Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in east Zoucheng City, Shandong Province
-
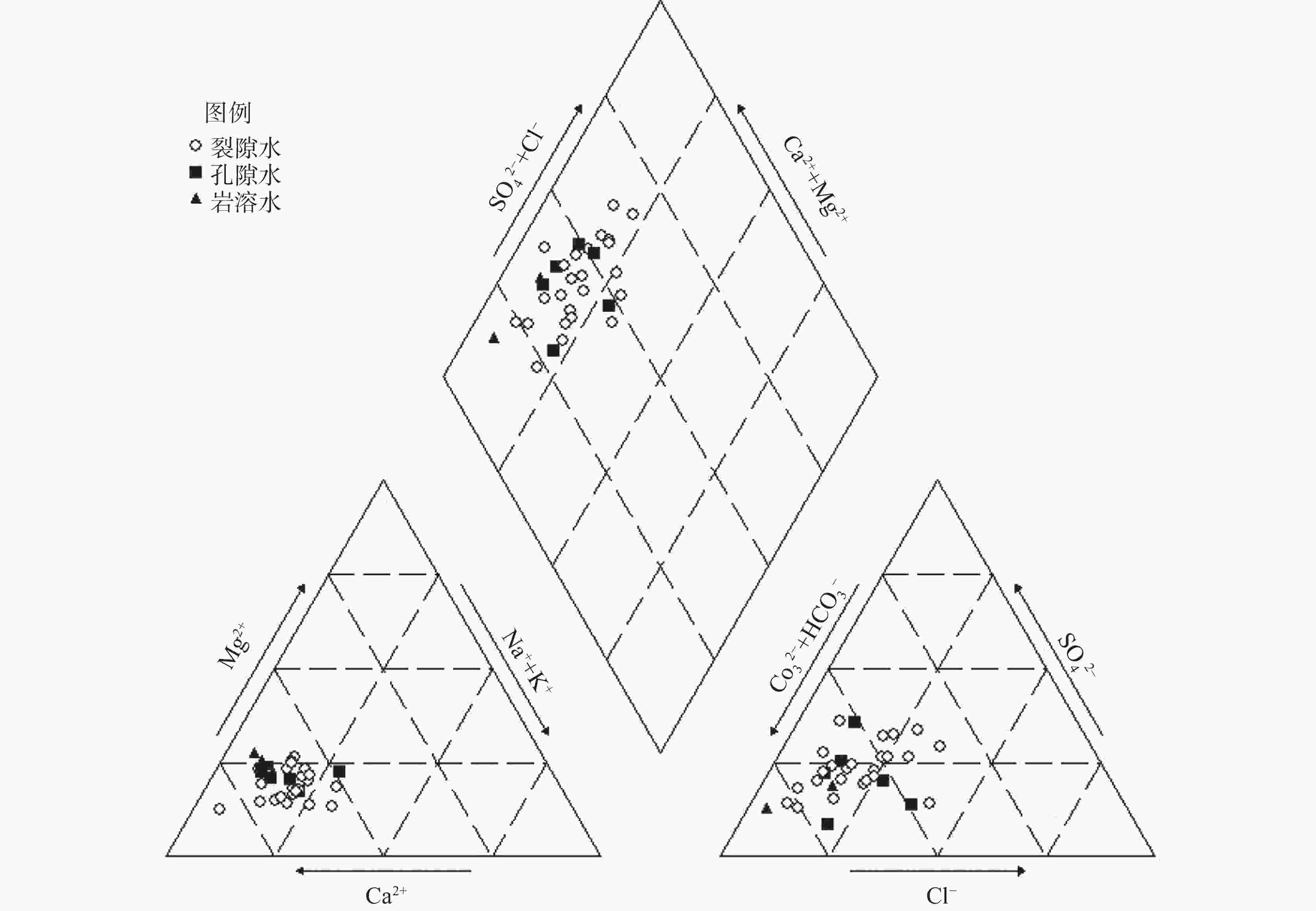
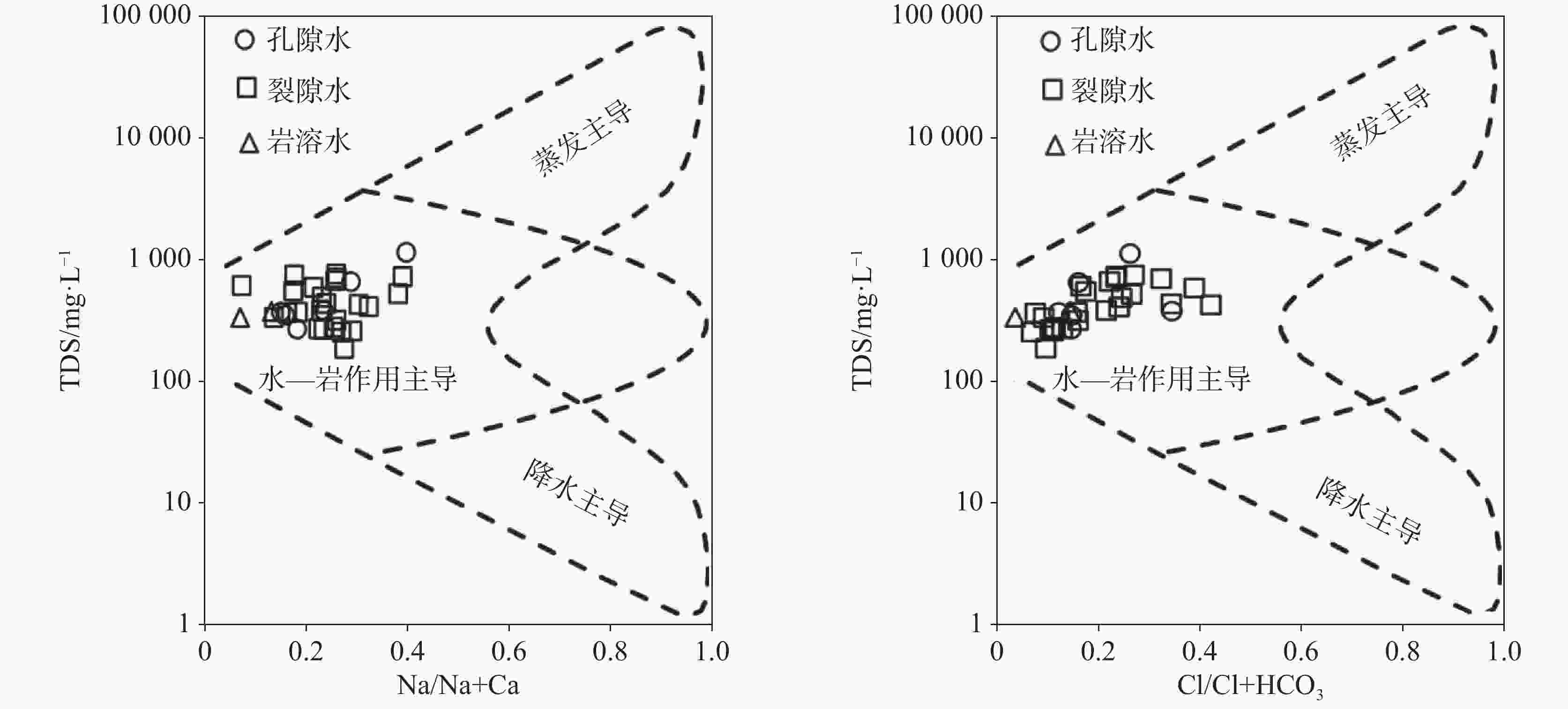
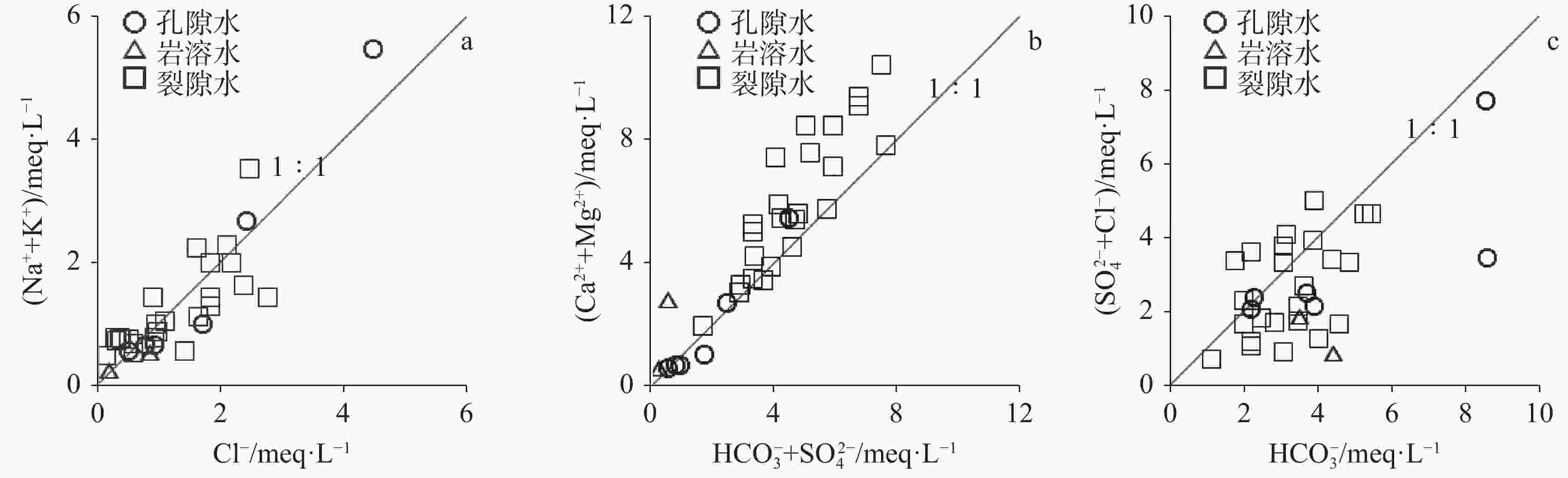
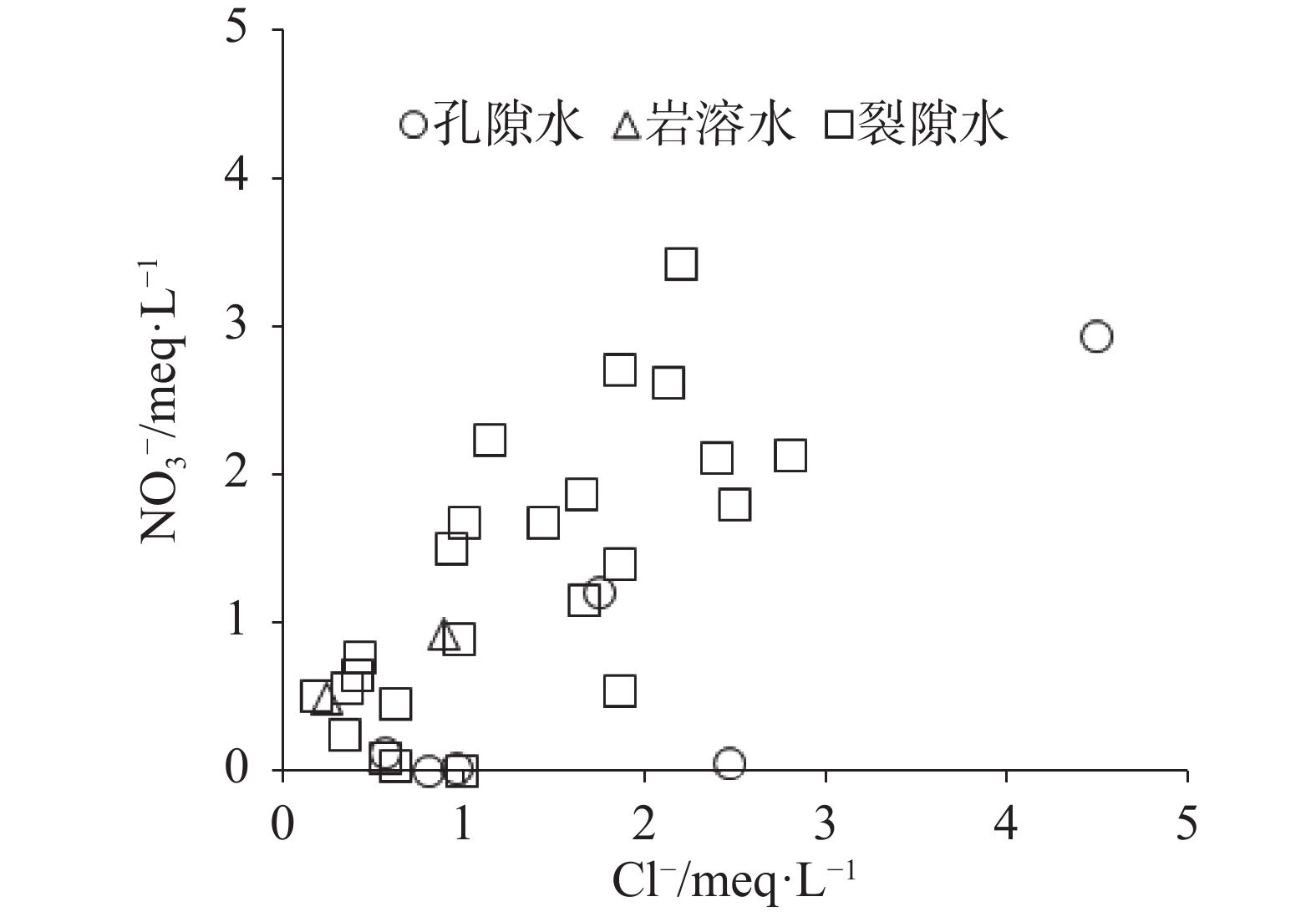
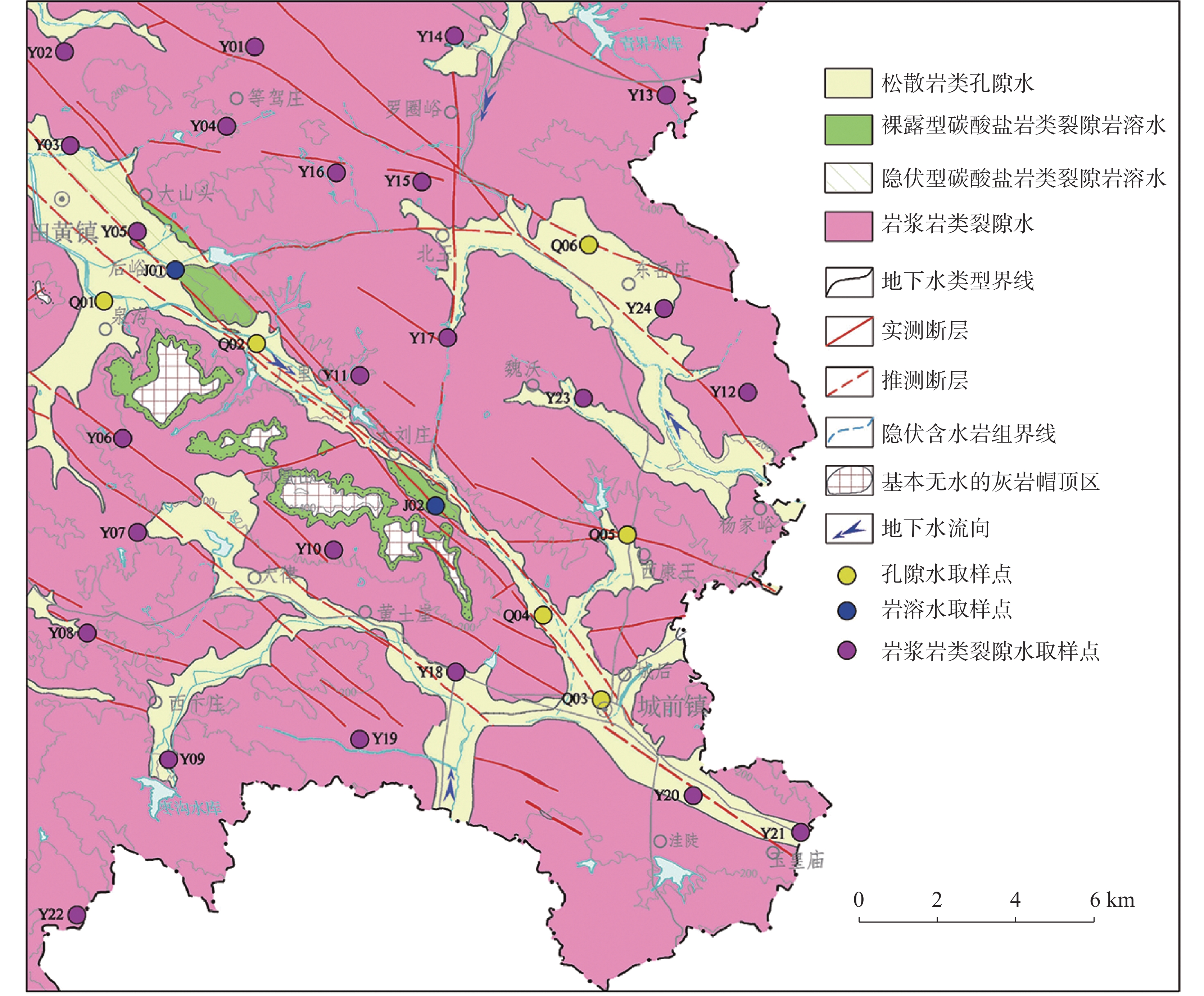
摘要: 为研究山东省邹城市东部缺水山区地下水水化学特征、水质状况和水化学过程,采集研究区各类型地下水样品32件,检测K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 、${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 、${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 、F−、TH和TDS等化学指标,综合利用图解法、相关性分析和主成分分析等方法探讨其地下水的水化学特征和形成机制。结果表明:(1)研究区裂隙水、孔隙水与岩溶水具有相似的水化学特征,裂隙水和孔隙水的水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型为主,而岩溶水水化学类型为HCO3 -Ca · Mg型;(2)孔隙水、裂隙水和岩溶水水化学形成机制主要以水−岩相互作用为主,其次还受到人类活动的影响。孔隙水受水−岩相互作用和人类活动影响的比例分别为77.7%和10.5%,而裂隙水受影响的比例分别为63.9%和11.3%。Abstract:The study area is located in the southwest of Shandong Province, which is a typical water shortage area in Shandong Province, and groundwater is an important water supply source in this area. There are distributed pore groundwater, karst groundwater, and fissure groundwater. The distribution of pore groundwater is small and discontinuous, with poor water-richness. Although the karst aquifer is relatively in good water-richness, its distribution is more limited. The fissure water presents a wide distribution, but its water-richness is extremely poor. In recent years, with the rapid development of economy and the continuous growth of urban population, the demand for groundwater resources is increasing, thus exacerbating the contradiction between supply and demand of water resources, which is bound to seriously restrict the improvement of local people's living standard and economic and social development. Therefore, the study on the hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in the water-scarce mountainous area of eastern Zoucheng City can provide a strong theoretical basis for promoting the construction of new rural areas and the implementation of drinking water safety projects. Based on this, 32 samples of different types of groundwater (24 fracture water samples, 6 pore water samples and 2 karst water samples) were collected in this study, and the water chemistry indexes such as K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ ,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ,${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ , F−, TH and TDS were measured in the water-scarce mountainous area in eastern Zoucheng city as a typical research area. The water chemistry characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in the region were explored in depth by graphical method, correlation analysis and principal component analysis.Results show that the cations of both fracture water and pore water are Ca2+ > Na+ > Mg2+ > K+, while the cations of karst water are Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ > K+, and the anions of all three types of groundwater are ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ >${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ > Cl− >${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ > F−. The water chemistry types of fracture water and pore water are mainly HCO3-Ca type, while the type of karst water is HCO3-Ca-Mg. The water chemistry formation mechanism of pore water, fracture water and karst water is mainly related to water-rock interaction, followed by the human activities. The results of principal component analysis show that water-rock interaction and human activities affect 77.7% and 10.5% of pore water, and 63.9% and 11.3% of fracture water, respectively. -
表 1 研究区水化学参数特征值统计表/mg·L−1
Table 1. Statistics of hydrochemical parameters of groundwater and surface water in the study area/mg·L−1
地下水类型 项目或编号 Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ Cl− F− ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$(N) TH TDS 裂隙水
(n=24)最小值 30.35 5.38 11.61 1.03 70.41 24.31 6.54 0.07 0.10 97.94 188.98 最大值 173.67 26.05 80.99 9.52 333.82 137.78 99.30 1.33 48.08 521.16 765.08 平均值 91.61 16.25 29.41 3.45 198.27 66.11 45.60 0.27 18.15 295.69 459.78 标准差 39.01 5.41 16.58 2.03 69.85 29.93 27.76 0.28 13.26 113.47 178.43 变异系数/% 42.59 33.28 56.36 58.87 35.23 45.27 60.88 103.14 73.06 38.38 38.81 孔隙水
(n=6)最小值 60.42 11.53 13.72 1.43 133.53 29.91 19.97 0.10 0.28 198.35 271.09 最大值 189.67 52.15 125.62 5.14 524.40 154.21 159.23 0.24 41.10 688.42 1152.00 平均值 107.57 23.40 42.68 2.71 297.20 73.91 65.14 0.17 10.90 364.98 532.97 标准差 50.86 14.86 44.48 1.53 180.21 42.81 52.32 0.05 16.04 185.68 331.25 变异系数/% 47.28 63.51 104.24 56.49 60.64 57.93 80.33 29.41 147.16 50.87 62.15 岩溶水
(n=2)J1 84.37 19.64 13.10 1.24 213.65 47.75 31.64 0.10 12.88 291.57 378.02 J2 79.82 19.80 6.31 5.69 269.49 31.01 8.55 0.17 6.91 280.86 337.78 表 2 研究区地下水水化学参数相关性系数矩阵
Table 2. Correlation matrices of hydrochemical parameters of groundwater in the study area
Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ Cl− F− ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ TH TDS Ca2+ 1 0.726** 0.677** 0.302 0.783** 0.731** 0.824** −0.403 0.650** 0.983** 0.935** Mg2+ 1 0.755** 0.265 0.750** 0.644** 0.792** −0.387 0.479** 0.839** 0.811** Na+ 1 0.367* 0.662** 0.701** 0.873** −0.115 0.592** 0.735** 0.870** K+ 1 0.186 0.171 0.344 −0.037 0.505** 0.309 0.399* ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 1 0.449** 0.628** −0.340 0.185 0.818** 0.723** ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 1 0.716** −0.240 0.598** 0.749** 0.803** Cl− 1 −0.274 0.676** 0.861** 0.924** F− 1 −0.187 −0.421 −0.311 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 1 0.641** 0.772** TH 1 0.954** TDS 1 注:*和**分别代表0.05和0.01显著水平。 表 3 地下水主成分分析结果
Table 3. Results of principal component analysis of groundwater
参数 孔隙水 裂隙水 RC1 RC2 RC1 RC2 Ca2+ 0.952 0.224 0.933 −0.154 Mg2+ 0.986 0.104 0.797 −0.231 Na+ 0.996 0.024 0.742 0.421 K+ 0.808 −0.458 0.433 0.568 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 0.837 0.358 0.703 −0.399 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 0.771 0.100 0.827 0.005 Cl− 0.987 −0.089 0.896 0.158 TDS 0.997 0.072 0.985 0.090 F− −0.290 0.765 −0.529 0.565 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 0.851 −0.341 0.800 0.355 TH 0.976 0.187 0.957 −0.178 特征值 8.547 1.159 7.033 1.246 方差百分数/% 77.703 10.538 63.938 11.332 累计方差百分数/% 77.703 88.241 63.938 75.270 -
[1] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 唐业旗, 李鹏岳. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4):1446-1456.YUAN Jianfei, DENG Guoshi, XU Fen, TANG Yeqi, LI Pengyue. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4):1446-1456. [2] 罗 飞, 苏春田, 潘晓东, 杨杨, 赵光帅. 典型岩溶丘陵区地下水水化学特征及地球化学敏感性分析: 以武冈东部地区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(2):211-217.LUO Fei, SU Chuntian, PAN Xiaodong, YANG Yang, ZHAO Guangshuai. Hydrochemical characteristics and geochemical sensitivity of groundwater in typical karst hilly regions: A case study of eastern Wugang[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(2):211-217. [3] 沈杨, 何江涛, 王俊杰, 杨广元, 刘丽雅. 基于多元统计方法的地下水水化学特征分析: 以沈阳市李官堡傍河水源地为例[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2):440-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.024SHEN Yang, HE Jiangtao, WANG Junjie, YANG Guangyuan, LIU Liya. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater based on multivariate statistical analyses: Taking the Liguanpu ripanian wellhead area in Shenyang City for example[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(2):440-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.024 [4] 刘伟江, 袁祥美, 张雅, 马燕华, 苏春利. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学特征及演化过程分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6):245-251. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0631LIU Weijiang, YUAN Xiangmei, ZHANG Ya, MA Yanhua, SU Chunli. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of karst groundwater in Guiyang City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6):245-251. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0631 [5] Peiyue Li, Rui Tian, Rong Liu. Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua Phosphorite mine, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Exposure and Health, 2019, 11(2): 81–94. [6] Heng Wang, Xiaowei Jiang, Li Wan, Guilin Han, Huaming Guo. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater flow systems in the discharge area of a river basin[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 527:433-441. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.04.063 [7] 李状, 苏晶文, 董长春, 叶永红, 杨洋. 安徽马鞍山市当涂地区地下水水化学特征及演化机制[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(5):1509-1526. doi: 10.12029/gc20210101LI Zhuang, SU Jingwen, DONG Changchun, YE Yonghong, YANG Yang. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution mechanisms of the groundwater in Dangtu area, Ma’anshan City, Anhui Province[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5):1509-1526. doi: 10.12029/gc20210101 [8] 张超, 张保祥, 张吉圣, 邸燕. 肥城市岩溶水水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(5):698-707.ZHANG Chao, ZHANG Baoxiang, ZHANG Jisheng, DI Yan. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of karst water in Feicheng City[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5):698-707. [9] 王瑞, 李潇瀚. 百泉泉域岩溶地下水水化学演化特征及成因[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):398-408.WANG Rui, LI Xiaohan. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of karst groundwater in the Baiquan spring catchment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3):398-408. [10] 盛婷, 杨平恒, 陈峰, 詹兆君, 谢国文. 典型岩溶泉主要化学成分来源及地球化学敏感性研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(6):827-834.SHENG Ting, YANG Pingheng, CHEN Feng, ZHAN Zhaojun, XIE Guowen. Study on sources of chemical elements and geochemical susceptibility of a typical karst spring[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(6):827-834. [11] 彭凯, 刘文, 魏善明, 刘传娥, 陈燕, 董浩, 苏动, 袁炜, 韩琳. 基于水化学、同位素特征的济南岩溶地下水补给来源研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(5):650-657.PENG Kai, LIU Wen, WEI Shanming, LIU Chuan'e, CHEN Yan, DONG Hao, SU Dong, YUAN Wei, HAN Lin. Study on the recharge source of karst groundwater in Jinan City based on hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(5):650-657. [12] 叶慧君, 张瑞雪, 吴攀, 李学先, 覃应机, 查学芳, 韩志伟. 基于主成分分析的岩溶水水化学组成及影响因素研究: 以贵州水城盆地为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(2):215-225. doi: 10.11932/karst20170209YE Huijun, ZHANG Ruixue, WU Pan, LI Xuexian, QIN Yingji, ZHA Xuefang, HAN Zhiwei. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater and surface water and their influencing factors based on principal component analysis: An example in the Shuicheng basin of Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(2):215-225. doi: 10.11932/karst20170209 [13] 管清花, 李福林, 王爱芹, 冯平, 田婵娟, 陈学群, 刘丹. 济南市岩溶泉域地下水化学特征与水环境演化[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5):653-662.GUAN Qinghua, LI Fulin, WANG Aiqin, FENG Ping, TIAN Chanjuan, CHEN Xuequn, LIU Dan. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of karst spring groundwater system in Jinan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5):653-662. [14] Qingchun Yang, Zijun Li, Hongyun Ma, Luchen Wang, Jordi Delgado Martín. Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the southeastern part of Ordos basin, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218:879-888. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.017 [15] Fei Liu, Xianfang Song, Lihu Yang. The role of anthropogenic and natural factors in shaping the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, Northwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 538:327-340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.057 [16] Peiyue Li, Yuting Zhang, Nuan Yang, Lijun Jing, Peiyuan Yu. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China[J]. Expo Health, 2016, 8:239-252. doi: 10.1007/s12403-016-0198-6 [17] Chengcheng Li, Xubo Gao, Yanxin Wang. Hydrogeochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater at Yuncheng Basin, Northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 508:155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.045 [18] 王晓曦, 王文科, 王周锋, 赵佳莉, 谢海澜, 王小丹. 滦河下游河水及沿岸地下水水化学特征及其形成作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1):25-32. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2014.01.005WANG Xiaoxi, WANG Wenke, WANG Zhoufeng, ZHAO Jiali, XIE Hailan, WANG Xiaodan. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of riverwater and groundwater along the downstream Luanhe river, Northeastern China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1):25-32. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2014.01.005 [19] 孙岐发, 贾林刚, 田辉, 李旭光, 郭晓东, 于慧明, 朱巍. 长春莲花山地区地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(5):476-482.SUN Qifa, JIA Lingang, TIAN Hui, LI Xuguang, GUO Xiaodong, YU Huiming, ZHU Wei. Chemical characteristics and genesis analysis of the groundwater in Lianhuashan area, Changchun City[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(5):476-482. [20] Peiyue Li, Jianhua Wu, Hui Qian. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China[J]. Water Quality, Exposure and Health, 2016, 8(3):331-348. doi: 10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y -










 下载:
下载: