Influence of initial fractures on the occurrence of karst turbulent flow
-
摘要: 岩溶地区地下发育着大量的溶洞和地下河管道,地下水流状态既有层流也有紊流,而紊流是溶洞管道形成的重要条件。紊流的形成受到岩石初始裂隙的影响,初始裂隙的张开度、分布、走向、迹长、密度等因素都影响着裂隙发育过程中水流状态的变化。通过对不同统计特征的初始裂隙网络进行水流和溶蚀的数值模拟发现,以张开度标准差反映的裂隙网络非均匀性越强,模拟紊流出现的时间就越早;主要裂隙的存在使裂隙网络的非均性增强,主要裂隙与水力梯度总方向的角度越小,紊流出现的时间就越早;当裂隙平均迹长过小时会导致裂隙连通性较差,影响裂隙水流和溶蚀作用;裂隙密度,尤其是主要裂隙密度,对岩溶发育的影响较大。相对于次要裂隙,如果主要裂隙密度偏小,紊流形成时间会大大增加,甚至很难形成紊流。当初始裂隙张开度小于0.001 cm,增大水力梯度仍没有紊流发生,岩溶几乎不发育。Abstract: In karst areas of China, there are many karst caves and underground river conduits in the underground aquifer. The development of large cave and conduit are controlled by many factors and it is not every karst aquifer would develop into conduit system, for example, the southern karst area with ample rainfall has many underground rivers, but in the northern arid and semi-arid karst area, underground rivers are relatively rare. The flow states in conduits may be laminar or turbulent. Turbulent flow is an important condition of forming large-scale caves and conduits. In turbulent state, the water flow begin to have the ability of mechanical transportation, which would carry the solid granule and cause the impact and erosion into surrounding rock. The powerful mechanical erosion of turbulence is very important for karst aquifer to develop into large scale conduits and caves. Furthermore, the dissolution rate of carbonate rock in turbulent flow is at least one order of magnitude faster than laminar flow condition. Therefore, the mechanical erosion and chemical dissolution in turbulent flow make the development of conduit and cave more possible. However, the occurrence of turbulent flow is rigidly affected by the hydraulic condition and the initial medium of the aquifer, such as the initial rock fracture, including the aperture, direction, length and density of initial fractures. So we designed different statistic features of fractures and different hydraulic gradients to study the flow state and dissolution widening rates of fractures by numerical simulation. The cubic law and Lomize equation were used to model the laminar and turbulent flow state in fracture. The Newton-Raphson iteration is high-performance to solve the nonlinear flow equation system of laminar and turbulent flow. Then the dissolution rate equation and the Ca2+ concentration equation system was employed to model the widening of the fractures. The simulation results and discussions were all under given outer environment with PCO2 0.8% and hydraulic gradient 0.02. The modeling results of fracture aperture showed that when the standard deviation of aperture was 0.0005 cm and the mean of aperture is 0.006, there was no turbulence in the modeling period of 5,000 thousand years. But when the standard deviation was increased to 0.001 cm, the turbulent flow emerged on 189 thousand year and the time was greatly shorten. In the 8 modeling aperture statistic situations, as the mean and the standard deviation of aperture increased and the heterogeneity of fractures was more intensive, the turbulent flow began to appear and the time of turbulence became earlier. The existence of primary fractures led to much heterogeneous aquifer and earlier turbulent time. The results of fracture direction modeling scenes showed that when the angle between the direction of primary fractures and the direction of main hydraulic gradient was smaller, the turbulence time would be shorter. If the mean of fracture length is too little, the connectivity of fracture would become poor and the karst dissolution would be heavily restricted. The fracture density, especially the primary fracture density, had much influence on the karst development. Compared with the secondary fractures, if the density of primary fractures was too smaller, the turbulence time would largely increase, and even no turbulence in the whole simulation. We also discussed the influence of hydraulic gradient on the turbulent time. The hydraulic gradient varied from 0.001 to 1 and the mean of aperture was from 0.001 to 0.005. The results showed that for each aperture, it had the corresponding smallest hydraulic gradient to the occurrence of turbulence and the greater gradient the turbulent time would become earlier. Below the smallest hydraulic gradient the turbulence would never occur. If the mean of aperture is less than 0.001cm, no matter how the hydraulic gradient is increased, the flow state in fractures remained laminar and no turbulence occurred, in which karst is nearly not developed in the aquifer. In conclusion, the occurrence time of turbulent flow reflects the possibility of forming large karst conduits and caves in present aquifer. The shorter the time is, the greater the possibility will be.
-
Key words:
- initial fractures /
- karst conduit /
- turbulent flow /
- dissolution /
- numerical modeling
-
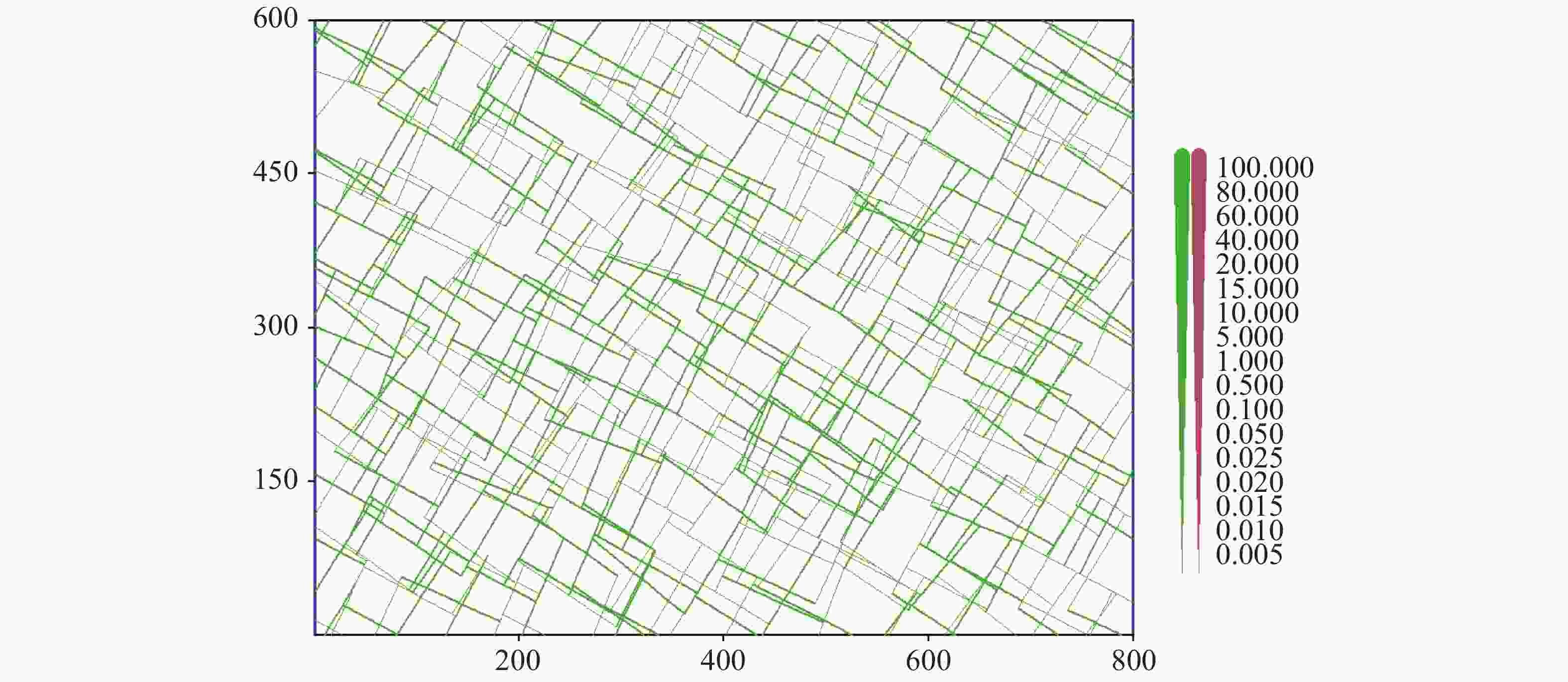
图 1 裂隙含水层模拟500万年的水流状态和张开度分布(含水层长宽单位为m,张开度单位为cm)
绿色代表层流,初始时刻模拟图与500万年相同
Figure 1. Flow state and apertures of the fracture aquifer at 5 million year which is similar to the initial state, where the green lines represent laminar flow, the unit of the aquifer length is m, the aperture is shown with the line width, and the unit of aperture is cm
图 2 第1组裂隙张开度增大后的含水层水流状态和张开度分布( 图中含水层长度单位为m, 张开度单位为cm)
(a)为初始时刻,(b)为50万年,(c)为70万年,(d)为83.9万年出现紊流,红色代表紊流
Figure 2. Flow state and apertures of the aquifer with the first group fracture aperture increased
(a) initial time, (b) 500 thousand year, (c) 700 thousand year, (d) 839 thousand year, where the red lines represent turbulent flow
图 4 (a)模拟情形E水平裂隙逆时针旋转45度的含水层在82.3万年出现紊流;(b)在图2中将第二组裂隙扩大为主要裂隙的含水层在21.7万年出现紊流, 图中含水层长度单位为m, 张开度单位为cm
Figure 4. (a) Turbulent time 823 thousand year of the aquifer based on model E in which the plane fractures were rotated 45° counterclockwise, (b) Turbulent time 217 thousand year with the second group of fractures widen into primary fractures
表 1 随机裂隙网络统计参数
Table 1. Statistic parameters of the random fracture network
裂隙组 统计参数 服从分布 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 走向 正态分布 30 5 15 45 第一组 迹长/m 对数正态分布 130 10 100 160 张开度/cm 正态分布 0.005 0.001 0.002 0.008 走向 正态分布 120 5 105 135 第二组 迹长/m 对数正态分布 130 10 100 160 张开度/cm 正态分布 0.005 0.001 0.002 0.008 表 2 不同模拟情形的初始裂隙张开度统计参数和紊流出现时间
Table 2. Statistic parameters of the initial aperture and the turbulent time in different simulations
模拟情形 均值/cm 标准差/cm 99.7%置信区间/cm 紊流出现时间/万年 A 0.005 0.001 0.002 0.008 >500 B 0.006 0.000 5 0.004 5 0.007 5 >500 C 0.006 0.001 0.003 0.009 18.9 D 0.006 0.001 5 0.001 5 0.010 5 12.0 E 0.008 − − − 42.7 F 0.008 0.000 5 0.006 5 0.009 5 20.3 G 0.008 0.001 0.005 0.011 14.3 H 0.008 0.001 5 0.003 5 0.012 5 9.0 -
[1] 袁道先, 朱德浩, 翁金桃, 朱学稳, 韩行瑞, 汪训一, 蔡桂鸿, 朱远峰, 崔光中, 邓自强. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993YUAN Daoxian, ZHU Dehao, WENG Jintao, ZHU Xuewen, HAN Xingrui, WANG Xunyi, CAI Guihong, ZHU Yuanfeng, CUI Guangzhong, DENG Ziqiang. Karst of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993. [2] 王大纯, 张人权, 史毅虹, 许绍倬, 于青春, 梁杏. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995WANG Dachun, ZHANG Renquan, SHI Yihong, XU Shaozhuo, YU Qingchun, LIANG Xing. Fundamentals of hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1995. [3] Yu Q, Shen J, Wan J, Ohnishi Y. Some investigation on early organization of karst system[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1999, 10:314-321. [4] Dreybrodt W. The role of dissolution kinetics in the development of karst aquifers in limestone: A model simulation of karst evolution[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1990, 98(5):639-655. doi: 10.1086/629431 [5] Liu Z, Dreybrodt W. Dissolution kinetics of calcium carbonate minerals in H2O CO2 solutions in turbulent flow: The role of the diffusion boundary layer and the slow reaction H2O+ CO2→ H++ HCO3−. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(14): 2879-2889. [6] Groves C G, Howard A D. Minimum hydrochemical conditions allowing limestone cave development[J]. Water Resources Research, 1994, 30(3):607-615. doi: 10.1029/93WR02945 [7] Gabrovšek F, Romanov D, Dreybrodt W. Early karstification in a dual-fracture aquifer: The role of exchange flow between prominent fractures and a dense net of fissures[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2004, 299(1-2):45-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.02.005 [8] Kaufmann G. Modelling karst geomorphology on different time scales[J]. Geomorphology, 2009, 106(1):62-77. [9] Reimann T, Rehrl C, Shoemaker W B, Geyer T, Birk S. The significance of turbulent flow representation in single‐continuum models[J]. Water Resources Research, 2011, 47(9):1-15. [10] Howard A D, Groves C G. Early development of karst systems: 2. turbulent flow[J]. Water Resources Research, 1995, 31(1):19-26. doi: 10.1029/94WR01964 [11] Gabrovšek F, Peric B, Kaufmann G. Hydraulics of epiphreatic flow of a karst aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 560:56-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.019 [12] Dreybrodt W. Principles of early development of karst conduits under natural and man‐made conditions revealed by mathematical analysis of numerical models[J]. Water Resources Research, 1996, 32(9):2923-2935. doi: 10.1029/96WR01332 [13] 于青春, 武雄, 大西有三. 非连续裂隙网络管状渗流模型及其校正[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(7):1469-1474.YU Qingchun, WU Xiong, Ohnishi Yuzo. Channel model for fluid flow in discrete fracture network and its modification[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(7):1469-1474. [14] 王云, 于青春, 薛亮, 马浩. 裂隙岩溶含水系统溢流泉演化过程的数值模拟[J]. 中国岩溶, 2010, 29(4):378-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.04.005WANG Yun, YU Qingchun, XUE Liang, MA Hao. Numerical simulation for the evolution of the overflow spring in fracture-karst aquifer system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2010, 29(4):378-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2010.04.005 [15] 高阳, 邱振忠, 于青春. 层流—紊流共存流场中岩溶裂隙网络演化过程的数值模拟方法[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(6):831-838.GAO Yang, QIU Zhenzhong, YU Qingchun. Numerical simulating method for the karst development of carbonate fracture networks with both laminar and turbulent flow[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(6):831-838. [16] 刘再华, Dreybrodt W. DBL理论模型及方解石溶解沉积速率预报[J]. 中国岩溶, 1998, 17(1):1-7.LIU Zaihua, DREYBRODT Wolfgang. The DBL model and prediction of calcite dissolution / precipitation rates[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1998, 17(1):1-7. -




 下载:
下载:







