Study on the intensity of boreal karstification under different geological conditions: A case study at the recharge area of Baotu Spring drainage area, Jinan, Northern China
-
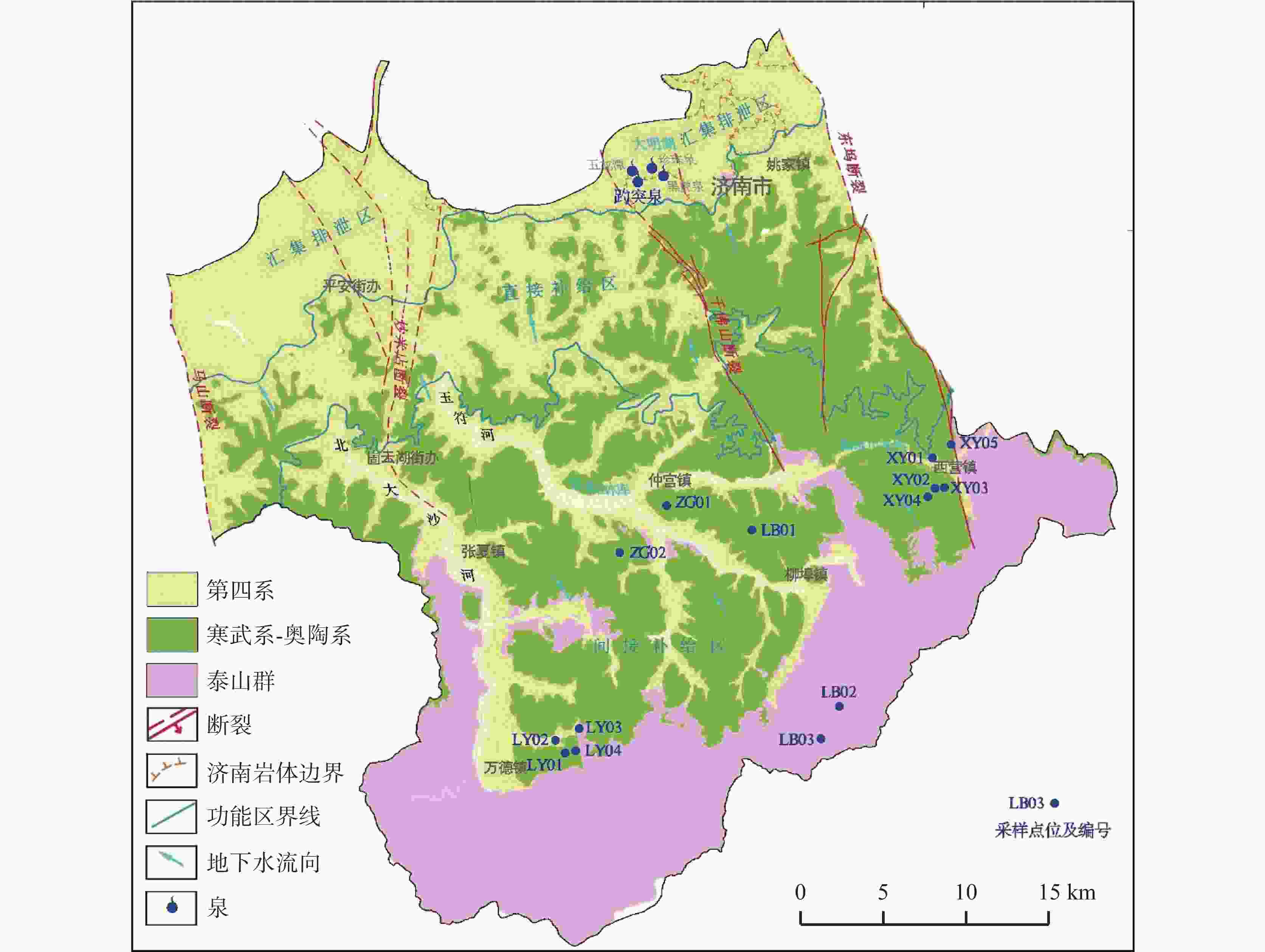
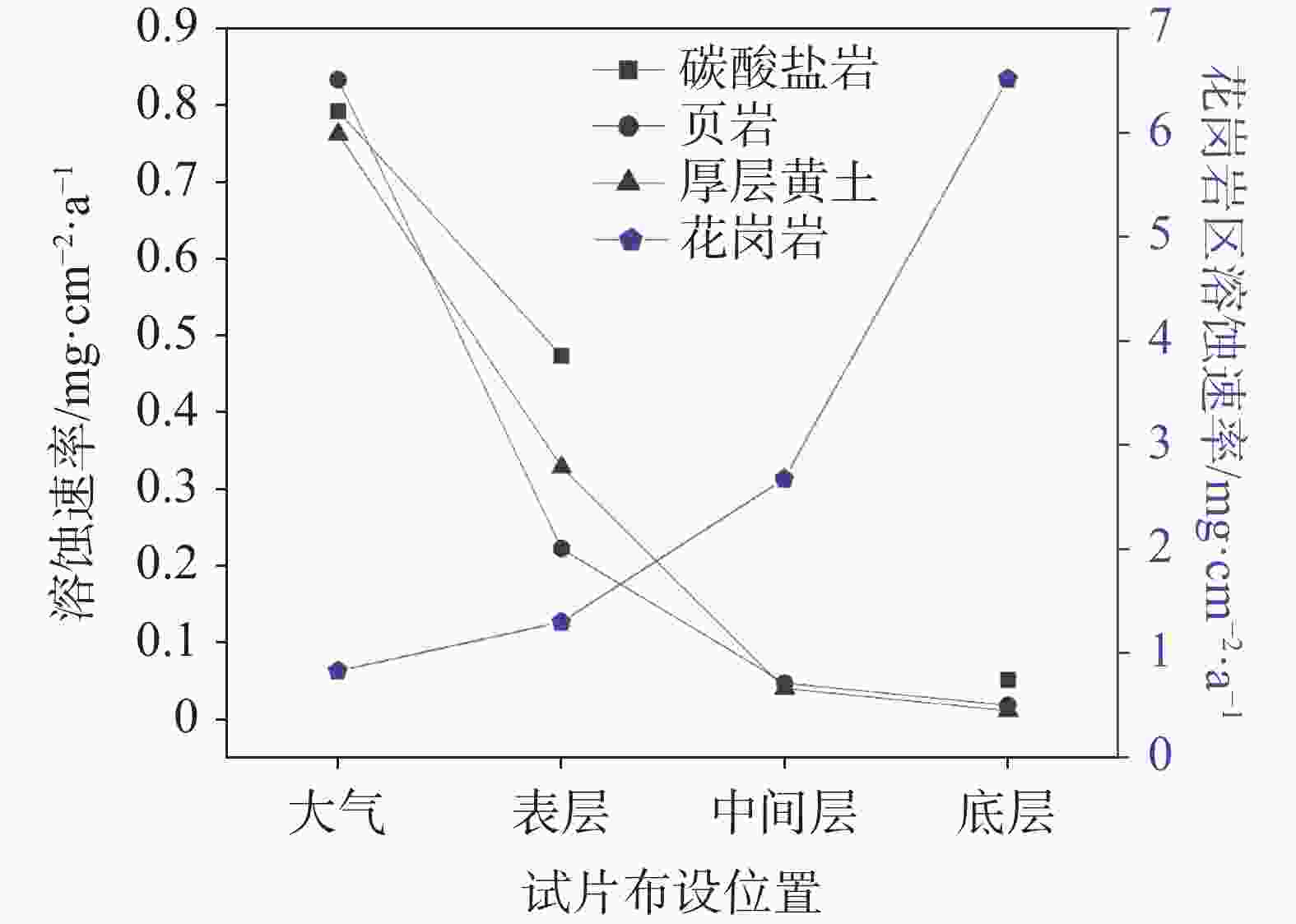
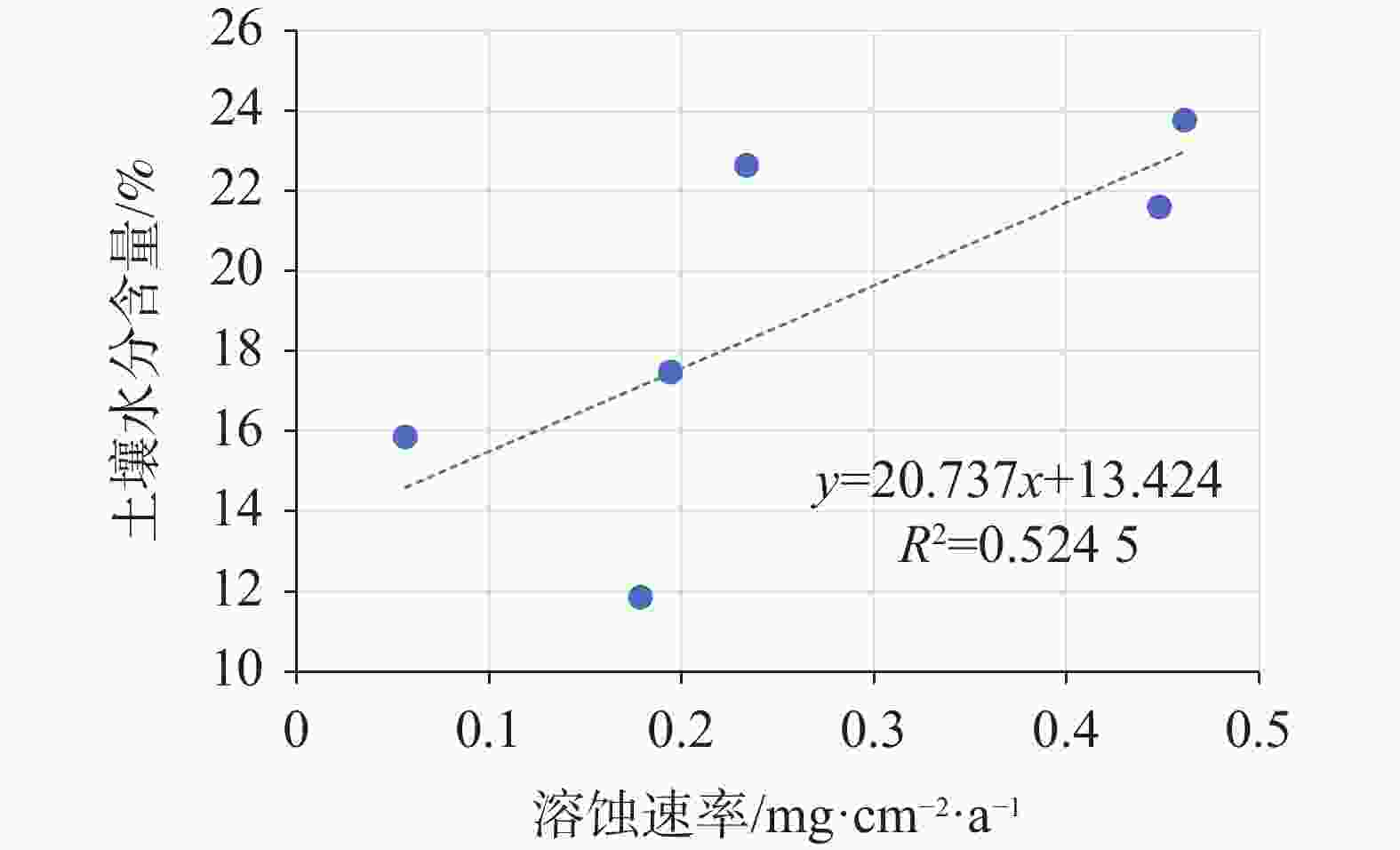
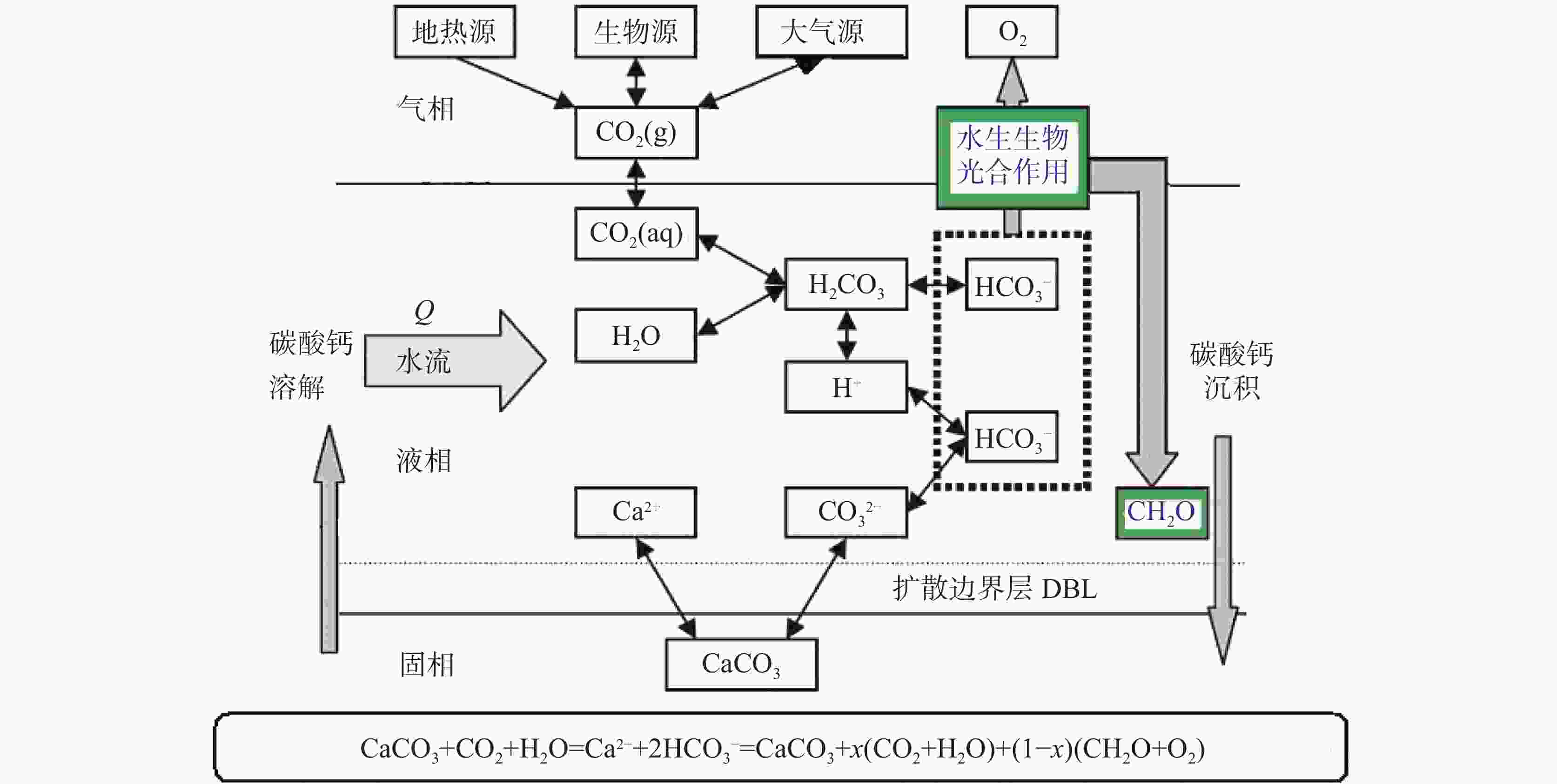
摘要: 岩溶作用过程可形成碳汇是不争的事实,为进一步探索不同地质背景对岩溶作用的影响机制,选取典型北方岩溶泉域−济南趵突泉泉域补给区为研究区,采用标准溶蚀试片法进行野外现场试验。结果表明,下伏岩性为花岗岩、碳酸盐岩、黄土、页岩的各试点平均溶蚀速率分别为:3.49、0.26、0.11、0.09 mg·cm−2·a−1;碳酸盐岩、黄土、页岩分布区溶蚀速率大气 > 地表 > 壤中,且壤中部分呈随深度增加而降低的趋势,而在花岗岩分布区则呈完全相反。分析发现,土壤水与溶蚀速率相关性远高于CO2,是北方岩溶区岩溶作用进行的限制因子。本研究结果有助于认识半湿润气候条件下岩溶碳汇机制,为北方其他岩溶区乃至整个同类型岩溶区相关研究的开展积累了经验。Abstract:
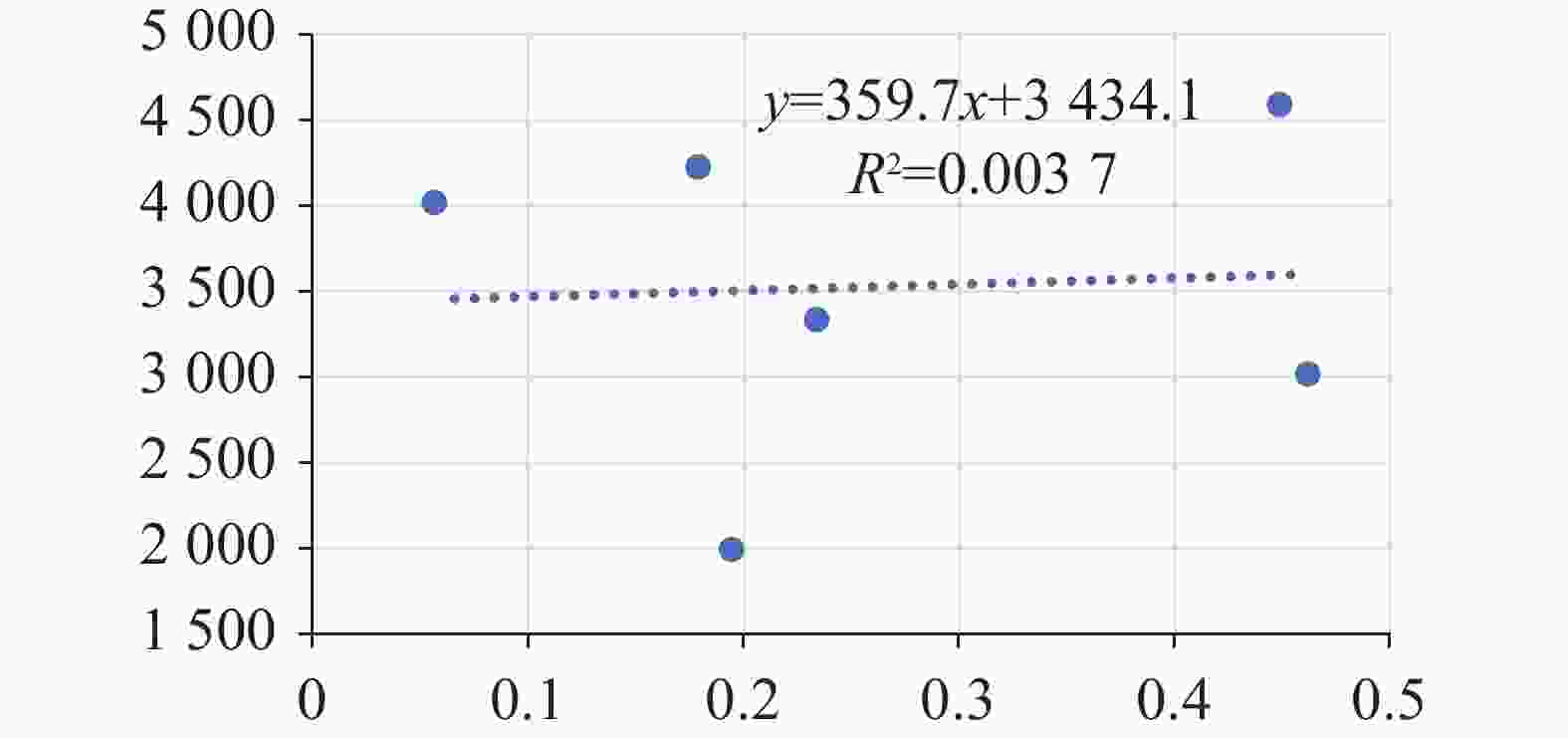
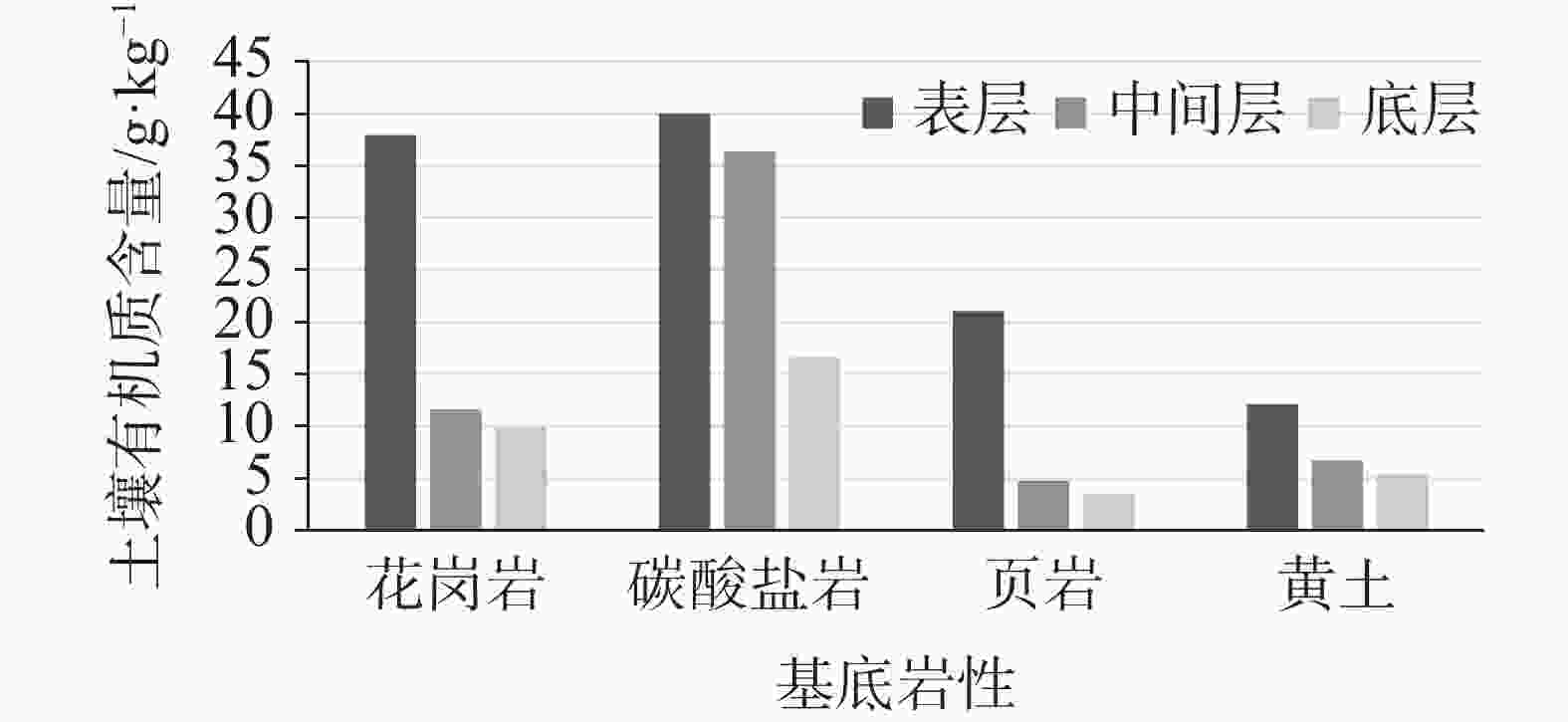
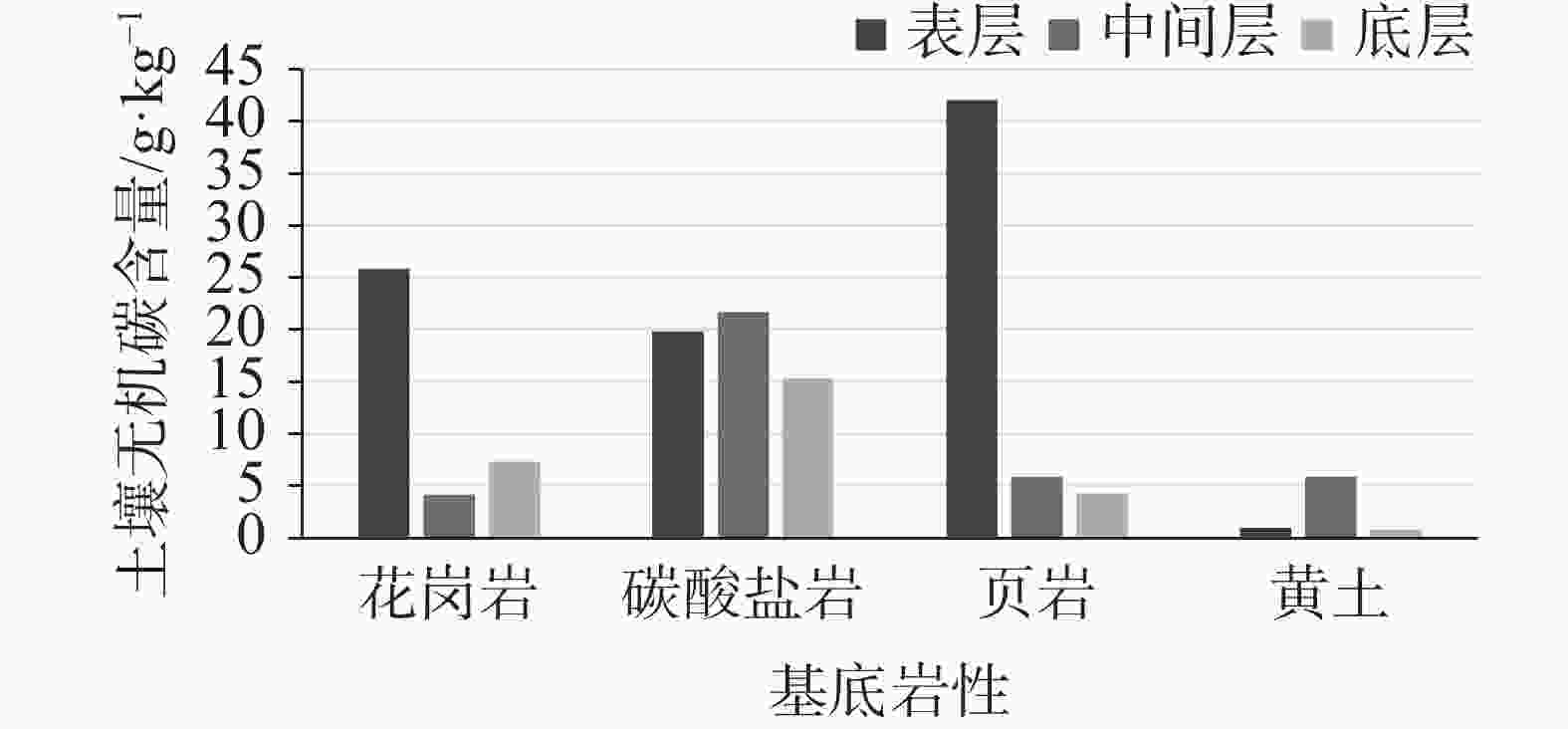
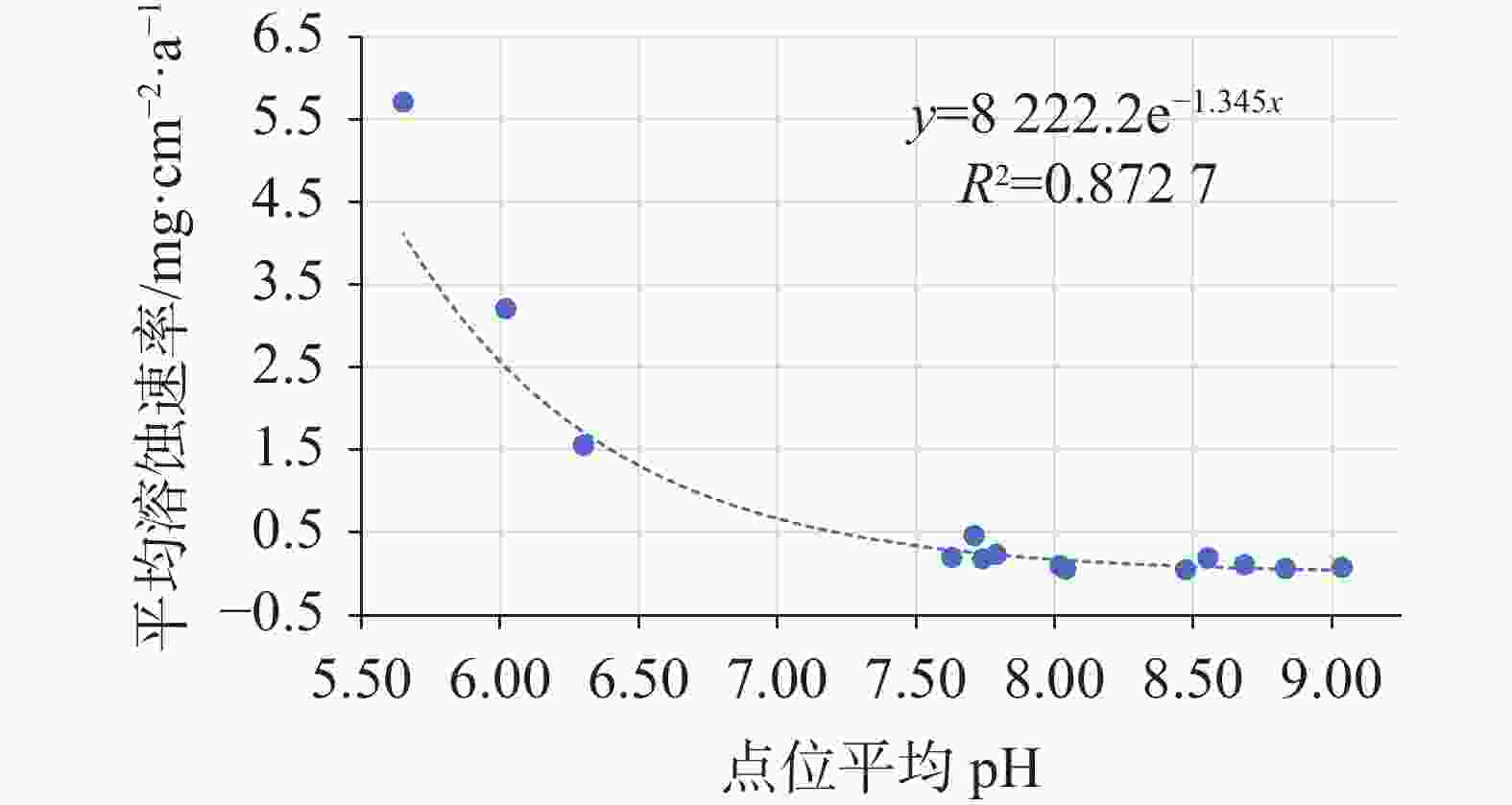
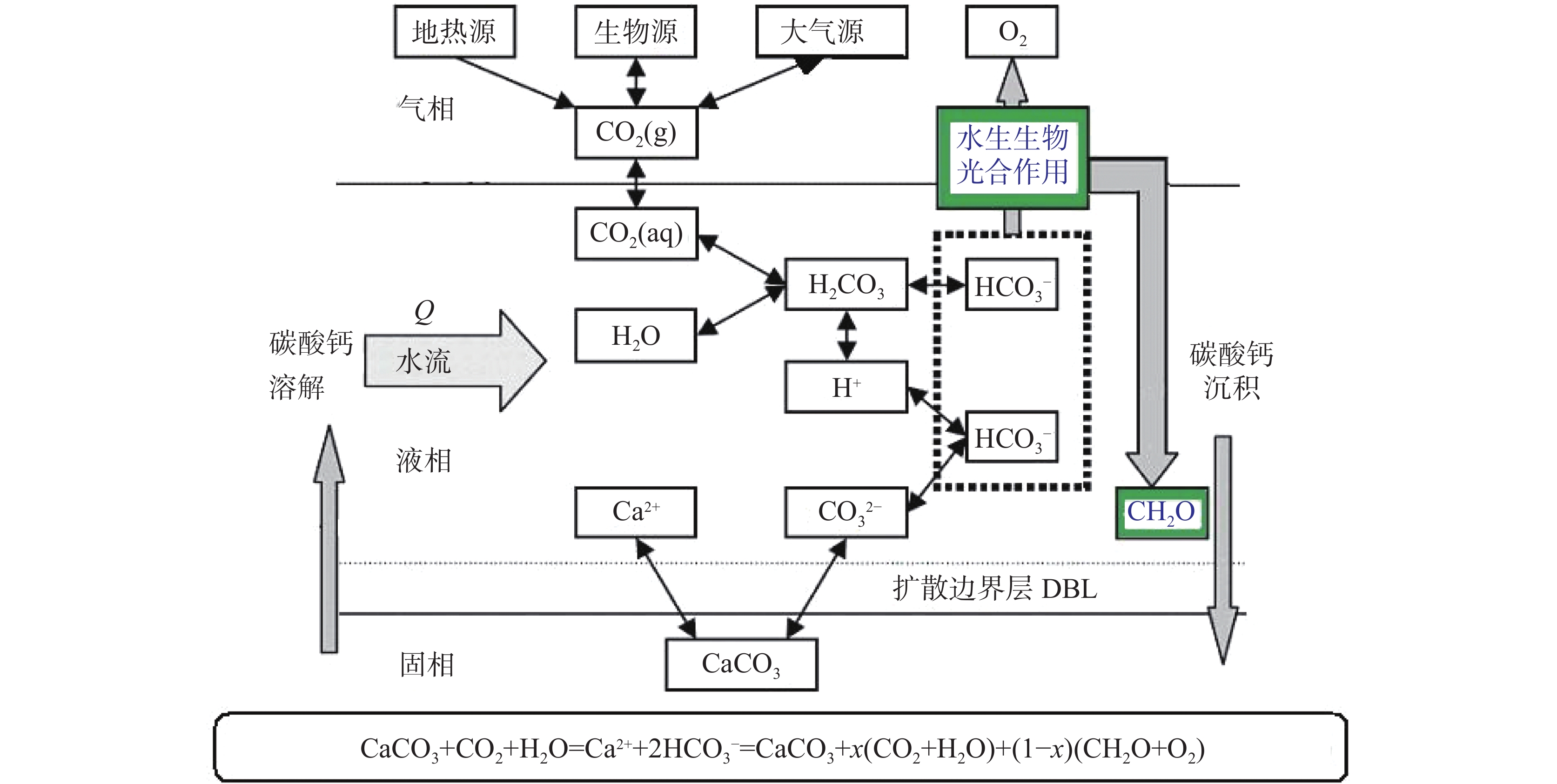
It is an indisputable fact that the process of karstification can form carbon sink, and the research on this process is in the ascendant. However, the factors affecting karstification process are very complicated, and the geological background is one of the most important aspects. The effect mechanism of different geological backgrounds on karstification and the data of dissolution rate under different geological backgrounds can provide a basis for understanding the karst process and its mechanism under sub-humid climate and improving the estimation accuracy of karst carbon sink. The recharge area of Baotu Spring area in Jinan, a typical boreal karst spring area, is selected as the research area, and the standard dissolution tablet test of carbonate rock is used for field measurement.At the northern edge of the mountainous region in central Shandong, the research area is located in the Baotu Spring area of Jinan, bordering Mount Tai in the south and the Yellow River in the north (116°40'30"-117°14'10"E; 36°14'50"-36°46'10"N). The spring area borders the Mashan fault and Dongwu fault to the west and east, respectively. These two faults are permeable in the north and weakly permeable in the south. The southern boundary is the ridgeline of Mount Tai, and the igneous body in the north is called "Jinan Rock". Constrained by the special topography and geological structure, precipitation infiltration in the southern mountainous area recharges the Cambrian-Ordovician karst aquifer which presents strong karst development, and then moves from south to north. According to the statistics of Jinan Meteorological Bureau, Jinan City is characterized by a warm temperate continental climate with four distinct seasons at an annual average temperature of 14.7 ℃. Its average precipitation per year is 647.9 mm, more than 70% of which is concentrated in July, August and September with less from December to March. During the four-year test, pH values of precipitation in Jinan (Guishan) National Basic Meteorological Station averaged between 6.96 and 7.61, which means there was no acid rain in this period.The standard dissolution tablet method is widely used in the study of karstification process because of its advantages such as short-term monitoring, simple preparation of sampling, mature embedding method and the condition closer to the natural state than that in a laboratory. The study area is located in the low mountainous but hilly area of the north wing of Mount Tai and the southern Jinan far away from the urban area, which is also the recharge area of Baotu Spring area. The area is forest and shrub land with less interference from human activities. We buried standard dissolution carbonate tablets around the end of November 2017, and retrieved them around the end of November 2021, with a total test period of four years. When burying these tablets, we selected test sites with different basement lithology in the same small watershed where the meteorological conditions are not significantly different, to ensure the relative consistency of test backgrounds such as precipitation and temperature. Meanwhile, we collected layered soil samples for testing physical and chemical indexes, atmospheric and soil CO2, soil water content, etc. Results show that the average dissolution rates of granite, carbonate, loess and shale are 3.49 mg·cm−2·a−1, 0.26 mg·cm−2·a−1, 0.11 mg·cm−2·a−1 and 0.09 mg·cm−2·a−1, respectively. In other words, the influence of basement lithology on dissolution rate is significant. The dissolution rate of granite area is much larger than that of the other ones. The dissolution rate of carbonate area is larger than that of loess and shale, and the lowest in shale area. From a vertical profile perspective, the dissolution rate of carbonate rock area, loess area and shale area is atmospheric>surface>soil, and the rate in soil decreases with the increase of depth, while the dissolution rate in granite area shows a completely opposite trend.It is found that there is no obvious correlation between soil CO2 and dissolution rate. The variation trend of soil organic matter content in the profiles of carbonate rock, loess and shale is consistent with that of dissolution rate, indicating that the former may have a direct effect on the latter, but the consistency does not show in the granite area. There is an exponential correlation between soil pH and dissolution rate at all sites, and the dissolution rate decreased significantly with the increase of pH. Soil water content has an obvious linear relationship with the dissolution rate, and is the limiting factor of karstification process in boreal karst area compared with soil CO2.This study is a useful exploration in the boreal karst area, the results of which help to deepen the understanding of the karstification process under the semi-humid and semi-arid climate conditions, and provide a comparative example for other karst areas in the north and even the whole karst area of the same type. -
表 1 标准溶蚀试验点位概况
Table 1. Overview of the test sites of standard dissolution
编号 埋放
日期取回
日期埋放
天数土地利用
类型优势
植被伴生
植被基底
岩性地貌
部位坡向/视
坡度LB01 2017年11月25日 2021年11月26日 1 462 林地 槐树 构树、灌丛 碳酸盐岩 山坡 135°/20° LB02 2017年11月28日 2021年11月25日 1 458 林地 柏树 黄荆 花岗岩 山坡 95°/10° LB03 2017年11月28日 2021年11月26日 1 459 林地 槐树 杂草 花岗岩 近山顶山坡 90°/60° LY01 2017年11月15日 2021年12月8日 1 484 林地、灌丛 杨树 黄荆、杂草 页岩 山坡 0°/3° LY02 2017年11月16日 2021年12月6日 1 481 林地 柏树 黄荆、杂草 页岩 山坡 345°/30° LY03 2017年11月16日 2021年12月7日 1 482 林地 柏树 黄荆、杂草 花岗岩 山坡 270°/8° LY04 2017年11月17日 2021年12月3日 1 477 林地 柏树 黄荆 碳酸盐岩 近山顶山坡 315°/45° XY01 2017年11月21日 2021年12月2日 1 472 园地 核桃树 山楂 黄土 山谷河漫滩 180°/1° XY02 2017年11月23日 2021年12月1日 1 469 园地 苹果树 杂草 页岩 山谷尾端 0°/3° XY03 2017年11月23日 2021年12月1日 1 469 园地 苹果树 杂草 页岩 山谷尾端 0°/3° XY04 2017年11月24日 2021年12月1日 1 468 林地 柏树 黄荆 碳酸盐岩 山坡 90°/45° XY05 2017年11月24日 2021年12月2日 1 469 未利用地 灌草丛 碳酸盐岩 山坡 225°/30° ZG01 2017年11月25日 2021年11月28日 1 464 林地 柏树 碳酸盐岩 山坡 180°/15° ZG02 2017年11月29日 2021年11月29日 1 461 林地 柏树 杂草 碳酸盐岩 山坡 190°/10° 表 2 按基底岩性分层溶蚀速率表/mg·cm−2·a−1
Table 2. Layered dissolution rate of different basement lithology/mg·cm−2·a−1
层位 碳酸盐岩 页岩 花岗岩 黄土 大气 0.791 7 0.832 5 0.829 0 0.761 9 表层 0.473 5 0.222 4 1.294 8 0.328 6 中间层 0.047 2 2.672 4 0.040 6 底层 0.051 1 0.018 4 6.504 1 0.011 6 壤中平均 0.262 3 0.093 8 3.490 4 0.105 4 表 3 平均溶蚀速率、土壤CO2含量及含水率
Table 3. Average dissolution rate, CO2 and water content in soil
点位 平均溶蚀速率/
mg·cm−2·a−1平均CO2含量/
×10−6含水率/
%LB02 5.708 6 2 733.33 16.17 LB03 1.556 2 2 750.00 9.08 LY03 3.206 5 2 783.33 17.22 LY01 0.073 5 1 760.00 22.52 LY02 0.046 8 4 514.29 29.22 XY02 0.065 7 2 100.00 37.12 XY03 0.189 0 5 200.00 33.70 LY04 0.194 4 1 991.67 17.47 XY04 0.448 5 4 587.50 21.60 XY05 0.461 7 3 016.67 23.77 ZG01 0.233 9 3 333.33 22.63 ZG02 0.056 5 4 016.67 15.86 LB01 0.178 8 4 225.00 11.85 XY01 0.105 4 1 960.00 35.81 注:含水率基于试片埋设和取回时测量的结果进行平均。
Note: Water content is averaged based on the results measured when the test tablet is buried and retrieved表 4 不同深度土壤CO2含量/×10−6
Table 4. CO2 content of soil in different depths/×10−6
点位 测试层位/cm 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 80 壤中平均 LB02 389 2 000 3 200 3 000 2 733.33 LB03 378 2 500 3 000 2 750 LY03 388 2 400 3 300 2 650 2 783 LY01 385 1 100 1 400 2 100 2 200 2 000 1 760 LY02 385 3 800 3 000 6 800 4 700 5 000 4 660 XY02 378 2 200 1 800 2 300 2 100 XY03 378 5 200 5 400 5 000 5 200 LB01 385 2 900 5 200 4 000 4 800 4 225 LY04 381 1 600 2 100 2 800 2 000 2 125 XY04 381 2 550 4 600 4 600 6 600 4 588 XY05 381 3 800 3 300 1 950 3 017 ZG01 388 3 800 4 400 1 800 3 333 ZG02 375 3 600 4 760 3 920 5 200 4 370 XY01 378 2 450 2 200 2 000 1 650 1 500 1 960 平均值 382 2 950 3 036 3 897 3 133 4 238 1 925 2 833 3 257 -
[1] YUAN Daoxian. Sensitivity of karst process to environmental change along the Pep II transect[J]. Quaternary International, 1997, 37:105-13. doi: 10.1016/1040-6182(96)00012-2 [2] 袁道先. 碳循环与全球岩溶[J]. 第四纪研究, 1993(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001YUAN Daoxian. Carbon cycle and global karst[J]. Quaternary Research, 1993(1):1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1993.01.001 [3] LIU Zaihua, LI Qiang, SUN Hailong, WANG Jinliang. Seasonal, diurnal and storm-scale hydrochemical variations of typical epikarst springs in subtropical karst areas of SW China: Soil CO2 and dilution effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337(1):207-223. [4] 章程, 肖琼, 孙平安, 高旭波, 郭永丽, 苗迎, 汪进良. 岩溶碳循环及碳汇效应研究与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5):190-198.ZHANG Cheng, XIAO Qiong, SUN Ping'an, GAO Xubo, GUO Yongli, MIAO Ying, WANG Jinliang. Progress on karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effect study and perspective[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5):190-198. [5] Nicolas Cassar, Edward A Laws, Robert R Bidigare, Brian N Popp. Bicarbonate uptake by Southern Ocean phytoplankton[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2004, 18(2):1-10. [6] 刘彦, 张金流, 何媛媛, 孙海龙, 刘再华. 单生卵囊藻对DIC的利用及其对CaCO3沉积影响的研究[J]. 地球化学, 2010, 39(2):191-196.LIU Yan, ZHANG Jinliu, HE Yuanyuan, SUN Hailong, LIU Zaihua. The utilization of dissolved inorganic carbon by Oocystis solitaria Wittr and its influence on the precipitation of calcium carbonate[J]. Geochemica, 2010, 39(2):191-196. [7] LIU Yan, LIU Zaihua, ZHANG Jinliu, HE Yuanyuan, SUN Hailong. Experimental study on the utilization of DIC by Oocystis solitaria Wittr and its influence on the precipitation of calcium carbonate in karst and non-karst waters[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2010, 25(1):21-26. doi: 10.1007/s13146-009-0002-9 [8] LIU Zaihua, Wolfgang DREYBRODT, WANG Haijing. A new direction in effective accounting for the atmospheric CO2 budget: Considering the combined action of carbonate dissolution, the global water cycle and photosynthetic uptake of DIC by aquatic organisms[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 99(3-4):162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.03.001 [9] 张强. 岩溶地质碳汇的稳定性:以贵州草海地质碳汇为例[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(6):947-952.ZHANG Qiang. The stability of carbon sink effect related to carbonate rock dissolution: A case study of the Caohai lake geological carbon sink[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(6):947-952. [10] 张陶, 李建鸿, 蒲俊兵, 李瑞, 吴飞红, 李丽. 小球藻对岩溶水体Ca2+、HCO3−利用效率实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):81-90.ZHANG Tao, LI Jianhong, PU Junbing, LI Rui, WU Feihong, LI Li. Experimental study on the utilization efficiency of Chlorella to Ca2+ and HCO3− in karst water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):81-90. [11] 章程. 岩溶作用时间尺度与碳汇稳定性[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):368-371.ZHANG Cheng. Time scale of karst processes and the carbon sink stability[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4):368-371. [12] 金泉. 岩溶区沉水植物无机碳利用策略的研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2019.JIN Quan. Study on inorganic carbon utilization strategy of submerged plants in karst area[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2019. [13] 张春来, 黄芬, 蒲俊兵, 曹建华. 中国岩溶碳汇通量估算与人工干预增汇途径[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4): 40-52.ZHANG Chunlai, HUANG Fen, PU Junbing, CAO Jianhua. Estimation of karst carbon sink fluxes and manual intervention to increase carbon sinks in China[ J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(4): 40-52. [14] SUN Ping'an, HE Shiyi, YUAN Yaqiong, YU Shi, ZHANG Cheng. Effects of aquatic phototrophs on seasonal hydrochemical, inorganic, and organic carbon variations in a typical karst basin, Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(32):32836-32851. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06374-6 [15] YAN Zhuang, SHEN Taiming, LI Wei, CHENG Wenli, WANG Xiayu, ZHU Min, YU Qiwen, XIAO Yutian, YU Longjiang. Contribution of microalgae to carbon sequestration in a natural karst wetland aquatic ecosystem: An in-situ mesocosm study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 768:144387. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144387 [16] YANG Mingxing, LIU Zaihua, SUN Hailong, ZHAO Min, HE Haibo. Lipid biomarker investigation of the delivery and preservation of autochthonous organic carbon in the Pearl River and its contribution to the carbon sink: Evidence from the water and surface sediment[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(22):15392. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215392 [17] 刘再华. 土壤碳酸盐是一个重要的大气CO2汇吗? [J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(26): 2209-2211.LIU Zaihua. Is pedogenic carbonate an important atmospheric CO2 sink?[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(26): 2209-2211. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4288-8. [18] 刘再华. 岩石风化碳汇研究的最新进展和展望[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(Suppl.1): 95-102.LIU Zaihua. New progress and prospects in the study of rock-weathering-related carbon sinks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(Suppl.1): 95–102. [19] Gabrovsek Franci. On concepts and methods for the estimation of dissolutional denudation rates in karst areas[J]. Geomorphology, 2009, 106(1-2):9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.09.008 [20] Krklec Kristina, Braucher Regis, Perica Dražen, Domínguez Villar David. Long-term denudation rate of karstic North Dalmatian Plain (Croatia) calculated from 36Cl cosmogenic nuclides[J]. Geomorphology, 2022, 413:108358. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2022.108358 [21] 徐胜, 刘丛强, FREEMAN Stewart, 郎赟超, SCHNABEL Christoph, 涂成龙, WILCKEN Klaus, 赵志琦. 贵州喀斯特地区碳酸盐岩的宇宙成因核素36Cl侵蚀速率[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(19): 1884.XU Sheng, LIU Congqiang, FREEMAN Stewart, LANG Yunchao, SCHNABEL Christoph, TU Chenglong, WILCKEN Klaus, ZHAO Zhiqi. In-situ cosmogenic 36Cl denudation rates of carbonates in Guizhou karst area[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(19): 1884. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-013-5756-8 [22] Yuki Matsushi, Kimikazu Sasa, Tsutomu Takahashi, Keisuke Sueki, Yasuo Nagashima, Yukinori Matsukura. Denudation rates of carbonate pinnacles in Japanese karst areas: Estimates from cosmogenic 36Cl in calcite[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2010, 268(7-8):1205-1208. [23] 曾成, 赵敏, 杨睿, 刘再华. 岩溶作用碳汇强度计算的溶蚀试片法和水化学径流法比较:以陈旗岩溶泉域为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1):106-111.ZENG Cheng, ZHAO Min, YANG Rui, LIU Zaihua. Comparison of karst processes-related carbon sink intensity calculated by carbonate rock tablet test and solute load method: A case study in the Chenqi karst spring system[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1):106-111. [24] 蒋忠诚, 覃小群, 曹建华, 蒋小珍, 何师意, 罗为群. 中国岩溶作用产生的大气CO2碳汇的分区计算[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.002JIANG Zhongcheng, QIN Xiaoqun, CAO Jianhua, JIANG Xiaozhen, HE Shiyi, LUO Weiqun. Calculation of atmospheric CO2 sink formed in karst progresses of the karst divided regions in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4):363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.002 [25] 刘再华. 岩溶作用及其碳汇强度计算的“入渗−平衡化学法”:兼论水化学径流法和溶蚀试片法[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4):379-382.LIU Zaihua. "Method of maximum potential dissolution" to calculate the intensity of karst process and the relevant carbon sink: With discussions on methods of solute load and carbonate-rock-tablet test[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4):379-382. [26] 何江湖, 肖时珍, 曾成, 狄永宁, 刘梦醒, 蓝家程, 肖华, 朱辉, 曾庆睿. 湿润亚热带典型白云岩流域的化学剥蚀速率:以贵州施秉黄洲河流域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(3):274-281.HE Jianghu, XIAO Shizhen, ZENG Cheng, DI Yongning, LIU Mengxing, LAN Jiacheng, XIAO Hua, ZHU Hui, ZENG Qingrui. Chemical denudation rate in typical humid subtropical dolomite catchments: A case study in the Huangzhou river basin, Shibing, Guizhou[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(3):274-281. [27] Corbel J. Erosion en terrain calcaire[J]. Annales de Géographie, 1959, 67:97-120. [28] 袁道光, 蔡桂鸿. 岩溶环境学[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988. [29] 孙平安, 肖琼, 郭永丽, 苗迎, 王奇岗, 章程. 混合岩溶流域碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率与岩溶碳汇:以漓江流域上游为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):825-384.SUN Ping'an, XIAO Qiong, GUO Yongli, MIAO Ying, WANG Qigang, ZHANG Cheng. Carbonate dissolution rate and karst carbon sink in mixed carbonate and silicate terrain: Take the upper reaches of the Lijiang river basin as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5):825-384. [30] 闫伟, 曾成, 肖时珍, 蓝家程, 代林玉, 邰治钦, 何江湖, 何春, 狄永宁. 湿润亚热带典型白云岩流域不同土地利用下的试片溶蚀速率及岩溶碳汇[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(5):529-538.YAN Wei, ZENG Cheng, XIAO Shizhen, LAN Jiacheng, DAI Linyu, TAI Zhiqin, HE Jianghu, HE Chun, DI Yongning. Dissolution rate and karst carbon sink of different land use in typical dolomite watershed with humid subtropical weather[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(5):529-538. [31] 刘再华. 外源水对灰岩和白云岩的侵蚀速率野外试验研究:以桂林尧山为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2000, 19(1):3-6.LIU Zaihua. Field experimental research on the corrosion kinetics of limestone and dolomite in allogenic water: Case from Yaoshan Mt., Guilin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2000, 19(1):3-6. [32] Dreybrodt W. Chemical kinetics, speleothem growth and climate[J]. Boreas, 1999, 28(3):347-356. [33] 侯满福, 刘雨婷, 张杰, 贺露炎, 梁江弈. 亚热带岩溶森林类型和坡位对碳酸盐岩溶蚀的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4): 842-852.HOU Manfu, LIU Yuting, ZHANG Jie, HE Luyan, LIANG Jiangyi. Influence of forest types and slope positions on dissolution rate of carbonate rock in karst area in subtropical China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 842-852. [34] 张春潮, 李向全, 王振兴, 侯新伟, 桂春雷, 白占学, 付昌昌. 不同碳酸盐岩岩性试片的溶蚀速率研究:以三姑泉域为例[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(5):218-223.ZHANG Chunchao, LI Xiangquan, WANG Zhenxing, HOU Xinwei, GUI Chunlei, BAI Zhanxue, FU Changchang. Dissolution rate of different carbonate rocks: A case study in Sangu spring basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2018, 29(5):218-223. [35] 章程, 李玉辉, 汪进良, 苗迎, 肖琼, 郭永丽. 云南石林地质公园土岩、土根界面过程和土下溶蚀速率[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(4):1019-1030. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.04.016ZHANG Cheng, LI Yuhui, WANG Jinliang, MIAO Ying, XIAO Qiong, GUO Yongli. Interface processes at soil-rock, soil-root contacts and subsoil dissolution rate in Shilin Geopark, Yunnan[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(4):1019-1030. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.04.016 [36] 黄奇波. 北方半干旱岩溶区岩溶碳汇过程及效应研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.HUANG Qibo. The carbon sequestration effect in semi-arid karst area: A case study of Liuling spring catchment, Shanxi Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2019. [37] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 蓝芙宁, 张连凯. 不同岩性试片溶蚀速率差异及意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(04): 379-385.HUANG Qibo, QIN Xiaoqun, LIU Pengyu, LAN Funing, ZHANG Liankai. Dissolution Rate and It's Significance of Different Lithological Tablets. [J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(04): 379-385. [38] 李涛, 赵东兴, 张美良, 曹建华, 朱晓燕. 土壤CO2、土壤水的动态特征及其对岩溶作用的驱动[J]. 热带地理, 2013, 33(5):575-581.LI Tao, ZHAO Dongxing, ZHANG Meilang, CAO Jianhua, ZHU Xiaoyan. Dynamic characteristics of the soil CO2 and soil water chemistry, and their driving action on karstification[J]. Tropical Geography, 2013, 33(5):575-581. [39] 刘文, 张强, 贾亚男. 气象要素及土壤理化性质对不同土地利用方式下冬夏岩溶作用的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(6): 1418-1428.LIU Wen, ZHANG Qiang, JIA Ya'nan. The influence of meteorological factors and soil physicochemical properties on karst processes in six land-use patterns in summer and winter in a typical karst valley[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica , 2014, 34(6): 1418-1428 [40] 肖琼, 赵丽芳, 陆来谋, 孙平安, 张陶, 郭永丽. 漓江源头大溶江流域土壤理化性质[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5):815-824. doi: 10.11932/karst20210508XIAO Qiong, ZHAO Lifang, LU Laimou, SUN Ping'an, ZHANG Tao, GUO Yongli. Spatial differences of soil physical and chemical properties in Darongjiang river watershed[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(5):815-824. doi: 10.11932/karst20210508 [41] 吴夏, 潘谋成, 殷建军, 汪智军, 朱晓燕, 杨会, 曹建华. 桂林典型岩溶区土壤CO2通量及其δ13C-CO2季节性特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(4):592-599.WU Xia, PAN Moucheng, YIN Jianjun, WANG Zhijun, ZHU Xiaoyan, YANG Hui, CAO Jianhua. Seasonal variation characteristics of soil respiration release and its isotopic composition in typical karst area, Guilin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(4):592-599. [42] 施晓, 杨琰, 李一冬, 田宁, 叶枝茂, 李建仓, 段军伟. 岩溶关键带土壤–洞穴系统CO2运移的时空变化:以河南鸡冠洞为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(4):580-591.SHI Xiao, YANG Yan, LI Yidong, TIAN Ning, YE Zhimao, LI Jiancang, DUAN Junwei. Analysis of temporal and spatial variations of CO2 migration in the soil cave system in karst critical zone: A case study of Jiguan cave, western Henan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(4):580-591. -




 下载:
下载: