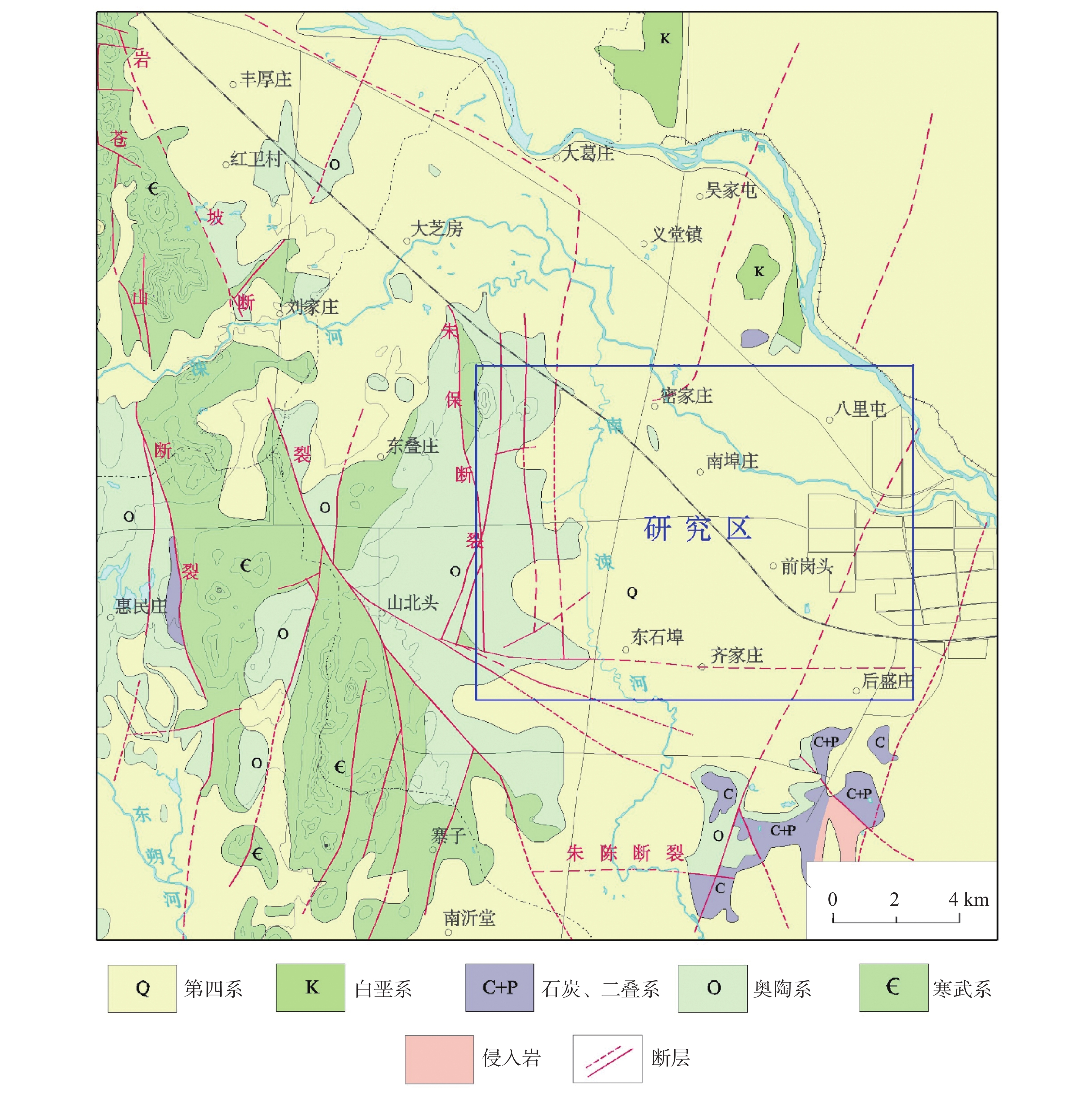
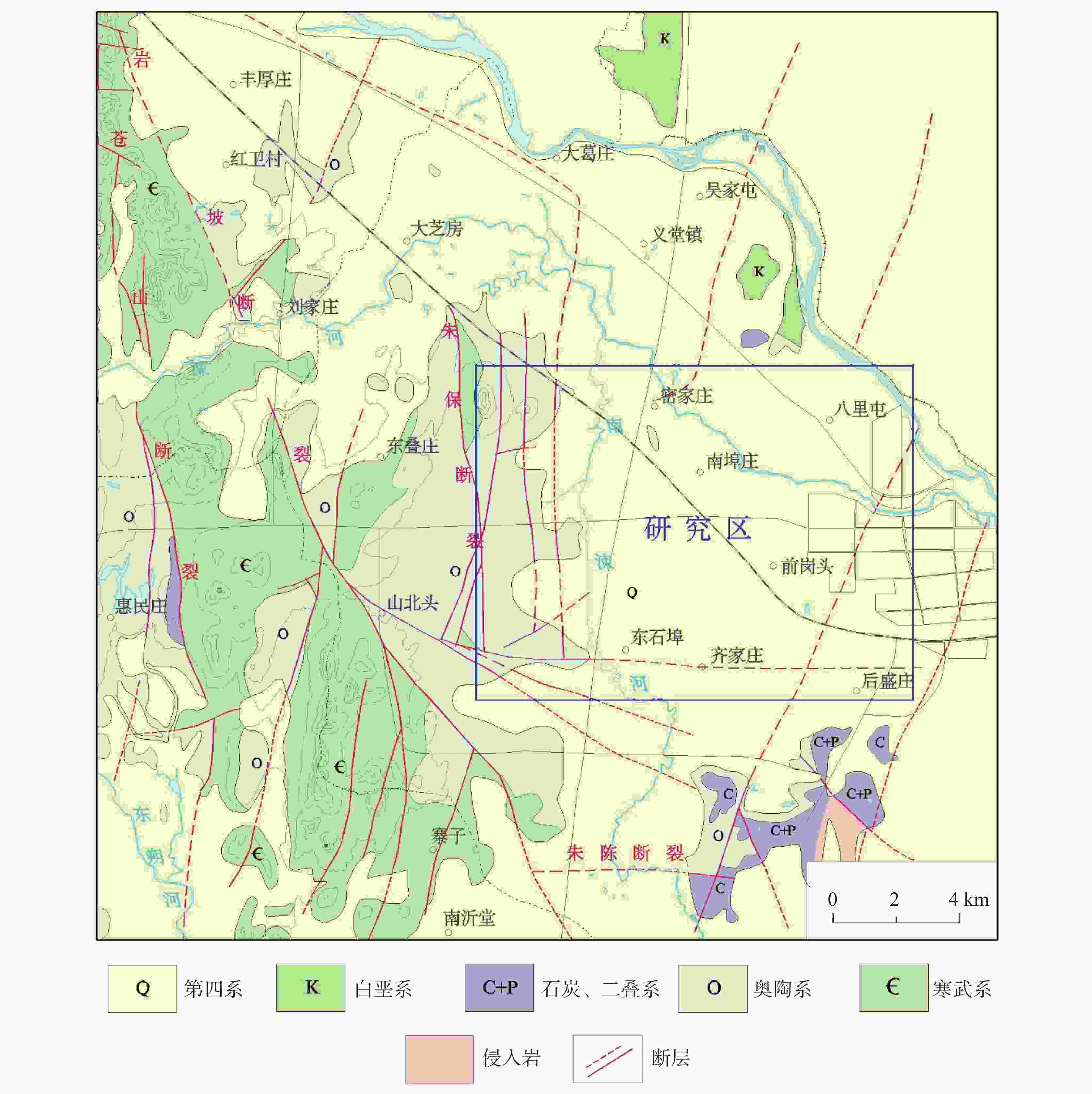
Study on the early warning model based on the occurrence index of karst collapse in Linyi City
-
摘要: 临沂市区中奥陶系灰岩岩溶发育,第四系覆盖层较薄,具备岩溶塌陷发育条件。20世纪80年代至21世纪初期岩溶塌陷灾害频发。文章以临沂市区岩溶塌陷作为研究对象,对其分布规律及影响因素进行了研究,提出了基于岩溶塌陷发生指数的预警模型,该模型以水位为主控监测因素,多因素叠加综合判定进行预警,并使用历史数据对模型进行验证,结果表明:该模型在临沂市城区重点监测区预警结果验证的可靠性较高,可为其他地区岩溶塌陷地质灾害监测预警提供借鉴。Abstract:
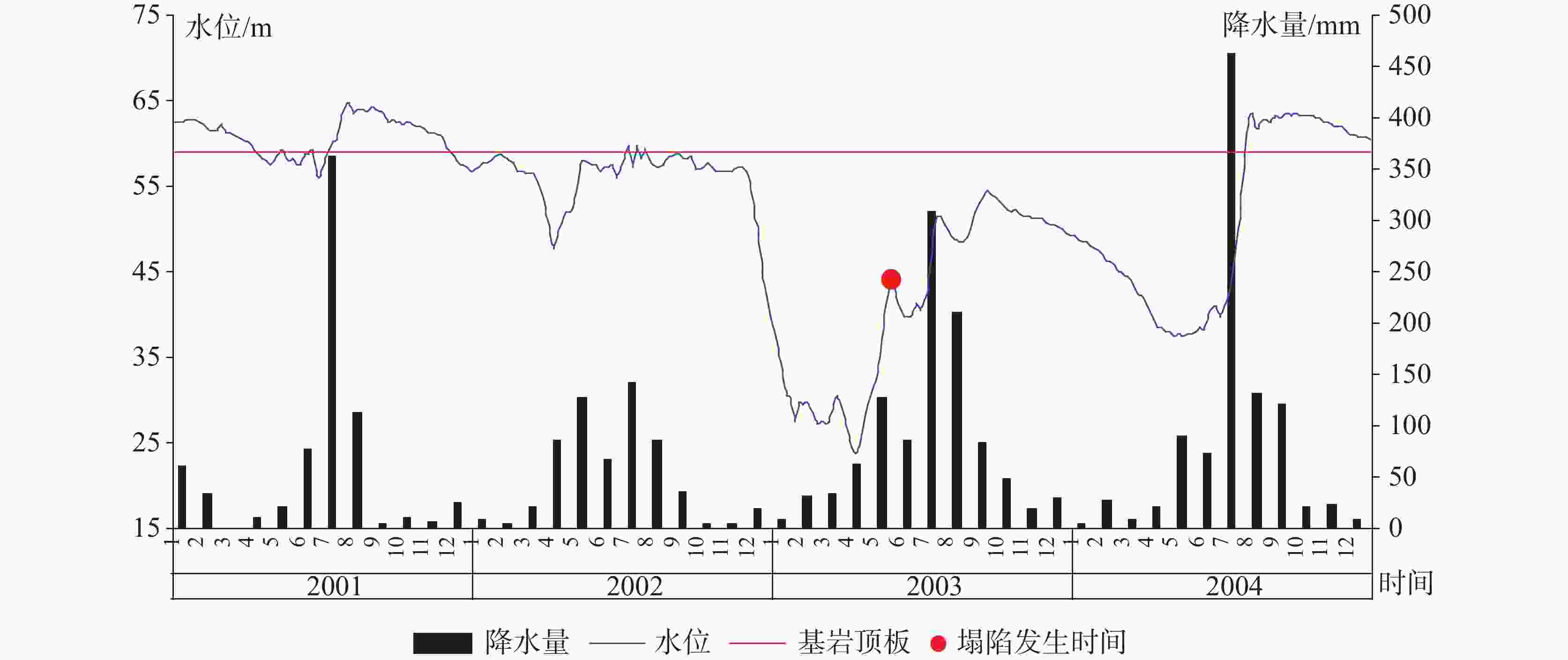
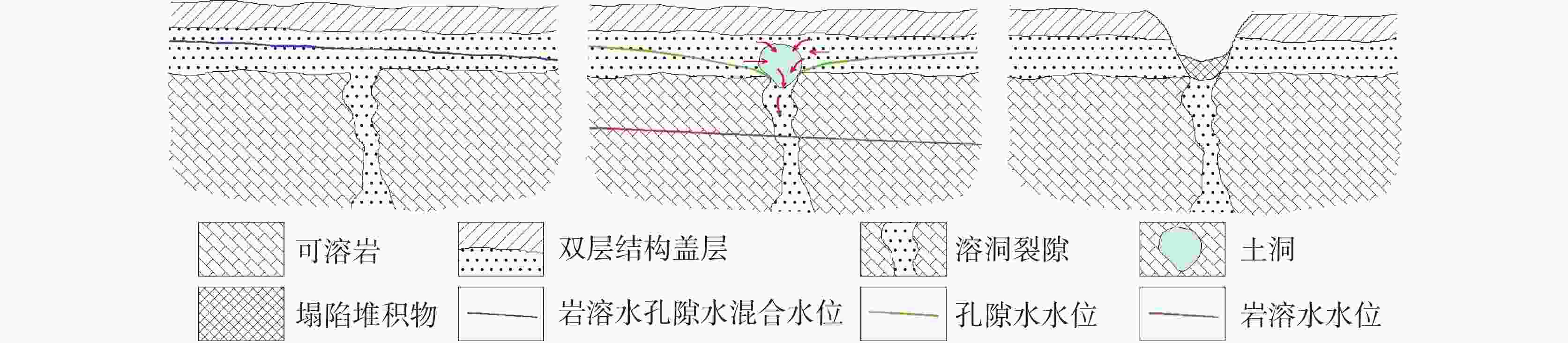
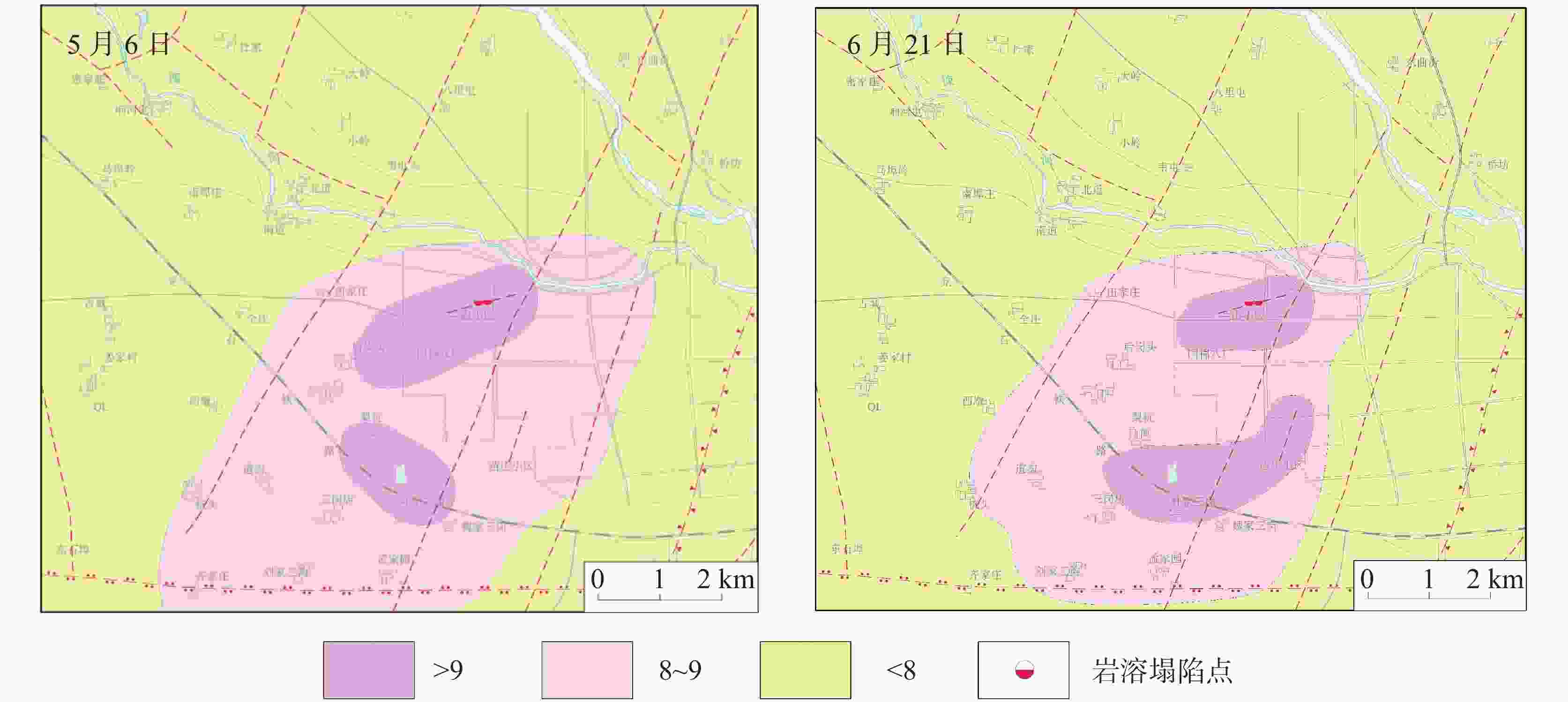
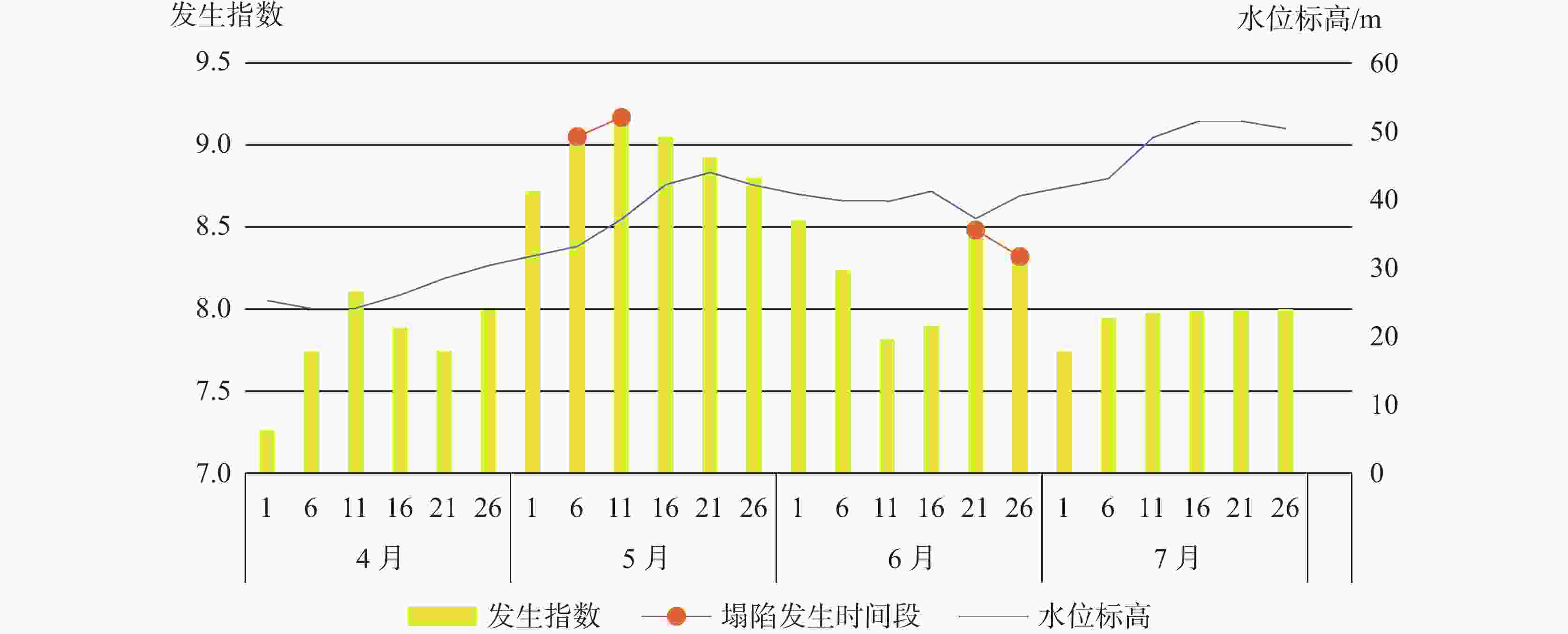
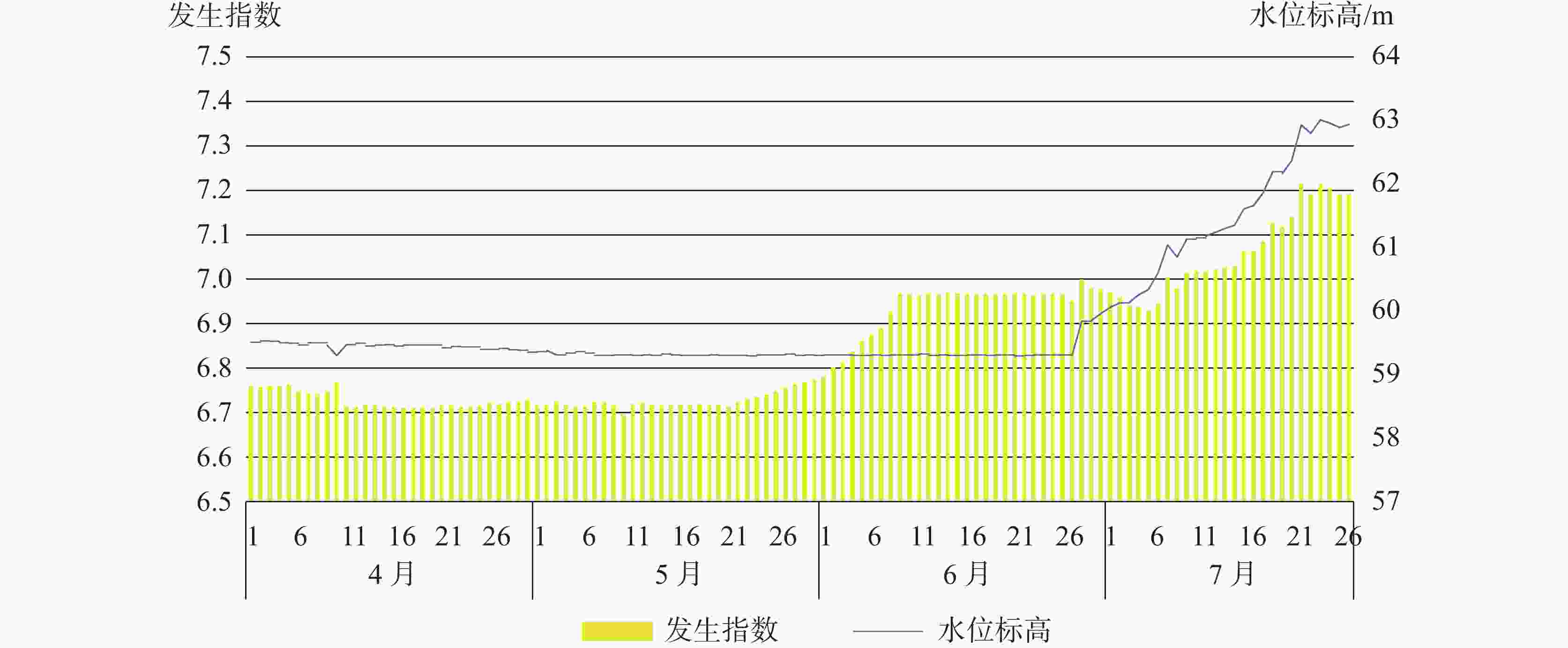
The urban area of Linyi City is endowed with the basic conditions for the development of karst collapse. In this area, Ordovician limestone with karst development is widely distributed, and the limestone is covered by a thin Quaternary overburden with a binary phase structure. From the 1980s to the early 21st century, the rapid development of Linyi City, the increase of groundwater exploitation and the decline of the overall regional water level led to the frequent occurrence of geological disasters of karst collapses, causing serious economic losses and social impact. In this study, the karst collapse in Linyi City is taken as the research object. The distribution law, geological conditions, and inducing factors of karst collapses are studied through statistical analysis. According to the analysis of the genesis mechanism of karst collapse in Linyi City, an early warning model based on the occurrence index of karst collapse is proposed. Taking the water level as the main monitoring factor, this model is constructed to comprehensively judge the early warning by the combination of multi-factors, and is verified by historical data. During the high incidence period from 1993 to 2012, a total of 17 karst collapses occurred in the study area. These karst collapses were caused by geological conditions such as topography, geological structure, and formation lithology, as well as inducing factors such as groundwater exploitation, human engineering activities, and precipitation. The distribution law of karst collapse reflects the consistency with its related influencing factors. Karst collapses are mainly distributed in the caprock area of double-layer structure with shallow karst development and small overburden thickness. They are also distributed near the surface water body and fault zone. Generally, karst collapses take place in the funnel areas and in the seasons with a large variation of water levels, They also occur in the influence range of human engineering activities. With a comprehensive index method, an early warning model based on the judgment made through multi-factors is established. The model comprehensively considers geological conditions and inducing factors and selects 10 influencing factors, including karst development degree, caprock thickness, caprock structure, distance from structure, distance from surface water, distance between water level and limestone roof, water level amplitude, distance from the center of depression cone, precipitation, and human engineering activities. Different weights of influencing factors and the range of influencing factors of each sub-condition are given and the early warning level is divided into four grades according to the occurrence index value. The model is verified by using historical data of the collapse when it occurred. For example, the data of 2003 was used for simulation and early warning validation. The karst collapse occurred in the east of the No.32 building in Lanshan community on May 8 and June 22 in 2003, and all the collapse points were located in the area at a high early warning level, and also fell into the time period of high early warning level. The results show that the model has high reliability in the verification of early warning in key monitoring areas of Linyi City, which can provide a reference for monitoring and early warning of karst collapse in other areas. -
表 1 主要岩溶塌陷情况一览表
Table 1. List of main karst collapses
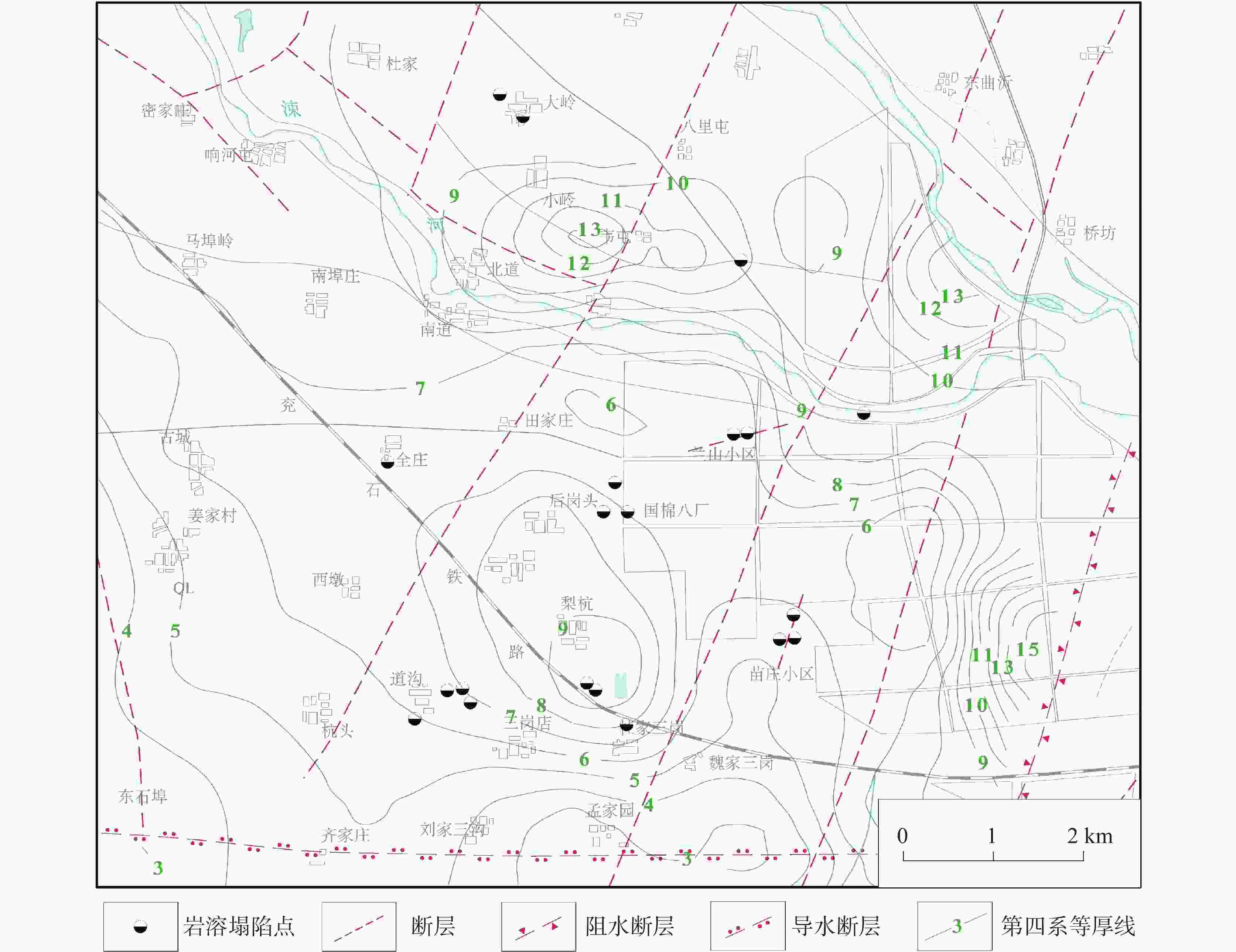
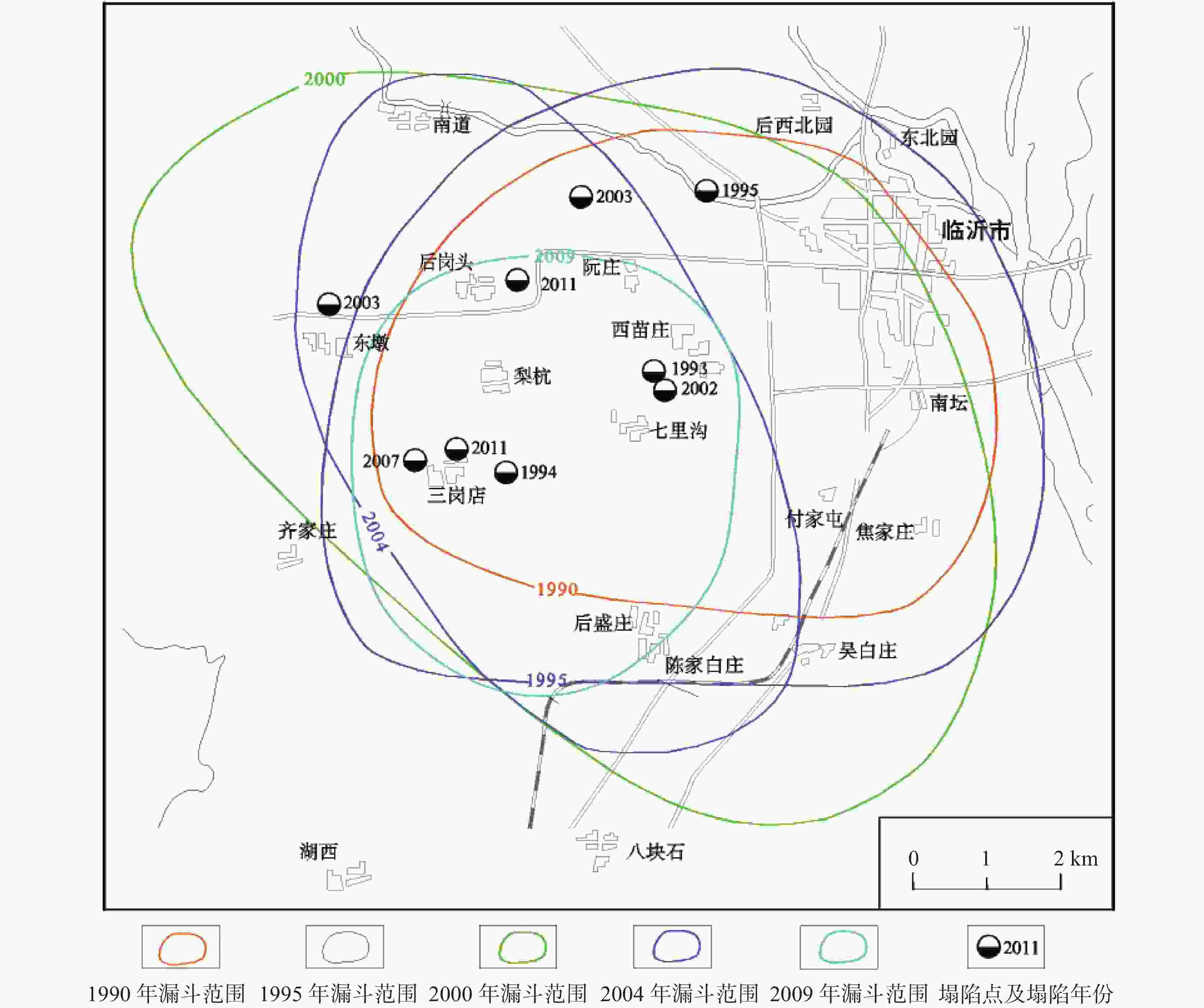
序号 塌陷年月 塌陷位置 陷坑个数 陷坑形态 地层结构 陷坑长度/m 陷坑宽度/m 陷坑深度/m 地层结构 覆层厚度/m 1 1993.6 苗庄小区 1 25.0 15.0 5.0 − − 2 1994.3 道沟村 1 3.0 3.0 2.8 二元相结构 3.0 3 1994.4 国棉八厂 3 6.3 6.3 2.3 二元相结构 8.0 8.0 8.0 5.0 2.2 2.2 2.1 4 1995.4 药材批发市场 多个 <3.0 <3.0 2.8 − − 5 2002.8 杜三岗村 3 10.0 10.0 2.5 − 6.1 4.5 4.5 2.5 1.5 1.5 2.5 6 2003.2 苗庄小区 − − − − 二元相结构 4.0 7 2003.5 临沂监狱 1 15.0 7.0 4.0 二元相结构 − 8 2003.6 兰山小区 1 4.7 4.7 4.0 二元相结构 10.0 9 2003.6 红埠寺村 1 0.8 0.8 − 二元相结构 − 10 2003.6 兰山小区 1 5.5 4.0 2.5 二元相结构 10.0 11 2005.6 雅禾纺织 1 20.0 10.0 5.0 二元相结构 − 12 2007.8 道沟村 1 1.0 1.0 9.0 二元相结构 − 13 2008.1 道沟村 1 1.5 1.5 − 二元相结构 − 14 2008.5 大岭村 9 − − − 二元相结构 6.0 15 2011.6 后岗头村 1 − − 2.5 二元相结构 − 16 2011.8 道沟村 1 0.5 0.5 − 二元相结构 − 17 2012.7 大岭村 2 5.0 3.0 2.0 二元相结构 − 3.3 1.2 1.5 表 2 岩溶塌陷分布规律(地质条件)
Table 2. Distribution law of karst collapse (geological conditions)
距离/km 塌陷数量/个 所占比例/% 地表水体 <1 16 76.2 >1 5 23.8 断裂带 <1 15 71.4 >1 6 28.6 表 3 岩溶塌陷分布规律(诱发因素)
Table 3. Distribution law of karst collapse (inducing factors)
距离/km 塌陷数量/个 所占比例/% 漏斗中心 <2 14 66.7 >2 7 33.3 表 4 指标权重取值表
Table 4. List of index weight value
基本条件 权重取值 分项条件 权重取值 地质条件 0.572 1 岩溶发育程度 0.257 4 盖层厚度 0.074 4 盖层结构 0.097 3 与构造距离 0.085 8 与地表水体距离 0.057 2 诱发因素 0.427 9 水位与界面距离 0.124 1 水位变幅 0.132 6 与降落漏斗中心距离 0.055 6 降水量 0.038 5 人类工程活动 0.077 1 表 5 影响因子取值范围表
Table 5. List of the value range of influencing factors
基本条件 分项条件 分项条件影响因素取值范围(0~10) 0~2 2~4 4~6 6~8 8~10 地质条件 岩溶发育程度 无 很不发育 不发育 发育 很发育 盖层厚度/m <0.5
>2520~25 15~20 0.5~3
11~153~11 盖层结构 无 一元结构 一元结构 二元结构 多元结构 与构造距离/m >1 000 700~1 000 400~700 200~400 <200 与地表水体距离/m >1 000 700~1 000 400~700 200~400 <200 诱发因素 水位与
基岩面
关系水位处于
基岩面
以上水位偶尔处
于基岩面以
下5~10 m水位偶尔处
于基岩面以
下10~20 m水位长期处
于基岩面以
下10~20 m基岩面附近5 m以
内波动或长期处于
基岩面20 m以下水位变幅/m <1 1~4 4~7 7~10 >10 与降落漏斗中心距离 >8 000或不处于
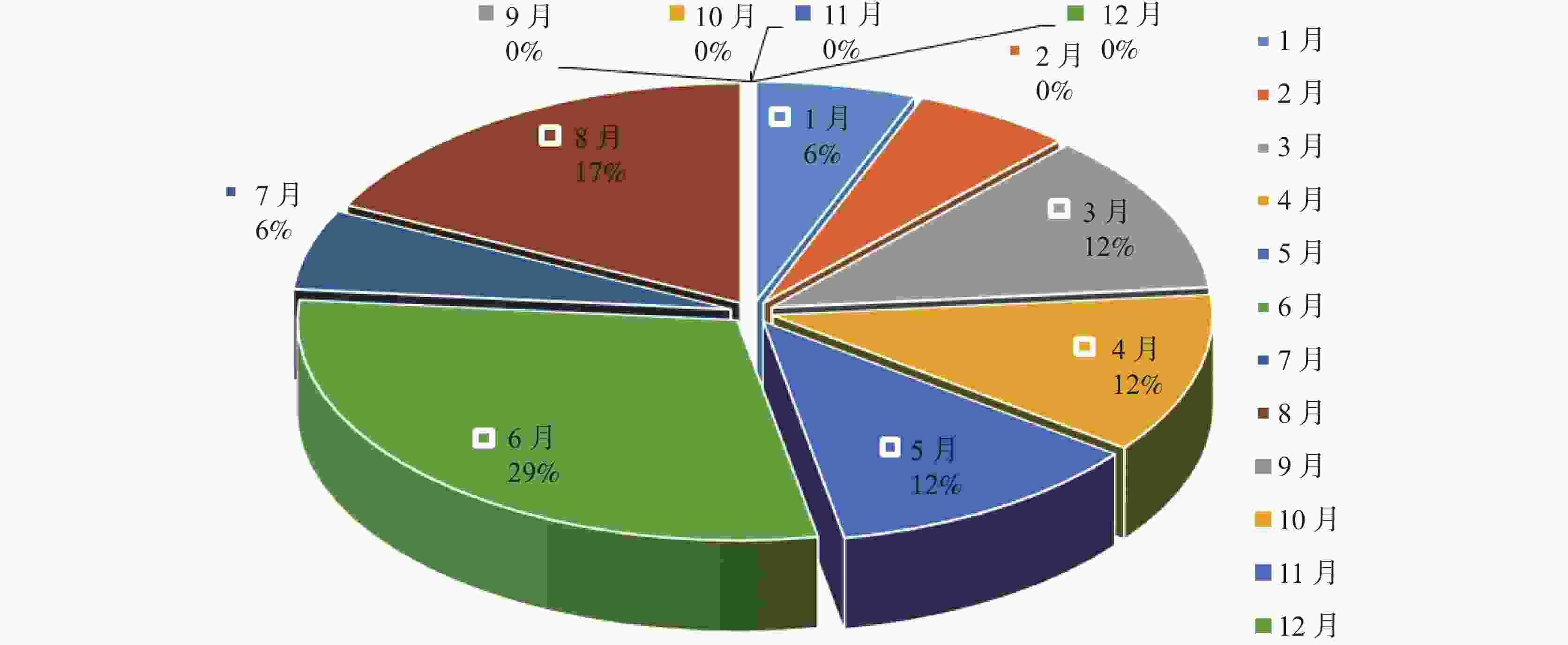
漏斗范围内5 000~8 000 3 000~5 000 2 000~3 000 <2 000 降水量/mm 小时降雨量 <2.6 2.6~8 8~12 12~16 >16 日降雨量 <10 10~25 25~50 25~50 >50 月降雨量
环比增长<40 40~60 60~80 80~100 >100 与抽水井距离/m >500 200~500 100~200 50~100 <50 -
[1] 贺可强, 王滨, 杜汝霖. 中国北方岩溶塌陷[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.HE Keqiang, WANG Bin, DU Rulin. Karst collapse in Northern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005. [2] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. 岩溶地面塌陷防治工程勘查规范(试行)T/CAGHP 076-2020[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2020.China Association of Geological Hazard Prevention. Code for geological investigation of karst collapse prevention (Trial) T/CAGHP 076-2020[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2020. [3] 王金晨, 吴迪, 娄万鹏, 吴远斌. 岩溶塌陷监测技术及发展趋势[J]. 工程技术研究, 2021, 6(8):55-57. [4] 蒙彦, 雷明堂. 岩溶塌陷研究现状及趋势分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(3):411-417.MENG Yan, LEI Mingtang. Analysis of situation and trend of sinkhole collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(3):411-417. [5] 王甫强, 张占彪, 李虎, 柯洋. 光纤传感技术在岩溶地面塌陷地质灾害监测中的应用[J]. 城市勘测, 2021(4):174-178.WANG Fuqiang, ZHANG Zhanbiao, LI Hu, KE Yang. Application of optical fiber sensing technology in geological hazard monitoring of karst ground collapse[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2021(4):174-178. [6] 梁明, 张观长. 地质雷达方法在城市岩溶塌陷隐患识别中的应用[J]. 西部资源, 2021(3):101-103.LIANG Ming, ZHANG Guanchang. The application of GPR method in the hidden danger identification of urban karst collapse[J]. Western Resources, 2021(3):101-103. [7] 汝亮, 张业智, 朱裕振, 高菡, 刘雪. 泰安市岩溶塌陷特征及探测方法研究[J]. 山东国土资源, 2020, 36(10):65-72.RU Liang, ZHANG Yezhi, ZHU Yuzhen, GAO Han, LIU Xue. Study on the characteristics and detection methods of karst collapse in Tai'an City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2020, 36(10):65-72. [8] 蒋小珍, 雷明堂. 岩溶塌陷灾害的岩溶地下水气压力监测技术及应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5):786-791. doi: 10.11932/karst20180517JIANG Xiaozhen, LEI Mingtang. Monitoring technique and its application of karst groundwater-air pressure in karst collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5):786-791. doi: 10.11932/karst20180517 [9] 蒙彦, 黄健民, 贾龙. 基于地下水动力特征监测的岩溶塌陷预警阈值探索:以广州金沙洲岩溶塌陷为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(3):408-414. doi: 10.11932/karst20180311MENG Yan, HUANG Jianmin, JIA Long. Early warning threshold of sinkhole collapse based on dynamic characteristics from groundwater monitoring: A case study of Jinshazhou of Guangzhou, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3):408-414. doi: 10.11932/karst20180311 [10] 李清春, 冯克印, 郑庭明, 董强. 临沂市城区岩溶塌陷特征及成因分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 2005(9):61-64.LI Qingchun, FENG Keyin, ZHENG Tingming, DONG Qiang. Characteristics and origin analysis of karst collapse in Linyi City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2005(9):61-64. [11] 杨全城, 姚春梅, 邵景力, 李景波, 卞加升. 模糊综合评判在临沂城区岩溶塌陷危险性评价中的应用[J]. 山东国土资源, 2010, 26(6):23-26.YANG Quancheng, YAO Chunmei, SHAO Jingli, LI Jingbo, BIAN Jiasheng. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in evaluating karst collapse risks in Linyi urban district[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2010, 26(6):23-26. [12] 姚春梅, 杨全城, 邵景力, 雷晓东. 山东临沂市城区岩溶塌陷易损性和期望损失评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(2):74-76.YAO Chunmei, YANG Quancheng, SHAO Jingli, LEI Xiaodong. Vulnerability and expectation loss assessment of karst collapse in Linyi City, Shandong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(2):74-76. [13] Yao Chunmei, Yuan Fang, Meng Fanqi, Yang Quancheng, Shan Jicheng. Study on risk assessment method of karst collapse: Taking the karst collapse in Linyi urban areas as an example[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 310(5):1-9. [14] 姚春梅, 徐品, 刘瑞峰, 张永伟, 姚英强, 王元波, 商婷婷, 王小燕. 临沂市城区岩溶塌陷预警系统建设及研究报告[R]. 山东省地质环境监测总站, 2008.YAO Chunmei, XU Pin, LIU Ruifeng, ZHANG Yongwei, YAO Yingqiang, WANG Yuanbo, SHANG Tingting, WANG Xiaoyan. Construction and research report of karst collapse early warning system in Linyi City[R]. Shandong Geological Environment Monitoring Station, 2008. [15] 邹连庆, 刘瑞峰, 姚英强, 王集宁, 商婷婷, 付娟, 王兆林, 王小燕, 刘建梅. 临沂市城区岩溶塌陷预警运行维护项目阶段总结报告(2008年—2018年)[R]. 山东省地质环境监测总站, 2018. [16] 马海会. 临沂市区岩溶地面塌陷成因机理与防治对策研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2010.MA Haihui. Formation mechanism and prevention countermeasures of karst ground collapse in Linyi urban district[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2010. [17] 吴远斌, 刘之葵, 殷仁朝, 杨建兴, 罗伟权, 雷明堂, 戴建玲, 潘宗源. 湖南怀化盆地岩溶发育特征与分布规律[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(5):759-772, 807.WU Yuanbin, LIU Zhikui, YIN Renchao, YANG Jianxing, LUO Weiquan, LEI Mingtang, DAI Jianling, PAN Zongyuan. Karst development characteristics and distribution law in Huaihua basin, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(5):759-772, 807. [18] 冯亚伟. 山东省岩溶塌陷分布规律及成因机制[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(2):205-214. doi: 10.11932/karst2021y01FENG Yawei. Distribution and genesis of karst collapse in Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(2):205-214. doi: 10.11932/karst2021y01 [19] 吴亚楠, 周绍智, 王延岭, 焦玉国, 陈伟清, 程凤, 赵志伟. 国内外岩溶塌陷监测方法综述[J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(12):1-6.WU Ya'nan, ZHOU Shaozhi, WANG Yanling, JIAO Yuguo, CHEN Weiqing, CHENG Feng, ZHAO Zhiwei. Summary of karst collapse monitoring methods in China and abroad[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2018, 34(12):1-6. [20] 王延岭. 山东省泰莱盆地岩溶地面塌陷影响因素分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(1):60-66.WANG Yanling. Research on influential factors of the karst collapse in the Tailai basin of Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(1):60-66. [21] 吴亚楠, 杨云涛, 焦玉国, 刘志涛, 王延岭, 翟代廷, 周绍智, 魏凯, 程凤. 山东省岩溶塌陷发育特征及诱因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(1):128-138, 148. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y007WU Ya'nan, YANG Yuntao, JIAO Yuguo, LIU Zhitao, WANG Yanling, ZHAI Daiting, ZHOU Shaozhi, WEI Kai, CHENG Feng. Analysis on development characteristics and inducement of karst collapse in Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(1):128-138, 148. doi: 10.11932/karst2023y007 [22] 高宗军, 鲁统民, 王敏, 冯建国, 刘书江, 王姝. 基于岩溶水动态的岩溶地面塌陷预测预报方法[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):739-745.GAO Zongjun, LU Tongmin, WANG Min, FENG Jianguo, LIU Shujiang, WANG Shu. Prediction of karst ground collapse based on karst water regime[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5):739-745. [23] 姜春露, 姜振泉. 基于Fisher判别分析法的岩溶塌陷预测[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2012, 34(1):91-95.JIANG Chunlu, JIANG Zhenquan. Prediction of karst collapse based on Fisher discriminant analysis method[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2012, 34(1):91-95. [24] 杨荣康, 杨元丽, 蒋镇涛, 王乾, 刘腾飞. 基于两级模糊数学综合评判法的岩溶塌陷危险性评价:以安顺市中心城市规划区为例[J]. 贵州地质, 2017, 34(2):109-115.YANG Rongkang, YANG Yuanli, JIANG Zhentao, WANG Qian, LIU Tengfei. Karst collapse risk assessment base on two-level fuzzy mathematical comprehensible evaluation: Taking the urban planning area in Anshuan as an example[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2017, 34(2):109-115. [25] 吴亚楠, 王延岭, 周绍智, 唐丽伟, 焦玉国. 基于综合指数法的泰莱盆地岩溶塌陷风险性评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):391-399.WU Ya'nan, WANG Yanling, ZHOU Shaozhi, TANG Liwei, JIAO Yuguo. Risk assessment of karst collapse in the Tailai basin based on the synthetic index method[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3):391-399. [26] 蒋小珍, 雷明堂, 管振德. 岩溶塌陷灾害的水动力条件危险性评价指标:以广西贵港青云村为例[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2012, 8(6):1316-1321.JIANG Xiaozhen, LEI Mingtang, GUAN Zhende. Characterization criteria of karst collapse hazard on groundwater fluctuations in Qingyun village, Guigang, Guangxi, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2012, 8(6):1316-1321. -




 下载:
下载: