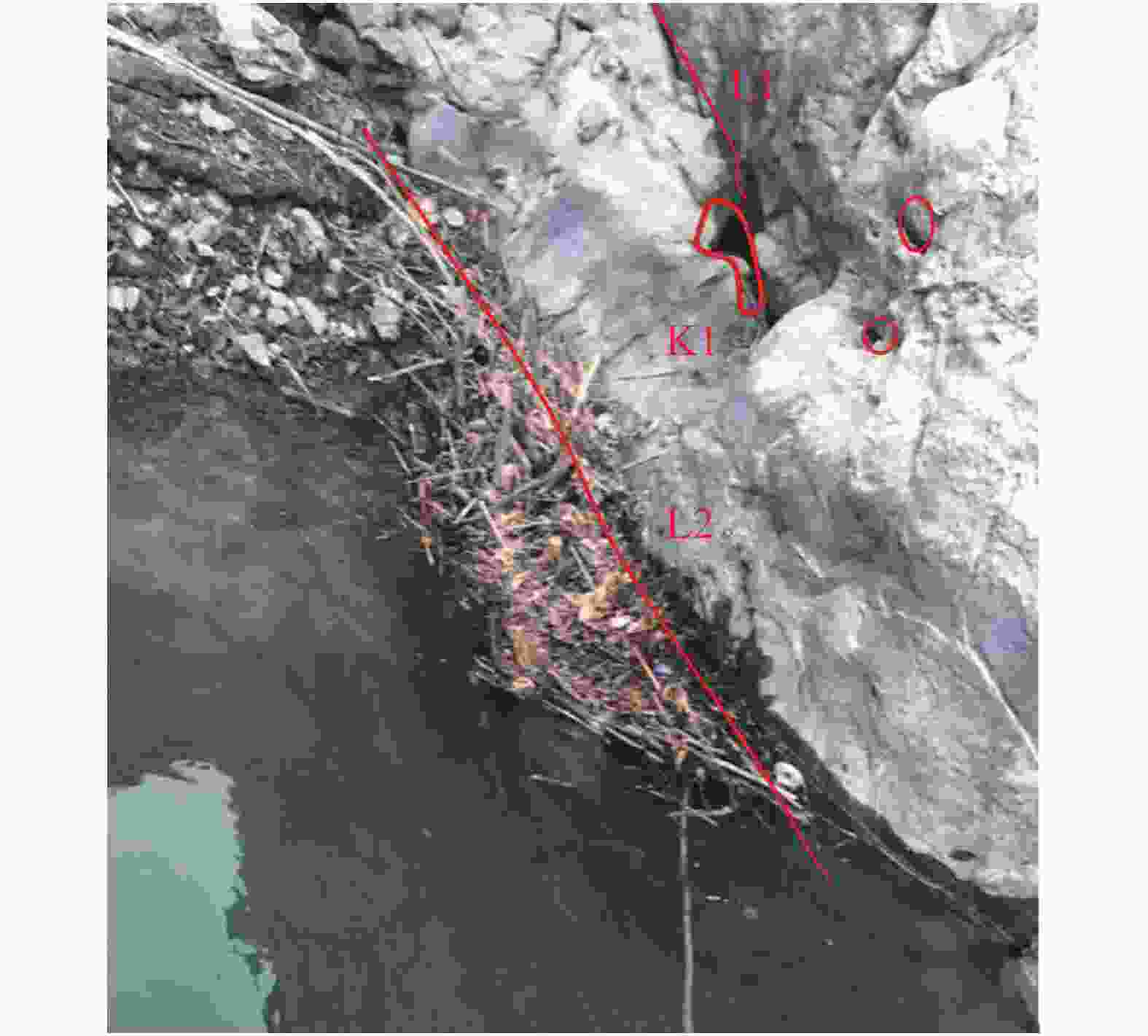
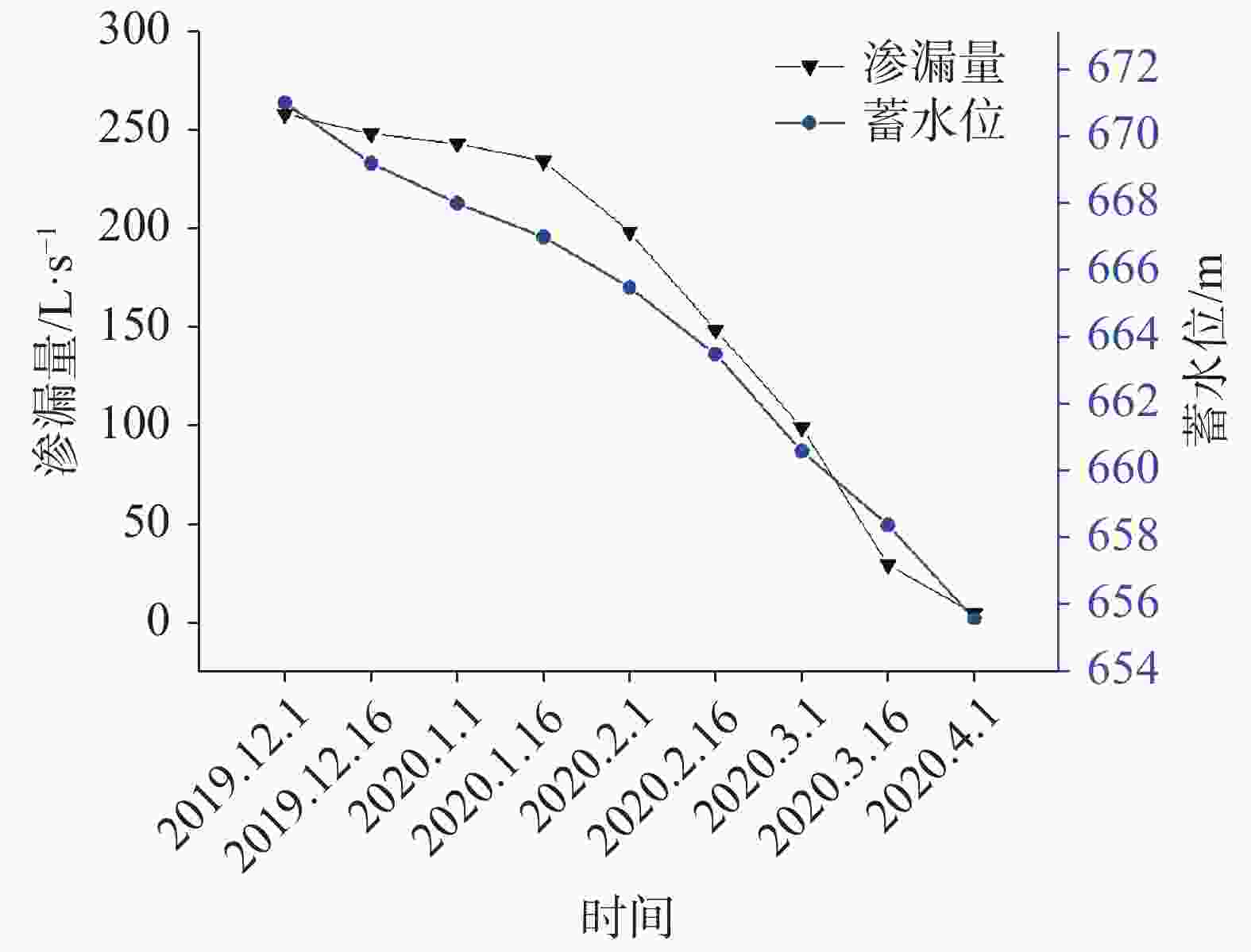
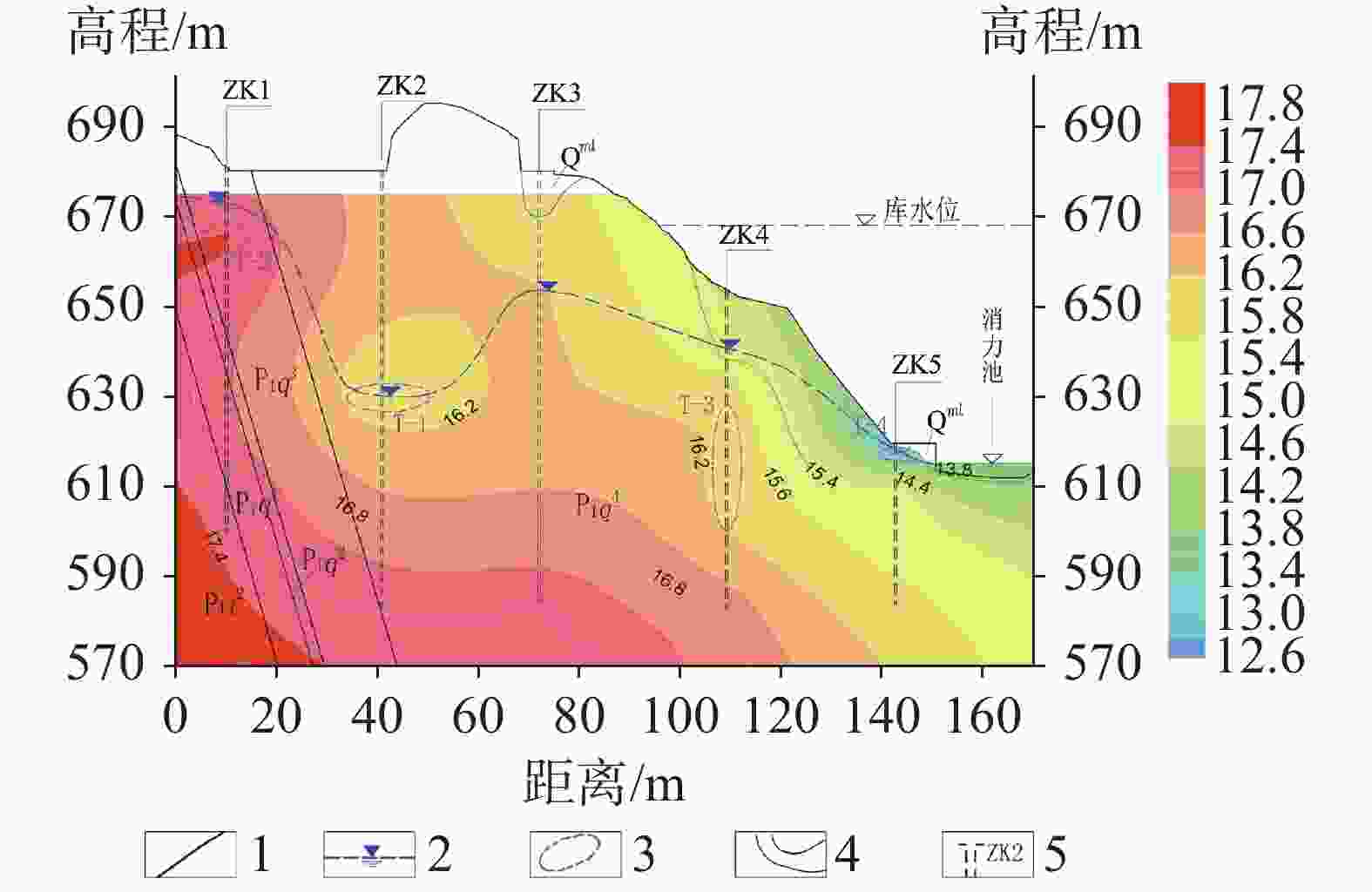
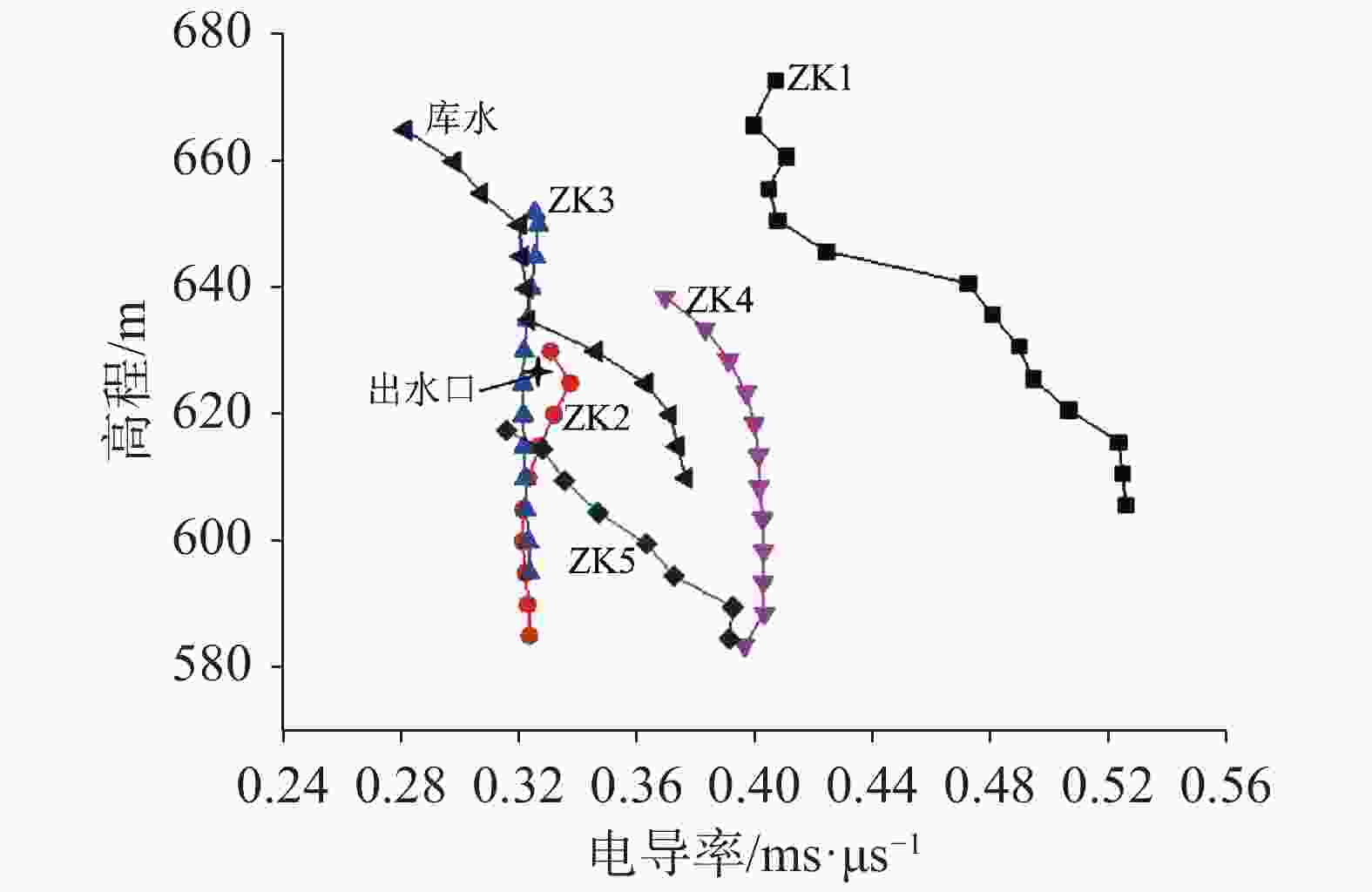
Investigation and evaluation of the leakage caused by seepage failure in karst reservoir
-
摘要: 以重庆市南川区肖家沟水库蓄水多年之后库首右岸发生的岩溶渗漏为例,探讨了岩溶水库长期运行过程中防渗体系因高压渗透破坏产生的岩溶渗漏的勘察与评价方法。通过地质分析、渗漏历史调查、钻孔、水文地质测试、物探及连通试验等方法,查明了水库右岸岩溶渗漏的范围及原因。水库渗漏边界清晰,渗漏范围主要是右岸可溶岩区的630 m高程以上,防渗体渗透破坏是水库产生渗漏主要原因。其渗漏途径一是沿原封堵堵头的薄弱区域或溶洞封堵体周边发生渗透破坏产生新的通道向下游溶洞出口集中的渗出,二是穿过右岸防渗线绕过右岸坝肩后沿岩体溶蚀裂隙或管道汇入下游右岸岸坡溶洞集中的渗出地表。通过此工程实例,提出了岩溶水库防渗体渗透破坏型渗漏的勘察与评价方法,宜以历史资料分析为基础,初判渗漏成因及范围,采用勘探、试验及物探等多种手段进行验证,为防渗处理提供可靠依据。Abstract:
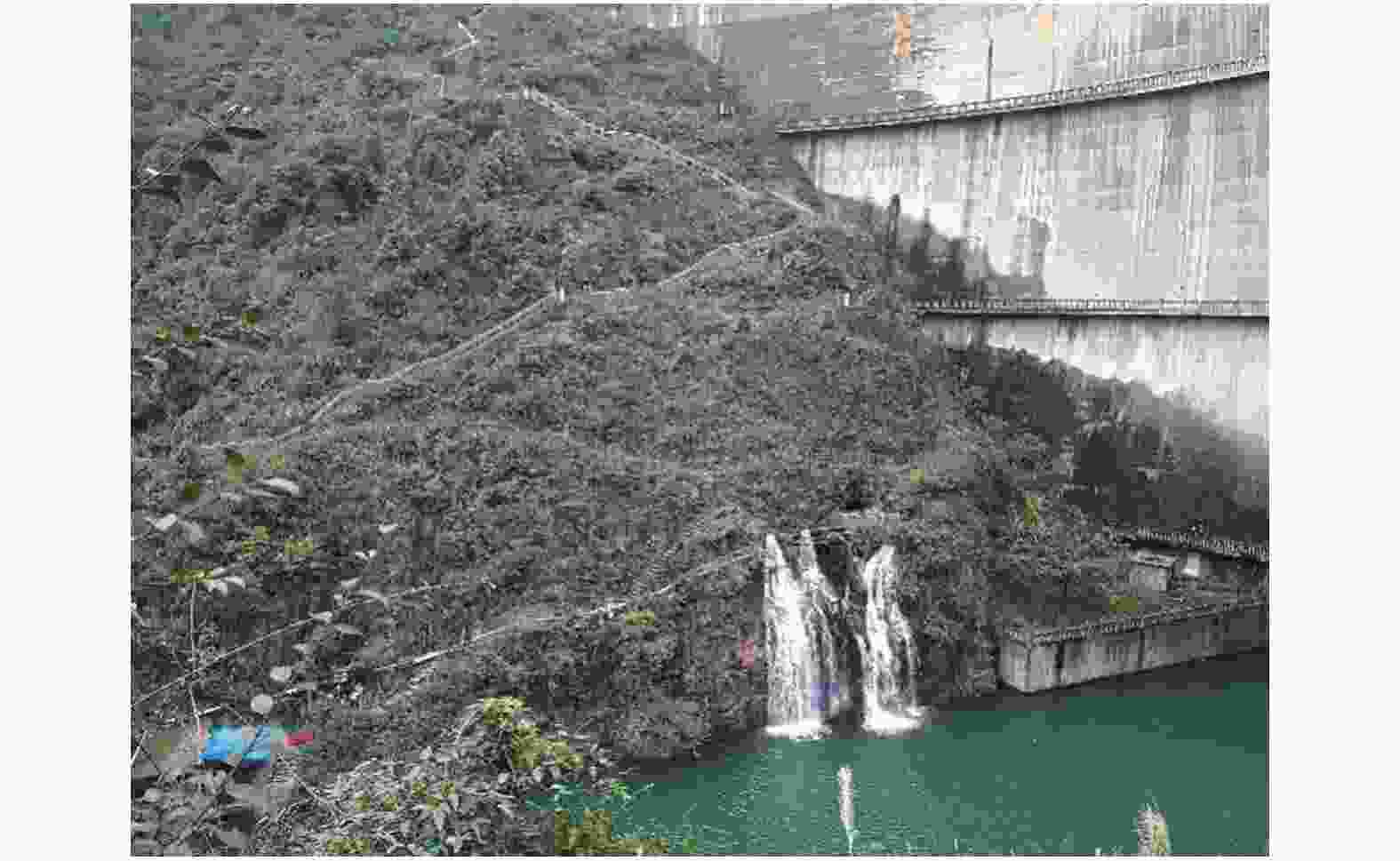
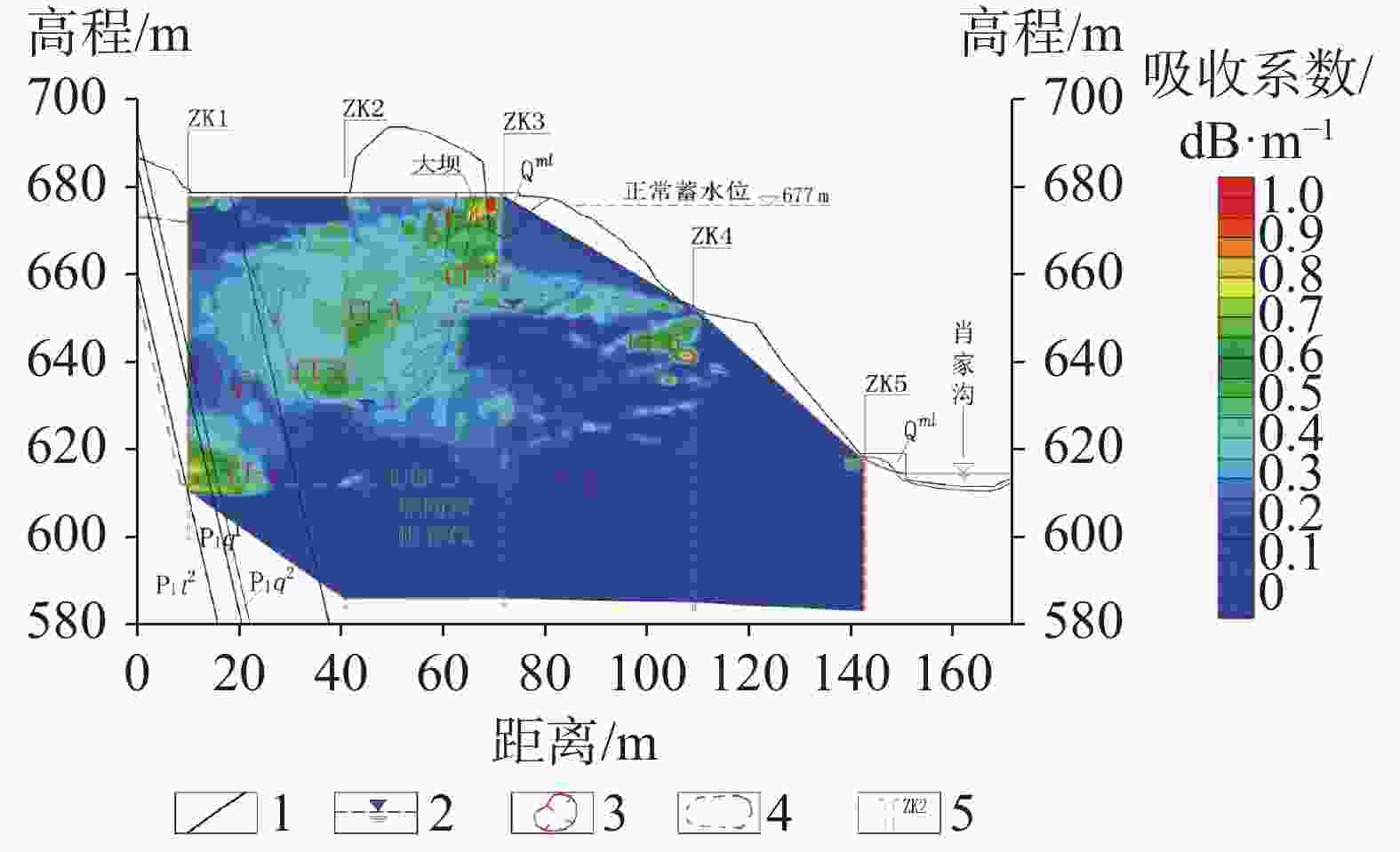
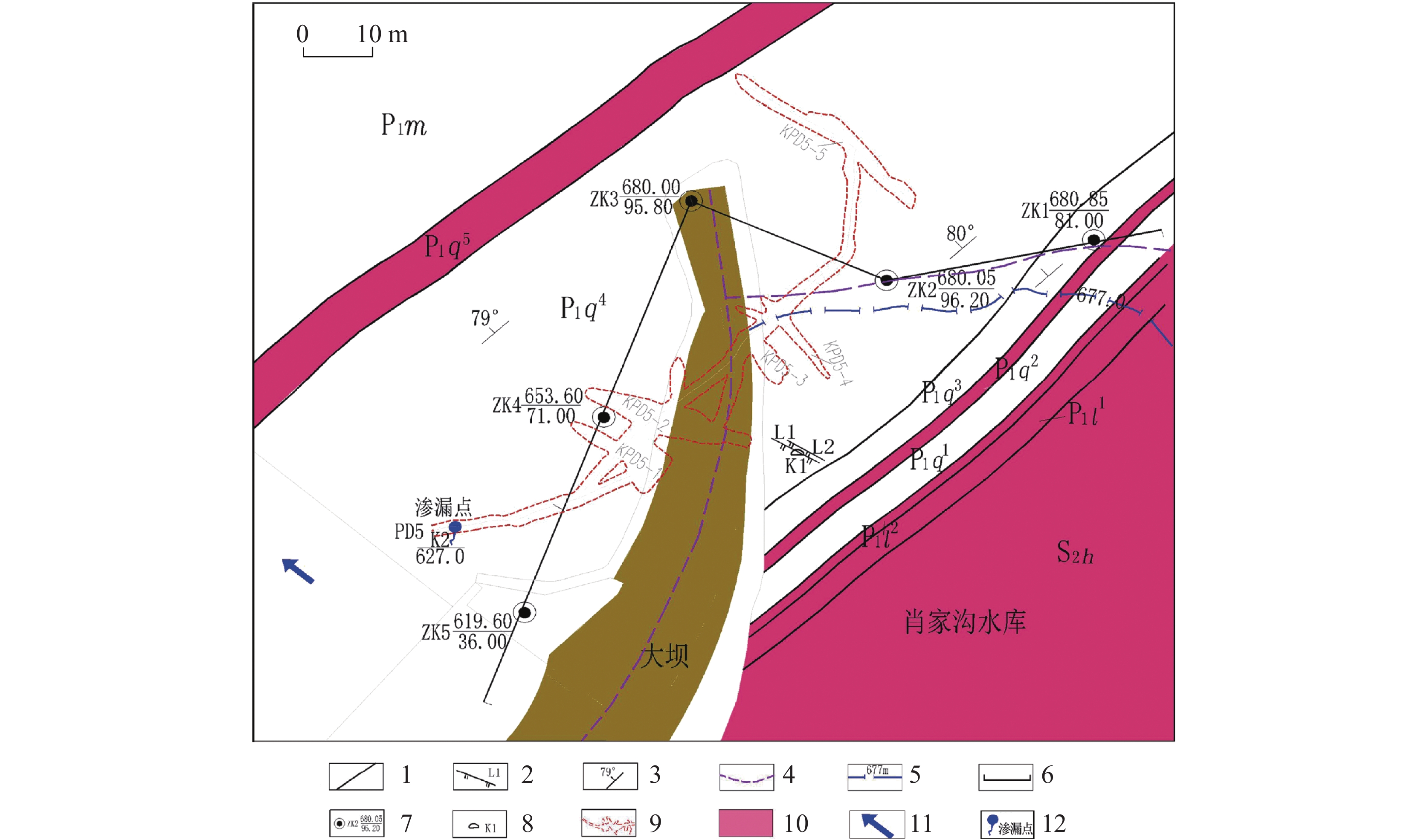
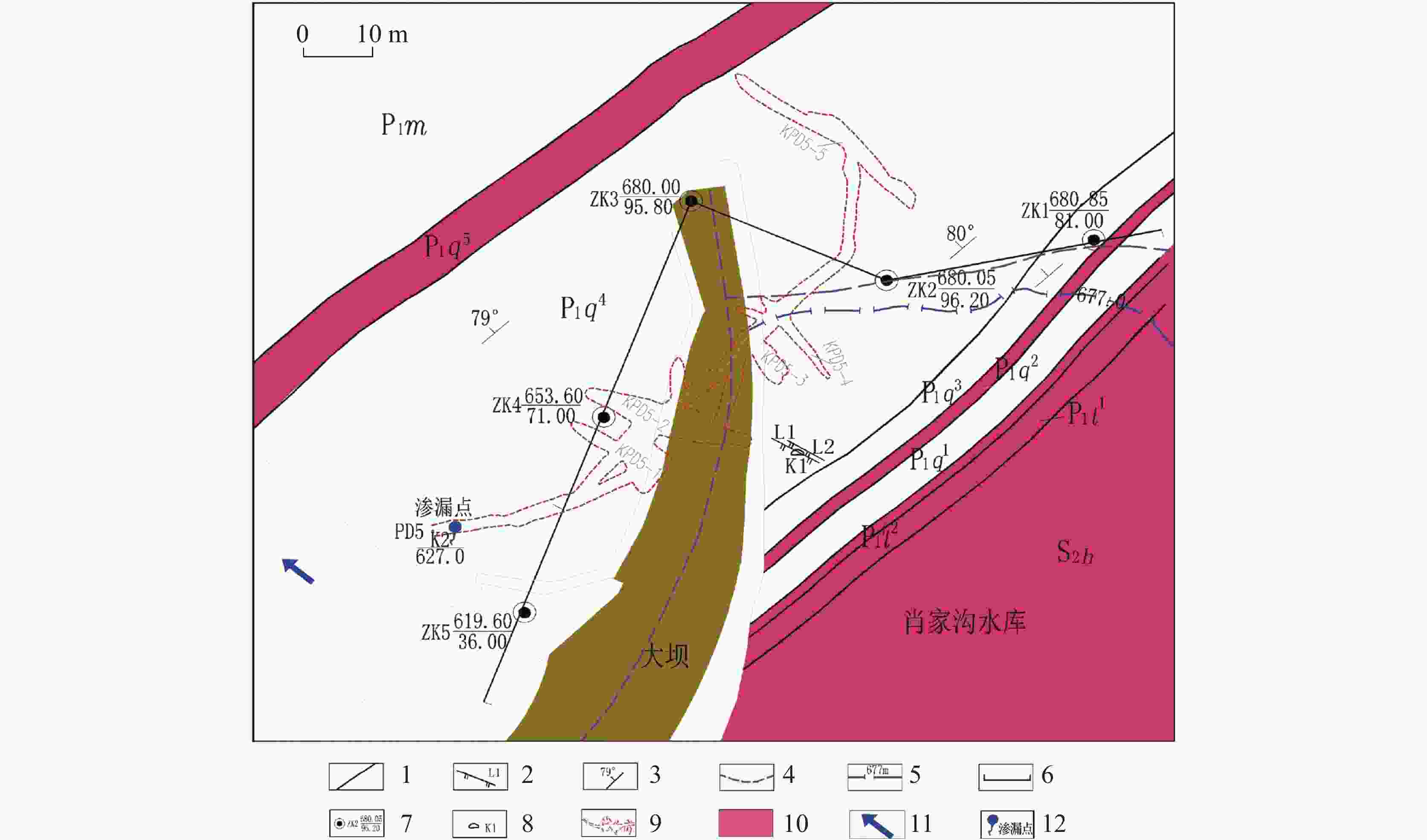
The karst leakage that occurred after the impoundment on the right bank of Xiaojiagou Reservoir in Nanchuan district of Chongqing has been taken as an example in the investigation and evaluation of karst leakage caused by high-pressure infiltration of the anti-seepage system during the long-term operation of karst reservoir. By means of geological analysis, historical investigation of leakage, drilling, hydrogeological test, geophysical prospecting and connectivity test, the range and causes of karst leakage on the right bank of the reservoir have been identified. According to the geological analysis, groundwater level observation and water permeability characteristics, the dam area is composed of karst rock, where dissolution occurs and fracture develops, and the local water permeability rate is large, hence there exist basic conditions for leakage. Besides, the limited groundwater recharge near the dam site and the low and flat groundwater level under the influence of limestone karst contribute to the hydrodynamic conditions for leakage. Combined with the analysis of temperature field, conductivity field and chemical field of reservoir and leakage point, the areas of abnormal groundwater temperature and conductivity on the right bank are mainly concentrated near the groundwater level of ZK2 and ZK4, and the water of the seepage point does not go through the deep groundwater circulation. The leakage path is short, which may penetrate through the dissolution fracture and small karst hole at the inlet on the right bank of the dam site to the PD5 flat cave section between the dam and anti-seepage line on the right bank. The connectivity test shows that the karst cave (dissolution fracture) on the right bank upstream of the dam have good connectivity with the leakage outlet. Geophysical exploration results show that CT-2, CT-3 and CT-5, the main channels of fracture-type leakage distributed above the elevation of 630 m on the right bank, mainly control the leakage of dam foundation and around dam. Study results are shown as follows. (1) The leakage boundary of the reservoir is clear, and the leakage range is mainly above the elevation of 630 m in the soluble rock area on the right bank. The seepage failure of the anti-seepage body is the main reason for the leakage of reservoir. (2) The first leakage path is through the weak area of the original plugging plug or the surrounding of the karst plugging body, resulting in a new channel for leakage to converge into the karst cave outlet downstream. The second bypasses the dam shoulder on the right bank through anti-seepage line before leakage converges into the karst cave downstream of the right bank slope along the erosion fissures or pipelines of rock mass, and then it seeps out on the surface. In this study, the method of investigating and evaluating the leakage caused by seepage failure of anti-seepage body in karst reservoir has been proposed as illustrated by the project. To preliminarily determine the cause and range of seepage, it is advisable for us to analyze historical data and use such methods as exploration, testing and geophysical prospecting. The study results may provide a reliable basis for anti-seepage treatment. -
表 1 库坝区含水岩组划分表
Table 1. Division of acquifer groups in the dam area
地层 厚度/m 岩性 含水岩组 志留系 中统 韩家店组(S2h) 570 页岩夹粉砂岩 隔水层 二叠系 下
统梁山组第一段(P1l1) 0.7~4.5 铝土岩 隔水层 梁山组第二段(P1l2) 0~3 页岩夹炭质页岩及煤线 隔水层 栖霞组第一段(P1q1) 5~6 灰岩夹钙质页岩 中等岩溶含水层 栖霞组第二段(P1q2) 2~3 粉砂质页岩及钙质页岩 隔水层 栖霞组第三段(P1q3) 1~5 灰岩夹薄层钙质页岩 中等岩溶含水层 栖霞组第四段(P1q4) 50~60 灰岩 强岩溶含水层 栖霞组第五段(P1q5) 8~10 钙质页岩夹灰岩 隔水层 茅口组(P1m) >200 生物碎屑灰岩 强岩溶含水层 表 2 钻孔地下水位统计表
Table 2. Statistics of groundwater level in borehole
孔号 高程/m 具体位置 地层揭露情况 地下水位特征 稳定地下水位
埋深及高程/m地下水位与
库水位关系/m地下水位与
河水关系/mZK1 680.85 坝前防渗线
端头P1l2页岩、P1q1-3灰岩、页岩 7.1/673.75 +5.75 +63.75 ZK2 680.05 坝前防渗线
中部P1q4灰岩 50.0/630.05 −37.95 +20.05 ZK3 680.00 坝端附近 P1q4灰岩 26.5/653.5 −14.5 +43.5 ZK4 653.60 坝下游岸坡
高位P1q4灰岩 13.8/639.8 −28.2 +29.8 ZK5 619.60 坝下游岸坡
低位P1q4灰岩 0.7/618.9 −49.1 +8.9 表 3 水质特征表
Table 3. Characteristics of water quality
取样位置 深度/m 离子浓度/mmol·L−1 Ca2+ Mg2+ K++Na+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 矿化度 泉水S2 2.92 0.23 2.13 4.67 507.97 右岸近坝库水 0.87 0.21 1.51 2.14 239.51 坝后渗漏点水 1.08 0.15 1.32 1.95 247.10 ZK2 60 0.76 0.38 1.15 1.75 216.90 70 0.8 0.32 1.35 1.95 230.62 80 0.74 0.25 1.19 1.75 203.56 ZK3 30 0.74 0.44 1.32 2.14 234.09 50 0.87 0.34 1.31 1.95 238.62 70 0.72 0.34 2.09 1.75 319.16 ZK4 30 1.33 0.17 1.61 2.53 297.20 45 1.23 0.23 1.72 2.73 297.09 60 1.29 0.17 3.02 3.8 414.76 ZK5 15 0.76 0.30 1.56 2.16 242.1 注:S2为大坝左岸上游附近泉水点。 -
[1] 薛伟, 袁宗峰, 周密. 西南地区某岩溶水库渗漏分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(4):508-514.XUE Wei, YUAN Zongfeng, ZHOU Mi. Analysis on leakage of a karst reservoir in Southwestern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(4):508-514. [2] 脱云飞, 王克勤, 张振伟, 郭涛, 杨路华. 斜孔帷幕灌浆在病险水库防渗处理中的应用[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2011, 9(1):145-147.TUO Yunfei, WANG Keqin, ZHANG Zhenwei, GUO Tao, YANG Luhua. Application of inclined-holes curtain grouting in the seepage control of the reservoir[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2011, 9(1):145-147. [3] 彭仕雄, 陈卫东, 肖强. 官地电站库首左岸河湾地块岩溶渗漏分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(S2):4030-4037.PENG Shixiong, CHEN Weidong, XIAO Qiang. Karst seepage analysis on left river bend in the head area of Guandi hydropower station reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(S2):4030-4037. [4] 郭铁柱, 谢宝瑜, 魏红. 海子水库岩溶渗漏分析及帷幕灌浆防渗效果评价[J]. 水利水电技术, 2009, 40(4):73-75.GUO Tiezhu, XIE Baoyu, WEI Hong. Anaysis on karstic seepage and evaluation on anti-seepage effect from curtain grouting for Haizi reservoir[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2009, 40(4):73-75. [5] 贺强. 基于渗透破坏试验的黏土临界坡降影响因素分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2017, 35(9):110-112, 21.HE Qiang. Influencing factor analysis of clay critical hydraulic gradient based on experiment of seepage failure[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2017, 35(9):110-112, 21. [6] 张贵金, 徐卫亚. 岩溶坝区溶蚀岩体的渗透性变异研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(9):1527-1534. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.010ZHANG Guijin, XU Weiya. Study on variability of permeability of corroded rock mass in karst dam region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(9):1527-1534. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.010 [7] 肖万春. 水库岩溶渗漏勘察技术要点与方法研究[J]. 水力发电, 2008, 34(7):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2008.07.016XIAO Wanchun. Keystones and methods study of karst reservoir leakage investigation[J]. Water Power, 2008, 34(7):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2008.07.016 [8] 李乐晨, 李子阳, 赵兆. 河口村水库坝肩裂隙岩体防渗处理分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2017, 39(10):98-101, 105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2017.10.021LI Lechen, LI Ziyang, ZHAO Zhao. Seepage control analysis of fractured rock mass at dam abutment of Hekoucun reservoir[J]. Yellow River, 2017, 39(10):98-101, 105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2017.10.021 [9] 张可能, 张岳, 廖阳, 万浩然, 许培浩, 张云毅. 贵阳某地铁车站岩溶发育特征及突水模式分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(2):300-306.ZHANG Keneng, ZHANG Yue, LIAO Yang, WAN Haoran, XU Peihao, ZHANG Yunyi. Analysis on karst development and water burst in a subway station[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(2):300-306. [10] 王家乐, 贾宝杰, 王志刚. 岩溶含水层地下水源热泵运行对地下水温度场的影响[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 37(2):55-58.WANG Jiale, JIA Baojie, WANG Zhigang. Influence of water source heat pump on groundwater temperature field in karst aquifer[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37(2):55-58. [11] 朱彪, 陈喜, 张志才, 彭韬, 张乐辰, 陈波, 赵美刚. 西南喀斯特流域枯季地下水电导率特征及水-岩作用分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(4):459-463.ZHU Biao, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Zhicai, PENG Tao, ZHANG Lechen, CHEN Bo, ZHAO Meigang. Characteristics of groundwater conductivity in dry season and water-rock interaction implications in a southwest karst basin[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(4):459-463. [12] 唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平. 龙子祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5): 2087-2095.TANG Chunlei, ZHENG Xiuqing, LIANG Yongping. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in Longzici spring catchment[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5): 2087-2095. [13] 张浪, 李俊, 潘晓东, 黄晓荣, 彭聪. 西南某岩溶区地下水系统示踪试验与解析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(1): 42-47.ZHANG Lang, LI Jun, PAN Xiaodong, HUANG Xiaorong, PENG Cong. Tracer test and analysis of karst groundwater system in karst area of Southwest China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1): 42-47. [14] 熊亮萍, 汪集旸. 钻孔地温分布与地下水活动[J]. 地质科学, 1992(S1):313-321.XIONG Liangping, WANG Jiyang. Geotemperature distribution in borehole and groundwater activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1992(S1):313-321. [15] 程亚平, 蒋灵芝, 黎柳月, 李善民, 冯志秦. 综合物探技术探测平果铝厂赤泥堆场岩溶发育特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(6):688-698.CHENG Yaping, JIANG Lingzhi, LI Liuyue, LI Shanmin, FENG Zhiqin. The application of integrated geophysical method to karst pipeline distribution[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(6):688-698. [16] 黄朝煊, 王贺瑶. 坝基渗流与坝肩绕渗实用计算方法探讨[J]. 水电能源科学, 2015, 33(3):71-75.HUANG Chaoxuan, WANG Heyao. Discussion on computing method of dam foundation seepage and bypass seepage of dam a butment[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2015, 33(3):71-75. [17] 康迎宾, 李琳. 涧里水库大坝右岸坝肩绕渗稳定分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2009, 31(4):109-110, 113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2009.04.051KANG Yingbin, LI Lin. Stability analysis of seepage around dam abutment on the right bank of Jianli reservoir[J]. Yellow River, 2009, 31(4):109-110, 113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2009.04.051 -




 下载:
下载: