴定与特性研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2017, 31(8):113-119.YI Zhe, YE Jiangyu, LI Darong, DOU Jianjun, SHI Yuzhu. Identification and characterization of bacterium with carbonic anhydrase in karst landform[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2017, 31(8):113-119. [14] 邓洁, 李建宏, 管章玲, 胡碧洋, 赵蕾, 李朋富. 一株产碳酸酐酶附生菌对铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)生长的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 2012, 24(3):429-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.03.015DENG Jie, LI Jianhong, GUAN Zhangling, HU Biyang, ZHAO Lei, LI Pengfu. Effect of attached bacteria of carbonic anhydrase on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2012, 24(3):429-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.03.015 [15] 陈羽. 会仙岩溶湿地藻与微生物及其碳酸酐酶的碳效应研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2014.CHEN Yu. Research on the carbon effects of algae and microorganisms and their carbonic anhydrase in Huixian karst wetland[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2014. [16] 吕现福. 岩溶洞穴微生物群落特征及微生物在碳酸钙沉积中的作用[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018.LYU Xianfu. Geomicrobiology of karst cave: Bacterial community and controls on calcium carbonate formation[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018. [17] Van Elsas J D, Duarte G F, Rosado A S, Smalla K. Microbiological and molecular biological methods for monitoring microbial inoculants and their effects in the soil environment[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 1998, 32(2):133-154. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(98)00025-6 [18] Kizilkaya Ridvan. Yield response and nitrogen concentrations of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum) inoculated with Azotobacter chroococcum strains[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2008, 33(2):150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.02.011 [19] 黄芬, 黄艳梅, 高喜, 曹建华. 岩溶环境因子对桂林毛村岩溶区土壤微生物胞外碳酸酐酶活性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2015, 46(10):1792-1797. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1792HUANG Fen, HUANG Yanmei, GAO Xi, CAO Jianhua. Effects of karst environmental factors on activity of soil microorganic extracellular Carbonic anhydrase of karst area in Maocun village, Guilin[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(10):1792-1797. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1792 [20] Lee Myungjin, Woo Sunggeun, Chae Myoungsoo, Shin Mincheol, Jung Haemin, Ten Leonid N. Stenotrophomonas daejeonensis sp. nov., isolated from sewage[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2011, 61(3):598-604. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.017780-0 [21] Ouattara Aboubakar Sidiki, Le Mer Jean, Joseph Manon, Macarie Hervé. Transfer of Pseudomonas pictorum Gray and Thornton 1928 to genus Stenotrophomonas as Stenotrophomonas pictorum comb. nov., and emended description of the genus Stenotrophomonas[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2017, 67(6):1894-1900. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001880 [22] Palleroni Norberto J, Bradbury John F. Stenotrophomonas, a new bacterial genus for Xanthomonas maltophilia (Hugh 1980) Swings et al. 1983[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 1993, 43(3):606-609. [23] Hagemann Martin, Ribbeck Busch Kathrin, Klähn Stephan, Hasse Dirk, Steinbruch Robert, Berg Gabriele. The plant-associated bacterium Stenotrophomonas rhizophila expresses a new enzyme for the synthesis of the compatible solute glucosylglycerol[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2008, 190(17):5898-5906. doi: 10.1128/JB.00643-08 [24] Suckstorff I, Berg Gabriele. Evidence for dose-dependent effects on plant growth by Stenotrophomonas strains from different origins[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2003, 95(4):656-663. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.02021.x [25] Horath Thomas, Bachofen Reinhard. Molecular characterization of an endolithic microbial community in dolomite rock in the central Alps (Switzerland)[J]. Microbial Ecology, 2009, 58:290-306. doi: 10.1007/s00248-008-9483-7 [26] 唐源, 连宾, 程建中. 贵州喀斯特地区碳酸盐岩表生古菌群落结构及多样性研究:以南江大峡谷为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(2):193-201. doi: 10.11932/karst20170206TANG Yuan, LIAN Bin, CHENG Jianzhong. Archaeal community structure and diversity of the carbonate rocks in karst regions, Guizhou: A case study of the Nanjiang canyon[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(2):193-201. doi: 10.11932/karst20170206 [27] Tang Yuan, Cheng Jianzhong, Lian Bin. Characterization of endolithic culturable microbial communities in carbonate rocks from a typical karst canyon in Guizhou (China)[J]. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 65(4):413-423. doi: 10.5604/17331331.1227667 -




 下载:
下载: