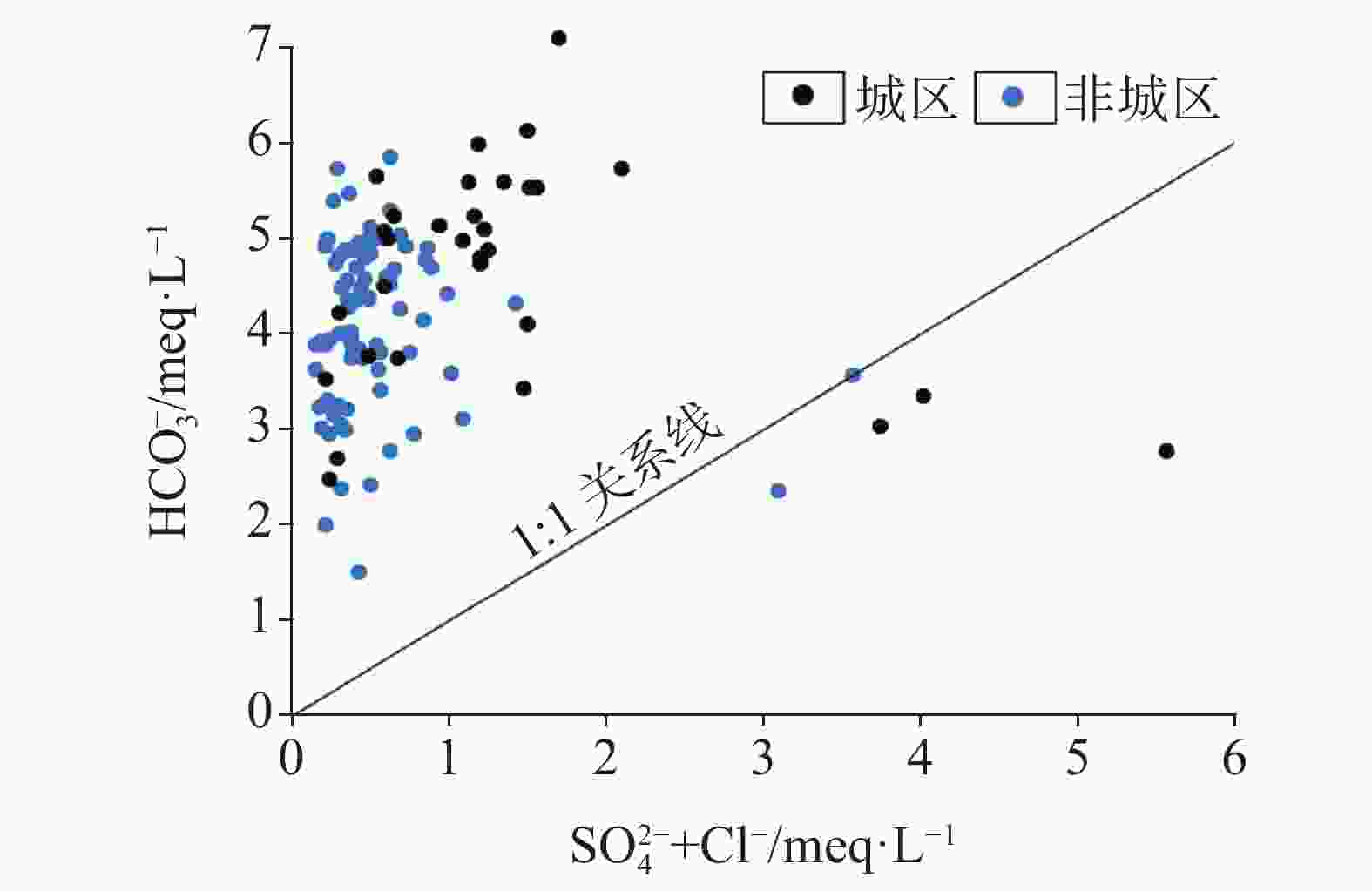
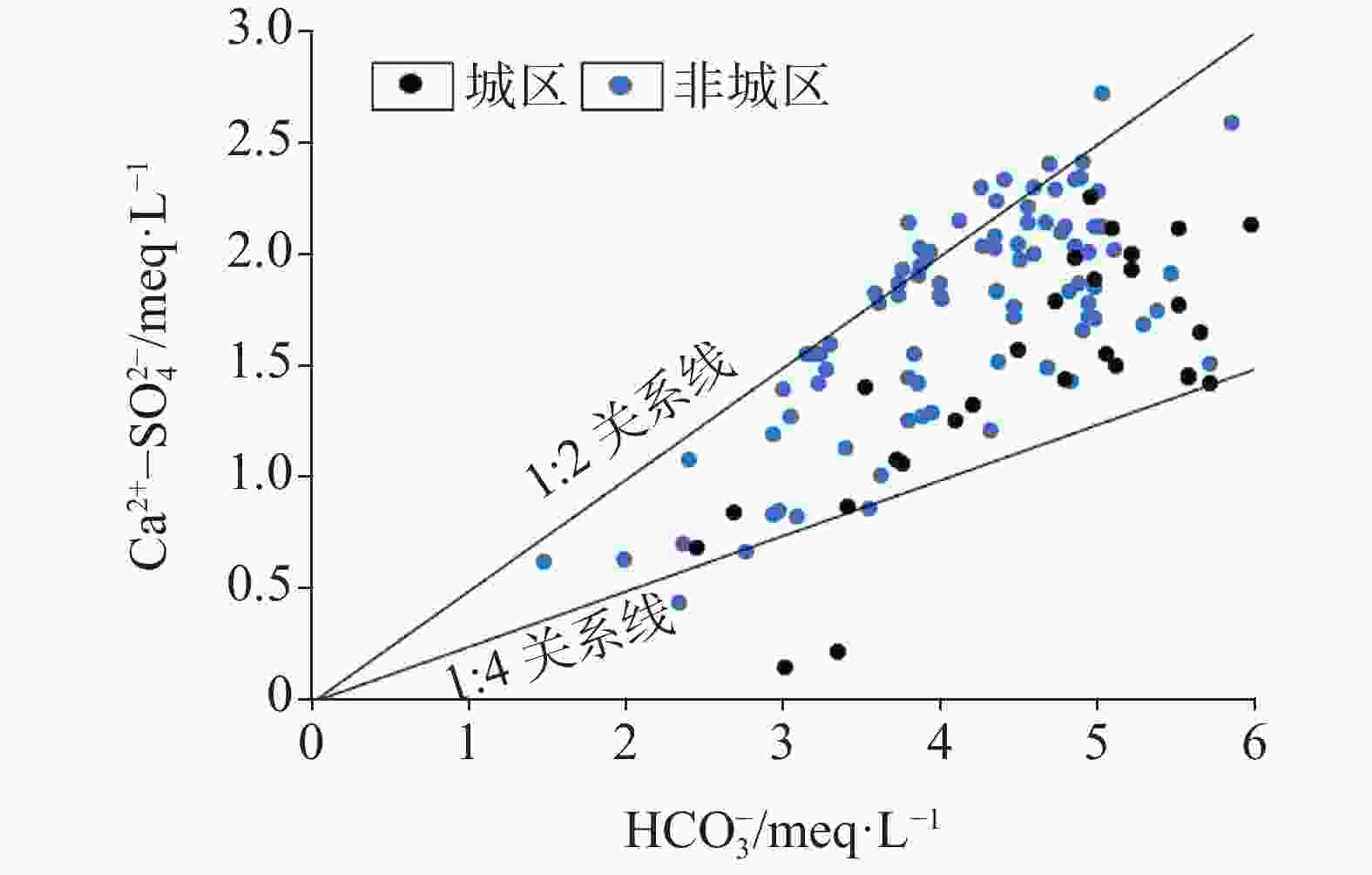
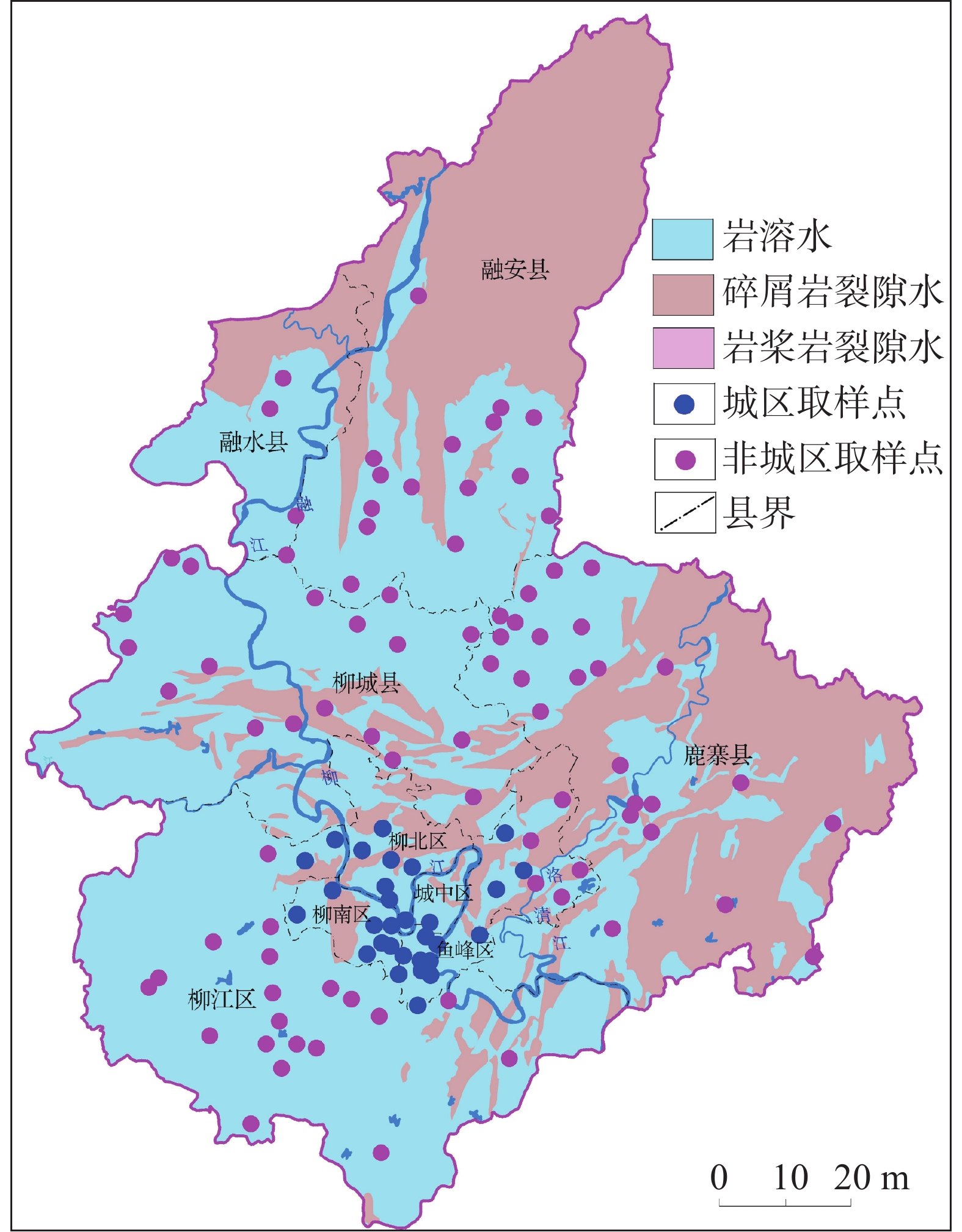
Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of karst groundwater in typical industrial cities
-
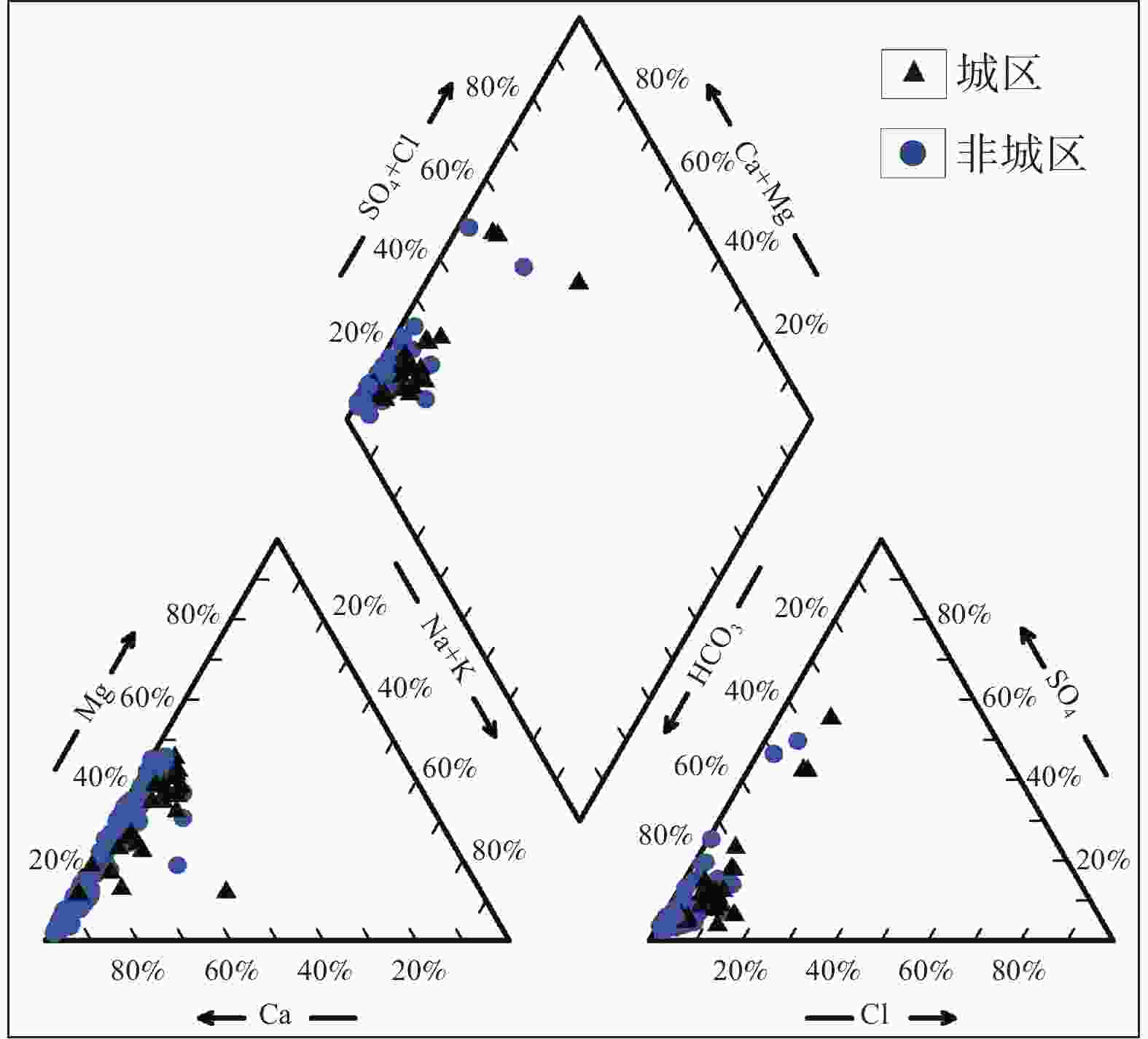
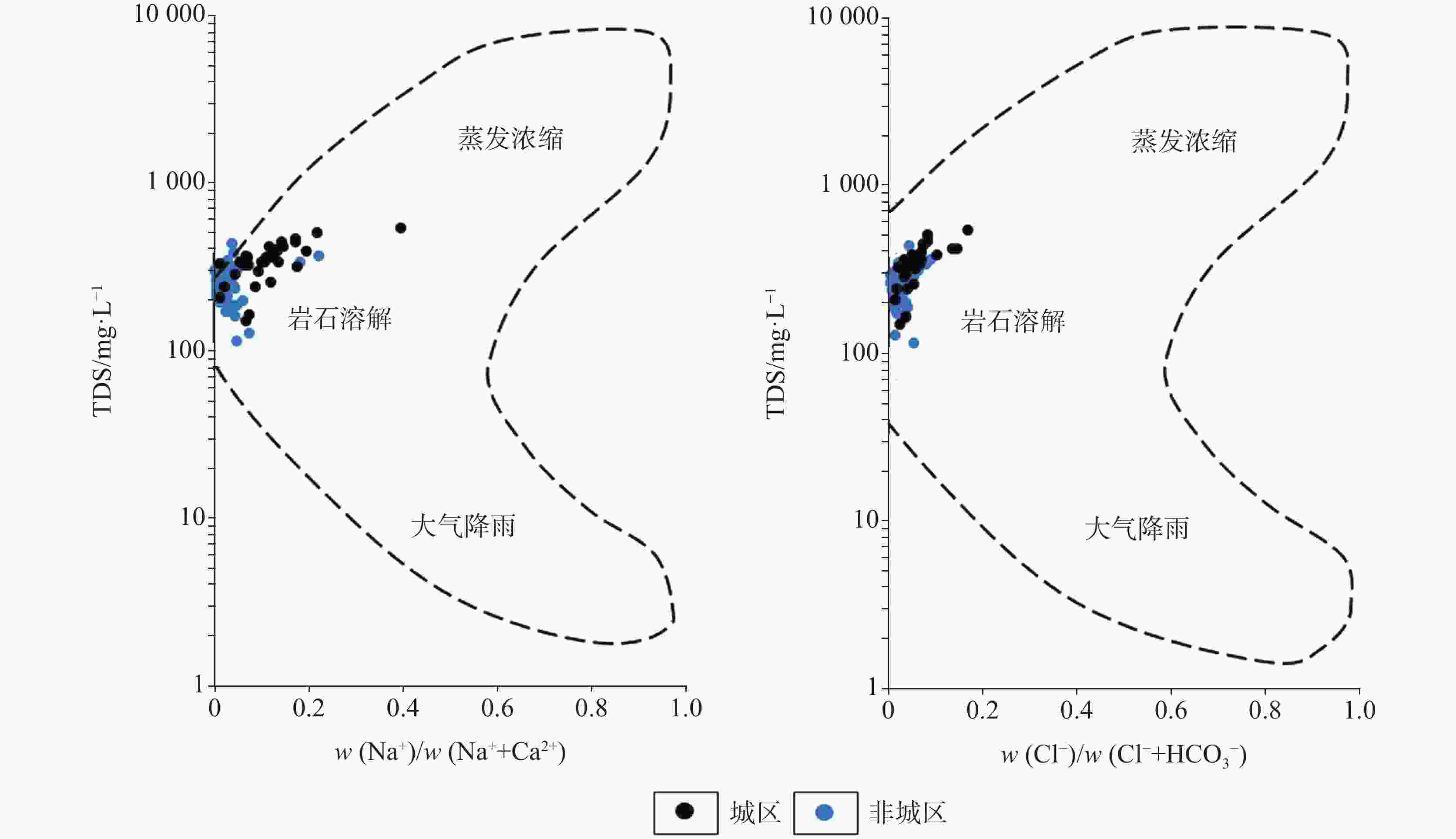
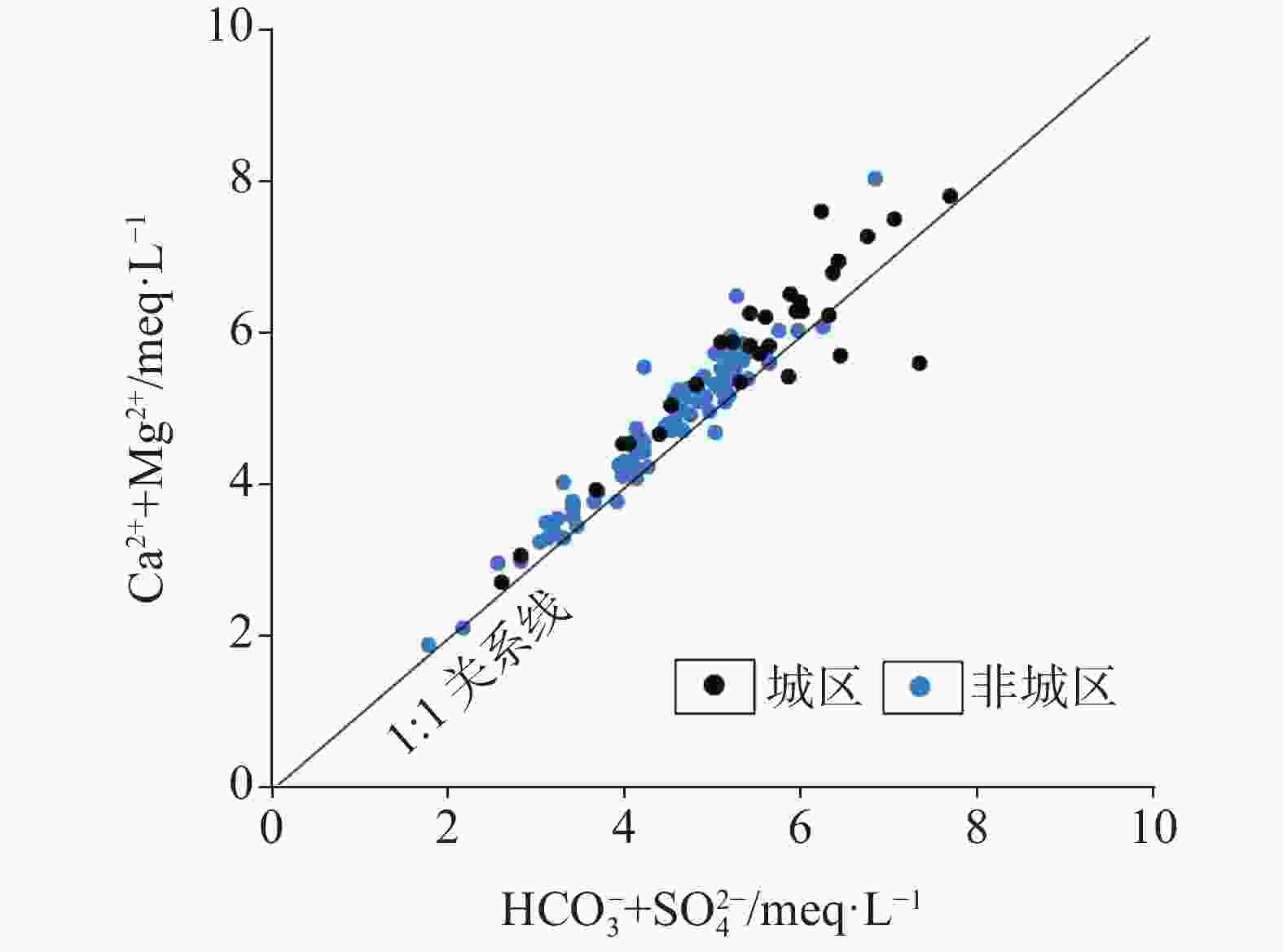
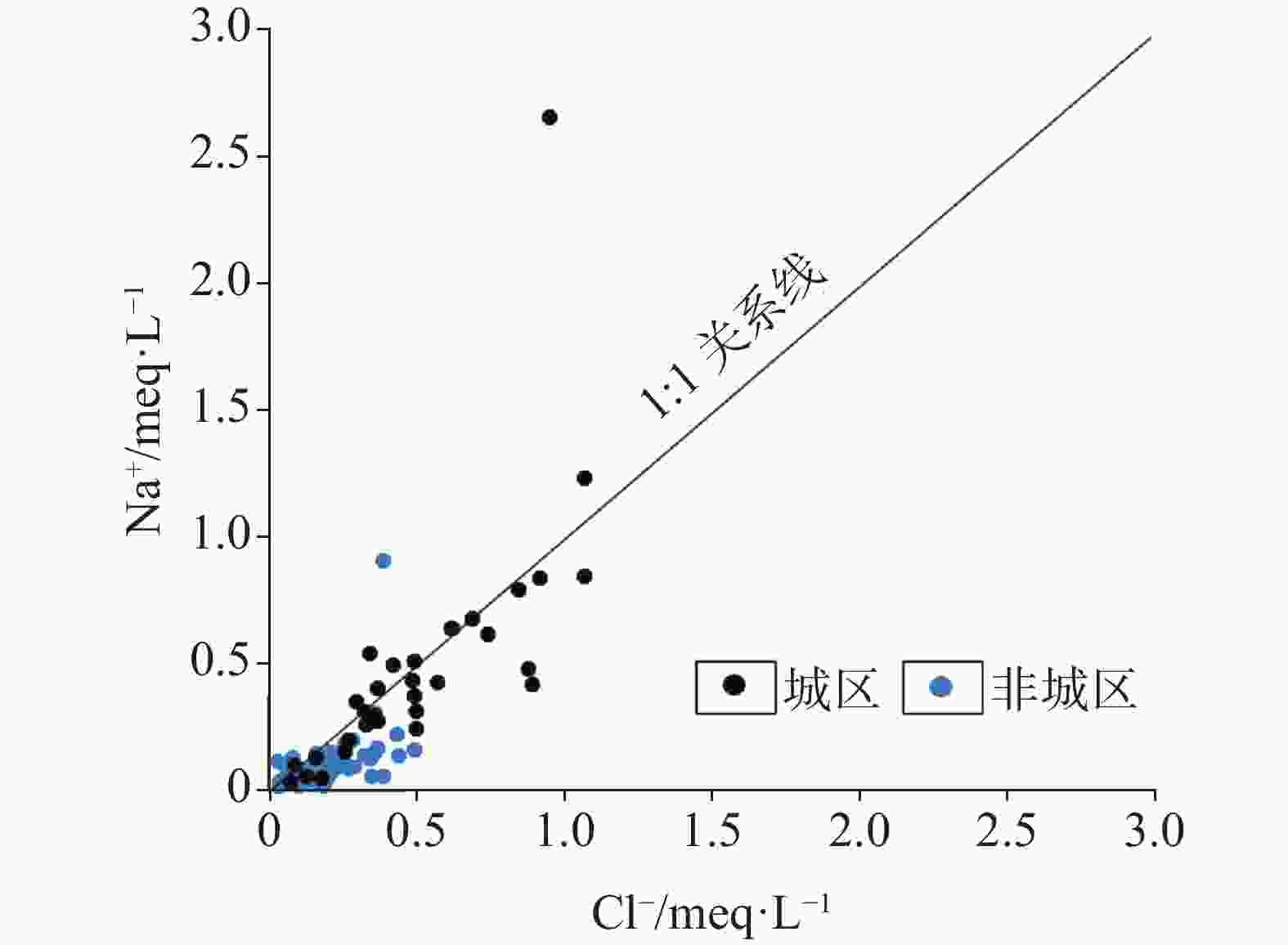
摘要: 文章以广西柳州市岩溶地下水为研究对象,在岩溶水文地质调查和样品采集测试的基础上,采用数理统计法、水化学方法(Piper图、Gibbs图、离子比值系数,矿物饱和指数计算)、因子分析法和模糊综合评价法,分析工业型城市岩溶地下水水化学特征及形成机制,开展岩溶地下水质量评价。结果表明,研究区岩溶地下水为中-弱碱性水,Ca2+、Mg2+、HCO3−、SO42−是主要的阴阳离子,水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Ca·Mg型为主,且城区的SO42−型水的比例远高于非城区。区内岩溶地下水水化学组分及演化主要受水-岩作用、工业污染、城镇生活污染和农业活动等主控因素的影响,贡献率分别为31.52%、25.15%、18.12%和10.74%。其中,城区的水化学组分受人类活动的影响程度大于非城区的。矿物饱和指数表明,区内方解石和绝大多数白云石为饱和状态,而石膏和盐岩均为溶解状态。不同功能区的水化学敏感指标有差异,工业区以重金属为主,农业区以三氮为主,生活区以K+、Na+、Cl−、SO42−为主。研究区整体水质较好,Ⅰ-Ⅲ类水的比例高达约87.39%;但不同区域的水质差异较大,其中城区的水质较差,超标因子主要为Al、Mn、Pb、Fe、Hg;非城区的水质较好,超标因子主要为三氮。研究成果可以为工业型城市岩溶地下水污染防治提供科学依据。Abstract:
As economic pillars of the karst area in south China, industrial cities located in this area play an important role in the promotion of national strategy and economic development. Karst groundwater, the main water source of industrial cities in the karst area, is vital for urban development. Therefore, studies on hydrochemical characteristics of karst groundwater and solutions to water pollution problems have always been working focuses of local governments, but little attention to the chemical problems of karst groundwater in industrial cities has been paid in previous studies. This study takes karst groundwater in Liuzhou City, Guangxi as the research object. Based on karst hydrogeological survey, a total of 119 groups of karst underground water samples were collected, including 31 groups of urban underground water samples and 88 groups of non-urban underground water samples. Using mathematical statistics, hydrochemistry method (Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram, ion ratio coefficient, mineral saturation index calculation), factor analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method, we analyzed the hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of karst groundwater in industrial cities, and carried out the quality evaluation of karst groundwater. Results show that karst groundwater in the study area is generally medium-weak alkaline water with a small amount of acidic water. The main cations are Ca2+ and Mg2+, and the main anions are HCO3- and SO42-. In terms of concentration and variation degree, karst groundwater in urban areas is larger than that in non-urban areas. In terms of water chemistry types, there are also obvious differences between the two kinds of areas, that is, water chemistry types in urban areas are mainly HCO3-Ca+Mg type, while those in non-urban areas are mainly HCO3-Ca type. The proportion of SO42- type water in urban areas is much higher than that in non-urban areas, reflecting that urban areas suffer serious pollution from more pollution sources than non-urban areas. The chemical composition of groundwater in the study area is mainly controlled by rock dissolution, industrial pollution, urban pollution and agricultural activities, with contribution rates of 31.52%, 25.15%, 18.12% and 10.74%, respectively. Dissolution factors of rock are mainly carbonate minerals such as calcite and dolomite, primarily from dolomite dissolution in urban areas and calcite dissolution in non-urban areas. The dissolution factors are mainly distributed in Liujiang district and northwestern Luzhai county of Liuzhou City. Industrial pollution factors are mainly distributed in Liunan district, Liubei district and other areas of Liuzhou City. The industrial pollution in these areas is related to the discharge of wastewater, waste gas and waste residue by a number of heavy industry enterprises, leading to the excessive concentration of heavy metals. Urban living pollution factors are mainly distributed in Chengzhong district, Yufeng district, Luzhai county, Liucheng county and other areas, and are related to domestic sewage discharge and domestic garbage leaching. The factors of agricultural activities are mainly distributed in Liujiang river, Luoqing river, Longjiang river and other river valleys, and are related to the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in agricultural activities and the direct discharge of animal feces from breeding. Hydrochemical sensitivity indexes of different functional areas are diverse, among which the industrial area is dominated by heavy metals, agricultural area by trinitrogen, and living area by K+, Na+, Cl- and SO42-. Mineral saturation indexes show that calcite and most dolomite are saturated, while gypsum and salt rocks are dissolved. The karst groundwater quality is good as a whole, mainly I-III water, accounting for 86.29%, but the water quality varies greatly in different areas. The water quality in the urban area is poor, with the proportion of IV-V water as high as 35.48%. The places with water exceeding permitted levels are mainly distributed in Liunan district and Liubei district of Liuzhou City, and factors exceeding levels are Al, Mn, Pb, Fe and Hg. Reasons for exceeding levels are related to the discharge of "three types of waste" and geochemical background of heavy industry enterprises. The water quality in non-urban areas is better, and the proportion of IV-V water is only 6.45%. The places with water quality exceeding permitted are only distributed in Liujiang river valley and Luoqing river valley, and the factor exceeding levels is trinitrogen, which is caused by the excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. -
表 1 研究区地下水水化学参数统计
Table 1. Test data of groundwater hydrochemical indexes in the study area
项目 总体 城区 非城区 最小值 最大值 平均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 平均值 Cv 最小值 最大值 平均值 Cv 总硬度 94.43 400.16 251.09 4.47 135.17 389.10 287.93 4.84 94.43 400.16 238.12 4.85 TDS 116.38 542.00 285.35 3.80 150.69 542.00 348.67 3.85 116.38 440.94 263.04 4.89 pH 6.30 8.56 7.41 21.15 6.87 8.56 7.48 23.00 6.30 8.17 7.38 20.69 Ca2+ 28.87 114.08 75.95 4.03 30.57 103.32 74.80 3.98 28.87 114.08 76.36 4.02 Mg2+ 0.85 39.88 14.91 1.45 10.01 39.88 24.55 2.98 0.85 36.10 11.52 1.33 K+ 0.03 7.61 1.13 1.03 0.35 4.18 1.73 1.61 0.03 7.61 0.93 0.89 Na+ 0.34 61.09 4.51 0.62 0.75 61.09 11.26 1.01 0.34 20.79 2.13 0.79 Cl− 1.14 38.15 9.18 1.11 2.62 38.15 18.07 1.74 1.14 22.32 6.05 1.42 SO42− 4.38 221.22 23.44 0.75 6.50 221.22 40.17 0.86 4.38 159.10 17.55 0.83 HCO3− 91.24 432.58 259.87 4.44 150.18 432.58 283.91 4.13 91.24 356.67 251.41 4.81 I− 0.00 0.56 0.02 0.29 0.00 0.56 0.07 0.51 0.00 0.02 0.00 1.44 F− 0.00 0.29 0.08 1.55 0.02 0.29 0.06 1.18 0.00 0.23 0.08 1.74 三氮 0.00 73.17 5.62 0.57 0.00 73.17 7.86 0.75 0.00 64.16 4.93 0.77 重金属 0.00 450.00×10−3 7.79×10−3 0.34 0.00 250.00×10−3 11.16×10−3 0.48 0.00 450.00×10−3 6.65×10−3 0.34 表 2 研究区矿物饱和指数计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of mineral saturation indexex in the study area
矿物 SI值 最小值 最大值 平均值 方解石 0.14 1.28 0.76 白云石 −0.32 2.46 1.40 石膏 −2.31 −0.38 −1.21 盐岩 −9.69 −5.85 −8.03 表 3 岩溶地下水因子载荷矩阵
Table 3. Factor load matrix of karst groundwater
项目 F1 F2 F3 F4 总硬度 0.972 0.040 0.150 0.141 TDS 0.868 0.167 0.423 0.192 pH 0.274 −0.216 −0.016 0.749 Ca2+ 0.881 0.220 −0.068 −0.155 Mg2+ 0.706 −0.225 0.334 0.446 K+ 0.075 0.163 0.724 0.241 Na+ 0.261 0.321 0.672 0.357 Cl− 0.420 0.093 0.636 0.438 SO42− 0.158 0.334 0.849 −0.119 HCO3− 0.958 −0.130 −0.137 0.133 NO3− 0.274 0.242 0.081 0.680 F− −0.011 0.731 −0.042 −0.187 Mn −0.131 0.138 0.507 0.213 Zn 0.016 0.693 0.293 0.250 Hg −0.093 0.648 −0.325 −0.236 As −0.091 0.613 0.045 −0.055 Pb 0.095 0.755 0.302 0.013 Cd 0.082 0.697 0.113 −0.058 特征值 4.559 3.638 2.621 1.554 贡献率/% 31.52 25.15 18.12 10.74 累计贡献率/% 31.52 74.79 49.64 85.53 表 4 研究区岩溶地下水水质评价结果
Table 4. Evaluation results of karst groundwater quality in the study area
区域 水质评价等级 数量 比例/% 城区 Ⅰ-Ⅲ类 20 64.52 Ⅳ-Ⅴ类 11 35.48 非城区 Ⅰ-Ⅲ类 84 95.45 Ⅳ-Ⅴ类 4 4.55 合计 Ⅰ-Ⅲ类 104 87.39 Ⅳ-Ⅴ类 15 12.61 -
[1] 夏日元, 卢海平, 曹建文, 赵良杰, 王喆, 栾崧. 南方岩溶区地下水资源特征与水资源保障对策[J]. 中国地质, 2021(网络版).XIA Riyuan, LU Haiping, CAO Jianwen, ZHAO Liangjie, WANG Zhe, LUAN Song. Characteristics of groundwater resources in southern karst areas and water resources guarantee countermeasures [J]. Geology in China, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20210726.1711.002.html [2] 袁道先. 岩溶地区的地质环境和水文生态问题[J]. 南方国土资源, 2003(1):22-25.YUAN Daoxian. Geological environment and hydrologic ecology in karst area[J]. Nanfang Guotu Ziyuan, 2003(1):22-25. [3] 曹建华, 袁道先, 童立强. 中国西南岩溶生态系统特征与石漠化综合治理对策[J]. 草业科学, 2008, 25(9):40-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2008.09.014CAO Jianhua, YUAN Daoxian, TONG Liqiang. Features of karst ecosystem and integrating measure for rock desertification in southwest China[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 25(9):40-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2008.09.014 [4] 朱丹尼, 邹胜章, 周长松, 李录娟, 谢浩. 不同城镇功能区岩溶地下水化学敏感因子识别[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):484-492.ZHU Danni, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHOU Changsong, LI Lujuan, XIE Hao. Identification of hydrochemical sensitive factors of karst groundwater in different functional urban areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4):484-492. [5] 张海月, 杨平恒, 王建力, 蓝家程, 詹兆君, 任娟, 张宇. 城市化对岩溶水系统化学组分演化的影响:以重庆市南山老龙洞地下河为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(4):541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416ZHANG Haiyue, YANG Pingheng, WANG Jianli, LAN Jiacheng, ZHAN Zhaojun, REN Juan, ZHANG Yu. Effect of urbanization on the hydrogeochemical evolution of karst groundwater system: A case of the Laolongdong watershed, Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(4):541-549. doi: 10.11932/karst20170416 [6] Wang Zhe, Li Jiang, Lu Li, Cao Jianwen, Zhao Liangjie, Luan Song. Source, partition and ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in karst underground river environment, southern China[J]. Water, 2021, 13(19):2655. doi: 10.3390/w13192655 [7] 刘长礼, 王秀艳, 吕敦玉, 赵悦文. 中国南方岩溶地下水面源污染风险评价及防控对策[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6):910-918. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.06LIU Changli, WANG Xiuyan, Lü Dunyu, ZHAO Yuewen. Risk assessment and control countermeasures of southern China's karst groundwater areal source pollution[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2017, 38(6):910-918. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.06 [8] 夏日元, 蒋忠诚, 邹胜章, 曹建华, 覃小群, 苏春田, 罗为群, 周立新. 岩溶地区水文地质环境地质综合调查工程进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(1):1-10. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2017.01.01XIA Riyuan, JIANG Zhongcheng, ZOU Shenzhang, CAO Jianhua, QIN Xiaoqun, SU Chuntian, LUO Weiqun, ZHOU Lixin. Progress of hydrogeology and environmental geology comprehensive survey in karst area[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(1):1-10. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2017.01.01 [9] 吴华英, 李腾芳, 程瑞瑞, 黄奇波, 潘晓东. 我国岩溶地下水受污染的原因与污染特征[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(S1):101-104. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.S1.095WU Huaying, LI Tengfang, CHENG Ruirui, HUANG Qibo, PAN Xiaodong. Causes and characteristics of the pollution of karst groundwater in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(S1):101-104. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.S1.095 [10] 唐春雷, 赵春红, 申豪勇, 梁永平, 王志恒. 娘子关泉群水化学特征及成因[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3):1416-1423. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202007047TANG Chunlei, ZHAO Chunhong, SHEN Haoyong, LIANG Yongping, WANG Zhiheng. Chemical characteristics and causes of groups water in Niangziguan Spring[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1416-1423. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202007047 [11] 高帅, 李常锁, 贾超, 孙斌, 张海林, 逄伟. 济南趵突泉泉域岩溶水化学特征时空差异性研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(S1):61-70. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019211GAO Shuai, LI Changsuo, JIA Chao, SUN Bin, ZHANG Hailin, PANG Wei. Spatiotemporal difference study of karst hydrochemical characteristics in the Baotu Spring area of Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(S1):61-70. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019211 [12] Li Xian, Wang Yixian, Shu Longcang, WANG Yanqiao, TONG Fang, HAN Junling, SHU Wenyu, LI Delong, WEN Jinmei. The controlling factors of the karst water hydrochemistry in a karst basin of southwestern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(24):793. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-10082-1 [13] 张春潮, 侯新伟, 李向全, 王振兴, 桂春雷, 左雪峰. 三姑泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及形成演化机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(3):62-71. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202004059ZHANG Chunchao, HOU Xinwei, LI Xiangquan, WANG Zhenxing, GUI Chunlei, ZUO Xuefeng. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution mechanism of karst groundwater in the catchment area of the Sangu spring[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(3):62-71. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202004059 [14] 王瑞, 李潇瀚. 百泉泉域岩溶地下水水化学演化特征及成因[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):398-408.WANG Rui, LI Xiaohan. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of karst groundwater in the Baiquan spring catchment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3):398-408. [15] 卢丽, 王喆, 裴建国, 邹胜章, 林永生, 樊连杰. 西南地区典型岩溶地下水系统污染模式[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2018, 16(6):89-96. doi: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2018.0158LU Li, WANG Zhe, PEI Jianguo, ZOU Shengzhang, LIN Yongsheng, FAN Lianjie. Study on pollution model of typical karst groundwater system in area of southwest China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2018, 16(6):89-96. doi: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2018.0158 [16] Li Jun, Zhu Danni, Zhang Si, et al. Application of the hydrochemistry, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model to identify nitrate sources and transformations in surface water and groundwater of an intensive agricultural karst wetland in Guilin, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 231:113205. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113205 [17] Qin Wenjing, Han Dongmei, Song Xianfang, Liu Shaohua. Sources and migration of heavy metals in a karst water system under the threats of an abandoned Pb-Zn mine, southwest China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 277:116774. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116774 [18] Ana I,Marín, José Francisco Martín Rodríguez, Juan Antonio Barberá. Groundwater vulnerability to pollution in karst aquifers, considering key challenges and considerations: application to the Ubrique springs in southern Spain[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2021, 29:379-396. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02279-8 [19] 乔肖翠, 李雪, 刘琰. 2种方法在典型岩溶区地下水质量评价中的对比: 以地苏地下河为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(2):291-297. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200120QIAO Xiaocui, LI Xue, LIU Yan. Comparison of two methods in groundwater quality assessment in typical karst areas: taking Disu underground river as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2021, 11(2):291-297. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200120 [20] 王亚维, 王中美, 王益伟, 褚双燕. 基于GRA-AHP模型的岩溶地下水水质评价[J]. 水力发电, 2019, 45(8):1-3, 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2019.08.001WANG Yawei, WANG Zhongmei, WANG Yiwei, CHU Shuangyan. Evaluation of karst groundwater quality based on GRA-AHP model[J]. Water Power, 2019, 45(8):1-3, 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2019.08.001 [21] 黄晨晖, 时坚, 吴华英. 土地利用对刁江流域岩溶水水质的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(3):522-527. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2014.03.007HUANG Chenhui, SHI Jian, WU Huaying. Effects of land use on karst groundwater quality in Diaojiang river basin[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(3):522-527. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2014.03.007 [22] 林云, 曹飞龙, 武亚遵, 任华鑫, 贾方建. 北方典型岩溶泉域地下水水文地球化学特征分析: 以鹤壁许家沟泉域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(3):294-306.LIN Yun, CAO Feilong, WU Yazun, REN Huaxin, JIA Fangjian. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in typical karst spring areas of North China: A case study in the Xujiagou spring area, Hebi[J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(3):294-306. [23] 唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平. 龙子祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5):2087-2095. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201910078TANG Chunlei, ZHENG Xiuqing, LIANG Yongping. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in the Longzici spring catchment[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5):2087-2095. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201910078 [24] 赵春红, 梁永平, 卢海平, 唐春雷, 申豪勇, 王志恒. 娘子关泉域岩溶水SO42−、δ34S特征及其环境意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(6):867-875.ZHAO Chunhong, LIANG Yongping, LU Haiping, TANG Chunlei, SHEN Haoyong, WANG Zhiheng. Chemical characteristics and environmental significance of SO42− and sulfur isotope in the karst watershed of the Niangziguan spring, Shanxi Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(6):867-875. [25] Hao Liu, Zhang Kaiyi, Tian Maozhong. Investigation on pollution sources of a karst underground river in southwest Guizhou[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 861(7):072115. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/861/7/072115 [26] 王喆, 李江, 卢丽. 岩溶地下河系统水环境中多环芳烃污染特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(5):186-193. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.05.025WANG Zhe, LI Jiang, LU Li. Pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water environment of karst underground river system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(5):186-193. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.05.025 [27] 蓝家程, 孙玉川, 胡宁. 重庆老龙洞岩溶地下水化学特征及影响因素[J]. 水资源保护, 2018, 34(3):37-44. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2018.03.06LAN Jiacheng, SUN Yuchuan, HU Ning. Hydrochemical characteristics of Laolongdong karst groundwater and its impact factors[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2018, 34(3):37-44. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2018.03.06 [28] 张睿东, 陈盟, 李强, 王櫹橦. 滇东高原牛栏江流域岩溶区地下水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12):3828-3837. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042002ZHANG Ruidong, CHEN Meng, LI Qiang, WANG Xiaotong. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater in karst area of Niulanjiang River watershed of eastern Yunnan Plateau[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12):3828-3837. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042002 [29] 陆石基, 周宏, 刘伟, 陈乾龙, 燕子琪, 陈丽. 秭归岩溶流域锶的分布特征与富集规律[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(6):1865-1874.LU Shiji, ZHOU Hong, LIU Wei, CHEN Qianlong, YAN Ziqi, CHEN Li. Distribution and enrichment of strontium in the Zigui karst watershed[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(6):1865-1874. [30] 张艳青, 张志才, 陈喜, 王刚, 程勤波, 刘皓, 彭韬. 西南喀斯特流域岩溶水氢氧同位素时空分布特征及水文意义: 以后寨河流域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(1):25-33.ZHANG Yanqing, ZHANG Zhicai, CHEN Xi, WANG Gang, CHENG Qinbo, LIU Hao, PENG Tao. Spatiotemporal features of deuterium and oxygen-18 in karst water and its relation to hydrological regime in the karst catchment of southwest china: A case study of Houzhai catchment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(1):25-33. [31] 苏春利, 张雅, 马燕华, 刘文波. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学演化机制: 水化学和锶同位素证据[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(9):2829-2838.SU Chunli, ZHANG Ya, MA Yanhua, LIU Wenbo. Hydrochemical evolution processes of karst groundwater in Guiyang City: Evidences from hydrochemistry and 87Sr/86Sr ratios[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9):2829-2838. [32] 张世旭, 王中美, 代天豪. 毕节地区岩溶地下水水化学特征与水质评价[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2019, 36(5):28-33, 41.ZHANG Shixu, WANG Zhongmei, DAI Tianhao. Chemical characteristics and water quality assessment of karst groundwater in Bijie[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(5):28-33, 41. [33] 李华, 文章, 谢先军, 罗朝辉, 顾栩. 贵阳市三桥地区岩溶地下水水化学特征及其演化规律[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5):804-812.LI Hua, WEN Zhang, XIE Xianjun, LUO Zhaohui, GU Xu. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of karst groundwater in Sanqiao district of Guiyang City[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5):804-812. [34] MING Xiaoxing, Chris Groves, WU Xinyu, CHANG longyan, ZHENG yanli, YANG Pingheng. Nitrate migration and transformations in groundwater quantified by dual nitrate isotopes and hydrochemistry in a karst World Heritage site[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 735:138907. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138907 [35] 杨婷婷, 许光泉, ANESU Mabaire. 淮南潘谢矿区岩溶水化学特征及其形成机制研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(3):238-249. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.024YANG Tingting, XU Guangquan, ANESU Mabaire. Chemical composition of karst groundwater of Panxie coal mining area in Huainan and its formation mechanism[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(3):238-249. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.024 [36] Li Bo, Zhang Huiling, Long Jie, Fan Juan, Wu Pan, Chen Mengyu, Liu Pu, Li Tao. Migration mechanism of pollutants in karst groundwater system of tailings impoundment and management control effect analysis: Gold mine tailing impoundment case[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 350:131434. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131434 [37] 宋煜, 李保珠. 云南会泽铅锌矿区地下水化学和同位素分析[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(5):1081-1089. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.05.013SONG Yu, LI Baozhu. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Analysis of Groundwater in the Huize Lead-Zinc Mining District, Yunnan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(5):1081-1089. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.05.013 [38] 韦虹, 吴锦奎, 沈永平, 张伟, 刘世伟, 周嘉欣. 额尔齐斯河源区融雪期积雪与河流的水化学特征[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(4):1345-1352.WEI Hong, WU Jinkui, SHEN Yongping, ZHANG Wei, LIU Shiwei, ZHOU Jiaxin. Hydrochemical characteristics of snow meltwater and river water during snow-melting period in the headwaters of the Ertis River, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(4):1345-1352. [39] Moran-Ramírez J, Ramos-Leal J A, Mahlknecht J, Santacruz-DeLeón G, Martín-Romero F, Fuentes Rivas R, Mora A. Modeling of groundwater processes in a karstic aquifer of Sierra Madre Oriental, Mexico[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 95:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.05.011 [40] Zhang Xiaobo, Li Xue, Gao Xubo. Hydrochemistry and coal mining activity induced karst water quality degradation in the Niangziguan karst water system, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23:6286-6299. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5838-z [41] 刘学娜, 李海明, 李梦娣, 章卫华, 肖瀚. 天津平原区加油站地下水石油烃污染特征及其生物降解机理研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 227-238.LIU Xuena, LI Haiming, LI Mengdi, ZHANG Weihua, XIAO Han. Pollution characteristics and biodegradation mechanism of petroleum hydrocar-bons in gas station groundwater in the Tianjin Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2022,29(3): 227-238. [42] 吴易雯, 李莹杰, 张列宇, 过龙根, 李华, 席北斗, 王雷, 李曹乐. 基于主客观赋权模糊综合评价法的湖泊水生态系统健康评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(5):1091-1102. doi: 10.18307/2017.0507WU Yiwen, LI Yingjie, ZHANG Lieyu, GUO Longgen, LI Hua, XI Beidou, WANG Lei, LI Caole. Assessment of lakes ecosystem health based on objective and subjective weighting combined with fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(5):1091-1102. doi: 10.18307/2017.0507 -




 下载:
下载: