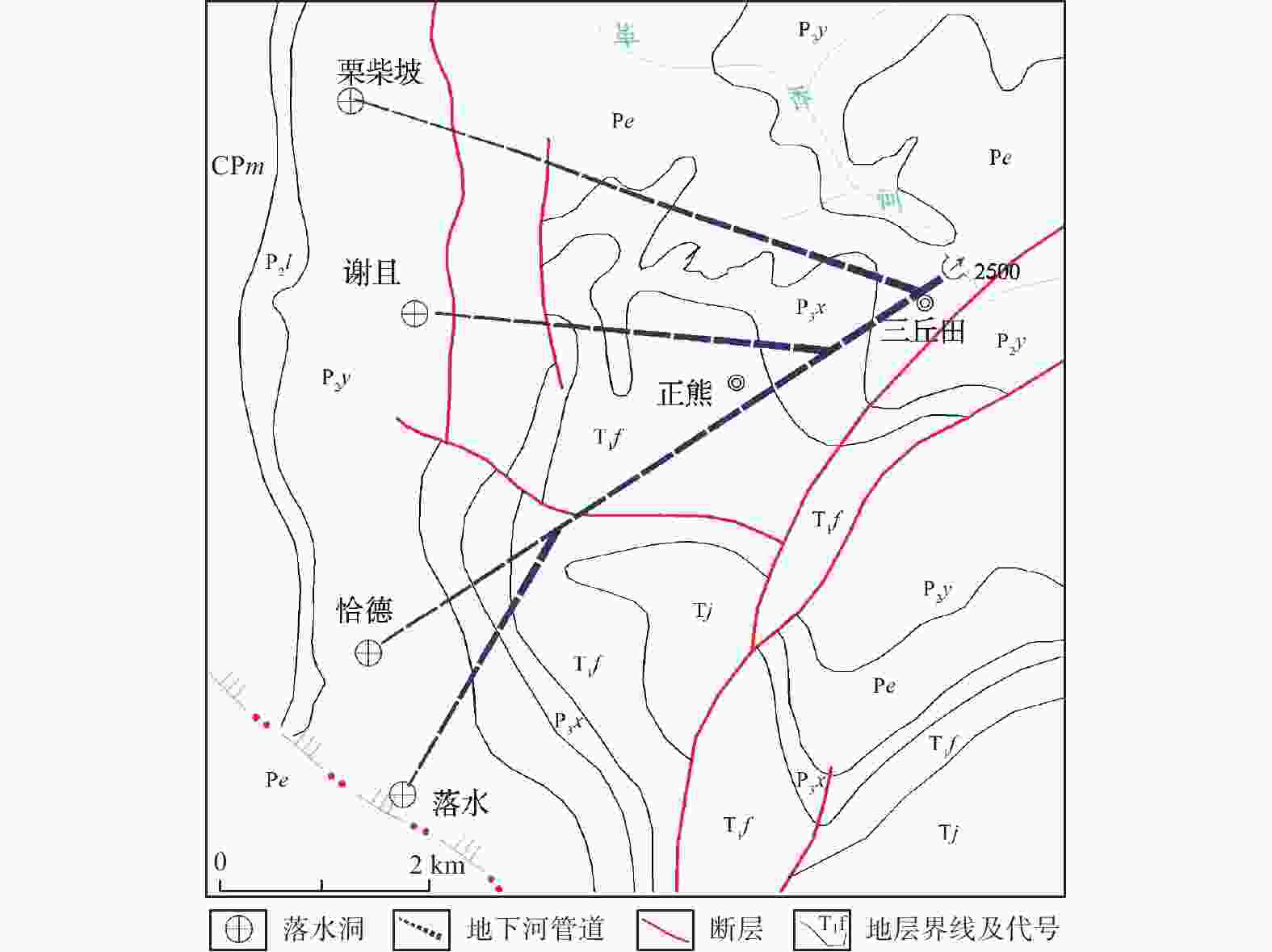
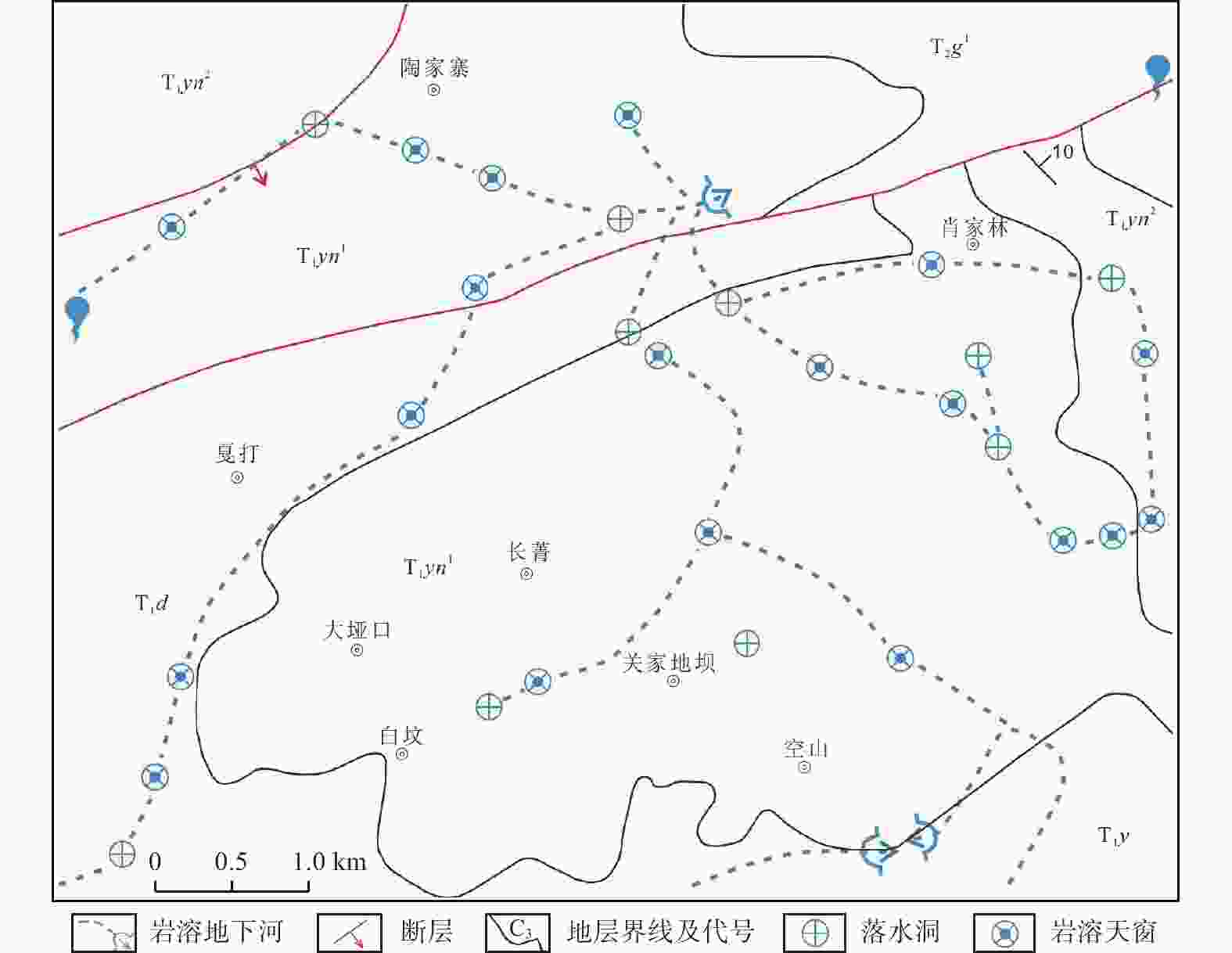
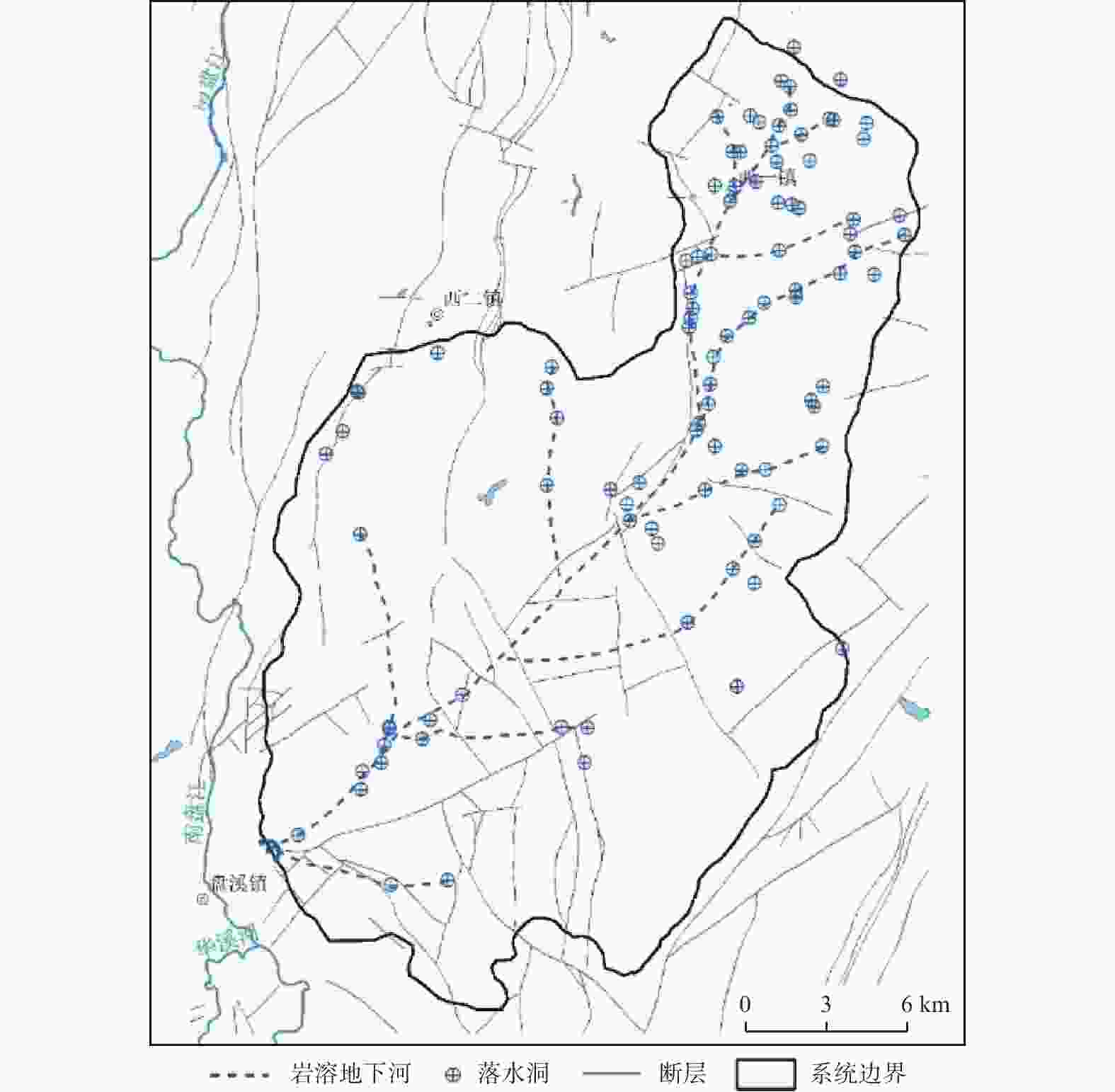
Distribution and influencing factors of karst underground rivers in the Pearl River Basin
-
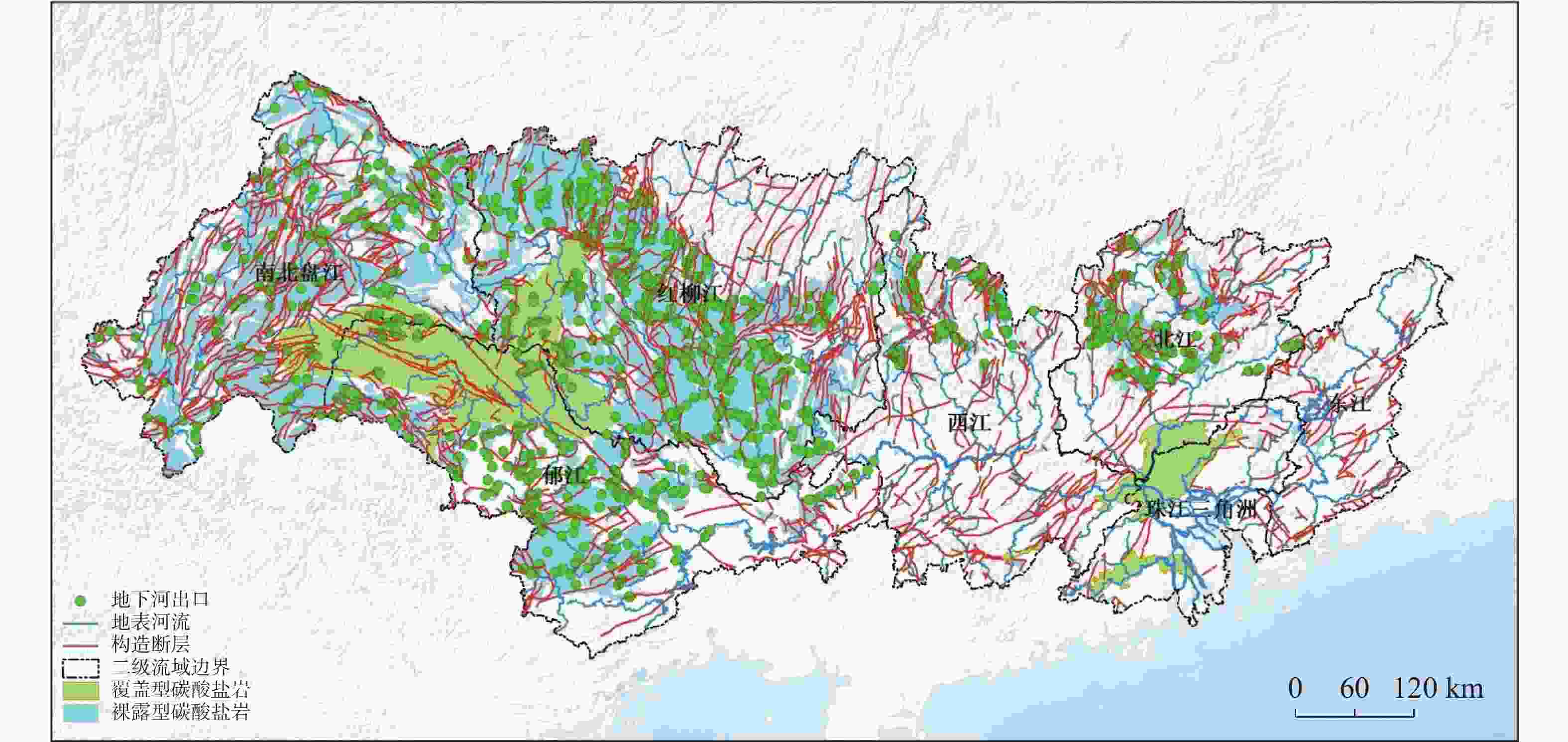
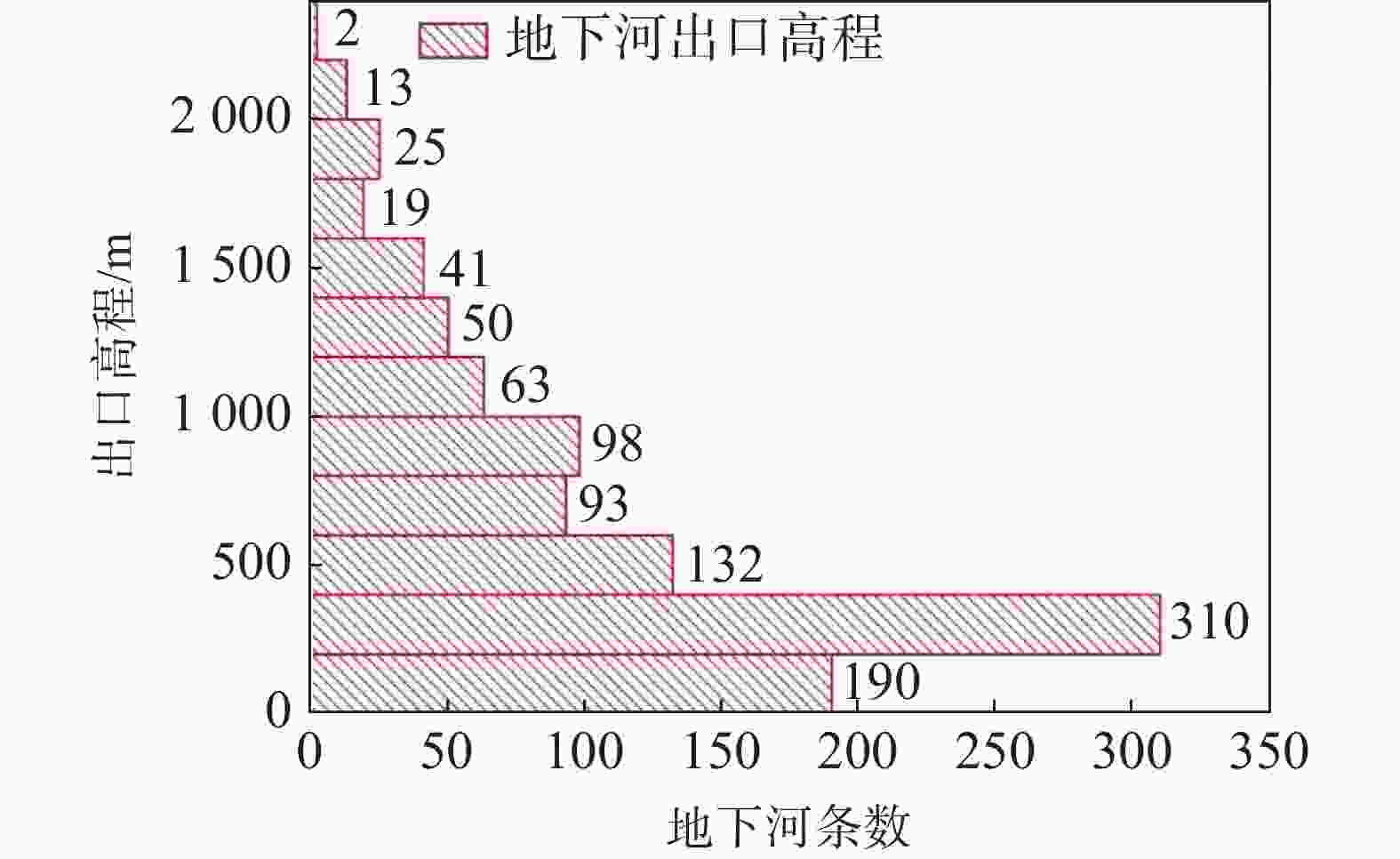
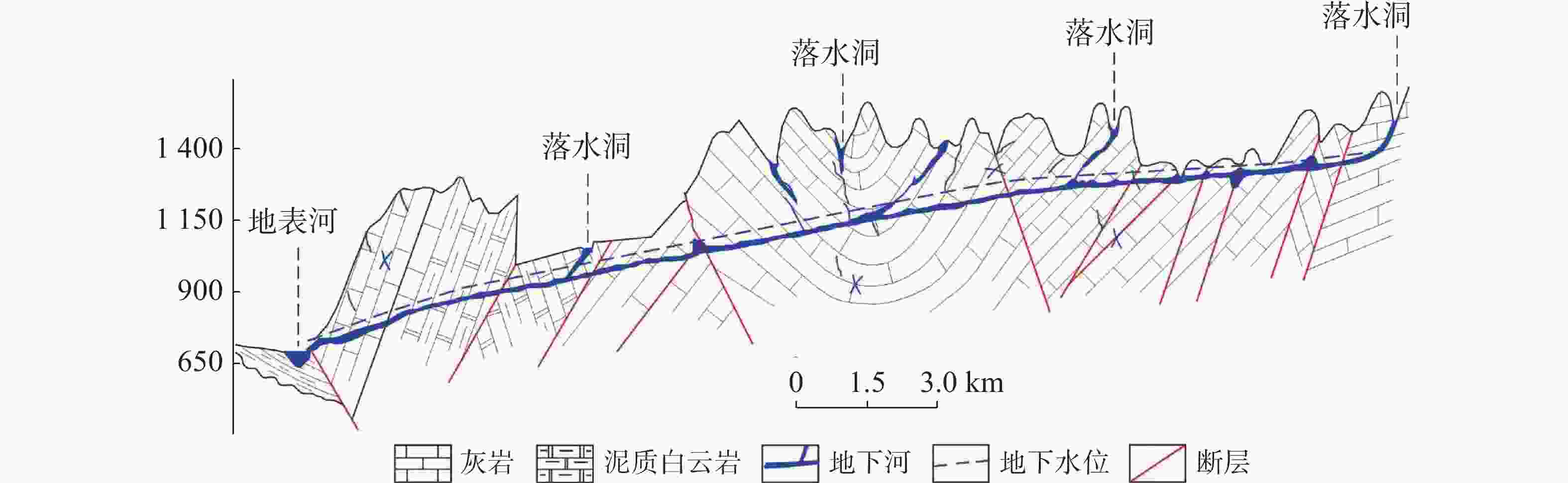
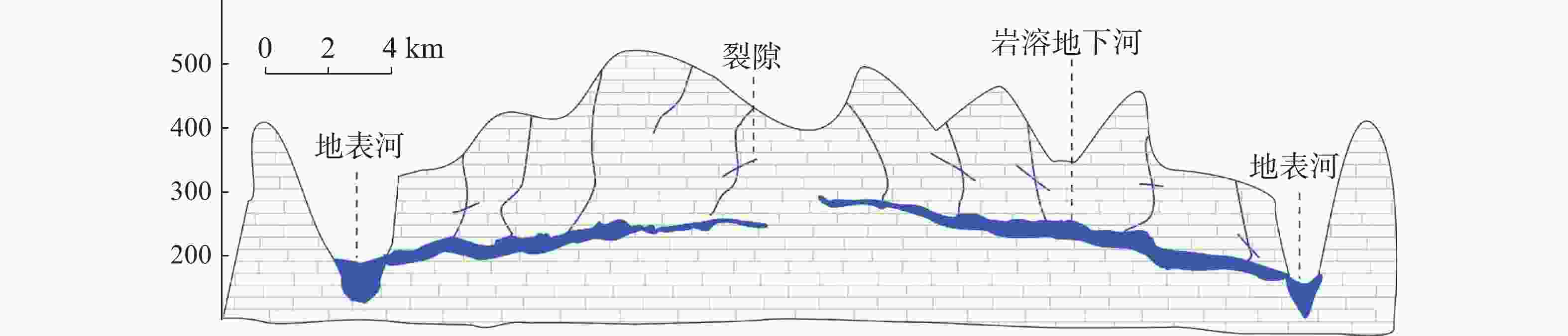
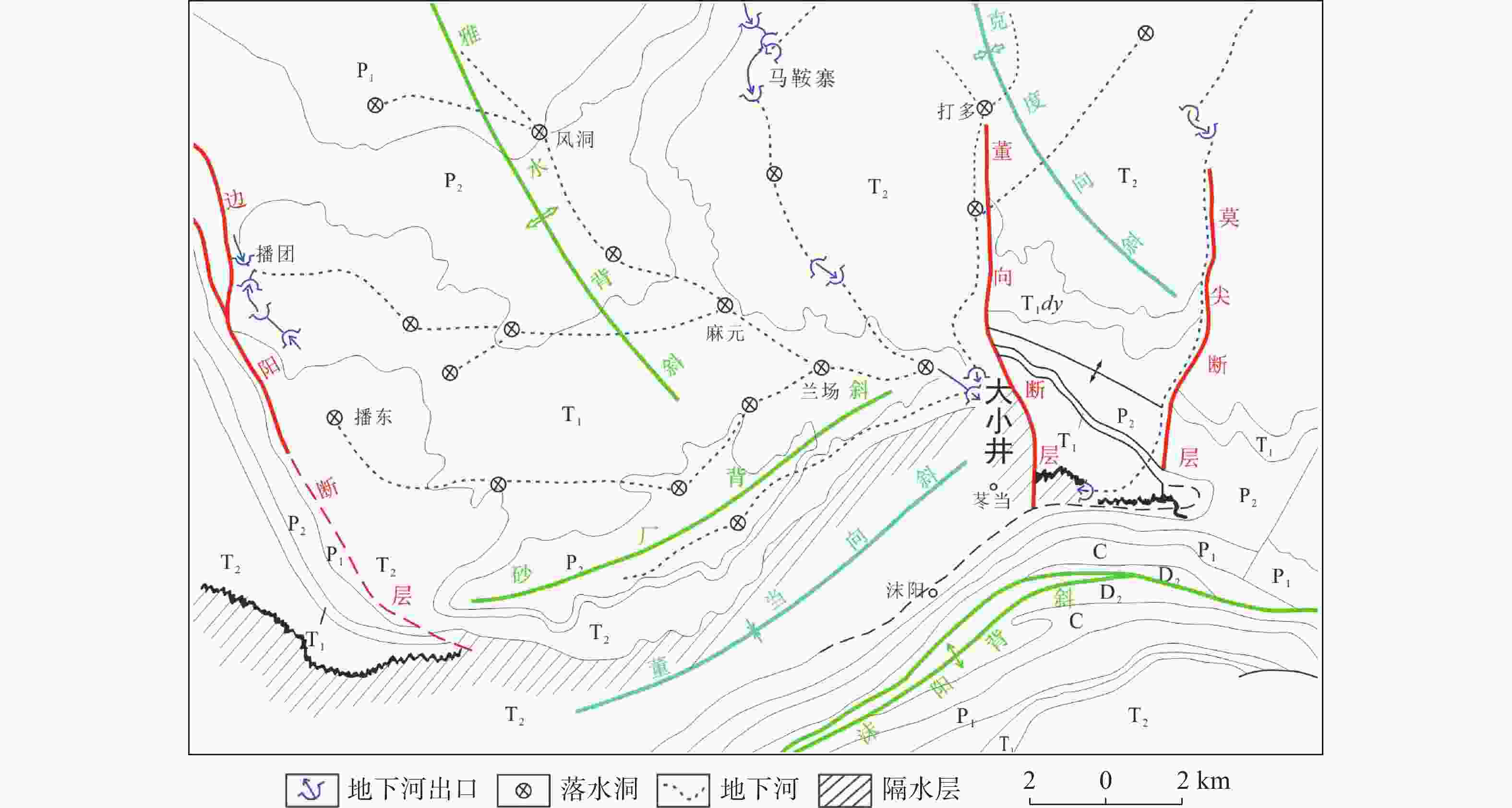
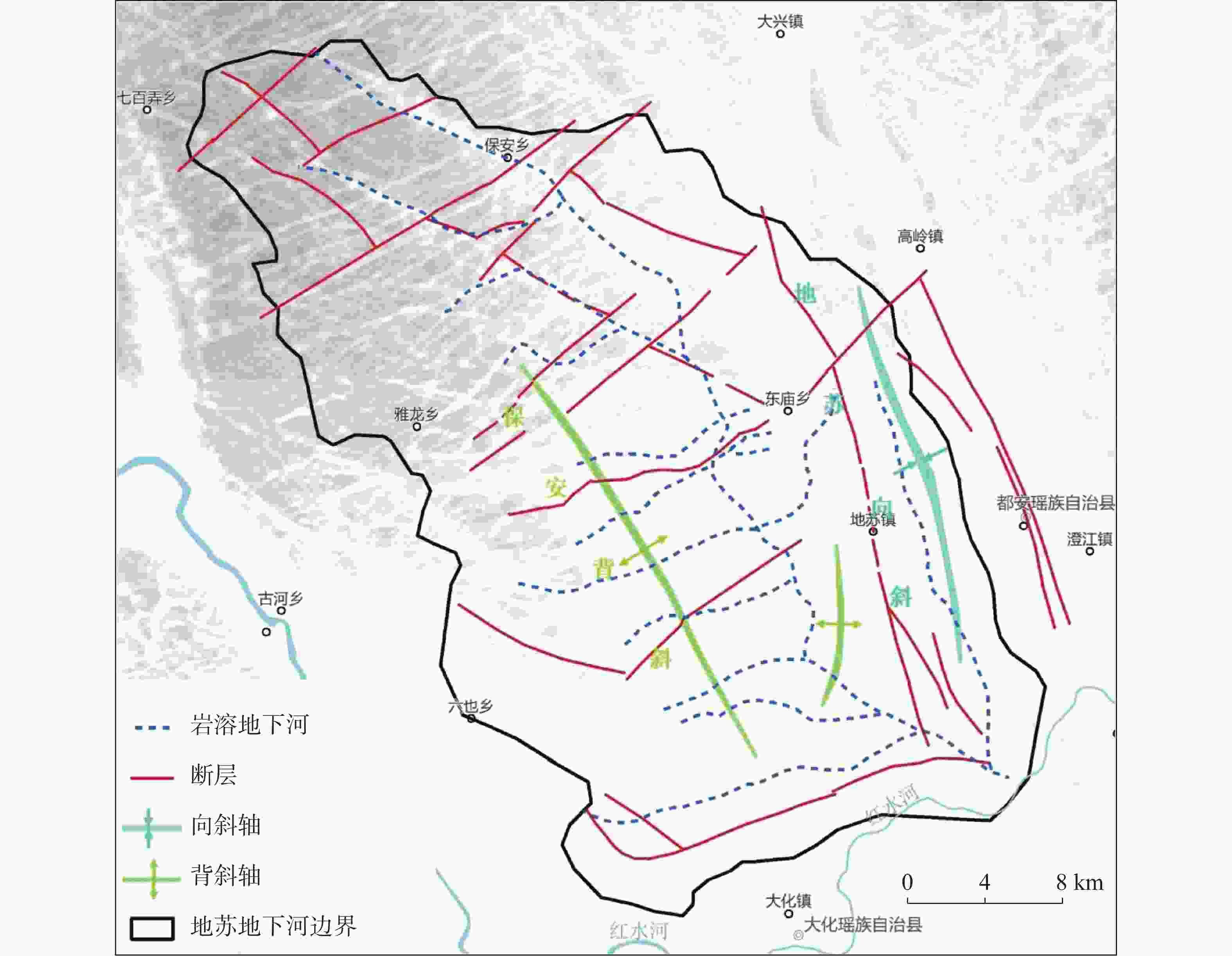
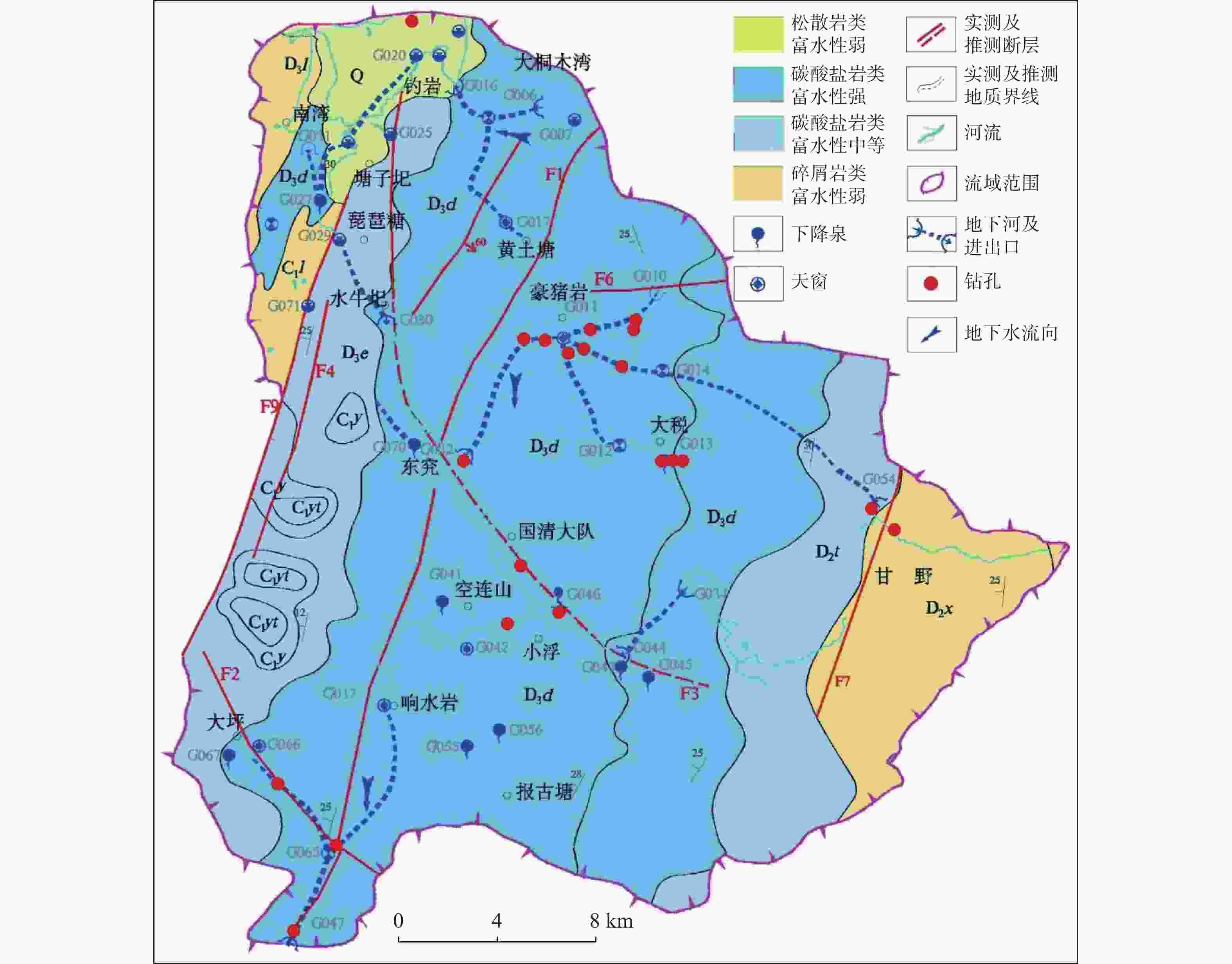
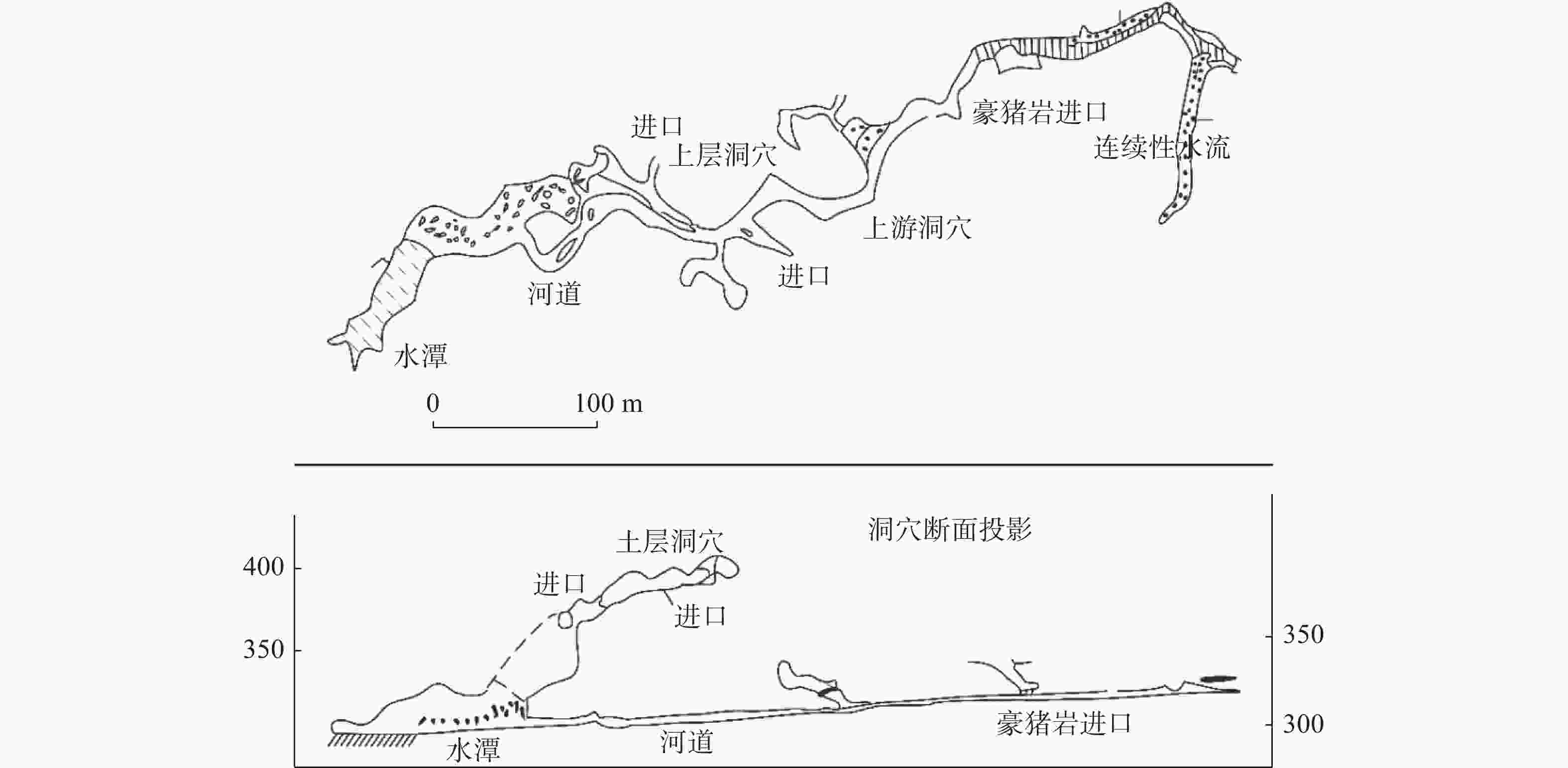
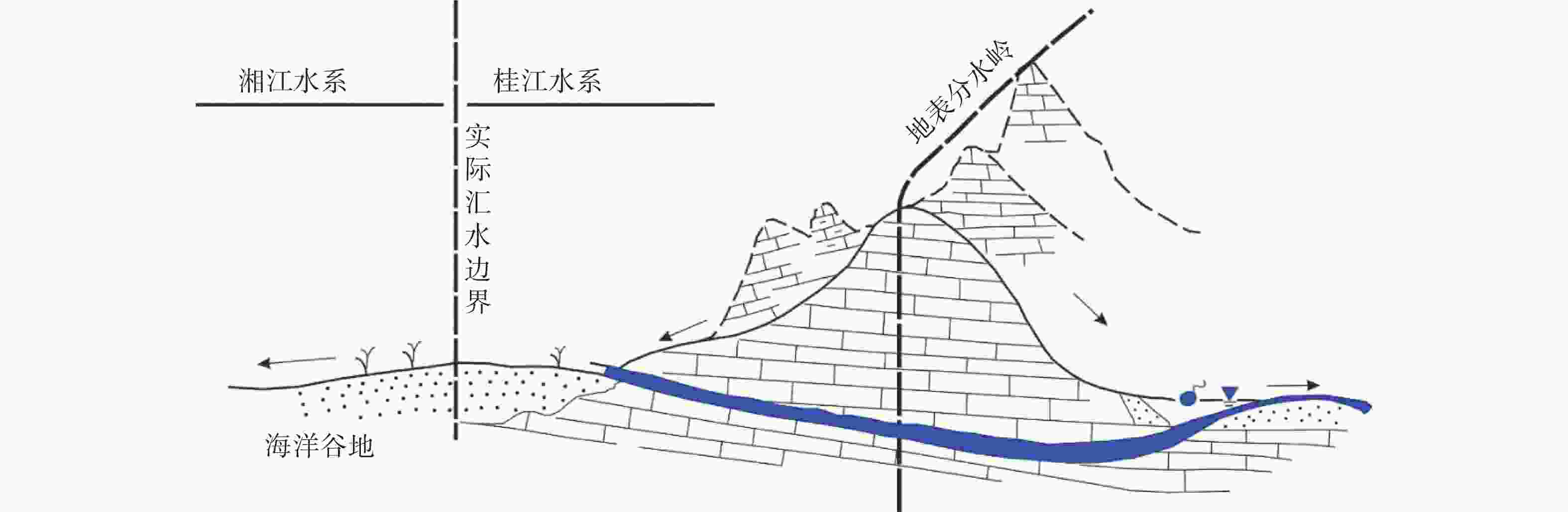
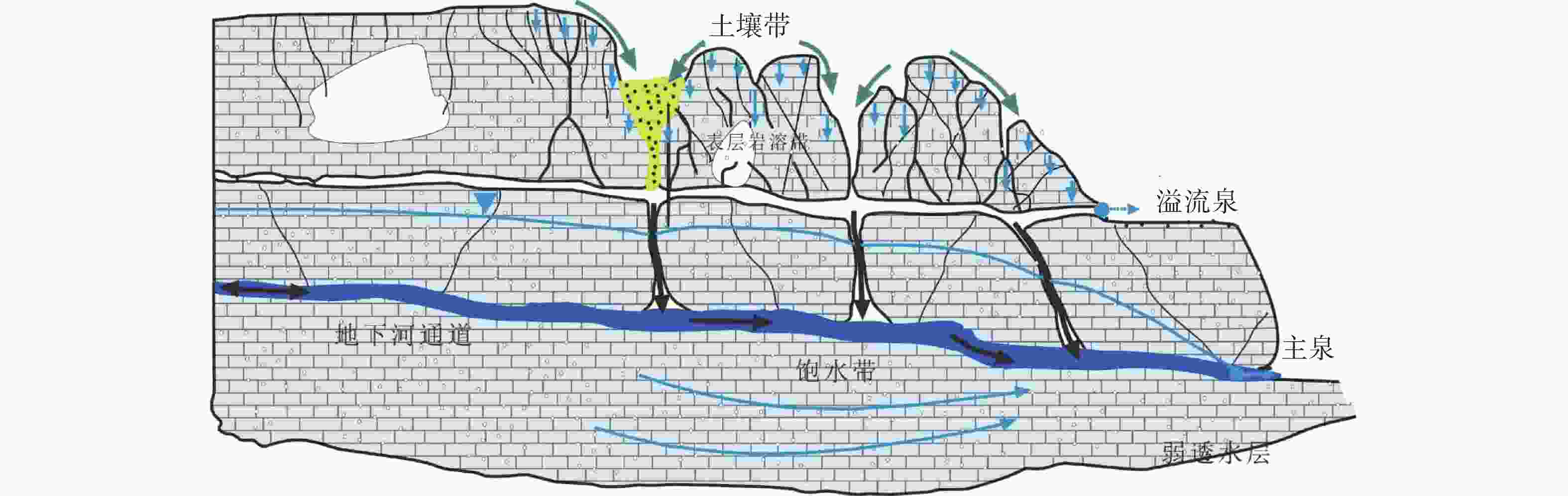
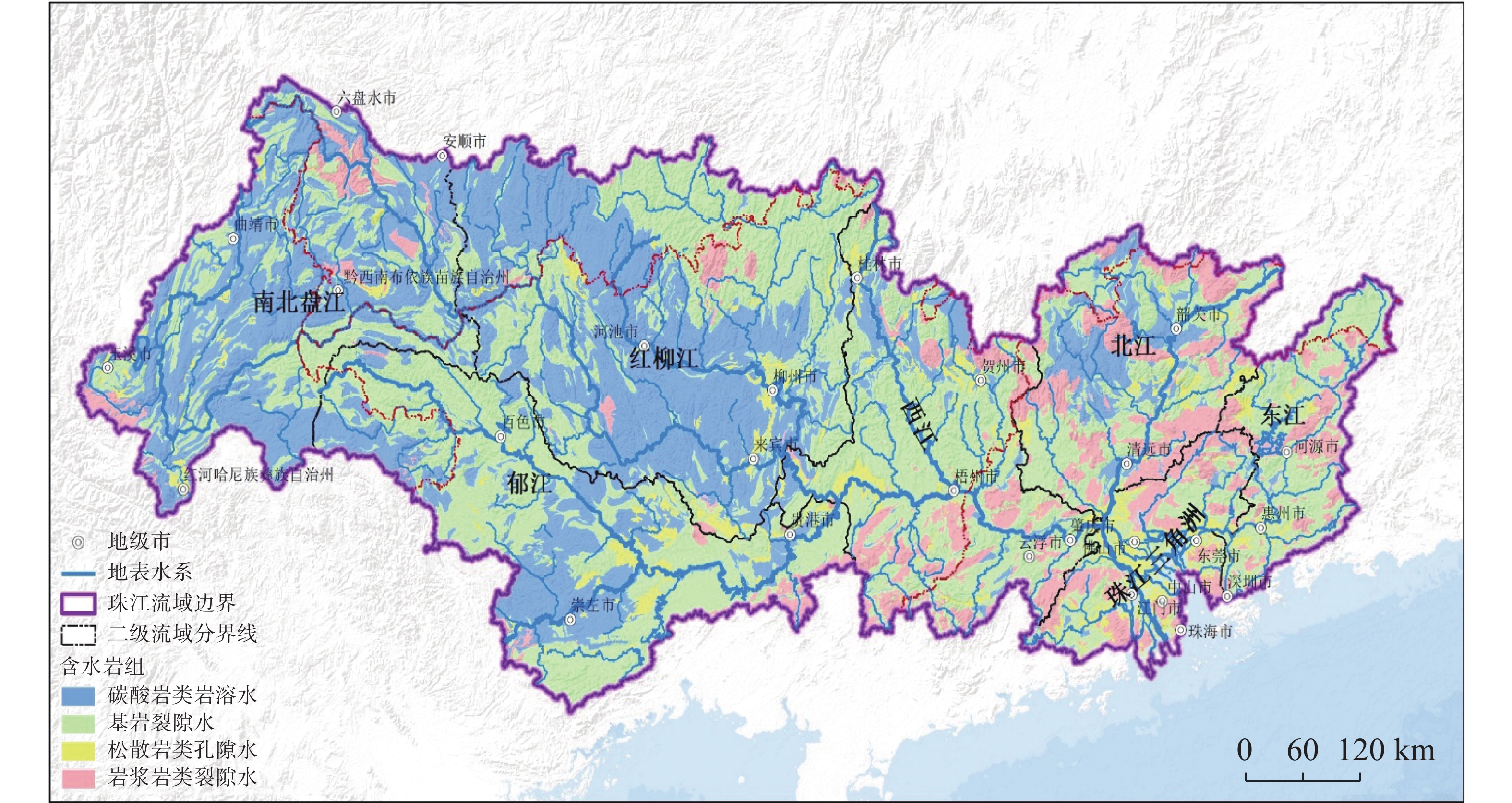
摘要: 珠江流域岩溶地下河枯季流量约4 738.69万m3·d−1,赋存丰富的地下水资源,探讨地下河分布和发育特征对我国南方岩溶水资源的开发利用具有重要的指导意义。文章以西南岩溶区大量的野外调查工作为基础,结合珠江流域内1∶20万水文地质普查报告,选择348组岩石样品和1 036条岩溶地下河,从岩性、地形地貌、构造、水动力条件和新构造运动等角度总结分析珠江流域地下河发育规律、分布特征及其影响因素。结果表明:地下河在比溶解度介于0.84~1.2的细粒−鲕粒生物碎屑纯灰岩中最为发育,在比溶解度介于0.43~0.61的泥质灰岩中发育较弱。根据地下河形态及水循环演化条件,将地下河分为发育初期单管型、发育多期羽毛型、新构造控制网络型、发育成熟期树枝型4种类型。地形地貌和地表河网决定岩溶地下河运动的趋势和方向;构造控制地下河发育的空间格局,其中构造反接复合部位、压扭性断裂两侧破碎带、与非可溶岩接触带、褶皱弯曲最大部位、背斜轴部破碎带和向斜轴部地下河发育尤为明显;水动力特征影响地下河发育规模和发育深度;新构造运动促进地下河发育向深性、继承性、新生性发展。Abstract: The Pearl River Basin is the area of first-class water resources at the southernmost end of China. Its geographical location is 102°14′-115°57′ E and 21°35′-26°50′N. The main stream of the Pearl River, with a total length of 2,214 km, flows through Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi and Guangdong. The total area of the Pearl River Basin is about 438,100 km2, including Nanbeipan river, Hongliu river, Yujiang river, Xijiang river, Beijiang river, the Pearl River Delta and the dongjiang river basin. The water-bearing rocks in the Pearl River Basin are divided into karst water of carbonate rock, fissure water of clastic rock, pore water of loose rock and fissure water of magmatic rock. The distribution area of exposed carbonate rocks is about 149,500 km2, and that of buried carbonate rocks is about 39,600 km2, accounting for 43.16% of the total area. Because there are 1,036 karst underground rivers, and the discharge of karst underground rivers of the Pearl River Basin in the dry season is about 47.39 million m3·d−1. the basin is rich in groundwater resources. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the distribution and karstification characteristics of underground rivers for the exploitation and utilization of karst water resources in southern China. Based on a large number of field investigations in the southwest karst area, 200,000 hydrogeological survey reports and the 1∶250,000 and 1∶50,000 karst hydrogeological surveys conducted from 2003 to 2016 in the Pearl River Basin, we selected 348 groups of rock samples and 1,036 karst underground rivers as study objects. Then, taking Dalongtan and Sanqiutian underground rivers in Yunnan Province, Sixiaojing, Tianshengqiao and Huachu underground rivers in Guizhou Province, and Disu, Zhaidi and Dizhou underground rivers in Guangxi as examples, we analyzed and summarized the development law, distribution characteristics and influencing factors of underground rivers in the Pearl River Basin from the perspectives of lithology, landform, structure, hydrodynamic conditions and neotectonic movement. According to the analysis, the outlets of 310 underground river are at an elevation between 200-400 m, accounting for the largest proportion. Among them, more than 30 underground rivers, mainly located in the river basins of Hongliu river, Yuhe river, South Panjiang river and north Panjiang river, respectively cover a catchment area greater than 200 km2. Their discharge in the dry season is greater than 1,000 L·s−1 and the length of main pipeline is greater than 10 km. The study result shows that the underground river is most developed in fine-grained oolitic bioclastic pure limestone with a specific solubility of 0.84-1.2, moderately developed in dolomite with a specific solubility of 0.62-0.83, and weakly developed in argillaceous limestone with a specific solubility of 0.43-0.61. Landform and surface river network determine the trend and direction of karst underground river movement. The structure controls the spatial pattern of underground river development. The development of underground river is particularly obvious in the reverse composite part of the structure, the fracture zone on both sides of the compressional torsional fault, the contact zone with the non-soluble rock, the part with the largest fold bending, and the fracture zone in the anticline axis and the syncline axis. Hydrodynamic characteristics affect the development scale and depth of underground rivers. The neotectonic movement facilitates the constant changes of cycle and alternation conditions of groundwater, as well as the deep, inherited and new development of underground rivers. Finally, according to the morphology of underground river and the evolution conditions of water circulation, the underground river can be divided into four types: single conduit type at the initial stage of development, multi-stage feather type, neotectonic control network type and mature dendritic type. All in all, this study is expected to provide data support for the exploitation and utilization of karst underground rivers, monitoring and evaluation of water resources, and the selection of backup water sources to meet urban emergency in the Pearl River Basin.
-
表 1 各二级流域岩溶地下河发育情况
Table 1. Development of karst underground rivers in each secondary watershed
二级
流域裸露型碳酸盐岩
面积/万km2占流域面
积比例/%岩溶地下
河条数密度/
条·100 km−2南北盘江 5.30 64.09 173 0.33 红柳江 5.90 52.07 440 0.75 郁江 2.06 26.44 216 1.05 西江 0.65 9.79 96 1.48 北江 1.04 22.27 111 1.07 合计 14.95 38.63 1036 0.69 表 2 大型地下河发育特征表
Table 2. Development characteristics of large underground rivers
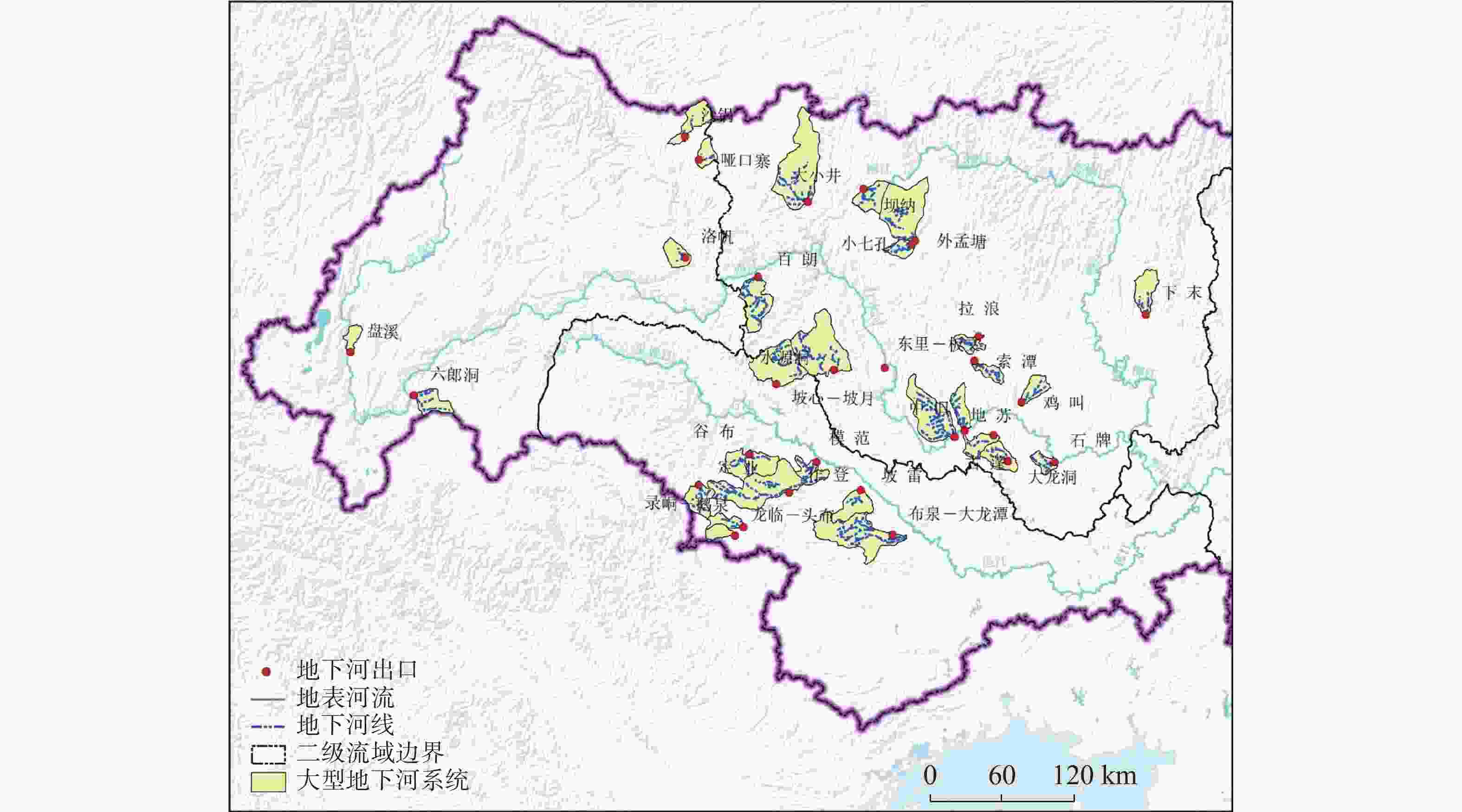
代码 地下河名称 出口位置 主管道长
度/km分布方向 地下河支流
数/个汇水面
积/km2枯季流
量/m3·s−1主要含水
岩组UGR1 六郎洞 云南丘北县 15.00 NE 2 2 064.00 10.50 T2g UGR2 水源洞 广西凌云县 80.30 SW 5 667.18 9.74 D2t UGR3 洛帆 贵州册亨县 11.25 SE 3 339.00 8.43 P1m UGR4 外孟塘 贵州荔波县 15.00 SE 2 1 418.80 6.60 P1m UGR5 谷 布 广西田阳区 19.20 NE 5 611.19 5.78 D3r UGR6 坡心-坡月 广西巴马瑶族自治县 47.30 SE 11 852.44 5.75 D2t UGR7 地 苏 广西都安瑶族自治县 55.90 SE 12 1 128.00 4.86 D3d-e UGR8 大小井 贵州罗甸县 35.00 SE 7 1 855.70 4.73 T1d UGR9 盘溪 云南弥勒市 13.75 NE 2 744.80 3.33 Dx UGR10 小七孔 贵州荔波县 20.00 SE 2 337.30 3.23 P1q-m UGR11 拉 浪 广西宜州区 20.90 SE转NE 7 221.20 3.00 C2d-h UGR12 定 业 广西那坡县 26.60 NNW 4 423.52 2.73 D1y UGR13 作 登 广西田东县 76.00 SEE转NE 4 1 409.05 2.16 D3r、C1yt UGR14 百 朗 广西乐业县 63.00 N 13 600.03 2.14 CPm UGR15 索 潭 广西都安瑶族自治县 31.20 N转NW 6 226.31 2.13 C2h、P1q UGR16 坡 雷 广西田东县 16.70 NE 2 377.37 1.79 D3r、CPm UGR17 鸡 叫 广西忻城县 28.80 SW 3 327.81 1.79 CPm、P1q UGR18 沙锅 贵州镇宁布依族苗族自治县 23.75 SW 4 480.20 1.70 T2f UGR19 东里-板文 广西东兰县 37.40 E 5 502.29 1.48 C1-2d UGR20 龙临-头布 广西靖西市 28.20 SE 3 320.81 1.46 D3r UGR21 录峒-鹅泉 广西靖西市 22.00 SE 2 226.95 1.40 D3r UGR22 哑口寨 贵州镇宁布依族苗族自治县 12.50 NE 5 252.20 1.36 P1m、P2w UGR23 布泉-大龙潭 广西隆安县 54.80 E 10 1 347.14 1.35 D3r UGR24 中 旧 广西都安瑶族自治县 35.90 SE 6 369.44 1.30 CPm、P1q UGR25 坝纳 贵州平塘县 17.50 NW 5 455.20 1.20 P1 UGR26 下 末 广西鹿寨县 20.00 S 3 463.60 1.20 D3g、C1h UGR27 石 牌 广西来宾市 23.00 SE转NEE 3 221.44 1.14 C1d、P1q UGR28 模 范 广西田东县 20.50 SE转NE 3 210.21 1.06 D3r、C1d UGR29 大龙洞 广西上林县 24.00 N转SSE 4 437.65 1.03 D2t、D3g UGR30 古 蓬 广西忻城县 17.00 NW转E 2 213.68 1.01 CPm、P1q 表 3 不同岩性化学成份及比溶解度对比
Table 3. Comparison of chemical composition and specific solubility of different lithologies
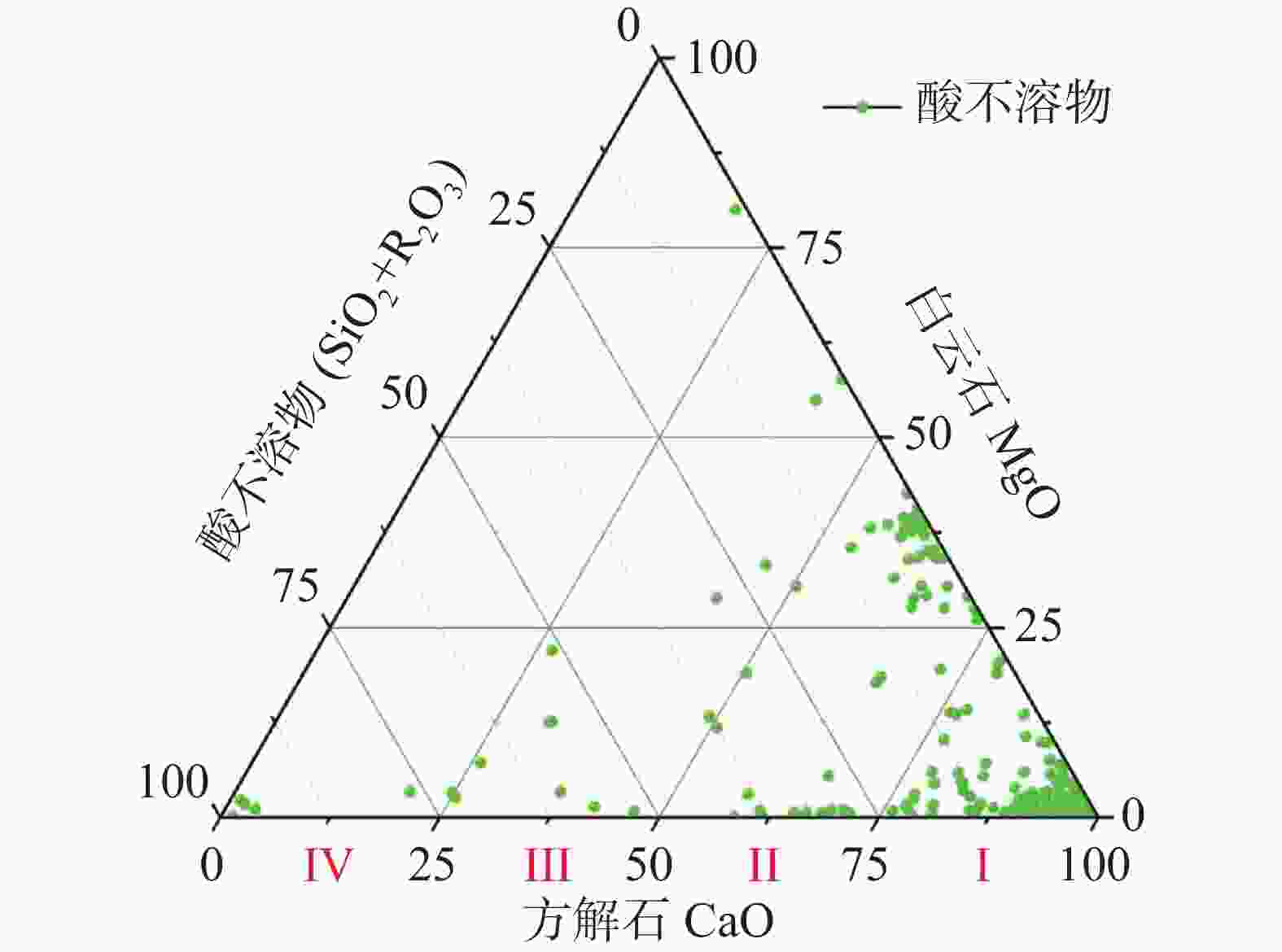
发育强弱 主要岩性结构 化学成份/% 比溶解度 CaO MgO 地下河发育强 细粒−鲕粒生物碎屑纯灰岩 52.58~56.03 0.08~1.62 0.84−1.20 地下河发育中等 微粒白云质灰岩 30.77~52.14 0.31~7.68 0.62~0.83 地下河发育弱 含泥质−燧石灰岩、细粒−中粒白云岩 30.72~34.84 10.94~21.11 0.43~0.61 无发育 非碳酸盐岩(粉砂岩) 1.15~3.33 0.12~2.14 / -
[1] 袁道先. 西南岩溶石山地区重大环境地质问题及对策研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.YUAN Daoxian. Study on major environmental geological problems and countermeasures in karst stone mountain area of southwest China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [2] ZOU S, ZHU M, TANG J, XIA R. Water resources security in karst area of southwest China: problems and countermeasures[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(10):637-642. [3] 夏日元. 西南岩溶石山区地下水资源调查评价与开发利用模式[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.XIA Riyuan. Investigation, evaluation and exploitation of groundwater resources in karst rocky mountainous areas of Southwest China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. [4] 赵良杰. 岩溶裂隙−管道双重含水介质水流交换机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.ZHAO Liangjie. Study of water exchange mechanism of karst matrix and conduit medium[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019. [5] Brkić Ž, Kuhta M, Hunjak T. Groundwater flow mechanism in the well-developed karst aquifer system in the western Croatia: Insights from spring discharge and water isotopes[J]. Catena, 2018, 161:14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.011 [6] 王宇. 岩溶区地表水与地下水资源及环境统一评价的流域边界划分研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(6):823-830.WANG Yu. Study on watershed boundary division for unified evaluation of surface water and groundwater resources and environment in karst areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(6):823-830. [7] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 潘晓东, 夏日元, 曹建文. 西南岩溶山区地下水资源评价方法对比研究: 以寨底地下河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1):111-123.YANG Yang, ZHAO Liangjie, PAN Xiaodong, XIA Riyuan, CAO Jianwen. Comparative analysis of groundwater resources evaluation methods in karst area of south China: Taking Zhaidi underground river system as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1):111-123. [8] 罗明明, 季怀松. 岩溶管道与裂隙介质间溶质暂态存储机制[J]. 水科学进展, 2022, 33(1):145-152.LUO Mingming, JI Huaisong. Mechanism of solute transient storage between karst conduit and fissures[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2022, 33(1):145-152. [9] Sağır Ç, Kurtuluş B, Razack M. Hydrodynamic characterization of Mugla karst aquifer using correlation and spectral analyses on the rainfall and springs water-level time series[J]. Water, 2019, 12(1):85. doi: 10.3390/w12010085 [10] Sauter M, Giese M, Bailly Comte V, Maré chal J C, Reimann T, Geyer T. Turbulent and laminar flow in karst conduits under unsteady flow conditions: Interpretation of pumping tests by discrete conduit-continuum modeling[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(3):1918-1933. doi: 10.1002/2017WR020658 [11] 蒋忠诚, 夏日元, 时坚, 裴建国, 何师意, 梁彬. 西南岩溶地下水资源开发利用效应与潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 2006(5):495-502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.012JIANG Zhongcheng, XIA Riyuan, SHI Jian, PEI Jianguo, HE Shiyi, LIANG Bin. The application effects and exploitation capacity of karst underground water resources in southwest China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2006(5):495-502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.012 [12] 王明章, 王伟, 周忠赋. 峰丛洼地区地下地表联合成库地下水开发模式: 贵州普定马官水洞地下河开发利用[J]. 贵州地质, 2005(4):279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2005.04.012WANG Mingzhang, WANG Wei, ZHOU Zhongfu. Development model for the coalition of surface and underground water into reservoir in the karst areas of peak-cluster depression: Taking example for exploitation of shuidong underground river at Maguan, Puding county, Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2005(4):279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2005.04.012 [13] 赵良杰, 王莹, 周妍, 曹建文, 杨杨, 王喆. 基于SWAT模型的珠江流域地下水资源评价研究[J/OL]. 地球科学: 1-19. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1634.006.html.ZHAO Liangjie, WANG Ying, ZHOU Yan, CAO Jianwen, YANG Yang, WANG Zhe. Groundwater resources evaluation in the pearl river basin based on swat model[J/OL]. Earth Science, 1-19 . https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1634.006.html. [14] Gallegos J J, Hu B X, Davis H. Simulating flow in karst aquifers at laboratory and sub-regional scales using MODFLOW-CFP[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2013, 21(8):1749-1760. doi: 10.1007/s10040-013-1046-4 [15] 姜光辉, 郭芳, 汤庆佳, 李鑫, 曾莘茹. 人工示踪技术在岩溶地区水文地质勘察中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3):503-511.JIANG Guanghui, GUO Fang, TANG Qingjia, LI Xin, ZENG Xinru. Application of tracer test techniques in hydrogeological survey in karst area[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 2016, 52(3):503-511. [16] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 易连兴, 杨杨, 王喆, 卢海平. 岩溶地下河浊度来源及对示踪试验影响的定量分析[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(2):241-246. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.02.12ZHAO Liangjie, XIA Riyuan, YI Lianxing, YANG Yang, WANG Zhe, LU Haiping. Quantitative analysis of the source and the effect of turbidity in karst river on tracer test[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(2):241-246. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.02.12 [17] Wang C, Wang X, Majdalani S, Guinot V, Jourde H. Influence of dual conduit structure on solute transport in karst tracer tests: An experimental laboratory study[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 590:125255. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125255 [18] 曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 夏日元, 章程. 岩溶动力系统与全球变化研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5):874-900. doi: 10.12029/gc20170504CAO Jianhua, JIANG Zhongcheng, YUAN Daoxian, XIA Riyuan, ZHANG Cheng. The progress in the study of the karst dynamic system and global changes in the past 30 years[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(5):874-900. doi: 10.12029/gc20170504 [19] 蒲俊兵, 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 章程. 岩石风化碳汇研究进展: 基于 IPCC 第五次气候变化评估报告的分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(10):1081-1090.PU Junbing, JIANG Zhongcheng, Yuan Daoxian, ZHANG Cheng. Some opinions on rock-weathering-related carbon sinks from the IPCC fifth assessment report[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2015, 30(10):1081-1090. [20] 赵小二, 常勇, 吴吉春. 岩溶地下河污染物运移模型对比研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(4):1250-1259. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0390ZHAO Xiaoer, CHANG Yong, WU Jichun. A comparative study on two contaminant transport models used in karst underground rivers[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4):1250-1259. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0390 [21] Madonia P, Cangemi M, Oliveri Y, Germani C. Hydrogeochemical characters of karst aquifers in central Italy and relationship with neotectonics[J]. Water, 2020, 12(7):1926. doi: 10.3390/w12071926 [22] 杨立铮. 我国南方某些地区地下河的结构特征及其形成和演化[J]. 成都地质学院学报, 1982, 2:54-61.YANG Lizheng. Structural characteristics, formation and evolution of underground rivers in some areas of southern China[J]. Journal of Chengdu Institute of Geology, 1982, 2:54-61. [23] 蒲俊兵. 重庆地区岩溶地下河发育与分布的基本特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(3):266-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.03.004PU Junbing. Development and distribution of karst subterranean streams in Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(3):266-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.03.004 [24] 陈思燕, 曾敏. 四川岩溶地下河空间分布规律研究[J]. 地下水, 2015(3):4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2015.03.003CHEN Siyan, ZENG Min. Study on the spatial distribution regularity of karst ground rivers in Sichuan[J]. Ground water, 2015(3):4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2015.03.003 [25] 韦王秋, 左天惠, 张沛全, 李海. 红水河流域岩溶地下河出口分布特征与控制因素[J]. 科学技术创新, 2017(34):17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2017.34.008WEI Wangqiu, ZUO Tinahui, ZHANG Peiquan, LI Hai. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of karst underground river outlet in Hongshuihe River basin[J]. Science and Technology Innovation, 2017(34):17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2017.34.008 -




 下载:
下载: