Study on "three-section and four-layer" reinforcement technology of tunnel vault subsidence in the karst basement
-
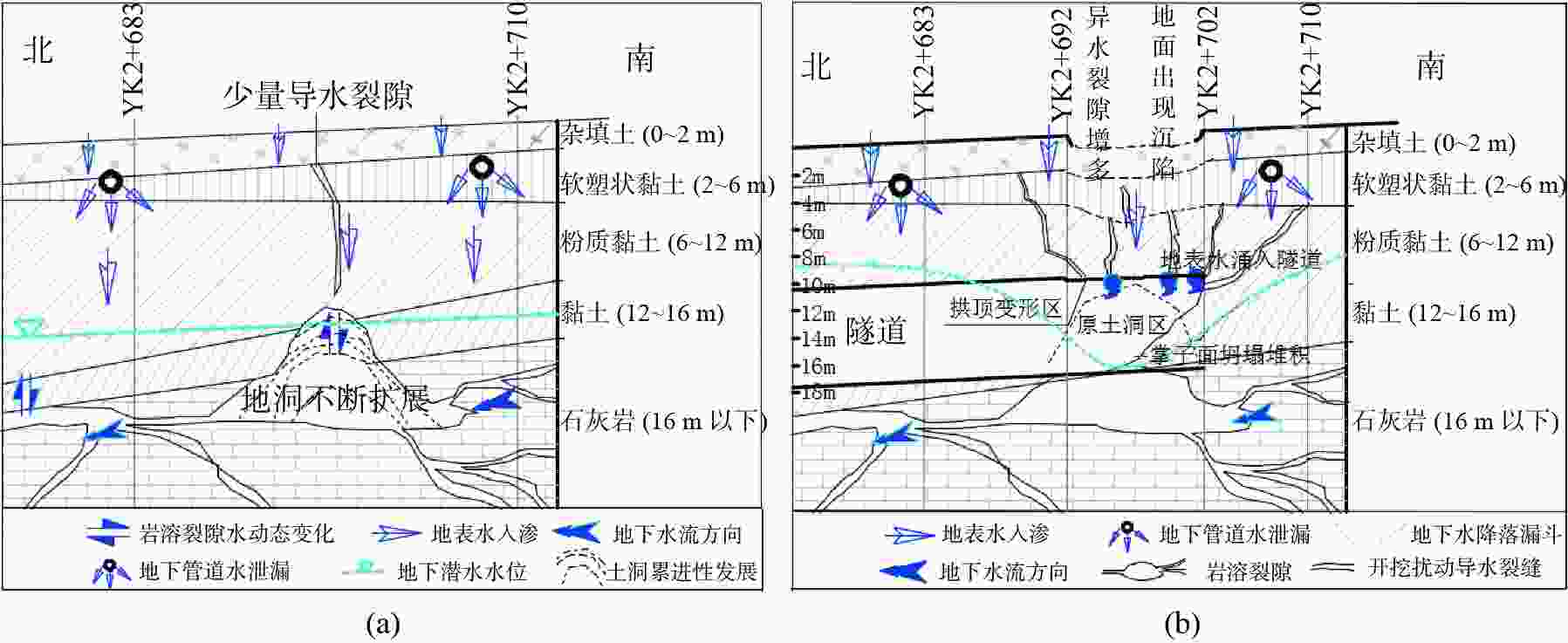
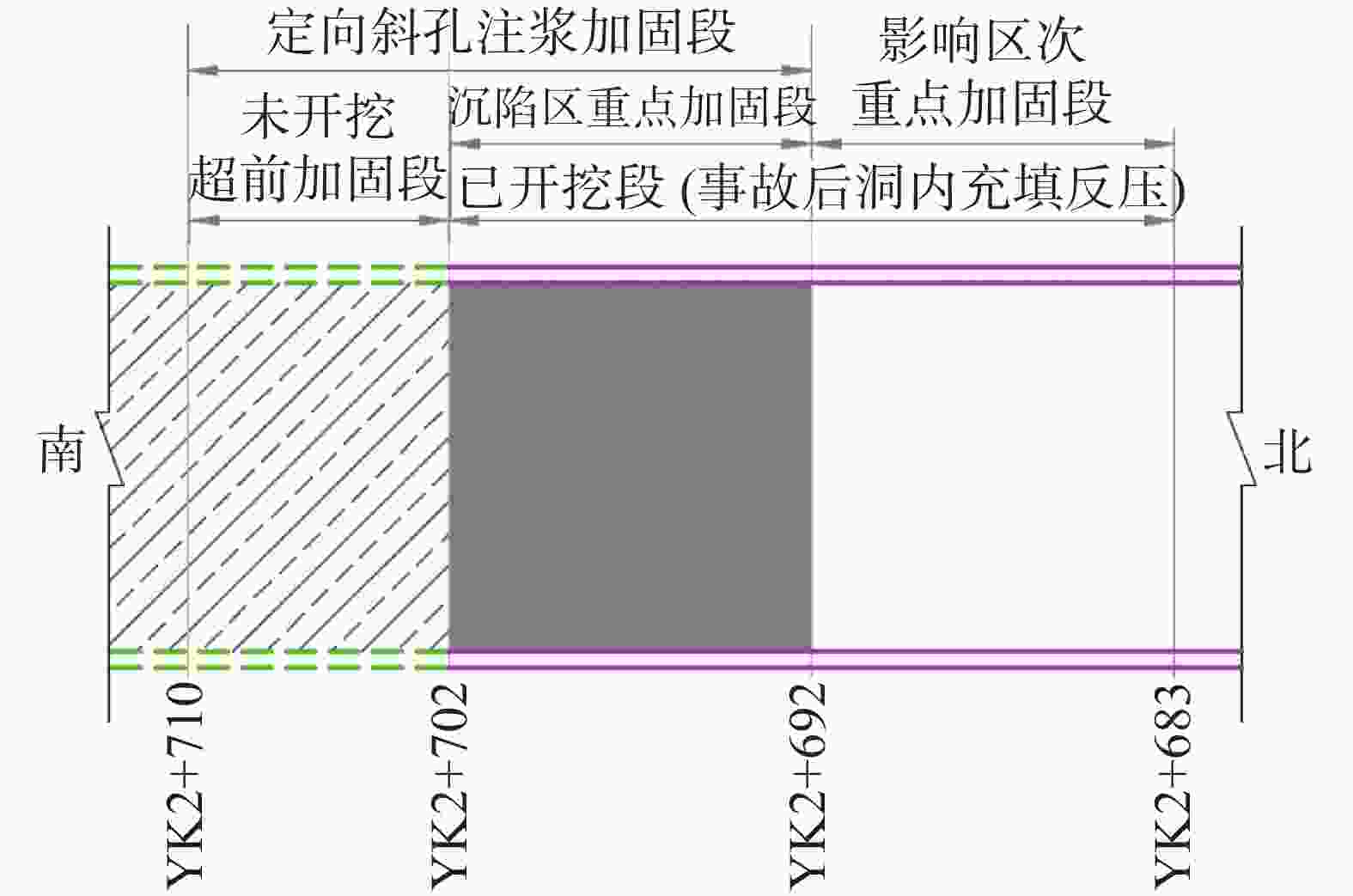
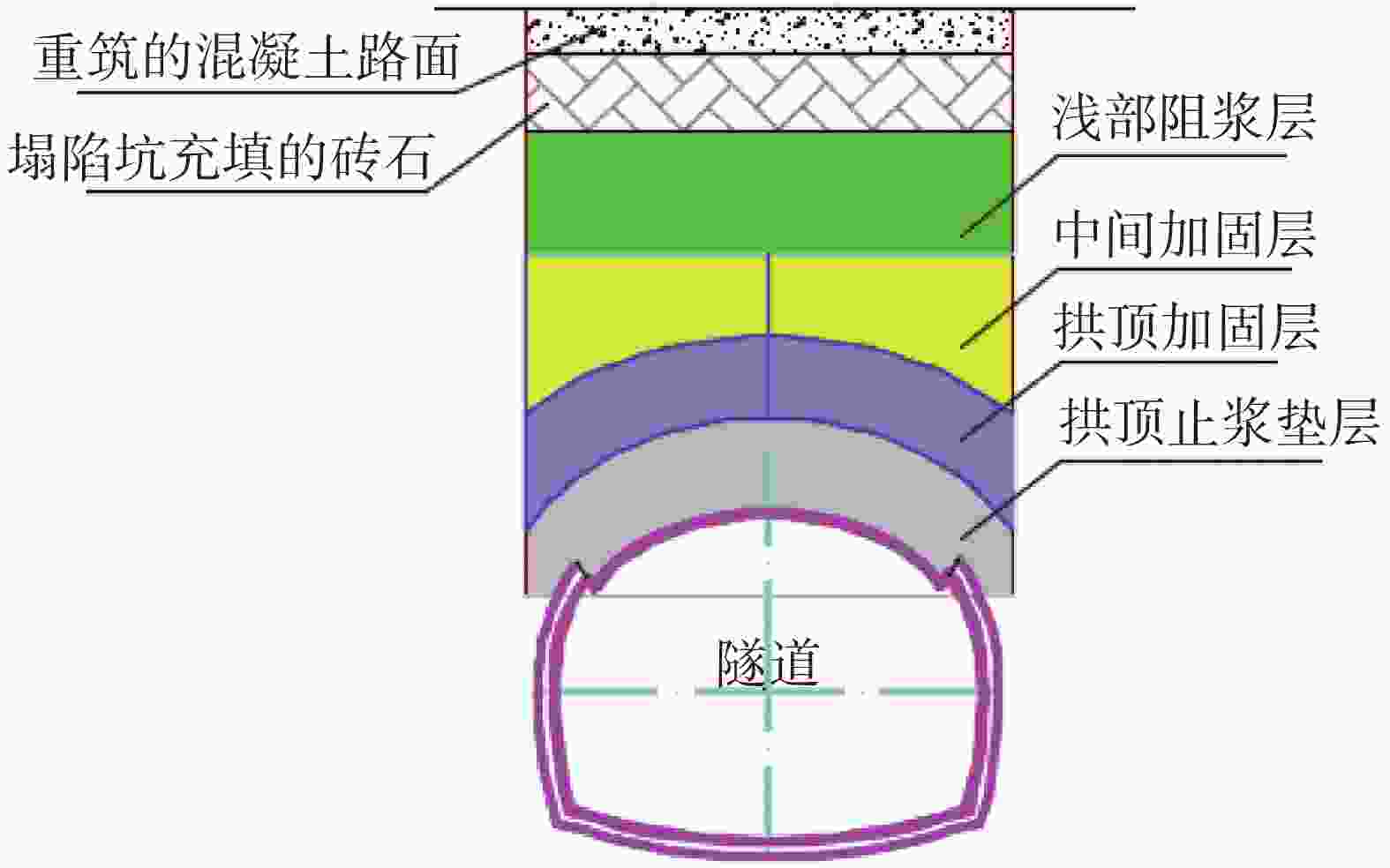
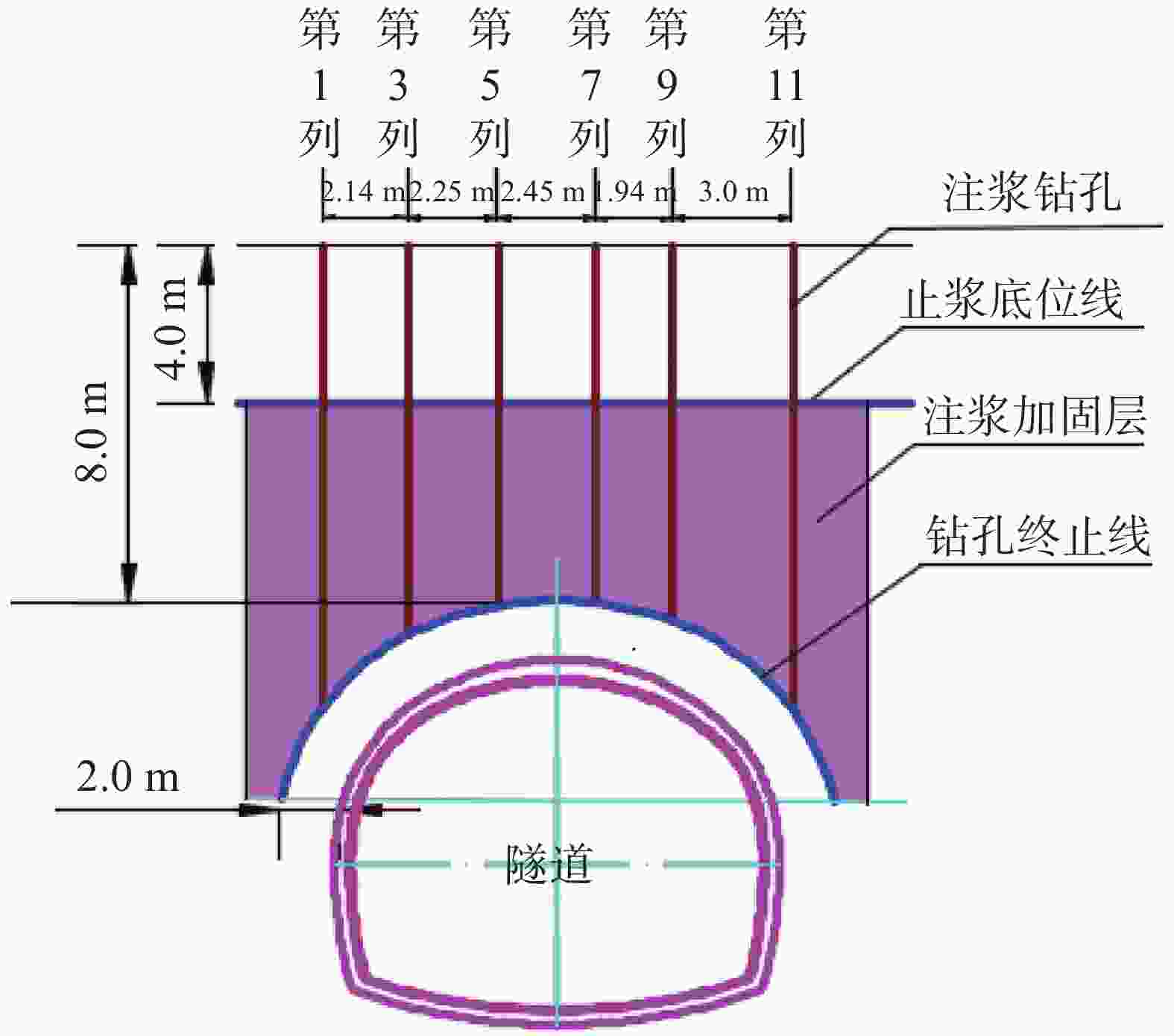
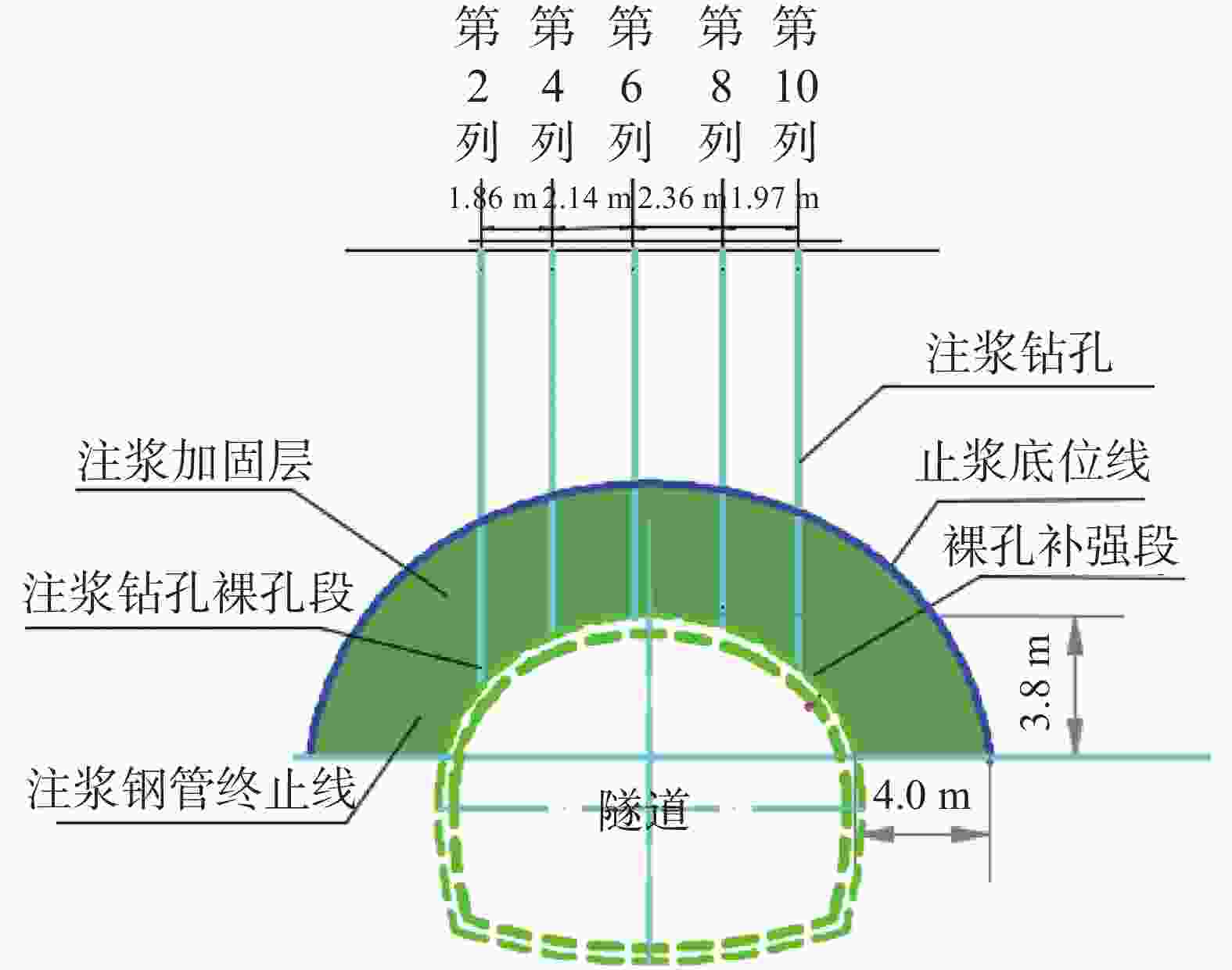
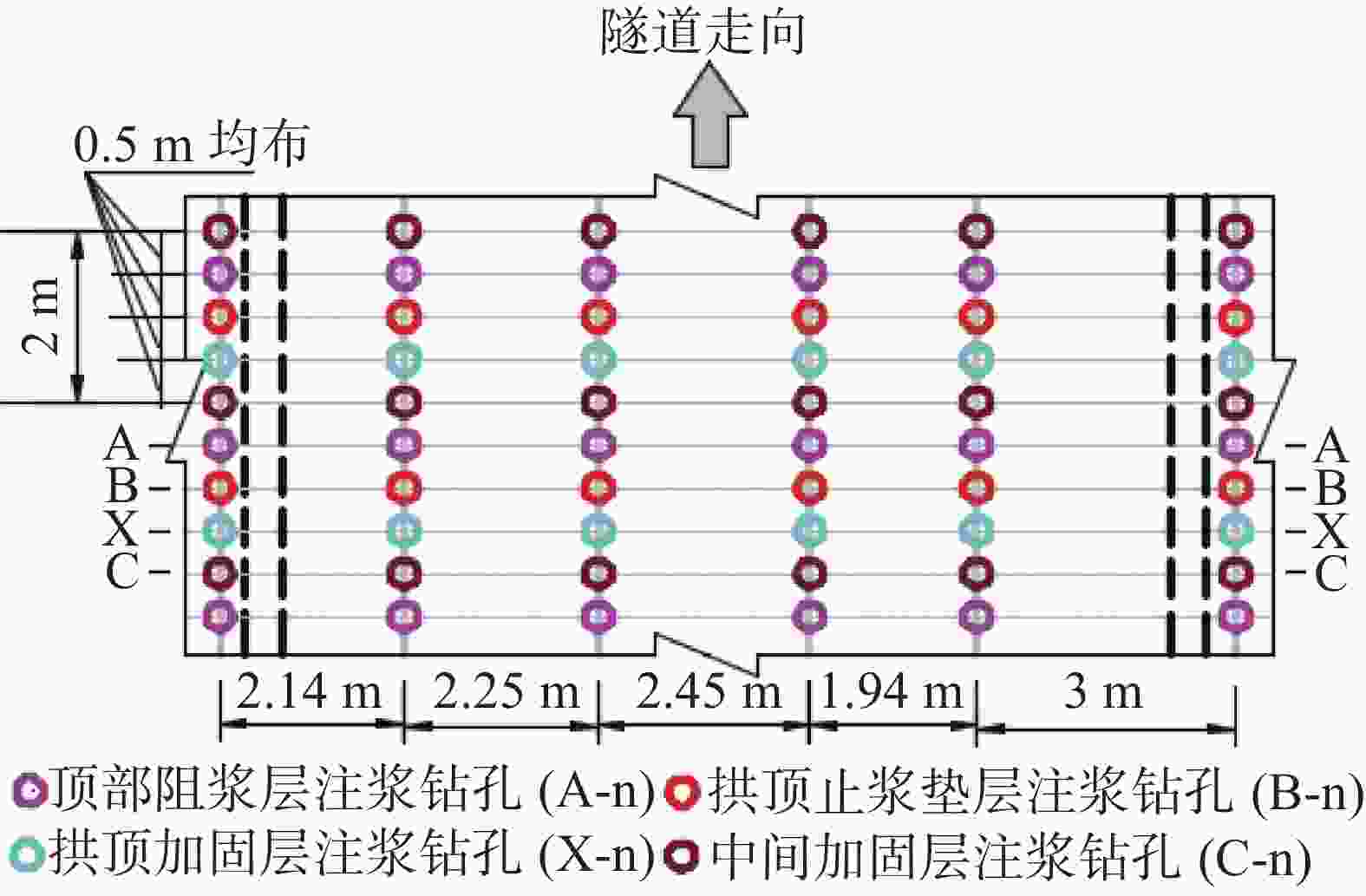
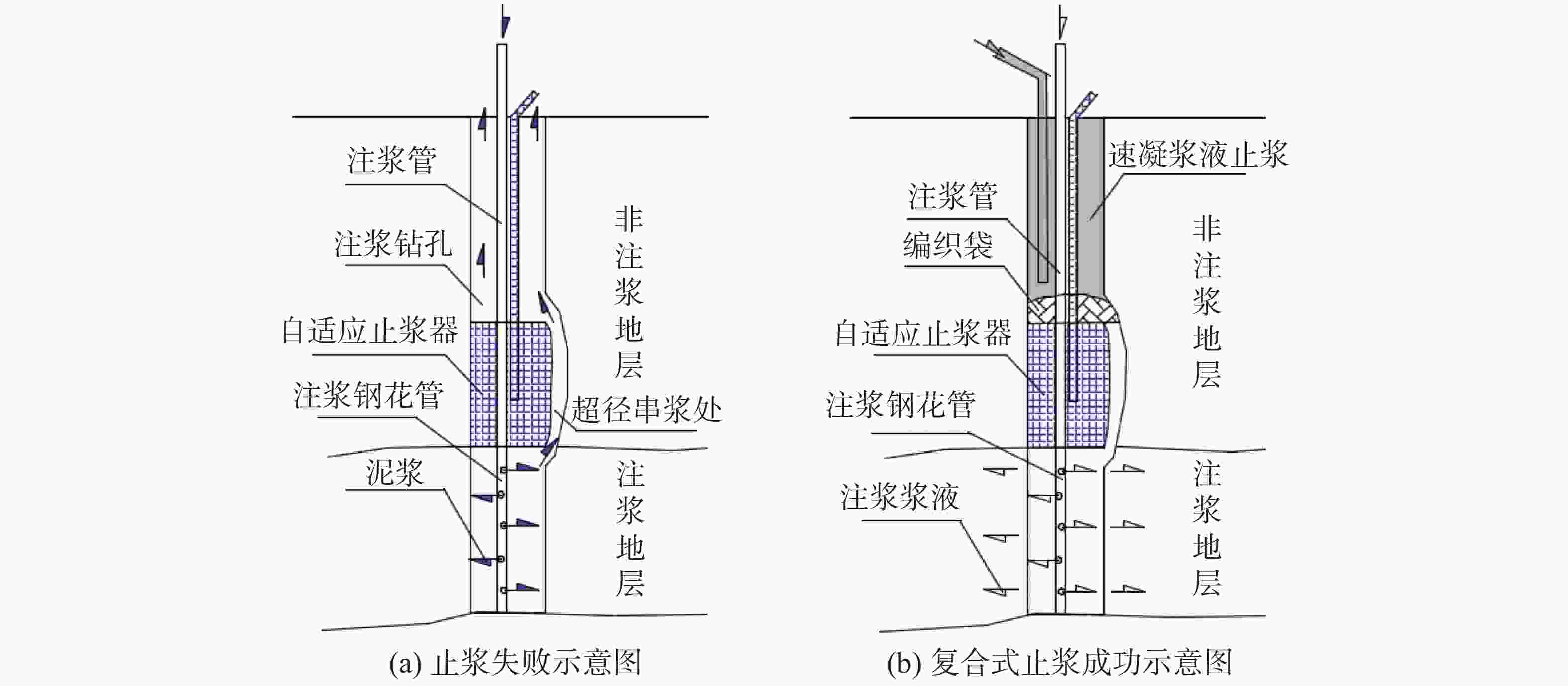
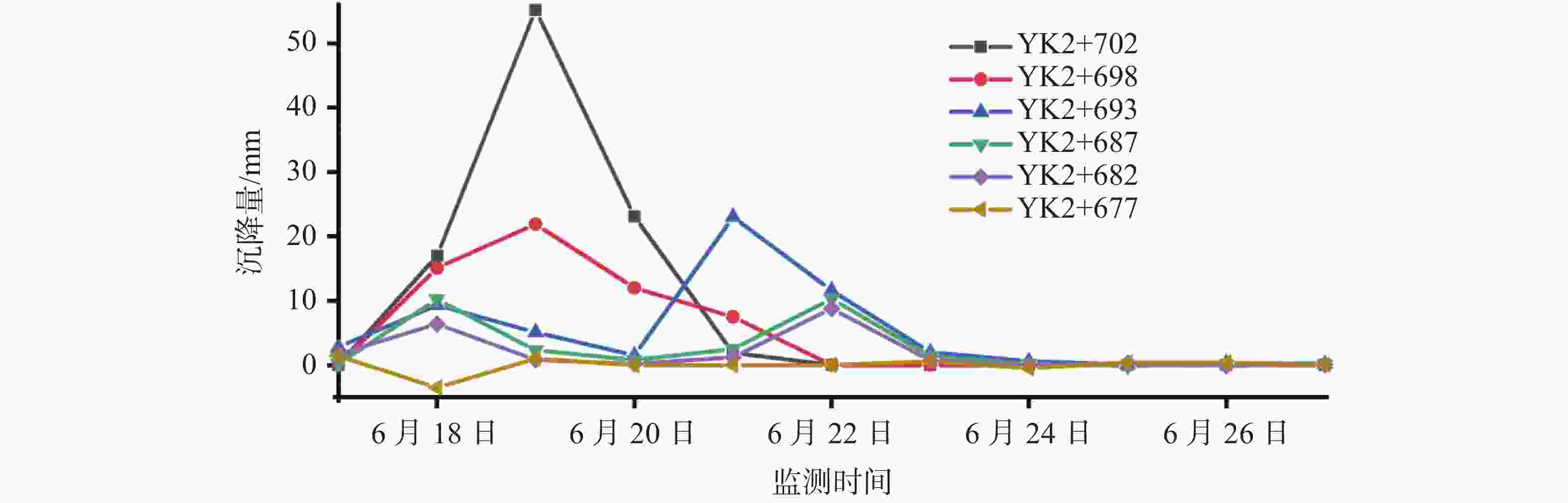
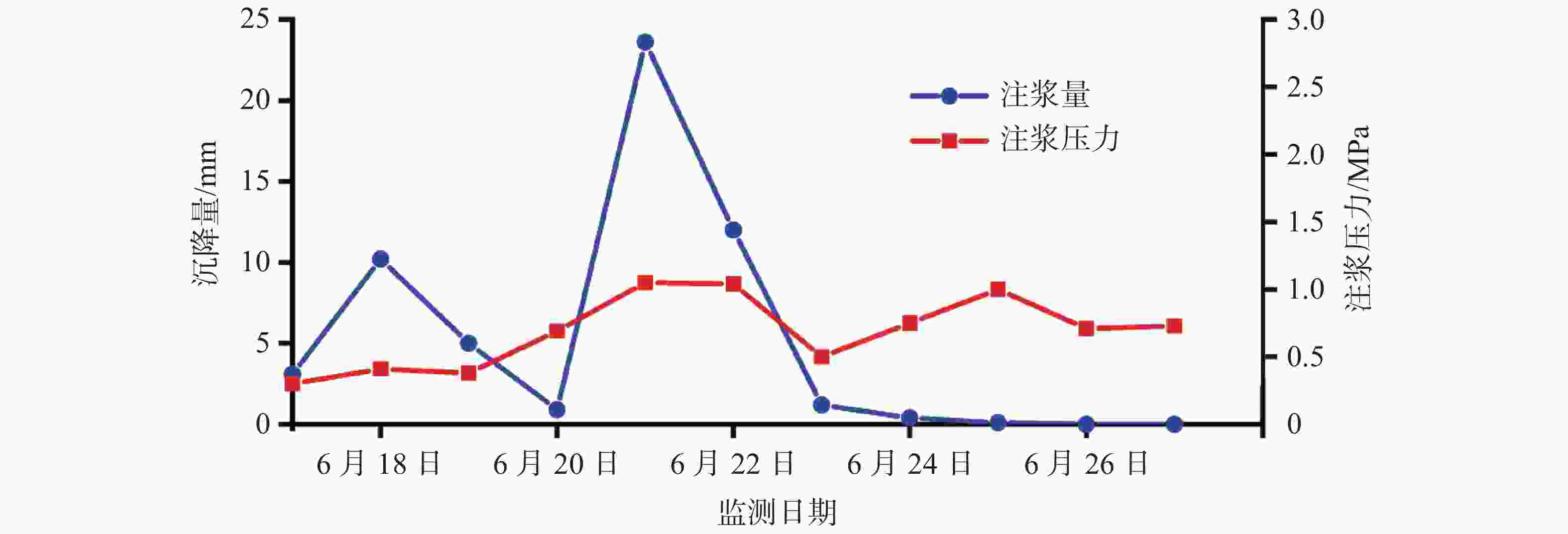
摘要: 为有效治理岩溶基底城市隧道拱顶地层沉陷地质灾害,在充分探明沉陷区水文地质、工程地质特征的基础上,提出了“三段四层控制技术”,将治理区划分为沉陷区重点加固段、影响区次重点加固段和超前加固段;再根据治理深度和治理顺序进一步把沉陷区重点加固段分为顶部阻浆层、拱顶止浆垫层、拱顶加固层和中间加固层,研究了每段、每层注浆加固机理、浆液类型选择和控制注浆参数。研究成果表明,采用孔内复合止浆技术满足不同深度地层分段注浆为主、垂直孔和定向斜孔相结合,充填注浆、劈裂-挤密注浆相结合,以速凝浆液为主、单液水泥浆为辅,严格控制安全注浆参数,是“三段四层控制技术”安全有效注浆的技术关键,该技术方案在岩溶基底城市隧道拱顶地层沉陷地质灾害治理方面,取得了较好的注浆加固效果,有良好的推广应用价值。Abstract:
In order to effectively control the geological disaster of tunnel vault subsidence in the karst basement, the "three-section and four-layer" control technology is proposed, based on the full analysis of engineering geology and hydrogeological characteristics of the subsidence stratum. In this technology, the treatment area is divided into the key reinforcement section, the sub-key reinforcement section of the affected area and the pre-excavated reinforcement section. According to the treatment depth and order, the key reinforcement section of the subsidence area is divided into the top slurry barrier layer, the vault cushion layer of slurry-stopping, the vault reinforcement layer and the intermediate reinforcement layer. In terms of grouting mechanism, filling grouting and splitting-compacting grouting are adopted in both the top slurry barrier layer and the intermediate reinforcement layer. The alternate mode with filling-splitting-compacting grouting is implemented in the intermediate reinforcement layer, and the filling grouting mode is adopted in the vault cushion layer of slurry-stopping. Splitting-compacting grouting is conducted in both the pre-excavated reinforcement section and the sub-key reinforcement section in the affected area. In order to reduce the leakage of grout in the top slurry barrier layer and vault cushion layer of slurry-stopping, C-GT quick setting mixed grout is selected, and the initial setting time of the grout is controlled at 30-50 seconds, while the final grouting pressure is no more than 0.5 MPa and 0.8 MPa. In order to realize the effective diffusion of slurry in the vault reinforcement layer and intermediate reinforcement layer, the initial setting time of C-GT mixed slurry is extended to 50-90 seconds, even up to 150 seconds, and the final grouting pressure is up to 0.8-1.2 MPa. To improve the slurry diffusion and overall reinforcement strength of the pre-excavated reinforcement layer and the sub-key reinforcement layer in the affected area, the alternate and continuous grouting mode of single and double cement slurry is implemented based on the high consolidation strength of single cement slurry and the quick setting characteristics of C-GT mixed slurry. The above-mentioned technology is the key to the success of grouting reinforcement. Besides, the combined grout-stopping method is used to effectively deal with the segmented grout-stopping at the place where the hole wall collapses and shrinks, and the diameter of borehole is greatly oversized. Hence, the isolated grouting at different depths of those four layers is realized. The directional inclined hole is used to effectively avoid the hidden underground pipeline, and the grouting pipe is used as the pipe roof to improve the shear resistance of stratum. Combined with grouting, this technology can effectively improve the overall strength and stability of the reinforcement stratum by tunnel vault grouting. Research results indicate that "the three-section and four-layer" treatment scheme is the basis to effectively control the subsidence of soil overlying the tunnel. The combined grout-stopping technology in the hole is the guarantee to meet the requirement of segmented grouting at different depths. The combination of vertical hole and directional inclined hole and of filling grouting and splitting-compacting grouting, taking quick setting slurry as the primary part supplemented with single cement slurry, and the strict control of safe grouting parameters are the technical keys of safe and effective grouting. The application of the above technology has achieved good grouting reinforcement effect and hence should be popularized. -
Key words:
- karst basement /
- tunnel /
- stratum subsidence /
- disaster control /
- segmented grouting
-
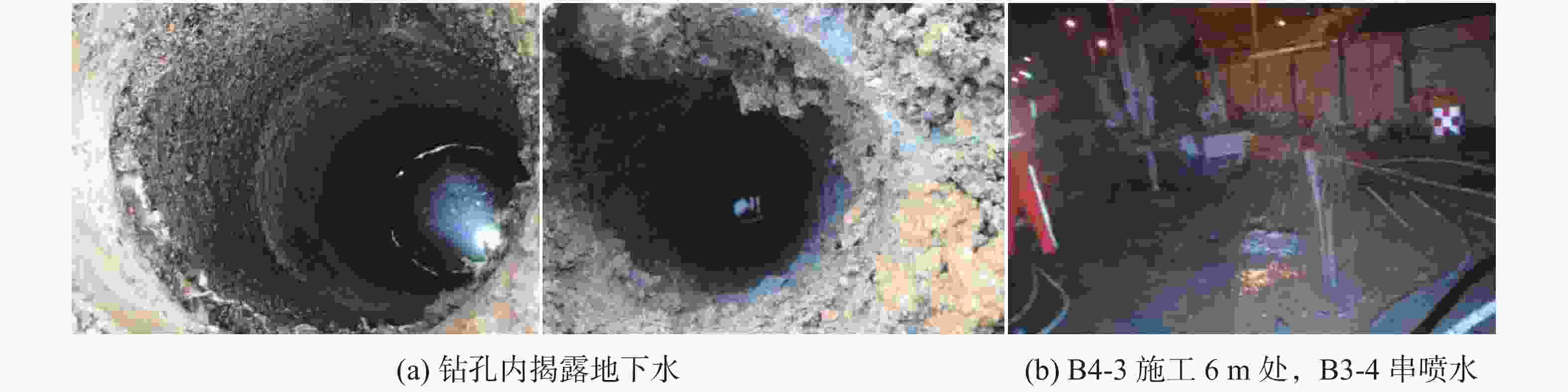
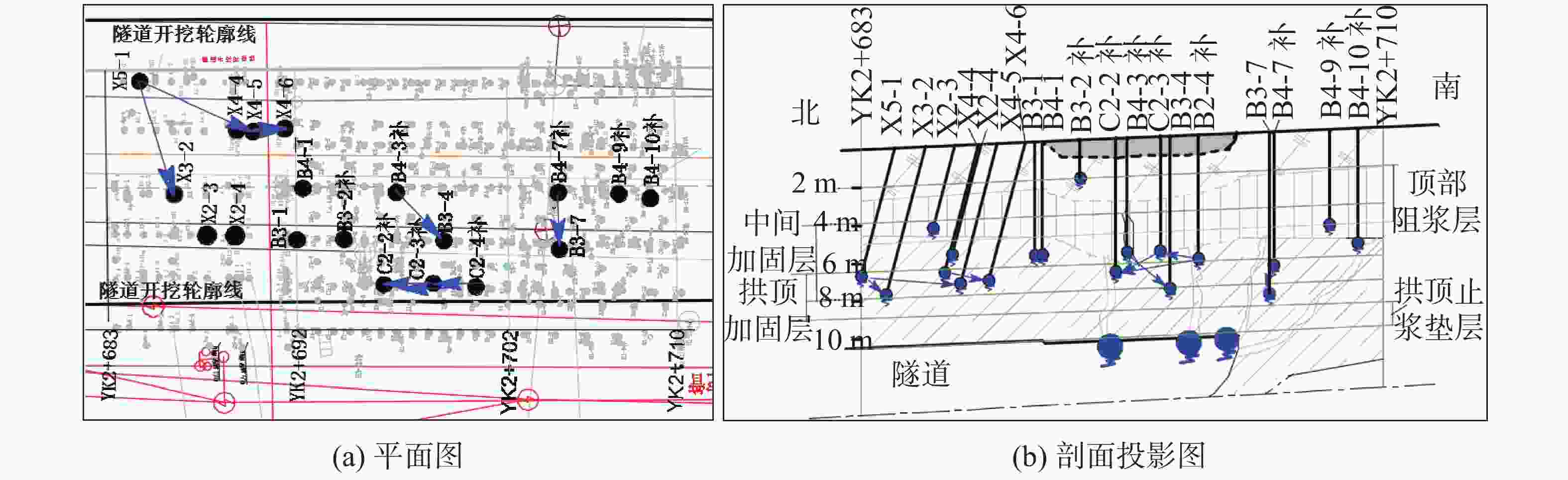
表 1 治理段部分钻孔地下水位及互相串通情况
Table 1. Groundwater levels and the interconnection of some boreholes in the treatment section
喷水孔号 喷水深度/m 串喷孔号 串喷深度/m 喷水孔号 喷水深度/m 串喷孔号 串喷深度/m B3-2补 2.0 X4-4 7.2 X4-6 7.5 B3-1 6.3 C2-3补 6.1 C2-2 7.0 B4-1 6.1 C2-4补 6.5 C2-2补
C2-3补7.0
6.2X5-1 7.2 X3-2
X4-58.0
7.5B4-7补 6.9 B3-7 8.5 X2-4 6.3 B4-10补 6.3 B4-9补 5.0 B4-3补 6.1 B3-4 8.0 X2-3 4.5 注:B3-2补是指原设计B3-2孔遇到障碍无法施工,移位重打的钻孔编号,以下同。 表 2 各加固层注浆机理、浆液类型和控制注浆参数表
Table 2. Grouting mechanism, slurry type and grouting control parameters of each reinforcement layer
序号 注浆加固
层位注浆
类型浆液
类型水泥浆平均
密度/g·cm−3Vc∶Vgt 混合浆液
初凝时间/s注浆速率
/L·min−1终压
(不大于)/MPa1 顶部阻浆层 充填注浆 C-Gt混合浆液 1.5 1∶1 50~90 40 0.3 2 劈裂—挤密注浆 C-Gt混合浆液 1.6 2∶1 30~50 20 0.8 3 拱顶止浆垫层 充填注浆 C-Gt混合浆液 1.6 1∶1~2∶1 30~50 20 0.5 4 拱顶加固层 充填注浆 C-Gt混合浆液 1.5 1∶1 50~90 40 0.5 5 劈裂—挤密注浆 C-Gt混合浆液 1.5 1∶1 30-50 20 0.8~1.0 6 中间加固层 充填—劈裂—挤密 单双液交替 1.5 1∶1 90~150 20~40 1.0~1.5 7 未开挖超前加固层 劈裂—挤密 单双液交替 1.5 1∶1 50~90 20~40 1.0~1.2 8 影响区加固层 劈裂—挤密 单双液交替 1.5 1∶1 50~90 20~40 1.0~1.2 注:配浆使用普通硅酸盐水泥,水泥标号P.O 42.5R;GT浆液密度控制在1.2-1.3 g·cm−3。单液浆密度平均1.5 g·cm−3。 表 3 沉陷区重点加固段各加固层钻孔数量、注浆量和注浆终压统计表
Table 3. Statistics of drilling quantity, grouting quantity and final grouting pressure of each reinforcement layer in the key reinforcement section of the subsidence area
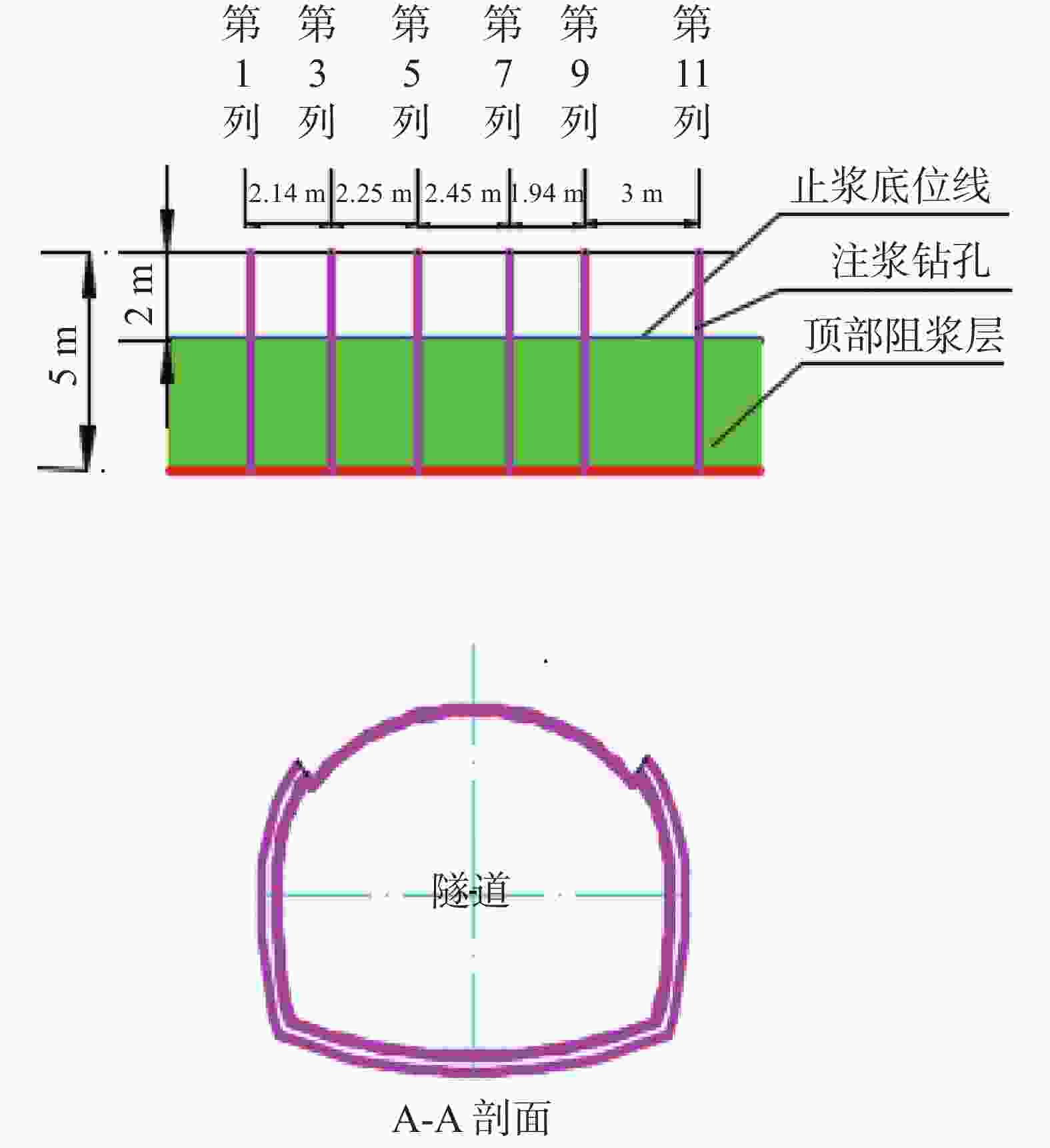
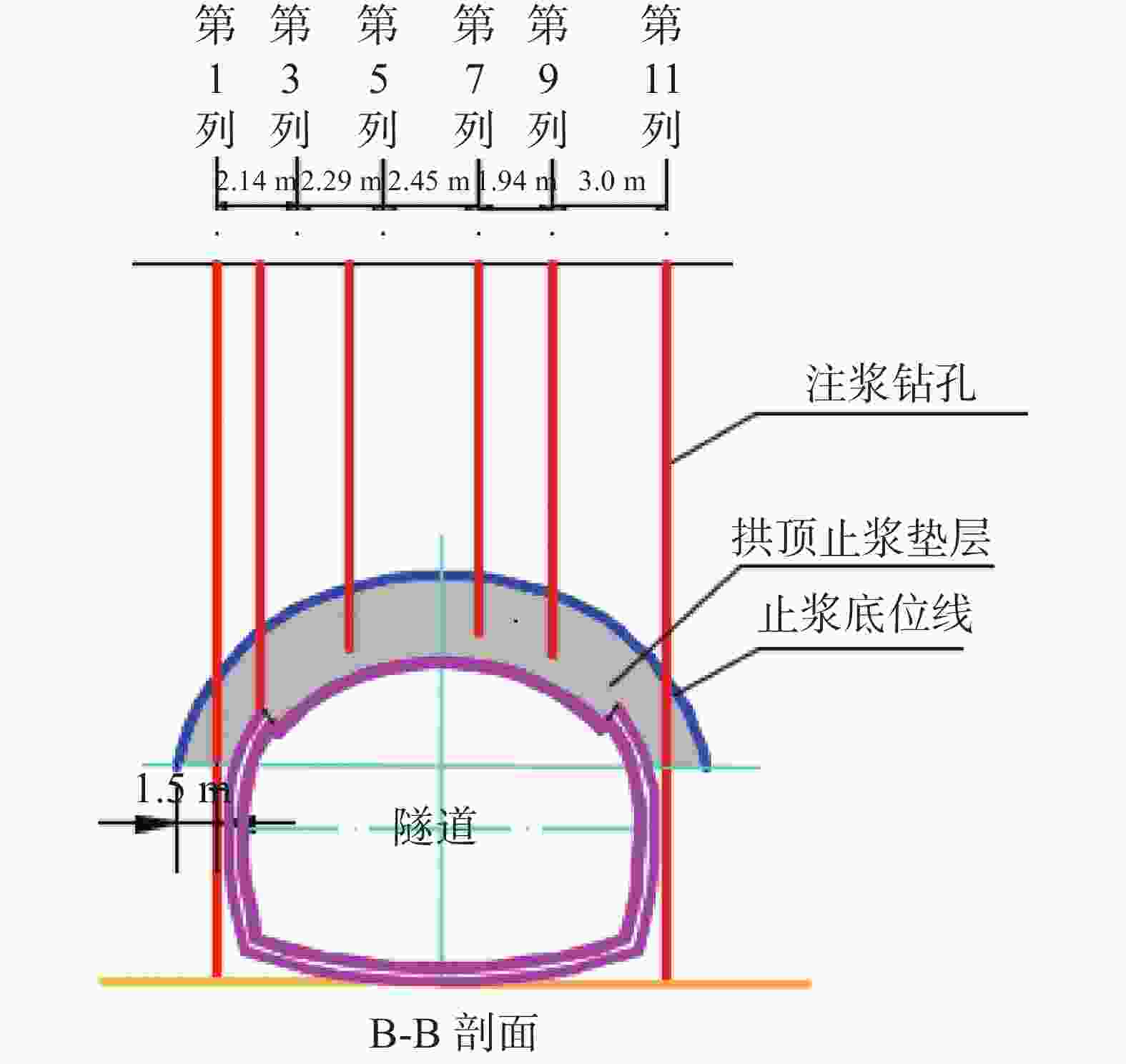
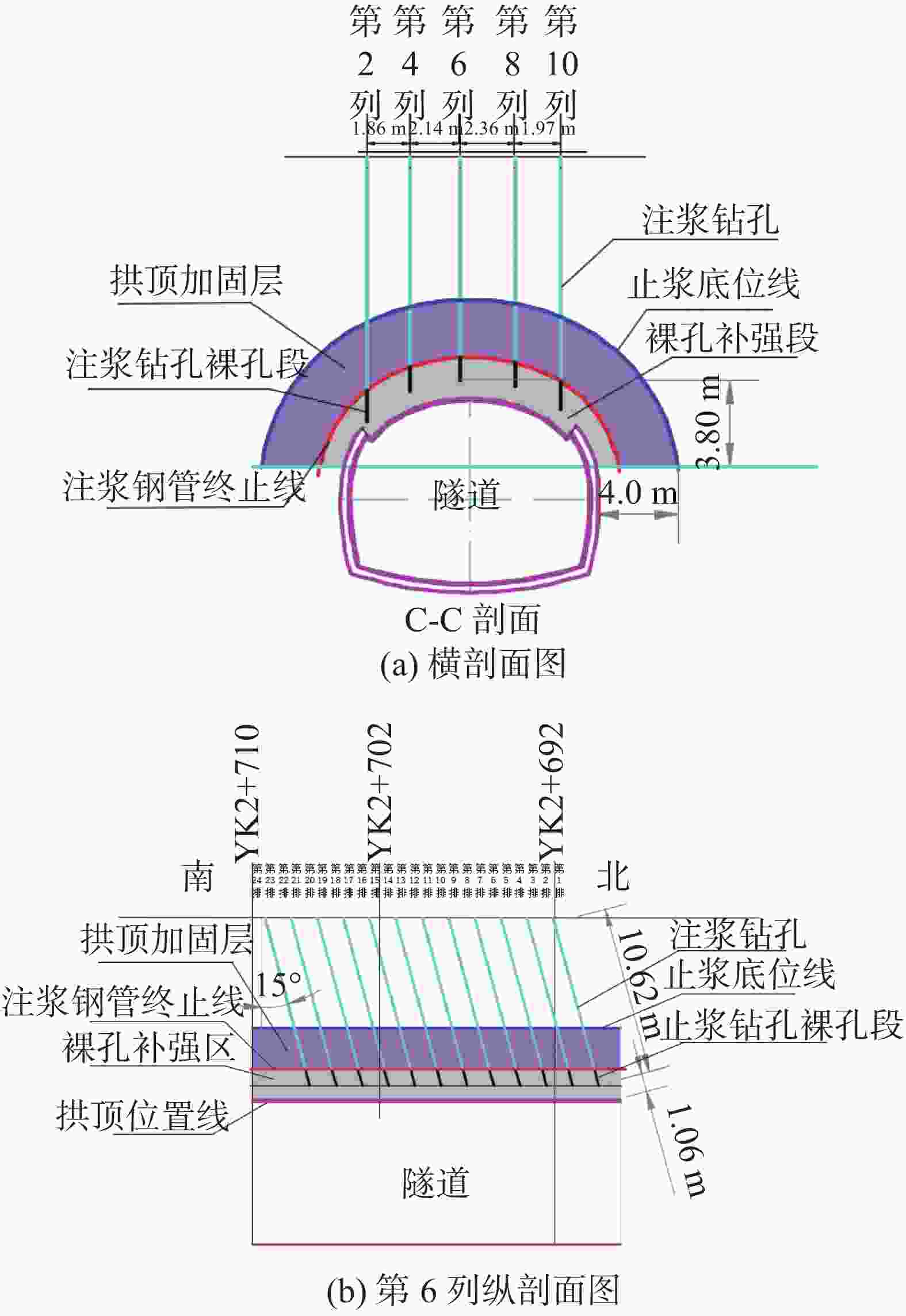
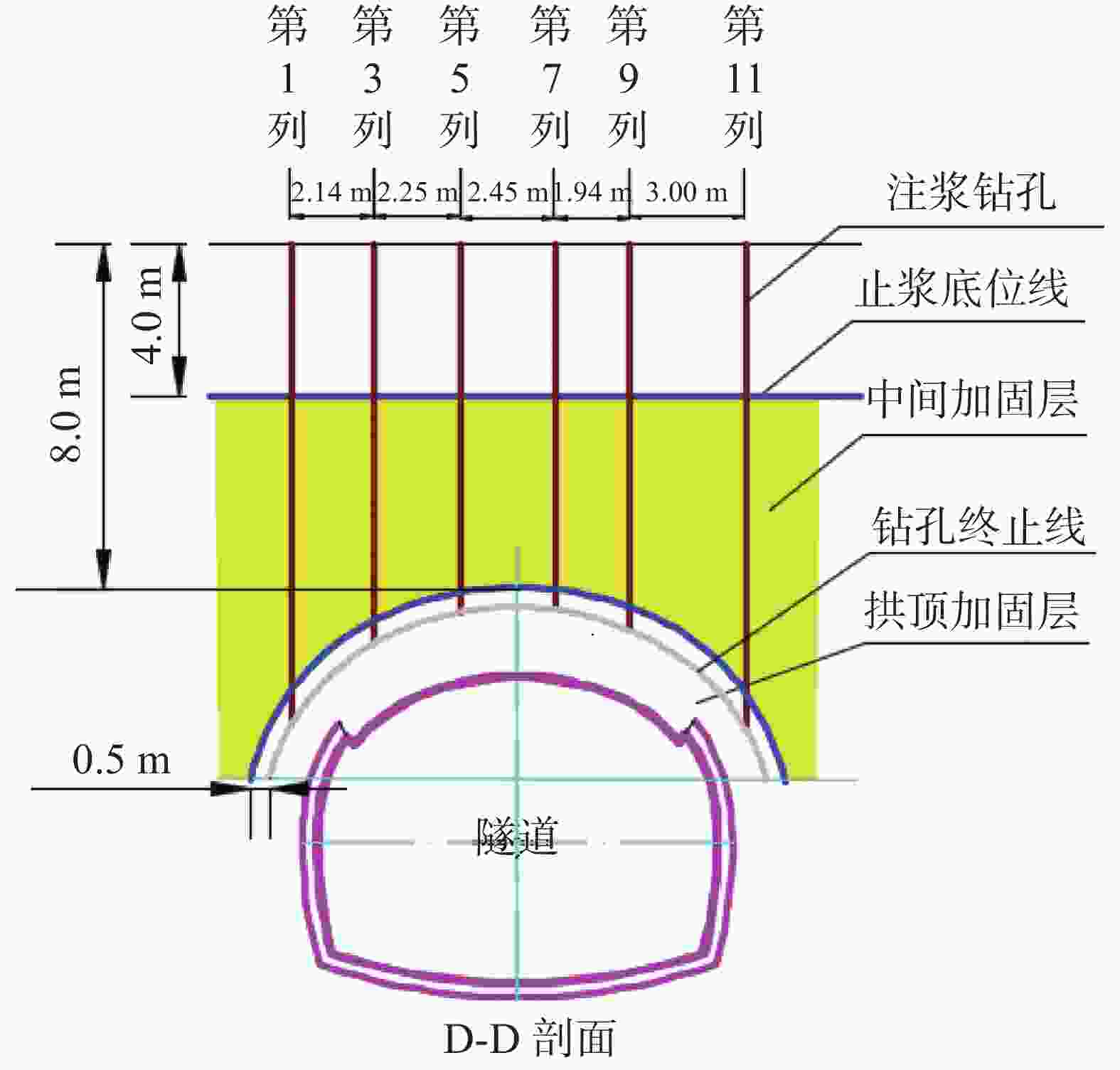
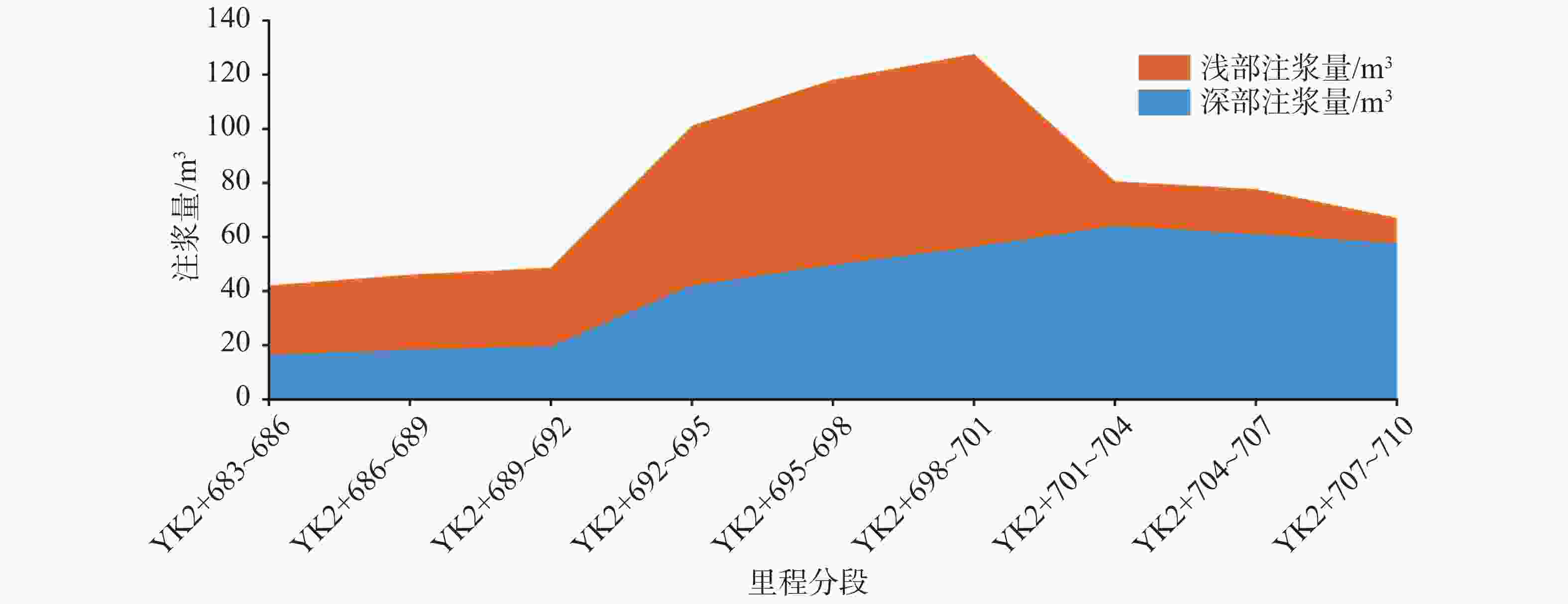
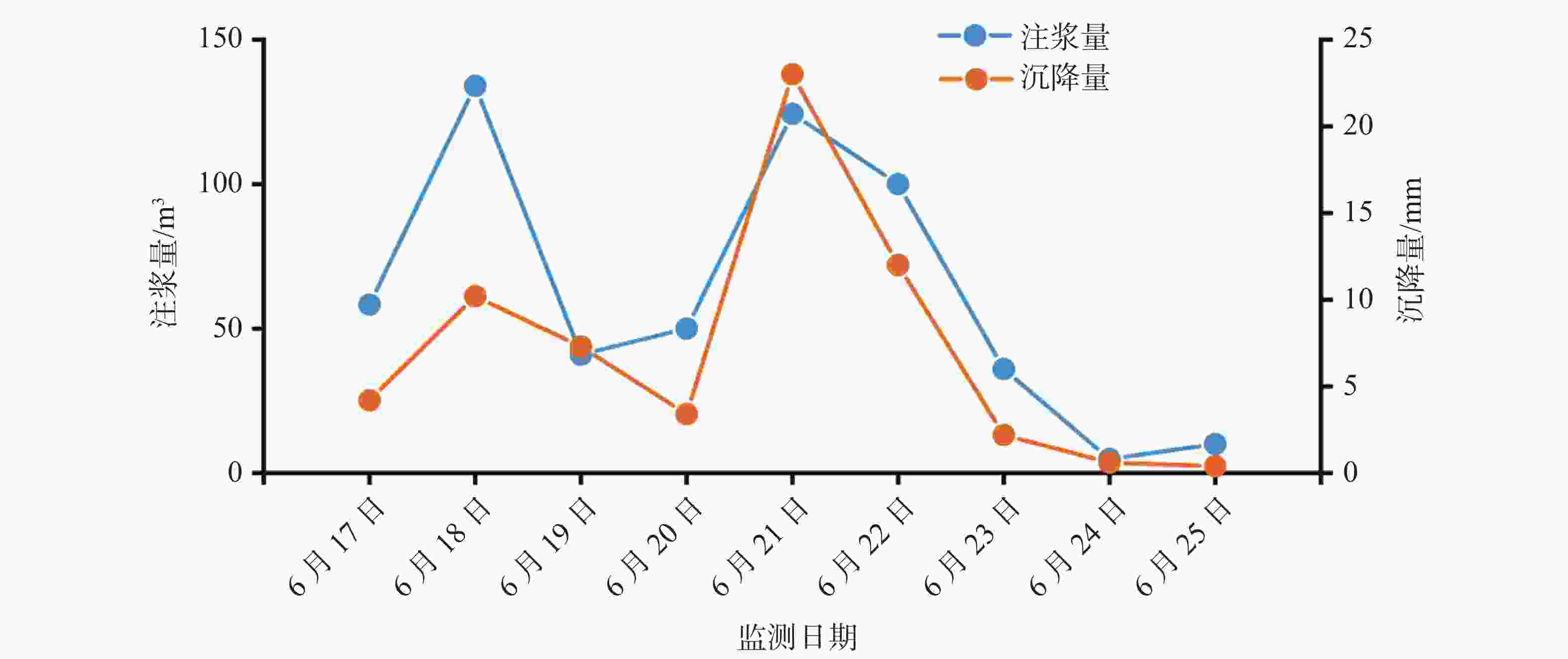
钻孔种类 设计钻孔数/个 优化后钻孔数/个 注浆量/m3 注浆终压范围/MPa 顶部阻浆层(A序)/垂直孔 30 26 91.59 0.3~0.8 拱顶止浆垫层(B序)/垂直孔 30 28 42.72 0.3~0.5 拱顶加固层(C序)/定向斜孔 35 31 96.60 0.5~1.0 中间加固层(D序)/垂直孔 30 24 108.63 1.0~1.5 补强孔/垂直孔 6 6 10.06 0.8~1.0 共计 131 115 349.54 -
[1] 蒋小珍, 雷明堂, 管振德. 单层土体结构岩溶土洞的形成机理[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(4):426-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2012.04.012JIANG Xiaozhen, LEI Mingtang, GUAN Zhende. Formation mechanism of karst soil cave with single-layer soil structure[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2012, 31(4):426-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2012.04.012 [2] 罗小杰, 罗程. 岩溶地面塌陷三机理理论及其应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(2):171-188.LUO Xiaojie, LUO Cheng. Three mechanism theory of karst ground collapse and its application[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(2):171-188. [3] 张健, 李术才, 张乾青, 李亮亮, 贺鹏. 覆盖型岩溶地基注浆处理与效果检测分析[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2017, 38(9):167-173. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2017.09.020ZHANG Jian, LI Shucai, ZHANG Qianqing, LI Liangliang, HE Pen. Analysis of covered karst foundation treatment and grouting effect[J]. Journal of Building Structure, 2017, 38(9):167-173. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2017.09.020 [4] 刘强, 张可能, 彭环云, 张云毅, 汪洋. 高速公路岩溶路基注浆效果综合评价[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2014(5): 591-595.LIU Qiang, ZHANG Keneng, PENG Huanyun, ZHANG Yunyi, WANG Yang. Comprehensive evaluation of grouting effect of expressway karst subgrade [J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2014 (5): 591-595 [5] 甘鹏路. 富水软弱地层浅埋暗挖隧道地层变形规律及预测研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016GAN Penglu. Study on formation deformation law and prediction of shallow buried tunnel in water rich soft stratum [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016 [6] 王鹏超. 贵阳浅埋暗挖地铁施工引起的地表变形规律及控制措施研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2021WANG Pengchao. Study on the deformation law and control measures of surface deformation caused by the construction of Guiyang shallow buried underground excavation subway [D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2021 [7] 牟翔. 地表注浆下浅埋暗挖地铁车站超前小导管支护参数研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2020MOU Xiang. Study on advance small conduit support parameters of shallow buried underground excavation subway station under surface grouting [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020 [8] 郑钦文. 浅埋暗挖黄土隧道下穿火车站场区变形控制技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017ZHENG Qinwen. Research on deformation control technology of shallow buried and concealed excavated loess tunnel under railway station [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017. [9] 王国强. 浅埋暗挖地铁隧道特殊黄土地层注浆预加固技术应用研究[J]. 四川建筑科学研究, 2015, 41(5):31-34,52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1933.2015.06.007WANG Guoqiang. Study on application of grouting pre-reinforcement technology in special loess stratum of shallow buried and concealed metro tunnel[J]. Sichuan Institute of Architectural Sciences, 2015, 41(5):31-34,52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1933.2015.06.007 [10] 赵朋. 粉细砂地层浅埋暗挖车站施工关键技术研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2016ZHAO Peng. Research on key technology of shallow buried and concealed excavation station construction in silty fine sand stratum [D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Railway University, 2016 [11] 宗振宇. 浅埋暗挖软弱富水渗流地层变形特征及控制研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018ZONG Zhenyu. Study on deformation characteristics and control of weak water-rich seepage stratum in shallow buried and concealed excavation [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018 [12] 于兆成. 砂土地层大断面浅埋隧道地表沉降规律及控制研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2018YU Zhaocheng. Study on surface settlement law and control of large section shallow buried tunnel in sandy soil [D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2018 [13] 王师. 地铁车站暗挖通道施工监测及数值模拟[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2019WANG Shi. Construction monitoring and numerical simulation of underground tunnel in subway station [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Architecture University, 2019 [14] 彭悦. 浅埋扩挖隧道大变形处治技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2019PENG Yue. Research on large deformation treatment technology of shallow buried expanded tunnel [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2019 [15] 刘鹏. 浅埋暗挖隧道衬砌外水压力分布及堵水限排技术研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2016LIU Peng. Study on external water pressure distribution and water plugging and drainage restriction technology of shallow buried and concealed tunnel lining [D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of technology, 2016 [16] 程飞. 淤泥质隧道暗挖施工加固方案优化分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018CHENG Fei. Optimization analysis of reinforcement scheme for mucky tunnel excavation [D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2018 [17] 张连震. 地铁穿越砂层注浆扩散与加固机理及工程应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017ZHANG Lianzhen. Mechanism and engineering application of grouting diffusion and reinforcement of subway crossing sand layer [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017 [18] 孙锋, 张顶立, 王臣, 房倩, 李兵. 劈裂注浆抬升既有管道效果分析及工程应用[J]. 岩土力学, 31(3): 932-938SUN Feng, ZHANG Dingli, WANG Chen, FANG Qian, LI Bing. Effect analysis and engineering application of splitting grouting to lift existing pipeline [J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2010,31 (3): 932-938 [19] 孙锋, 张顶立, 陈铁林, 张晓平. 土体劈裂注浆过程的细观模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 32(3):474-480.SUN Feng, ZHANG Dingli, CHEN Tielin, ZHANG Xiaoping. Meso-simulation of soil splitting grouting process[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 32(3):474-480. [20] 陈立生, 沈成明, 彭惠, 廖少明, 孙连元. 一种复杂环境条件下隧道内微扰动注浆控制方法[P]. CN101255798A, 2008年CHEN Lisheng, SHEN Chengming, PENG Hui, LIAO Shaoming, SUN Lianyuan. A micro disturbance grouting control method in tunnel under complex environmental conditions [P]. CN101255798A, 2008 [21] 葛以衡, 赵国强, 夏晨欢, 廖少明. 隧道内微扰动注浆工艺[P]. CN 101255799A , 2008GE Yiheng, ZHAO Guoqiang, XIA Chenhuan, LIAO Shaoming. Micro-disturbance grouting technology in tunnel [P]. CN101255799A, 2008. [22] 王松根, 宋修广, 李英勇, 张思峰, 张宏博, 管延华. 分层多次调压调浆注浆方法[P]. CN 101230570A, 2008WANG Songgen, SONG Xiuguang, LI Yingyong, ZHANG Sifeng, ZHANG Hongbo, GUAN Yanhua. Layered multiple pressure and slurry regulating grouting method [P]. CN101230570A, 2008 [23] 刘人太, 张庆松, 李术才, 李海燕, 原小帅, 张霄, 韩伟伟, 张伟杰, 王凤刚. 一种膏状速凝注浆材料及其制备方法[P]. CN102001847A, 2010LIU Rentai, ZHANG Qingsong, LI Shucai, LI Haiyan, YUAN Xiaoshuai, ZHANG Xiao, HAN Weiwie, ZHANG Weijie, WANG Fenggang. The invention relates to a paste quick setting grouting material and a preparation method [P]. CN102001847A, 2010. -





 下载:
下载: