Study and prospect of karst collapse columns and their water inrush in the coalfield of North China
-
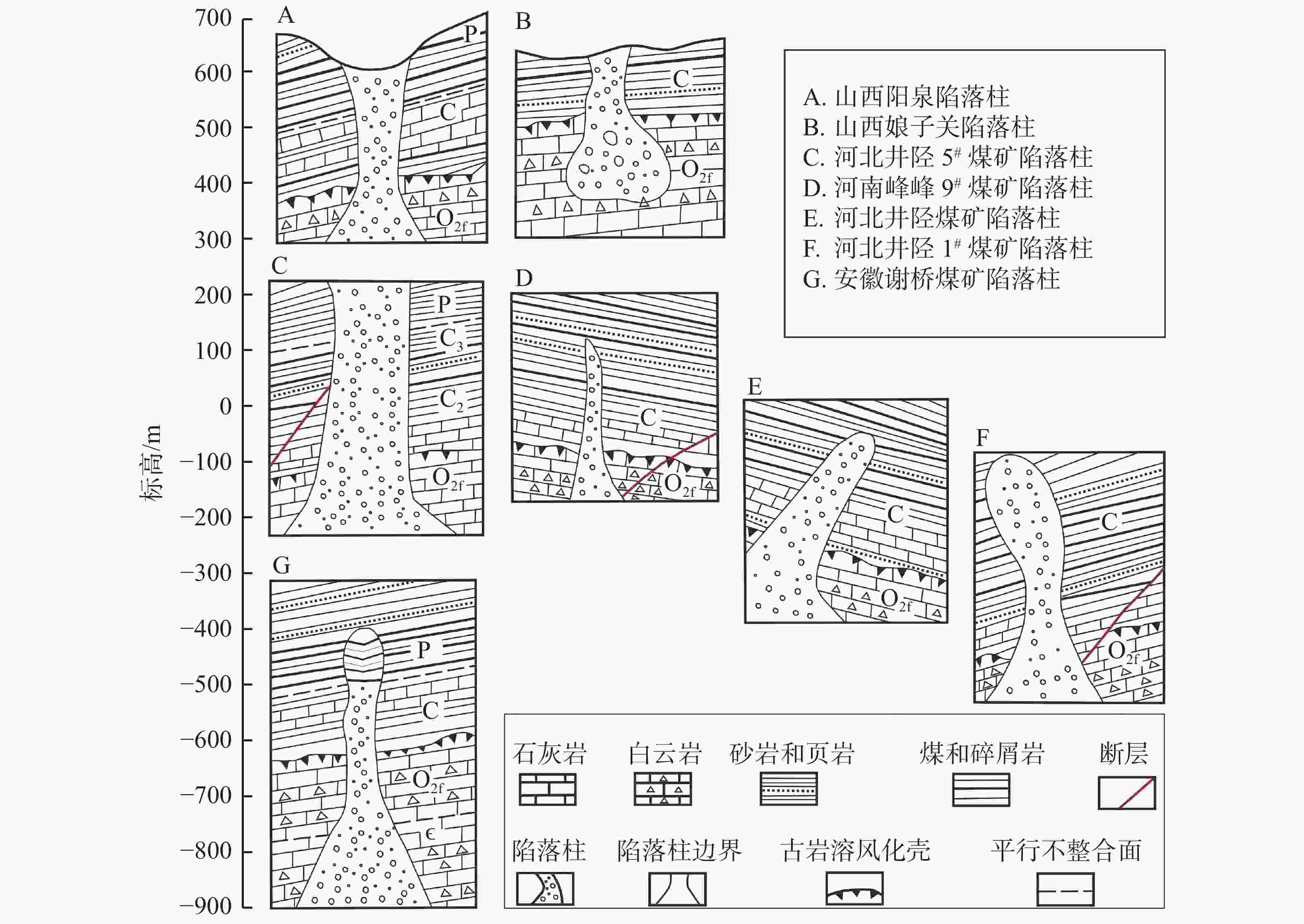
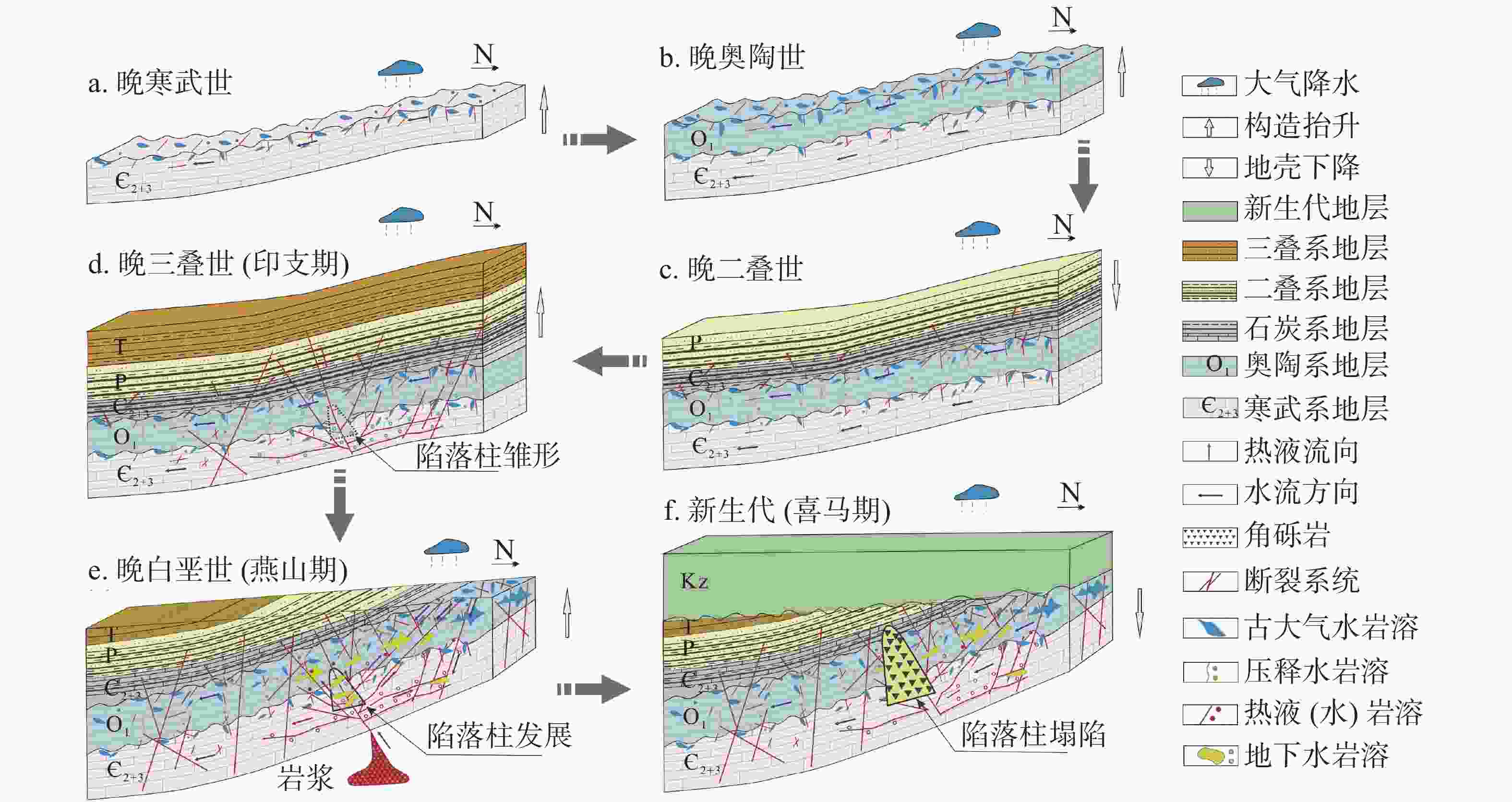
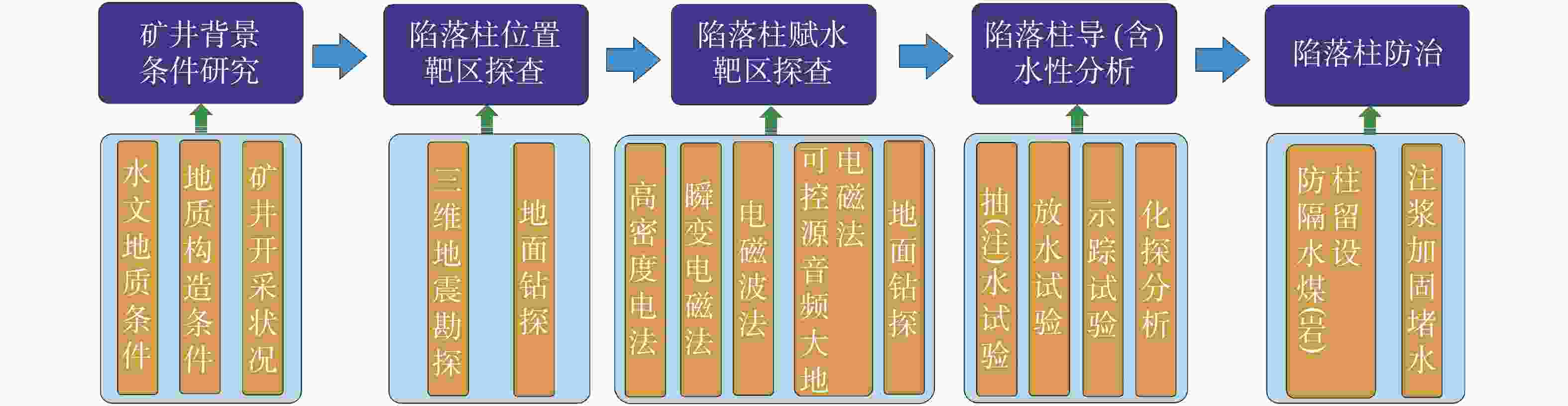
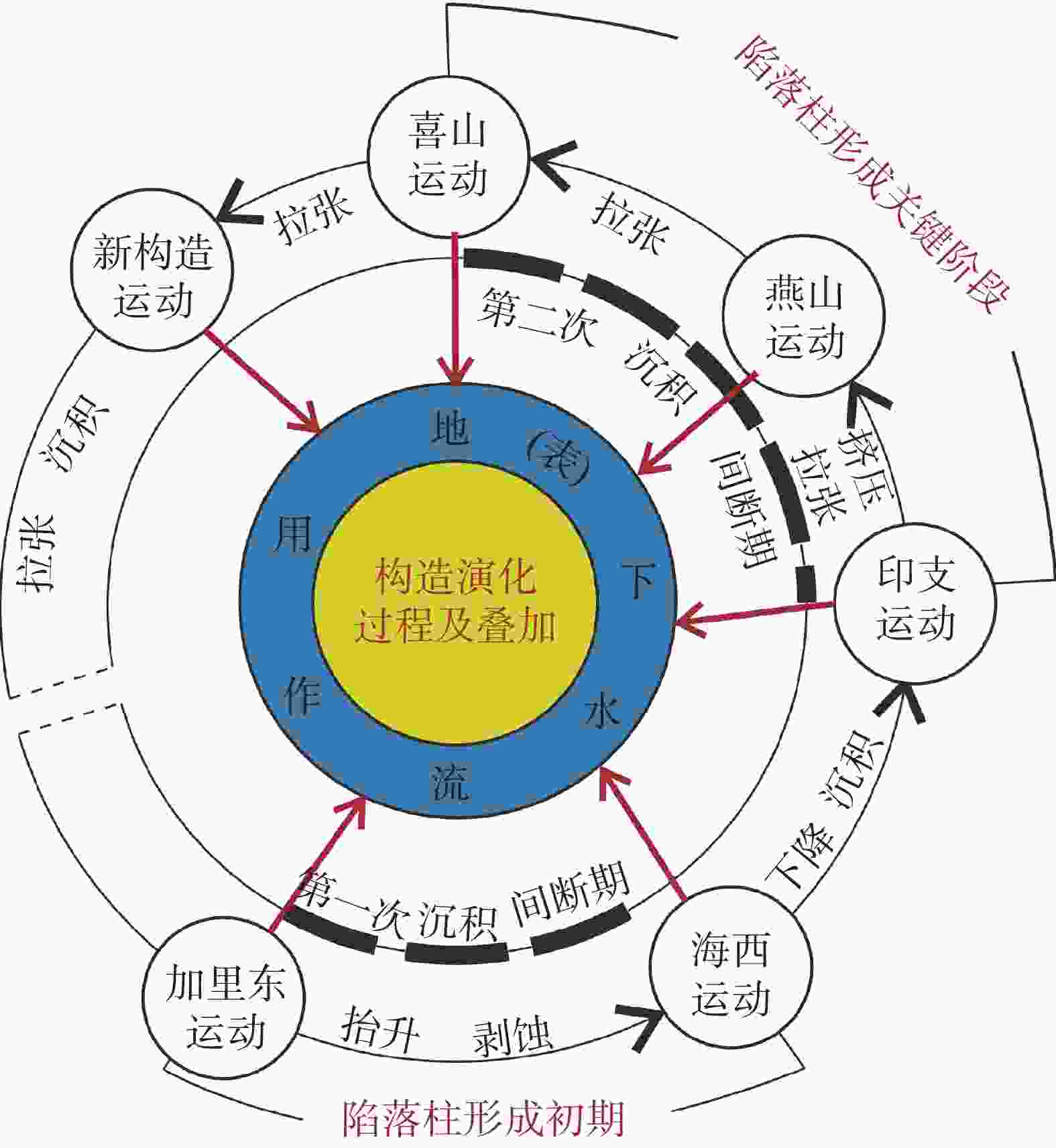
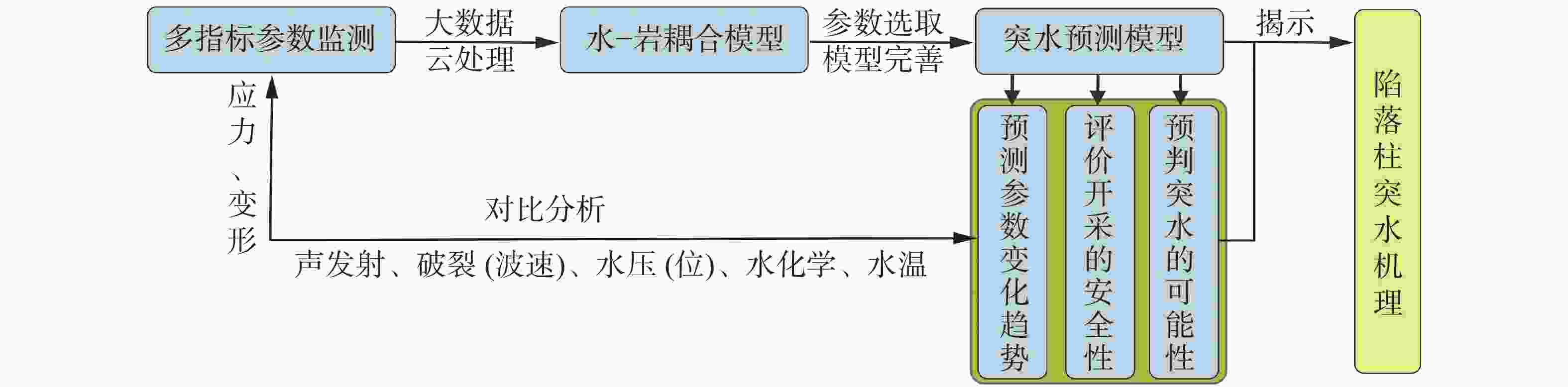
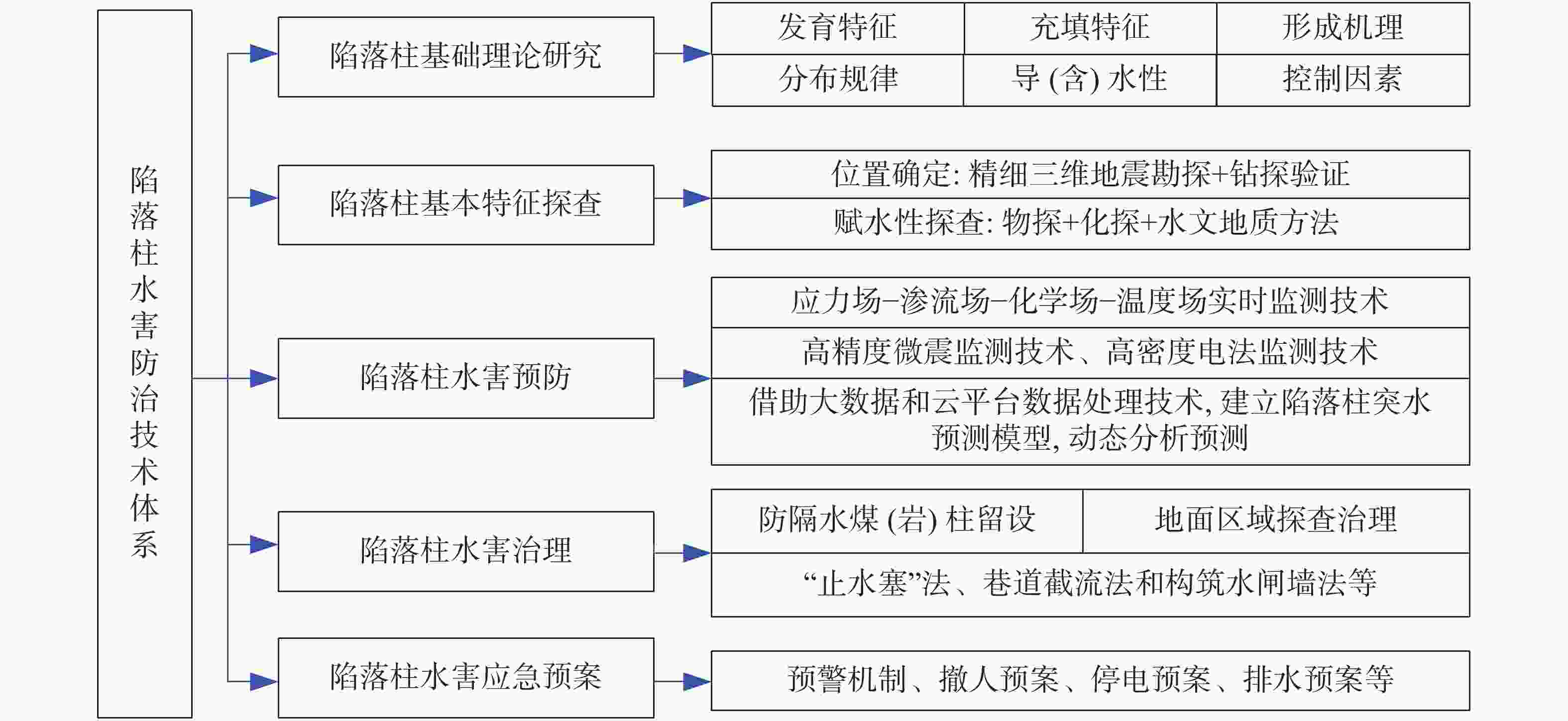
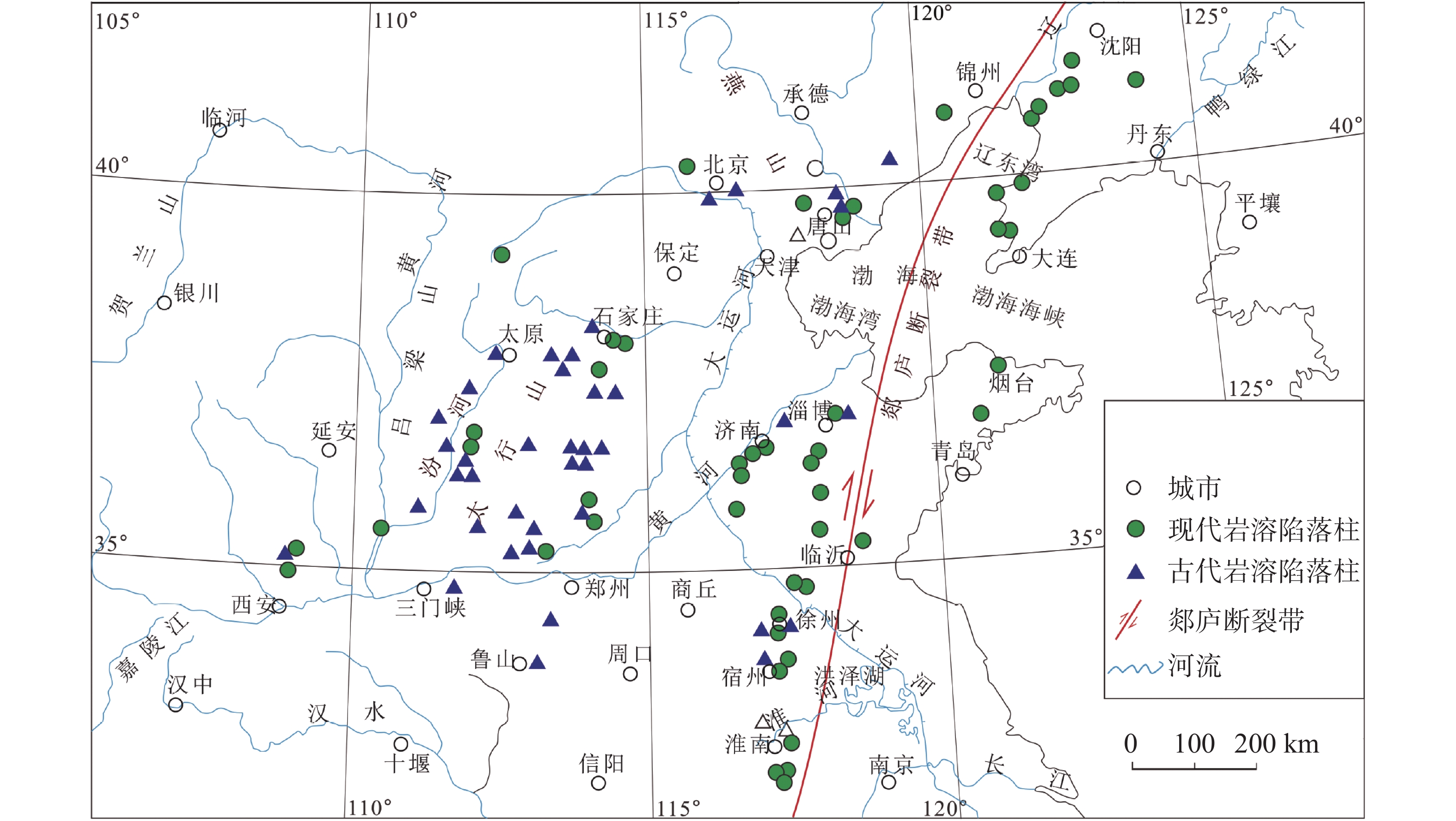
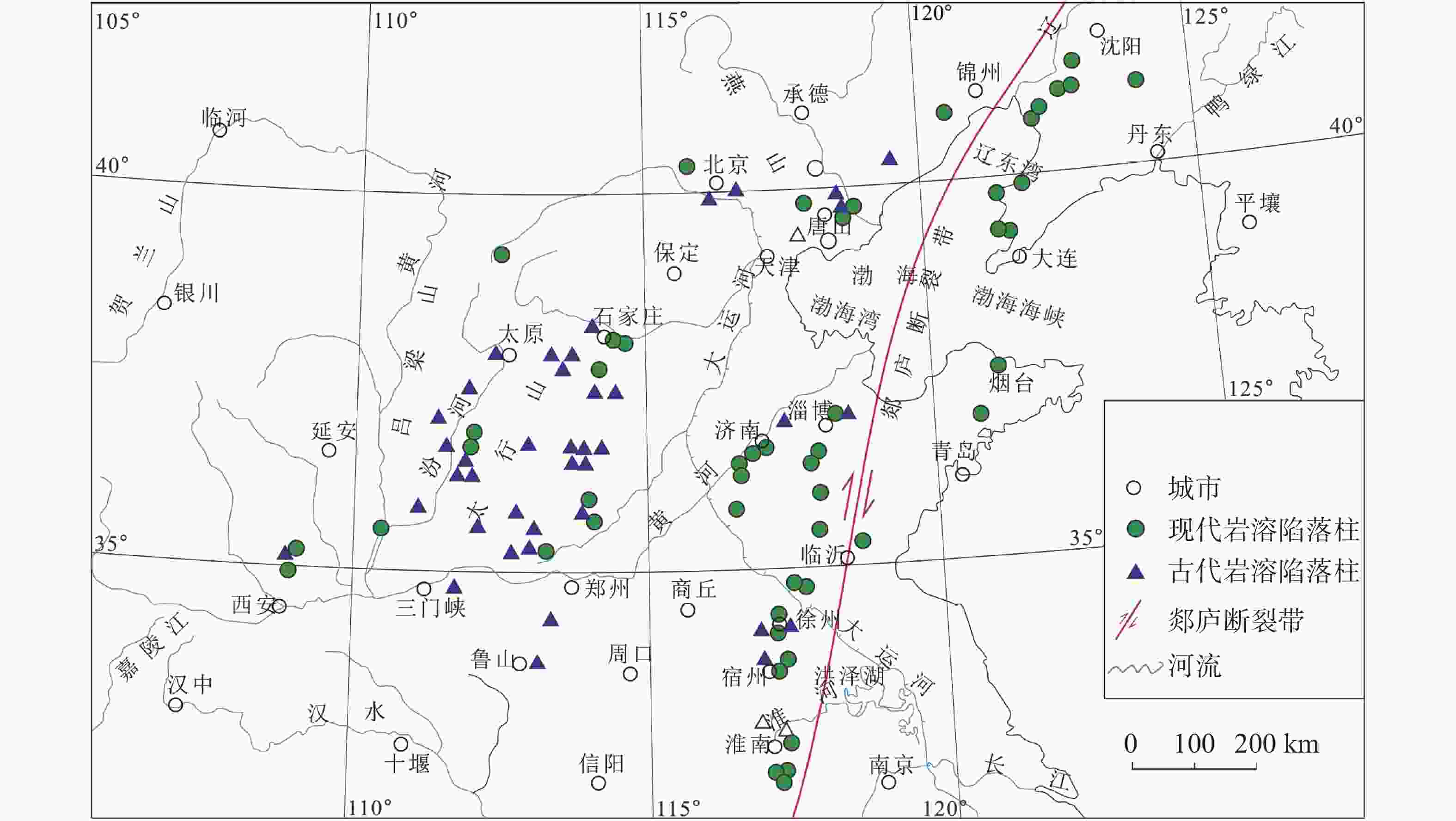
摘要: 华北煤田岩溶陷落柱(简称“陷落柱”)是地质历史演化过程中形成的产物。80多年来,在中国华北煤田39个矿区煤矿开采过程中共揭露10 000多个陷落柱,因其导致的重大突水淹井事故20余起,研究岩溶陷落柱对系统认识中国矿山岩溶水文地质条件以及防治岩溶水害具有十分重要的理论与现实意义。文章系统梳理、总结了华北煤田陷落柱的发育特征、成因机理、突水机理、探查与防治方法,归纳出近年来华北南缘陷落柱的研究成果,并结合目前华北煤田生产过程中陷落柱研究与水害防治中存在的问题,从陷落柱形成机理与演化过程、小型隐伏陷落柱精细化探查与解译、陷落柱“动态监测—预测模型—突水机理”模式以及陷落柱水害防治技术体系等方面展望了其今后研究趋势及水害防治的方向。Abstract: Karst collapse columns (KCCs) are formed in the process of geological evolution in North China coalfield. Their roots are developed in the Ordovician or Cambrian carbonate rocks, and pass upward through Carboniferous, Permian, Triassic strata, and even enter the Jurassic, Cretaceous and Quaternary loose rock strata. Over the past 80 years, more than 10,000 mines have been exposed in 39 mining areas in the coalfields of North China, resulting in more than 20 major water inrush accidents. Therefore, the study on KCCs is of important theoretical and practical significance for the systematic understanding of karst hydrogeological conditions of mines in North China and of prevention and control of karst water disaster as well.This study systematically summarized the spatial distribution characteristics of KCCs in the coalfields of North China, mainly focusing the areas along the Fenhe river, the western foothills of Taihang mountain, the foothills of eastern and southeastern Taihang mountain, the foothills of southern Yanshan mountain, and the west side of the Tanlu fault zone. The plane shapes of KCCs are mostly circular and elliptical, and their cross-sections are mainly cone-shaped. KCCs are usually filled and cemented by broken debris of wall rock and secondary minerals, so most of the collapsed columns in the coalfields do not conduct (contain) water, and only few cases of water inrush occur there. KCCs usually form in such basic conditions as soluble rocks and special stratigraphic structures, multi-stage and multi-source fluid erosiveness, geological tectonic evolution, and paleokarst groundwater flow. Five theories on the genesis mechanism have been put forward, namely “karst gravity collapse”, “gypsum dissolution collapse”, “vacuum absorption collapse”, “hydrothermal origin” and “groundwater internal circulation”.According to the current research on the formation and evolution of KCCs in the Huainan coalfield in the southern margin of North China, this study shows that consisting of Ordovician or Cambrian carbonate rocks, KCCs move through fluid migration channels of faults and fractures generated by multi-stage tectonic movements in this area, and are accommodated with the paleokarst formed by dissolution in the carbonate rocks. After a long-term process of dissolution, transportation, and collapse, KCCs are finally formed with the joint effect of the self-gravity of the rock mass, the in-situ stress, and the vacuum negative pressure in the cave. The formation of KCCs is related to the multi-stage tectonic movements in Mesozoic, and the Yanshan movement might be the key stage of its formation and development.In this study, the water inrush mechanism of KCCs in the mining process is reviewed from the aspects of mining-induced water inrush mechanism, seepage transformation mechanism, and water inrush model. Four modes of water inrush of KCCs in working face or roadway, as well as the mechanical mechanism and seepage transformation mechanism of water inrush are analyzed, and the reasons for the sudden and hysteresis of water inrush are also explained. The technical route for KCC detection and prevention are determined by geophysical prospecting, geochemical prospecting, roadway prospecting, drilling, and hydrogeological conditions.At present, the prevention and control of KCC water disaster is mainly carried out from two aspects,exploration and treatment. In terms of exploration, several methods can be used. The technology of three-dimensional seismic exploration can be adopted to preliminarily determine the impacted area of collapse columns. The comprehensive geophysical method can be used to detect the water-bearing area of KCCs. The exact location, shape and hydrogeological characteristics of KCCs can be determined by methods of drilling, the test of pumping (draining) water, geochemical exploration and others. In terms of treatment, two methods can be mainly adopted,water-proof coal (rock) pillar retention and grouting reinforcement/water blocking to cut off the hydraulic connection between the KCCs water channel and the water inrush source. This technology has been successfully applied in the treatment of KCCs in the mining areas subject to karst water disaster such as Hebei and Anhui.As to the research gap and deficiency in the prevention of water disaster caused by KCCs, the following suggestions are put forward,(1) Under the guidance of earth system science, the study on evolution of KCCs can be conducted combined with the formation mechanism of KCCs. Meanwhile, a multidisciplinary method involving petrology, structural geology, hydrology, geomorphology, karst hydrogeology, GIS, RS, and others can also be applied based on the time axis of evolution of regional geological structure.(2) For the precise detection, data and interpretation of small hidden collapse columns, efforts should be made to perfect the basic theory of full-space physics, to develop new equipment, new technologies and new methods, to further improve the precision, resolution, anti-interference competence of geophysical exploration, and to increase the detection depth.(3) Research on the KCCs model of “dynamic monitoring-prediction model-water inrush mechanism” should be conducted. Firstly, a dynamic monitoring system to obtain parameters such as stress, deformation, acoustic emission, rupture (wave velocity), water pressure (position), water chemistry, and water temperature during the water inrush process of KCCs can be established, and an indicator monitoring instrument of stable multi-parameter can be developed. Secondly, with the help of big data and data processing technology of cloud platform, a multi-parameter integrated water inrush prediction model of KCCs can be established based on the dynamic monitoring system characterized by information transmission and the existing water-rock coupling numerical model.(4) The prevention and control technology system of KCCs water disaster should be established and improved. This system will mainly include the technical subsystem such as basic theoretical research on KCCs formation, exploration of KCC basic characteristics, prevention, management and emergency planing of KCC water disaster. In short, the establishment of the system is of important theoretical and practical significance for the research of KCCs and water disaster control.
-
表 1 华北煤田部分煤矿陷落柱突水淹井事故
Table 1. Water inrush accidents of KCCs in some coal mines in North China
序号 突水煤矿 突水日期 最大突水量 /m3·min−1 危害程度 1 河南焦作利丰煤矿 1967年3月29日 120 矿井被淹 2 河北开滦范各庄煤矿 1984年6月2日 2053 相邻4对矿井被淹 3 山东肥城国家庄煤矿 1993年1月5日 550 矿井被淹 4 安徽皖北任楼煤矿 1996年3月4日 576 矿井被淹 5 江苏徐州张集煤矿 1997年2月18日 402 矿井被淹 6 河北邢台东庞煤矿 2003年4月12日 1167 矿井被淹 7 河北峰峰九龙煤矿 2009年1月8日 120 矿井被淹 8 内蒙古桌子山骆驼山煤矿 2010年3月1日 1000 矿井被淹 9 河北峰峰黄沙煤矿 2011年12月11日 380 矿井被淹 10 安徽皖北桃园煤矿 2013年2月3日 167 矿井被淹 11 安徽淮南潘二煤矿 2017年5月25日 242 矿井巷道被淹 -
[1] 王锐. 论华北地区岩溶陷落柱的形成[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1982, 9(1):41-45.WANG Rui. Formation of karst subsidence column in North China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1982, 9(1):41-45. [2] 尹尚先, 吴文金, 李永军. 华北煤田岩溶陷落柱及其突水研究[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2008.YIN Shangxian, WU Wenjin, LI Yongjun. Research on karst collapse column and water inrush in North China coalfield[M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press, 2008. [3] 尹尚先, 连会青, 刘德民,尹慧超. 华北型煤田岩溶陷落柱研究70年: 成因·机理·防治[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(11):1-29.YIN Shangxian, LIAN Huiqing, LIU Demin, YIN Huichao. 70 years of investigation on karst collapse column in North China coalfield: cause of origin, mechanism and prevention[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(11):1-29. [4] He K Q, Dong G, Wen D, Wang R L. The effects of karst collapse on the environments in north China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2007, 52(3):449-455. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0478-8 [5] He K, Yu G, Lu Y. Palaeo-karst collapse pillars in northern China and their damage to the geological environments[J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 58(5):1029-1040. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1583-7 [6] 李金凯, 周万芳. 华北型煤矿床陷落柱作为导水通道突水的水文地质环境及预测[J]. 中国岩溶, 1989, 8(3):192-199.LI Jinkai, ZHOU Wanfang. The hydrogeological environment and prediction of the water inrush from the collapse column of the North China-type coal deposit as an aqueduct[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1989, 8(3):192-199. [7] Xu W, Zhao G. Mechanism and prevention of karst collapse near mine areas in China[J]. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences, 1988, 12(1):37-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02574825 [8] 侯恩科, 夏玉成. 矿井陷落柱的成因分析及其预测[J]. 西北地质, 1994, 15(2):18-22.HOU Enke, XIA Yucheng. Genetic analysis and prediction of mine collapse column[J]. Northwest Geology, 1994, 15(2):18-22. [9] 贾贵廷, 胡宽瑢. 华北型煤田陷落柱的形成及分布规律[J]. 中国岩溶, 1989, 8(4):261-267.JIA Guiting, HU Kuanrong. Formation and distribution of collapse columns in North China coalfield[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1989, 8(4):261-267. [10] 许光泉, 孙丰英, 刘丽红, 李佩全, 汪敏华, 刘满才. 淮南潘谢矿区岩溶类地质异常体演化过程及预测[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(1):62-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.01.012XU Guangquan, SUN Fengying, LIU Lihong, LI Peiquan, WANG Minhua, LIU Mancai. Evolution process and prediction of karst geological abnormal bodies in Panxie coal mining area in Huainan[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2016, 44(1):62-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.01.012 [11] Zuo J P, Peng S P, Li Y J, Chen Z H,Xie H P. Investigation of karst collapse based on 3-D seismic technique and DDA method at Xieqiao coal mine, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2009, 78(4):276-287. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.02.003 [12] 程广琪, 刘登宪, 傅先杰, 王峻莺. 淮南煤田北西向断裂与岩溶陷落柱关系研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2013, 41(10):108-111.CHENG Guangqi, LIU Dengxian, FU Xianjie, WANG Junying. Study on relationship between northwest directional failure and karst sinkhole in Huainan coalfield[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2013, 41(10):108-111. [13] 尹尚先, 武强, 王尚旭. 北方岩溶陷落柱的充水特征及水文地质模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(1):77-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.01.013YIN Shangxian, WU Qiang, WANG Shangxu. Water-bearing characteristics and hydro-geological models of karstic collapse columns in north China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(1):77-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.01.013 [14] Ma D, Bai H, Miao X, Pu H,Jiang B Y,Chen Z Q. Compaction and seepage properties of crushed limestone particle mixture: an experimental investigation for Ordovician karst collapse pillar groundwater inrush[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(1):2-14. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4790-z [15] Gui H, Xu J, Zhang D. Relationship between hydraulic conductivity of karst collapse column and its surrounding lithology[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(5):215. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6541-9 [16] Li H, Bai H, Wu J, Ma Z G,Ma K,Wu G M,Du Y B,He S X. A cascade disaster caused by geological and coupled hydro-mechanical factors-water Inrush mechanism from karst collapse column under confining pressure[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(12):1-19. [17] 桂辉, 杨志斌, 韩翔旭. 皖北矿区岩溶陷落柱导水性差异原因研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(6):165-169.GUI Hui, YANG Zhibin, HAN Xiangxu. Study on reason for differences of hydraulic conductivity of karst collapse columns in Wanbei Mining Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(6):165-169. [18] 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 蒲俊兵,肖琼. 现代岩溶学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Yongjun, SHEN Licheng,PU Junbing, XIAO Qiong. Modern karst science [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [19] 李定龙, 周治安, 王桂梁. 马家沟灰岩(古)岩溶研究中的若干问题探讨[J]. 地质科技情报, 1997, 16(1):23-28.LI Dinglong, ZHOU Zhian, WANG Guiliang. Approaching problems in karstic studying of MaJiaGou limestone in area of north China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1997, 16(1):23-28. [20] Tian F, Jin Q, Lu X B, Lei Y H,Zhang L K,Zheng S Q,Zhang H F,Rong Y S,Liu N G. Multi-layered ordovician paleokarst reservoir detection and spatial delineation: A case study in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, Western China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 69(3):53-73. [21] 李定龙. 皖北奥陶系古岩溶及其环境地球化学特征研究[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001.LI Dinglong. Research on Ordovician paleokarst and its environmental geochemical characteristics in northern Anhui [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001. [22] 尹尚先, 武强, 王尚旭. 华北煤矿区岩溶陷落柱特征及成因探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(1):120-123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.01.023YIN Shangxian, WU Qiang, WANG Shangxu. Studies on characters and forming mechanism of collapse columns at mine area of north China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(1):120-123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.01.023 [23] 史俊德, 连冬香, 杨士臣. 论岩溶塌陷问题[J]. 华北地质矿产杂志, 1998, 5(3):264-267.SHI Junde, LIAN Dongxiang, YANG Shicheng. Discussions on the engineering geologic problems relevant to karst collapse[J]. Jour Geoland Min Res North China, 1998, 5(3):264-267. [24] 钱学溥. 石膏喀斯特陷落柱的形成及其水文地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 1988, 7(4):344.QIAN Xuepu. The formation of gypsum karst collapse-collum and its hydrogeological significance[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1988, 7(4):344. [25] 徐卫国, 赵桂荣. 试论岩溶矿区地面塌陷的真空吸蚀作用[J]. 地质论评, 1981, 27(2):86-95.XU Weiguo, ZHAO Guirong. The implication of suction action for ground subsidence in karst mining areds[J]. Geological Review, 1981, 27(2):86-95. [26] 徐卫国, 赵桂荣. 真空吸蚀作用引起的塌陷实例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988, 15(3):54-55.XU Weiguo, ZHAO Guirong. Example of collapse caused by vacuum aspiration[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1988, 15(3):54-55. [27] 潘彤. 火山侵蚀和塌陷: 以侵入体为中心的矿床叠生的成因[J]. 世界地质, 1996, 15(1):35-38.PAN Tong. Volcanic erosion and subsidence: the genesis of deposits centered on intrusions[J]. World Geology, 1996, 15(1):35-38. [28] 丁博钊, 张光荣, 陈康,耿玮,朱兴卉,范畅. 四川盆地高石梯地区震旦系岩溶塌陷储集体成因及意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(8):1211-1218.DING Bozhao, ZHANG Guangrong, CHEN Kang, GENG Wei,ZHU Xinghui,FAN Chang. Genesis research of collapsed-paleo-cave systems in Sinian carbonate strata in central Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(8):1211-1218. [29] 王经明, 刘文生, 关永强,王军现,吴燔. 华北煤田陷落柱的地下水内循环形成机理: 以峰峰矿区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2007, 26(1):11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2007.01.002WANG Jingming, LIU Wensheng, GUAN Yongqiang, WANG Junxian,WU Fan. Mechanism of groundwater inner circulation in sinking column formation in North China coal field-A case study at Fengfeng mine[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2007, 26(1):11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2007.01.002 [30] Zhang H T, Xu G Q, Zhan H B, Zheng J B,Wang M H,Liu M C,Pan S Q,Wang N. Formation mechanisms of paleokarst and karst collapse columns of the Middle Cambrian-Lower Ordovician carbonates in Huainan coalfield, Northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 601(1):126634. [31] 赵金贵, 郭敏泰. 平顺老马岭岩溶陷落柱的发现及形成时段探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8):1716-1724.ZHAO Jingui, GUO Mintai. Discover and formation time of karst collapse pillar in Laomaling, Pingshun County[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8):1716-1724. [32] 啜晓宇, 滕吉文. 强导(含)水隐伏陷落柱底板突水机理研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(1):430-440.CHUAI Xiaoyu, TENG Jiwen. Water inrush mechanism research of strong conductiong (water including) karstic collapse column[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(1):430-440. [33] 李连崇, 唐春安, 左宇军, 李根,刘超. 煤层底板下隐伏陷落柱的滞后突水机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(9):1212-1216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.09.013LI Lianchong, TANG Chunan, ZUO Yujun, LI Gen,LIU Chao. Mechanism of hysteretic groundwater inrush from coal seam floor with karstic collapse columns[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(9):1212-1216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.09.013 [34] 李见波, 许延春. 承压水渗流条件下预防陷落柱突水力学模型及应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(2):217-224.LI Jianbo, XU Yanchun. Mechanical model of the collapse column water inrush prevention considering the confined water seepage and its application[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2016, 45(2):217-224. [35] 王家臣, 李见波. 预测陷落柱突水灾害的物理模型及理论判据[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2010, 32(10):1243-1247.WANG Jiachen, LI Jianbo. Physical model and theoretic criterion of the forecast of water inrush caused by collapse columns[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(10):1243-1247. [36] 张文忠. 陷落柱突水三维大型模拟实验系统研制及应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(1):56-61.ZHANG Wenzhong. Development and application of 3D large-scale simulation experiment system of water inrush caused by collapse column[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2016, 45(1):56-61. [37] 李振华, 李见波, 贺志宏. 双柳煤矿陷落柱发育特征及突水危险性分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2014, 31(1):84-89.LI Zhenhua, LI Jianbo, HE Zhihong. Analysis on development characteristics of karst collapse column and water inrush risk in Shuangliu coal mine[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2014, 31(1):84-89. [38] 王家臣, 王树忠, 熊崇山. 五阳煤矿陷落柱发育特征及突水危险性评价[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(7):922-926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.07.012WANG Jiachen, WANG Shuzhong, XIONG Chongshan. The collapse column development characteristics and the evaluation onwater bursting risk of Wuyang CoalMine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(7):922-926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.07.012 [39] 张勃阳, 白海波, 张凯. 采动影响下陷落柱的滞后突水机理研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(3):447-454.ZHANG Boyang, BAI Haibo, ZHANG Kai. Study on the mechanism of delayed water inrushof collapse column under the influence of mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2016, 45(3):447-454. [40] 尹尚先, 王尚旭. 陷落柱影响采场围岩破坏和底板突水的数值模拟分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2003, 28(3):264-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2003.03.009YIN Shangxian, WANG Shangxu. A numerical simulation analysis of influence of karstic collapse columns on rock mass yield and water inrush from coal floor[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2003, 28(3):264-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2003.03.009 [41] 尹尚先, 武强. 煤层底板陷落柱突水模拟及机理分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(15):2551-2556. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.15.014YIN Shangxian, WU Qiang. Simulation and mechanism analysis of water inrush from karstic collapse columns in coal floor[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(15):2551-2556. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.15.014 [42] 张均锋, 张华玲, 孟达, 曹杰. 采动影响下强充水型隐伏岩溶陷落柱围岩变形与渗流场数值模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(s1):2824-2829.ZHANG Junfeng, ZHANG Hualing, MENG Da, CAO Jie. Numerical simulation of rock deformation and seepage field with a fully-water karstic collapse column under mining influence[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(s1):2824-2829. [43] 宋彦琦, 王兴雨, 程鹏, 彭长剑,徐爽. 椭圆形陷落柱厚壁筒突水模式力学判据及数值模拟[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(3):452-455.SONG Yanqi, WANG Xingyu, CHENG Peng, PENG Changjian,XU Shuang. The mechanical criterion and numerical simulation of thick-walled elliptical cylinder collapse column model under water inrush[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(3):452-455. [44] 刘志军, 熊崇山. 陷落柱突水机制的数值模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(s2):4013-4018.LIU Zhijun, XIONG Chongshan. Numerical simulation study on water inrush mechanism from collapse column[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(s2):4013-4018. [45] 尹尚先, 王尚旭. 不同尺度下岩层渗透性与地应力的关系及机理[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2006, 36(5):472-480.YIN Shangxian, WANG Shangxu. Relationship between rock permeability and ground stress and mechanism under different scales[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2006, 36(5):472-480. [46] 武强, 朱斌, 李建民, 洪益清, 钱增江. 断裂带煤矿井巷滞后突水机理数值模拟[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2008, 37(6):780-785. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2008.06.010WU Qiang, ZHU Bin, LI Jianmin, HONG Yiqing, QIAN Zengjiang. Numerical Simulation of Lagging Water-Inrush Mechanism of Rock Roadways Near Fault Zone[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2008, 37(6):780-785. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2008.06.010 [47] 武强, 朱斌, 刘守强. 矿井断裂构造带滞后突水的流—固耦合模拟方法分析与滞后时间确定[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(1):93-104.WU Qiang, ZHU Bin, LIU Shouqiang. Flow-solid coupling simulation method analysis and time identification of lagging water-inrush near mine fault belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(1):93-104. [48] 杨天鸿, 师文豪, 刘洪磊, 杨斌,杨鑫,刘再斌. 基于流态转捩的非线性渗流模型及在陷落柱突水机理分析中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(2):315-321.YANG Tianhong, SHI Wenhao, LIU Honglei,YANG Bin, YANG Xin, LIU Zaibin. A non-linear flow model based on flow translation and its application in the mechanism analysis of water inrush through collapse pillar[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(2):315-321. [49] 张勃阳, 白海波, 张凯. 类陷落柱介质渗流突变机制试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(3):745-752.ZHANG Boyang, BAI Haibo, ZHANG Kai. Experimental research on seepage mutation mechanism of collapse column medium[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(3):745-752. [50] 杨天鸿, 陈仕阔, 朱万成, 孟召平,高延法. 矿井岩体破坏突水机制及非线性渗流模型初探[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(7):1411-1416. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.07.014YANG Tianhong, CHEN Shikuo, ZHU Wancheng, MENG Zhaoping,GAO Yanfa. Water inrush mechanism in mines and nonlinear flow model for fractured rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(7):1411-1416. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.07.014 [51] 张凯, 姚邦华, 吴松刚, 张宏图. 陷落柱的变质量渗流特性及其突水危险性数值模拟[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2013, 30(6):892-896.ZHANG Kai, YAO Banghua, WU Songgang, ZHANG Hongtu. Study on the characteristics of variable mass seepage and water inrush mechanism of collapse column[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2013, 30(6):892-896. [52] 姚邦华, 茅献彪, 魏建平, 王登科. 考虑颗粒迁移的陷落柱流固耦合动力学模型研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(1):30-35.YAO Banghua, MAO Xianbiao, WEI Jianping, WANG Dengke. Study on coupled fluid-solid model for collapse columns considering the effect of particle transport[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2014, 43(1):30-35. [53] 张勃阳, 白海波, 张凯. 陷落柱填隙物全应力—应变过程的渗流特性研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2016, 33(4):734-740.ZHANG Boyang, BAI Haibo, ZHANG Kai. Research on permeability characteristics of karst collapse column fillings in complete stress-strain process[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2016, 33(4):734-740. [54] 师文豪, 杨天鸿, 刘洪磊, 杨斌, 杨鑫, 周永发. 矿山岩体破坏突水非达西流模型及数值求解[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(3):446-455.SHI Wenhao, YANG Tianhong, LIU Honglei, YANG Bin, YANG Xin, ZHOU Yongfa. Non-Darcy flow model and numerical simulation for water-inrush in fractured rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(3):446-455. [55] 赵延林, 张盛国, 万文, 王卫军, 蔡璐, 彭青阳. 基于流态转换理论巷道前伏溶洞突水的流固耦合–强度折减法分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(9):1852-1862.ZHAO Yanlin, ZHANG Shengguo, WAN Wen, WANG Weijun, CAI Lu, PENG Qingyang. Solid-fluid coupling-strength reduction method for karst cave water inrush before roadway based on flow state conversion theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(9):1852-1862. [56] 尹尚先, 武强. 陷落柱概化模式及突水力学判据[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2006, 28(9):812-817. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2006.09.003YIN Shangxian, WU Qiang. Generalized modes and academic criterions of water inrush from paleo-sinkholes[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2006, 28(9):812-817. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2006.09.003 [57] 刘国林, 尹尚先, 王延斌. 华北型煤田岩溶陷落柱侧壁厚壁筒突水模式研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2007, 15(2):284-287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.02.026LIU Guolin, YIN Shangxian, WANG Yanbin. Model of water inrush for thick wall cylinder at side face of paleo-sinkholes in north-china-type coalfields[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007, 15(2):284-287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.02.026 [58] 尹尚先, 王尚旭, 武强. 陷落柱突水模式及理论判据[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(6):964-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.06.015YIN Shangxian, WANG Shangxu, WU Qiang. Water inrush patterns and theoretic criteria of karstic collapse columns[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(6):964-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.06.015 [59] 杨为民, 司海宝, 吴文金. 岩溶陷落柱导水类型及其突水风险预测[J]. 煤炭工程, 2005, 38(8):60-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2005.08.025YANG Weimin, SI Haibao, WU Wenjin. Water conducted type karst sink hole and prediction of water inrush risk[J]. Coal Engineering, 2005, 38(8):60-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2005.08.025 [60] Zhang S H, Lin C R. Study on the genesis of karstic collapse column and characteristics of high resolution seismic data in one coal field[J]. International Journal of Coal Science and Technology, 2008, 14(4):648-650. [61] 杨武洋. 煤矿陷落柱赋水特征的综合物探探查原理与方法[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2013, 30(1):45-50.YANG Wuyang. Integrated geophysical prospecting principle and method of explorating the water enrichment of coal mine collapse column[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2013, 30(1):45-50. [62] 朱国维, 王怀秀, 韩堂惠. 地面—井下联合地震勘探确定岩溶陷落柱空间分布[J].煤炭科学技术, 2008, 31(5): 33-36.ZHU Guowei, WANG Huaixiu, HAN Tanghui. Surface and underground combined seism ic survey to define space distribution of karst sink hole[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2008, 31(5): 33-36. [63] 彭苏萍, 杜文凤, 赵伟,师素珍, 何登科. 煤田三维地震综合解释技术在复杂地质条件下的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(s1):2760-2765.PENG Suping, DU Wenfeng, ZHAO Wei, SHI Suzhen, HE Dengke. 3D coalfield seismic integrated interpretation technique in complex geological condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(s1):2760-2765. [64] 刘礼农, 崔凤林, 张剑锋. 三维复杂构造中地震波模拟的单程波方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(3):514-520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.03.023LIU Linong, CUI Fenglin, ZHANG Jianfeng. Seismic modeling with one-way wave equation in 3D complex structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(3):514-520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.03.023 [65] 贾东, 李一泉, 王毛毛, 李海滨. 断层相关褶皱的三维构造几何学分析: 以川西三维地震工区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3):732-740.JIA Dong, LI Yiquan, WANG Maomao, LI Haibin. Three-dimensional structural geometry of faultrelated folds: Examples from 3-D seismic explored blocks in the western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(3):732-740. [66] 勾精为, 程增庆, 陈加林. 三维地震探测陷落柱的可行性研究[C]//计算机在地学中的应用国际讨论会论文摘要集, 1991.GOU Jingwei, CHENG Zengqing, CHEN Jialin. Feasibility study of three-dimensional seismic detection of collapsed columns [C]//Abstracts of International Symposium on the Application of Computers in Geoscience, 1991. [67] 李艳芳, 程建远, 熊晓军, 聂爱兰,张宪旭. 陷落柱三维地震正演模拟及对比分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(3):456-460.LI Yanfang, CHENG Jianyuan, XIONG Xiaojun, NIE Ailan,ZHANG Xianxu. 3D seismic forward modeling of collapse column and comparison[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(3):456-460. [68] 查文锋. 山西某矿陷落柱三维地震成果可靠程度评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 45(5):147-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.05.025CHA Wenfeng. Evaluation of the reliability of the collapse column interpreted by 3D seismic in a mine in Shanxi Province[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2017, 45(5):147-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.05.025 [69] 庄益明, 宋利虎, 刘镜竹. 蚂蚁追踪技术在三维地震精细解释中的应用: 以淮北祁南煤矿82采区为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 4(2):173-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.02.026ZHUANG Yiming, SONG Lihu, LIU Jingzhu. Application of ant tracking technology in 3D seismic fine interpretation of faults: A case study on mining district No. 82 in Huaibei Qinan coal mine[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2018, 4(2):173-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.02.026 [70] 杨双安, 张淑婷, 郭勇洪, 魏书宏, 李连英, 张胤彬. 时间剖面上分析陷落柱充水性的探讨[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2001, 30(5):503-505. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2001.05.020YANG Shuangan, ZHANG Shuting, GUO Yonghong, WEI Shuhong, LI Lianying, ZHANG Yinbin. Analysis of water-filling of subsided column based on time section[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2001, 30(5):503-505. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2001.05.020 [71] 刘志新, 刘树才, 于景邨. 综合矿井物探技术在探测陷落柱中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(2):212-215.LIU Zhixin, LIU Shucai, YU Jingcun. The application of integrated mining geophysical technology to detecting the collapse column[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(2):212-215. [72] 袁伟, 李天亮, 李东北, 熊键. 音频大地电磁法在某灰岩地区煤炭资源勘查中探测岩溶和陷落柱的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2016, 38(6):727-733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2016.06.03YUAN Wei, LI Tianliang, LI Dongbei, XIONG Jian. Audio magneto-telluric method to detect karst and collapse column in the limestone region in the exploration of coal resources[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 38(6):727-733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2016.06.03 [73] 原文涛. 瞬变电磁法在采空区及陷落柱探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(10):164-167.YUAN Wentao. The application of transient electromagnetic method to the detection of goaf and collapse columns[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(10):164-167. [74] 程久龙, 李飞, 彭苏萍, 孙晓云. 矿井巷道地球物理方法超前探测研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8):1742-1750.CHENG Jiulong, LI Fei, PENG Shuping, SUN Xiaoyun. Research progress and development direction on advanced detection in mine roadway working face using geophysical methods[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8):1742-1750. [75] 桂和荣, 陈陆望. 矿区地下水水文地球化学演化与识别[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.GUI Herong, CHEN Luwang. Hydrogeochemical evolution and identification of groundwater in mining areas [M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 2007. [76] 尹尚先, 徐斌, 徐慧, 夏向学. 化学示踪连通试验在矿井充水条件探查中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(1):129-134.YIN Shangxian, XU Bin, XU Hui, XIA Xiangxue. The application of chemical tracer experiments on exploring the mine water filling conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(1):129-134. [77] 李霞, 陈文芳, 万利勤, 夏飞雪, 张一博, 袁梦丽. 河南嵩县北部基岩山区地下水水化学特征和环境同位素特征分析[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3):403-412. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.03.10LI Xia, CHEN Wenfang, WAN Liqin, XIA Feixue, ZHANG Yibo, YUAN Mengli. An Analysis of Hydrochemical Characteristics and Environmental Isotopic Characteristics of the Groundwater in the Bedrock Mountain Area in Northern Songxian County, Henan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(3):403-412. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.03.10 [78] 刘人太, 李术才, 张庆松, 张伟杰, 孙子正, 朱明听. 示踪试验分析方法在地下工程水害治理中的应用研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(4):814-821.LIU Rentai, LI Shucai, ZHANG Qingsong, ZHANG Weijie, SUN Zizheng, ZHU Mingting. Research on application of tracer experiment analysis method to water hazards management in underground engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(4):814-821. [79] 徐占杰, 刘钦甫, 宋璞, 姬景超, 毋应科. 寺家庄井田陷落柱对煤层气井产出水地球化学特征的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 45(2):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.02.009XU Zhanjie, LIU Qinfu, SONG Pu, JI Jingchao,WU Yingke. Effect of karstic collapse column on hydrogeochemistry of produced water from coalbed methane wells in Sijiazhuang mine field[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2017, 45(2):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.02.009 [80] 田多, 师皓宇, 梁兴旺,牛国星. 综放工作面过陷落柱阶段划分及其顶板结构分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2015, 32(1):49-53.TIAN Duo, SHI Haoyu, LIANG Xingwang, NIU Guoxing. Stage division and roof structure analysis during fully mechanized caving face passing a collapse column[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2015, 32(1):49-53. [81] 国家安全生产监督管理总局. 煤矿防治水规定[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2009.State administration of work safety. Regulations on prevention and control of water in coal mine [M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press, 2009. [82] 张村, 屠世浩, 白庆升, 张艳伟, 杨乾龙. 陷落柱周边应力变化及推采控制研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(6):974-980.ZHANG Cun, TU Shihao, BAI Qingsheng, ZHANG Yanwei, YANG Qianlong. Stress changes around collapse column and the control technology by directly passing operation in longwall working face[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2014, 43(6):974-980. [83] 郝兵元, 张玉江, 戚庭野, 冯国瑞, 白锦文, 章敏, 康立勋. 综采面过陷落柱采动应力与柱体应力相互影响模拟研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2015, 32(2):192-198.HAO Bingyuan, ZHANG Yujiang, QI Tingye, FENG Guorui, BAI Jinwen, ZHANG Min, KANG Lixun. Simulation of interaction between mine-induced stress and stress of collapse column with fully-mechanized working face advancing[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2015, 32(2):192-198. [84] 郑士田, 马培智. 陷落柱中“止水塞”的快速建立技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 1998, 26(3):51-53.ZHENG Shitian, MA Peizhi. The technique building"concrete plug" quickly in collapse column[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 1998, 26(3):51-53. [85] 段中稳. 隐伏导水陷落柱的综合防治[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2004, 21(2):115-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2004.02.047DUAN Zhongwen. Integrated prevention and control of concealed water guiding collapse column[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2004, 21(2):115-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2004.02.047 [86] 南生辉, 蒋勤明, 郭晓山, 李抗抗, 刘再斌, 石磊. 导水岩溶陷落柱堵水塞建造技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2008, 36(4):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2008.04.008NAN Shenghui, JIANG Qinming, GUO Xiaoshan, LI Kangkang, LIU Zaibin, SHI Lei. Construction technique of groundwater-preventing piston in Karst flow collapse column[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2008, 36(4):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2008.04.008 [87] 何思源. 开滦范各庄矿岩溶陷落柱特大突水灾害的治理[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 1986, 14(2):37-44.HE Siyuan. Treatment of extraordinary water inrush disaster in karst collapse column of Fanzhizhuang coal mine[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 1986, 14(2):37-44. [88] 郑士田. 两淮煤田煤层底板灰岩水害区域超前探查治理技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(4):142-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.04.023ZHENG Shitian. Advanced exploration and control technology of limestone water hazard in coal seam floor in Huainan and Huaibei coalfields[J]. Coalfield Geology and Exploration, 2018, 46(4):142-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.04.023 [89] 郑士田. 地面定向钻进技术在煤矿陷落柱突水防治中的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(7):234-238.ZHENG Shitian. Application of ground directional borehole technology to control prevention karst collapsed column water inrush in coal mines[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(7):234-238. [90] Howard J E. Global invariants for variable-mass systems[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(16):1-4. [91] 杨天鸿, 唐春安, 芮勇勤, 朱万成, 李元辉, 谭国焕. 不同围压作用下非均匀岩石水压致裂过程的数值模拟[J]. 计算力学学报, 2004, 21(4):419-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2004.04.006YANG Tianhong, TANG Chunan, RUI Yongqin, ZHU Wancheng, LI Yuanhui, TAN Guohuan. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing process in heterogeneous rocks under different confining pressures[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2004, 21(4):419-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2004.04.006 [92] 周创兵, 陈益峰, 姜清辉, 卢文波. 论岩体多场广义耦合及其工程应用[C]//全国岩石力学与工程学术大会, 2008: 1329-1340.ZHOU Chuangbing, CHEN Yifeng, JIANG Qinghui, LU Wenbo. On multi-field generalized coupling of rock mass and its engineering application [C]//National Conference on Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008: 1329-1340. [93] 荆自刚, 李白英, 孙振鹏. 峰峰二矿开采活动与底板突水关系研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 1984, 21(2):81-87.JING Zigang, LI Baiying, SUN Zhenpeng. Study on the relationship between the mining activities of Fengfeng No. 2 Mine and the water inrush from the floor[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1984, 21(2):81-87. [94] 王作宇, 刘鸿泉. 承压水上采煤[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1993.WANG Zuoyu, LIU Hongquan. Confined water mining [M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press, 1993. [95] 杨映涛. 论岩石体积应变与孔隙中流体压力的关系及其应用途径[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1989, 33(1):29-33.YANG Yingtao. The relation between volumetric strain of the rock and fluid pressure in the pores and its application[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1989, 33(1):29-33. [96] 王经明. 承压水沿煤层底板递进导升突水机理的模拟与观测[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(5):546-549. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.05.004WANG Jingming. In-situ measurement and physical analogue on water inrush from coal floor induced by progressive intrusion of artesian water into protective aquiclude[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(5):546-549. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.05.004 [97] 杨天鸿, 唐春安, 谭志宏, 朱万成, 冯启言. 岩体破坏突水模型研究现状及突水预测预报研究发展趋势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(2):268-277.YANG Tianhong, TANG Chunan, TAN Zhihong, ZHU Wancheng, FENG Qiyan. State of the art of inrush models in rock mass failure and developing trend for prediction and forecast of groundwater inrush[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(2):268-277. [98] 姜福兴, 叶根喜, 王存文, 张党育, 关永强. 高精度微震监测技术在煤矿突水监测中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(9):1932-1938. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.09.023JIANG Fuxing, YE Genxi, WANG Cunwen, ZHANG Dangyu, GUAN Yongqiang. Application of high-precision microseismic monitoring technique to water inrush monitoring in coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(9):1932-1938. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.09.023 [99] 徐佩芬, 李传金, 凌甦群, 张胤彬, 侯超, 孙勇军. 利用微动勘察方法探测煤矿陷落柱[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(7):1923-1930. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.028XU Peifen, LI Chuanjin, LING Suqun, ZHANG Yinbin, HOU Chao, SUN Yongjun. Mapping collapsed columns in coal mines utilizing mierotremor survey methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(7):1923-1930. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.028 [100] 姜福兴, 刘伟建, 叶根喜, 李伟. 构造活化的微震监测与数值模拟耦合研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2):3590-3597.JIANG Fuxing, LIU Weijian, YE Genxi, LI Wei. Coupling study of microseismic monitoring and numerical simulation for tectonic activation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2):3590-3597. -




 下载:
下载: