Evaluation of rocky desertification comprehensive control based on orchard intercropped by herbage: A case study of the Xingyi City, Guizhou Province
-
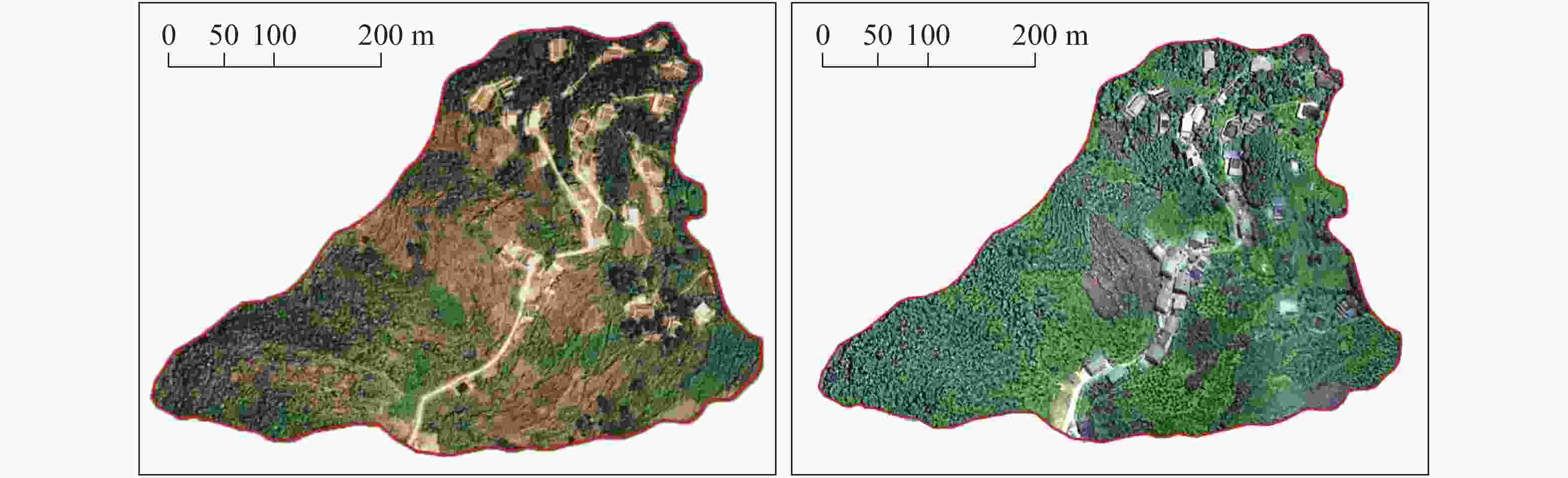
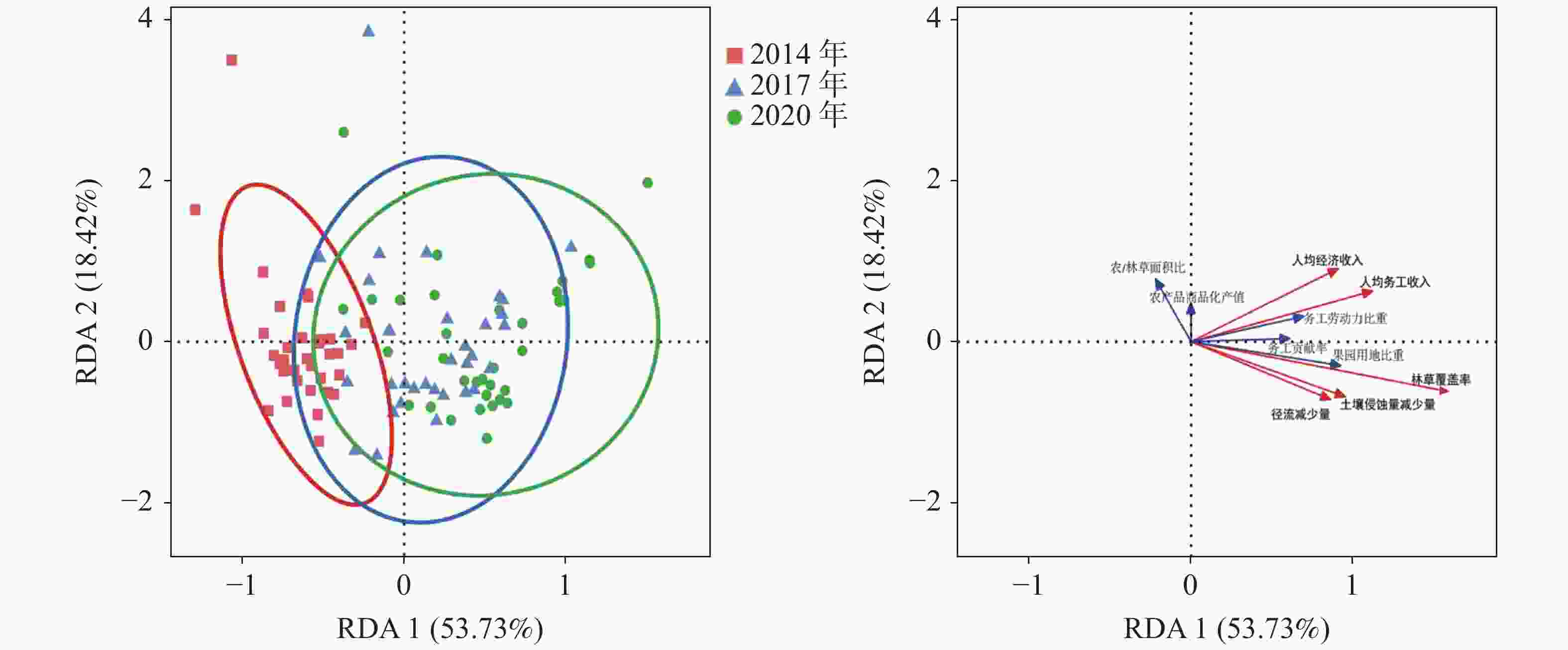
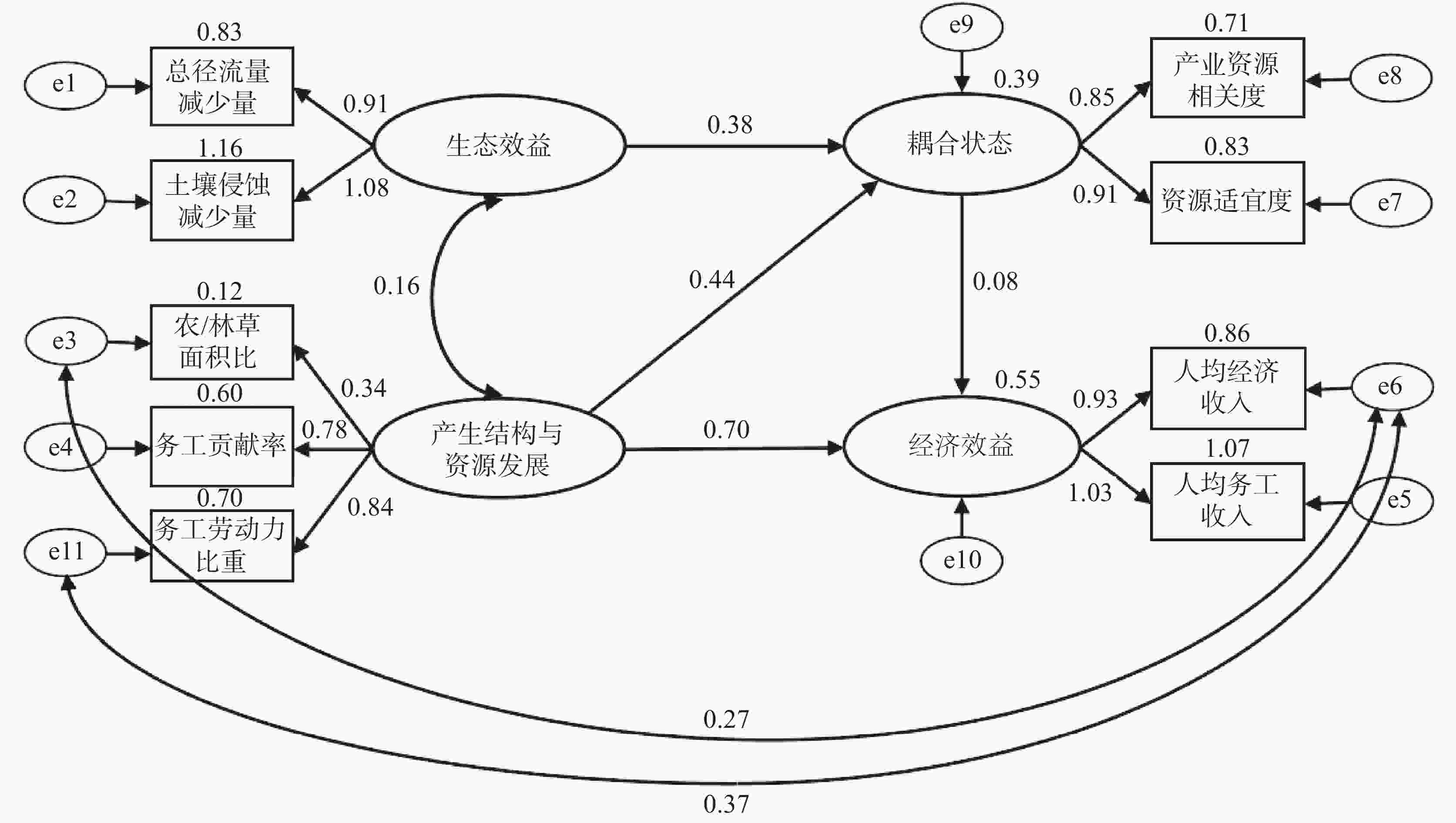
摘要: 开展石漠化综合治理效益评价,对于石漠化综合治理模式的优化和改进至关重要。文章以贵州兴义市南盘江镇田房村为研究对象,分析热带果树+覆盖作物措施的石漠化综合治理效益。通过调查兴义市南盘江镇田房村治理前(2014年)和治理后(2017年和2020年)的农业产业结构、产业资源发展、经济效益和生态效益,利用冗余分析(RDA)和结构方程建模(SEM)评价了田房村石漠化治理的综合效益。结果表明:通过将耕地转变为园地(芒果和澳洲坚果间作牧草或绿肥),综合治理6年后,该示范区农业产业结构、产业资源发展、经济效益和生态效益均呈现向好趋势;除了农/林草面积比和农产品商品产值两个观测变量,农业产业结构和产业资源发展与经济效益和生态效益之间观测指标均呈显著相关;果园用地比重、务工劳动力比重、务工贡献率、农产商品化产值、农/林草面积比5个变量是引起经济效益和生态效益变化的重要驱动因子;石漠化治理能耦合生态环境与产业资源的协调发展,同时实现生态恢复和经济增收。热带果树+覆盖作物相结合综合治理石漠化是该村生态恢复和经济增收的有效措施。研究结果为喀斯特石漠化综合治理提供了依据。Abstract: An evaluation of rocky desertification comprehensive control is very important to optimize and improve strategy for rocky desertification control modes. This paper aims to (Ⅰ) analyze the relationship among agricultural structure, industrial resources situation, economy benefit and ecology benefit; (Ⅱ) evaluate the comprehensive benefit of karst rocky desertification control by orchard-herbage intercropping, and further find its own advantages and disadvantages; (Ⅲ) provide ecological economic and sustainable development reference for rocky desertification control in the southwest karst area of China.A comprehensive prevention and control of rocky desertification area has been implemented in combination with tropical fruit tree intercropped by legume herb in Tianfang village, Nanpanjiang town, Xingyi City of Guizhou Province,where the rocky desertification is serious. To evaluate the comprehensive benefit of the demonstration area, we investigated the agricultural structure, industrial resources situation, and the benefits of economy and ecology before (2014) and after (2017 and 2020) karst rocky desertification control, and then adopted correlation analysis, Redundancy Analysis (RDA) and Structure Equation Modeling (SEM).By converting cultivated land to orchard (mango and Macadamia intercropped with herbage or green manure) the agricultural industrial structure ,industrial resources development,economic benefit and ecological benefit of the demonstration area showed a good trend after 6 years of rocky desertification comprehensive control. Correlation analysis showed that the agricultural industrial structure and industrial resources development situation were significantly correlated with economic benefit and ecological benefit, except for farming/forest-grass area ratio and commodity output value of agricultural products. RDA analysis showed that there are five variables which are the important contributing factors to the changes of economic benefit and ecological benefit such as, proportion of orchard land, migrant worker population, economic contribution rate of migrant workers, commodity output value of agricultural products farming/forest-grass area ratio SEM further showed that the rocky desertification control are able to couple the coordinated development of ecological environment and industrial resources, and at the same time achieve ecological restoration and economic benefit.Conclusions are drawn as follows, (Ⅰ) The rocky desertification control in orchards intercropped by fruit tree has increased the number of labor force and migrant workers,and improved the economic benefits by increasing commodity output value of agricultural products and migrant workers income. (Ⅱ) The ecological environment has been improved by increasing forest and grass coverage,soil erosion and water loss and surface runoff loss in the comprehensive control area of rocky desertification has been reduced. (Ⅲ) The rocky desertification control by orchard covered with fruit tree and intercropped by crops controlling rocky desertification will improve both economic benefit and ecological benefit. Overall, rocky desertification control by fruit tree intercropping orchard is an effective way to achieve sustainable development in the southwest karst area of China The study results provide a basis for the comprehensive control of karst rocky desertification.
-
表 1 调研基本信息
Table 1. Basic situation of investigation
类别 研究内容 家庭基本信息 人口数量、耕地数量、劳动力数量 农业产业 一年生农作物种类和种植面积、多年生果树种类和种植面积、果园种草面积、商品化农产品种类 产业资源发展 农产品商品率、务农劳动力数量、外出务工劳动力数量 经济效益 务农收益(一年生作物经济收益、多年生果树经济收益、
畜禽养殖收益)、本地务工收益、外地务工收益生态效益 地表径流量、土壤侵蚀量、林草覆盖率 表 2 石漠化综合治理区农业产业-资源-经济-生态系统耦合变量解释
Table 2. Coupling variable interpretation of agricultural industry-industrial resources- economic-ecological system in rocky desertification comprehensive control area
潜变量 观测变量 定义方法 产业结构与资源发展 农/林草面积比 农用地面积:果园和牧草用地面积 务工劳动力比重 务工劳动力/总劳动力 务工贡献率 务工经济收入/总经济收入 经济效益 人均经济收入 家庭总收入/家庭人口数 人均务工收入 家庭务工总收入/家庭人口数 生态效益 径流量减少量 治理后径流量-治理前径流量 侵蚀减少量 治理后侵蚀量-治理前侵蚀量 林草覆盖率 林地和草地面积之和/土地确权的耕地面积 耦合状态 产业资源相关度 具体赋值方法参考王继军[19]的研究成果 资源适宜度(各项得分
加总值;0~12)耕地适宜性(1 不适宜 /2 临界适宜 /3 适宜,下同)+
园地适宜性(1 /2 / 3)+
林地适宜性(1 / 2 / 3) +草地适宜性(1 /2 /3)
(赵晓翠,2019)[16]表 3 石漠化综合治理后农业产业结构、产业资源发展、经济效益和生态效益变化情况
Table 3. Changes of agricultural industrial structure, industrial resources development, economic benefit and ecological benefit after rocky desertification comprehensive control
年度 农业产业结构 产业资源发展 经济效益 生态效益 果园用地
比重/
%农/林草
面积比务工劳动
力比重/
%农产品商品
产值/
万元·人-1务工贡
献率/
%人均经济
收入/
万元·人-1人均务工
收入/
万元·人-1年总径流
量/m3·hm-2年总侵蚀
量/t·hm-2林草覆
盖率/%2014 0.47a 0.58a 45.74a 0.20b 67.44a 1.24a 0.85a 870.1a 11.89a 0.53a 2017 78.43b 0.58b 67.09b 0.00a 86.68b 1.85b 1.66b 557.99b 7.68b 80.27b 2020 80.12b 0.35b 74.56b 0.20b 86.53b 2.23b 1.93b 484.76b 4.42b 84.62b 表 4 石漠化治理后农业产业结构和产业资源发展与经济效益和生态效益的相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of agricultural industrial structure and industrial resources development with economic benefit and ecological benefit after rocky desertification control
观测项目 观测变量 农业产业结构 产业资源发展 果园用地比重 农/林草面积比 务工劳动力比重 农产品商品产值 务工贡献率 经济效益 人均经济收入 0.272** 0.176 0.474** 0.311** 0.273** 人均务工收入 0.384** 0.111 0.551** 0.032 0.505** 生态效益 总径流量 −0.473** 0.405** −0.233* 0.202 −0.324** 总侵蚀量 −0.514** 0.414** −0.262** 0.152 −0.321** 林草覆盖率 0.995** −0.343** 0.457** −0.115 0.430** -
[1] 王克林, 岳跃民, 陈洪松, 曾馥平. 科技扶贫与生态系统服务提升融合的机制与实现途径[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(10):1264-1272.WANG Kelin, YUE Yuemin, CHEN Hongsong, ZENG Fuping. Mechanisms and realization pathways for integration of scientific poverty alleviation and ecosystem services enhancement[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(10):1264-1272. [2] 国家林业和草原局. 中国·岩溶地区石漠化状况公报 [N]. 2018.National forestry and grassland administration. bulletin on the status of rocky desertification in karst areas of China [N]. 2018 [3] 朱斌, 刘丹一. 岩溶地区石漠化综合治理经验、问题及策略[J]. 林业经济, 2015, 37(5):76-81.ZHU Bin,LIU Danyi. Comprehensive taming of karst rock desertification in karst region: experience, problems and strategy[J]. Forestry Economics, 2015, 37(5):76-81. [4] 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 杜虎, 王克林, 曾馥平. 中国西南喀斯特石漠化时空演变特征、发生机制与调控对策[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(18):5328-5341.SONG Tongqing, PENG Wanxia, DU Hu, WANG Kelin, ZENG Fuping. Occurrence, spatial-temporal dynamics and regulation strategies of karst rocky desertification in southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(18):5328-5341. [5] 黄秋昊, 蔡运龙, 王秀春. 我国西南部喀斯特地区石漠化研究进展[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2007, 16(2): 106-111.HUANG Qiuhao, CAI Yunlong, WANG Xiuchun. Progress of research on rocky desertifica tion in karst area s of southwestern China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters. 2007, 16(2): 106-111 [6] 蒋忠诚, 罗为群, 童立强, 程 洋, 杨奇勇, 吴泽燕, 梁建宏. 21世纪西南岩溶石漠化演变特点及影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(5):461-468.JIANG Zhongchen, LUO Weiqun, TONG Liqian, CHENG Yan, YANG Qiyong, WU Zeyan, LIANG Jianhong. Evolution features of rocky desertification and influence factors in karst areas of southwest China in the 21st century[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(5):461-468. [7] 吴协保. 继续推进岩溶地区石漠化综合治理二期工程的现实意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(5):469-475.WU Xiebao. Realistic significance of carrying forward the project phase Ⅱ for comprehensive treatment of rocky desertification in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(5):469-475. [8] 李阳兵, 王世杰, 熊康宁. 花江峡谷石漠化土地生态重建及其启示[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2005, 15(1):138-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2005.01.030LI Yangbing, WANG Shijie, XIONG Kangning. Ecological reconstruction of karst rocky desertification and its significance in Huajian Gorge[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2005, 15(1):138-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2005.01.030 [9] 陈洪松, 岳跃民, 王克林. 西南喀斯特地区石漠化综合治理: 成效、问题与对策[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):37-42. doi: 10.11932/karst20170101CHENG Honglin, YUE Yuemin, WANG Kelin. Comprehensive control on rocky desertification in karst regions of southwestern China: achievements, problems, and countermeasures[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):37-42. doi: 10.11932/karst20170101 [10] 蒋忠诚, 李先琨, 覃小群, 吕仕洪, 罗为群, 蓝芙宁, 曹建华. 论岩溶峰丛洼地石漠化的综合治理技术:以广西平果果化示范区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(1):50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.009JIANG Zhongcheng, LI Xiankun, QIN Xiaoqun, LU Shihong, LUO Weiqun, LAN Funing, CAO Jianhua. Comprehensive improving technique to rocky desertification in karst peak-cluster depression: A case study at Guohua Ecological Experimental Area, Pingguo, Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(1):50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.009 [11] 吴鹏, 朱军, 崔迎春, 赵文君, 侯娜, 张喜. 喀斯特地区石漠化综合治理生态效益指标体系构建及评价:以杠寨小流域为例[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(10):95-101.WU Peng, ZHU Jun, CUI Yingchun, ZHAO Wenjun, HOU Na, ZHANG Xi. Construction of eco-efficiency index system for preventing and controlling rocky desertification in Gangzhai karst small watershed, Kaiyang, Guizhou and system evaluation[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology (Natural Science), 2014, 34(10):95-101. [12] 尹育知. 岩溶地区石漠化综合治理及其生态效益评价研究[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学, 2013.YIN Yunzhi. Study on the comprehensive treatment and eco-benefit evaluation on karst rocky desertification area-a case study on Xihua county[D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2013 [13] 杜雪莲, 王世杰, 熊强辉, 彭 韬, 程安云, 张 林, 蔡先立. 基于模糊综合评价法的小流域喀斯特石漠化治理综合效益评价:以贵州省普定县陈家寨小流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(5):586-593.DU Xuelian, WANG Shijie, XIONG Qianghui, PENG Tao, CHEN Anyun, ZHANG Lin, CAI Xianli. Evaluation on effect of small catchment comprehensive control in karst rocky desertification areas based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method: A case study of Chenjiazhai catchment in Puding county, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(5):586-593. [14] 顾剑红. 广西石漠化地区小流域水土保持综合效益评价[D]. 北京:北京林业大学, 2016.GU Jianhong. Assessment on comprehensive benefits of soil and water conservation at small watersheds in the rocky desertification region, Guangxi[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University, 2016 [15] 李昂, 王云琦, 张会兰, 王彬, 黎宏祥. 广西石漠化地区水土保持效应评价指标体系研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(11):67-78.LI Ang, WANG Yunqi, ZHANG Huilan, WANG Bin, LI Hongxiang. Research on evaluation index system of soil and water conservation effect of rocky desertification region in Guangxi of southern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(11):67-78. [16] 荣泰生. AMOS与研究方法 [M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2009.RONG Tai-sheng. AMOS and research method[M]. Chongqing:Chongqing University Press, 2009 [17] 赵晓翠, 王继军, 乔梅, 韩晓佳, 李玥. 水土保持技术对农业产业-资源系统的耦合路径分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16):5820-5828.ZHAO Xiaocui, WANG Jijun, QIAO Mei, HAN Xiaojia, LI Yue. Coupling path analysis of soil and water conservation technology to the agricultural industry-resource system[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16):5820-5828. [18] 苏鑫, 王继军, 郭满才, 姜志德, 李慧, 牛艳利. 基于结构方程模型的吴起县农业生态经济系统耦合关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(4):937-944.SU Xin, WANG Jijun, GUO Mancai, JIANG Zhide, LI Hui, NIU Yanli. Coupling relationship of agricultural eco-ceonomic systems in Wuqi county based on structural model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 21(4):937-944. [19] 王继军. 黄土丘陵区纸坊沟流域农业生态经济安全评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2008, 06(4):109-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.04.020WANG Jijun. Safety evaluation of the Zhifanggou watershed in the agricultural eco-economics of Hilly-gully region of Loess Plateau[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 06(4):109-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.04.020 [20] 王克林, 岳跃民, 陈洪松, 吴协保, 肖峻, 祁向坤, 张伟, 杜虎. 喀斯特石漠化综合治理及其区域恢复效应[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20):7432-7440.WANG Kelin, YUE Yuemin, CHEN Hongsong, WU Xiebao, XIAO Jun, QI Xiangkun, ZHANG Wei, DU Hu. The comprehensive treatment of karst rocky desertification and its regional restoration effects[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20):7432-7440. [21] LI Changjia, PAN Chengzhong. The relative importance of different grass components in controlling runoff and erosion on a hillslope under simulated rainfall[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 558:90-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.01.007 [22] 程汉亭, 李勤奋, 王晓敏, 卢天禹, 张显波. 不同植被恢复策略对贵州喀斯特生态系统土壤渗透特性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2020. 34(6): 110-116.CHENG Hanting, LI Qinfen, WANG Xiaomin, LU Tianyu, ZHANG Xianbo. Effects of different vegetation restoration strategies on soil penetrability of karst ecosystem in Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020,34(6): 110-116 [23] ZHAN Chesheng, ZHAO RUxin, HU Shi. Emergy-based sustainability assessment of forest ecosystem with the aid of mountain eco-hydrological model in Huanjiang county, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 251:119638. [24] HU Mengmeng, XIA Beicheng. Significant increase in the normalized difference vegetation index during the rapid economic development in the Pearl River Delta of China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2019, 30:359e370. [25] 侯宁, 王勇, 赵虎, 张校棱, 梁心蓝. 耕作侵蚀对不同坡度下紫色土侵蚀产沙的影响[J]. 山地学报, 2021, 39(4):495-505.HOU Ning, WANG Yong, ZHAO Hu, ZHANG Xiaoling, LIANG Xinlan. Effects of tillage erosion on sediment yield of purple soil under different slopes[J]. Mountain Research, 2021, 39(4):495-505. [26] 张黎鸣, 王红瑞, 潘成忠, 何继宏. 资源型地区产业结构调整对水资源利用效率影响的实证分析:来自中国10个资源型省份的经验证据[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(3):353-362.ZHANG Liming, WANG Hongrui, PAN Chengzhong, HE Jihong. Empirical analysis on the influence of industrial structure adjustment on water resource utilization efficiency in resource-based regions: empirical evidence from 10 resource-based provinces in China[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2021, 57(3):353-362. [27] 叶鑫, 顾羊羊, 张琨, 邹长新, 徐梦佳, 黄贤. 西南喀斯特地区石漠化治理现状分析与对策研究:以贵州省黔西南州为例[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48(22):30-34.YE Xin, GU Yangyang, ZHANG Kun, ZOU Changxin, XUN Mengjia, HUANG Xian. Current situation analysis and countermeasures of rocky desertification control in southwest karst region: A case study of Qianxinan Prefecture in Guizhou Province[J]. Environmental Protection, 2020, 48(22):30-34. [28] 李海燕, 丁剑宏, 柏勇, 吴昊, 张凤. 岩溶区水土保持综合治理技术效益分析:以官脉地小流域、高枧槽小流域为例[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2018, 16(3):68-78.LI Haiyan, DING Jianhong, BAI Yong, WU Hao, ZHANG Feng. Promotion effects of comprehensive control technologies of soil and water conservation in Karst region: A case study of the Guanmaidi Watershed and the Gaojiancao Watershed[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 16(3):68-78. [29] TONG Xiaowei, BRANDT Martin, YUE Yuemin, HORION Stephanie, WANG Kelin, KEERSMEACHER Wanda, TIAN Feng, SCHURGERS Guy, XIAO Xiaoming, LUO Yiqi, CHEN Chi, MYNENI Ranga, SHI Zheng, CHEN Hongsong, FENSHOLT Rasmus. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2018, 1(1):44-50. doi: 10.1038/s41893-017-0004-x -





 下载:
下载: