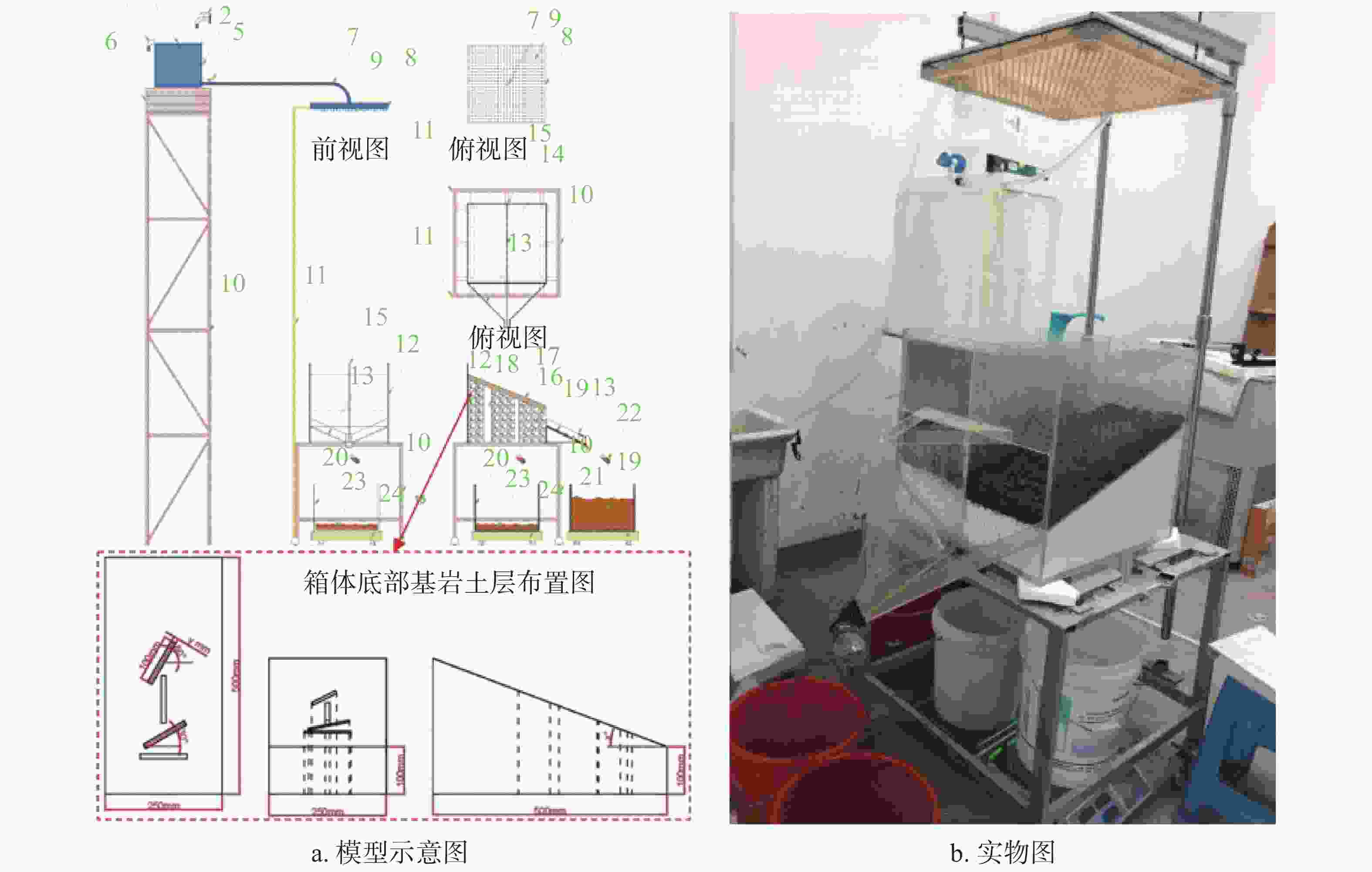
Laboratory simulation study on soil surface loss and underground leakage in the epikarst fissure zone
-
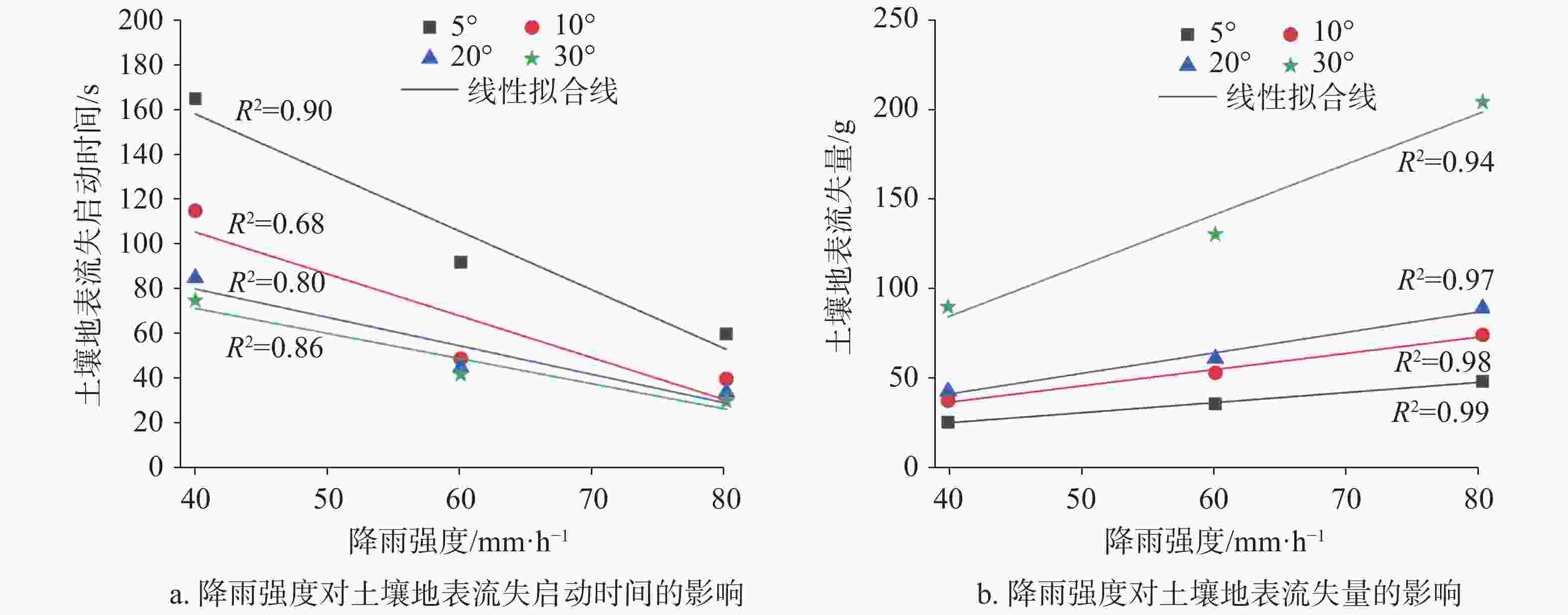
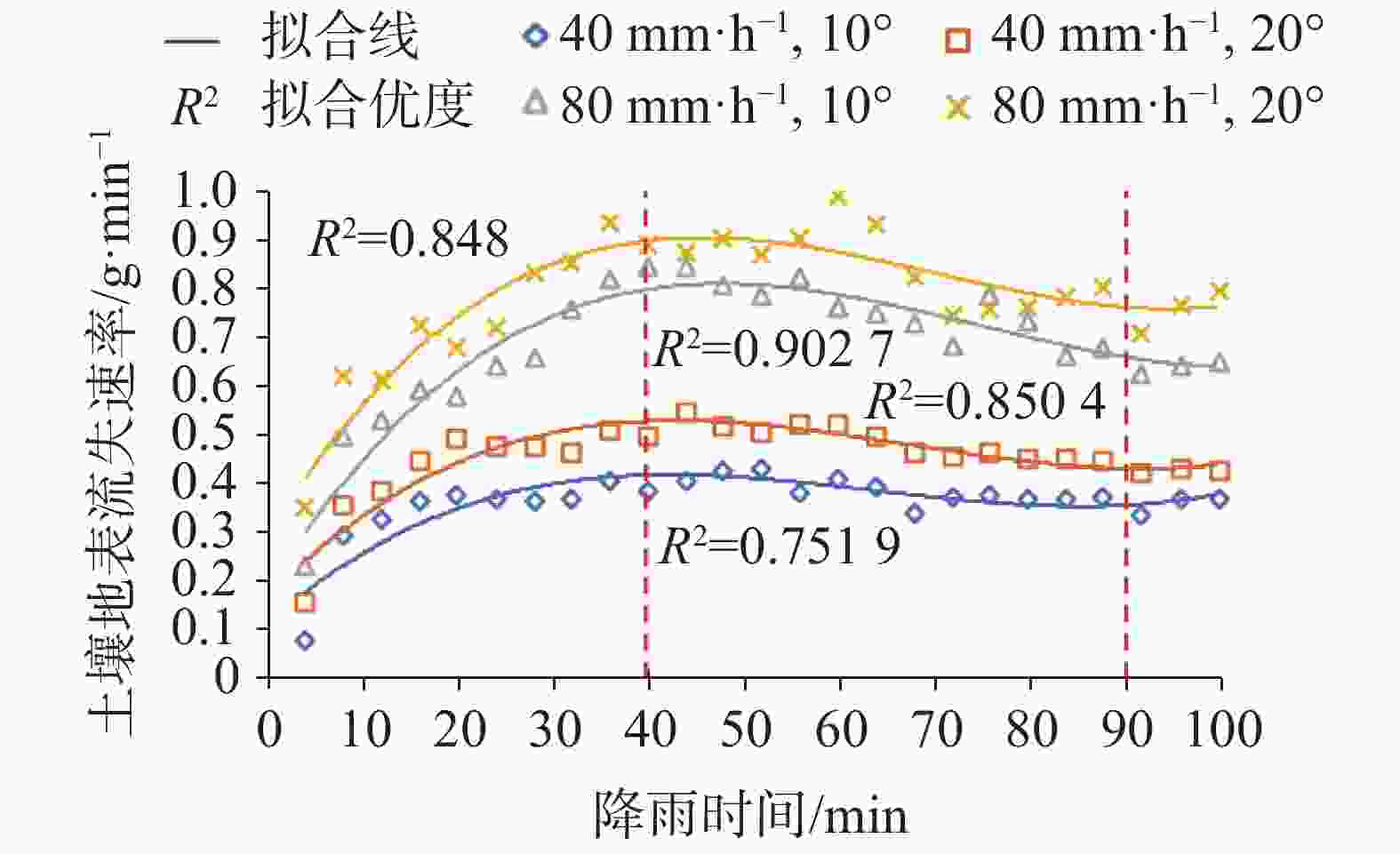
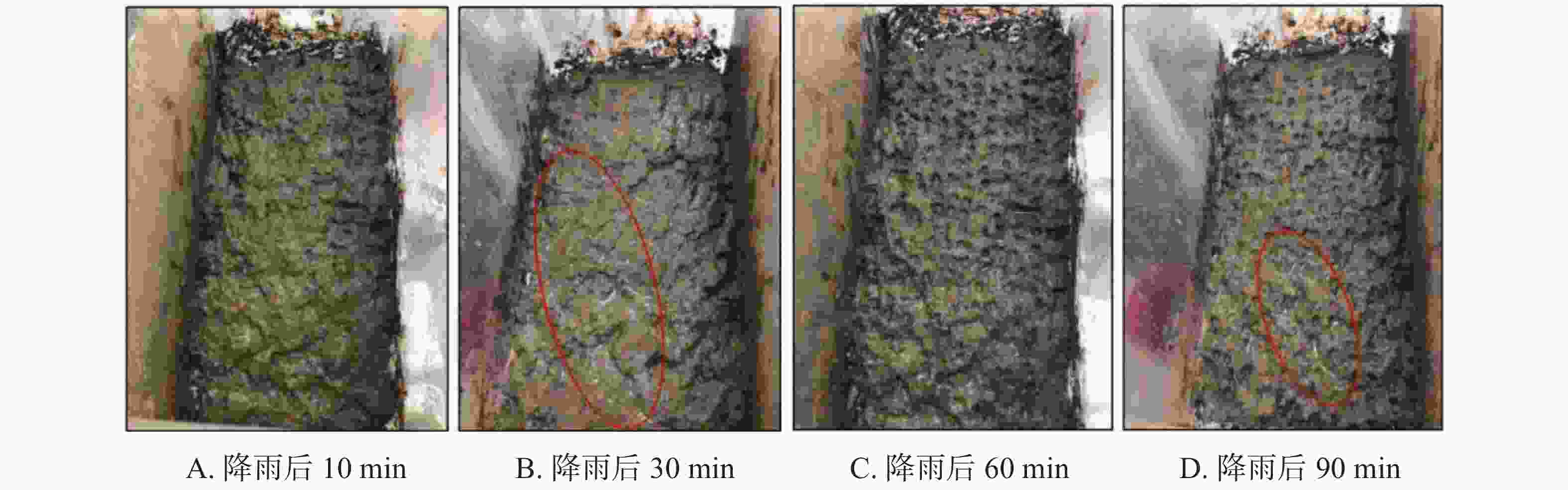
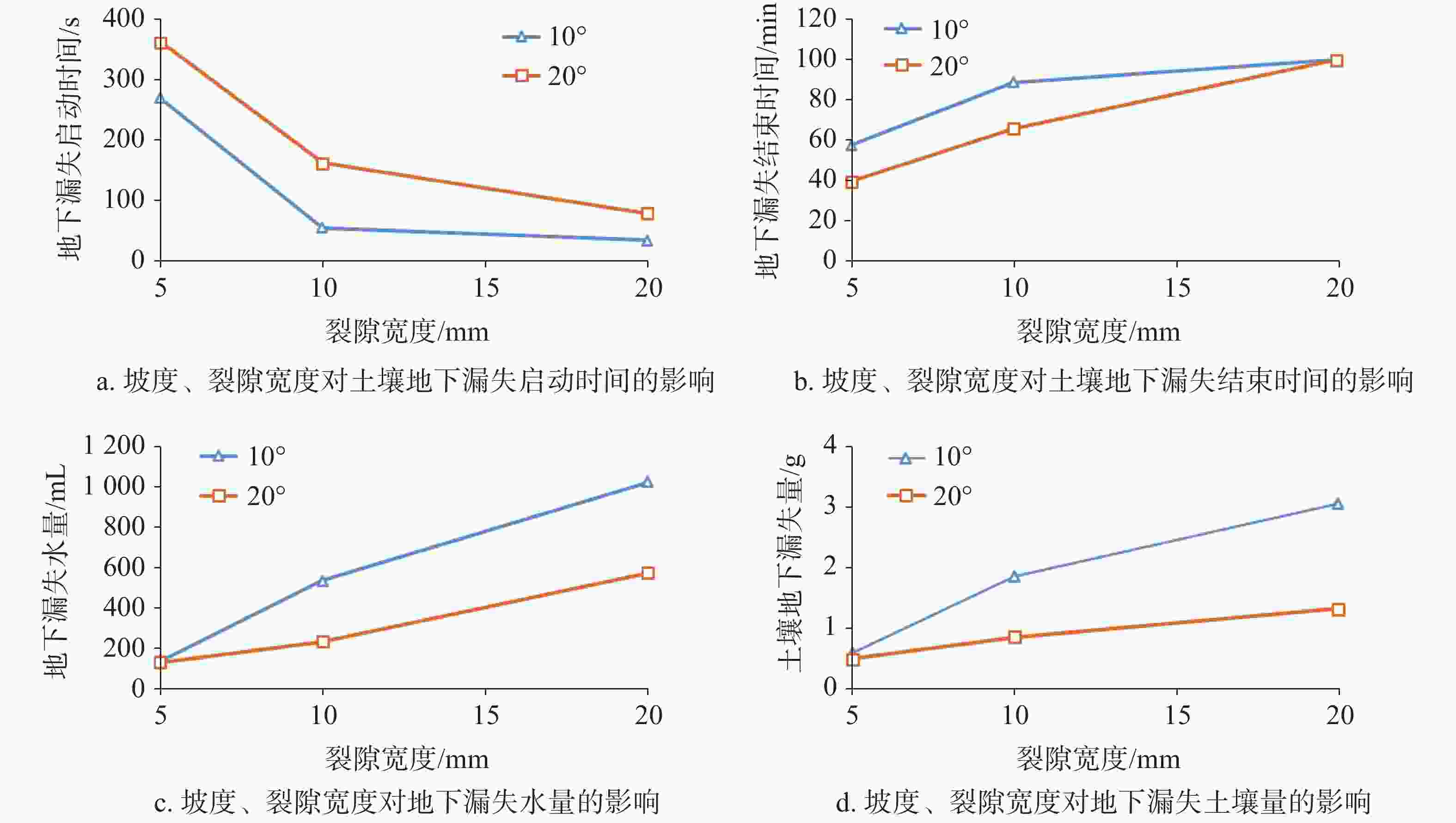
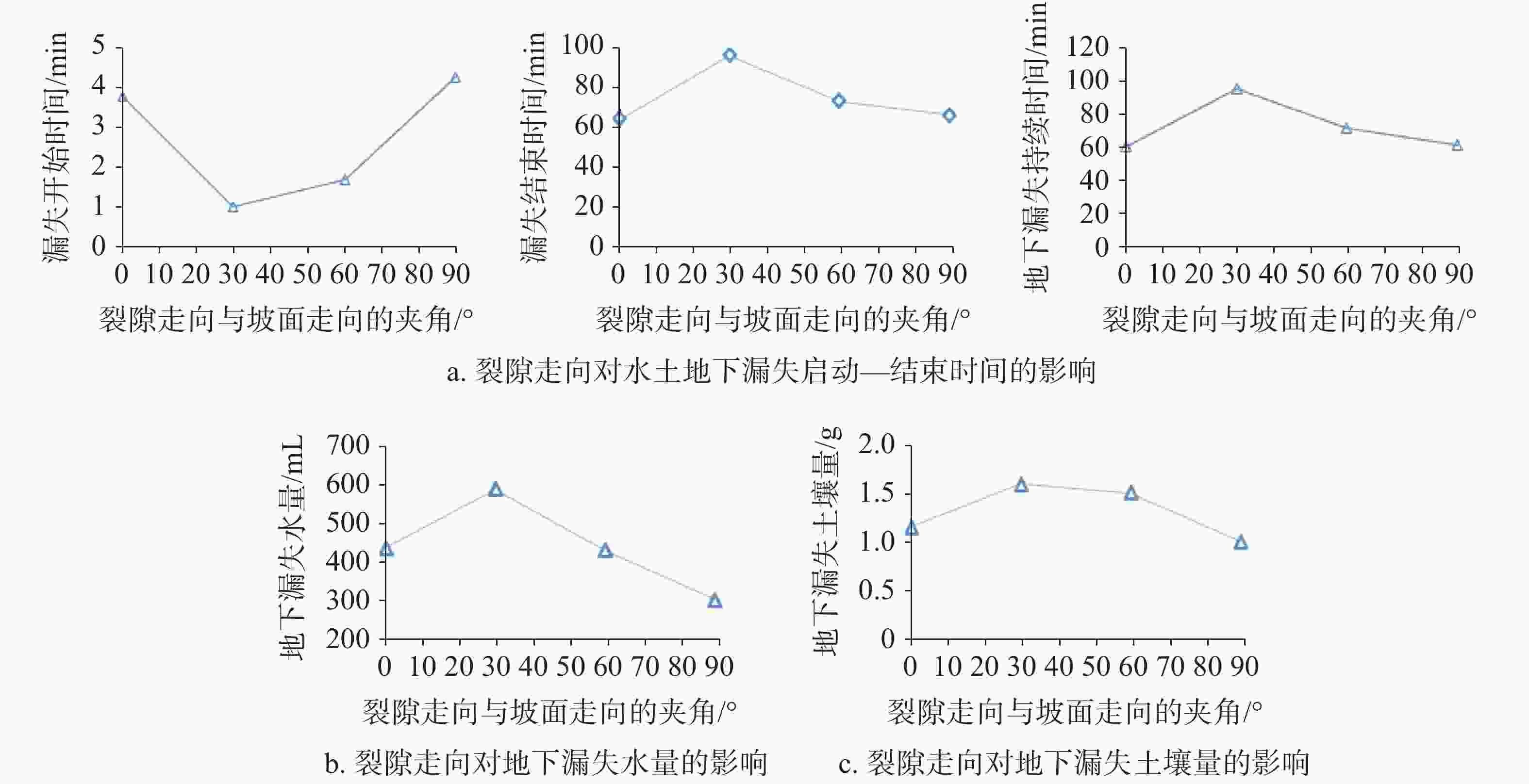
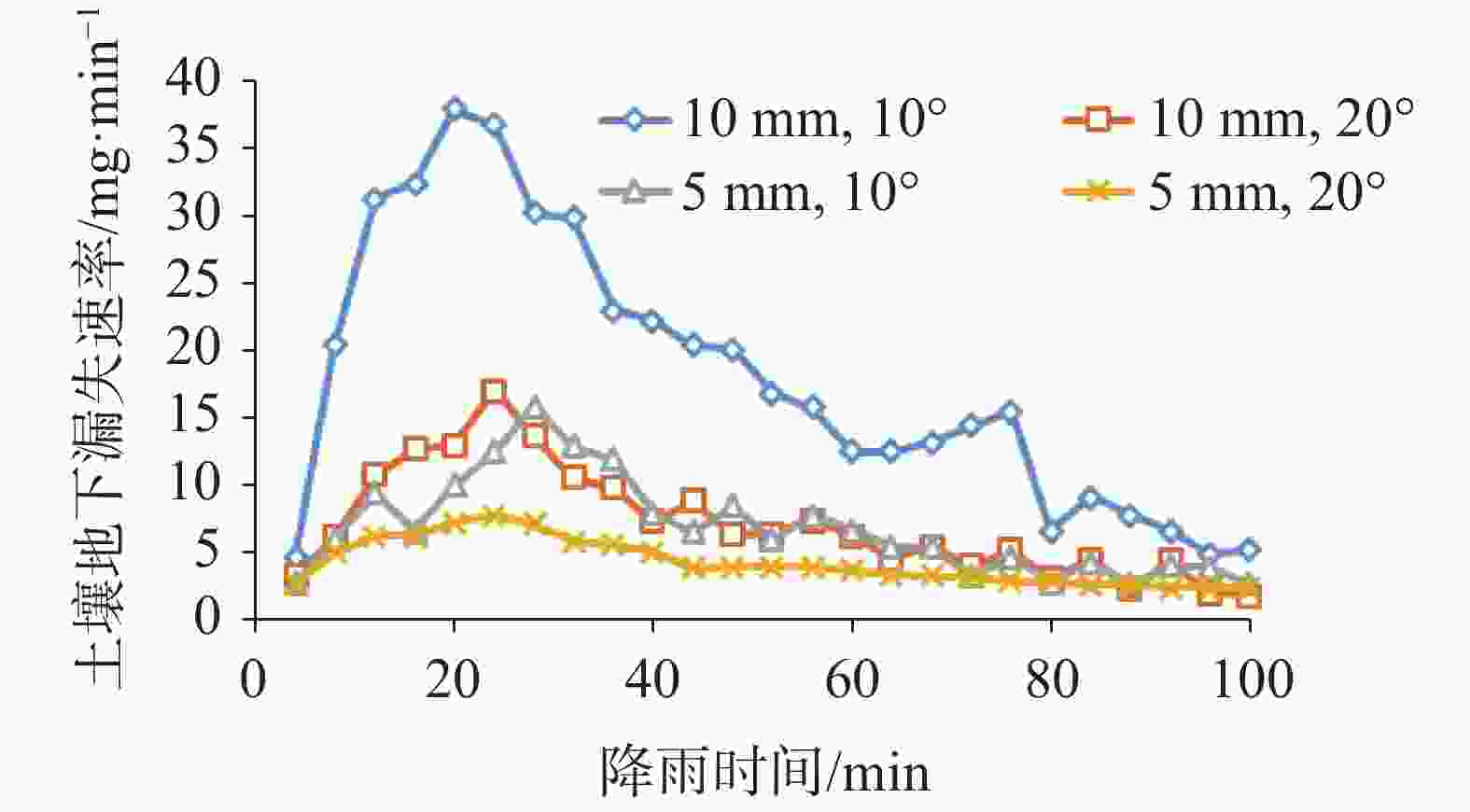
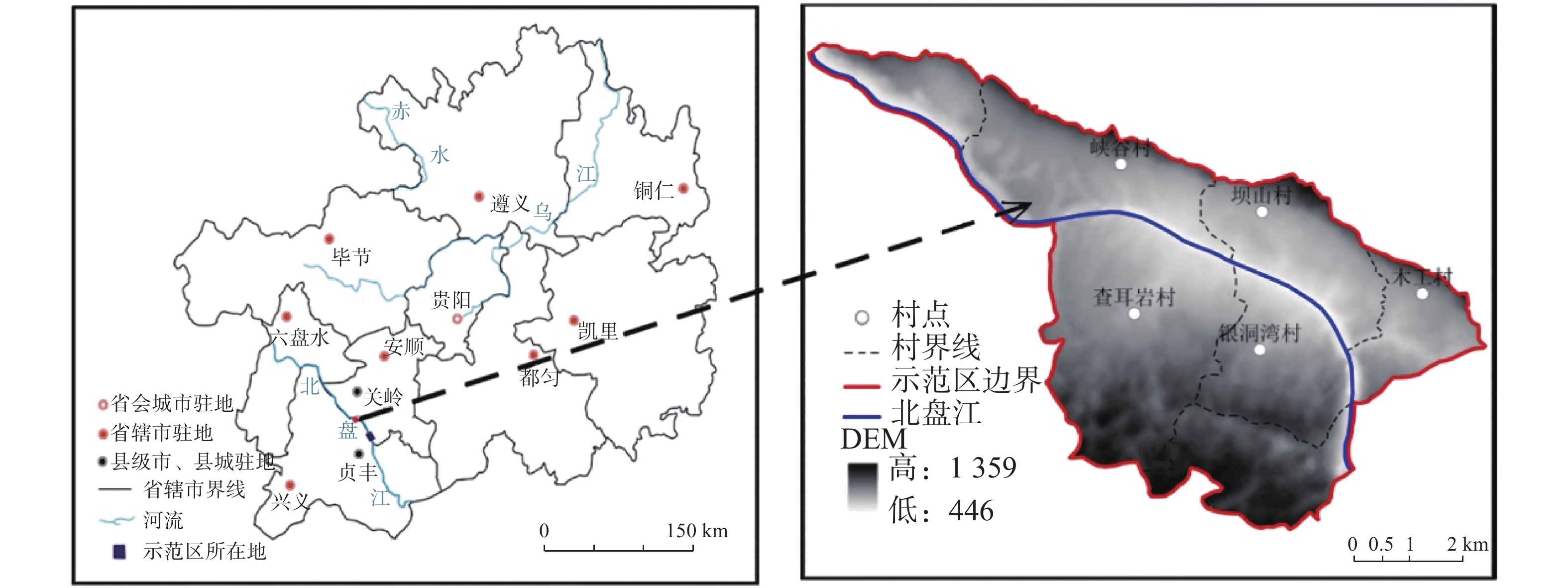
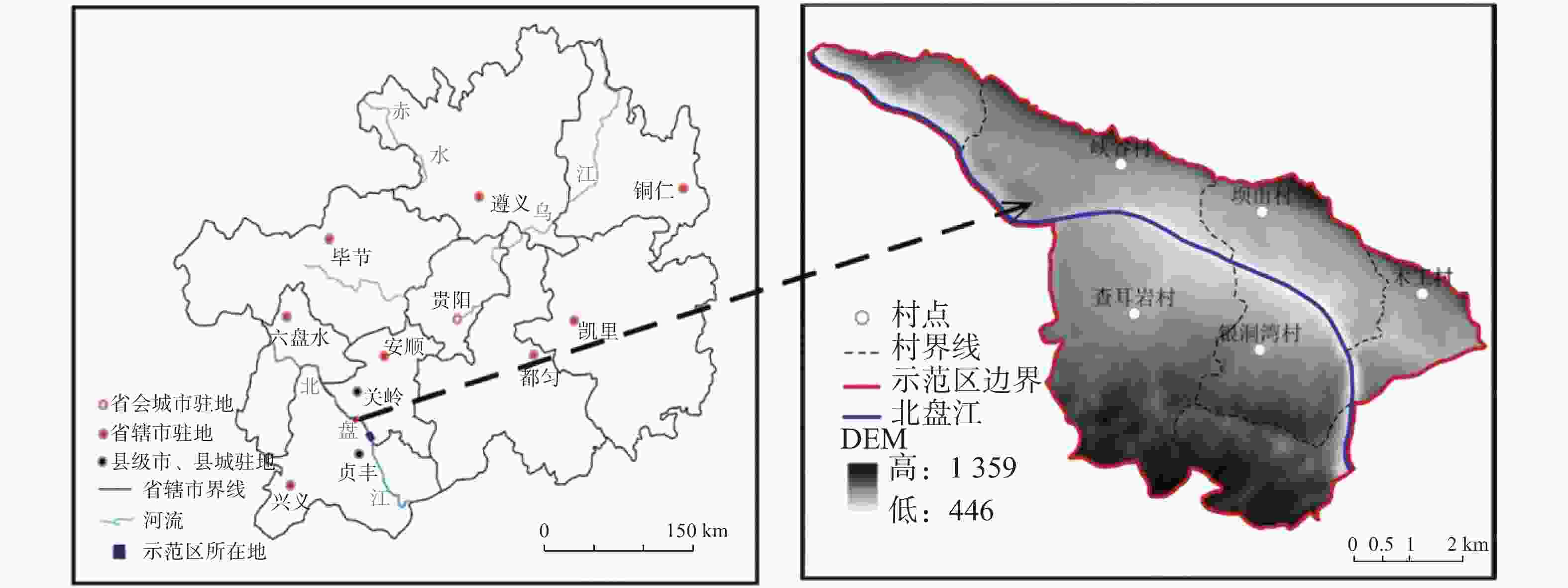
摘要: 以表层岩溶裂隙带为研究对象,采用室内模拟降雨的方法,通过控制降雨强度、坡度、裂隙宽度、裂隙产状,研究其对土壤地表流失、地下漏失的影响。结果表明:(1)土壤地表流失主要受降雨强度和坡度的影响,土壤地表流失量随降雨强度的增大而增大、随坡度的增大而增大,30°坡面土壤地表流失量最高。(2)土壤地下漏失主要受裂隙宽度、产状和坡度的影响,对降雨强度的响应不明显;土壤地下漏失量与裂隙宽度大小呈正相关关系,裂隙走向与坡面走向呈30°时最容易发生土壤地下漏失;坡度与土壤地下漏失的发生呈负相关关系;伴随降雨,土壤地下漏失速率变化幅度较大,漏失速率先增加后减小直至停止。无落水洞、漏斗等管道的岩溶坡面土壤流失的主要形式是地表流失,而土壤地下漏失的主要通道是落水洞、漏斗等大型岩溶管道,土壤地下漏失对土壤流失的总贡献率小于5%。Abstract: The study area, Guanling-Zhenfeng Huajiang demonstration area of karst plateau canyon, covers 51.62 km2 with the karst area of 45.39 km2. It is a typical area of karst plateau canyon on the Guizhou plateau with an elevation difference between 370 and 1,355 meters. In this study, a simulation device was developed by researchers to investigate soil surface loss and underground leakage in the epikarst fissure zone. By simulating indoor rainfall and controlling the rainfall intensity, slope, fracture width and fracture occurrence, a 90-minute experiment was carried out to probe into the influence of soil surface loss and underground leakage. During the experiment, the data such as run-up time of underground leakage, water and soil surface loss and underground leakage was obtained every 4 minutes. EXCEL 2016 was used for statistical analysis of the data, and Origin 2017 for mapping.Results show that soil surface loss is mainly affected by rainfall intensity and slope. The lose increases with the intensifying of rainfall and the rising of slope, reaching the highest at 30° slope gradient. Besides, soil underground leakage is mainly affected by fissure width, occurrence and slope, but not obviously affected by rainfall intensity. The leakage is positively correlated with the fissure width, and most likely to occur when the fissure direction is 30° to the slope direction. The slope gradient is negatively correlated with the occurrence of soil underground leakage. During the rainfall, the underground leakage rate changes greatly, experiencing a decrease after an increase and finally reducing to 0. Surface loss is the main form of soil loss on the karst slope without sinkholes and funnels, and soil underground loss contributes less than 5% of the soil loss. Large karst pipelines such as sinkholes and funnels are the main channels of soil underground leakage. These experimental results can provide theoretical reference to the control of soil and water loss as well as the ecological restoration of karst sloping land in southwest China.
-
Key words:
- karst /
- simulation experiment /
- soil surface loss /
- soil underground leakage
-
表 1 实验土样物理性质
Table 1. Physical properties of soil samples
取样深度/cm 含水量/% 密度/g·cm−3 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数/% 天然孔隙比 10~15 10.9 1.31 54 36 18 1.165 表 2 实验条件的设置
Table 2. Test conditions
实验条件 实验设置 坡度/° 5、10、20、30 降雨强度/mm·h−1 40、60、80 裂隙宽度/mm 5、10、20 裂隙走向/° 0、30、60、90 表 3 不同降雨强度和坡度情况下的实验条件
Table 3. Test conditions under different rainfall intensities and slopes
实验条件 实验设置 坡度/° 10、20 降雨强度/mm·h-1 40、80 裂隙宽度/mm 5 裂隙走向/° 90 -
[1] 卢耀如. 地质—生态环境与可持续发展: 中国西南及邻近岩溶地区发展途径[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2003.LU Yaoru. Geology-ecological environment and sustainable development: Approaches to development of southwest China and adjacent karst areas[M]. Nanjing: Hohai University Press, 2003. [2] 李箐. 石灰岩地区开发与治理[M]. 贵阳: 贵州人民出版社, 1996.LI Jing. Development and management of limestone area [M]. Guiyang: Guizhou People's Publishing House, 1996. [3] 蒋忠诚, 李先琨, 胡宝清. 广西岩溶山区石漠化及其综合治理研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.JIANG Zhongcheng, LI Xiankun, HU Baoqing. Study on rocky desertification and its comprehensive control in karst mountainous areas of Guangxi[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing & Media Ltd. (CSPM), 2011. [4] 王世杰. 喀斯特石漠化:中国西南最严重的生态地质环境问题[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2003, 22(2):120-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.02.007WANG Shijie. The Most Serious Eco-geologically environmental Problem in Southwestern China–Karst Rocky Desertification[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2003, 22(2):120-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.02.007 [5] 曾发明, 吴泽燕, 章程, 杨奇勇. 峰丛洼地区石漠化治理的碳汇研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):67-73.ZENG Faming, WU Zeyan, ZHANG Cheng, YANG Qiyong. Carbon sink in rocky desertification restoration, Southwest China: A case of the peak-cluster depression areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):67-73. [6] 袁道先. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.YUAN Daoxian. Chinese karst Science[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993. [7] 张殿发, 王世杰, 周德全, 李瑞玲. 贵州省喀斯特地区土地石漠化的内动力作用机制[J]. 水土保持通报, 2001, 21(4):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2001.04.001ZHANG Dianfa, WANG Shijie, ZHOU Dequan, LI Ruiling. Intrinsic driving mechanism of land rocky Desertification in karst regions of Guizhou Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 21(4):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2001.04.001 [8] 张信宝, 王世杰, 贺秀斌, 汪阳春, 何永彬. 碳酸盐岩风化壳中的土壤蠕滑与岩溶坡地的土壤地下漏失[J]. 地球与环境, 2007, 35(3):202-206.ZHANG Xinbao, WANG Shijie, HE Xiubin, WANG Yangchun, HE Yongbin. Soil creeping in weathering crusts of carbonate rocks and underground soil losses on karst slopes[J]. Earth and Environment, 2007, 35(3):202-206. [9] 曹建华, 袁道先, 章程, 蒋忠诚. 受地质条件制约的中国西南岩溶生态系统[J]. 地球与环境, 2004, 32(1):1-8.CAO Jianhua, YUAN Daoxian, ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Zhongcheng. Karst ecosystem constrained by geological conditions in southwest China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2004, 32(1):1-8. [10] 龙健, 江新荣, 邓启琼, 刘方. 贵州喀斯特地区土壤石漠化的本质特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(3): 419-427.LONG Jian, JIANG Xinrong, DENG Qiqiong, LIU Fang. Characteristics of soil rocky desertification in the karst region of Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2005, 42(3): 419-427. [11] 王世杰. 喀斯特石漠化概念演绎及其科学内涵的探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2002, 21(2):101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.006WANG Shijie. Concept deduction and its connotation of karst rocky desertification[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2002, 21(2):101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.006 [12] Panos Panagos,Cristiano Ballabio,Pasquale Borrelli, Katrin Meusburger, Andreas Klik, Svetla Rousseva ,Melita Perčec Tadić, Silas Michaelides , Michaela Hrabalíková, Preben Olsen, Juha Aalto,Mónika Lakatos , Anna Rymszewicz , Alexandru Dumitrescu, Santiago Beguería, Christine Alewell. Rainfall erosivity in Europe[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 511:801-814. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.008 [13] Jomaa S,Barry D A,Brovelli A,Heng B C P,Sander G C, Parlange J Y,Rose C W. Rain splash soil erosion estimation in the presence of rock fragments[J]. Catena, 2012, 92:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.008 [14] 黄晓亚, 陈喜, 张志才, 张增信, 吴杨青, 黄远洋. 西南喀斯特地区降雨集中度及其变化特征分析: 以乌江流域中上游为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2013, 41(3):203-208.HUANG Xiaoya, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Zhicai, ZHANG Zengxin, WU Yangqing, HUANG Yuanyang. Analysis of daily rainfall concentration and Its change characteristics in southwestern karst regions: A case study of Wujiang catchment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2013, 41(3):203-208. [15] 高阿娟, 刘子琦, 李渊, 李凯萍. 喀斯特峡谷区不同经济林地土壤水分变化特征: 以贵州花江示范区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(6):863-872.GAO Ajuan, LIU Ziqi, LI Yuan, LI Kaiping. Study on soil moisture variation characteristics of different economic forest lands in karst gorge area: A case study of Huajiang demonstration area in Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(6):863-872. [16] 李春茂, 陈洪松, 徐勤学, 吴攀, 付智勇. 典型岩溶峰丛洼地坡面土壤水分空间变异性[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(2):159-167.LI Chunmao, CHEN Hongsong, XU Qinxue, WU Pan, FU Zhiyong. Spatial variability of soil moisture on hillslope in typical karst peak-cluster depression areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(2):159-167. [17] 熊康宁, 李晋, 龙明忠. 典型喀斯特石漠化治理区水土流失特征与关键问题[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(7):878-888. doi: 10.11821/xb201207002XIONG Kangning, LI Jin, LONG Mingzhong. Features of soil and water loss and key issues in demonstration areas for combating karst rocky desertification[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(7):878-888. doi: 10.11821/xb201207002 [18] Xingping Wei, Yaner Yan, Deti Xie, Jiupai Ni, Hugo A. Loáiciga. The soil leakage ratio in the Mudu watershed, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(8):721. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5351-9 [19] 白占国, 万国江. 滇西和黔中表土中7Be与137Cs分布特征对比研究[J]. 地理科学, 2002, 22(1):43-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2002.01.009BAI Zhanguo, WAN Guojiang. A comparative study on distribution of 7Be and 137Cs in the surface soils in the Western Yunnan and the central Guizhou Provinces[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2002, 22(1):43-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2002.01.009 [20] 曾凌云, 汪美华, 李春梅. 基于RUSLE的贵州省红枫湖流域土壤侵蚀时空变化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(2):113-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.020ZENG Lingyun, WANG Meihua, LI Chunmei. Study on soil erosion and its spatio-temporal change at Hongfeng lake watershed based on RUSLE model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2):113-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.020 [21] FENG Teng, CHEN Hongsong, WANG Kelin, ZHANG Wei, QI Xiangkun. Modeling soil erosion using a spatially distributed model in a karst catchment of northwest Guangxi, China[J]. Earth Surface Processes & Landforms, 2015, 39(15):2121-2130. [22] DAI Quanhou, PENG Xudong, YANG Zhi, ZHAO Longshan. Runoff and erosion processes on bare slopes in the Karst Rocky Desertification Area[J]. CATENA, 2017, 152:218-226. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.01.013 [23] YAN Youjin, DAI Quanhou, YUAN Yingfei, PENG Xudong, ZHAO Longshan, YANG Jing. Effects of rainfall intensity on runoff and sediment yields on bare slopes in a karst area, SW China[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 330:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.05.026 [24] DAI Quanhou, PENG Xudong, ZHAO Longshan, SHAO Hongbao, YANG Zhi. Effects of underground pore fissures on soil erosion and sediment yield on karst slopes: soil erosion and sediment on karst slopes[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2017, 28(7):1922-1932. [25] DAI Quanhou, LIU Zhengtang, SHAO Hongbao, YANG Zhi. Karst bare slope soil erosion and soil quality: a simulation case study[J]. Solid Earth, 2015, 6(3):985-995. doi: 10.5194/se-6-985-2015 [26] 刘琦, 顾展飞, 卢耀如, 刘之葵. 贵州施秉白云岩溶蚀特性及孔隙特征实验研究[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(4):413-418. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.04.04LIU Qi, GU Zhanfei, LU Yaoru, LIU Zhikui. The experimental study of dolomite dissolution and pore characteristics in Shibing, Guizhou[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(4):413-418. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.04.04 [27] 刘琦, 王涵, 廖启迪, 邓大鹏, 姚邦杰. 一种表层岩溶裂隙带土壤地表流失和地下漏失模拟装置[P]. 中国: CN112611850A, 2021-04-06. [28] 王涵, 刘琦, 任标, 姚邦杰,廖启迪. 典型喀斯特石漠化地区降雨产流产沙特征[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37(3):6-12.WANG Han, LIU Qi, REN Biao,YAO Bangjie,LIAO Qidi. Characteristics of rainfall runoff and sediment yield in typical Karst rocky desertification area[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 37(3):6-12. [29] 张信宝, 王世杰. 浅议喀斯特流域土壤地下漏失的界定[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(5):602-603.ZHANG Xinbao, WANG Shijie. A discussion on the definition of soil leaking in a karst catchment[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(5):602-603. [30] 魏兴萍, 谢德体, 倪九派, 苏程烜. 重庆岩溶槽谷区山坡土壤的漏失研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2015, 23(3):462-473.WEI Xingping, XIE Deti, NI Jiupai, SU Chenxuan. Soil erosion and loss on slope in karst valley area, Chongqing with 137Cs[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2015, 23(3):462-473. [31] 严友进, 戴全厚, 伏文兵, 彭旭东, 靳丽. 喀斯特裸坡产流产沙过程实验研究[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(6):2067-2079.YAN Youjin, DAI Quanhou, FU Wenbing, PENG Xudong, JIN Li. Runoff and sediment production processes on a karst bare slope[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(6):2067-2079. -




 下载:
下载: