Study on ecological restoration strategy of karst spring region in north China:Taking Jinci spring as an example
-
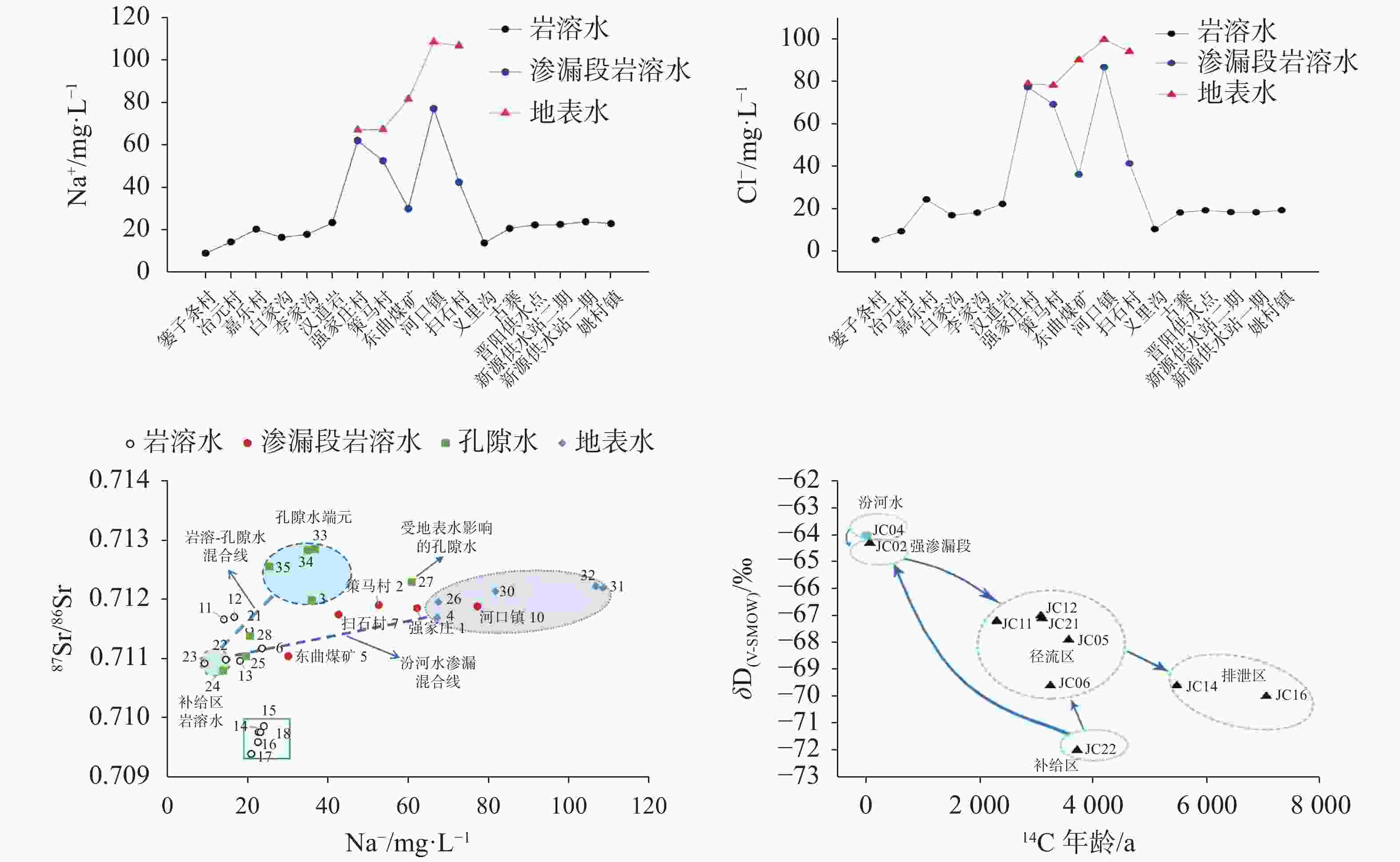
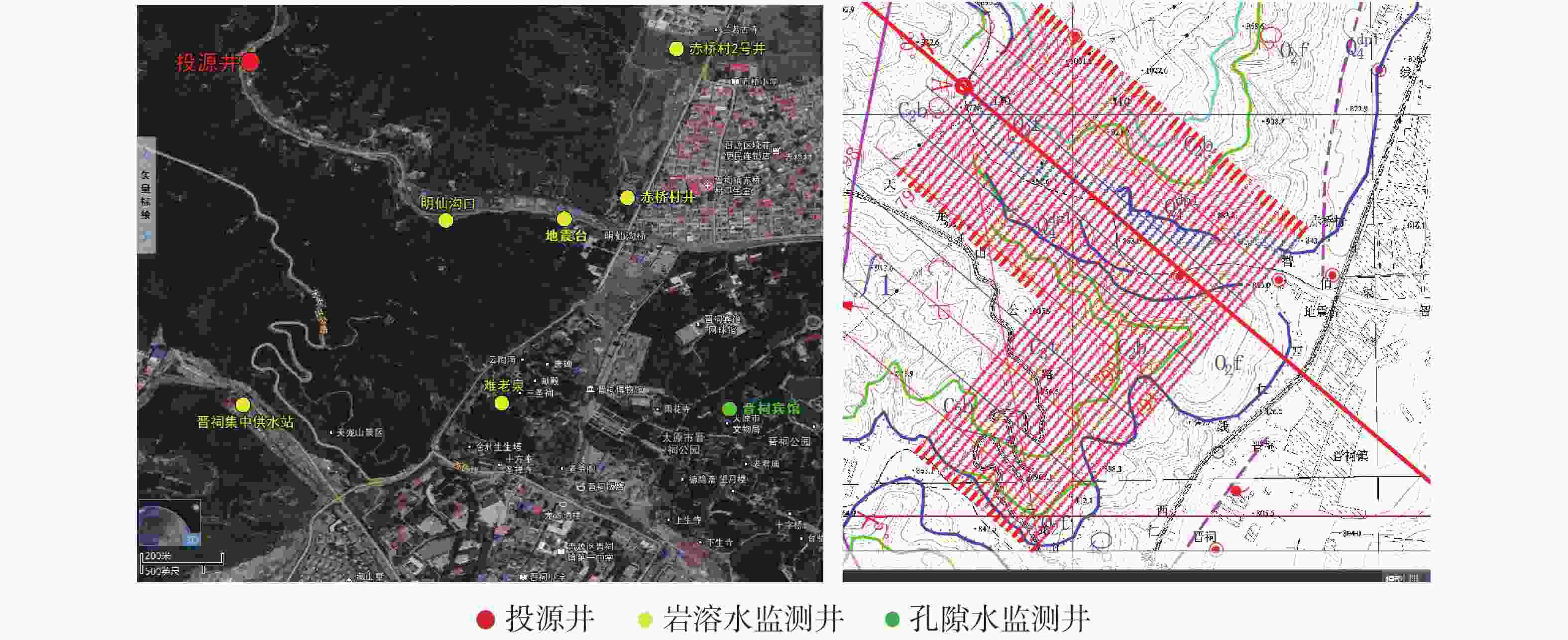
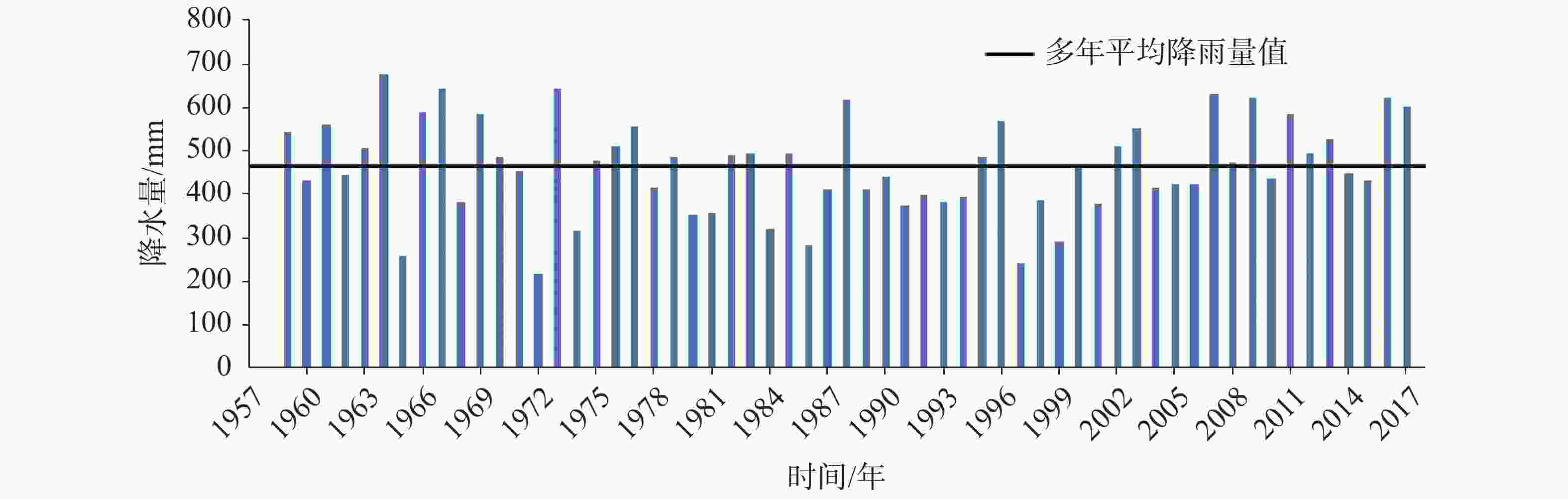
摘要: 我国北方岩溶分布面积广,岩溶泉水资源丰富,是岩溶区工农业及居民生活的优质供水水源。但在全球气候变化和采煤等强烈人类活动的叠加作用下,我国北方岩溶泉水流量衰减,水质恶化,岩溶泉域生态环境功能下降。通过合理、适度的人工干预,强化岩溶大泉的自然恢复机能,并最终实现泉域生态环境修复,是当前我国生态文明建设的先行区和重点领域。论文在分析研究晋祠泉断流原因的基础上,针对性地提出并科学地评估了汾河二库强化渗漏补给、泉域岩溶水关井压采、煤矿区保水限采、近源生态补水和远源河道渗漏补给等一系列措施及预期效果,以期推进晋祠泉域岩溶地下水生态环境得到根本性改善。该研究工作有望对我国北方岩溶大泉的生态修复形成示范效应,为遏制我国岩溶区生态恶化现象提供科学依据。Abstract: In northern China, karst is widely distributed and rich in karst spring water resources. It is a high-quality water supply source for industry, agriculture and residents’ life in karst areas. However, under the superposition of global climate change, coal mining and other strong human activities, the flow of karst springs in northern China has declined, the water quality has deteriorated, and the ecological environment function of karst springs has declined. Therefore, how to take reasonable measures, strengthen the natural recovery function of karst springs through appropriate manual intervention, and finally realize the ecological environment restoration of spring area is the leading area and key field of ecological civilization construction in China. On the basis of analyzing and studying the causes of Jinci spring cutoff, the paper puts forward and scientifically evaluates a series of measures and expected results, such as strengthening leakage recharge of Fenhe ReservoirⅡ, closing and pressure mining of karst water in spring area, water conservation and limited mining in coal mine area, near source ecological water replenishment and far source river leakage recharge, in order to promote the fundamental improvement of karst groundwater ecological environment in Jinci spring area. The research work of this paper is expected to form a demonstration effect on the ecological restoration of karst springs in northern China, and provide a scientific basis for curbing the ecological deterioration in karst areas in China.
-
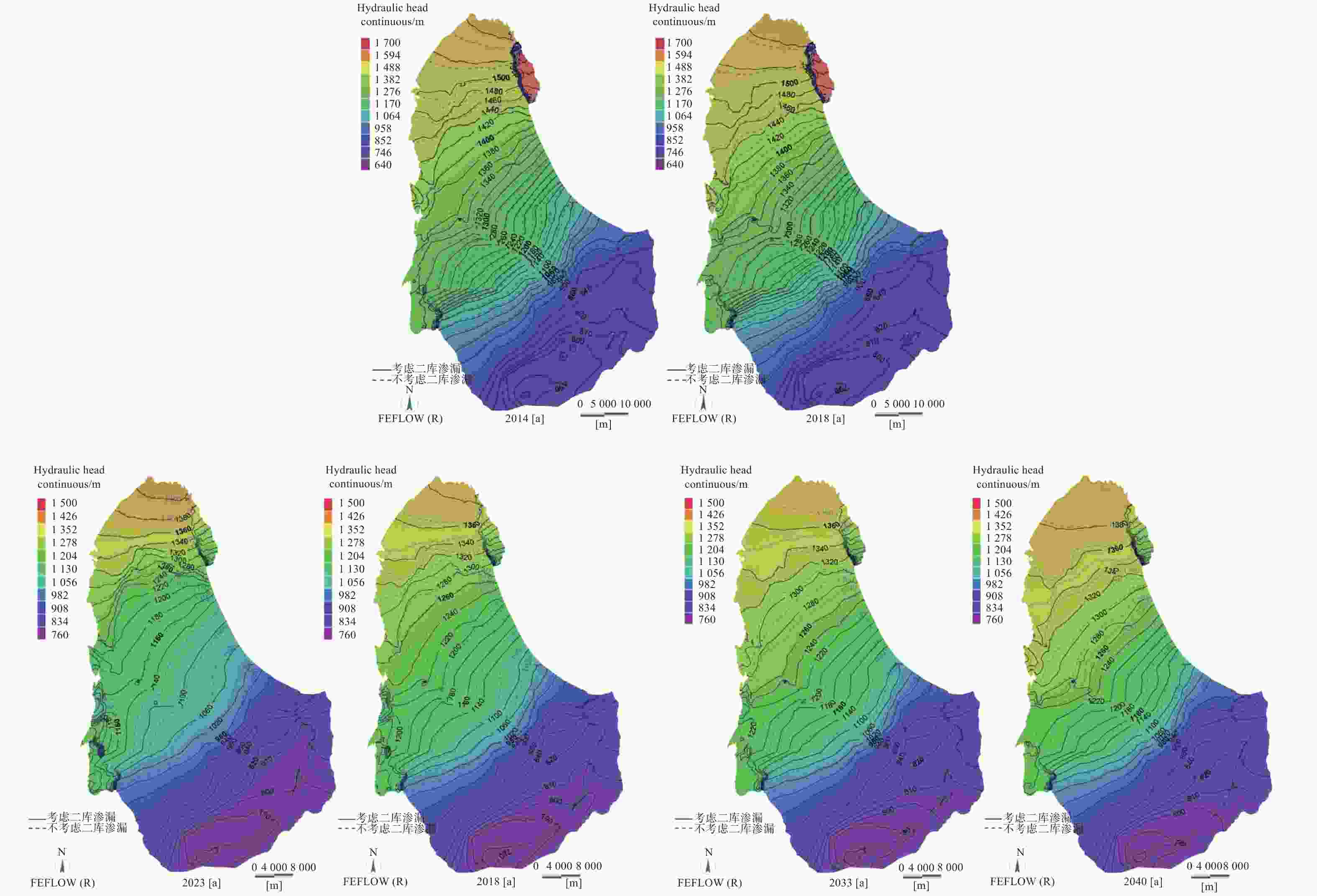
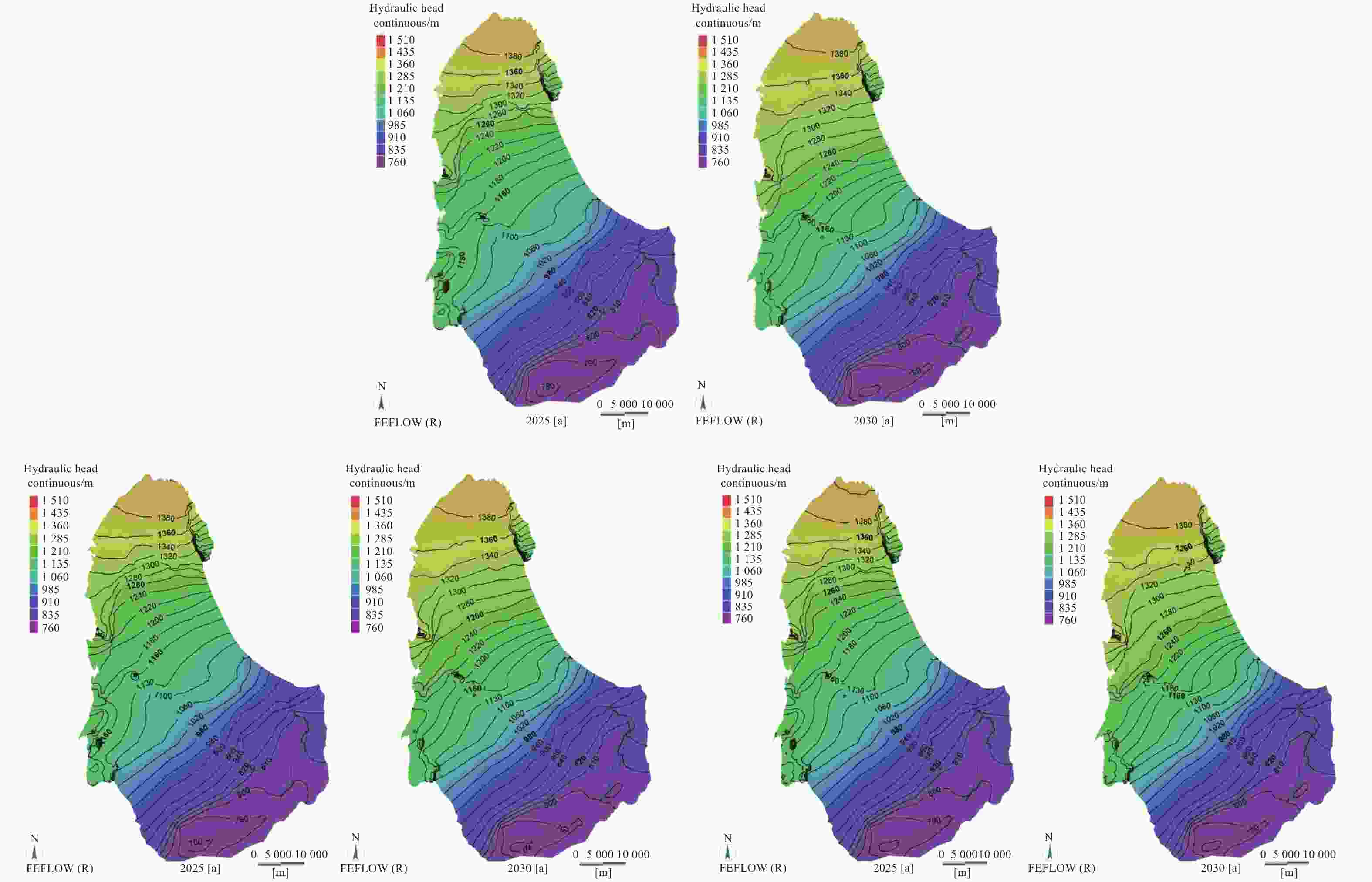
表 1 泉域岩溶地下水水均衡摘要表
Table 1. Summary of karst groundwater balance in spring area
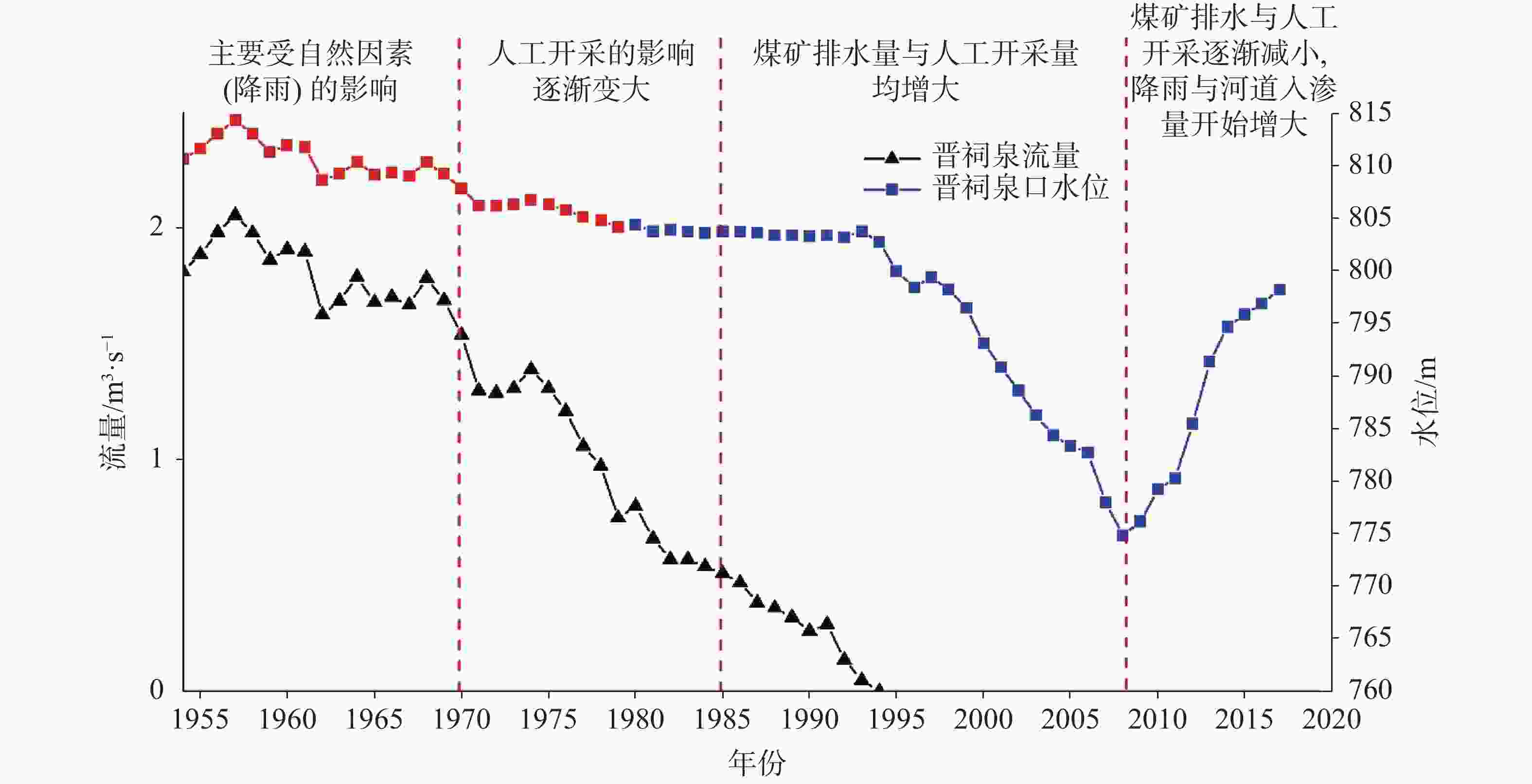
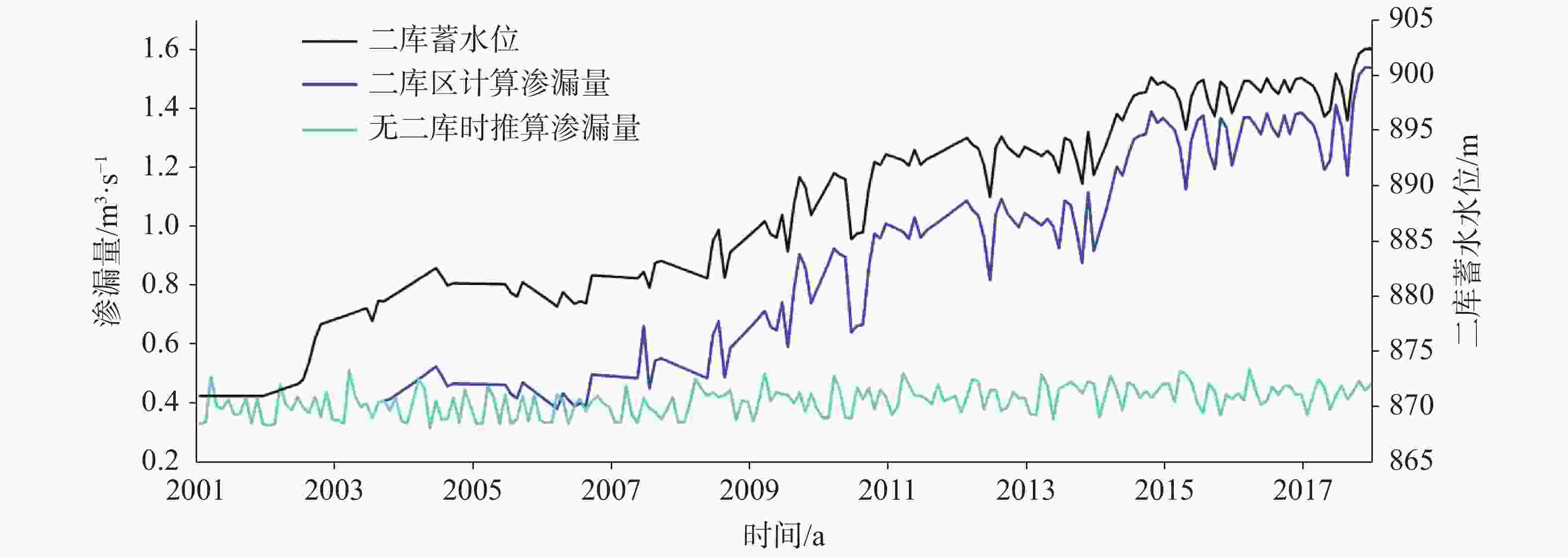
收入/m3·s−1 支出/m3·s−1 1959-1963 1984-1988 2013-2017 1959-1963 1984-1988 2013-2017 降雨入渗 3.299 2.823 3.418 泉(自流井) 1.798 0.959 0.261 河流渗漏量 0.955 0.742 1.022(2.254*) 开采 0.307 1.289 1.251 侧向排泄 1.954 1.889 2.059 总计 4.254 3.565 4.44 4.059 4.137 3.572 注:(*)为考虑了汾河二库渗漏的情况。 -
[1] 梁永平, 赵春红. 中国北方岩溶水功能[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(s2):297-299,305.LIANG Yongping ZHAO Chunhong. Karst water function in norther China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(s2):297-299,305. [2] 张晓博. 采煤活动影响下娘子关岩溶水系统演化研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.ZHANG Xiaobo. Study on the evolution of Niangziguan karst water system under the influence of coal mining activities[D]. China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017. [3] 吴潇. 柳林泉岩溶水系统水文地球化学演化及污染溯源研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2021.WU Xiao. Study on hydrogeochemical evolution and Pollution Tracing of liulinquan karst water system[D] . Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2021. [4] 梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 王志恒, 唐春雷, 赵 一, 谢 浩, 石维芝. 对中国北方岩溶水研究方向的思考与实践[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):363-380.LIANG Yongping, SHEN Haoyong, ZHAO Chunhong, WANG Zhiheng, TANG Chunlei, ZHAO Yi, XIE Hao, SHI Weizhi. Thinking and practice on the research direction of karst water in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3):363-380. [5] 廖资生. 论北方岩溶水资源的开发与管理问题[J]. 中国岩溶, 1985, 4(Z1):107-114.LIAO Zisheng. On development and management of karst water resource in north China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1985, 4(Z1):107-114. [6] 刘启仁, 张凤岐, 秦毅苏, 周俊业, 董玉良, 马潭, 何斌, 白世英, 贾秀梅. 中国北方岩溶水资源的形成、分布与合理开发利用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1992(4):41-44.LIU Qiren, ZHANG Fengqi, QIN Yisu, ZHOU Junye, DONG Yuliang, MA Tan, HE Bin, BAI Shiying, JIA Xiumei. Formation, distribution and rational development and utilization of karst water resources in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1992(4):41-44. [7] Zhang Xiaobo, Guo Jing, Hu Qianhong, et al. Effects of Fe-rich Acid Mine Drainage on Percolation Features and Porestructure in Carbonate Rocks[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 591:125571. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125571 [8] 薛凤海. 采煤保水:实现水资源的可持续利用[J]. 山西水利, 2011, 27(8):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7042.2011.08.004XUE Fengmei. Coal mining to protect water resources: Realizing the sustainable utilization of water resources[J]. Shanxi Water resources, 2011, 27(8):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7042.2011.08.004 [9] Li Chengcheng, Gao Xubo, Wang Wanzhou, et al. Hydro-biogeochemical processes of surface water leakage into groundwater in large scale karst water system: A case study at Jinci, northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology: 125691. [10] Jiang Chunfang, Gao Xubo, Hou Baojun, et al. Occurrence and environmental impact of coal mine goaf water in karstareas in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 275: 123813. [11] 李向全, 张春潮, 侯新伟. 采煤驱动下晋东大型煤炭基地地下水循环演变特征:以辛安泉域为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(9):3015-3026.LI Xiangquan, ZHANG Chunchao, HOU Xinwei1. Characteristics of groundwater circulation and evolution in Jindong large coal base driven by coal mining: An example of Xin’an spring area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(9):3015-3026. [12] 刘振明, 张仁豪, 杨萌, 候乐,托蓝河. 中国主要聚煤区含水层水文地球化学特性[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济, 2016(7):154-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0155.2016.07.089LIU Zhenming, ZHANG Renhao, YANG Men, HOU Le,TUO Lanhen. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of aquifers in major coal rich areas in China[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy, 2016(7):154-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0155.2016.07.089 [13] 许伟. 采煤影响下长治盆地含水层空间分区变化研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 2013. [14] 王志恒, 梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红,唐春雷,谢浩 ,赵一. 自然与人类活动叠加影响下晋祠泉域岩溶地下水动态特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(6):1823-1837.WANG Zhiheng, LIANG Yongping, SHEN Haoyong, ZHAO Chunhong, TANG Chunlei, XIE Hao, ZHAO Yi. Dynamic Characteristics of Karst Groundwater in Jinci Spring Under Superimposed Influence of Natural and Human Activities[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(6):1823-1837. [15] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 高列波, 张建友, 张松涛, 李成城, 姜春芳. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3):287-298.GAO Xubo, WANG Wanzhou, HOU Baojun, GAO Liebo, ZHANG Jianyou, ZHANG Songtao, LI Chengcheng, JIANG Chunfang. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3):287-298. [16] 刘盼, 李鹏翔, 陈斌,胡祥云,陈玲玉,廖卫阳. 山西晋祠泉复流:地球物理应用研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(25):58-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.25.009Liu Pan, Li Pengxiang, Chen Bin, HU Xiangyun, CHEN Lingyu, LIAO Weiyang. Reflow project of jinci spring in shanxi province: Application research of comprehensive geophysical prospecting methods[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(25):58-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.25.009 [17] 梁永平, 张发旺, 申豪勇, 唐春雷, 赵春红, 王志恒, 侯宏冰, 任建会, 郭芳芳. 山西太原晋祠—兰村泉水复流的岩溶水文地质条件新认识[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(1):11-18,34.LIANG Yongping, ZHANG Fawang, SHEN Haoyong, TANG Chunlei, ZHAO Chunhong, WANG Zhiheng, HOU Hongbin, REN Jianhui, GUO Fangfang. Recognition of the critical hydrogeological conditions of the Jinci Spring and Lancun Spring in Shanxi[J]. Hydrogeology&Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(1):11-18,34. [18] 冉曦, 顾盼, 连雷雷, 左 建, 邱瑞明. 采煤和岩溶水开采对晋祠泉出流影响的随机模型分析[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2018, 35(6):154-158.RAN Xi, GU Pan, LIAN Leilei, ZUO Jian, QIU Ruiming. Impact of Coal Mining and Karst Water Exploitation on Outflow of Jinci Spring: Stochastic Model Analysis[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2018, 35(6):154-158. [19] 钱鸣高, 许家林. 煤炭开采与岩层运动[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(4):973-984.QIAN Minggao, XU Jialin. Behaviors of strata movementin coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(4):973-984. [20] 唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平, 张发旺, 景泽. 山西太原晋祠—平泉水力联系及对晋祠泉复流的贡献[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1755-1764. doi: 10.12029/gc20200612TANG Chunlei, ZHENG Xiuqing, LIANG Yongping, ZHANG Fawang, JING Ze. The hydraulic connection between Jinci and Pingquan in Taiyuan andits contribution to the reflow of Jinci spring[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1755-1764. doi: 10.12029/gc20200612 [21] 石桂萍. 晋祠泉泉域变化分析与保护措施设计[J]. 水利技术监督, 2014, 22(1):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1305.2014.01.015SHI Guiping. Analysis on the change of water resources in Jinci spring area and design of protection measures[J]. Technical Supervision in Water Resources, 2014, 22(1):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1305.2014.01.015 [22] 李悦, 刘家宏, 桑学锋, 袁飞. 汾河清水复流生态调水量研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2013, 44(9): 21-24, 30.LI Yue , LIU Jiahong, SANG Xuefeng, YUAN Fei . Study on eco-water diversion quantity for clean water restoration of Fenhe River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering , 2013, 44(9): 21-24, 30. [23] 菅宇翔, 范永平, 孙瑞, 魏路峰. 晋祠泉补水工程的地下水环境影响及保护措施分析[J]. 水利水电工程设计, 2016, 35(3):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6980.2016.03.008JIAN Yuxiang, FAN Yongping, SUN Rui, WEI Lufeng. Analysis of groundwater environmental impact and protection measures of Jinci spring water replenishment project[J]. Design of Water Resources & Hydroelectric Engineering, 2016, 35(3):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6980.2016.03.008 [24] 李昕生. 明仙沟引蓄水工程设计方案比选[J]. 山西水利, 2017(3): 39-40.LI Xinsheng. Comparison and selection of design schemes of mingxiangou water diversion and storage project [J]. Shanxi Water Resources, 2017(3): 39-40. [25] 辛雁清. 汾河二库与太原市城市防洪[J]. 山西科技, 2013, 28(5): 22-23.XIN Yanqing . Fenhe Second Reservoir and Taiyuan City’s Urban Flood Control[J]. Shanxi Science and Technology, 2013, 28(5): 22-23. [26] 郭芳芳, 梁永平, 王志恒, 申豪勇,赵春红. 山西太原西山汾河二库的泉域归属及其渗漏量计算[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):493-500.GUO Fangfang, LIANG Yongping, WANG Zhiheng, SHEN Haoyong, ZHAO Chunhong. Attribution of spring fields and seepage calculation of Fenhe second reservoir in Xishan, Taiyuan, Shanxi Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4):493-500. [27] 李劭宁, 贾晓鹏. 格尔木河 222Rn同位素变化及其对地表水-地下水交互关系的指示意义[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(4):1190-1199.LI Shaoning, JIA Xiaopeng. Variability of 222Rn in Golmud River and its implication for surface-groundwater interaction[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2021, 43(4):1190-1199. [28] Bicalho C, Batiot-guilhe C, Taupin J, et al. A Conceptual Model for Groundwater Circulation Using Isotopes and Geochemical Tracers Coupled with Hydrodynamics: a Case Study of the Lez Karst System, France[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 528:118442. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.08.014 [29] 常建忠. 山西省岩溶大泉地下水超采治理保护措施与经验[J]. 中国水利, 2021(7):43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2021.07.018CHANG Jianzhong. Control of overdraft of karst spring groundwater in Shanxi Province: measures and experiences[J]. China Water Resources, 2021(7):43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2021.07.018 [30] 王志恒, 梁永平, 唐春雷, 申豪勇,赵春红,郭芳芳,谢浩,赵一. 北方断流岩溶大泉复流的生态修复模式与复流措施效果的定量评价:以山西太原晋祠泉为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1726-1738. doi: 10.12029/gc20200610WANG Zhiheng, LIANG Yongping, TANG Chunlei, SHEN Haoyong, ZHAO Chunhong, GUO Fangfang, XIE Hao, ZHAO Yi. Ecological restoration pattern and quantitative evaluation of recirculation measures for northern discontinuous karst spring: A case study of Jinci Spring in Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1726-1738. doi: 10.12029/gc20200610 [31] 陆帅帅, 郑秀清, 李旭强, 陈军锋, 张永波, 臧红飞. 晋祠泉域岩溶水生态系统健康评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(1):34-41.LU Shuaishuai, ZHENG Xiuqing, LI Xuqiang, CHEN Junfeng, ZHANG Yongbo, ZANG Hongfei. Health assessment of karst groundwater ecosystem of Jinci spring area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1):34-41. -




 下载:
下载: