Trend analysis of groundwater quality in major basins of Yunnan Province
-
摘要: 云南省的高原山间盆地是重要的水源汇集区,人口聚集和经济活动中心,也是对水环境影响和变化具有指标意义的环境水文地质单元。文章阐述了云南省高原主要山间盆地地下水质监测概况,并依据多年地下水水质监测数据,按照孔隙水、裂隙水、岩溶水三种地下水类型进行了水质评价。通过数据统计法、Piper三线图、小波神经网络时间序列分析,预测云南省地下水化学特征及水质变化趋势。研究发现:地下水化学类型种类复杂多样,以HCO3-Ca · Mg、HCO3-Ca型为主。氨氮、锰、氟化物、硝酸根离子等含量超标率较高,是导致地下水水质超标的主要指标,不同污染指标的污染来源不同,主要为生活污染和工业污染。根据统计分析结果显示云南高原主要盆地水质总体上呈稳定趋势,针对研究结果提出了地下水环境保护的措施建议。Abstract:
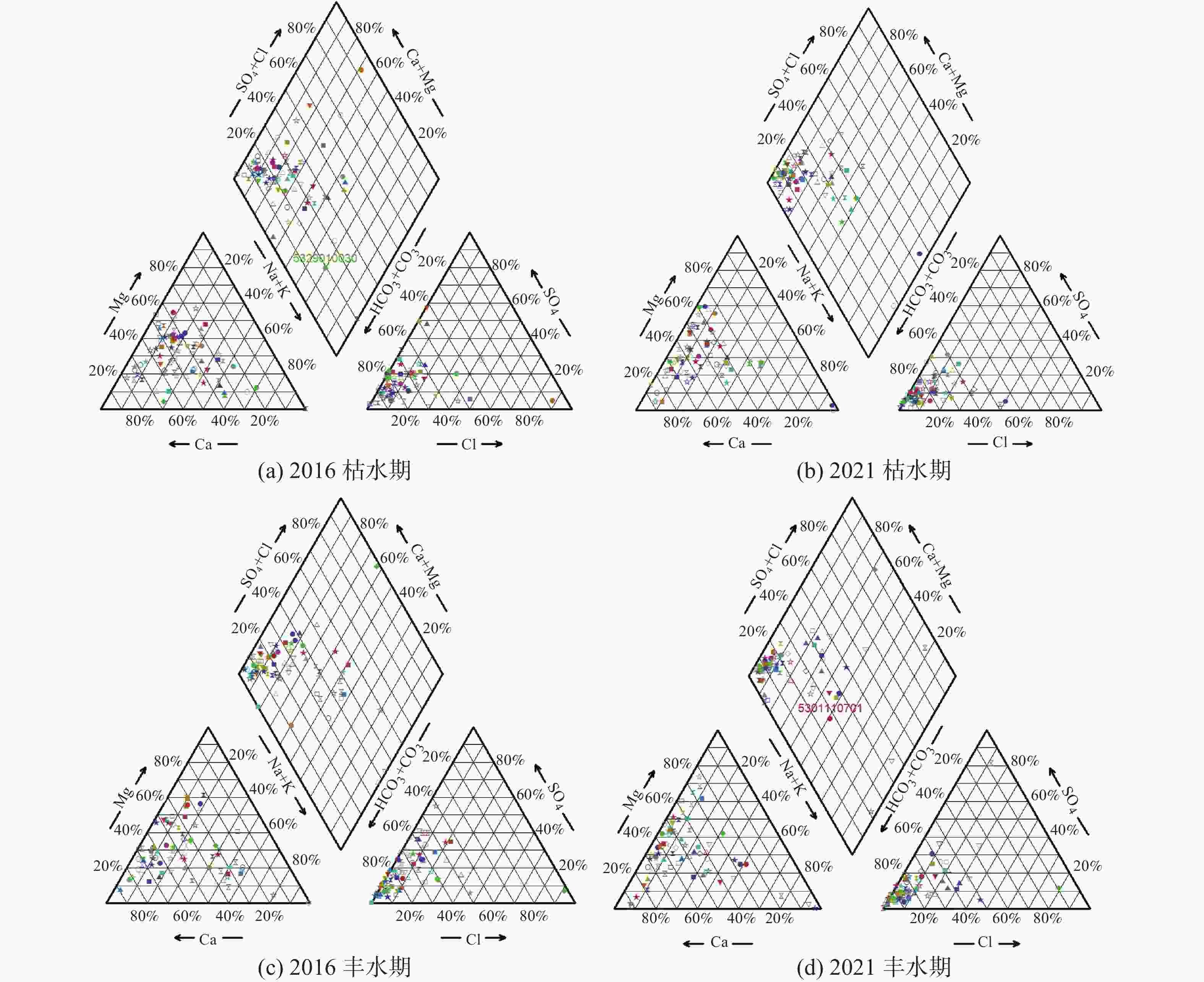
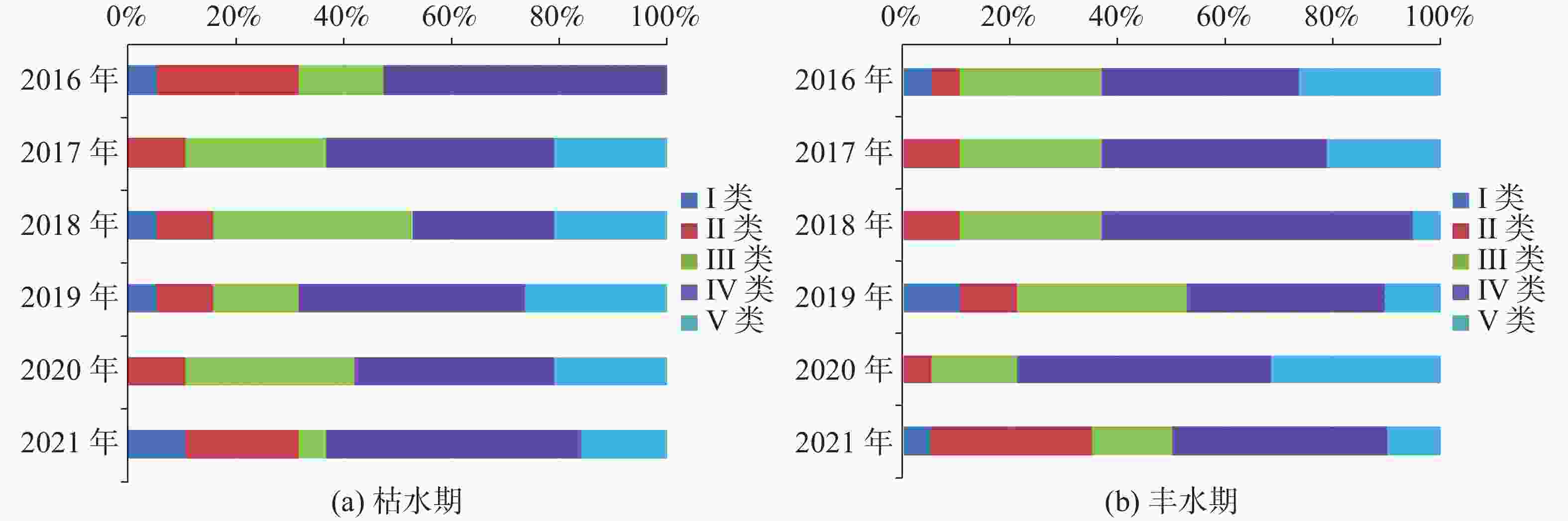
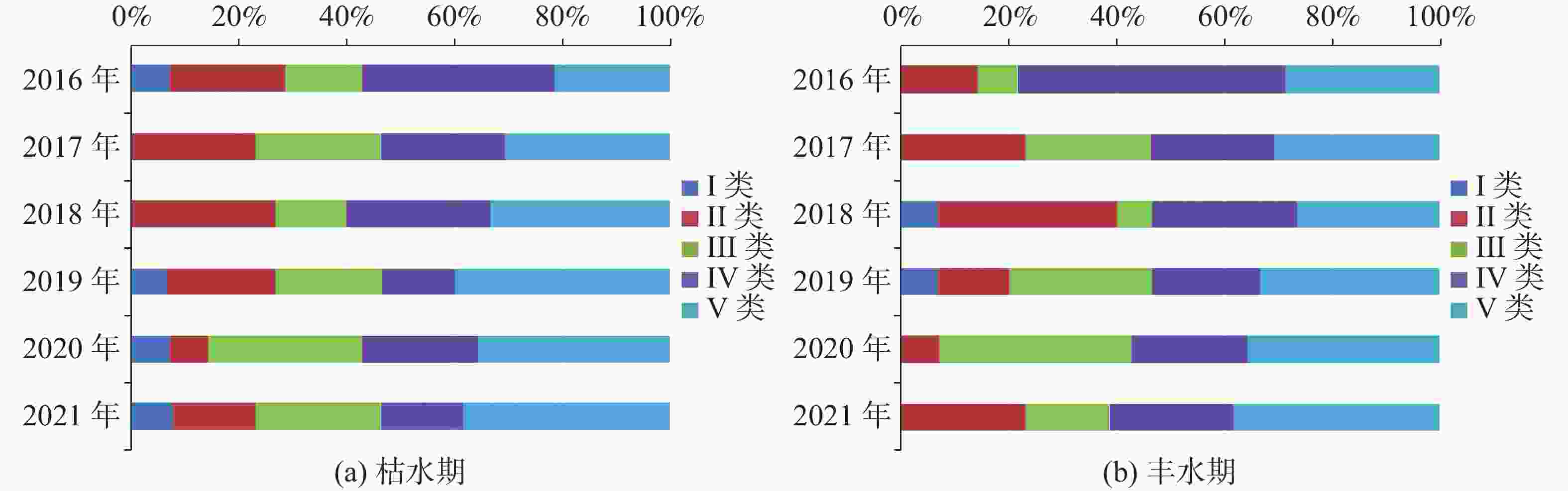
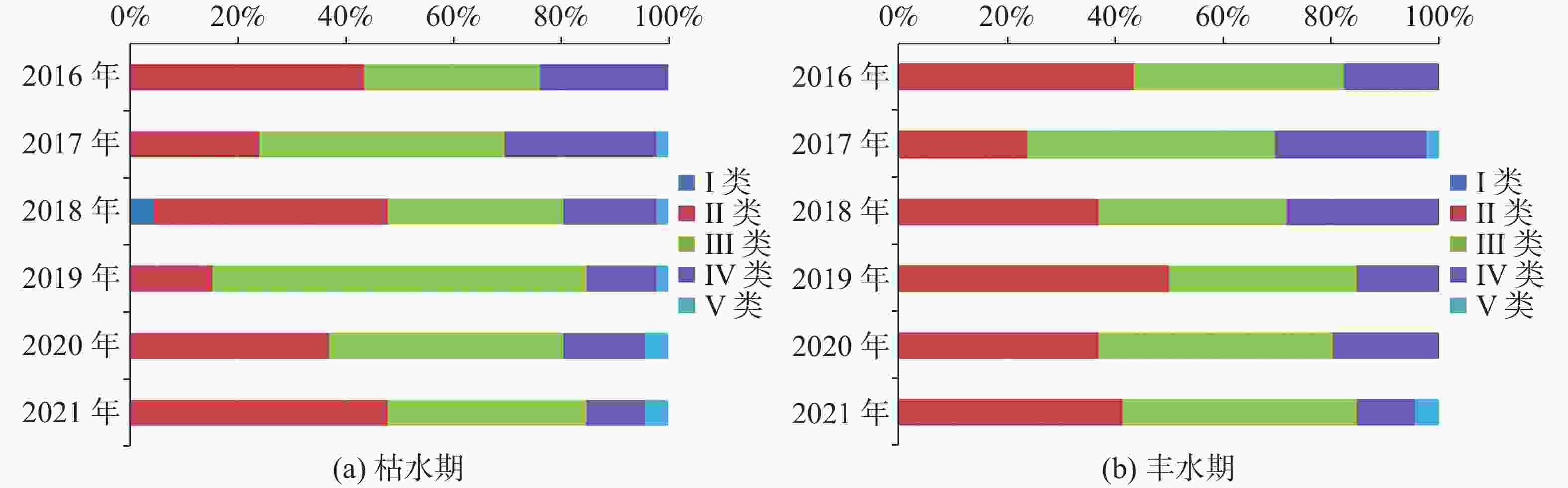
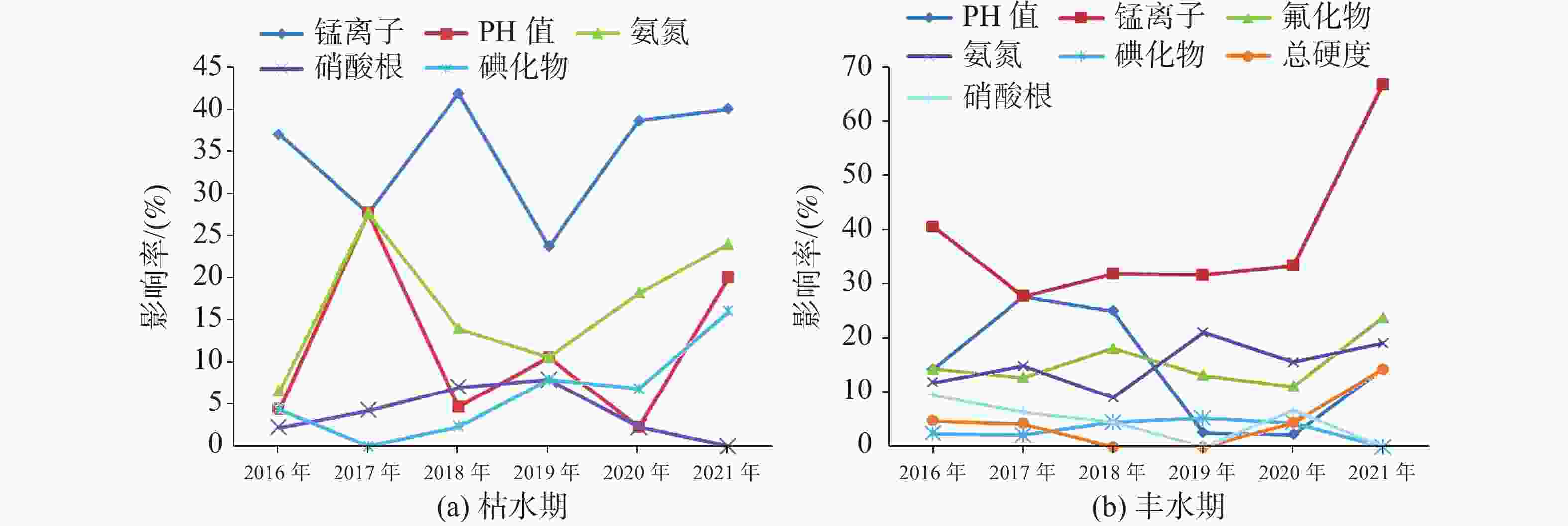
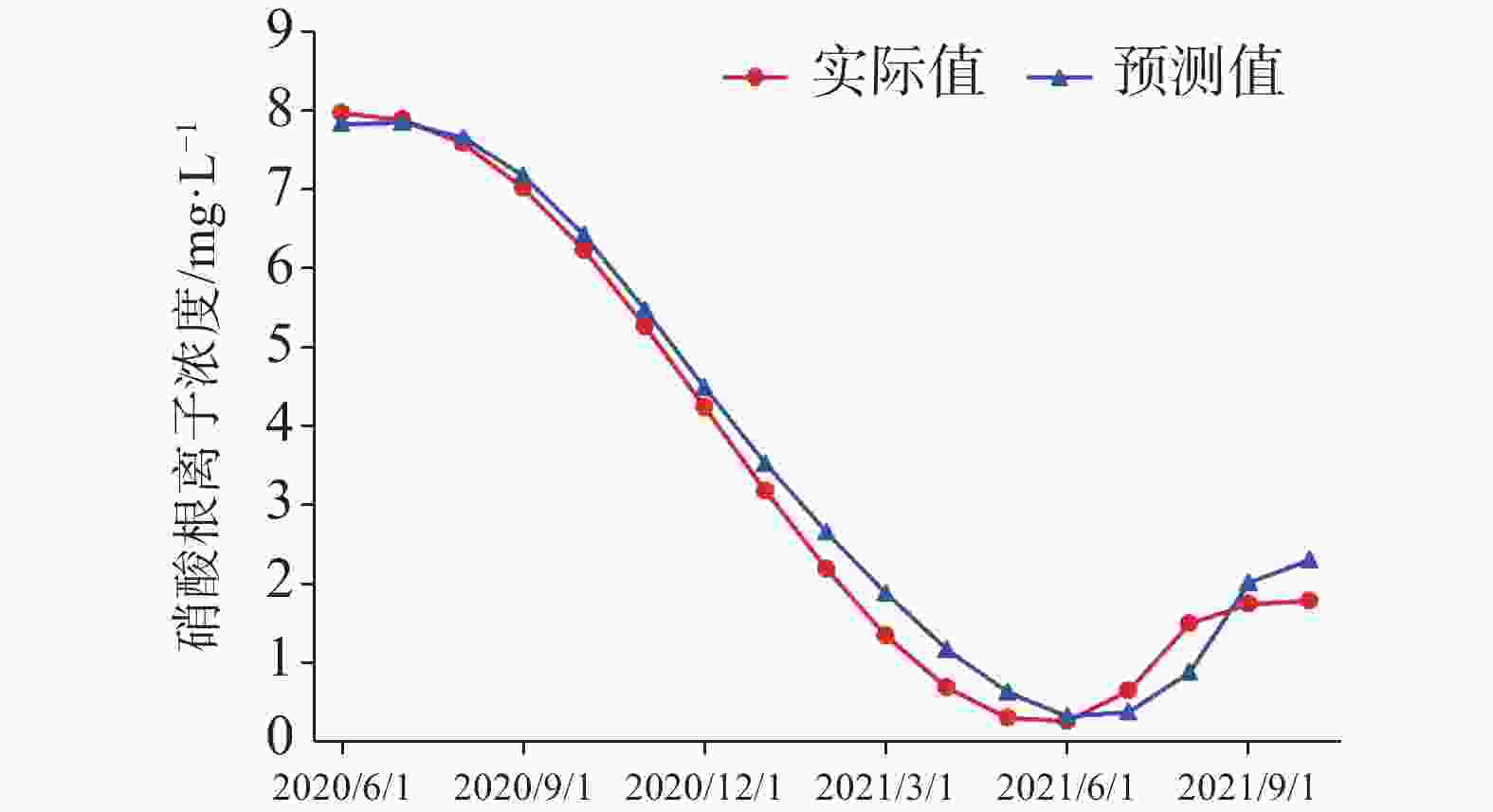
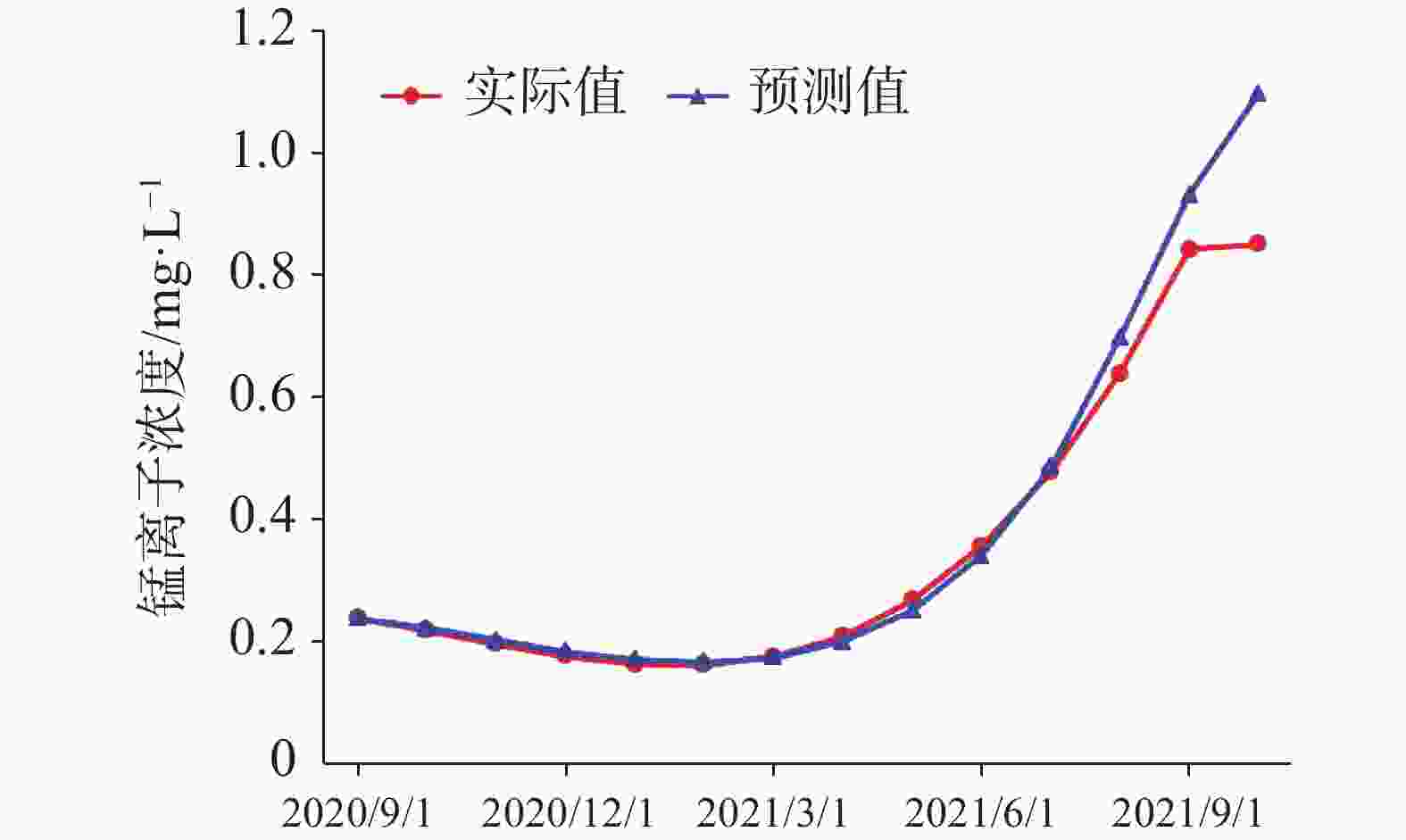
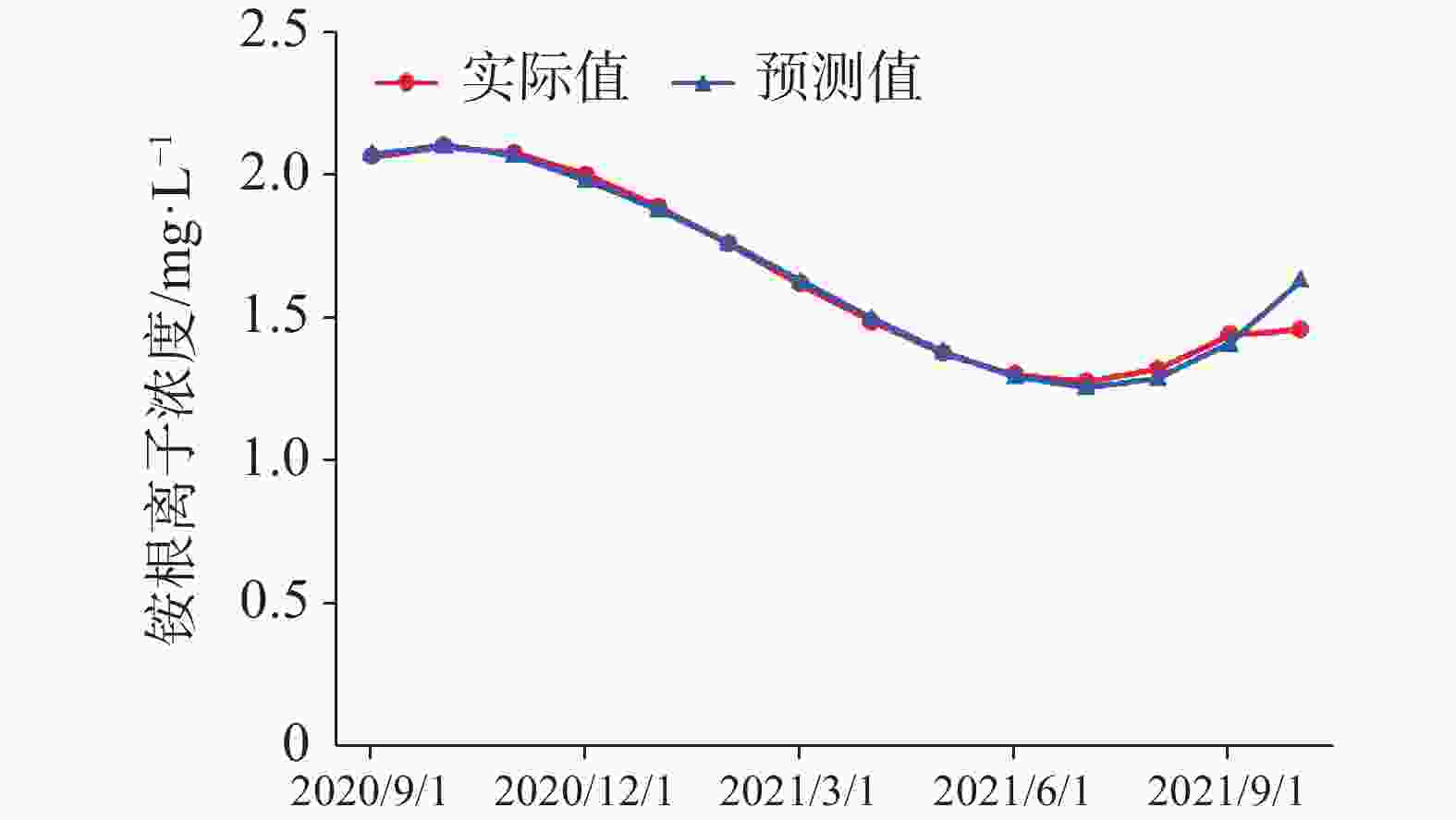
The plateau intermountain basin in Yunnan Province is an important water source gathering area, a population gathering and economic activity center, as well as an environmental hydrogeological unit with index significance of the impact and change of water environment. This article reviews the general monitoring situation of groundwater quality in the main intermountain basins of Yunnan Province. Among nearly 50 basins with an area of more than 100 square kilometers each, 7 have been laid out groundwater monitoring sites, respectively in Kunming, Yuxi, Dali, Chuxiong, Qujing, Jinghong and Kaiyuan. On the basis of dynamic monitoring data for groundwater quality in these basins from 2016 to 2021, the quality of pore water, fissure water and karst water is evaluated. Besides, the groundwater chemical characteristics are analyzed and the change trend of water quality in Yunnan are predicted with data statistics, Piper trilinear diagrams and time series analyses of wavelet neural network. The simulation results of wavelet neural network show that nitrate ion concentration in Hole 152 of Kunming basin increased in a short term, but then slowed down and leveled off. The concentration of manganese ion in Hole 101 of Chuxiong showed an increasing trend, while the concentration of ammonium ion showed a gradual but continual increase in the recent 1 or 2 years after an initial decrease reached the bottom. The high fitting accuracy of wavelet neural network and the average percentage error (less than 10%) demonstrated a satisfactory prediction, which may provide reference for groundwater treatment, protection and prediction, and the building of an early warning platform. It is found that the chemical types of groundwater are complex and diverse, mainly HCO3-Ca·Mg and HCO3-Ca. The content of ammonia nitrogen, manganese, fluoride and nitrate ion exceeds permitted levels, which may mainly indicate the exceedance of an acceptable level of groundwater quality. Over the past six years, the rates of exceeding permitted levels of pore water quality remained stable at about 70%. The components exceeding permitted levels were mainly pH value, total hardness, iodine ion, nitrate, ammonia nitrogen, etc. As for fissure water quality, its rates of exceeding permitted levels were basically unchanged, but the proportion of Class V water was on the rise, mainly in Kunming, Chuxiong and Yuxi. During 2017 and 2019, the rates of exceeding permitted levels were relatively low, but the fissure water quality was deteriorating. The components exceeding permitted levels were mainly manganese ions, pH values, fluorides, etc. The rates of exceeding permitted levels in terms of karst water quality gradually decreased, and in dry season the rate for Class II and Class III water decreased from 23.91% to 15.22%. Components were mainly manganese ions, arsenic ions, ammonia nitrogen, etc. Different indicators show different pollution causes. Pore water may be polluted with infiltration and recharge brought by atmospheric precipitation in pore aquifer. It may also be polluted when laterally recharged by surface water and by agricultural irrigation. Consequently, the deterioration of pore water is closely connected with the discharge of urban domestic sewage, industrial “three wastes” emissions, the use of chemical fertilizer and pesticide, agricultural irrigation and others. Compared with pore water, fissure water was less affected by pollution. Its pollution was mainly caused by the high background values of red beds and metamorphic rocks. Karst water may pollute karst aquifers through low-lying karst fissures, sinkholes and groundwater drainage. According to the statistical results, the water quality in the main basins of Yunnan Plateau shows a stable trend on the whole, which can provide a scientific basis for local economic and social development, territorial space planning, and rational exploitation and effective protection of groundwater resources. -
Key words:
- water environment /
- groundwater quality /
- groundwater monitoring /
- pollution index /
- plateau basin
-
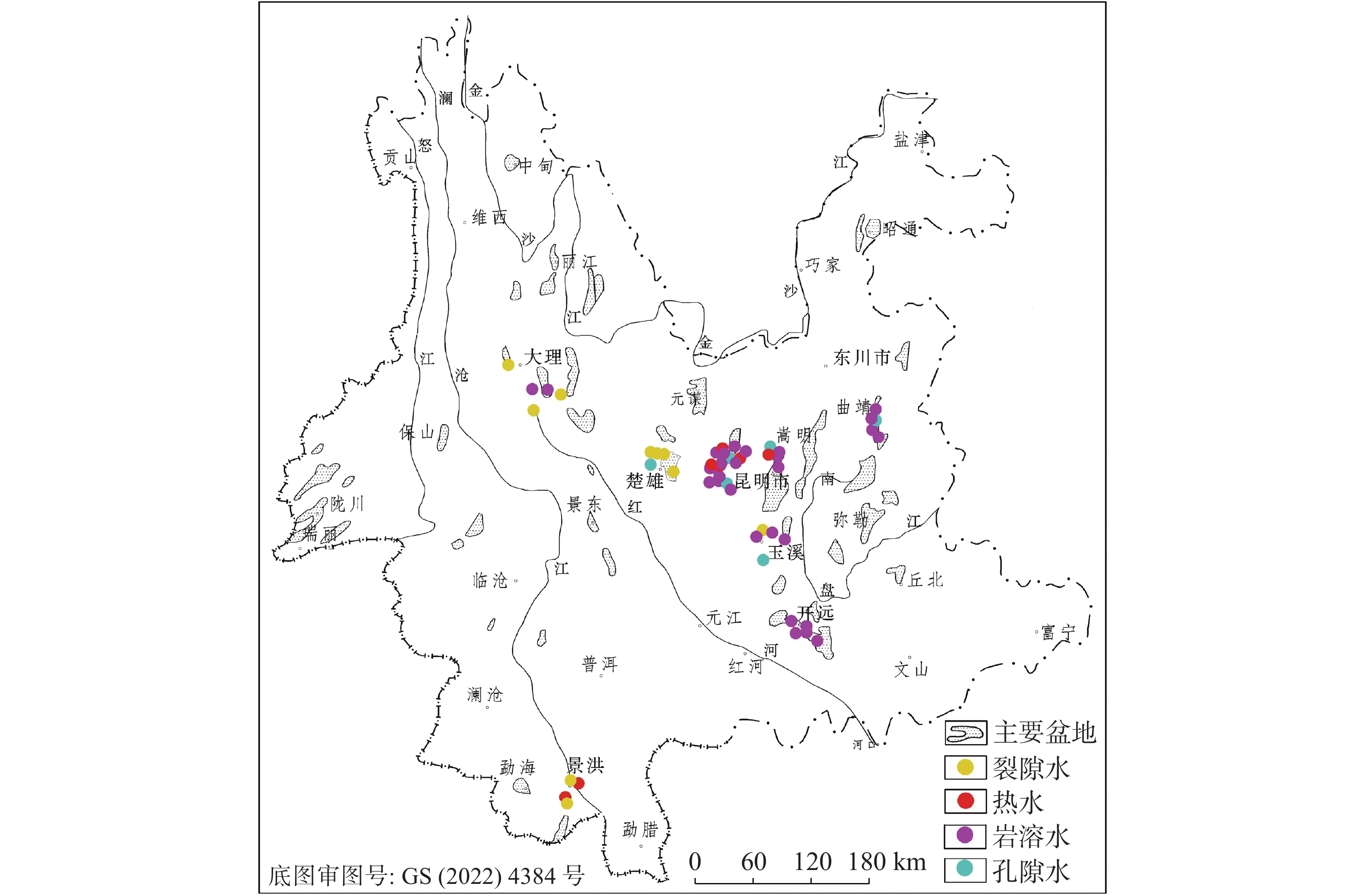
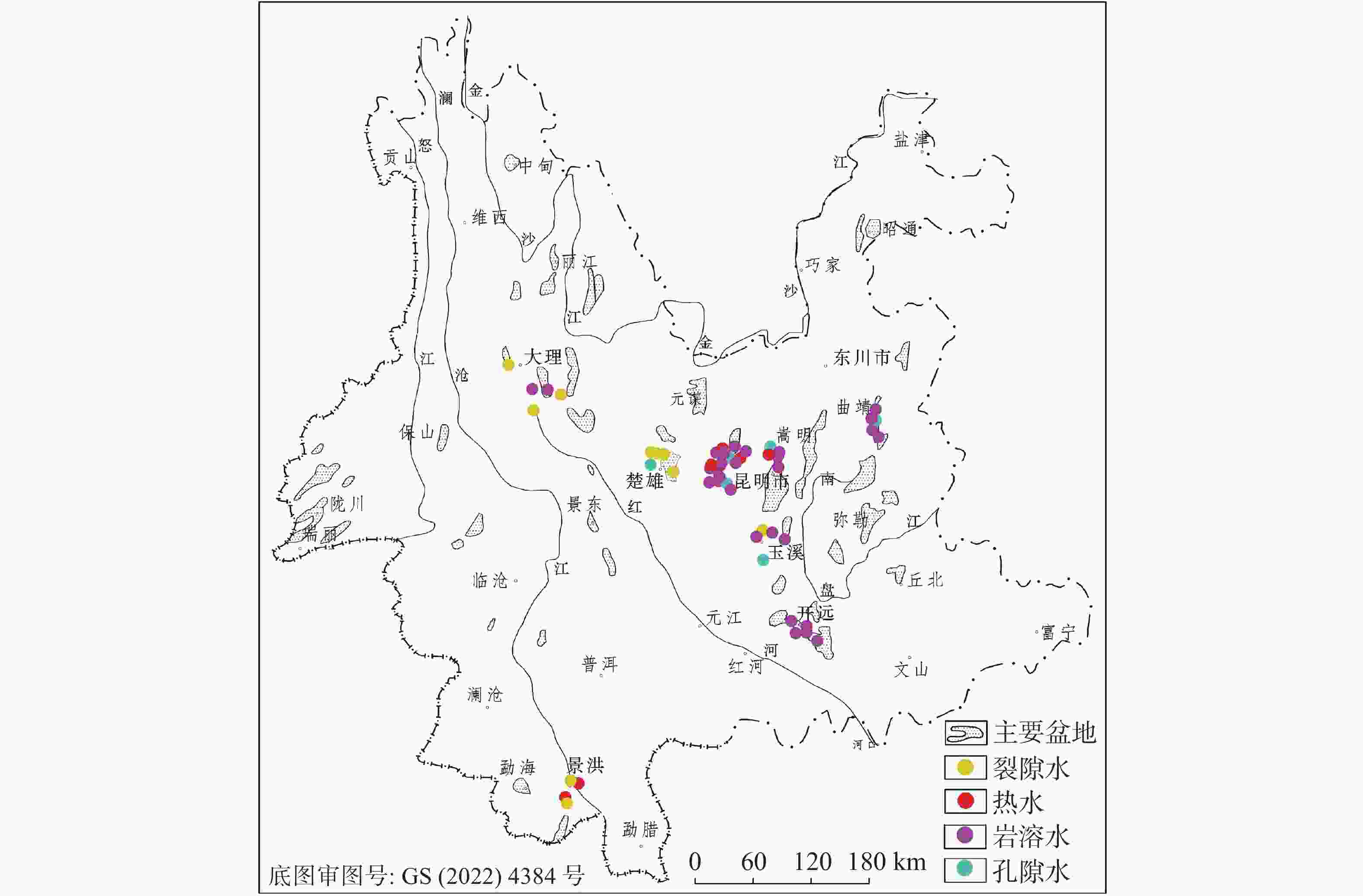
表 1 云南省地下水监测站点分布情况表
Table 1. Distribution of groundwater monitoring sites in Yunnan Province
州市 数量 监测项目分类/个 水位 流量 水质 水温 流量、水温共用 水位、水质共用 流量、水质共用 水位、水温共用 昆明 110 68 9 50 14 9 11 4 5 玉溪 12 7 3 6 3 3 1 3 0 开远 21 11 3 5 3 3 0 0 0 大理 11 7 2 5 2 2 1 2 0 楚雄 11 9 1 5 1 1 3 1 0 曲靖 10 6 2 5 2 2 1 2 0 景洪 8 5 2 3 2 2 1 1 0 合计 183 113 22 79 27 22 18 13 5 表 2 昆明盆地152号孔硝酸根离子浓度预测结果误差分析表
Table 2. Error analysis of prediction results of nitrate ion concentration in Hole 152 of Kunming basin
实际值/
mg·L−1预测值/
mg·L−1偏差/
%平均百分比
误差/%均方根
误差7.974 032 7.836 001 −6.90 7.33 0.16 7.898 648 7.856 258 −2.12 7.599 509 7.661 768 3.11 7.029 46 7.195 764 8.32 6.232 3 6.439 032 10.34 5.279 58 5.494 991 10.77 4.242 854 4.494 204 12.57 3.193 681 3.529 283 16.78 2.203 616 2.663 838 23.01 1.344 214 1.882 355 26.91 0.687 033 1.181 627 24.73 0.303 629 0.635 833 16.61 0.265 557 0.334 812 3.46 0.644 374 0.377 119 −13.36 1.511 637 0.890 394 −31.06 1.75 2.030 851 14.04 表 3 楚雄101号孔锰离子浓度预测结果误差分析表
Table 3. Error analysis of prediction results of manganese ion concentration in Hole 101 of Chuxiong
实际值
mg·L−1预测值
mg·L−1偏差/
%平均百分比
误差/%均方根
误差0.239 386 0.239 68 0.12 1.84 0.05 0.219 571 0.223 052 1.59 0.197 511 0.203 475 3.02 0.177 614 0.185 628 4.51 0.164 399 0.173 083 5.28 0.162 388 0.167 336 3.05 0.176 101 0.175 076 −0.58 0.210 056 0.200 816 −4.40 0.268 775 0.251 975 −6.25 0.356 778 0.342 704 −3.94 0.478 584 0.487 297 1.82 0.638 714 0.697 465 9.20 0.841 688 0.930 564 10.56 表 4 楚雄101号孔铵根离子浓度预测结果误差分析表
Table 4. Error analysis of prediction results of ammonium ion concentration in Hole 101 of Chuxiong
实际值
/mg·L−1预测值
/mg·L−1偏差
/%平均百分比
误差/%均方根
误差2.062 402 2.075 19 0.62 0.35 0.01 2.100 669 2.102 612 0.09 2.075 476 2.067 837 −0.37 2.000 217 1.983 028 −0.86 1.889 264 1.880 876 −0.44 1.756 986 1.763 891 0.39 1.617 755 1.632 051 0.88 1.485 943 1.499 617 0.92 1.375 92 1.382 616 0.49 1.302 058 1.297 05 −0.38 1.278 726 1.259 742 −1.48 1.320 298 1.290 263 −2.27 1.441 143 1.410 574 −2.12 -
[1] 周仰效, 李文鹏. 地下水水质监测与评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2008(1): 1-9.ZHOU Yangxiao, LI Wenpeng. Groundwater quality monitoring and assessment[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2008(1): 1-9. [2] 田振君. 沧州市浅层地下水水质变化趋势分析[J]. 河北水利水电学院院报, 2020, 30(4): 54-57.TIAN Zhenjun. Trend analysis of shallow groundwater quality in Cangzhou City[J].JoumaI of Hebei University of water Resources and Electric Engineering. 2020, 30(4): 54-57. [3] 雷天雷, 马运革, 郝仁琪. 成都平原浅层地下水水质变化趋势浅析[J]. 水利技术监督, 2021(4):23-26,146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1305.2021.04.007LEI Tianlei, MA Yunge, HAO Renqi. Analysis on variation trend of shallow groundwater quality in Chengdu Plain[J]. Water Conservancy Technical Supervision, 2021(4):23-26,146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1305.2021.04.007 [4] 王波, 王宇, 张贵, 张华, 代旭升, 康晓波. 滇东南泸江流域岩溶地下水质量及污染影响因素研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(3): 352-362.WANG Bo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, ZHANG Hua, DAI Xusheng, KANG Xiaobo. A Study of quality and pollution factors of karst groundwater in Lujiang River basin in Southeast Yunnan [J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 352-362. [5] 王宇, 张贵, 张华, 康晓波, 彭淑惠, 王波, 王劲, 周翠琼. 云南省岩溶水文地质环境地质调查与研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 2018.WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, ZHANG Hua, KANG Xiaobo, PENG Shuhui, WANG Bo, WANG Jin, ZHOU Cuiqiong. Investigation and study on karst hydrogeology and environmental geology in Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. 2018. [6] 张华, 王宇, 张贵. 云南重点岩溶流域水文地质及环境地质调查成果评析[J]. 云南地质, 2014, 33(2):259-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2014.02.021ZHANG Hua, WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui. Evaluation of hydrogeological and environmental geological survey results in key karst basins in Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2014, 33(2):259-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2014.02.021 [7] 王宇. 云南省地下水资源潜力评价现状与问题分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(2):137-146.WANG Yu. Evaluation status and problems of groundwater resource potential in Yunnan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(2):137-146. [8] 卢丽, 王喆, 裴建国, 杜毓超, 林永生, 樊连杰. 红水河中上游流域岩溶地下水水质影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4): 415-419.LU Li, WANG Zhe, PEI Jianguo, DU Yuchao, LIN Yongsheng, FAN Lianjie. R-mode analysis for influencing factors of karst groundwater quality in middle and upper reaches of the Hongshuihe river[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 415-419. [9] 李从仁, 杨艳华. 云南省地下水资源分布特征及地下水环境问题[C]. 中国地质矿产经济学会2005年学术年会论文集. 2005: 512-516.LI Congren, YANG Yanhua. Geological characteristics of groundwater and groundwater resources in Yunnan Province[C]. Proceedings of 2005 academic annual meeting of China Society of Geology and mineral economics, 2005: 512-516. [10] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 李成城, 姜春芳. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):287-298.GAO Xubo, WANG Wanzhou, HOU Baojun, LI Chengcheng, JIANG Chunfang. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3):287-298. [11] 章程, 蒋勇军, Michèle Lettingue, 王松. 岩溶地下水脆弱性评价“二元法”及其在重庆金佛山的应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2007, 26(4):334-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2007.04.010ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Yongjun, Michèle Lettingue, WANG Shong. Duality method for assessing karst groundwater vulnerability and its application in Jinfo mountain of Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2007, 26(4):334-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2007.04.010 [12] 周巾枚, 蒋忠诚, 徐光黎, 覃小群, 黄奇波, 张连凯. 崇左响水地区地下水水质分析及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6):2675-2685.ZHOU Jinmei, JIANG Zhongcheng, XU Guangli, QIN Xiaoqun, HUANG Qibo, ZHANG Liankai. Water quality analysis and health risk assessment for groundwater at Xiangshui, Chongzuo[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6):2675-2685. [13] 刘伟. 云南异龙湖水质及富营养化变化趋势分析[J]. 人民长江, 2014, 45(S1):48-50, 56.LIU Weng. Analysis on water quality and eutrophication trend of Yilong Lake in Yunnan Province[J]. Yangtze River, 2014, 45(S1):48-50, 56. [14] 赵军, 张祯宇, 谢哲宇, 黄金良, 黄祖亚. 基于BP人工神经网络的闽江口水厂水质模拟[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(S1):198-203.ZHAO Jun, ZHANG Zhenyu, XIE Zheyu, HUANG Jinliang, HUANG Zhuya. Water quality modeling for water works in the Minjiang River estuary based on BP neural network model[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(S1):198-203. [15] 李芸, 张楠, 张坤. 云南省地下水监测及开发利用浅析[J]. 人民珠江, 2016, 37(8):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.08.010LI Yun, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Kun. Analysis of groundwater monitoring, exploitation and utilization in Yunnan Province[J]. Pearl River, 2016, 37(8):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.08.010 [16] 王雅茹. 基于Piper三线图的矿井水化学特征分析[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2019(4):145-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2019.04.057WANG Yaru. Analysis of chemical characteristics of mine water based on Piper three line diagram[J]. Shandong Coal Technology, 2019(4):145-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2019.04.057 [17] 刘世强, 吕海滨, 彭波. 兰陵县地下水的水化学分布特征及其形成条件分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(6):151-158.LIU Shiqiang, LV Haibin, PENG Bo. Hydrochemical distribution characteristics and formation conditions of groundwater in Lanling county, Shandong coal science and technology[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(6):151-158. [18] GB/T14848-2017, 地下水质量标准[S].2017.GB/T14848-2017, Groundwater quality standard[S].2017. [19] 袁忠玉, 彭淑惠. 近年昆明市茨坝一岗头村富水块段地下水位持续下降原因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(3): 313-317.YUAN Zhongyu, PENG Shuhui. Analysis on the reasons for the continuous decline of groundwater level in Fushui block of yigangtou village, Ciba, Kunming in recent years[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(3): 313-317. [20] 张华, 王波, 王宇, 张贵, 何绕生, 代旭升, 康晓波, 蓝芙宁. 云南泸西岩溶断陷盆地水循环系统及水资源循环利用方案[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(3):313-323. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.090603ZHANG Hua, WANG Bo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Gui, HE Raosheng, DAI Xusheng, KANG Xiaobo, LAN Funing. Water circulation system and water resources recycling scheme in Luxi karst depression basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(3):313-323. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.090603 [21] 叶许春. 近20年来昆明盆地北端孔隙水化学场演变过程及其驱动因素分析[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2006.YE Xuchun. Evolution process and driving factors of pore water chemical field in the northern end of Kunming Basin in recent 20 years[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2006. [22] 吴香根, 朱春林, 吴尚谦, 叶十五. 滇中红层水文地质特征与找水方向[J]. 路基工程, 2011(5):46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2011.05.015WU Genxiang, ZHU Chunlin, WU Shangqian, YE Shiwu. Hydrogeological characteristics and water prospecting direction of red beds in Central Yunnan[J]. Subgrade works, 2011(5):46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2011.05.015 [23] 莫美仙, 王宇, 李峰. 滇东断陷盆地地下水污染的水文地质模式[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 39(5):88-95.MO Meixian, WANG Yu, LI Feng. Hydrogeological model of groundwater pollution in east Yunnan fault basin[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Technology (NATURAL SCIENCE EDITION), 2014, 39(5):88-95. [24] 刘长礼, 王秀艳, 吕敦玉, 赵悦文. 中国南方岩溶地下水面源污染风险评价及防控对策[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6):910-918. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.06LIU Changli, WANG Xiuyan, LV Dunyu, ZHAO Yuwen. Risk assessment and control countermeasures of karst groundwater non-point source pollution in South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(6):910-918. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.06 [25] 孟维伟. 基于神经网络的交通量预测技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学,2006.MENG Weiwei. Research on traffic volume prediction technology based on Neural Network[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Technology, 2006. [26] MATLAB中文论坛. MATLAB神经网络30个案例分析[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社,2010.Matlab Chinese Forum Analysis of 30 cases of MATLAB neural network[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2010. [27] 王鑫东. 小波神经网络模型在水库水质预测中的应用研究[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 2016, 26(3): 54-56.WANG Xindong. Application of wavelet neural network model for prediction of water quality in the reservoirs[J]. Flood control and drought relief in China, 2016,26(3): 54-56. [28] 卢志娟, 朱玲, 裴洪平, 汪勇. 基于小波分析与BP神经网络的西湖叶绿素a浓度预测模型[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(10):4965-4973. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.10.042LU Zhijuan, ZHU Ling, PEI Pongpin, WANG Yong. The model of chlorophyll-a concentration forecast in the West Lake based on wavelet analysis and BP neural networks[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(10):4965-4973. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.10.042 [29] 朱文龙, 龙艳萍, 贾磊. 基于RBF神经网络的交通流量预测算法[J]. 山东大学学报, 2007, 37(4):24-27.ZHU Wenlong, LONG Yanping, JIA Lei. Traffic flow prediction algorithm based on RBF neural network[J]. Journal of Shandong University, 2007, 37(4):24-27. [30] 张国彬. 小波神经网络算法的改进与应用[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2005.ZHANG guobin. Improvement and application of wavelet neural network algorithm[D]. Fuzhou : Fuzhou University, 2005. [31] 王宇, 张华, 张贵, 王波, 彭淑惠, 何绕生, 周翠琼. 喀斯特断陷盆地环境地质分区及功能[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3):283-295. doi: 10.11932/karst20170316WANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, ZHANG Gui, WANG Bo, PENG Shuhui, HE Raosheng, ZHOU Chuiqiong. Division and function of environmental geology in Karst faulted basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3):283-295. doi: 10.11932/karst20170316 [32] 赵贵章, 王淑丽, 李志萍, 龚建师, 王赫生. 基于小波分析的水质变化及预测研究: 以涡河为例[J]. 人民珠江, 2022, 43(2):79-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2022.02.011ZHAO Guizhang, WANG Shuli, LI Zhiping, GONG Jianshi, WANG Hesheng. Study on water quality change and prediction based on wavelet analysis: Taking Wohe River as an example[J]. Pearl River, 2022, 43(2):79-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2022.02.011 -




 下载:
下载: